Abstract
Background: Thrombotic microangiopathies (TMAs) can be induced by drugs. Recent works have indicated proteasome inhibitors, including carfilzomib, as a possible new causative agent. Although the physiopathology and management of carfilzomib-induced TMA are still unknown, eculizumab seems to be efficient. Results: We report a clinical case of TMA during carfilzomib treatment for multiple myeloma, possibly triggered by a concomitant influenza infection, suggesting a multi-hit process. Histologic analysis of the kidney biopsy proved renal TMA. Eculizumab allowed rapid and long-lasting renal and hematologic recovery. We enriched our work with a systemic review of published cases of carfilzomib-induced TMA treated by eculizumab. Twelve patients were included, all of whom presented acute renal failure and nine of them required hemodialysis. Eculizumab led to TMA resolution in eleven patients and complete renal recovery with hemodialysis withdrawal for seven of them within a month. One patient died from multiple myeloma progression. Two patients presented inter-current viral infection. Soluble complement fragment Bb and C5b9s were found in two patients and genetic benign variant of Factor H (CFH3–CFH1) in four. Conclusion: Our results suggest that eculizumab is effective in carfilzomib-induced TMA, which could support its inclusion as a treatment option. Further studies are required to clarify its physiopathology, complement role, and management.
1. Introduction
Thrombotic microangiopathies (TMAs) are life-threatening syndromes, with various etiologies requiring prompt and efficient treatment [1,2,3]. Drug-induced TMAs (DITMAs) consist of secondary TMAs related to medication exposure, occurring through two main pathogenic mechanisms: either an immune reaction or a toxic effect. The first occurs within hours or days of drug exposure and can be proven by drug-dependent antibody detection, while a toxic dose-dependent mechanism usually arises after long-lasting use, suggesting a cumulative dose toxicity [1,2,4,5]. In particular, the pathophysiology of toxic dose-related DITMAs is unclear and many hypotheses have been proposed, including endothelial cell dysfunction, increased secretion of von Willebrand factor, decreased production of prostacyclin and nitric oxide, and dysregulation of the complement pathway [2,4]. Many other factors may lead to TMAs, including drug molecular properties, individual genetic susceptibility, and potential triggers such as infections [1,2]. Approximately 75 drugs have been described as TMA inductors, the most classical of which are gemcitabine, anti-VEGF, calcineurin inhibitors, and mitomycin [2,4,5,6]. Recent works have described DITMA development with proteasome inhibitors (PIs).
PIs are able to block the ubiquitin–proteasome reaction and especially the NF-κB molecular downstream pathway and VEGF production. Although phases II and III of both bortezomib and carfilzomib studies have not identified TMAs as possible adverse drug events, clinical evidence of TMA onset during PI employment has been described [7,8,9]. Indeed, more than 65 DITMA clinical cases have been associated with carfilzomib use [7,10], among which only a few patients have benefited from empiric and successful eculizumab treatment [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20].
While the physiopathology and management of DITMAs are still poorly understood, complement alternative pathway activation seems to play a key role in the pathogenic process, and complement blockage therapies could be indicated.
Because of the rising use of carfilzomib, it is important to underline its potential severe side effects and suggest possible treatments for clinical practice.
Herein, we present a case of histologically proven TMA (CFZ TMA), induced by carfilzomib, which was successfully treated with eculizumab. We then review and discuss published cases of carfilzomib-induced CFZ TMA treated with eculizumab.
2. Case Report
A 48-year-old woman was diagnosed in 2013 with IgG-Kappa multiple myeloma (MM). She underwent induction chemotherapy with VTD (bortezomib–thalidomide–dexamethasone), followed by an autologous bone marrow transplantation. Upon disease progression, she received lenalidomide, followed by a pheno-allogenic stem cell transplantation three years later. Despite these treatments, she rapidly developed a serologic relapse, which was treated with daratumumab–pomalidomide–dexamethasone. In 2020, bone lytic progression required radiation and she was initiated on carfilzomib–dexamethasone, achieving complete remission. At the time of presentation, she had completed 20 cycles of carfilzomib maintenance therapy over almost two years, with a cumulative dose of 7761 mg. Her glomerular filtration rate was >60 mL/min/1.73 m2.
Five days after the last injection, the patient presented to the emergency department with complaints of new onset of an impaired general condition, incoercible vomiting, and flu syndrome with hyperthermia. Initially, she presented grade 4 thrombocytopenia (13 g/L) and grade 1 anemia (12 g/dL) with a schistocyte count at 1.5%, as well as anuric acute kidney failure KDIGO III requiring hemodialysis at day 1 from hospital admission, orienting toward thrombotic microangiopathy. Importantly, her blood pressure was normal.
