Abstract
The emergence of COVID-19 has evolved into a global pandemic, causing an unprecedented public health crisis marked by unprecedented levels of morbidity never seen in the recent past. Considerable research efforts have been made in the scientific community to establish an optimal method to identify severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infections and to understand the induced immune response. This review examined the development of serological tests during the COVID-19 pandemic, considering the factors affecting sensitivity and specificity, which are key to promote an efficient vaccination strategy for public health. The market has witnessed the introduction of various serological tests for the detection of SARS-CoV-2, such as the chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA), which emerged as a powerful and rapid tool to monitor the antibody response before and after vaccination or infection. Therefore, developing serological tests by studying antibody trends and persistence is essential for creating long-term strategies. Our analysis underscores the multifaceted applications of serological tests in pandemic management with a focus on the critical insights they provide into antibody dynamics that help in managing the ongoing pandemic and shaping future public health initiatives, providing a basis for optimizing the future response to viral threats.
1. Introduction
Coronaviruses are a group of enveloped viruses with a large single-stranded positive RNA genome ranging in size from 26 kb to 32 kb [1]. They belong to the Coronaviridae family, order Nidovirales, and are classified into four genera: α, β, γ, and δ coronaviruses (CoV). α- and β-CoVs infect mammals, γ-CoVs infect avian species, and δ-CoVs infect both mammals and aves. Among the coronaviruses infecting mammals, seven are known to infect humans, including α-CoVs HCoV-229E and NL63 and β-CoVs HCoVOC43, HCoV-HKU1, MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2. The last three coronaviruses are of zoonotic origin and spread throughout the population through close contact. The estimated mean reproduction numbers (R0) of the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 and the following delta and omicron variants were 2.79, 5.08, and 9.5, respectively [2]. To date, the omicron variant BA.2.86 represents the dominant circulating variant [3]. BA.2.86 carries several mutations in the spike protein that confer to BA.2.86 a high immune evasion capability, although its infecting efficiency in vitro is low [4]. However, additional mutations acquired during transmission could increase BA.2.86 infectivity [5,6]. A BA.2.86 Genome analysis demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2 is very similar to two SARS-like bat CoVs, bat-SL-CoVZC45 and bat-SL-CoVZXC21, compared to SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV [5,6]. At the genome level, SARS-CoV-2 is approximately 88% identical to bat-SL-CoVZC45 and 87.23% identical to bat-SL-CoVZXC21 [3]. Lower levels of identity are observed with SARS-CoV (~79%) and MERS-CoV (~50%) [7].
The SARS-CoV-2 genome encodes four major structural proteins within the 3′ end of the genome: the spike (S), membrane (M), envelope (E), and nucleocapsid (N) proteins. The S protein mediates adhesion to host–cell surface receptors, resulting in fusion and subsequent viral entry. The M protein is the most abundant and defines the shape of the viral envelope. The E protein is the smallest of this group and participates in viral assembly and development. The N protein is the only one that binds to the RNA genome and is involved in viral assembly and growth [2].
The S protein is a homotrimer transmembrane glycoprotein on the viral surface and is composed of two functional subunits: the S1 and S2 subunits. The receptor binding domain (RBD) present in S1 identifies and binds to angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE 2) present on the host surface, while the S2 subunit anchors the S protein to the membrane to mediate fusion [8]. The S protein is a key target for neutralizing antibodies (Abs), which are produced either through natural infection or vaccination, highlighting its critical role in vaccine development and diagnostic assays. Vaccines administered during the world vaccine campaign were developed based on the RBD [9,10]. The RBD, in turn, includes two structural domains: the core, which has five highly conserved antiparallelβ strands, and external subdomains, which are dominated by the loop. Both are stabilized by the disulfide bond. The receptor binding motif (RBM), defined by a loop and α helices, is located between the antiparallel β4 and β7 strands. The RBM contains most of the binding sites for SARS-CoV-2 and ACE-2, providing information on potential antiviral compounds and antibody targets [10]. Understanding the conformational transitions of the spike protein, specifically the “up” and “down” states, helps to decipher the infectivity and involvement of the host receptor [2].
The nucleocapsid protein (N) is the other multifunctional primary protein in SARS-CoV-2. As a structural component, the N protein engages in complex interactions with genomic RNA, contributing significantly to virion assembly, transcription efficiency, and the initiation of RNA synthesis during the early stages of infection. It has a multifaceted role in viral pathogenesis, including the stabilization of the complex between the membrane protein and the nucleocapsid, thus improving the efficiency of virus transcription and assembly [11]. Its implication in viral pathogenesis is exemplified by studies that demonstrate protection against lethal infection with anti-N monoclonal Abs [12]. Some serological assays are performed based on the detection of anti-N Abs [13], while others rely on anti-S Abs [14].
This narrative review describes the serological tests developed during the pandemic to diagnose SARS-CoV-2 infection and/or the immune response induced by vaccination.
Search Strategy
Biology, structure, serological assay validation, and vaccine development were considered in studies found in bibliographical databases and web search engines, such as PubMed, the National Library of Medicine, the World Health organization (WHO), and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The research for this narrative review was conducted using the following keywords: SARS-CoV-2, COVID-19, COVID-19 assay, anti-N antibodies, anti-S antibodies, S-RBD, RBD, SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, SARS-CoV-2 OR COVID-19 AND serological assay, SARS-CoV-2 OR COVID-19 AND immune response, SARS-CoV-2 OR COVID-19 AND method validation. All of the included studies used serological assays with IVD marking to assure their reliability.
Titles and abstracts were used to filter the articles in the databases. The exclusion criteria were the use of biomolecular docking and outdated information.
2. Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2: Immunoglobulins as Useful Markers of Infection
The diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection relied mainly on RT-PCR performed on nasal and throat swabs and cycle threshold (Ct) values [7]. Coronavirus infections induce neutralizing and non-neutralizing antibody responses as well as catalytically active antibodies for COVID-19; however, the scientific interest was focused on neutralizing antibodies due to vaccine development and the break of the virus infection. Given the unknown rate of asymptomatic infections, there has been a pressing need for a serological diagnosis to determine the real number of infections. This information is essential to define the case fatality rate and determining the scale and duration of social lockdowns [7].
Immunoglobulins play an important role in the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in serum. The activation and differentiation of B cells into plasma cells, which secrete antibodies (Abs), are initiated by a series of immunological events that culminate in antibody production. Generally, anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgA Abs increase sharply in response to infection, and this result could significantly increase the sensitivity of the COVID-19 diagnosis when combined with molecular tests. Most serological assays rely on IgM and IgG detection, although IgA plays an important role in mucosal immunity [2].
Anti-SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing Abs defend the host by binding to specific antigens in the virus, deactivating its entry into the host cell; moreover, it activates the phlogistic process and the immune response [15].
The highest levels of anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulins usually occur in the second and third weeks of infection, as shown in Figure 1, for IgM, IgG, and IgA [13,16,17]. The level of IgG shows whether a putative immune response against the virus has developed (at least 14 days after contact); however, the presence of IgG does not guarantee immunity over time. In addition, more in-depth tests are necessary to exclude/confirm that the infection is in progress. The IgM assay instead provides information on a possible recent infection at least 10 days before sample collection.
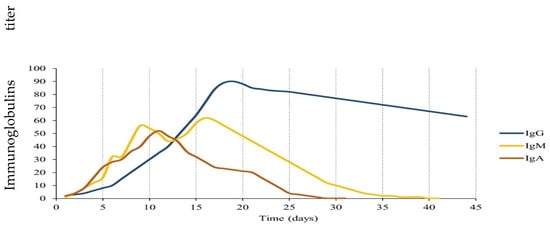
Figure 1.
Kinetics of anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulins G (IgG), A (IgA), and M (IgM) [13,18].
IgAs are secreted immunoglobulins whose level provides information on a possible infection that occurred in a very recent period. Most IgAs are secreted as dimers in mucosal tissues, where they represent the first line of the immune response against pathogen adhesion. They have recently been investigated as salivary biomarkers in patients with COVID-19 [18]; however, their half-life (and, therefore, their presence in the blood) is limited to a few days.
IgG Abs, including IgGs against S and N proteins, persist for several months in most individuals; however, they gradually decrease to minimum levels after reaching the immunological peak [19]. In patients with severe COVID-19, a stronger antibody response has been reported with higher levels and longer persistence of the IgM, IgG, and IgA immunoglobulins [20,21].
