Abstract
Graphene oxide (GO) has been successfully used as a filler to modify various properties of polymers and fiber-reinforced composites. The resulting properties depend on the filler content and on the distribution of GO in the polymer matrix. In this work, for the first time, we introduced GO into the highly viscous DEN-438 epoxy novolac resin and investigated rheological properties of the resulting compositions. In particular, we studied the functions of complex viscosity, storage and loss moduli, and mechanical loss tangent on temperature and GO content. The unusual behavior of the newly prepared formulations compared to typical GO/epoxy mixtures was discovered. At low GO content, introduction of GO led not to an increase, but to a decrease in the resin viscosity, with the minimum registered at 0.29 wt.% GO. After this threshold value, viscosity increased with GO content, which we explained by formation of the liquid crystalline structure. At higher GO concentrations, the formulations changed their state from solid-like at rest to liquid-like under load, with the properties being highly desired for film binders. The discovered properties of the GO/novolac epoxy resin formulations suggest their potential use as the new generation of film binders for Resin Film Infusion technology.
1. Introduction
Graphene oxide (GO) is a two-dimensional nanomaterial with micron-scale linear dimensions and a ~1 nanometer thickness. It possesses great potential for developing new materials due to the combination of specific features of chemical composition and structure, which provide the possibility of strong non-covalent interactions with surrounding objects, including macromolecules, as well as due to the possibility of large-scale production. Recently, the potential of GO as an active 2D filler in polymer composites has attracted considerable interest. For example, epoxy nanocomposites containing exfoliated GO sheets have recently been proposed as anticorrosive [1,2] or hydrogen barrier [3] coatings, as well as shape-memory polymers [4]. The reduction of GO to RGO in composites imparts new properties, such as heat dissipation [5] or an antistatic effect [6]. GO is used to modify various properties of polymers and fiber-reinforced composites, and can also affect interactions at the matrix/fiber interface. The latter depends on GO/fiber and GO/matrix interactions as well as on the distribution of GO in the polymer matrix. The main challenge in designing GO-based polymer nanocomposites (as, indeed, with any other nanofillers) is to uniformly disperse the individual graphene oxide sheets in the polymer matrix. Various approaches are used to solve this problem, among which the most commonly used are the chemical modification of GO [7,8,9] and using surfactants or polymers [10,11]. GO-based composites have been prepared with epoxy resins [1,2,3,4,5,6,12,13,14], which are widely used as a matrix for fiber-reinforced plastics, and GO has been used for modification of epoxy matrix in composites comprising glass [15] or carbon fibers [12,14,16,17,18,19]. However, direct introduction of GO into polymers does not let one achieve uniform distribution and sufficient exfoliation of GO in the matrix. The use of solvents is a convenient means for introducing GO into the polymer matrix [20,21,22]. To assess the degree of GO exfoliation both in a solvent and in a liquid polymer matrix, it is advisable to study the rheological properties of such systems [21,23,24] [https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b07450, https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c02208] (accessed on 16 November 2025).
The rheology of GO solutions has been the subject of intensive study in recent years, especially for practical applications [25,26,27,28,29]. In [30], the authors found the concentrations of aqueous GO dispersions at which isotropic solutions and liquid crystals are formed. Dilute suspensions of graphene oxide (0.05 to 0.5 mg/mL) exhibit a shear-thinning behavior at low shear rates followed by a shear-independent region that starts at shear rates between 5 and 100 s−1 depending on the concentration [31]. With high GO content in the dispersion, and especially in the presence of salts, the formation of various types of liquid crystalline phases is possible [32]. GO dissolves in a limited number of organic solvents [33,34], and the structure of dispersions and their rheology greatly depends on the GO concentration [35,36].
Currently, the Resin Film Infusion (RFI) technology based on the film binders, made from thermosetting resins, is gaining growing interest in the manufacture of carbon fiber-reinforced plastics with high-elastic-strength characteristics and due to its cost-effectiveness [37,38,39,40]. In this technology, the solid sticky film binder is in direct contact with the preform, including the reinforcing filler. When heated, the binder softens and impregnates the filler due to a sharp decrease in its viscosity. Thus, when developing a film binder for the RFI process, it is important to fine-tune the rheological properties of the binder, i.e., the polymer matrix. At rest and at ambient temperature, the film binder for RFI technology should possess elasticity and tackiness, while upon heating and under shear deformations, its viscosity should decrease sharply. In this regard, the modification of the rheological properties of highly viscous epoxy resins, to be used as a film binder, becomes an important challenge.
Nanoscaled materials are very effective modifiers of the viscosity of liquids [41]. Thus, the use of GO as a nanomodifier appears to be a promising approach in this regard. In our earlier studies, we developed the Homogeneous Liquid Phase Transfer method for introducing GO into epoxy resins [21]. Also, we studied the rheological properties of the resulting liquid formulations [22,23,24]. It was demonstrated that introduction of GO sharply increases viscosity of the low-viscosity epoxy resin NPEL-128. This was attributed to the highly exfoliated level of GO in the resin. In this work, we introduce GO into the highly viscous epoxy resin DEN-438 and investigate rheological properties of the as-prepared formulations. This is important because NPEL-128-based formulations, while applicable for fabrication of carbon fabric prepregs, are poorly applicable for making film binders usable in RFI technologies due to their low elasticity and tackiness. The goal of this study is to investigate if introduction of GO into highly viscous DEN-438 novolac resin can modify its properties in a way so as to be usable as a basis of the RFI–film binder.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
DEN-438 epoxy novolac resin (supplied by Dow Chemical Co., Midland, MI, USA)) is a semi-solid reaction product of epichlorohydrin and phenol-formaldehyde novolac (Scheme 1) with a functionality of approximately 3.6, epoxy equivalent weight of 176–181 g/eq, dynamic viscosity of 500–1200 mPa·s, boiling point of 56 °C, and vapor pressure of 181.7 mmHg (20 °C).
