Residual Kidney Function and the Impact of Dialysis Modality
Abstract
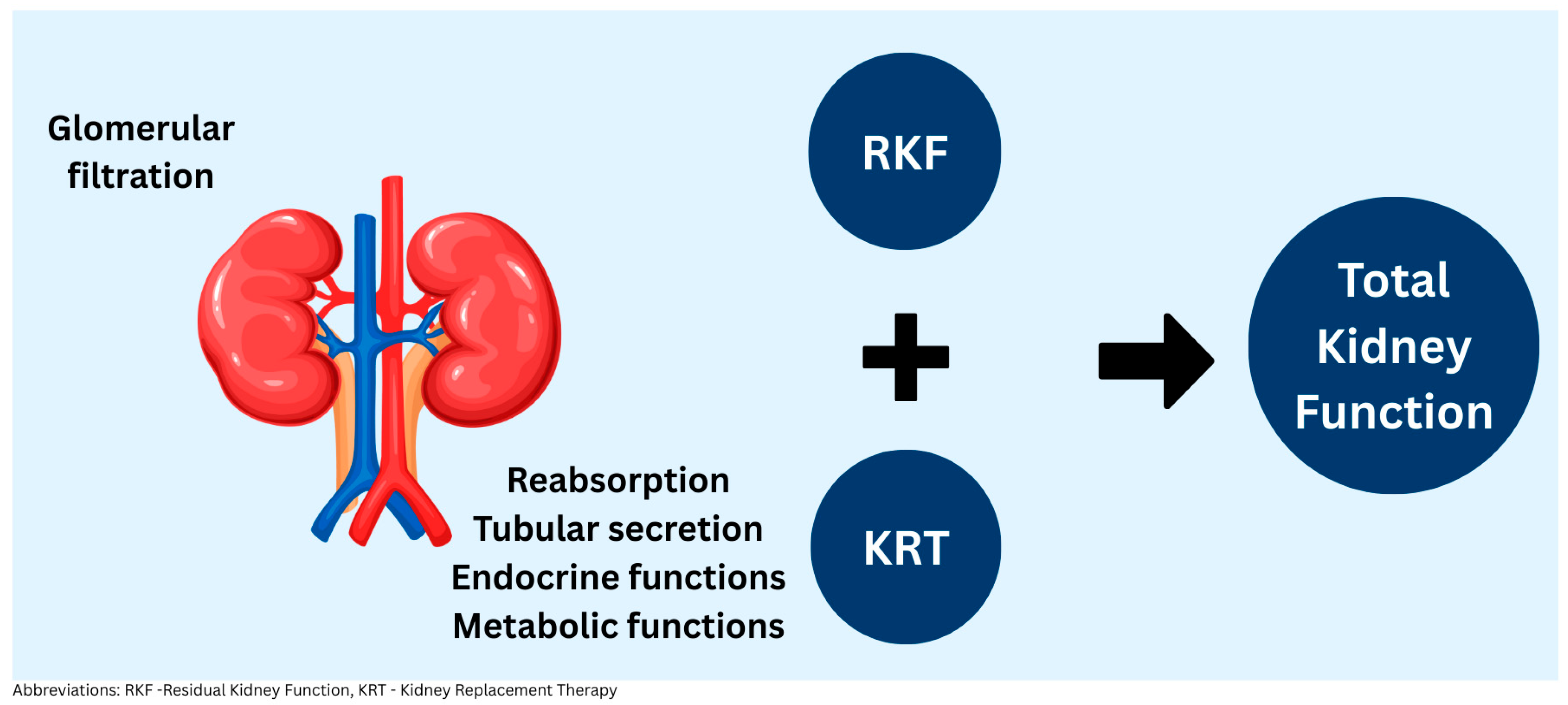
1. Residual Kidney Function Definition
2. Importance of RKF for Dialysis Patients
3. Mortality and Cardiovascular Benefits of RKF
4. RKF and Volume Management in Dialysis Patients
5. Other Benefits of RKF in Dialysis Patients
6. Approach to RKF-PD vs. HD
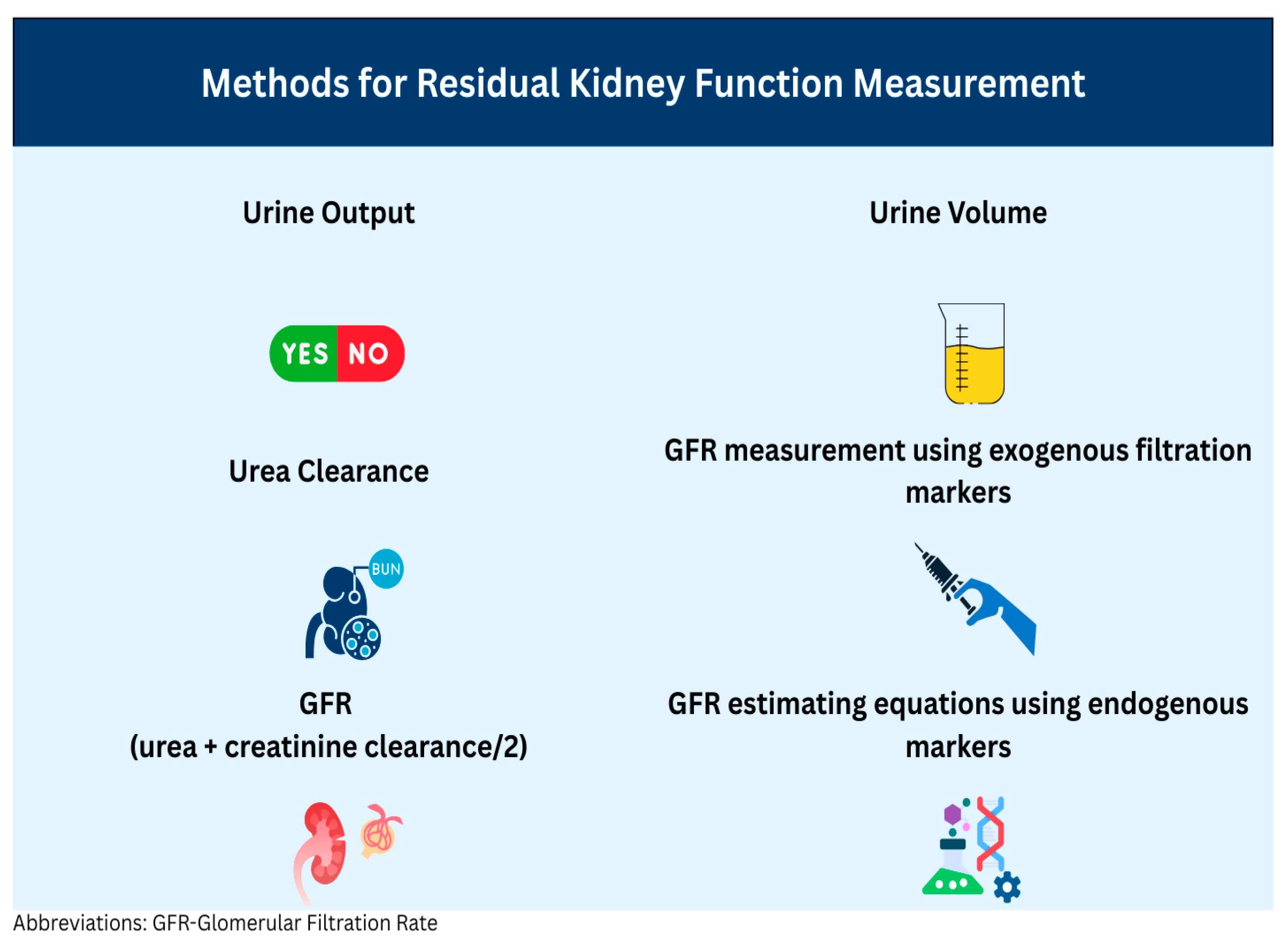
7. Methods for Residual Kidney Function Measurement
8. Influence of Dialysis Modality on Residual Kidney Function Loss
9. Factors Affecting Residual Kidney Function and Strategies for Preservation
10. Conclusions and Future Directions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shafi, T.; Levey, A.S. Measurement and Estimation of Residual Kidney Function in Patients on Dialysis. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Renal Data System. 2024 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States; National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2024.
