Signs of Alveolar Collapse in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis and Systemic Sclerosis Revealed by Inspiration and Expiration Computed Tomography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Thorax CT and Imaging Modalities
2.3. Segment-Based CT Densitometry
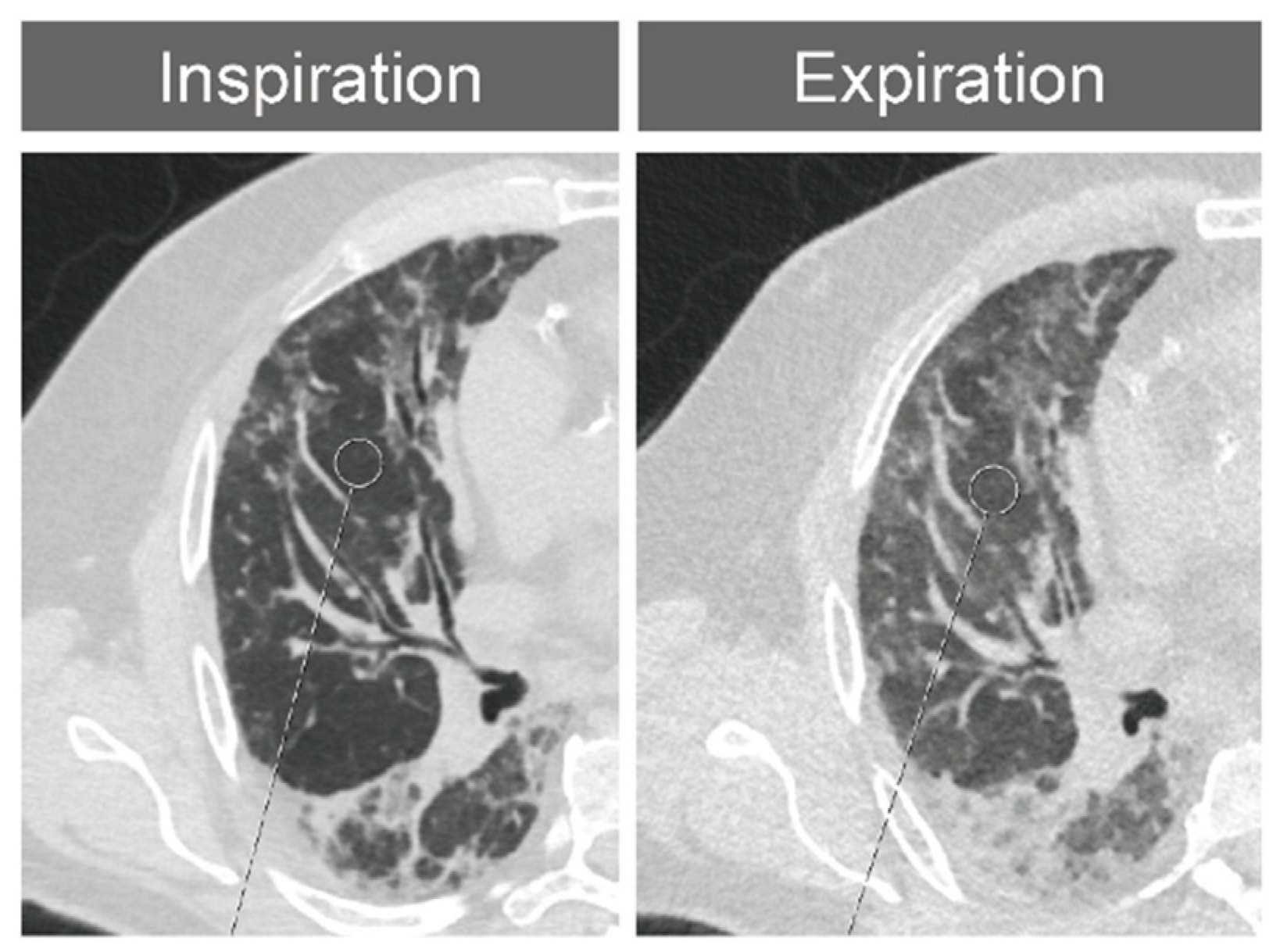
2.4. Expansion Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
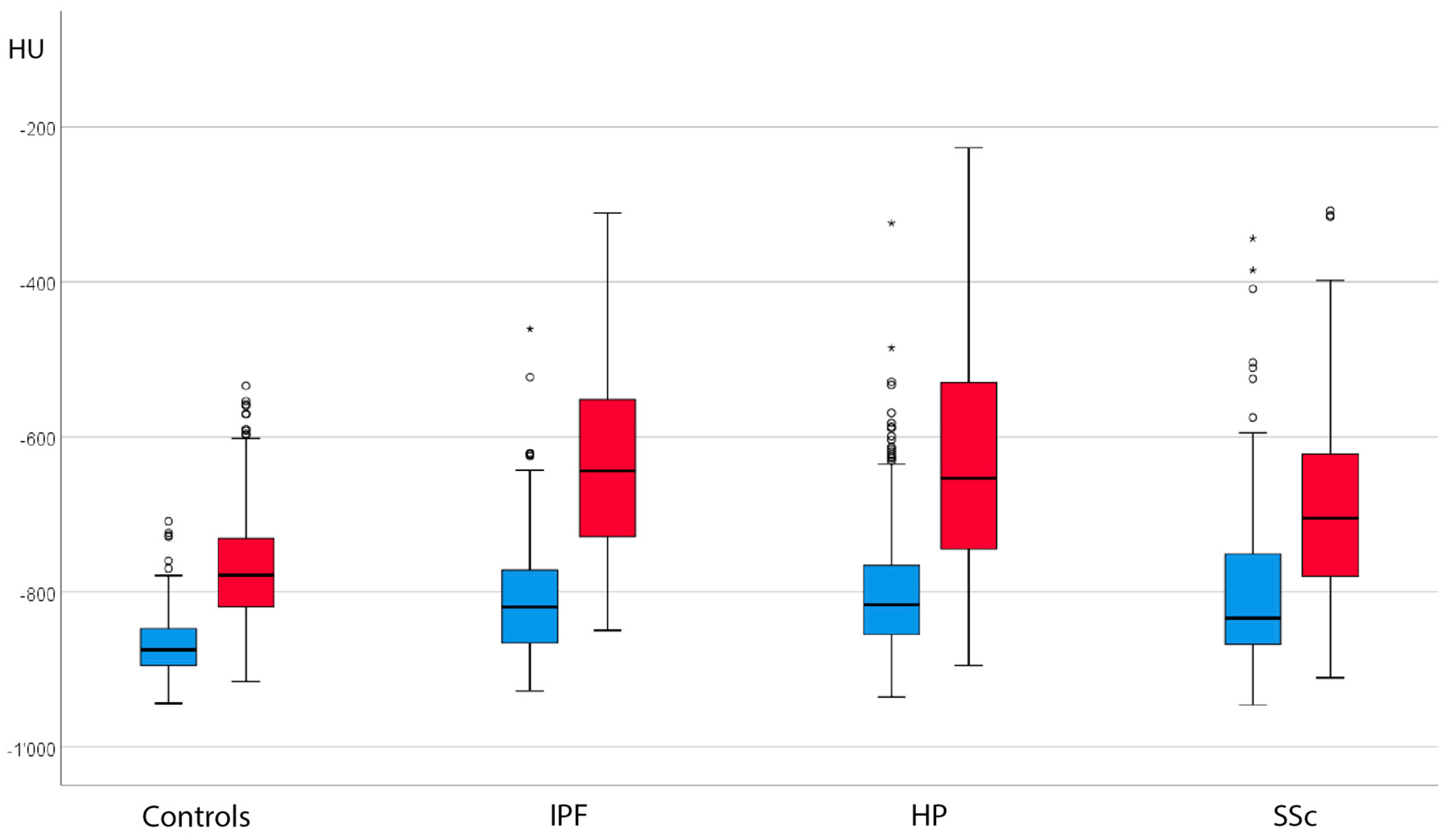
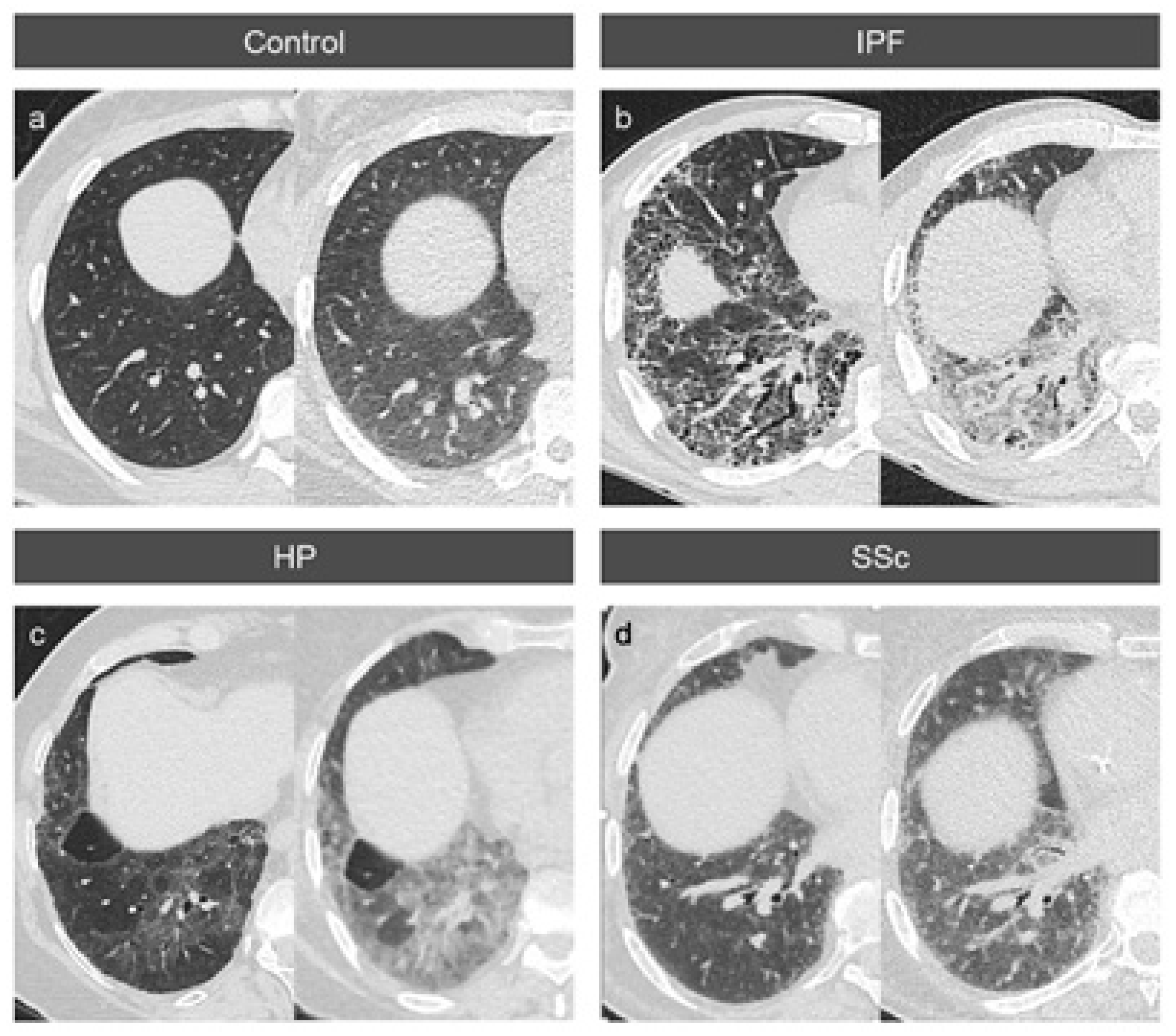
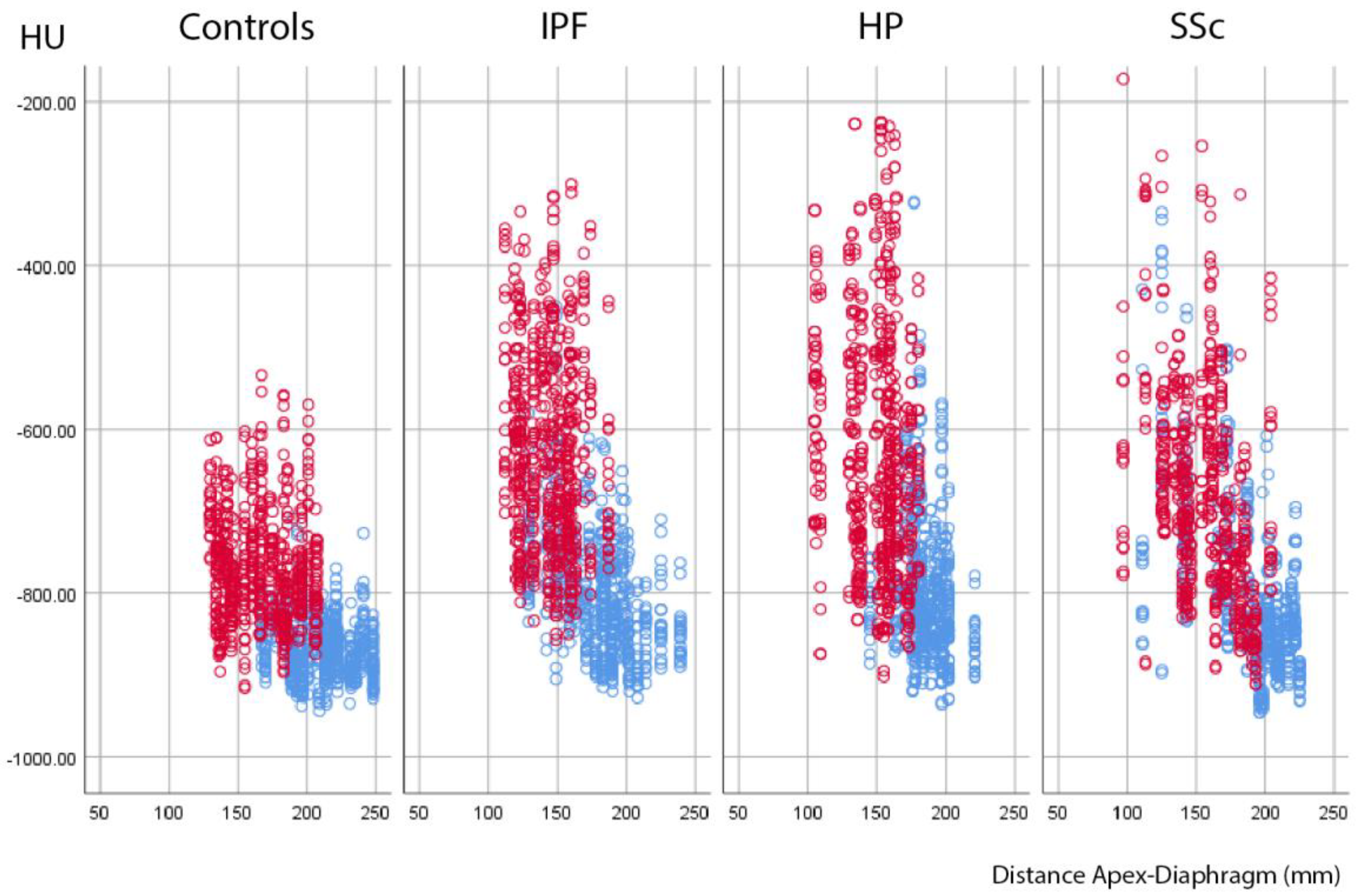
3.2. Absolute Attenuation Values
3.3. Attenuation Differences between Inspiration and Expiration
3.4. Variable Density Increases in the Lung Lobes
3.5. Expansion Measurements
3.6. Correlation between Density Increase and Expansion
3.7. Interobserver Variability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI: | Artificial intelligence |
| CT: | Computed tomography |
| CTD-ILD: | Connective tissue disease-associated ILD |
| DLCOc | Corrected diffusion capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide |
| GGO: | Ground-glass opacities |
| FEV1 | Forced first-second volume |
| FVC | Forced vital capacity |
| HP: | Hypersensitivity pneumonitis |
| HRCT: | High-resolution computed tomography |
| HU: | Hounsfield units |
| ILD: | Interstitial lung disease |
| IPF: | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| NSIP: | Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia |
| ROI: | Region of interest |
| SSc: | Systemic sclerosis |
| UIP: | Usual interstitial pneumonia |
References
- Saldana, D.C.; Hague, C.J.; Murphy, D.; Coxson, H.O.; Tschirren, J.; Peterson, S.; Sieren, J.P.; Kirby, M.; Ryerson, C.J. Association of Computed Tomography Densitometry with Disease Severity, Functional Decline, and Survival in Systemic Sclerosis-associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2020, 17, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeh, B.; Brylski, L.T.; von