Several studies analyzed the kinetics of anti-SARS-CoV-2 Abs over a period (Figure 1). The three Ig classes, IgM, IgA, and IgG, increase rapidly after the onset of symptoms, and their increase appears to be already significant from the first days after the onset of symptoms. The simultaneous measurement of IgM/IgA and IgG may be useful, especially in the early stage of infection [20,21].
The early production of IgA has been confirmed by a study carried out on 82 hospitalized patients, followed by the synthesis of IgM and IgG. In addition, this study evaluated the level of IgA in relation to the severity and duration of symptoms [13].
In general, at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, IgA detection was used both as a guide to contain the spread of infection and for rapid diagnosis.
However, on 12 September 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) published the authorization for the use of the antigen test, using the antigen–antibody interaction principle, for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection [6]. The antigen test, based on lateral flow test methodology, shows a lower sensitivity than RT-PCR, while its specificity is generally high. It can detect cases with a high viral load, for instance, pre-symptomatic or early symptomatic cases (up to five days or with a RT-PCR cycle threshold of <25 cycles), which are responsible for a significant number of transmissions. Furthermore, the antigen test is easy to perform and takes about 15 min to obtain results. Due to its features, the antigen test quickly replaced serology tests for the rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection [22].
2.1. Serological Tests
In the current pandemic, reliable serological tests have been key elements of the public health policy, initially to control the spread of the disease and then as a tool to monitor vaccination campaigns to gradually return to normality [23]. In addition, serological diagnostic tests are increasingly being used to better understand the incidence of COVID-19, assess the immunity status of the population, and identify individuals who were previously infected or vaccinated [24].
Serological tests are based on the detection of specific antibodies produced by plasma cells during the humoral response to SARS-CoV-2 in order to neutralize and prevent the further spread of the virus.
Studies on patients with COVID-19 enabled the characterization of the RBD antigenic map, leading to the identification of major specific antigenic sites towards which the antibody is directed, improving the understanding of the humoral immune response against SARS-CoV-2 [25].
2.1.1. Detection Methods
Currently, several serological assays are available on the market for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and they are distinguished into two generations.
Table 1 reports the classification of serological tests by the type of detection.

Table 1.
Serological assay [Abs: Antibodies; N: Nucleocapsid; S: Spike; RBD: Receptor Binding Domain; RLU: Relative Luminescence Unit; TAT: Turn Around Time].
2.1.2. Immunochromatographic Enzyme Immunoassay
The immunochromatographic enzyme immunoassay is a rapid serological assay performed in a card for the qualitative determination of IgM and IgG against SARS-CoV-2. It uses chromatographic technology with colloidal gold as a solid phase for the qualitative determination of Abs to SARS-CoV-2 in human serum, plasma, or whole blood [26]. Since it is portable, it can be used at the point of care.
2.1.3. Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay
An electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA) is a quantitative method for the measurement of antigens or antibodies based on the change in the electrochemiluminescence signal (ECLIA) following immunoreaction. An ECLIA employs electrochemical compounds capable of generating light electrochemically, facilitated by the cyclic reaction of oxidative reduction. This process involves species generated at the electrode undergoing a high-energy electron transfer reaction, leading to the formation of excited states that emit light. Unlike the chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) (Section 2.1.4 below), an ECLIA does not require the use of external light sources. In the context of COVID-19, it is a useful screening tool. It can detect the total Abs against the S or N antigen.
2.1.4. Chemiluminescence Immunoassay
A chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) is a test that combines chemiluminescence techniques with immunochemical reactions and is used for the detection and analysis of antigens, antibodies (Abs), enzymes, drugs, and more. In chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassays, an enzyme such as horseradish peroxidase (HRP) is used to label an antigen or antibody. Following the immunoreaction, luminol, as a luminescent substrate, emits light through a reduction or oxidative reaction facilitated by the enzyme-labeled immunoreacting complex and the luminescent reagent. The antigen or antibody concentration is determined by measuring the intensity of the luminescence in relative luminescence units (RLUs). A CLIA is typically a semiquantitative laboratory assay that utilizes plasma or serum samples. A variation of this test, known as the chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay, employs magnetic, protein-coated microparticles. In the context of COVID-19, this test may be useful for the detection of multiple types of Abs, including IgG, IgM, and IgA.
2.1.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a rapid and sensitive method for the evaluation and quantification of an antigen using an enzyme-labeled antibody. The general ELISA protocol is described below.
Ninety-six-well plates are coated with specific antigens or antibodies to bind to the corresponding Abs or antigen of the sample. After the wells are washed to remove all unbound sample material, a blocking buffer is added to prevent nonspecific binding. In the second washing step, the unbound conjugate is removed. The sample containing the target analyte is then added and incubated, followed by another washing step. An enzyme-conjugated detection antibody is added to bind to the target and then washed again. A substrate solution is added, and the enzyme catalyzes a reaction that produces a measurable color change. The immune complex, formed through the substrate, gives a color or fluorescent reaction product. The intensity of this product is proportional to the amount of specific Abs/antigen in the sample.
An ELISA can be qualitative or quantitative, strictly dependent on the laboratory. These tests typically employ whole blood, plasma, or serum samples from patients. The assay involves coating a plate with a viral protein of interest, such as the spike protein. Patient samples are then incubated with the protein, and if antibodies against the viral protein are present, they bind together. The resulting antibody–antigen immune complex can be detected using anti-Fc antibodies, which produce a color or fluorescent readout. In the context of COVID-19, these assays commonly test for patient antibodies, including IgG and IgM.
2.2. The Evaluation of Serological Tests
The parameters used to evaluate the performance of diagnostic tests are sensitivity and specificity. Sensitivity measures the true positive rate of the serological test, while specificity measures the true negative rate of the serological test. A highly sensitive serological test will identify almost everyone who has the disease and will generate a few false negative results, while a highly specific serological test will correctly exclude almost everyone who does not have the disease and will generate a few false positive results.
Sensibility is the ability of the test to detect the disease agent or host response to the infectious agent (i.e., Abs) when it is truly present, while specificity is the ability of the test to correctly return a negative result when the disease or host response is absent [10].
Sensitivity and specificity data from studies demonstrate that commercially available serological tests present significantly different performances. Ghaffari et al. reported on the discrepancies between the claimed performance and those measured in the daily routine for the marketed serological assays [11]. Anyhow, the sensibility and the specificity, as well as the cross-reactivity, can vary when using different assays and methods.
Differences in the diagnostic assay performance could be partially explained by differences in target antigens (N and S), as described in the following paragraphs.
2.2.1. Anti-Nucleocapsid Antigen Tests
The most used antigens in the available serological assays are as follows: N protein, S protein, or protein S subunits (RBD). Whatever method is used, the nature of the antigen is important, considering that the detection of Abs directed against the S protein, or its subunits, is more likely to have neutralizing activity and would better describe the immunization state [27,28]. According to these observations, Nuccetelli and Pieri obtained better results when using assays based on the presence of both N and S proteins [13,29]. Anti-N Abs are useful for monitoring a natural infection; instead, anti-S Abs that can neutralize virus entry into host cells are used for monitoring the response to the vaccine [30]. Furthermore, the S1 or receptor binding domain regions of the spike protein (S-RBD) are more specific than the N protein [31].
Another possible cause of the differences in the performance of serological assays could be the detection time. The presence of Abs can be revealed in the patient’s sera within days after the onset of symptoms. Studies on COVID-19 suggest that seroconversion, when antibody levels become detectable in the blood, can occur even days after the viral load reaches its peak [6]. Therefore, serological tests would be less effective in the early stages of COVID-19.
Ghaffari et al. confirmed that serological tests perform better at later stages of the disease when higher levels of IgG and IgM are present in the blood [11].
Pieri and coworkers estimated the precision of a new chemiluminescent immunoassay for the detection of anti-SARSCoV2 IgG and IgM. The study was carried out on three different cohorts of patients: a control group and patients with SARS-CoV-2 with early and late infection times [32]. The results show high sensitivity and specificity for IgM for the new assay and the usefulness of IgM in the first phases of infection.
2.2.2. Anti-Spike and Anti-S-RBD Antigen Tests
As it is known, coronaviruses use the homotrimeric spike glycoprotein (comprising the S1 and S2 subunits in each spike monomer) inserted into the envelope to bind to their cellular receptors; the interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and the ACE-2 cell receptor is a critical step for SARS-CoV-2 to enter target cells. In particular, the virus binds to the ACE-2 receptor with high affinity through the specific receptor binding domain (RBD) of the S protein [33].