- Chan, C.T.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Dember, L.M.; Gallieni, M.; Harris, D.C.H.; Lok, C.E.; Mehrotra, R.; Stevens, P.E.; Wang, A.Y.-M.; Cheung, M.; et al. Dialysis initiation, modality choice, access, and prescription: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosner, M.H.; Reis, T.; Husain-Syed, F.; Vanholder, R.; Hutchison, C.; Stenvinkel, P.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Cozzolino, M.; Juillard, L.; Kashani, K.; et al. Classification of Uremic Toxins and Their Role in Kidney Failure. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2021, 16, 1918–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Kazama, J.J.; Wakamatsu, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Kaneko, Y.; Goto, S.; Narita, I. Removal of uremic toxins by renal replacement therapies: A review of current progress and future perspectives. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2016, 2, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalim, S.; Wald, R.; Yan, A.T.; Goldstein, M.B.; Kiaii, M.; Xu, D.; Berg, A.H.; Clish, C.; Thadhani, R.; Rhee, E.P.; et al. Extended Duration Nocturnal Hemodialysis and Changes in Plasma Metabolite Profiles. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2018, 13, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eknoyan, G.; Beck, G.J.; Cheung, A.K.; Daugirdas, J.T.; Greene, T.; Kusek, J.W.; Allon, M.; Bailey, J.; Delmez, J.A.; Depner, T.A.; et al. Effect of dialysis dose and membrane flux in maintenance hemodialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 2010–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth-Manikowski, S.M.; Sirich, T.L.; Meyer, T.W.; Hostetter, T.H.; Hwang, S.; Plummer, N.S.; Hai, X.; Coresh, J.; Powe, N.R.; Shafi, T. Contribution of “clinically negligible” residual kidney function to clearance of uremic solutes. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2020, 35, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargman, J.M.; Thorpe, K.E.; Churchill, D.N. Relative contribution of residual renal function and peritoneal clearance to adequacy of dialysis: A reanalysis of the CANUSA study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2001, 12, 2158–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua, R.; Amato, D.; Vonesh, E.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Ramos, A.; Moran, J.; Mujais, S. Effects of increased peritoneal clearances on mortality rates in peritoneal dialysis: ADEMEX, a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2002, 13, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termorshuizen, F.; Korevaar, J.C.; Dekker, F.W.; van Manen, J.G.; Boeschoten, E.W.; Krediet, R.T. The relative importance of residual renal function compared with peritoneal clearance for patient survival and quality of life: An analysis of the Netherlands Cooperative Study on the Adequacy of Dialysis (NECOSAD)-2. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2003, 41, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termorshuizen, F.; Dekker, F.W.; van Manen, J.G.; Korevaar, J.C.; Boeschoten, E.W.; Krediet, R.T. Relative contribution of residual renal function and different measures of adequacy to survival in hemodialysis patients: An analysis of the Netherlands Cooperative Study on the Adequacy of Dialysis (NECOSAD)-2. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2004, 15, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Wal, W.M.; Noordzij, M.; Dekker, F.W.; Boeschoten, E.W.; Krediet, R.T.; Korevaar, J.C.; Geskus, R.B. Full loss of residual renal function causes higher mortality in dialysis patients; findings from a marginal structural model. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2011, 26, 2978–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, T.; Jaar, B.G.; Plantinga, L.C.; Fink, N.E.; Sadler, J.H.; Parekh, R.S.; Powe, N.R.; Coresh, J. Association of residual urine output with mortality, quality of life, and inflammation in incident hemodialysis patients: The Choices for Healthy Outcomes in Caring for End-Stage Renal Disease (CHOICE) Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 56, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obi, Y.; Rhee, C.M.; Mathew, A.T.; Shah, G.; Streja, E.; Brunelli, S.M.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Mehrotra, R.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Residual Kidney Function Decline and Mortality in Incident Hemodialysis Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2016, 27, 3758–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, A.S.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Obi, Y.; Novoa, A.; Peralta, R.A.; Streja, E.; Nakata, T.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Nguyen, D.V.; Rhee, C.M. Residual Urine Output and Mortality in a Prospective Hemodialysis Cohort. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, M.; Obi, Y.; Shafi, T.; Rhee, C.M.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Residual Kidney Function and Cause-Specific Mortality Among Incident Hemodialysis Patients. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 1989–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.J.; Coyle, D.; Lindley, E.J.; Keane, D.; Belcher, J.; Caskey, F.J.; Dasgupta, I.; Davenport, A.; Farrington, K.; Mitra, S.; et al. Bio-impedance spectroscopy added to a fluid management protocol does not improve preservation of residual kidney function in incident hemodialysis patients in a randomized controlled trial. Kidney Int. 2023, 104, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcher, J.; Coyle, D.; Lindley, E.J.; Keane, D.; Caskey, F.J.; Dasgupta, I.; Davenport, A.; Farrington, K.; Mitra, S.; Ormandy, P.; et al. Impact of the Preservation of Residual Kidney Function on Hemodialysis Survival: Results from the BISTRO Trial. Kidney360 2025, 6, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, M.K.; Naimark, D.M.; Bargman, J.M.; Vas, S.I.; Oreopoulos, D.G. Long-term blood pressure control in a cohort of peritoneal dialysis patients and its association with residual renal function. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2001, 16, 2207–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.Y.M.; Woo, J.; Wang, M.; Sea, M.M.M.; Sanderson, J.E.; Lui, S.F.; Li, P.K.-T. Important differentiation of factors that predict outcome in peritoneal dialysis patients with different degrees of residual renal function. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2005, 20, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struijk, D.G. The solution to better preservation of the peritoneal membrane still lies hidden in the solution. Perit. Dial. Int. 2015, 35, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.L.; Cho, J.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, C.D.; Park, S.H. Systemic and local impact of glucose and glucose degradation products in peritoneal dialysis solution. J. Ren. Nutr. 2013, 23, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Perl, J.; Teitelbaum, I. Prescribing high-quality peritoneal dialysis: The role of preserving residual kidney function. Perit. Dial. Int. 2020, 40, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.H.; Lee, S.C.; Ahn, S.V.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, T.H.; Moon, S.J.; Kim, B.S.; Kang, S.-W.; Choi, K.H.; et al. Reduced residual renal function is a risk of peritonitis in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2007, 22, 2653–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.T.; Chen, Y.M.; Shiao, C.C.; Hu, F.C.; Huang, J.W.; Kao, T.W.; Chuang, H.-F.; Hung, K.-Y.; Wu, K.-D.; Tsai, T.-J. Rate of decline of residual renal function is associated with all-cause mortality and technique failure in patients on long-term peritoneal dialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2009, 24, 2909–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, A.T.; Fishbane, S.; Obi, Y.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Preservation of residual kidney function in hemodialysis patients: Reviving an old concept. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 262–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, C.W. Effects of hemodialysis on cardiac function. Kidney Int. 2009, 76, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorairajan, S.; Chockalingam, A.; Misra, M. Myocardial stunning in hemodialysis: What is the overall message? Hemodial. Int. 2010, 14, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, M.A.M.; Hart, A.A.M.; Korevaar, J.C.; Dekker, F.W.; Boeschoten, E.W.; Krediet, R.T. Predictors of the rate of decline of residual renal function in incident dialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugirdas, J.T.; Greene, T.; Rocco, M.V.; Kaysen, G.A.; Depner, T.A.; Levin, N.W.; Chertow, G.M.; Ornt, D.B.; Raimann, J.G.; Larive, B.; et al. Effect of frequent hemodialysis on residual kidney function. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marants, R.; Qirjazi, E.; Grant, C.J.; Lee, T.Y.; McIntyre, C.W. Renal Perfusion during Hemodialysis: Intradialytic Blood Flow Decline and Effects of Dialysate Cooling. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2019, 30, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suda, T.; Hiroshige, K.; Ohta, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Iwamoto, M.; Kanegae, K.; Ohtani, A.; Nakashima, Y. The contribution of residual renal function to overall nutritional status in chronic haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2000, 15, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, S.; Bird, T.A.; Selkirk, S.; Gaines-Das, R.E.; Choudry, Y.; Stephenson, S.L.; John Kenny, A.; Saklatvaa, J. Fate of injected interleukin 1 in rats: Sequestration and degradation in the kidney. Cytokine 1990, 2, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bemelmans, M.H.; Gouma, D.J.; Buurman, W.A. Influence of nephrectomy on tumor necrosis factor clearance in a murine model. J. Immunol. 