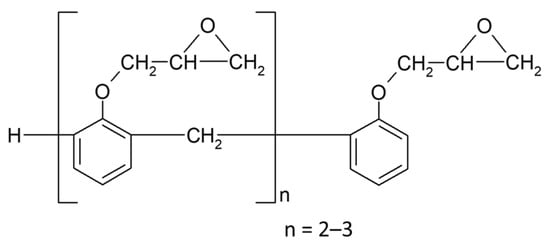
Scheme 1.
The structure of novolac glycidyl ether (DEN-438).
2.2. Synthesis of GO
GO was prepared and characterized as described in our previous reports [21,22,23,24,42]. Graphite flakes were dispersed in the commercial ~96% sulfuric acid at room temperature using a mechanical stirrer. Then, 4 wt equiv. of KMnO4 was added iteratively in four portions after consumption of a previous portion. After the complete consumption of KMnO4, the reaction was quenched with ice water, and the 30% H2O2 was added until the color changed. The resulting mixture was centrifuged; the separated GO precipitate was redispersed in DI water and centrifuged again to separate the GO product. This constituted one purification cycle. Such cycles of GO purification were repeated five more times. The 3% HCl was used instead of water during the last three washing cycles. The GO precipitate, obtained after the final wash, was air dried at ambient conditions.
2.3. Preparation of GO/DEN-438 Formulations Using Homogeneous Liquid Phase Transfer Method
The GO–epoxy formulations were prepared as follows: GO was taken as a 2.8 wt.% gel with i-propyl alcohol (IPA), prepared by the solvent exchange method as described elsewhere [21,22,23,24]. A part (approx. 25%) of the needed amount of epoxy resin, preheated to 50 °C, was manually blended with the required amount of the GO-IPA gel with a mortar and pestle. After achieving the uniform mixture, the rest of the preheated epoxy resin was added in portions and manually blended again until the mixture became homogeneous. Then the sample was placed in the oven and heated at 80 °C for 6 h to remove IPA. Next, the mixture was degassed under vacuum until reaching constant weight to completely remove IPA from the mixture.
2.4. Characterization of GO–Epoxy Dispersions
2.4.1. Rheological Measurements
Rheological studies were performed with the DHR-2 (TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA) rheometer. All the viscosity data for the GO/DEN-438 dispersions were obtained by using a 25 mm diameter parallel plate with a 1 mm plate–plate gap. After being loaded, the GO/DEN-438 sample was left at rest for 3 min to eliminate the effects of the aging history. Steady and dynamic tests were carried out to analyze the rheological behavior of the GO/DEN-438 dispersions with different GO loadings at various temperatures. The temperature of the system was controlled using an advanced Pelletier system unit with a temperature accuracy of 0.1 °C. All rheological measurements were performed with the three replicate samples, and the average values were reported.
Steady Test
Shear rate sweep tests were used to investigate the flow properties of the material by recording the shear stress (σ) and viscosity (η) with increasing shear rates (γ) from 0.01 to 650 s−1. The temperature was varied from 30 to 70 °C and from 50 to 90 °C for the highest GO loading of 1.87 wt.%.
Dynamic Test
Under oscillatory shear measurements at a low strain amplitude of 0.001 (viscoelastic range), the dynamic rheological parameters, such as the storage shear modulus (G′), loss shear modulus (G″), mechanical loss tangent (Tan(delta)), and complex shear viscosity (|η*|) in the frequency range (ω) 0.05–100 rad/s were collected. The dynamic tests, including a strain sweep and frequency sweep, differentiated the fluid and solid responses.
2.4.2. DSC Experiments
The glass transition temperature of GO/DEN-438 dispersions was determined with DSC 214 Polyma (NETZCH Instruments, Selb, Germany). The samples weighing 5–7 mg underwent cooling–heating cycles at a ramping rate of 5 °C/min in the N2 environment in the (−20) ÷ (+40) °C temperature range.
2.4.3. Optical Microscopy
Optical images of GO/DEN-438 formulations were obtained using a PLM-030 (Lacopa, China) optical polarization microscope in polarized light at 20× magnification. The studied compositions were applied as a thin film onto a glass substrate and placed between crossed polarizers.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Glass Transition Properties and Optical Microscopy
According to DSC measurements, neat DEN-438 epoxy resin has a glass transition temperature (Tg) of +2.1 °C. The introduction of GO into the resin up to 0.0155 wt.% leads to a slight decrease in Tg by 0.7 °C. However, a further increase in GO content up to 0.29 wt.% successively reduces Tg up to −15.7 °C (Figure 1).