In this sense, human anti-S-RBD IgG is directed against the RBD; therefore, since the RBD is the primary target of SARS-CoV-2 within subunit S1, these immunoglobulins can disrupt the interaction between S-RBD and the ACE-2 receptor. Therefore, anti-S-RBD Abs could prevent the virus from entering and infecting a cell by neutralizing or inhibiting its biological effect (Figure 2). However, it is not known whether these responses are associated with protection against subsequent infections [24].
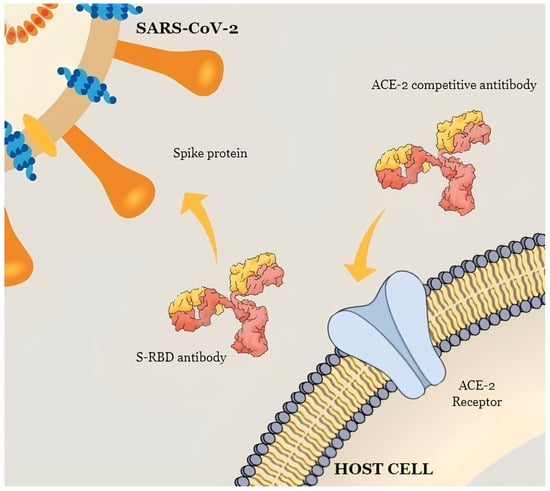
Figure 2.
A schematic illustration of the mechanism that shows the neutralizing activity of anti-S-RBD IgG and ACE-2 competitive Abs.
Several studies reported that S-RBD Abs binds with high affinity to the ACE-2 receptor, completely preventing virus–host cell interaction. Other studies investigating the performance of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) described the neutralization power of these Abs, which could have therapeutic applications [27,34].
In some studies, Abs levels were found to be correlated with symptomatology [20,35]. Hospitalized patients exhibiting severe symptoms showed higher levels of S-RBD IgGs compared to non-hospitalized patients with mild to moderate symptoms. It may be inferred that the observed response after six months in hospitalized patients has led to the development of memory and immune defense following natural infection. Nonetheless, the progression in non-hospitalized patients remains unclear, particularly regarding reinfection [28].
A large Italian observational study [24] evaluated the level of anti-S-RBD IgG after natural infection, vaccination, and vaccination after recovering from SARS-CoV-2 infection. This study found that the anti-S-RBD IgG levels were significantly lower in patients who recovered from COVID-19 than in vaccinated subjects, both with and without previous SARS-CoV-2 infection. Age, adverse effects of vaccination, and sex were independent predictors of the anti-S-RBD IgG levels among all vaccinated subjects. Specifically, females and subjects developing adverse effects showed the highest levels of Abs, while older subjects showed the lowest levels. Finally, a significant decrease in the anti-S-RBD IgG levels occurred rapidly. Interestingly, the rate of decrease was not influenced by age or sex.
The value of serological assays has resulted in the widespread availability of commercially available kits. Even so, current anti-S protein assays exhibit high variability in clinical practice, likely attributed to the differences in neutralizing activities. The need for assay standardization has driven the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to adopt the first international standard (IS) of the WHO for anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulin [20] to harmonize the evaluation of the immune response after natural infection or vaccination, using BAU/mL as a reference value. The international standard is based on a pool of human plasma from convalescent patients, which is lyophilized in vials, with an assigned unit of 250 international units (IU) per vial for neutralizing activity. For binding tests, a unit of 1000 binding antibody units (BAUs) per mL can be used to compare tests that detect the same immunoglobulin class with the same specificity (e.g., anti-IgG receptor domain, anti-N IgM, etc.). The international standard, thanks to the accurate calibration of tests to an arbitrary unit, reduces inter-laboratory variation, creating a common language for data reporting.
In a study, a head-to-head comparison of six commercially available anti-SARS-CoV-2 serological tests was carried out, which confirmed the effect of the WHO’s IS in reducing the variability of the results using BAU/mL. The average agreement among the methods for positive/negative results assessed by Cohen’s Kappa was almost perfect (κ = 0.820), better than the average of the correlation coefficients (ρ = 0.786) [22].
In conclusion, immunity to SARS-CoV-2 is provided through the contribution of B and T cell populations, but even if immunological memory can be maintained over time in the absence of measurable serum Abs levels, serological assays could be used as surrogates to determine the protection against infection and vaccine-induced immunity to SARS-CoV-2. Since the S protein constitutes the main target of all current vaccines, serological assays are increasingly geared toward using this protein or parts of it; the S protein is likely to be the target of neutralizing Abs, particularly the RBD.
2.2.3. Neutralizing Antibody Assays
The detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies (NT) is a critical step in assessing immunity against COVID-19. These antibodies effectively mimic the virus–host interaction, leveraging the specific ACE2-RBD protein interaction to prevent the binding of the viral spike domain RBD to the ACE2 cell surface receptor [36] (Figure 2).
Usually, NT abs tests employ a competitive immunoassay that mimics the natural virus–host interaction by blocking the highly specific ACE2-RBD protein interaction using surrogate virus-neutralizing antibodies. In the presence of surrogate virus-neutralizing antibodies, this crucial binding is inhibited due to the competitive action of these antibodies with RBD antigens. This method allows for the quantitative determination of SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus-neutralizing antibodies in human serum or plasma, which is essential for evaluating the immune response [37,38,39,40]. Most neutralizing antibody assays are built as described above, though some can also target the N-terminal domain (NTD) of the S protein. These NTD antibodies freeze the S protein and inhibit its conformational changes in the active form [41].
In natural infections, most patients develop varying levels of NT Abs between 2 and 3 weeks post-infection [42], with detectable responses lasting up to 1 year [39]. The peak NAb response depends on the disease severity, with severe cases showing higher titers, which are good predictors of survival [40,43,44,45]. This may be due to prolonged B cell receptor stimulation or increased interferon type I (IFN-I) production during severe disease [46]. Furthermore, the booster vaccine dose has been shown to significantly enhance the immune response, leading to increased levels of both binding and neutralizing antibodies [39,47]. On the other hand, the emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants has presented a challenge, as some variants can evade the neutralizing antibody response elicited by vaccines [38]. While virus-neutralizing antibodies are widely considered a correlate of protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection, uncertainties remain regarding which immune components provide the best protection. Nonetheless, pathogen-neutralizing antibodies are generally recognized as protective against most vaccine-preventable infections, and virus-neutralizing IgG has demonstrated protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection [48,49].
2.3. International Guidelines for the Use of Serological Assays
The WHO, as the first leading health organization, since the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic, has issued significant recommendations on the use of serological tests, acknowledging their importance as a tool for surveillance in the population. Initially, the use of a serological assay was limited to the detection of SARS-CoV-2 positivity; its application has evolved alongside the progression of the pandemic, being used to determine immunological status, assess the risk of reinfection, and evaluate fatality [50].
The public health value of serological testing has been recognized by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), including their value in understanding COVID-19 immunity and in providing patient care in a clinical setting. Positive serological results could indicate infection whether the test was performed after a week from the illness onset and with no positive molecular test. Serology testing also helps in confirming COVID-19-related complications. Furthermore, the serosurvey is a valuable method to differentiate natural infection from vaccination by measuring antibodies against the target proteins [25,51].
In contrast, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the CDC strongly discourage the use of serology tests to assess the strength and duration of immunity after COVID-19 vaccination. Furthermore, these organizations advise against relying on serological tests to determine the need for vaccination in people who have not yet received the COVID-19 vaccine [51].
3. The Persistence and Duration of the Humoral Immune Response
In the current COVID-19 pandemic, the duration of serological responses and the trend in antibody titers over time have been crucial concerns.
The level of Abs, as well as its duration, has been shown to be associated with protection against infection, reinfection, and/or severe symptoms, but there is still no agreement on the duration of protection against COVID-19 achieved by vaccine, natural infection, or reinfection [20,35,52]. To explore this point, there are many parameters to consider. First is the differences in the vaccines administered, also considering that different vaccines were administered to different age groups. Then, individual immune responses must be considered. In addition, the vaccine-induced immune response may be different from that stimulated by viral infection or after reinfection. In fact, the current vaccination strategies differ from natural infection in a variety of ways, including the method of generating or introducing viral antigens into the body, the site of exposure, and the presence of adjuvants [32,36,53]; Abs titers can differ between a vaccinated subject and a subject who was naturally infected. Moreover, misclassifications can occur in the Abs titer due to the inherent inaccuracy of serological tests [54].