1993, 150, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penne, E.L.; van der Weerd, N.C.; Grooteman, M.P.; Mazairac, A.H.; van den Dorpel, M.A.; Nubé, M.J.; Bots, M.L.; Lévesque, R.; ter Wee, P.M.; Blankestijn, P.J. Role of residual renal function in phosphate control and anemia management in chronic hemodialysis patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2011, 6, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendy, A.; Abdelsalam, A.I.; Mansour, M.; Nassar, M.K. Can residual kidney function affect quality of life and cognitive function in hemodialysis patients? BMC Nephrol. 2022, 23, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Jia, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Shao, F.; Shi, Y.; Li, Z. Research on cognitive impairment and potential risk factors in peritoneal dialysis patients: An observational study. Medicine 2024, 103, e38374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Okuda, Y.; Sy, J.; Lee, Y.K.; Obi, Y.; Cho, S.; Chen, J.L.T.; Jin, A.; Rhee, C.M.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; et al. Ultrafiltration Rate, Residual Kidney Function, and Survival Among Patients Treated With Reduced-Frequency Hemodialysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, T.; Levey, A.S.; Inker, L.A.; Schwartz, G.J.; Knight, C.; Abraham, A.G.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Coresh, J. Plasma Iohexol Clearance for Assessing Residual Kidney Function in Dialysis Patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 728–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Milutinovic, J.; Cutler, R.E.; Hoover, P.; Meijsen, B.; Scribner, B.H. Measurement of residual glomerular filtration rate in the patient receiving repetitive hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 1975, 8, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Teplan, V.; Schück, O.; Nádvorníková, H. Differences in the effect of hemodialysis on the residual clearance of inulin, endogenous creatinine, and urea. Artif. Organs 1984, 8, 488–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Olden, R.W.; van Acker, B.A.; Koomen, G.C.; Krediet, R.T.; Arisz, L. Time course of inulin and creatinine clearance in the interval between two haemodialysis treatments. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 1995, 10, 2274–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Olden, R.W.; Krediet, R.T.; Struijk, D.G.; Arisz, L. Measurement of residual renal function in patients treated with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 1996, 7, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, S.K.; Halstenson, C.E.; Kasiske, B.L.; Collins, A.J. Determination of residual renal function with iohexol clearance in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 1996, 49, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sacamay, T.E.; Bolton, W.K. Use of iohexol to quantify hemodialysis delivered and residual renal function: Technical note. Kidney Int. 1998, 54, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sterner, G.; Frennby, B.; Månsson, S.; Ohlsson, A.; Prütz, K.G.; Almén, T. Assessing residual renal function and efficiency of hemodialysis--an application for urographic contrast media. Nephron 2000, 85, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjaergaard, K.D.; Jensen, J.D.; Jespersen, B.; Rehling, M. Reliability of 51Cr-EDTA plasma and urinary clearance as a measure of residual renal function in dialysis patients. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2011, 71, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.L.; Lane, C.E.; Fan, S.L.; Lamb, E.J. Estimation of residual glomerular filtration rate in peritoneal dialysis patients using cystatin C: Comparison with 51Cr-EDTA clearance. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2011, 26, 3729–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kjaergaard, K.D.; Rehling, M.; Jensen, J.D.; Jespersen, B. Reliability of endogenous markers for estimation of residual renal function in haemodialysis patients. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2013, 33, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, F.J.; Korevaar, J.C.; Dekker, F.W.; Boeschoten, E.W.; Krediet, R.T. Estimation of residual glomerular filtration rate in dialysis patients from the plasma cystatin C level. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2007, 22, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Li, R.; Zhong, Z.; Mao, H.; Fan, J.; Lin, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Yu, X. Is cystatin C a better marker than creatinine for evaluating residual renal function in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis? Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2011, 26, 3358–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Sridharan, S.; Berdeprado, J.; Vilar, E.; Viljoen, A.; Wellsted, D.; Farrington, K. Predicting residual kidney function in hemodialysis patients using serum β-trace protein and β2-microglobulin. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, E.; Boltiador, C.; Wong, J.; Viljoen, A.; Machado, A.; Uthayakumar, A.; Farrington, K. Plasma Levels of Middle Molecules to Estimate Residual Kidney Function in Haemodialysis without Urine Collection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafi, T.; Michels, W.M.; Levey, A.S.; Inker, L.A.; Dekker, F.W.; Krediet, R.T.; Hoekstra, T.; Schwartz, G.J.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Coresh, J. Estimating residual kidney function in dialysis patients without urine collection. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steubl, D.; Fan, L.; Michels, W.M.; Inker, L.A.; Tighiouart, H.; Dekker, F.W.; Krediet, R.T.; Simon, A.L.; Foster, M.C.; Karger, A.B.; et al. Development and Validation of Residual Kidney Function Estimating Equations in Dialysis Patients. Kidney Med. 2019, 1, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, S.; Akbari, A.; Brahm, G.; Dorie, J.; Tamasi, T.; Penny, J.; McIntyre, C.W. Redefining the concept of residual renal function with kidney sodium MRI: A pilot study. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2024, 39, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, A.; McIntyre, C.W. Recent Advances in Sodium Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Its Future Role in Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, P. Peritoneal dialysis and preservation of residual renal function. Perit. Dial. Int. 2009, 29, S108–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjaergaard, K.D.; Jensen, J.D.; Peters, C.D.; Jespersen, B. Preserving residual renal function in dialysis patients: An update on evidence to assist clinical decision making. NDT Plus 2011, 4, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lysaght, M.J.; Vonesh, E.F.; Gotch, F.; Ibels, L.; Keen, M.; Lindholm, B.; Nolph, K.D.; Pollock, C.A.; Prowant, B.; Farrell, P.C. The influence of dialysis treatment modality on the decline of remaining renal function. ASAIO Trans. 1991, 37, 598–604. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Lang, S.M.; Bergner, A.; Töpfer, M.; Schiffl, H. Preservation of residual renal function in dialysis patients: Effects of dialysis-technique-related factors. Perit. Dial. Int. 2001, 21, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, M.; Vonesh, E.; Churchill, D.N.; Moore, H.L.; Van Stone, J.C.; Nolph, K.D. Preservation of glomerular filtration rate on dialysis when adjusted for patient dropout. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Misra, M.; Vonesh, E.; Van Stone, J.C.; Moore, H.L.; Prowant, B.; Nolph, K.D. Effect of cause and time of dropout on the residual GFR: A comparative analysis of the decline of GFR on dialysis. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKane, W.; Chandna, S.M.; Tattersall, J.E.; Greenwood, R.N.; Farrington, K. Identical decline of residual renal function in high-flux biocompatible hemodialysis and CAPD. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moist, L.M.; Port, F.K.; Orzol, S.M.; Young, E.W.; Ostbye, T.; Wolfe, R.A.; Hulbert-Shearon, T.; Jones, C.A.; Bloembergen, W.E. Predictors of loss of residual renal function among new dialysis patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2000, 11, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jager, D.J.; Halbesma, N.; Krediet, R.T.; Boeschoten, E.W.; Le Cessie, S.; Dekker, F.W.; Grootendorst, D.C. Is the decline of renal function different before and after the start of dialysis? Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2013, 28, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocco, M.V.; Lockridge, R.S.; Beck, G.J.; Eggers, P.W.; Gassman, J.J.; Greene, T.; Larive, B.; Chan, C.T.; Chertow, G.M.; Copland, M.; et al. The effects of frequent nocturnal home hemodialysis: The Frequent Hemodialysis Network Nocturnal Trial. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecking, M.; McCullough, K.P.; Port, F.K.; Bieber, B.; Morgenstern, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Suri, R.S.; Jadoul, M.; Gesualdo, L.; Perl, J.; et al. Self-reported Urine Volume in Hemodialysis Patients: Predictors and Mortality Outcomes in the International Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS). Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 7, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethier, I.; Hayat, A.; Pei, J.; Hawley, C.M.; Johnson, D.W.; Francis, R.S.; Wong, G.; Craig, J.C.; Viecelli, A.K.; Htay, H.; et al. Peritoneal dialysis versus haemodialysis for people commencing dialysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2024, 6, CD013800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.W.; Brown, F.G.; Clarke, M.; Boudville, N.; Elias, T.J.; Foo, M.W.Y.; Jones, B.; Kulkarni, H.; Langham, R.; Ranganathan, D.; et al. Effects of biocompatible versus standard fluid on peritoneal dialysis outcomes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2012, 23, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.W.; Brown, F.G.; Clarke, M.; Boudville, N.; Elias, T.J.; Foo, M.W.Y.; Jones, B.; Kulkarni, H.; Langham, R.; Ranganathan, D.; et al. The effect of low glucose degradation product, neutral pH versus standard peritoneal dialysis solutions on peritoneal membrane function: The balANZ trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2012, 27, 4445–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htay, H.; Johnson, D.W.; Wiggins, K.J.; Badve, S.V.; Craig, J.C.; Strippoli, G.F.; Cho, Y. Biocompatible dialysis fluids for peritoneal dialysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 10, CD007554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Xu, C.; Yan, H.; Ma, J. Comparison of icodextrin and glucose solutions for long dwell exchange in peritoneal dialysis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Perit. Dial. Int. 2011, 31, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zeng, X.; Fu, P.; Wu, H.M. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers for preserving residual kidney function in peritoneal dialysis patients. Cochrane Kidney and Transplant Group, editor. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD009120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Davies, M.; Mount, P. The importance of residual kidney function in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Carlton Vic. 2018, 23, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; Li, H.; Yu, P.; Yuan, L.; Hao, C.; Chen, J.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Association of initial twice-weekly hemodialysis treatment with preservation of residual kidney function in ESRD patients. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 40, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragg-Gresham, J.L.; Fissell, R.B.; Mason, N.A.; Bailie, G.R.; Gillespie, B.W.; Wizemann, V.; Cruz, J.M.; Akiba, T.; Kurokawa, K.; Ramirez, S.; et al. Diuretic use, residual renal function, and mortality among hemodialysis patients in the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Pattern Study (DOPPS). Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 49, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Seo, Y.J.; Jeon, Y.; Jeon, Y.H.; Jung, H.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, C.-D.; Kang, S.H.; Ryu, J.-H.; et al. Expanded Hemodialysis with Theranova Dialyzer and Residual Kidney Function in Patients Starting Long-Term Hemodialysis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2025, 36, 1614–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takkavatakarn, K.; Jintanapramote, K.; Phannajit, J.; Praditpornsilpa, K.; Eiam-Ong, S.; Susantitaphong, P. Incremental versus conventional haemodialysis in end-stage kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Kidney J. 2024, 17, sfad280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Exogenous Marker | Assay | Studies | Year | Study Population (n) | Dialysis Modality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Inulin (5200 Da)
| HPLC, LC-MS/MS | Milutinovic et al. [41] | 1975 | 38 | HD |
| Teplan et al. [42] | 1984 | 20 | HD | ||
| Van olden et al. [43] | 1995 | 11 | HD | ||
| Van olden et al. [44] | 1996 | 10 | PD | ||
Iohexol (821 Da)
| HPLC, LC-MS/MS | Swan et al. [45] | 1996 | 33 | HD |
| Sacamay et al. [46] | 1998 | 10 | HD | ||
| Sterner et al. [47] | 2000 | 12 | HD | ||
| Shafi et al. [40] | 2016 | 40 | HD + PD | ||
Cr51-EDTA (339 Da)
| SPECT | Kjaergaard et al. [48] | 2011 | 24 | HD + PD |
| Carter et al. [49] | 2011 | 28 | HD | ||
| Kjaergaard et al. [50] | 2013 | 12 | HD |
| Endogenous Markers | Assay | Studies | Year | Study Population (n) | Modality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Cystatin C
| Immunonephelometric | Hoek et al. [51] | 2007 | 310 (D) + 155 (V) | HD + PD PD |
| Yang et al. [52] | 2011 | 120(D) + 40 (V) | |||
Beta 2 Microglobulin
| Immunonephelometric | Wong et al. [53] | 2016 | 191(D) + 40 (V) | HD |
| Vilar et al. [54] | 2016 | 341(D) +50 (V) | HD | ||
| Shafi et al. [55] | 2016 | 44 (D) + 826 (V) | HD + PD | ||
| Steubl et al. [56] | 2019 | 823 (D) + 826 (V) | PD | ||
Beta Trace Protein
| Immunonephelometric | Wong J et al. [53] | 2016 | 191(D) + 40 (V) | HD |
| Shafi et al. [55] | 2016 | 44 (D) + 826 (V) | HD + PD | ||
| Steubl et al. [56] | 2019 | 823 (D) + 826 (V) | PD |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mangalgi, S.; Joshi, V.; Misra, M.; Chaudhary, K. Residual Kidney Function and the Impact of Dialysis Modality. Kidney Dial. 2025, 5, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial5030043
Mangalgi S, Joshi V, Misra M, Chaudhary K. Residual Kidney Function and the Impact of Dialysis Modality. Kidney and Dialysis. 2025; 5(3):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial5030043
Chicago/Turabian StyleMangalgi, Shreepriya, Vijay Joshi, Madhukar Misra, and Kunal Chaudhary. 2025. "Residual Kidney Function and the Impact of Dialysis Modality" Kidney and Dialysis 5, no. 3: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial5030043
APA StyleMangalgi, S., Joshi, V., Misra, M., & Chaudhary, K. (2025). Residual Kidney Function and the Impact of Dialysis Modality. Kidney and Dialysis, 5(3), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial5030043