The following day, her anemia and thrombocytopenia worsened (Hg 6 g/dL and PLT 15 g/L) (Figure 1), schistocytes elevating up to 4.3%, with high LDH of 1653UI/L and undetectable haptoglobin, with a negative Coombs test. Normal activity of ADAMTS13 at 43% and a PLASMIC score at 0% ruled out thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). Stool cultures and PCRs were negative for shiga-like toxin activity bacteria, which did not support a typical hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) diagnosis. Functional exploration of alternative complement protein (CD46 activity, Factor H, Factor I, anti-FH, and anti-FI antibodies) disorders was normal. Autoimmune explorations of anti-nuclear factor, anti-DNA antibodies, ANCA, and anti-phospholipid antibody dosage were negative. Complement C3 and C4 levels were normal. Moreover, B12 vitamin level was normal, excluding the pseudo-TMA diagnosis.
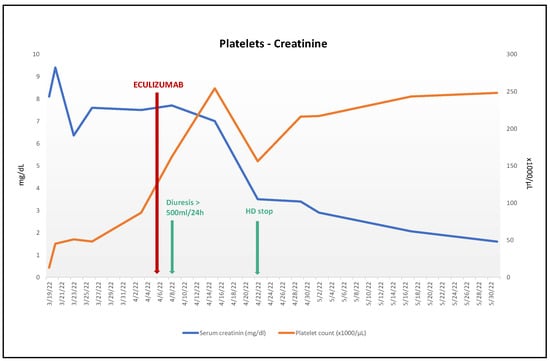
Figure 1.
Evolution platelets count and serum creatinine after eculizumab treatment. Hematologic response with platelet count normalization without relapses. Renal response with creatinine almost normalized, regular diuresis recovery, and hemodialysis weaning off.
Concurrently, laboratory tests revealed hemophagocytic lympho-histiocytosis syndrome with increased ferritin (13,600 g/L), hypertriglyceridemia (4.42 mmol/L), liver function alteration, and clear macrophagic activation signs on the bone marrow aspiration (6% of monocyte vacuolized mature cells with cytoplasmic extensions and hemophagocytosis by macrophages on platelets, erythroblasts, and polynuclear neutrophil cells), resulting in a H-score of 96%. Serum and urine protein electrophoresis with immunofixation did not identify any monoclonal protein, and there was no plasmacytoid infiltration on the bone marrow aspiration.
The microbiological investigations revealed an influenza-A-H1N1v upper respiratory tract infection, without major symptoms. Concomitantly, the patient developed self-limited colitis, complicated by an Enterococcus faecalis bacteremia. A colonoscopy showed colonic inflammatory petechiae, while anatomopathological examination found nonspecific lymphocytic infiltrate, without signs of vascular thrombosis on the biopsy.
The hemophagocytic lympho-histiocytosis syndrome progressively faded after treatment of the infectious episode, while the MAHA features and AKI lasted.
The hypothesis of a graft-versus-host disease was raised, but there was no evidence of any other GVHD clinical, biologic, or histologic signs, and the patient was no longer receiving calcineurine, which could have been a TMA drug inductor.
Complement alternative pathway functional tests were normal and research of genetic complement mutations in the blood sample could not be performed because of a previous allogenic stem cell transplantation.
Upon persistence of AKI and TMA, CFZ-induced TMA was suspected, with a viral and/or bacterial infection as the causal trigger. Because of the persistent anuric KDIGO III AKI without any sign of recovery from the CFZ suspension, 900 mg/w of eculizumab for four weeks, followed by 1200 mg every two weeks, was started 19 days after hospital admission, with previous anti-meningococcal prevention. Within two days of the first dose, the hemolytic parameters, platelet count, and renal function improved, and dialysis was stopped 15 days after starting eculizumab (Figure 1).
After platelet normalization, a kidney biopsy was performed, and one glomerulus was apoplectic. The other revealed endothelial swelling and nonspecific ischemic glomerular lesions. We observed mesangiolysis in a few glomeruli, interstitial edema, and acute tubular injury. Several arterioles showed intimal mucoid edema with narrowed lumina. The immunohistochemical analysis was positive for C3 depositions on the arteriolar walls, with a nonsignificant glomerular C4d marking, sustaining the diagnosis of TMA (Figure 2). C5b9s staining on the frozen sample did not reveal arteriolar- or glomerular-specific staining.
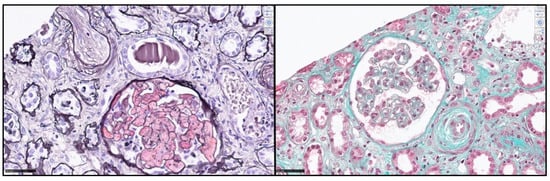
Figure 2.