Numerous recent studies have provided data on the duration of immunity; however, a definitive and unambiguous response has yet to be provided.
The primary infection develops high levels of anti-SARS-CoV-2 Abs in 90% of patients, which remain detectable for months, although they reduce over time [55]. Data from the literature reveal a heterogeneous antibody response, highlighting the variability between individuals and the dependence of Abs production on the severity of the disease (asymptomatic, mild, moderate, or severe) [20]. However, recent works demonstrated circulating Abs persisting for 5 to 11 in convalescent patients [56].
Furthermore, a population-based study on the longevity of SARS-CoV-2 antibody seroprevalence revealed that nucleocapsid antibody positivity based on IgG assays increased to 90% within the first month after infection and showed linear decay afterward, declining to 65% around 10 months [57].
Most studies have found that naturally occurring Abs due to SARS-CoV-2 infection usually last between 3 and 6 months, with few studies reporting persistence of up to 11 months [58].
It seems reasonable that the IgG antibody response after COVID-19 infection increases for months after infection and that the duration of the antibody response is long-lasting, reasonably up to 1 year. Those who had a previous COVID-19 infection are expected to retain the Abs beyond 1.5 years; however, it should be considered that the rate of decline can vary by age, body mass index, smoking, and the severity of the disease. Although immune responses can vary for different pathogens and between individuals, reports in the literature demonstrate that anti-SARS-CoV-2-Ab kinetics follows a relatively normal pattern of high levels that peak shortly after the onset of symptoms, followed by a gradual decrease in the following months [59].
Concerning SARS-CoV-2-specific natural antibodies (NAbs), most patients with COVID-19 developed NAbs in the convalescent phase of infection with a peak titer between 10 and 15 days after the onset of the disease, remaining stable thereafter. However, the NAb levels were variable, with about 30% of patients who did not develop high NAb titers after COVID-19 infection [60].
Furthermore, studies have identified variations with weaker immune responses in asymptomatic and mild cases compared to cases with more severe symptoms [61,62]. Although the anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody response can be long lasting, the level of neutralizing antibodies is related to the severity of symptoms [35,60,61,63]. The first report on antibody longevity published in June 2020 showed that 40% of asymptomatically infected individuals lost their antibody titers over a 2-month period [64].
The data available in the literature for vaccinated patients show a decrease in antibody levels after the immunological peak (after 21 days for Pfizer-BioNTech, and after 2 months for ChAdOx1 nCoV19), while stabilization in the antibody levels occurs from the fourth month. However, a common fact reported is that the antibody levels obtained with the ChAdOx1 nCoV19 vaccine were lower than that obtained with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Moreover, heterologous vaccination resulted in an effective antibody response. Indeed, the homologous vaccination results, referring to the observed circulating levels of S-RBD Abs, show a significant increase even after 1 month. Three months after booster administration, the heterologous antibody levels continued to be significantly higher than that with Pfizer-BioNTech and/or ChAdOx1 nCoV19. Therefore, heterologous vaccination has been proven to be capable of generating a robust persistent immunogenicity with high antibody levels that remain stable for up to at least three months after administration [39]. Furthermore, the COVID-19 convalescent patient who received a booster dose of the vaccine reached higher and more enduring antibody levels [52,65].
Figure 3 shows the typical antibody trend for heterologous vaccination, where a Pfizer-BioNTech dose was administered as the third or booster dose after the first two doses of ChAdOx1 nCoV19 [39]. Likewise, several studies have shown that mixing the ChAdOx1 nCoV19 and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines triggers an immune response like or even more significant than two doses of either vaccine. The mixing of vaccines from different platforms can result in higher IgG and neutralizing Abs levels as well as a stronger cellular immune response; the use of heterologous COVID-19 vaccines has resulted in higher neutralizing antibody levels against Variants of Concern (VOCs) compared to homologous vaccines [66].
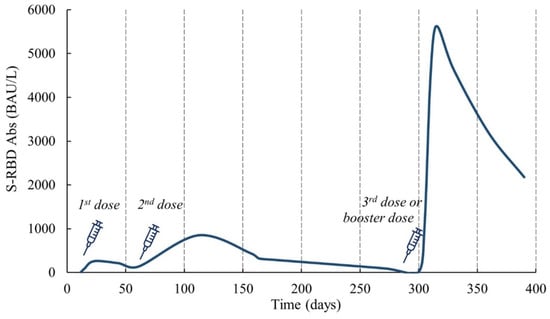
Figure 3.
Antibody trend in heterologous vaccination (1st and 2nd doses of ChAdOx1 nCoV19 and 3rd or booster dose of Pfizer-BioNTech) [39].
The lack of vaccines, especially in poor regions, the emergence of new VOCs that have been partially resistant to available vaccines, and several adverse reactions have forced several countries to mix COVID-19 vaccines.
The factors that can influence and affect differences among vaccinations can be various, comprising differences in age in tested populations and the individual variability in the immune response after the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, as well as the compositions and technical properties of the different vaccines [56].
Cross-sectional studies reported that the presence of receptor binding domain Abs can occur in all vaccinated individuals and in up to 97% of individuals with previous infections that occur several months before antibody tests, suggesting persistence several months after [67].
Another study involving participants with the first dose of the CoronaVac inactivated vaccine revealed low levels of neutralizing antibodies, total anti-RBD antibodies, anti-spike IgG, anti-spike IgM, and anti-spike IgA. However, at the second dose, all antibody levels increased rapidly, reaching the immunological peak within two weeks. Subsequently, the antibody levels began to decrease at 35.61 days, 36.46 days, 30.33 days, and 13.54 days, respectively, for total anti-RBD antibodies, anti-spike IgG, and anti-spike IgM. These findings indicate an intense and comprehensive immune response to the vaccine, albeit with an observed antibody decrease over time [68].
In conclusion, the longest time interval currently reported in the literature at which a positive antibody titer appears to be present is around 1 year. However, it should be noted that this limit is imposed by the timing of the clinical studies conducted so far.
4. The Use of the Interferon Gamma (IFN-γ) Release Assay to Assess the Cellular Response to SARS-CoV-2
Since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, the most frequently asked questions were and still are the severity of symptoms during infection and the vaccine protection rate. Consistent with other viral infections, the development of SARS-CoV-2-specific humoral and cellular immunity controls and limits viral propagation [59]. There is growing evidence of the importance of T cells response to vaccination or SARS-CoV-2 infection. A study on patients with COVID-19 revealed that CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes play a significant role in reducing the severity of the disease during the initial phase of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Furthermore, cellular immunity to SARS-CoV-2 variants has been shown to persist even when the virus escapes humoral immunity [69]. Since SARS-CoV-2 T cells are detectable after infection or stimulation by vaccination, they should have diagnostic value. To consistently assess SARS-CoV-2 immunity and protection, several studies have focused on T cell surveillance using the interferon-ϒ release assay (IGRA). As it is accurate and completely automated, it can be easily performed in clinical laboratories [70] and can be used to quantify the responses of T cells. Many findings support the notion that T cell reactivity is commonly applied to measure responses to other viral infections using different procedures [71], including variations of the ELISPOT assay [72] and the interferon gamma release immunoassay (IGRA) [73]. The ELISPOT assay evaluates IFN-γ production and intracellular cytokine staining (ICS) by flow cytometry, but being outmoded, it is usually replaced by the IGRA test in routine diagnosis. The IGRA test is also used for the diagnosis of tuberculosis (Quantiferon assay).
The IGRA is a whole blood lithium-heparinized test that can aid in the diagnosis of infection. The test consists of two different phases: T cell stimulation and IFN-γ detection. In the first step, the Antigen Presenting Cell (APC) shows the viral antigen to CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, which switch to an activated status and release interferon-ϒ. Then, mitogens are added to the blood samples to produce cells that overexpress interferon-ϒ. IFN-γ release can be detected indirectly by ELISA.
Immunity against COVID-19 infection or vaccination produces an immune response consisting of Abs and T cells specific to the virus. Neutralizing Abs was believed to be the key to preventing SARS-CoV-2 from entering host cells and for host defense [74]. In contrast, SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing Abs induced by vaccination or spontaneous infection may no longer be adequate for host protection due to their decay over the months and/or the appearance of viral escape variants [75,76]. On the other hand, memory T cells persist for a long period and can contribute significantly to controlling SARS-CoV-2 and protecting against hospitalization or death [77,78].
