Can the European Hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) Be a Sentinel for One Health Concerns?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
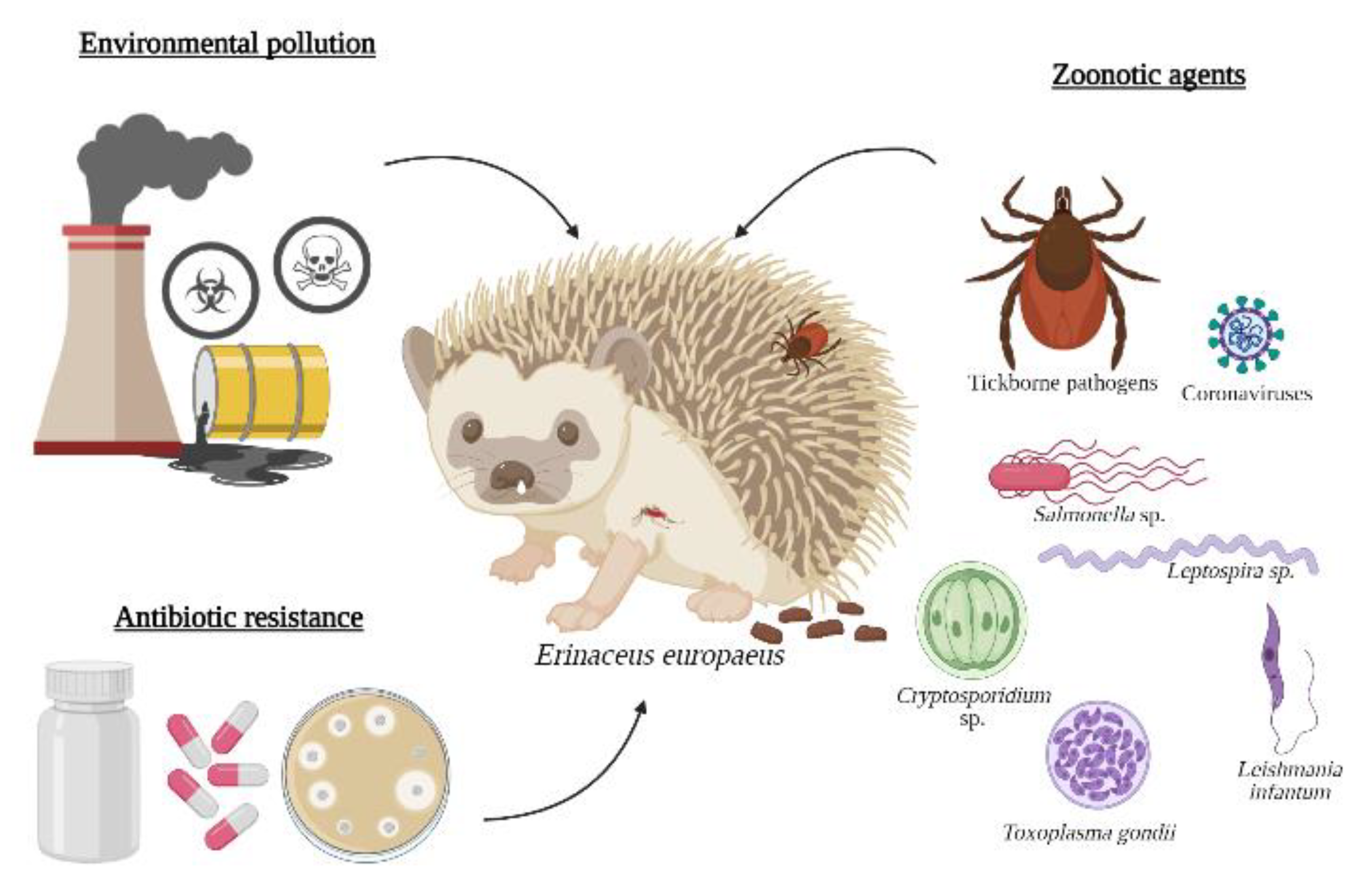
3. Zoonotic Agents
4. Environmental Pollution
5. Antibiotic Resistance
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amori, G. Erinaceus europaeus. IUCN Red List Threat. Species 2016, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.L.; Larsen, J.; Van Wijk, R.E.; Jones, O.R.; Berg, T.B.; Angen, O.; Larsen, A.R. European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) as a natural reservoir of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying mecC in Denmark. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.M.; Baker, P.J.; Thomas, E.; Wilson, G.; Judge, J.; Yarnell, R.W. Reduced occupancy of hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in rural England and Wales: The influence of habitat and an asymmetric intra-guild predator. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettett, C.E.; Johnson, P.J.; Moorhouse, T.P.; Macdonald, D.W. National predictors of hedgehog Erinaceus europaeus distribution and decline in Britain. Mamm. Rev. 2018, 48, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencatel, J.; Sabino-Marques, H.; Álvares, F.; Moura, A.E.; Barbosa, A.M. Atlas de Mamíferos de Portugal, 2nd ed.; Universidade de Évora: Évora, Portugal, 2019; ISBN 9789898550804. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell-Jones, A.J.; Amori, G.; Bogdanowicz, W.; Krystufek, B.; Reijnders, P.J.H.; Spitzenberger, F.; Stubbe, M.; Thissen, J.B.M.; Vohralik, V.; Zima, J. The Atlas of European Mammals; Poyser: London, UK, 1999; ISBN 9780856611308. [Google Scholar]
- European Hedgehog (Erinaceus Europaeus)|Natural History Museum. Available online: https://www.nhm.ac.uk/discover/hedgehog-erinaceus-europaeus.html (accessed on 24 April 2021).