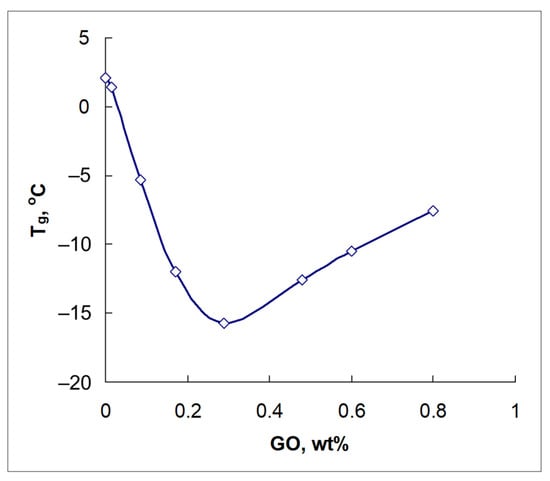
Figure 1.
Glass transition temperatures (Tg) of GO/DEN-438 dispersions according to DSC data.
At the same time, a further increase in GO content reverses the trend, and Tg increases up to −7.6 °C at 0.8 wt.% (Figure 1). Thus, the minimum glass transition temperature is reached at a GO concentration of 0.29 wt.%. As will be shown below, this composition also exhibits specific rheological properties.
It is known that the glass transition temperature of a polymer reflects manifestation of the diffusion motion by its molecules, as in the case of molecules in liquids. Although much is known about the effects of various additives [43], including GO [19], on the glass transition temperature of cured epoxy polymers, such information for uncured epoxy oligomers is lacking. One of the most important factors determining the glass transition temperature of neat epoxy resin is intermolecular interactions [44]. The oligomer molecules in the DEN-438 resin contain oxirane rings which provide formation of multiple intermolecular bonds along with the π-π stacking of aromatic fragments. With this in mind, lower Tg values of the GO/DEN-438 compositions can be interpreted as “unfreezing” of molecular motions in the resin due to disruption of intermolecular bonds in oligomer molecules. As a result, the network of new stronger bonds (especially hydrogen bonds) between DEN-438 molecules and functional groups of exfoliated GO sheets are formed. This leads to the fact that in GO/DEN-438 mixtures, with an increase in GO content to 0.29 wt.%, a sequential Tg decrease occurs. However, with a GO content in dispersions greater than 0.29 wt.%, Tg reversely increases. This effect may indicate a change in the state of GO in the dispersion and, accordingly, the change in the nature of intermolecular interactions that affect the molecular motions of oligomeric molecules. The ability of GO to form liquid crystals in aqueous or alcoholic solutions was noted above. It is possible indeed that with GO content over 0.29 wt.%, the increase in Tg is caused by the ordering of GO sheets with the formation of a liquid crystalline phase. Thus, the DEN-438 molecules, which previously participated in interactions with GO sheets, are now “liberated”, and return to their “usual” intermolecular interactions, which restores the “freezing” of their motion. Formation of a GO liquid crystalline phase in DEN-438 was proved by polarized optical microscopy (POM) (Figure S1, Supplementary Materials) and was consistent with the rheology data presented in the next section. POM images demonstrated birefringence, typical for ordered structures like liquid crystals. Namely, individual textures appeared at low GO contents (0.015 and 0.17 wt.%). Near 0.29 wt.% GO, a noticeable number of textures were visible in the image, occupying almost the entire image field at high GO contents (0.8 wt.%). Thus, these data confirmed the formation of liquid crystalline structures in DEN-438-GO dispersions and demonstrated the noticeable formation of such textures at GO contents of 0.29 wt.% and higher.
The obtained results are important for demonstrating the suitability of GO-loaded DEN-438 resin for manufacturing film binders, since even at low temperatures, the resin retains elasticity at any GO content.
3.2. Rheological Properties
3.2.1. Oscillatory Shear Sweeps
- Temperature factor
At room temperature, neat DEN-438 is a very viscous liquid. A change in its viscosity with temperature was determined in oscillatory shear sweep tests, and is shown in Figure S2, Supplementary Materials. Similar experiments were carried out for all GO/DEN-438 formulations prepared according to the procedure described in the experimental section (Section 2.3). A sufficiently low viscosity (20 Pa·s and less) of the neat resin, needed to make the impregnation of the binder into the preform possible, is achieved by heating to about 65–67 °C. The temperatures T20 at which a viscosity of 20 Pa·s is attained for neat DEN-438 and all the GO/DEN-438 formulations are presented in the graph (Figure 2). For clarity, this is presented in comparison with the data on Tg (presented above in Figure 1).
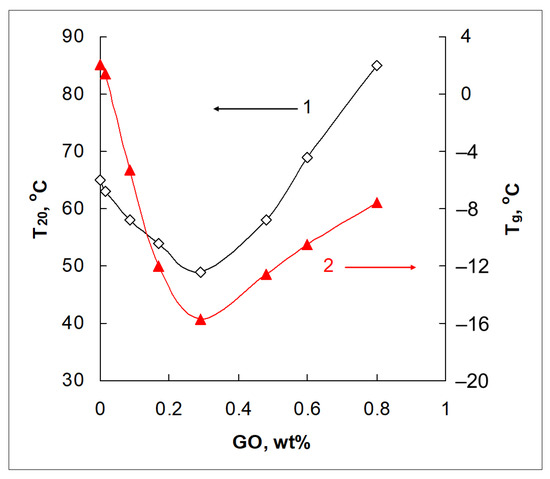
Figure 2.