Kidney biopsy: Light microscopic features of thrombotic microangiopathy during carfilzomib use. Left: Apoplectic glomerulus with myxoid intimal oedema in interlobular arteriol (Jones stain). Right: Mesangiolysis, subendothelial clear space, and myxoid intimal oedema (Trichrome stain). Scale bar 50 µm.
Follow-up at 12 weeks after eculizumab initiation indicated that the patient remained off dialysis, with a serum creatinine dose of 108 µmol/L (GFR 54 mL/min/1.73 m²), normalized levels of hemoglobin and platelet count, and no sign of myeloma relapse nor eculizumab side effects. Carfilzomib is currently still in suspension.
3. Systematic Review
3.1. Materials and Methods
The PubMed and Google Scholar databases were searched from their inception up to 16 May 2022 for relevant studies, limited to English-language articles. The search strategy was based on the following keywords: “Thrombotic microangiopathy AND carfilzomib” and “Thrombotic microangiopathy AND carfilzomib AND eculizumab”. A systematic review was conducted and reported in compliance with the PRISMA statement, and the case report adhered to the CARE guidelines.
Articles were selected for review if their title or abstract suggested that they reported individual patients or group data on patients with a diagnosis of carfilzomib-induced TMA treated with eculizumab. The selected articles were analyzed independently by two reviewers by reading the full texts. Articles mentioning eculizumab but not using it were excluded, as well as previous reviews and posters.
We collected data regarding patients’ age, sex, underlying malignant blood disorder, previous treatments received, time from carfilzomib to DITMA and total dose of carfilzomib received, peak serum creatinine and hemodialysis treatment, time from DITMA diagnosis to eculizumab use, and outcomes.
The results are reported as the median and interquartile (IQR) and percentages, as appropriate. Statistical analyses were performed using Excel.
3.2. Results
The search strategy resulted in 200 records; following the removal of duplicates, 171 abstracts were screened. Of these, 157 were declared not suitable and 14 full-text articles were assessed for eligibility. Four further articles were excluded (two posters and two previous reviews). Our systematic review thus included 10 articles (Figure 3).
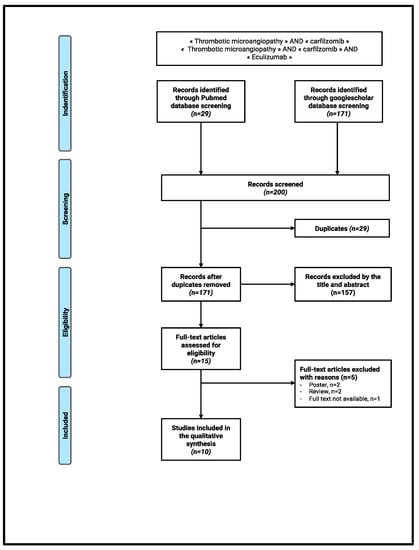
Figure 3.
Flow chart.
All reported patients among the included articles presented TMA with severe renal injury after carfilzomib exposition and were treated with eculizumab. None of the articles described histological findings from a kidney biopsy. The results are described in Table 1.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the reported clinical case and the 12 reviewed reported cases. Legend. A: adriamycin/doxorubicin; ASCT: autologous stem cells transplantation; C: cisplatin; CFZ: carfilzomib; CR: complete response; Cy: cyclophosphamide; D: dexamethasone; Dara: daratumumab; E: etoposide; Flu: fludarabine; HD: hemodialysis; K: carfilzomib; M: melphalan; MM: multiple myeloma; MTX: methotrexate; NA: not available; P: pomalidomide; PR: partial response; R: lenalidomide; SCr: serum creatinine; T: thalidomide; TMA: thrombotic microangiopathy; V: bortezomib.
Altogether, 12 patients were included, 5 (42%) females and 7 (58%) males, with a median age of 48 years. All patients presented a malignant plasma cell disorder: nine (75%) multiple myeloma, two plasmacytoma, and one plasma cell leukemia.
All patients presented features of microthrombotic hemolytic anemia (MAHA) and consumption thrombopenia associated with acute oligo-anuric renal failure KDIGO III, requiring hemodialysis for nine (75%) patients. The median serum creatinine was 5.4 mg/dL, ranging from 3.2 to 14.4 mg/dL. In all cases, TTP diagnosis was eliminated by normal ADAMTS13 activity.