According to recent research, anti-COVID-19 cellular immune responses persist for months after infection, while memory B cells and antibody levels are no longer detectable at that time. However, the duration of Abs and T cell memory against SARS-CoV-2 in vaccinated individuals is still not clear. Only a few studies were conducted to investigate the persistence of T cells against SARS-CoV-2, and fewer studies were conducted on the discrimination between convalescent and vaccinated patients [78,79,80]. Fernández-González [81] reported that the IGRA accurately distinguished the vaccinated from previously infected individuals and the IFN-γ levels correlated proportionally with the level of neutralizing Abs. In their study, COVID-19 convalescent patients were investigated at 3 and 12 months after diagnosis, and vaccinated subjects were investigated for a period of 3 months, including healthy donors (negative control). The sensitivity of the first group has emerged to be largely dependent on disease severity and time since primary infection, while the second group, as expected, had IFN-γ levels significantly lower than those in patients infected with severe symptoms.
Furthermore, the presence of the cellular immune response could be very important in the absence of specific Abs to understand immune protection not only in infected patients but also in vaccinated patients.
Furthermore, Murugesan’s paper studied the IFN-γ levels in 82 adult convalescent patients with COVID-19 and 48 healthy adults without infection (negative control), showing values that were extremely high in the convalescent patients compared to the healthy negative controls. The median IFN-γ response was 0.36 (interquartile range, IQR, 0.14–0.74) IU/mL in the COVID-19 cases vs. 0.01 (IQR, 0–0.01) IU/mL in the controls, with p < 0.001 [82].
SARS-CoV-2 T cells were shown to be expressed after vaccine administration and after viral infection [83]. Antibody and cell responses were tested with different methods in a population of 153 healthcare workers with two complete doses of ChAdOx1 nCov-19 and BNT162b2 as a booster, and it was found that the antibody levels peaked after the second dose was administered and then linearly increased again with cell reactivity after the booster dose, as determined in 95.1% of the subjects. The median IFN-γ value in the first kit used was 1.3 IU/mL (IQR: 0.7–2.6 IU/mL), and in the second kit, it was 0.8 IU/mL (IQR: 0.4–1.7 IU/mL) (p: without significance).
Unlike the previous study, Seraceni’s work showed a strong T cell immune response in 23 healthcare workers with double BNT162b2 vaccination doses, which appeared not to be antibody-related [84]. Individuals were tested for S-RBD (receptor binding domain) and neutralizing Abs and divided into three groups according to their antibody levels: Group 1, with low antibody levels, N = 8; Group 2, with high antibody levels, N = 9; and Group 3, the control negative group, N = 6. However, no significant differences were found between Groups 1 and 2 in the IFN-γ concentrations despite the significant antibody difference observed. This last finding could suggest that T cell immunity is stimulated even if the antibody response is low.
To summarize, IFN-γ release can be used to indirectly measure the T cell response to SARS-CoV-2 infection or vaccination. In addition, the assay could be further refined using more sensitive and specific peptides that discriminate SARS-CoV-2 from seasonal coronaviruses or identify SARS-CoV-2 variants that circulate in the population [81], confirming that the IGRA test is a useful diagnostic tool for managing the COVID-19 pandemic.
5. Possible Laboratory Algorithm for COVID-19 Serological Tests
The correct interpretation of laboratory test results is fundamental for clinicians. Laboratory algorithms may help avoid misdiagnoses and improve patient management.
Firstly, it is suggested to divide the possible patients into vaccinated, unvaccinated, and unknown vaccine status. In unvaccinated individuals, a positive result in anti-N, S, or RBD antibody tests indicates a prior infection. Conversely, negative results across all tests suggest that the individual has neither been vaccinated nor previously infected. In vaccinated individuals who have not been previously infected with SARS-CoV-2, positive antibody tests against the vaccine antigen, the S protein, are expected, while tests for other antigens such as the N protein would yield negative results. However, a positive result in antibody tests for antigens such as the N protein suggests an infection with SARS-CoV-2, which may have occurred before or after vaccination.
If the status of vaccination is unknown and the test is positive for Abs against N and S, the individual surely has been previously infected and may or may not have been vaccinated. If this group is positive for the anti-S Abs and negative for the anti-N Abs, it means the individuals have been vaccinated with no previous infection. If the result is negative for both types of Abs, they have not been previously vaccinated or infected (Table 2).

Table 2.
An interpretation of the serological antibody test against the anti-S and anti-N proteins of COVID-19.
6. Understanding the Evolution and Implications of the Serological Test in COVID-19 Variants
The emergence of COVID-19 variants has presented a significant challenge in the battle against the pandemic. These variants, characterized by specific mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 virus, have raised concerns due to their potential to affect the virus’s transmissibility, disease severity, and ability to evade immunity [85]. Among the notable variants, the alpha, beta, gamma, and delta variants were distinguished by their heightened transmissibility, which manifested in a viral load 2.5 times higher than that of the original strain. These features increased the risk of reinfection and presymptomatic transmission, amplifying concerns about its rapid spread within communities [86]. Furthermore, evidence points to a higher secondary attack rate and an increase in hospitalizations among delta cases, underscoring the clinical impact of the variant. Despite these challenges, vaccination and serological assays remain a crucial tool in combating delta spread.
In the third and last wave of the COVID-19 saga, the emergence of omicron, designated a Variant of Concern (VOC), requires new strategies to fight infection and symptomatology. The omicron lineage, marked by descendant lineages such as BA.1 and BA.2, among others, introduces complexities in understanding its epidemiological footprint [85]. The WHO acknowledges the multifaceted drivers behind the surge of omicron, attributing its rapid spread to immune escape properties and regional epidemiological dynamics. Such insights underscore the imperative of continuous genomic surveillance and international collaboration to follow the evolutionary trajectory of COVID-19 variants and inform targeted public health interventions. In this regard, the European Commission authorized the Comirnaty XBB.1.5-adapted COVID-19 vaccine on 1 September 2023. The goal was to protect the most fragile population from the complications of COVID-19 infection.
Despite these new challenges of COVID-19 variants, vaccination remains a crucial tool in combating the spread of the virus. Studies indicate that while vaccines retain protective efficacy, particularly with the adoption of heterologous vaccine doses (Comirnaty + Vaxvrevia), there may be slight reductions in the prevention of symptomatic disease. Some studies elucidate the critical role of vaccination in mitigating the spread of COVID-19 variants and conferring durable immunity against evolving variants, underscoring the importance of comprehensive vaccination strategies, including booster doses and an active serological surveillance program [45,87,88].
7. Conclusions
Various serological tests have been launched on the market for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Lateral flow assays (LFAs) often demonstrate lower sensitivity than ELISAs and CLIAs. LFAs are powerful diagnostic tools for large-scale population screening and community surveillance for the identification of SARS-CoV-2. Numerous LFIA-based rapid POC tests have been developed by various companies, which enable the detection of IgM and IgG Abs produced in response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. It does not require any instrument or trained personnel and can therefore be employed anywhere and at any time, especially in developing countries with limited healthcare resources and remote settings.
In conclusion, antibody testing could provide valuable epidemiological data and help in assessing the immunization status of the population [89]. In addition, it could be a useful tool for detecting and selecting hyperimmune plasma for convalescent plasma therapy.
Additionally, today, serological assays are critically needed to determine the immune response after vaccination or infection to plan a correct vaccination campaign. It has been proven that different amounts of Abs are produced after vaccine administration, and individuals with a previous natural infection develop higher Abs titer levels. Among people without a history of previous SARS-CoV-2 infection, up to 5% had an Abs level of the same order of magnitude as infected people, suggesting that they acquired an asymptomatic infection [90,91]. In such individuals, one dose of vaccine may be sufficient to obtain a protective immune response. A serological investigation right after the first dose of vaccine could be a useful tool to identify people with asymptomatic infection and avoid the administration of a second dose that is not necessary but detrimental in some circumstances. If one dose of vaccine is sufficient for patients who recovered from COVID-19, we could distribute the spare doses to other people [77].
The use of serological tests in clinical laboratory practice represents an important element for long-term strategies, such as the recent hypothesis of booster vaccine doses and the identification of a previous infection with the N antibody assay.