The temperature of reaching a viscosity value of 20 Pa·s, T20, (1) and the glass transition temperature, Tg, (2) as functions of GO content for GO/DEN-438 dispersions.
A linear decrease in viscosity occurs up to a GO content of 0.29 wt.%, at which the T20 value is reached at 50 °C. However, with a higher GO loading (up to 0.8 wt.%), the viscosity increases. Thus, comparing curves 1 and 2 in Figure 2, one can easily find that a GO content of 0.29 wt.% is an obvious threshold for the change in the two different properties of GO/epoxide formulations. According to the known literature [24,27,28], an increase in viscosity of aqueous GO dispersions is usually associated with the appearance of ordered structures, presumably liquid crystals. In our previous works [21,22,24,45], we also demonstrated that the change in the rheological properties of dispersions of the low-viscosity NPEL-128 resin with GO content higher than 0.2 wt.% is caused by the formation of organized structures.
- Angular frequency dependencies
The angular frequency dependencies of the complex viscosity (|η*|), storage modulus (G′), loss modulus (G″), and loss angle tangency for neat epoxy resin and GO/epoxy dispersions at 30 °C are shown in Figure 3a–d, respectively. The data at other temperatures are presented in Figure S3, Supplementary Materials.
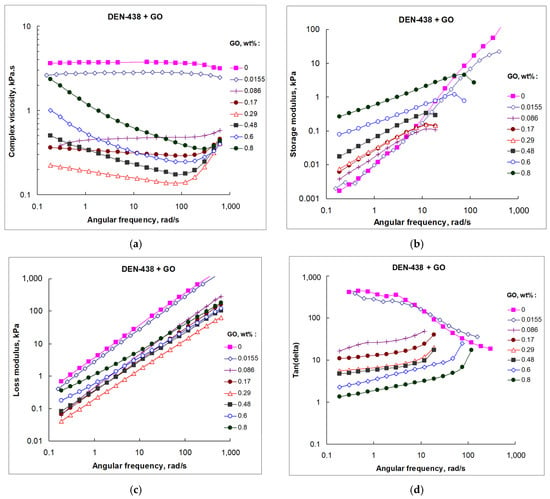
Figure 3.
Complex viscosity (a), storage (b), and loss (c) moduli, and loss angle tangency (d) of GO/DEN-438 dispersions, measured at 30 °C.
The first thing that is evident when analyzing data on the influence of GO on the complex viscosity of DEN-438 epoxy resin (Figure 3a) is the effect, opposite to that previously observed for NPEL-128, where viscosity gradually increases at a whole range of GO concentrations [21,22,23]. Surprisingly, with DEN-438, the introduction of GO leads not to the increase, as one might expect, but to the decrease in viscosity over the entire range of angular frequencies (an order of magnitude for a sample with only 0.086 wt.% GO). Moreover, starting from 0.17 wt.%, addition of GO gives rise to shear-thinning behavior (with lowest |η*| values of 0.29 wt.% GO), and this is especially pronounced at a GO content of 0.8 wt.% (Figure 3a). Apparently, at such high content, GO structurizes epoxy resin with formation of the nematic phase, as was found earlier [22] at lower GO contents for the less viscous NPEL-128 epoxy resin. The decrease in viscosity with an increase in the angular frequency can be explained by disorientation of the liquid crystalline phase due to the rupture of the viscoelastic GO network and acquisition of liquid-like behavior. Such behavior is highly desirable for film binders used in the RFI process. Film binders should have the properties of an elastic solid in the absence of load (or at low loads), but should acquire liquid-like behavior when heated and compression molded.
The storage (G′) and loss (G″) moduli of the neat DEN-438 epoxy resin both exhibited frequency-dependent behavior and their values increased with increasing frequency with scaling laws G′~ω2 and G″~ω (Figure 3b,c). Introduction of GO into the resin at up to 0.29 wt.% resulted in a moderate enhancement of storage modulus, registered at low frequencies. At higher GO loadings, the G′ values rose more than an order of magnitude in all frequency ranges (Figure 3b). Alongside modulus values, the slope of the curve also changed significantly (G′~ω1/2). The loss modulus graphs had approximately the same slope, but lower positions for samples with GO content up to 0.29 wt.%, while the slope change and G″ value increase were found during the transition to the highest loading (0.8 wt.%) (Figure 3c).
Comparison of both the G′ and G″ modulus values gives an answer to the question of whether the object behaves as a solid or a liquid at the given frequency range. As the G′ > G″ case is typical to solids, and G″ > G′ to fluids, the loss angle tangent, tan(δ), defined as tan(δ) = G″/G′, can be used as a criterion for fluid–solid transition (tan(δ) = 1 for fluid–solid crossover). At 30 °C, the neat DEN-438 epoxy resin demonstrates presumably fluid-like behavior in the low-frequency region, and the tan(δ) values only tend to reduce with frequency, not reaching the unity value (Figure 3d). At a low GO content (0.0155 wt.%), the “tan(δ) − ω” function is practically the same as that for neat epoxy resin. At higher GO loadings, the “tan(δ) − ω” function changes sharply, showing that the solid-like behavior may be achieved at low frequencies. The reproducibility of the results of the oscillatory experiments was confirmed by the measurements performed with the same 0.29 wt.% GO sample after two months of storage at ambient temperature (Figure S4, Supplementary Materials).