der Beck, D.; Seeger, W.; Krauss, E.; Bonniaud, P.; Crestani, B.; Vancheri, C.; Wells, A.U.; Markart, P.; et al. Lung CT Densitometry in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis for the Prediction of Natural Course, Severity, and Mortality. Chest 2019, 155, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosch, H.; Schaefer-Prokop, C.M.; Eisenhuber, E.; Kienzl, D.; Herold, C.J. CT protocols in interstitial lung diseases—A survey among members of the European Society of Thoracic Imaging and a review of the literature. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Myers, J.L.; Richeldi, L.; Ryerson, C.J.; Lederer, D.J.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Danoff, S.K.; Morell, F.; et al. Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, e44–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroulia, V.; Funke, M.; Zumstein, P.; Berezowska, S.; Ebner, L.; Geiser, T.; Torbica, N.; Heverhagen, J.; Poellinger, A. Increased Expiratory Computed Tomography Density Reveals Possible Abnormalities in Radiologically Preserved Lung Parenchyma in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Investig. Radiol. 2018, 53, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, V.; Hirani, N.A.; Hotchkin, D.L.; Nambiar, A.M.; Ogura, T.; Otaola, M.; Skowasch, D.; Park, J.S.; Poonyagariyagorn, H.K.; Wuyts, W.; et al. Presentation, diagnosis and clinical course of the spectrum of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 180076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salciccioli, J.D.; Marshall, D.C.; Goodall, R.; Crowley, C.; Shalhoub, J.; Patel, P.; Molyneaux, P.L. Comparison of registries of interstitial lung diseases in three European countries. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 18 (Suppl. 