- One Health Basics. One Health|CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/onehealth/basics/index.html (accessed on 3 June 2021).
- World Bank. People, Pathogens and our Planet; Agriculture and Rural Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Available online: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/2012/06/16360943/people-pathogens-planet-economics-one-healt (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Kelly, T.R.; Karesh, W.B.; Johnson, C.K.; Gilardi, K.V.K.; Anthony, S.J.; Goldstein, T.; Olson, S.H.; Machalaba, C.; Mazet, J.A.K.; Aguirre, A.; et al. One Health proof of concept: Bringing a transdisciplinary approach to surveillance for zoonotic viruses at the human-wild animal interface. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 137, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (US) Committee on Animals as Monitors of Environmental Hazards. Animals as Sentinels of Environmental Health Hazards; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Delogu, M.; Cotti, C.; Lelli, D.; Sozzi, E.; Trogu, T.; Lavazza, A.; Garuti, G.; Castrucci, M.R.; Vaccari, G.; De Marco, M.A.; et al. Eco-virological preliminary study of potentially emerging pathogens in hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) recovered at a wildlife treatment and rehabilitation center in Northern Italy. Animals 2020, 10, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, A.I.; Van Leeuwen, A.D.; Jacobs-Reitsma, W.; Wijnands, L.M.; Bouw, E.; Jahfari, S.; Van Hoek, A.H.A.M.; Van Der Giessen, J.W.B.; Roelfsema, J.H.; Kroes, M.; et al. Presence of zoonotic agents in engorged ticks and hedgehog faeces from Erinaceus europaeus in (sub) urban areas. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeble, E.; Koterwas, B. Salmonellosis in Hedgehogs. Vet. Clin. North. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2020, 23, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.Q.; Xiao, X.; Liu, J.W.; Han, H.J.; Qin, X.R.; Lei, S.C.; Yu, X.J. Occurrence and Genotyping of Coxiella burnetii in Hedgehogs in China. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2020, 20, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahfari, S.; Ruyts, S.C.; Frazer-Mendelewska, E.; Jaarsma, R.; Verheyen, K.; Sprong, H. Melting pot of tick-borne zoonoses: The European hedgehog contributes to the maintenance of various tick-borne diseases in natural cycles urban and suburban areas. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydeskov, H.B.; Amar, C.F.L.; Fernandez, J.R.-R.; John, S.K.; MacGregor, S.K.; Cunningham, A.A.; Lawson, B. Listeria monocytogenes infection of free-living western european hedgehogs (erinaceus Europaeus). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2019, 50, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collares-Pereira, M.; Korver, H.; Terpstra, W.J.; Santos-Reis, M.; Ramalhinho, M.G.; Mathias, M.L.; Oom, M.M.; Fons, R.; Libois, R.; Petrucci-Fonseca, F. First epidemiological data on pathogenic leptospires isolated on the Azorean islands. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 13, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sixl, W.; Kock, M.; Withalm, H.; Stunzner, D. Serological investigations of the hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) in Styria. Geogr. Med. Suppl. 1989, 2, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schönbächler, K.; Hatt, J.-M.; Silaghi, C.; Merz, N.; Fraefel, C.; Bachofen, C. Confirmation of tick-borne encephalitis virus in an european hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus)|Détection du virus de la méningo-encéphalite verno-estivale chez le hérisson d’europe (Erinaceus europaeus)|Frühsommer-meningoenzephalitis-virus nachweis beim. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2018, 161, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, J.R.; Bergeron, É.; Rollin, P.E. Seroepidemiological Studies of Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus in Domestic and Wild Animals. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medlock, J.M.; Snow, K.R.; Leach, S. Possible ecology and epidemiology of medically important mosquito-borne arboviruses in Great Britain. Epidemiol. Infect. 2021, 135, 466–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubálek, Z.; Rödl, P.; Juricová, Z. Experimental infection of hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) with Bhanja virus. Folia Parasitol. 1984, 31, 189–190. [Google Scholar]