In order to verify the temperature impact on GO/DEN-438 fluid–solid transitions, their rheological behavior was investigated at several temperatures. The results for both moduli for selected GO loadings are presented in Figure 4.
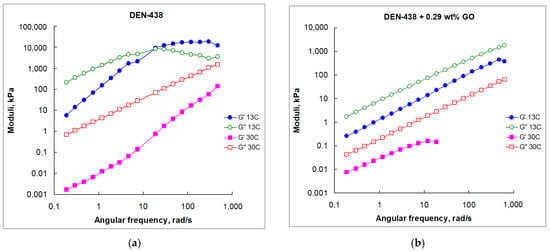
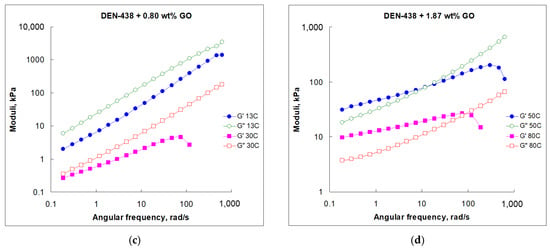
Figure 4.
Frequency dependence of G′ and G″ moduli for neat DEN-438 epoxy resin (a) and with various GO loadings (b–d) at different temperatures.
Contrary to the fluid-like behavior of the neat DEN-438 epoxy resin at 30 °C, the crossover to solid-like behavior was unexpectedly discovered at 13 °C with the critical point at nearly 10 rad/s frequency (Figure 4a). The formulation with 0.8 wt.% GO demonstrated the domination of fluid-like behavior at both temperatures within the entire tested frequency range (Figure 4b,c). The question that arises is if the DEN-438/GO systems can exhibit a solid–fluid crossover. To answer this question, we prepare a sample containing 1.87 wt.% GO and test its rheological properties (Figure 4d). The frequency sweep demonstrates the solid–fluid crossover at both tested temperatures (50 and 80 °C) with critical points at, respectively, nearly 10 and 100 rad/s frequencies (Figure 4d). According to this preliminary data the GO content at which solid–liquid transition in GO/DEN-438 dispersions occurs at ambient temperature may be estimated as more than 0.8 wt.%.
3.2.2. Steady Shear Sweeps
The results of the steady shear measurements for neat DEN-438 and some of the GO/epoxy dispersions with the same GO loadings as in the oscillatory experiments (Figure 4) are presented in Figure 5. The measurements were performed at several selected temperatures (data for several other GO loadings and temperatures are given in Figure S5 in Supplementary Materials).
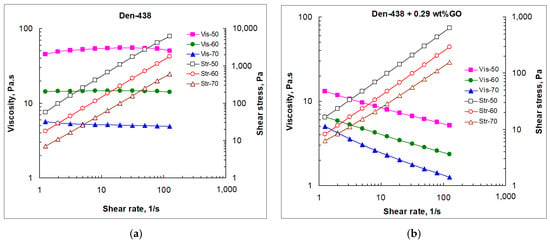
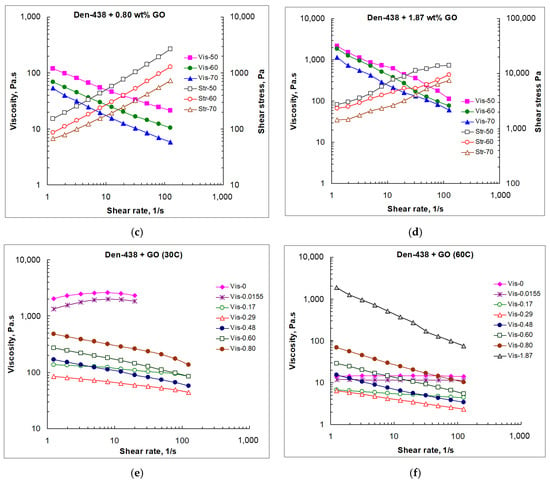
Figure 5.
Viscosity (a–f) and shear stress (a–d) vs. shear rate at various temperatures (Vis-T, Str-T) and GO loadings (Vis-[GO]) for neat DEN-438 (a) and GO/DEN-438 dispersions (b–f).
As can be seen from Figure 5, the steady shear viscosity of the epoxy resin and the GO/epoxy dispersions follow the same trends as described above for the dynamic rheological parameters. An analysis of the values of shear stress shows that up to a GO content of 0.29 wt.%, they are close to those for a neat resin.
However, upon transition to the region of formation of liquid crystal structures (0.80 wt.% GO), they increase several times at all shear rates, and at the maximum GO content (1.87 wt.%), they increase additionally by an order of magnitude. For a given temperature, at low GO content, the viscosity of GO/epoxy compositions only slightly depends on the shear rate. However, for the formulations, in the liquid crystalline state, the viscosity at low and high shear rates differs by an order of magnitude. As in oscillatory shear sweeps, the presence of GO leads to appearance of shear-thinning behavior, as the viscosity is very high at low shear rates and decreases progressively at higher shear rates.