Complement functional activity explorations were measured in seven (58%) patients, finding a normal activity for six of them, except for one case [19]. Interestingly C5b9s and Bb fragments were found to be elevated in two cases [15,16], reflecting a complement overactivation. When described, genetic complement pathway research found heterozygous CFHR3–CFHR1 deletions in four patients [14,18], orienting toward a genetic susceptibility to uncontrolled complement alternative pathway activation, in which case the diagnosis of atypical HUS, possibly triggered by carfilzomib introduction, was suggested.
Time from carfilzomib therapy exposure and TMA onset considerably differed among the cases: TMA was diagnosed within a few days after the first cycle for only two patients, orienting toward an immune-mediated mechanism, while for eight (67%) patients, TMA occurred between the 2nd and 10th cycles, and for two patients, it occurred after long-standing carfilzomib utilization (18th and the 22nd cycles), suggesting a dose-dependent toxicity. When the total cumulative dose was available (three patients), the median dose received was 6628 mg (ranging between 329 and 7761 mg).
Similar to our patient, Rassner et al. described a TMA case that appeared after CFZ exposure and during septic status with influaenzae H3N2 throat infection and Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteremia and speculated a possible CFZ-induced TMA triggered by infectious stimulus.
Darwin et al. reported a patient treated with allogenic stem cell transplantation, complicated by cutaneous and ocular GHVD controlled by sirolimus administration. Likewise, with our patient, their case did not present any clinical sign of GVHD relapsing during the TMA episode. In this case, mTOR inhibition could be involved in TMA.
Plasmapheresis therapy was employed for eight patients, justified by the suspicion of a TTP, and was discontinued after normal ADAMTS13 activity results.
All patients were empirically treated with eculizumab, an anti-C5a monoclonal antibody, with different injection protocols, the most frequent of which was 900 mg/w for four weeks followed by 1200 mg every two weeks injections. Eculizumab treatment was successful for 11 (92%) patients, with hematological recovery (TMA resolution) and renal function recovery, enabling hemodialysis withdrawal within a median period of one month for seven of the nine (89%) patients on kidney replacement therapy. Unfortunately, data regarding renal evolution were not always described, but at least 7 of 10 patients recovered a completely normal renal function. Only one patient [18] did not respond after five eculizumab injections and died after 154 days of follow-up, due to multiple myeloma progression and sepsis.
Eculizumab was successfully stopped for four patients within three months of treatment (one case after three months [16], one case after five administrations [17], and two cases after four administrations [19]). Information regarding the reintroduction of Carfilzomib was not available for all described cases.
4. Discussion
This is the first reported case of CFZ TMA, with glomerular injury proven by histological and immunohistochemical analyses successfully treated with eculizumab.
In our case, the pathogenesis of TMA could have been the result of complement activation and direct endothelial damage. Understanding the mechanism of CFZ TMA and identifying triggers and predisposing factors is likely to have significant therapeutic impact.
Our patient developed TMA after several cycles of carfilzomib treatment (20th cycle), which was infrequent among the reviewed cases (Table 1), associated with the onset of an influenza-A-H1N1 infection and an Enterococcus faecalis bacteremia. Viral infections have been suspected to be a trigger in other cases of CFZ TMA (rhinovirus, parainfluenza B, and influenza) [19,21,22]. The observation suggests that viral infection could represent a second hit that triggers acute disease [23,24,25], especially in late-onset CFZ TMA.
In a retrospective review including all types of TMA addressed to a clinical apheresis unit, infection was suspected to act as an acute trigger in 69% of patients with preexisting predisposing factors of TMA (autoimmune disease, drug, genetic, predisposition) [26]. In a recent retrospective analysis in four French hospitals, infection was present at the onset of TMA in 27% of patients, of which 3% were reported to have an influenza infection [27].
Pathogenesis could be the consequence of inflammation-induced damage to platelets or the endothelium [28], or infection-induced release of DNA and histones, stimulating thrombosis and causing cytotoxicity [24]. More specifically for influenza infection, neuraminidase has been demonstrated to cause erythrocyte fusion and hemolysis, activation of platelets, and generation of thrombin by exposing the Thomsen–Friedenreich antigen on the glomerular endothelium, erythrocytes, and platelets, leading to TMA [29,30,31]. Thus, in light of the concomitant CFZ exposure and due to its barely asymptomatic presentation, influenza infection has been deemed as a trigger.
CFZ TMA could also be driven by complement activation, explaining the effectiveness of eculizumab. Interestingly, Bb fragments and C5b9s were found to be elevated in one and four cases, respectively [15,16], reflecting complement alternative pathway activation. Unfortunately, genetic analyses were not carried out in most reported cases. Heterozygous CFHR3/CFHR1 deletions, which are considered a common benign variant in proteins regulating complement activation, were reported in three patients with CFZ TMA [14,18]. It is unclear whether these variants could be predisposed to a genetic susceptibility for uncontrolled complement activation over a multi-hit process, including carfilzomib toxic effect and intercurrent infection.