32), 114s–118s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyldgaard, C.; Hilberg, O.; Muller, A.; Bendstrup, E. A cohort study of interstitial lung diseases in central Denmark. Respir. Med. 2014, 108, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capobianco, J.; Grimberg, A.; Thompson, B.M.; Antunes, V.B.; Jasinowodolinski, D.; Meirelles, G.S.P. Thoracic manifestations of collagen vascular diseases. Radiographics 2012, 32, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamasco, A.; Hartmann, N.; Wallace, L.; Verpillat, P. Epidemiology of systemic sclerosis and systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 11, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehbock, B. Pulmonale Beteiligung bei Kollagenosen. Radiologe 2015, 55, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Thoracic Society; European Respiratory Society. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elicker, B.M.; Jones, K.D.; Henry, T.S.; Collard, H.R. Multidisciplinary Approach to Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis. J. Thorac. Imaging 2016, 31, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Ryerson, C.J.; Myers, J.L.; Kreuter, M.; Vasakova, M.; Bargagli, E.; Chung, J.H.; Collins, B.F.; Bendstrup, E.; et al. Diagnosis of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis in Adults. An Official ATS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, e36–e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasakova, M.; Morell, F.; Walsh, S.; Leslie, K.; Raghu, G. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Perspectives in Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magee, A.L.; Montner, S.M.; Husain, A.; Adegunsoye, A.; Vij, R.; Chung, J.H. Imaging of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 54, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varone, F.; Iovene, B.; Sgalla, G.; Calvello, M.; Calabrese, A.; Larici, A.R.; Richeldi, L. Fibrotic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Diagnosis and Management. Lung 2020, 198, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.