The viscosity value at a low shear rate (approximately of 1.5 s−1) depends on the filler content and is minimal at 0.29 wt.%, while it substantially rises with [GO] > 0.29 wt.%. The viscosity level at low shear rates largely reflects the intensity of the interactions between the epoxy oligomer molecules. GO nanosheets, highly dispersed within the resin at [GO] < 0.29 wt.%, disturb the abovementioned intermolecular bonds in the resin, and, thus, reduce the viscosity of the GO/DEN-438 dispersions. At higher GO loadings, liquid crystals hinder the motion of DEN-438 oligomeric molecules resulting in the rise in viscosity. At high shear rates (~100 s−1) and high GO loading (0.80 wt.%), the viscosity tends to decrease and reaches values close to those for the neat DEN-438. In this case, the higher GO loading destroys GO liquid crystals, and individual GO sheets are aligned with the flow direction. At the highest GO content (1.87 wt.%), the shear-thinning effect becomes the most pronounced (Figure 5f). Together with the results of the oscillatory shear sweeps (Figure 4d), this means that in a state of rest or light loading, the DEN-438 dispersion containing 1.87 wt.% GO behaves as a solid not only at low but even at elevated temperatures (50–60 °C). At the same time, at high shear loads, it exhibits fluid-like properties. At first glance, such behavior is ideal for the film binder used in the RFI process. However, very high viscosity values at such a high GO content require very high pressures for impregnating the carbon fiber fabric in preform. Meanwhile, even at relatively low GO content (near 0.3 wt.%), dispersions remain practically solid at rest, and have reduced viscosity under load.
A higher GO content in dispersions is accompanied by undesirable filtering of its big aggregates during carbon fiber fabric impregnation and uneven distribution of GO in the composite. Carbon plastics have recently been prepared by the RTM process using GO-modified binders based on other epoxy resins [16,19]. It was found that at a content of 0.3 wt.% GO, the maximum strength properties of the cured composites were achieved. At the same time, at a higher GO content (0.6 wt.%) in the polymer matrix, GO aggregates were found that acted as stress concentration centers. Thus, it is possible to preliminarily estimate the content of 0.3 wt.% GO in the epoxy novolac matrix as the threshold above which GO aggregation (liquid crystals formation) takes place. An increase in the physicomechanical properties of carbon plastics based on GO-modified epoxy binders can be expected when the GO content is below the aggregation threshold.
4. Conclusions
Calorimetry and rheometry methods are used to analyze the properties of compositions made from the highly viscous epoxy resin DEN-438 with GO as a filler. According to the DSC data, the glass transition temperature (Tg) of the GO/DEN-438 formulations with a wide range of GO content (0.08–0.8 wt.%) is 7–17 degrees lower compared to the neat resin. Subsequently, the elasticity of this system is maintained even at low temperatures, with the lowest Tg at 0.29 wt.% GO. Lower Tg values of the GO/DEN-438 compositions can be interpreted as “unfreezing” of molecular motions in the resin, when the network of intermolecular bonds of oligomer molecules is disrupted due to the formation of new bonds with groups on the surface of exfoliated GO sheets.
The rheological behavior of GO/DEN-438 formulations is very different from those of aqueous and organic solvent GO dispersions, and even the low-viscosity GO/NPEL-128 formulations. Both steady and dynamic tests showed a linear decrease in viscosity of the DEN-438 resin with an increase in GO content from 0 through 0.29 wt.% due to the abovementioned disruption in intermolecular bonds of oligomer molecules. Then, at a higher GO content (from 0.29 wt.% through to 0.8 wt.%, and higher), the viscosity begins to increase. At high GO content, the decrease in complex viscosity with an increase in the angular frequency can be explained by the disorientation of the formed ordered phase due to the rupture of the viscoelastic GO network and acquisition of liquid-like behavior. The GO content of 0.29 wt.% in DEN-438 is also a threshold for changing the values of the storage and loss moduli. The neat DEN-438 epoxy resin reveals fluid-like behavior at 30 °C; the modulus values increased with frequency with the scaling laws G′~ω2 and G″~ω. The observed features of the rheological behavior of GO/DEN-438 with GO content above 0.29 wt.% can be attributed to formation of ordered (liquid crystalline) structures, in accordance with the DSC data. The results show the promise of developing a new generation of film binders used in the RFI process in fabricating epoxy resin-based composite materials.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/liquids5040032/s1: Figure S1: Polarized optical microscopy (POM) images of DEN-438/graphene oxide formulations with different GO contents (wt.%): 0.015 (a), 0.17 (b), 0.29 (c), 0.8 (d); Figure S2: Temperature dependence of complex viscosity of DEN-438 epoxy resin during initial heating, cooling, and reheating; Figure S3: Complex viscosity of GO/DEN-438 dispersions as a function of angular frequency at various temperatures and GO contents; Figure S4: The results of the measurement of complex viscosity (squares), storage modulus (circles), loss modulus (triangles), and loss tangent (rhombs) of GO/DEN-438 dispersions taken with a difference of two months (unfilled and filled figures); Figure S5: Viscosity (a–d) and shear stress (a,b) of GO/DEN-438 dispersions as a function of shear rate at various temperatures.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.M.A.; methodology, L.M.A.; validation, L.M.A., R.R.A., and A.K.; formal analysis, A.K.; investigation, L.M.A. and A.K.; resources, A.M.D.; data curation, R.R.A.; writing—original draft preparation, L.M.A. and R.R.A.; writing—review and editing, L.M.A. and A.M.D.; visualization, R.R.A.; supervision, L.M.A.; project administration, A.M.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article and are included in the associated Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| GO | graphene oxide |