A few other mechanisms may be involved in CFZ TMA. Indeed, carfilzomib is an irreversible inhibitor of the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway, which results in VEGF inhibition that could induce endothelial damage [8]. Moreover, inhibition of proteasome activity leads to accumulation of unfolded proteins, which causes endoplasmic reticulum stress, resulting in oxidative stress and oxidative hemolysis [30,32,33]. Extracellular heme may then conduct to TMA by activation of a complement alternative pathway and endothelial and platelet activation [34,35].
Jindal et al. published a CFZ TMA review of 17 patients [36], 2 of which had concomitant viral infections (rhinovirus and parainfluenza) and 13 of which did not receive eculizumab for treatment. Of these 13 patients, 4 reached complete renal remission in a median of 60 days (4–270), 5 reached partial renal remission in a median of 42 days (3–56), and 3 patients did not experience renal recovery. One patient died from TMA complications. Our systematic review highlights the effectiveness of eculizumab for CFZ TMA. Indeed, 11 (92%) of the 12 patients were successfully treated with eculizumab within an average of eight days, with hematological recovery (TMA resolution) and renal function recovery enabling hemodialysis discontinuation within a median time of a month in seven out of nine (89%) patients (Table 1). Eculizumab use seems to lead to more frequent and faster responses.
It should be noted that our patient presented a partial hematological response even before eculizumab introduction (Figure 1), possibly due to carfilzomib interruption and sepsis treatment. Meanwhile, a renal response was obtained only after eculizumab introduction, with recovery of diuresis in 3 days and withdrawal of hemodialysis within 15 days. Although there is no consensual administration regimen, eculizumab appears to be effective in the management of CFZ TMA. Even its late introduction appears to be beneficial, with a favorable outcome reported after a 17-day delay between TMA onset and eculizumab introduction [17].
Similar to our case, Yui et al. [9] showed a complete platelet recovery in 5 of 11 patients within 21 days after IP discontinuation, which could indicate a direct toxic effect of IP on platelets.
Another interesting feature about our case is colitis. Some intestinal TMAs have been reported [37,38,39,40,41], usually characterized by edema, redness, and ulcers in endoscopy and fibrin insulations in the vascular walls, endothelial swelling, and fresh microthrombi leading to lumen obliteration in histopathology, which does not match our patient’s data. Gastrointestinal toxicity is also one of the most common adverse events reported with PIs [42] and a few cases of bortezomib-induced colitis have been published [43,44,45]. Some pre-clinical studies have also suggested bortezomib-induced gastrointestinal damage related to a proinflammatory cytokine secretion [46,47,48]. No case of carfilzomib-induced colitis has been reported thus far to the best of our knowledge. Although no definitive conclusions can be drawn from our case, this association should be further investigated.
Our study has some limitations. Unfortunately, C5b9s analysis could not be performed in our case and genetic research is not informative because of allogenic stem cell transplantation. Data about complement testing were lacking in most of the reported cases. Some data were also missing from our review due to the retrospective nature of our analysis. Finally, the cases included in our review were limited in number, and the presence of unpublished cases cannot be excluded as far as treatment failure with eculizumab is concerned.
However, we hereby provide the first reported case of TMA histologically proven and treated by eculizumab, developed during carfilzomib use. It occurred after a long-lasting carfilzomib exposure, which is infrequent in the reported cases (Table 1) and suggests a sustained toxic mechanism. The viral infection trigger, simultaneous colitis, and rapid evolution under eculizumab point to a multi-hit process, characterized by complement overactivation. Our review of the cases with CFZ TMA treated with eculizumab allows summarizing the knowledge on this rare occurrence.
Our results suggest that eculizumab is effective in carfilzomib-induced TMA, which could support its inclusion as a treatment option. Further studies are required to clarify its physiopathology, complement role, and management.
5. Conclusions
We report the first case of histologically proven TMA associated with long-term carfilzomib treatment and presumably triggered by influenza infection, successfully treated with eculizumab. The review of the literature suggested a favorable response of carfilzomib-induced TMA to treatment with eculizumab. This indirectly suggests an activation of a complement alternative pathway. This finding remains to be confirmed by further studies. Because of the increasing use of CFZ, it is crucial to assess its side effects, including TMA.