-F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Statement: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Evidence-based Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, S.B.; Dirksen, A.; Lo, P.; Skovgaard, L.T.; de Bruijne, M.; Pedersen, J.H. Factors influencing the decline in lung density in a Danish lung cancer screening cohort. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckler, A.J.; Danagoulian, J.; Johnson, K.; Peskin, A.; Gavrielides, M.A.; Petrick, N.; Obuchowski, N.A.; Beaumont, H.; Hadjiiski, L.; Jarecha, R.; et al. Inter-Method Performance Study of Tumor Volumetry Assessment on Computed Tomography Test-Retest Data. Acad. Radiol. 2015, 22, 1393–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbach, H.; Karlinskaya, M.; Fruchter, O. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D.A.; Godwin, J.D.; Safrin, S.; Starko, K.M.; Hormel, P.; Brown, K.K.; Raghu, G.; King, T.E., Jr.; Bradford, W.Z.; Schwartz, D.A.; et al. High-resolution computed tomography in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Diagnosis and prognosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, A.C.; Meng, J.; Lynch, A.M.; Bozic, C.M.; Miller, D.; Grunwald, G.K.; Lynch, D.A. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Physiologic tests, quantitative CT indexes, and CT visual scores as predictors of mortality. Radiology 2008, 246, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jung, J.; Yoon, S.H.; Goo, J.M.; Hong, H.; Yoon, J.-H. Inspiratory Lung Expansion in Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease: CT Histogram Analyses. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhyadhom, A. On the molecular relationship between Hounsfield Unit (HU), mass density, and electron density in computed tomography (CT). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Yu, Y.; Huang, H.; Hu, Y.; Fu, S.; Wang, Z.; Shi, M.