- Monchatre-Leroy, E.; Boué, F.; Boucher, J.M.; Renault, C.; Moutou, F.; Gouilh, M.A.; Umhang, G. Identification of alpha and beta coronavirus in wildlife species in france: Bats, rodents, rabbits, and hedgehogs. Viruses 2017, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bao, C.; Hu, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Ji, Z.; Feng, Z.; Li, L.; Shen, A.; et al. Ecology of the Tick-Borne Phlebovirus Causing Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in an Endemic Area of China. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekeres, S.; Docters van Leeuwen, A.; Tóth, E.; Majoros, G.; Sprong, H.; Földvári, G. Road-killed mammals provide insight into tick-borne bacterial pathogen communities within urban habitats. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilvers, B.L.; Cowan, P.E.; Waddington, D.C.; Kelly, P.J.; Brown, T.J. The prevalence of infection of Giardia spp. and Cryptosporidium spp. in wild animals on farmland, southeastern North Island, New Zealand. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 1998, 8, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangster, L.; Blake, D.P.; Robinson, G.; Hopkins, T.C.; Sa, R.C.C.; Cunningham, A.A.; Chalmers, R.M.; Lawson, B. Detection and molecular characterisation of Cryptosporidium parvum in British European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus). Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 217, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmannová, L.; Juránková, J. Survey of Toxoplasma gondii and Trichinella spp. in hedgehogs living in proximity to urban areas in the Czech Republic. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Madrid, R.; Belinchón-Lorenzo, S.; Iniesta, V.; Fernández-Cotrina, J.; Parejo, J.C.; Serrano, F.J.; Monroy, I.; Baz, V.; Gómez-Luque, A.; Gómez-Nieto, L.C. First detection of Leishmania infantum kinetoplast DNA in hair of wild mammals: Application of qPCR method to determine potential parasite reservoirs. Acta Trop. 2013, 128, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingmueller, G.; Heymer, T.; Sobich, E. Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. erinacei-infection of hedgehog. Trichophyton-mentagrophytes-var.-erinacei-infektion VOM IGEL. Hautarzt 1979, 30, 140–143. [Google Scholar]
- Majerová, K.; Hönig, V.; Houda, M.; Papežík, P.; Fonville, M.; Sprong, H.; Rudenko, N.; Golovchenko, M.; Bolfíková, B.Č.; Hulva, P.; et al. Hedgehogs, squirrels, and blackbirds as sentinel hosts for active surveillance of borrelia miyamotoi and borrelia burgdorferi complex in urban and rural environments. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skuballa, J.; Petney, T.; Pfäffle, M.; Oehme, R.; Hartelt, K.; Fingerle, V.; Kimmig, P.; Taraschewski, H. Occurrence of different Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato genospecies including B. afzelii, B. bavariensis, and B. spielmanii in hedgehogs (Erinaceus spp.) in Europe. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silaghi, C.; Skuballa, J.; Thiel, C.; Pfister, K.; Petney, T.; Pfäffle, M.; Taraschewski, H.; Passos, L.M.F. The European hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus)-A suitable reservoir for variants of Anaplasma phagocytophilum? Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, B.; Franklinos, L.H.V.; Rodriguez-Ramos Fernandez, J.; Wend-Hansen, C.; Nair, S.; Macgregor, S.K.; John, S.K.; Pizzi, R.; Núñez, A.; Ashton, P.M.; et al. Salmonella Enteritidis ST183: Emerging and endemic biotypes affecting western European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) and people in Great Britain. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heir, E.; Lindstedt, B.A.; Nygård, I.; Vardund, T.; Hasseltvedt, V.; Kapperud, G. Molecular epidemiology of Salmonella typhimurium isolates from human sporadic and outbreak cases. Epidemiol. Infect. 2002, 128, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayral, F.; Djelouadji, Z.; Raton, V.; Zilber, A.-L.; Gasqui, P.; Faure, E.; Baurier, F.; Vourc’h, G.; Kodjo, A.; Combes, B. Hedgehogs and Mustelid Species: Major Carriers of Pathogenic Leptospira, a Survey in 28 Animal Species in France (20122015). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hathaway, S.C.; Hathaway, S.C. Leptospirosis in New Zealand: An ecological view. N. Z. Vet. J. 1981, 29, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corman, V.M.; Kallies, R.; Philipps, H.; Gopner, G.; Muller, M.A.; Eckerle, I.; Brunink, S.; Drosten, C.; Drexler, J.F. Characterization of a Novel Betacoronavirus Related to Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus in European Hedgehogs. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldanha, I.F.; Lawson, B.; Goharriz, H.; Rodriguez-Ramos Fernandez, J.; John, S.K.; Fooks, A.R.; Cunningham, A.A.; Johnson, N.; Horton, D.L. Extension of the known distribution of a novel clade C betacoronavirus in a wildlife host. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sabato, L.; Di Bartolo, I.; De Marco, M.A.; Moreno, A.; Lelli, D.; Cotti, C.; Delogu, M.; Vaccari, G. Can Coronaviruses Steal Genes from the Host as Evidenced in Western European Hedgehogs by EriCoV Genetic Characterization? Viruses 2020, 12, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, D.K.; Alkhovsky, S.V.; Kolobukhina, L.V.; Burtseva, E.I. Etiology of epidemic outbreaks COVID-19 in Wuhan, Hubei province, Chinese People Republic associated with 2019-nCoV (Nidovirales, Coronaviridae, Coronavirinae, Betacoronavirus, Subgenus Sarbecovirus): Lessons of SARS-CoV outbreak. Vopr. Virusol. 2020, 65, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drexler, J.F.; Corman, V.M.; Lukashev, A.N.; Van Den Brand, J.M.A.; Gmyl, A.P.; Brünink, S.; Rasche, A.; Seggewiβ, N.; Feng, H.; Leijten, L.M.; et al. Evolutionary origins of hepatitis A virus in small mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Havé, H.; Scheirs, J.; Mubiana, V.K.; Verhagen, R.; Blust, R.; De Coen, W. Nondestructive pollution exposure assessment in the European hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus): I. Relationships between concentrations of metals and arsenic in hair, spines, and soil. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 2356–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, F.; Covaci, A.; D’Havé, H.; Van den Brink, N.W.; Blust, R.; De Coen, W.; Bervoets, L. Accumulation of background levels of persistent organochlorine and organobromine pollutants through the soil-earthworm-hedgehog food chain. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; Covaci, A.; Voorspoels, S.; Schepens, P. The distribution of octachlorostyrene (OCS) in environmental samples from Europe. J. Environ. Monit. 2003, 5, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, F.; D’Havé, H.; Mubiana, V.K.; Van den Brink, N.W.; Blust, R.; Bervoets, L.; De Coen, W. Relevance of hair and spines of the European hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) as biomonitoring tissues for arsenic and metals in relation to blood. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcês, A.; Soeiro, V.; Lóio, S.; Sargo, R.; Sousa, L.; Silva, F.; Pires, I. Outcomes, Mortality Causes, and Pathological Findings in European Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europeus, Linnaeus 1758): A Seventeen Year Retrospective Analysis in the North of Portugal. Animals 2020, 10, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleva, E.; Francia, N.; Pandolfi, M.; De Marinis, A.M.; Chiarotti, F.; Santucci, D. Organochlorine and heavy-metal contaminants in wild mammals and birds of Urbino-Pesaro Province, Italy: An analytic overview for potential bioindicators. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 51, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinecke, A.J.; Reinecke, S.A.; Musilbono, D.E.; Chapman, A. The transfer of lead (Pb) from earthworms to shrews (Myosorex varius). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautio, A.; Kunnasranta, M.; Valtonen, A.; Ikonen, M.; Hyvärinen, H.; Holopainen, I.J.; Kukkonen, J.V.K. Sex, age, and tissue specific accumulation of eight metals, arsenic, and selenium in the European Hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 59, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowding, C.V.; Shore, R.F.; Worgan, A.; Baker, P.J.; Harris, S. Accumulation of anticoagulant rodenticides in a non-target insectivore, the European hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus). Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rast, W.; Barthel, L.M.F.; Berger, A. Music festival makes Hedgehogs move: How individuals cope behaviorally in response to human-induced stressors. Animals 2019, 9, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Antibiotic Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antibiotic-resistance (accessed on 3 June 2021).