Furthermore, it should be associated with the IGRA test to assess the protection rate and determine the best individual-specific way to manage the administration of the vaccine schedule. Finally, in terms of vaccine application, we can highlight the utility of antibody assays as a highly cost-effective tool for an effective vaccination strategy to promote public health.
Nevertheless, new variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, especially the Variants of Concern (VOCs), could impact diagnostic tests in several ways, considering that some mutations in the viral genome, particularly for the VOCs, affected the spike protein and other key regions. Some specific mutations can potentially affect the accuracy of both serological and antigen-based tests, especially in sensitivity, potentially causing false negative results [92]. To mitigate this, manufacturers and health authorities continuously monitor and update the test components to ensure they remain effective against new variants.
The development of post-COVID-19 pathologies could include the involvement of both a transient immunosuppression (both innate and acquired immunity) and an inappropriate form of immune reconstitution that amplifies the process.
Lymphoplasmocyte cell infiltrates are involved as the expressions of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin (IL) IL-1, IL-6, IL-17, and TNF-α, and markers of systemic inflammation [91].
The development of pathologic conditions subsequent to COVID-19 infection may be associated with factors such as the transient immunosuppression of innate and acquired immunity, leading to a form of inappropriate immune system reconstitution in individuals with predisposing conditions such as immunological frailty.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: U.B. and M.C.; Data Curation: E.N., F.T., S.P. and S.R.; Original draft preparation: E.N., F.T. and M.M.; Review and editing: M.M. and U.B.; Supervision: M.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic Characterisation and Epidemiology of 2019 Novel Coronavirus: Implications for Virus Origins and Receptor Binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brochot, E.; Demey, B.; Handala, L.; François, C.; Duverlie, G.; Castelain, S. Comparison of Different Serological Assays for SARS-CoV-2 in Real Life. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 130, 104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrou, A.S.; South, E.; Ballou, E.S.; Paden, C.R.; Fuller, J.A.; Bart, S.M.; Butryn, D.M.; Novak, R.T.; Browning, S.D.; Kirby, A.E.; et al. Early Detection and Surveillance of the SARS-CoV-2 Variant BA.2.86—Worldwide, July–October 2023. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2023, 72, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Rocklöv, J. The Reproductive Number of the Delta Variant of SARS-CoV-2 Is Far Higher Compared to the Ancestral SARS-CoV-2 Virus. J. Travel Med. 2021, 28, taab124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Yu, Y.; Jian, F.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; et al. Antigenicity and Infectivity Characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, e457–e459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Li, T.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Liu, J. The Genetic Sequence, Origin, and Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1629–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, R.J.; O’Donnell, S.; LeBlanc, D.; McMahon, M.; Natin, D. The Importance of Cycle Threshold Values in Interpreting Molecular Tests for SARS-CoV-2. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 98, 115130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.; Peng, Y.; Huang, B.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Niu, P.; Meng, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Genome Composition and Divergence of the Novel Coronavirus (2019-NCoV) Originating in China. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Gao, G.F. Viral Targets for Vaccines against COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrekar, J.N. Simple Statistical Measures for Diagnostic Accuracy Assessment. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 763–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, A.; Meurant, R.; Ardakani, A. COVID-19 Serological Tests: How Well Do They Actually Perform? Diagnostics 2020, 10, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, B.; Wang, X.-Y.; Yuan, J.-W.; Vabret, A.; Wu, X.-D.; Yang, R.-F.; Tian, L.; Ji, Y.-Y.; Deubel, V.; Sun, B. Characterization and Application of Monoclonal Antibodies against N Protein of SARS-Coronavirus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 336, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieri, M.; Ciotti, M.; Carlozzi, N.; Frassanito, M.L.; Meloni, A.; Cistera, A.; Turchetti, G.; Niscola, S.; Labate, G.; Calugi, G.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Serology Validation of Different Methods: Usefulness of IgA in the Early Phase of Infection. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 511, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, M.; Nuccetelli, M.; Nicolai, E.; Sarubbi, S.; Grelli, S.; Bernardini, S. Clinical Validation of a Second Generation Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgM Automated Chemiluminescent Immunoassay. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 2523–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, D.J. The Immune System in Health and Disease. Baillieres Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1992, 6, 393–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuccetelli, M.; Pieri, M.; Gisone, F.; Bernardini, S. Combined Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgA, IgG, and IgM Detection as a Better Strategy to Prevent Second Infection Spreading Waves. Immunol. Investig. 2022, 51, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuccetelli, M.; Pieri, M.; Gisone, F.; Sarubbi, S.; Ciotti, M.; Andreoni, M.; Bernardini, S. Evaluation of a New Simultaneous Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgA, IgM and IgG Screening Automated Assay Based on Native Inactivated Virus. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 92, 107330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napodano, C.; Callà, C.; Fiorita, A.; Marino, M.; Taddei, E.; di Cesare, T.; Passali, G.C.; di Santo, R.; Stefanile, A.; Fantoni, M.; et al. Salivary Biomarkers in Covid-19 Patients: Towards a Wide-Scale Test for Monitoring Disease Activity. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassetti, F.; Nuccetelli, M.; Sarubbi, S.; Gisone, F.; Ciotti, M.; Spinazzola, F.; Ricotta, C.; Cagnoli, M.; Borgatti, M.; Iannetta, M.; et al. Evaluation of S-RBD and High Specificity ACE-2-Binding Antibodies on SARS-CoV-2 Patients after Six Months from Infection. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 99, 108013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO International Standard First WHO International Standard for Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Immunoglobulin (Human); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Infantino, M.; Pieri, M.; Nuccetelli, M.; Grossi, V.; Lari, B.; Tomassetti, F.; Calugi, G.; Pancani, S.; Benucci, M.; Casprini, P.; et al. The WHO International Standard for COVID-19 Serological Tests: Towards Harmonization of Anti-Spike Assays. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 100, 108095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Options for the Use of Rapid Antigen Detection Tests for COVID-19 in the EU/EEA—First Update, 26 October 2021; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chotpitayasunondh, T.; Fisher, D.A.; Hsueh, P.-R.; Lee, P.-I.; Nogales Crespo, K.; Ruxrungtham, K. Exploring the Role of Serology Testing to Strengthen Vaccination Initiatives and Policies for COVID-19 in Asia Pacific Countries and Territories: A Discussion Paper. Int. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 2, 275–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Sasso, B.; Giglio, R.V.; Vidali, M.; Scazzone, C.; Bivona, G.; Gambino, C.M.; Ciaccio, A.M.; Agnello, L.; Ciaccio, M. Evaluation of Anti-SARS-Cov-2 S-RBD IgG Antibodies after COVID-19 MRNA BNT162b2 Vaccine. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, L.; Park, Y.-J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Czudnochowski, N.; Walls, A.C.; Beltramello, M.; Silacci-Fregni, C.; Pinto, D.; Rosen, L.E.; Bowen, J.E.; et al. Mapping Neutralizing and Immunodominant Sites on the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain by Structure-Guided High-Resolution Serology. Cell 2020, 183, 1024–1042.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; He, P.; Liu, H.; Wei, H.; Yu, J. A Luciferase Based Automated Assay for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1238, 340633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meira, C.; Silva, D.; Santos, I.; Barreto, B.; Rocha, V.; Santos, E.; Dos Reis, B.; Evangelista, A.; Ribeiro Dos Santos, R.; Machado, B.; et al. Diagnostic Performance of Three ELISAs for Detection of Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in Human Samples. Sci. World J. 2022, 2022, 7754329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montesinos, I.; Dahma, H.; Wolff, F.; Dauby, N.; Delaunoy, S.; Wuyts, M.; Detemmerman, C.; Duterme, C.; Vandenberg, O.; Martin, C.; et al. Neutralizing Antibody Responses Following Natural SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Dynamics and Correlation with Commercial Serologic Tests. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 144, 104988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuccetelli, M.; Pieri, M.; Grelli, S.; Ciotti, M.; Miano, R.; Andreoni, M.; Bernardini, S. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Serology: A Useful Tool to Overcome Lockdown? Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. The Species Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus: Classifying 2019-NCoV and Naming It SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, W.N.; Tan, C.W.; Foo, R.; Kang, A.E.Z.; Peng, Y.; Sivalingam, V.; Tiu, C.; Ong, X.M.; Zhu, F.; Young, B.E.; et al. Serological Differentiation between COVID-19 and SARS Infections. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folegatti, P.M.; Ewer, K.J.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Becker, S.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Bellamy, D.; Bibi, S.; Bittaye, M.; Clutterbuck, E.A.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of the ChAdOx1 NCoV-19 Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: A Preliminary Report of a Phase 1/2, Single-Blind, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.A.; Anderson, E.J.; Rouphael, N.G.; Roberts, P.C.; Makhene, M.; Coler, R.N.; McCullough, M.P.; Chappell, J.D.; Denison, M.R.; Stevens, L.J.; et al. An MRNA Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2—Preliminary Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1920–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.; Park, Y.-J.; Beltramello, M.; Walls, A.C.; Tortorici, M.A.; Bianchi, S.; Jaconi, S.; Culap, K.; Zatta, F.; de Marco, A.; et al. Cross-Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 by a Human Monoclonal SARS-CoV Antibody. Nature 2020, 583, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röltgen, K.; Powell, A.E.; Wirz, O.F.; Stevens, B.A.; Hogan, C.A.; Najeeb, J.; Hunter, M.; Wang, H.; Sahoo, M.K.; Huang, C.; et al. Defining the Features and Duration of Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection Associated with Disease Severity and Outcome. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabe0240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Yuan, M.; Keating, C.; Shaabani, N.; Limbo, O.; Joyce, C.; Woehl, J.; Barman, S.; Burns, A.; Tran, Q.; et al. Broadening a SARS-CoV-1–Neutralizing Antibody for Potent SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization through Directed Evolution. Sci. Signal. 2023, 16, eabk3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedan, H.T.; Yassine, H.M.; Al-Sadeq, D.W.; Liu, N.; Qotba, H.; Nicolai, E.; Pieri, M.; Bernardini, S.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Nasrallah, G.K. Evaluation of Commercially Available Fully Automated and ELISA-Based Assays for Detecting Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos da Silva, E.; Servais, J.-Y.; Kohnen, M.; Arendt, V.; Staub, T.; The Con-Vince Consortium; The CoVaLux Consortium; Krüger, R.; Fagherazzi, G.; Wilmes, P.; et al. Validation of a SARS-CoV-2 Surrogate Neutralization Test Detecting Neutralizing Antibodies against the Major Variants of Concern. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolai, E.; Tomassetti, F.; Pelagalli, M.; Sarubbi, S.; Minieri, M.; Nisini, A.; Nuccetelli, M.; Ciotti, M.; Pieri, M.; Bernardini, S. The Antibodies’ Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination: 1-Year Follow Up. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieri, M.; Infantino, M.; Manfredi, M.; Nuccetelli, M.; Grossi, V.; Lari, B.; Tomassetti, F.; Sarubbi, S.; Russo, E.; Amedei, A.; et al. Performance Evaluation of Four Surrogate Virus Neutralization Tests (SVNTs) in Comparison to the in Vivo Gold Standard Test. Front. Biosci. 2022, 27, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Sempowski, G.D.; Saunders, K.O.; Acharya, P.; Haynes, B.F. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies for COVID-19 Prevention and Treatment. Annu. Rev. Med. 2022, 73, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, E.H.Y.; Tsang, O.T.Y.; Hui, D.S.C.; Kwan, M.Y.W.; Chan, W.; Chiu, S.S.; Ko, R.L.W.; Chan, K.H.; Cheng, S.M.S.; Perera, R.A.P.M.; et al. Neutralizing Antibody Titres in SARS-CoV-2 Infections. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, A.; Pieri, M.; Sarubbi, S.; Pelagalli, M.; Calugi, G.; Tomassetti, F.; Bernardini, S.; Nuccetelli, M. Evaluation of Serological Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Chemiluminescent Immunoassays Correlated to Live Virus Neutralization Test, for the Detection of Anti-RBD Antibodies as a Relevant Alternative in COVID-19 Large-Scale Neutralizing Activity Monitoring. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 234, 108918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristiano, A.; Nuccetelli, M.; Pieri, M.; Sarubbi, S.; Pelagalli, M.; Calugi, G.; Tomassetti, F.; Bernardini, S. Serological Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies Association to Live Virus Neutralizing Test Titers in COVID-19 Paucisymptomatic/Symptomatic Patients and Vaccinated Subjects. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 108215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciola, A.K.; La Raja, M.; Pacenti, M.; Salata, C.; De Silvestro, G.; Rosato, A.; Pasqual, G. Neutralizing Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 in Recovered COVID-19 Patients Are Variable and Correlate With Disease Severity and Receptor-Binding Domain Recognition. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 830710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Núñez, J.J.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Torres-Hernández, P.C.; Hernández-Bello, J. Overview of Neutralizing Antibodies and Their Potential in COVID-19. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzati, L.; Milazzo, L.; Carrozzo, G.; Kullmann, C.; Oreni, L.; Beltrami, M.; Caronni, S.; Lai, A.; Caberlotto, L.; Ottomano, C.; et al. Evaluation of Residual Humoral Immune Response against SARS-CoV-2 by a Surrogate Virus Neutralization Test (SVNT) 9 Months after BNT162b2 Primary Vaccination. J. Infect. Chemother. 2023, 29, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abebe, E.C.; Dejenie, T.A. Protective Roles and Protective Mechanisms of Neutralizing Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Their Potential Clinical Implications. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1055457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhani, K.; Cheng, S.; Binder, R.A.; Mantis, N.J.; Crawford, J.M.; Okoye, N.; Braun, J.G.; Joung, S.; Wang, M.; Lozanski, G.; et al. Clinical Utility of SARS-CoV-2 Serological Testing and Defining a Correlate of Protection. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeri, I.; Lewis, H.C.; Subissi, L.; Nardone, A.; Valenciano, M.; Cheng, B.; Glonti, K.; Williams, B.; Abejirinde, I.O.; Simniceanu, A.; et al. Early Epidemiological Investigations: World Health Organization UNITY Protocols Provide a Standardized and Timely International Investigation Framework during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2022, 16, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Interim Guidelines for COVID-19 Antibody Testing—Interim Guidelines for COVID-19 Antibody Testing in Clinical and Public Health Settings; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Schipani, M.C.; Tomassetti, F.; Polidori, I.; Ricci, P.; Frassanito, M.L.; Seraceni, S.; Morello, M.; Nicolai, E.; Aquaro, S.; Bernardini, S.; et al. Evaluation of Natural and Vaccine-Induced Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Immunity: A Comparative Study between Different Groups of Volunteers. Diseases 2022, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, M.J.; Lyke, K.E.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Raabe, V.; Bailey, R.; Swanson, K.A.; et al. Phase I/II Study of COVID-19 RNA Vaccine BNT162b1 in Adults. Nature 2020, 586, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.A. Serological Tests for COVID-19 Antibodies: Limitations Must Be Recognized. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2020, 57, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, J.M.; Mateus, J.; Kato, Y.; Hastie, K.M.; Yu, E.D.; Faliti, C.E.; Grifoni, A.; Ramirez, S.I.; Haupt, S.; Frazier, A.; et al. Immunological Memory to SARS-CoV-2 Assessed for up to 8 Months after Infection. Science 2021, 371, eabf4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzetto, B.; Legros, V.; Djebali, S.; Barateau, V.; Guibert, N.; Villard, M.; Peyrot, L.; Allatif, O.; Fassier, J.-B.; Massardier-Pilonchéry, A.; et al. Immunogenicity and Efficacy of Heterologous ChAdOx1-BNT162b2 Vaccination. Nature 2021, 600, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfego, D.; Sullivan, A.; Poirier, B.; Williams, J.; Grover, A.; Gillim, L.; Adcock, D.; Letovsky, S. A Population-Based Analysis of the Longevity of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Seropositivity in the United States. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 36, 100902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, D.; di Resta, C.; Tomaiuolo, R.; Sabetta, E.; Pontillo, M.; Motta, A.; Locatelli, M. Long-Term Antibody Persistence and Exceptional Vaccination Response on Previously SARS-CoV-2 Infected Subjects. Vaccine 2021, 39, 4256–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sette, A.; Crotty, S. Adaptive Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Cell 2021, 184, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criscuolo, E.; Diotti, R.A.; Strollo, M.; Rolla, S.; Ambrosi, A.; Locatelli, M.; Burioni, R.; Mancini, N.; Clementi, M.; Clementi, N. Weak Correlation between Antibody Titers and Neutralizing Activity in Sera from SARS-CoV-2 Infected Subjects. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 2160–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, K.H.D.; Dingens, A.S.; Eguia, R.; Wolf, C.R.; Wilcox, N.; Logue, J.K.; Shuey, K.; Casto, A.M.; Fiala, B.; Wrenn, S.; et al. Dynamics of Neutralizing Antibody Titers in the Months After Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Xiao, M.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Long, P.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, X.; Lei, Y.; et al. Dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response up to 10 Months after Infection. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1832–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addetia, A.; Crawford, K.H.D.; Dingens, A.; Zhu, H.; Roychoudhury, P.; Huang, M.-L.; Jerome, K.R.; Bloom, J.D.; Greninger, A.L. Neutralizing Antibodies Correlate with Protection from SARS-CoV-2 in Humans during a Fishery Vessel Outbreak with a High Attack Rate. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e02107-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.-X.; Tang, X.-J.; Shi, Q.-L.; Li, Q.; Deng, H.-J.; Yuan, J.; Hu, J.-L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, F.-J.; et al. Clinical and Immunological Assessment of Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infections. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plebani, M.; Cosma, C.; Padoan, A. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Assay after Vaccination: One Size Does Not Fit All. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2021, 59, e380–e381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashedi, R.; Samieefar, N.; Masoumi, N.; Mohseni, S.; Rezaei, N. COVID-19 Vaccines Mix-and-Match: The Concept, the Efficacy and the Doubts. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 1294–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, N.; Pernet, O.; Lam, C.N.; Klipp, A.; Kotha, R.; Kovacs, A.; Hu, H. Seroprevalence of Antibodies Specific to Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 and Vaccination Coverage Among Adults in Los Angeles County, April 2021: The LA Pandemic Surveillance Cohort Study. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2144258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Núñez, J.J.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Meza-López, C.; Wang, L.-F.; Machado Sulbarán, A.C.; Torres-Hernández, P.C.; Bedolla-Barajas, M.; de la O-Gómez, B.; Balcázar-Félix, P.; Hernández-Bello, J. Neutralizing Antibodies Titers and Side Effects in Response to BNT162b2 Vaccine in Healthcare Workers with and without Prior SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Vaccines 2021, 9, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarke, A.; Sidney, J.; Methot, N.; Yu, E.D.; Zhang, Y.; Dan, J.M.; Goodwin, B.; Rubiro, P.; Sutherland, A.; Wang, E.; et al. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Variants on the Total CD4+ and CD8+ T Cell Reactivity in Infected or Vaccinated Individuals. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, I.; Gilberg, L.; Bruger, J.; Garí, M.; Wieser, A.; Eser, T.M.; Frese, J.; Ahmed, M.I.M.; Rubio-Acero, R.; Guggenbuehl Noller, J.M.; et al. Broad T Cell Targeting of Structural Proteins After SARS-CoV-2 Infection: High Throughput Assessment of T Cell Reactivity Using an Automated Interferon Gamma Release Assay. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 688436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalvani, A.; Pareek, M. Interferon Gamma Release Assays: Principles and Practice. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2010, 28, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, M.; Dark, C.; Aspden, M.; Cochrane, D.; Competiello, R.; Peltz, M.; Torres, L.; Wrighton-Smith, P.; Dudek, M. Performance of the T-SPOTⓇ.COVID Test for Detecting SARS-CoV-2-Responsive T Cells. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 113, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaudineau, Y.; Abravanel, F.; Izopet, J.; Bost, C.; Treiner, E.; Congy, N.; Blancher, A. Novel T Cell Interferon Gamma Release Assay (IGRA) Using Spike Recombinant Protein for COVID19 Vaccine Response and Nucleocapsid for SARS-Cov2 Response. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 237, 108979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadarangani, M.; Marchant, A.; Kollmann, T.R. Immunological Mechanisms of Vaccine-Induced Protection against COVID-19 in Humans. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarrondo, F.J.; Fulcher, J.A.; Goodman-Meza, D.; Elliott, J.; Hofmann, C.; Hausner, M.A.; Ferbas, K.G.; Tobin, N.H.; Aldrovandi, G.M.; Yang, O.O. Rapid Decay of Anti–SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Persons with Mild Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1085–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, P.; Barmania, F.; Mellet, J.; Peta, K.; Strydom, A.; Viljoen, I.M.; James, W.; Gordon, S.; Pepper, M.S. SARS-CoV-2 Variants, Vaccines, and Host Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 809244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broccolo, F. Optimizing Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccination: Will Laboratory Stewardship Play a Role? Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2022, 60, 64–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, P. The T Cell Immune Response against SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cromer, D.; Juno, J.A.; Khoury, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Wheatley, A.K.; Kent, S.J.; Davenport, M.P. Prospects for Durable Immune Control of SARS-CoV-2 and Prevention of Reinfection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- le Bert, N.; Tan, A.T.; Kunasegaran, K.; Tham, C.Y.L.; Hafezi, M.; Chia, A.; Chng, M.H.Y.; Lin, M.; Tan, N.; Linster, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-Specific T Cell Immunity in Cases of COVID-19 and SARS, and Uninfected Controls. Nature 2020, 584, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-González, M.; Agulló, V.; Padilla, S.; García, J.A.; García-Abellán, J.; Botella, Á.; Mascarell, P.; Ruiz-García, M.; Gutiérrez, F. Clinical Performance of a Standardized SARS-CoV-2 Interferon-γ Release Assay for Simple Detection of T-Cell Responses after Infection or Vaccination. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, ciab1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, K.; Jagannathan, P.; Pham, T.D.; Pandey, S.; Bonilla, H.F.; Jacobson, K.; Parsonnet, J.; Andrews, J.R.; Weiskopf, D.; Sette, A.; et al. Interferon-γ Release Assay for Accurate Detection of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 T-Cell Response. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e3130–e3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Lee, N.; Lee, S.K.; Cho, E.-J.; Hyun, J.; Park, M.-J.; Song, W.; Kim, H.S. Humoral and Cellular Responses to BNT162b2 as a Booster Following Two Doses of ChAdOx1 NCov-19 Determined Using Three SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Assays and an Interferon-Gamma Release Assay: A Prospective Longitudinal Study in Healthcare Workers. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 859019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraceni, S.; Zocca, E.; Cervone, T.E.; Tomassetti, F.; Polidori, I.; Valisi, M.; Broccolo, F.; Calugi, G.; Bernardini, S.; Pieri, M. T-Cell Assay after COVID-19 Vaccination Could Be a Useful Tool? A Pilot Study on Interferon-Gamma Release Assay in Healthcare Workers. Diseases 2022, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. SARS-CoV-2 Variant Classifications and Definitions; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Smirnova, A.; Baroonian, M. Reconstruction of Incidence Reporting Rate for SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant of COVID-19 Pandemic in the US. Infect. Dis. Model. 2024, 9, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, M.S.; Farias, J.P.; Andreata-Santos, R.; Silva, M.P.; Brito, R.D.d.S.; Duarte Barbosa da Silva, M.; Peter, C.M.; Cirilo, M.V.d.F.; Luiz, W.B.; Birbrair, A.; et al. Neutralizing Antibody Response after Immunization with a COVID-19 Bivalent Vaccine: Insights to the Future. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chittrakarn, S.; Siripaitoon, P.; Chusri, S.; Kanchanasuwan, S.; Charoenmak, B.; Hortiwakul, T.; Kantikit, P.; Kositpantawong, N. Comparative Immunogenicity and Neutralizing Antibody Responses Post Heterologous Vaccination with CoronaVac (Sinovac) and Vaxzevria (AstraZeneca) in HIV-Infected Patients with Varying CD4+ T Lymphocyte Counts. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2024, 20, 2309734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awwad, S.; Al-Hamdani, M.; Abdallah, A.M.; Abu-Madi, M. Laboratory Testing Efficiency during the COVID Pandemic: Findings from the Primary Health Care Corporation Laboratories in the State of Qatar. J. Infect. Public Health 2024, 17, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieri, M.; Nicolai, E.; Ciotti, M.; Nuccetelli, M.; Sarubbi, S.; Pelagalli, M.; Bernardini, S. Antibody Response to COVID-19 Vaccine: A Point of View That Can Help to Optimize Dose Distribution. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 102, 108406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejo, A.; Vizcarra, P.; Quereda, C.; Moreno, A.; Casado, J.L. IFN-Γ+ Cell Response and IFN-γ Release Concordance after in Vitro SARS-CoV-2 Stimulation. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, R.K. State of the Globe: Navigating the Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Mutations on COVID-19 Testing. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2023, 15, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).