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, J.; et al. Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis Is Caused by Elevated Mechanical Tension on Alveolar Stem Cells. Cell 2019, 180, 107–121.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, D.; Gazdhar, A.; Lopez-Rodriguez, E.; Ruppert, C.; Mahavadi, P.; Günther, A.; Klepetko, W.; Bates, J.H.; Smith, B.; Geiser, T.; et al. Alveolar Derecruitment and Collapse Induration as Crucial Mechanisms in Lung Injury and Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 52, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, M.; Vašáková, M. The natural history of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, P.M.; Spagnolo, P.; Kreuter, M.; Altinisik, G.; Bonifazi, M.; Martinez, F.J.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Renzoni, E.A.; Richeldi, L.; Tomassetti, S.; et al. Progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease: Clinical uncertainties, consensus recommendations, and research priorities. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Thomson, C.C.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; Kreuter, M.; Lynch, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, e18–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.T.; Chatzkel, J.; Hewitt, M.G. Expiratory Air Trapping on Thoracic Computed Tomography. A Diagnostic Subclassification. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, J.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Rajagopalan, S.; van Moorsel, C.H.M.; van Es, H.W.; van Beek, F.T.; Struik, M.H.L.; Kokosi, M.; Egashira, R.; Brun, A.L.; et al. Predicting Outcomes in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Using Automated Computed Tomographic Analysis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.R.; Veeraraghavan, S.; Hansell, D.M.; Nikolakopolou, A.; Goh, N.S.L.; Nicholson, A.G.; Colby, T.V.; Denton, C.P.; Black, C.M.; du Bois, R.M.; et al. CT Features