| DEN-438 | brand of epoxy novolac resin |
| NPEL-128 | brand of epoxy dianic resin |
| RFI | Resin Film Infusion process |
| RTM | Resin Transfer Molding process |
| DSC | differential scanning calorimetry |
| IPA | i-propyl alcohol |
| Tg | glass transition temperature |
| σ | shear stress |
| η | viscosity |
| γ | shear rate |
| G′ | storage shear modulus |
| G″ | loss shear modulus |
| Tan(delta) | mechanical loss tangent |
| |η*| | complex shear viscosity |
| ω | frequency range |
| T20 | temperature at which a viscosity of 20 Pa·s is achieved |
References
- Hao, S.; Hou, S.; Liu, Y.; Nan, D.; Xu, D.; Shen, W.; Kang, F.; Huang, Z.-H. Enhanced anticorrosion of waterborne epoxy coatings by electrochemical exfoliated graphene oxide. Prog. Org. Coat. 2025, 202, 109147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, H.; Lin, B.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, C. Graphene oxide loaded dopamine modified zirconium dioxide nanocomposites to enhance the corrosion resistance of epoxy resin coatings. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 35, 5717–5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Min, W.; Geng, L.; Li, Y.; Song, D.; Chen, C. Design a new type of composite coating of functionalized graphene oxide-composite pyrrhotite/waterborne epoxy resin with excellent hydrogen barrier performance. Corros. Sci. 2025, 256, 113261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Song, Q. Synergistic effect of graphene oxide and glass fiber on mechanical and thermal properties of composites: Experimental and simulation investigations. React. Funct. Polym. 2025, 210, 106201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, J. Graphene/epoxy coating with radiation heat dissipation properties for spacecraft thermal management. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 519, 165105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, T.; Pan, X.; Tang, E.; Yuan, M.; Xing, X.; Chu, X.; Liu, S.; Li, H.; Cui, J. Enhancing antistatic property of epoxy resin coatings via formation of conductive networks with fibrous polyaniline/reduced graphene oxide. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 478, 141191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, D.R.; Park, S.; Bielawski, C.W.; Ruoff, R.S. The chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.J.; Zhu, W.J.; Zhang, S.F.; Gao, Q.; Li, J.Z.; Zhang, W. Amine-terminated hyperbranched polyamide covalent functionalized graphene oxide-reinforced epoxy nanocomposites with enhanced toughness and mechanical properties. Polym. Test. 2019, 76, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.G.; Costa, V.O.; Martinez, A.H.G.; Régnier, B.M.; Gomes, G.C.B.; Zarbin, A.J.G.; Orth, E.S. Functionalization of graphene oxide via epoxide groups: A comprehensive review of synthetic routes and challenges. Front. Carbon 2024, 3, 1393077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Song, J.; Tian, X.; Liu, T.; Wu, Z. High-performance epoxy nanocomposites via constructing a rigid-flexible interface with graphene oxide functionalized by polyetheramine and f-SiO2. Carbon 2024, 216, e118591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, Y.H.; Lee, K.E.; Shin, T.J.; Kim, S.O.; Kim, S.Y. Wide concentration liquid crystallinity of graphene oxide aqueous suspensions with interacting polymers. Mater. Horiz. 2017, 4, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Fernandez, G.; Muñoz, M.; García-Quesada, J.C.; Rodriguez-Pastor, I.; Martin-Gullon, I. Role of graphene oxide surface chemistry on the improvement of the interlaminar mechanical properties of resin infusion processed epoxy-carbon fiber composites. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, E2116–E2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallés, C.; Beckert, F.; Burk, L.; Mülhaupt, R.; Young, R.J.; Kinloch, I.A. Effect of the C/O ratio in graphene oxide materials on the reinforcement of epoxy-based nanocomposites. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2016, 54, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortz, D.R.; Heras, E.G.; Martin-Gullon, I. Impressive Fatigue Life and Fracture Toughness Improvements in Graphene Oxide/Epoxy Composites. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, M.; Nitzsche, F.; Laliberte, J.; Hind, S.; Robitaille, F.; Labrosse, M. Thermal properties of doubly reinforced fiberglass/epoxy composites with graphene nanoplatelets, graphene oxide and reduced-graphene oxide. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 164, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.K.; Borah, M.; Gupta, A.; Yokozeki, T.; Dhakate, S.R. Improved mechanical properties of carbon fiber/graphene oxide-epoxy hybrid composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 135, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, G.; Starost, K.; Bari, P.; Faisal, N.; Mishra, S.; Njuguna, J. Tensile and flexural properties of hybrid graphene oxide/epoxy carbon fibre reinforced composites. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 195, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyte, J.; Pancholi, K.; Njuguna, J. Recent Developments in Graphene Oxide/Epoxy Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Composites. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 224–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.K.; Garg, H.; Singh, M.; Yokozeki, T.; Dhakate, S.R. Enhanced interfacial properties of graphene oxide incorporated carbon fiber reinforced epoxy nanocomposite: A systematic thermal properties investigation. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vryonis, O.; Virtanen, S.T.H.; Andritsch, T.; Vaughan, A.S.; Lewin, P.L. Understanding the cross-linking reactions in highly oxidized graphene/epoxy nanocomposite systems. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 3035–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirova, L.; Surnova, A.; Balkaev, D.; Musin, D.; Amirov, R.; Dimiev, A.M. Homogeneous liquid phase transfer of graphene oxide into epoxy resins. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 11909–11917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surnova, A.; Balkaev, D.; Musin, D.; Amirov, R.; Dimiev, A.M. Fully exfoliated graphene oxide accelerates epoxy resin curing, and results in dramatic improvement of the polymer mechanical properties. Compos. Part B 2019, 162, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimiev, A.M.; Surnova, A.; Lounev, I.; Khannanov, A. Intrinsic Insertion Limits of Graphene Oxide into Epoxy Resin and the Dielectric Behavior of Composites Comprising Truly 2D Structures. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 3461–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimiev, A.M.; Lounev, I.; Khamidullin, T.; Surnova, A.; Valimukhametova, A.; Khannanov, A. Polymer Composites Comprising Single-Atomic-Layer Graphenic Conductive Inclusions and Their Unusual Dielectric Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 13715–13725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Giudice, F.; Cunning, B.V.; Ruoff, R.S.; Shen, A.Q. Filling the gap between transient and steady shear rheology of aqueous graphene oxide dispersions. Rheol. Acta 2018, 57, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalghatgi, S.R.; Kumar, S.K.; Mani, E. Molecular Dynamics Study of the Role of Nanoparticle Assemblies on Polymer Nanocomposite Rheology. Macromolecules 2024, 57, 9555–9564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Tong, X.; Wang, Y.; Bao, J.; Wang, Z.M. Graphene oxide liquid crystals—Synthesis, phase transition, rheological property, and applications in optoelectronics and display. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallés, C.; Young, R.J.; Lomax, D.J.; Kinloch, I.A. The rheological behaviour of concentrated dispersions of graphene oxide. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 6311–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corker, A.; Ng, H.C.H.; Poole, R.J.; Garcia-Tunon, E. 3D printing with 2D colloids: Designing rheology protocols to predict “printability” of soft-materials. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 1444–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikala, S.P.; Lim, J.; Kim, I.H.; Jung, H.J.; Yun, T.; Han, T.H.; Kim, S.O. Graphene oxide liquid crystals: A frontier 2D soft material for graphene-based functional materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 6013–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfai, W.; Singh, P.; Shatilla, Y.; Iqbal, M.Z.; Abdala, A.A. Rheology and microstructure of dilute graphene oxide suspension. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konkena, B.; Vasudevan, S. Glass, Gel, and Liquid Crystals: Arrested States of Graphene Oxide Aqueous Dispersions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 21706–21713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, R.; Aboutalebi, S.H.; Esrafilzadeh, D.; Konstantinov, K.; Moulton, S.E.; Razal, J.M.; Wallace, G.G. Organic Solvent-Based Graphene Oxide Liquid Crystals: A Facile Route toward the Next Generation of Self-Assembled Layer-by-Layer Multifunctional 3D Architectures. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3981–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, J.I.; Villar-Rodil, S.; Martınez-Alonso, A.; Tascon, J.M.D. Graphene oxide dispersions in organic solvents. Langmuir 2008, 24, 10560–10564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, R.; Gong, J.; Xu, D.; Tang, T.; Sun, Z.Y. Relationship between structures and rheological properties of plate-like particle suspensions. Colloids Surf. A 2015, 470, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Chamoli, P.; Sachdev, S.; Raina, K.K.; Shukla, R.K. Structural, optical and rheological behavior investigations of graphene oxide/glycerol based lyotropic liquid crystalline phases. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 509, 144710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, F.C. Thermoset Composite Fabrication Processes. In Structural Composite Materials; Campbell, F.C., Ed.; ASM International: Almere, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 119–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.-M.; Zheng, S.-R.; Zheng, Y.-P. Forming technology of polymer matrix composites. In Polymer Matrix Composites and Technology; Wang, R.-M., Zheng, S.-R., Zheng, Y.-P., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 253–319. [Google Scholar]
- Umer, R.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y.; Haroosh, H.J.; Liao, K. The effect of graphene oxide (GO) nanoparticles on the processing of epoxy/glass fiber composites using resin infusion. Intern. J. Adv. Manufact. Technol. 2015, 81, 2183–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, D.I.; Chursova, L.V.; Petrova, A.P. A manufacturing technology of polymeric composite materials by resin film infusion. Polym. Sci. Ser. D 2012, 5, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshed, S.M.S.; Estellé, P. A state of the art review on viscosity of nanofluids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 1134–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirov, R.R.; Shayimova, J.; Nasirova, Z.; Dimiev, A.M. Chemistry of graphene oxide. Reactions with transition metal cations. Carbon 2017, 116, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Sue, H.-J. Epoxy/Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites. In Epoxy Polymers. New Materials and Innovations; Pascault, J.-P., Williams, R.J.J., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; pp. 185–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenberg, B.A. Kinetics, Thermodynamics and Mechanism of Reactions of Epoxy Oligomers with Amines. In Epoxy Resins and Composites II; Dusek, K., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA; Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; pp. 115–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solodov, A.N.; Balkaev, D.; Amirov, R.; Gataullina, R.; Nurtdinova, L.; Yusupov, R.; Kharintsev, S.S.; Dimiev, A.M. Polymer Composites with Magnetically Tunable Optical Anisotropy. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 6338–6345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).