Author Contributions
F.P.: Medical care of the patient. Preparation, creation of the published work, specifically writing the initial draft. Conducting a research and investigation process, specifically performing the experiments, or data/evidence collection. Preparation, creation, and presentation of the published work, specifically visualization/data presentation. C.Q.: Medical care of the patient. Preparation, creation and/or presentation of the published work, specifically writing the initial draft. Conducting a research and investigation process, specifically performing the experiments, or data/evidence collection. M.B.: Medical care of the patient. Preparation, creation of the published work, specifically writing the initial draft. B.J.-J.: Histologic data and interpretation. A.-C.G.: Medical care of the patient and responsible for the hematologic care of the patient. V.C.: Medical care of the patient, HUS referent of Caen University Hospital, and responsible of the nephrological care of the patient. A.B.: Medical care of the patient. Preparation, creation of the published work, specifically writing the initial draft. Conducting a research and investigation process, specifically performing the experiments, or data/evidence collection. Development or design of the methodology; creation of models. Preparation, creation of the published work, specifically visualization/data presentation. Preparation, creation of the published work by those from the original research group, specifically critical review, commentary, or revision—including the pre- or post-publication stages. V.G.: Medical care of the patient. Preparation, creation of the published work, specifically writing the initial draft. Conducting a research and investigation process, specifically performing the experiments, or data/evidence collection. Development or design of the methodology; creation of models. Preparation, creation of the published work by those from the original research group, specifically critical review, commentary, or revision—including the pre- or post-publication stages. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors declare that there was no funding support.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki 2008, and approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Caen University Hospital (file number 3499).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor of this journal on request.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article. Laboratory testing data are available on Caen University Hospital Software, but publication of this dataset could compromise patient privacy. The literature review’s data are available on analyzed articles from the PubMed and Google Scholar databases.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the patient for consent, as well as the whole medical and paramedical team.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare having no competing interests.
List of Abbreviations
| ADAMTS13 | a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, member 13 |
| ANCA | anti-neutrophilic cytoplasmatic antibody |
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| ASCT | autologous stem cell transplantation |
| CFZ | carfilzomib |
| D | dexamethasone |
| GFR | glomerular filtration rate |
| GVHD | graft-versus-host disease |
| HD | hemodialysis |
| Hg | hemoglobin |
| IQR | interquartile |
| KDIGO | kidney disease improving global outcomes |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| PIs | proteasome inhibitors |
| PLT | platelet |
| SCr | serum creatinine |
| TMA | thrombotic microangiopathy |
| T | thalidomide |
| TTP | thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura |
| VEGF | vascular epithelial growth factor |
| V | Velcade®, bortezomib |
References
- Coppo, P. Microangiopathies thrombotiques secondaires. Rev. Méd. Intern. 2017, 38, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masias, C.; Vasu, S.; Cataland, S.R. None of the above: Thrombotic microangiopathy beyond TTP and HUS. Blood 2017, 129, 2857–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, J.N.; Nester, C.M. Syndromes of thrombotic microangiopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1847–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, L.M.P.; Sridharan, M.; Sethi, S. Complement in Secondary Thrombotic Microangiopathy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Nouri, Z.L.; Reese, J.A.; Terrell, D.R.; Vesely, S.K.; George, J.N. Drug-induced thrombotic microangiopathy: A systematic review of published reports. Blood 2015, 125, 616–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, P.J.; Sipols, J.M.; George, J.N. Drug-associated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2001, 8, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, B.E.; Venner, C.P.; Reece, D.E.; Kew, A.K.; Lalancette, M.; Garland, J.S.; Shepherd, L.E.; Pater, J.L.; Hay, A.E. Drug-induced Thrombotic Microangiopathy with Concurrent Proteasome Inhibitor Use in the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma: A Case Series and Review of the Literature. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020, 20, e791–e800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodhi, A.; Kumar, A.; Saqlain, M.U.; Suneja, M. Thrombotic microangiopathy associated with proteasome inhibitors. Clin. Kidney J. 2015, 8, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yui, J.C.; Van Keer, J.; Weiss, B.N.; Waxman, A.J.; Palmer, M.B.; D’Agati, V.D.; Kastritis, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Vij, R.; Bansal, D.; et al. Proteasome inhibitor associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, E348–E352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terao, T.; Tsushima, T.; Miura, D.; Ikeda, D.; Fukumoto, A.; Kuzume, A.; Tabata, R.; Narita, K.; Takeuchi, M.; Matsue, K. Carfilzomib-induced thrombotic microangiopathy is underestimated in clinical practice: A report of five patients and literature review. Leuk Lymphoma 2022, 63, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moliz, C.; Gutiérrez, E.; Cavero, T.; Redondo, B.; Praga, M. Eculizumab as a treatment for atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome secondary to carfilzomib. Nefrología (Engl. Ed.) 2019, 39, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwin, A.; Malpica, L.; Dhanoa, J.; Hashmi, H. Carfilzomib-induced atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome: A diagnostic challenge and therapeutic success. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e239091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosain, R.; Gill, A.; Fuqua, J.; Volz, L.H.; Kessans Knable, M.R.; Bycroft, R.; Seger, S.; Gosain, R.; Rios, J.A.; Chao, J.-H. Gemcitabine and carfilzomib induced thrombotic microangiopathy: Eculizumab as a life-saving treatment. Clin. Case Rep. 2017, 5, 1926–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portuguese, A.J.; Lipe, B. Carfilzomib-induced aHUS responds to early eculizumab and may be associated with heterozygous CFHR3-CFHR1 deletion. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 3443–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasco, M.; Martínez-Roca, A.; Rodríguez-Lobato, L.G.; Garcia-Herrera, A.; Rosiñol, L.; Castro, P.; Fernández, S.; Quintana, L.F.; Cibeira, M.T.; Bladé, J.; et al. Complement as the enabler of carfilzomib-induced thrombotic microangiopathy. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 193, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutani, D.; Assal, A.; Mapara, M.Y.; Prinzing, S.; Lentzsch, S. Case Report: Carfilzomib-induced Thrombotic Microangiopathy With Complement Activation Treated Successfully with Eculizumab. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020, 20, e155–e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiez, C.; Pica, G.M.; Bally, S. Syndrome hémolytique et urémique lié au carfilzomib: Évolution favorable sous éculizumab. Néphrol. Thér. 2020, 16, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyer, C.W.; Bange, E.M.; Skuli, S.; Hsu, M.; Lin, J.; Cuker, A.; Cohen, A.D.; Garfall, A. Carfilzomib-Induced Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome in a Patient With Heterozygous CFHR3/CFHR1 Deletion Treated with Eculizumab. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 21, e845–e849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassner, M.; Baur, R.; Wäsch, R.; Schiffer, M.; Schneider, J.; Mackensen, A.; Engelhardt, M. Two cases of carfilzomib-induced thrombotic microangiopathy successfully treated with Eculizumab in multiple myeloma. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheggi, V.; Merilli, I.; Cesaroni, E.; Alterini, B. Carfilzomib-induced thrombotic microangiopathy: A case report. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2022, 28, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ooi, M.; Lim, S.F.; Lin, A.; Lee, J.; Nagarajan, C.; Phipps, C.; Lee, Y.S.; Grigoropoulos, N.F.; Lao, Z.; et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy during carfilzomib use: Case series in Singapore. Blood Cancer J. 2016, 6, e450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, C.D.; Hoelscher, Z.C.; Tchakarov, A.; Kala, J. Influenza-induced thrombotic microangiopathy in a patient with cancer on proteasome inhibitor: A diagnostic dilemma. CEN Case Rep. 2022, 11, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, T.; Fan, X. A second hit for TMA. Blood. 2012, 120, 1152–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Schatzberg, D.; Wagner, D.D.; Lämmle, B. Circulating DNA and myeloperoxidase indicate disease activity in patients with thrombotic microangiopathies. Blood 2012, 120, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes da Silva, R. Viral-associated thrombotic microangiopathies. Hematol./Oncol. Stem Cell Ther. 2011, 4, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, K.W.; Pollock, K.G.J.; Young, D.; Catlow, J.; Green, R. Infection Frequently Triggers Thrombotic Microangiopathy in Patients with Preexisting Risk Factors: A Single-Institution Experience. J. Clin. Apher. 2010, 25, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoreau, B.; von Tokarski, F.; Bauvois, A.; Bayer, G.; Barbet, C.; Cloarec, S.; Mérieau, E.; Lachot, S.; Garot, D.; Bernard, L.; et al. Infection in Patients with Suspected Thrombotic Microangiopathy Based on Clinical Presentation. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujii, N.; Nogami, K.; Yoshizawa, H.; Hayakawa, M.; Isonishi, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Shima, M. Influenza-associated thrombotic microangiopathy with unbalanced von Willebrand factor and a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with a thrombospondin type 1 motif, member 13 levels in a heterozygous protein S-deficient boy. Pediatr. Int. 2016, 58, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitzan, M.; Zieg, J. Influenza-associated thrombotic microangiopathies. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018, 33, 2009–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, E.E.; Mannava, S.; Bagati, A.; Bianchi-Smiraglia, A.; Nair, J.R.; Moparthy, K.; Lipchick, B.C.; Drokov, M.; Utley, A.; Ross, J.; et al. Mitochondrial thioredoxin reductase regulates major cytotoxicity pathways of proteasome inhibitors in multiple myeloma cells. Leukemia 2016, 30, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubovic, E.; Miljkovic, P.; Zivic, S.; Jovancic, D.; Kostic, G. Hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with novel influenza A H1N1 infection. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2011, 26, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fribley, A.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, C.Y. Proteasome Inhibitor PS-341 Induces Apoptosis through Induction of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Reactive Oxygen Species in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 9695–9704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopal, R.; Bennett, R.; Liang, J.; Royle, G. High dose carfilzomib proteasome inhibition induces anemia by oxidative hemolysis: A case series of 8 patients from a single centre. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, E215–E216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frimat, M.; Tabarin, F.; Dimitrov, J.D.; Poitou, C.; Halbwachs-Mecarelli, L.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Roumenina, L.T. Complement activation by heme as a secondary hit for atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood 2013, 122, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumenina, L.T.; Rayes, J.; Lacroix-Desmazes, S.; Dimitrov, J.D. Heme: Modulator of Plasma Systems in Hemolytic Diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, N.; Jandial, A.; Jain, A.; Lad, D.; Prakash, G.; Khadwal, A.; Nada, R.; Sethi, J.; Ahluwalia, J.; Malhotra, P. Carfilzomib-induced thrombotic microangiopathy: A case based review. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Ther. 2020; ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- El-Bietar, J.; Warren, M.; Dandoy, C.; Myers, K.C.; Lane, A.; Wallace, G.; Davies, S.M.; Jodele, S. Histologic Features of Intestinal Thrombotic Microangiopathy in Pediatric and Young Adult Patients after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015, 21, 1994–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narimatsu, H.; Kami, M.; Hara, S.; Matsumura, T.; Miyakoshi, S.; Kusumi, E.; Kakugawa, Y.; Kishi, Y.; Murashige, N.; Yuji, K.; et al. Intestinal thrombotic microangiopathy following reduced-intensity umbilical cord blood transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2005, 36, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Komeno, Y.; Ogawa, S.; Ishida, T.; Takeuchi, K.; Tsujino, S.; Kurokawa, M.; Aoki, K.; Kanda, Y.; Chiba, S.; Motokura, T.; et al. Ischemic colitis as a manifestation of thrombotic microangiopathy following bone marrow transplantation. Intern Med. 2003, 42, 1228–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nishio, M. Small intestinal thrombotic microangiopathy following kidney transplantation diagnosed by balloon-assisted enteroscopy. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2021, 34, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunius, C.; Büttner-Herold, M.; Bertz, S.; Schiffer, M.; Buchholz, B. Isolated thrombotic microangiopathy of the small intestine in a patient with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome—A case report. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stansborough, R.L.; Gibson, R.J. Proteasome inhibitor-induced gastrointestinal toxicity. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2017, 11, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogales Rincón, O.; Huerta Madrigal, A.; Merino Rodriguez, B.; González Asanza, C.; Cos Arregui, E.; Menchén Fernández-Pacheco, P. Rectal bleeding and diarrhea caused by bortezomib-induced colitis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 33, 753–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siniscalchi, A.; Tendas, A.; Ales, M.; Fratoni, S.; Cupelli, L.; Dentamaro, T.; Scaramucci, L.; Giovannini, M.; Caravita, T.; Santeusanio, G.; et al. Bortezomib-related colon mucositis in a multiple myeloma patient. Support Care Cancer 2009, 17, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.J.; Min, C.K.; Lee, D.G.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.W.; Min, W.S.; Kim, C.-C.; Kim, M.; Park, G.; Kim, Y. Pseudomembranous Colitis following Bortezomib Therapy in a Myeloma Patient. Acta Haematol. 2007, 117, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Wilkins, D.E.C.; Anver, M.R.; Sayers, T.J.; Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A.; Blazar, B.R.; Welniak, L.A.; Murphy, W.J. Differential effects of proteasome inhibition by bortezomib on murine acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD): Delayed administration of bortezomib results in increased GVHD-dependent gastrointestinal toxicity. Blood 2005, 106, 3293–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritts, T.A.; Hungness, E.S.; Hershko, D.D.; Robb, B.W.; Sun, X.; Luo, G.J.; Fischer, J.E.; Wong, H.R.; Hasselgren, P.-O. Proteasome inhibitors induce heat shock response and increase IL-6 expression in human intestinal epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2002, 282, R1016–R1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghouzali, I.; Azhar, S.; Bôle-Feysot, C.; Ducrotté, P.; Déchelotte, P.; Coëffier, M. Proteasome inhibitors exacerbate interleukin-8 production induced by protease-activated receptor 2 in intestinal epithelial cells. Cytokine 2016, 86, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).