of Lung Disease in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: Comparison with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia. Radiology 2004, 232, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Disease | IPF | HP | SSc-ILD | Controls |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age (years) | 64.8 | 65.5 | 62.2 | 63.7 |
| Gender | F = 0 M = 15 | F = 5 M = 10 | F = 13 M = 2 | F = 6 M = 9 |
| Extent of Honeycombing | 15 ± 14.5 | 6 ± 7.8 | 11 ± 14.9 | None |
| Extent of Reticulations | 52 ± 14.2 | 42 ± 24.2 | 34 ± 15.9 | None |
| Extent of Traction-bronchiectasis | 40 ± 13.6 | 31 ± 20.1 | 21 ± 11.7 | None |
| Extent of Ground-glass Opacities | 17 ± 18.8 | 40 ± 24.5 | 20 ± 9.7 | None |
| Visual Fibrosis Score (incl. GGO) | 124 ± 35.2 | 119 ± 59.0 | 86 ± 34.7 | None |
| Visual Fibrosis Score (excl. GGO) | 107 ± 28.4 | 79 ± 44.1 | 65 ± 33.9 | None |
| FVC (L) | 2.5 ± 0.7 | 2.7 ± 0.7 | 2.4 ± 0.9 | 3.7 ± 1.1 |
| FVC % Predicted | 58.9 ± 15.5 | 70.2 ± 21.7 | 72.5 ± 27.9 | 103.3 ± 11.0 |
| FEV1 (L) | 2.1 ± 0.7 | 2.1 ± 0.5 | 1.8 ± 0.6 | 2.6 ± 0.6 |
| FEV1 % Predicted | 65.3 ± 18.6 | 71.2 ± 20.2 | 70.7 ± 26.1 | 93.5 ± 12.1 |
| DLCOc (mmol/(min*kPa) | 4.1 ± 1.3 | 4.3 ± 1.4 | 4.5 ± 1.8 | 6.3 ± 2.0 |
| DLCOc % Predicted | 45.1 ± 13.3 | 51.3 ± 17.7 | 57.3 ± 21.5 | 77.9 ± 14.0 |
| All Lobes | Upper Lobe | Middle Lobe/Lingula | Lower Lobe | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insp., HU | Exp., HU | Insp., HU | Exp., HU | Insp., HU | Exp., HU | Insp., HU | Exp., HU | |
| Controls | −872.1 ± 33.1 | −772.6 ± 64.8 | −873.3 ± 27.9 | −793.7 ± 48.6 | −889.2 ± 28.6 | −817.9 ± 47.7 | −864.5 ± 35.7 | −741.7 ± 63.6 |
| IPF | −809.4 ± 69.4 | −632.7 ± 115.8 | −838.1 ± 48.6 | −698.5 ± 82.8 | −818.4 ± 65.8 | −682.8 ± 89.7 | −788.3 ± 74.6 | −572.4 ± 111.2 |
| HP | −798.9 ± 84.1 | −628.0 ± 149.7 | −815.3 ± 85.4 | −678.5 ± 123.6 | −826.2 ± 70.3 | −700.7 ± 117.1 | −777.2 ± 83.5 | −566.2 ± 152.0 |