- Martin, J.F.; Liras, P. Organization and expression of genes involved in the biosynthesis of antibiotics and other secondary metabolites. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1989, 43, 173–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Rodríguez, C.; Alt, K.; Grobbel, M.; Hammerl, J.A.; Irrgang, A.; Szabo, I.; Stingl, K.; Schuh, E.; Wiehle, L.; Pfefferkorn, B.; et al. Wildlife as Sentinels of Antimicrobial Resistance in Germany? Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 7821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucur, I.; Dumitrescu, V.; Imre, K.; Herman, V.; Nichita, I.; Cristina, R.T.; Tirziu, E. Research on the Frequency of Resistance Phenotypes in Bacterial Strains Isolated From Chamois (Rupicapra Rupicapra Carpatica). Rev. Rom. Med. Vet. 2020, 30, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, M.C. Tetracycline Resistance Determinants: Mechanisms of Action, Regulation of Expression, Genetic Mobility, and Distribution. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 19, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Francesco, A.; Renzi, M.; Borel, N.; Marti, H.; Salvatore, D. Detection of tetracycline resistance genes in european hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) and crested porcupines (Hystrix cristata). J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monecke, S.; Gavier-Widen, D.; Mattsson, R.; Rangstrup-Christensen, L.; Lazaris, A.; Coleman, D.C.; Shore, A.C.; Ehricht, R. Detection of mecC-Positive Staphylococcus aureus (CC130-MRSA-XI) in Diseased European Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in Sweden. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-López, R.A.; Vidal, A.; Obón, E.; Martín, M.; Darwich, L. Multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium monophasic variant 4,12:i:- Isolated from asymptomatic wildlife in a catalonian wildlife rehabilitation center, Spain. J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Agents | Ref | |
|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | Campylobacter jejuni | [13] |
| Salmonella sp. 1 | [14] | |
| Shiga toxin-producing E. coli | [13] | |
| ESC-resistant E. coli | [13] | |
| Yersinia pseudotuberculosis | [14] | |
| Mycobacterium marinum | [13] | |
| Coxiella burnetii | [15] | |
| Borrelia burgdorferi sensu latum (s.l.) 2 | [16] | |
| Borrelia miyamotoi | [16] | |
| Listeria monocytogenes | [17] | |
| Leptospira interrogans s.l. | [18] | |
| Klebsiella sp. | [13] | |
| Virus | Herpesvirus 3 | [19] |
| TBEV 4 | [20] | |
| CCHFV 5 | [21] | |
| Tahyna virus | [22] | |
| Bhanja virus | [23] | |
| Influenza A virus | [12] | |
| Influenza D virus | [12] | |
| Coronavirus | [24] | |
| SFTSV 6 | [25] | |
| Parasites | Anaplasma phagocytophilum | [26] |
| Giardia sp. | [27] | |
| Cryptosporidium parvum | [28] | |
| Cryptosporidium hominis | [13] | |
| Rickettsia helvetica | [26] | |
| Toxoplasma gondii | [29] | |
| Leishmania infantum | [30] | |
| Fungi | Trychophyton mentagrophytes var. erinacei | [31] |
| Microsporum spp. | [13] | |
| Candida albicans | [13] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jota Baptista, C.V.; Seixas, F.; Gonzalo-Orden, J.M.; Oliveira, P.A. Can the European Hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) Be a Sentinel for One Health Concerns? Biologics 2021, 1, 61-69. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics1010004
Jota Baptista CV, Seixas F, Gonzalo-Orden JM, Oliveira PA. Can the European Hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) Be a Sentinel for One Health Concerns? Biologics. 2021; 1(1):61-69. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics1010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleJota Baptista, Catarina Vinhas, Fernanda Seixas, José Manuel Gonzalo-Orden, and Paula A. Oliveira. 2021. "Can the European Hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) Be a Sentinel for One Health Concerns?" Biologics 1, no. 1: 61-69. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics1010004
APA StyleJota Baptista, C. V., Seixas, F., Gonzalo-Orden, J. M., & Oliveira, P. A. (2021). Can the European Hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) Be a Sentinel for One Health Concerns? Biologics, 1(1), 61-69. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics1010004