| SSc-ILD | −806.8 ± 95.5 | −692.5 ± 114.8 | −822.7 ± 78.9 | −723.4 ± 97.9 | −828.1 ± 76.7 | −733.1 ± 94.7 | −786.4 ± 109.0 | −653.4 ± 121.5 |
| Evaluation | Comparison | All Lobes | Upper Lobe | Middle Lobe/Lingula | Lower Lobe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control—IPF | 0.0031 | 0.0735 | 0.0002 | 0.0028 | |
| Control—HP | 0.0005 | 0.0038 | 0.0009 | 0.0007 | |
| Inspiration | Control—SSc | 0.0019 | 0.0109 | 0.0012 | 0.0015 |
| IPF—HP | 0.5580 | 0.2425 | 0.6713 | 0.6558 | |
| IPF—SSc | 0.8696 | 0.4273 | 0.6037 | 0.8365 | |
| HP—SSc | 0.6732 | 0.7049 | 0.9241 | 0.8112 | |
| Control—IPF | <0.0001 | 0.0009 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| Control—HP | <0.0001 | 0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| Expiration | Control—SSc | 0.0047 | 0.0127 | 0.0010 | 0.0069 |
| IPF—HP | 0.8743 | 0.4694 | 0.4745 | 0.9654 | |
| IPF—SSc | 0.0428 | 0.3665 | 0.0489 | 0.0303 | |
| HP—SSc | 0.0296 | 0.1062 | 0.2028 | 0.0274 | |
| Control—IPF | <0.0001 | 0.0005 | 0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| Control—HP | 0.0001 | 0.0008 | 0.0009 | 0.0001 | |
| Absolute | Control—SSc | 0.3542 | 0.2324 | 0.1301 | 0.5263 |
| Difference | IPF—HP | 0.6630 | 0.8642 | 0.5177 | 0.6510 |
| IPF—SSc | 0.0007 | 0.0160 | 0.0118 | 0.0002 | |
| HP—SSc | 0.0025 | 0.0246 | 0.0568 | 0.0011 | |
| Control—IPF | <0.0001 | 0.0017 | 0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| Control—HP | <0.0001 | 0.0003 | 0.0002 | <0.0001 | |
| Relative | Control—SSc | 0.2665 | 0.2056 | 0.1048 | 0.3482 |
| Difference | IPF—HP | 0.5942 | 0.5918 | 0.8427 | 0.5442 |
| IPF—SSc | 0.0019 | 0.0504 | 0.0143 | 0.0012 | |
| HP—SSc | 0.0003 | 0.0137 | 0.0236 | 0.0002 |
| All Lobes, HU and % | Upper Lobe, HU and % | Middle Lobe/Lingula, HU and % | Lower Lobe, HU and % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controls | −100 ± 47 14 ± 8 | −80 ± 32 10 ± 5 | −71 ± 31 9 ± 5 | −123 ± 47 17 ± 8 |
| IPF | −177 ± 79 31 ± 21 | −140 ± 54 21 ± 11 | −136 ± 62 21 ± 12 | −216 ± 79 42 ± 23 |
| HP | −171 ± 99 34 ± 31 | −137 ± 84 23 ± 20 | −126 ± 75 21 ± 18 | −211 ± 101 46 ± 37 |
| SSc-ILD | −114 ± 57 18 ± 11 | −99 ± 43 15 ± 8 | −95 ± 49 14 ± 8 | −133 ± 62 22 ± 13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wittwer, M.F.; Kim, S.-Y.; Leichtle, A.; Berezowska, S.; Guler, S.A.; Geiser, T.; Heverhagen, J.; Maurer, B.; Poellinger, A. Signs of Alveolar Collapse in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis and Systemic Sclerosis Revealed by Inspiration and Expiration Computed Tomography. BioMed 2023, 3, 471-483. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed3040038
Wittwer MF, Kim S-Y, Leichtle A, Berezowska S, Guler SA, Geiser T, Heverhagen J, Maurer B, Poellinger A. Signs of Alveolar Collapse in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis and Systemic Sclerosis Revealed by Inspiration and Expiration Computed Tomography. BioMed. 2023; 3(4):471-483. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed3040038
Chicago/Turabian StyleWittwer, Marco Fabian, Soung-Yung Kim, Alexander Leichtle, Sabina Berezowska, Sabina A. Guler, Thomas Geiser, Johannes Heverhagen, Britta Maurer, and Alexander Poellinger. 2023. "Signs of Alveolar Collapse in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis and Systemic Sclerosis Revealed by Inspiration and Expiration Computed Tomography" BioMed 3, no. 4: 471-483. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed3040038
APA StyleWittwer, M. F., Kim, S.-Y., Leichtle, A., Berezowska, S., Guler, S. A., Geiser, T., Heverhagen, J., Maurer, B., & Poellinger, A. (2023). Signs of Alveolar Collapse in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis and Systemic Sclerosis Revealed by Inspiration and Expiration Computed Tomography. BioMed, 3(4), 471-483. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomed3040038






