Exploring Solvation Properties of Protic Ionic Liquids by Employing Solvatochromic Dyes and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
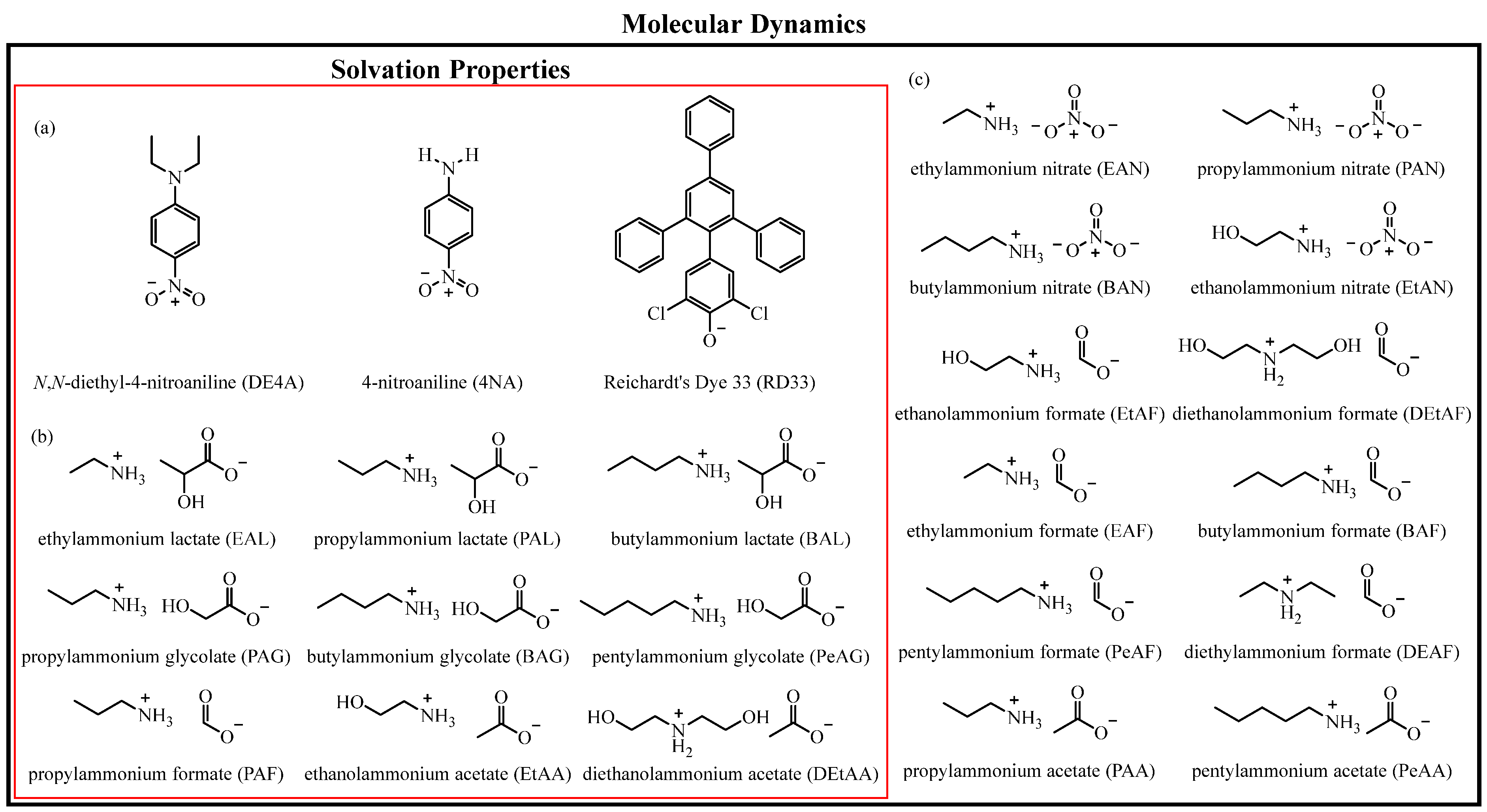
2.1. PIL Synthesis
2.2. UV/Visible Spectroscopy Analysis
2.3. KAT Formulation
2.4. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
3. Results
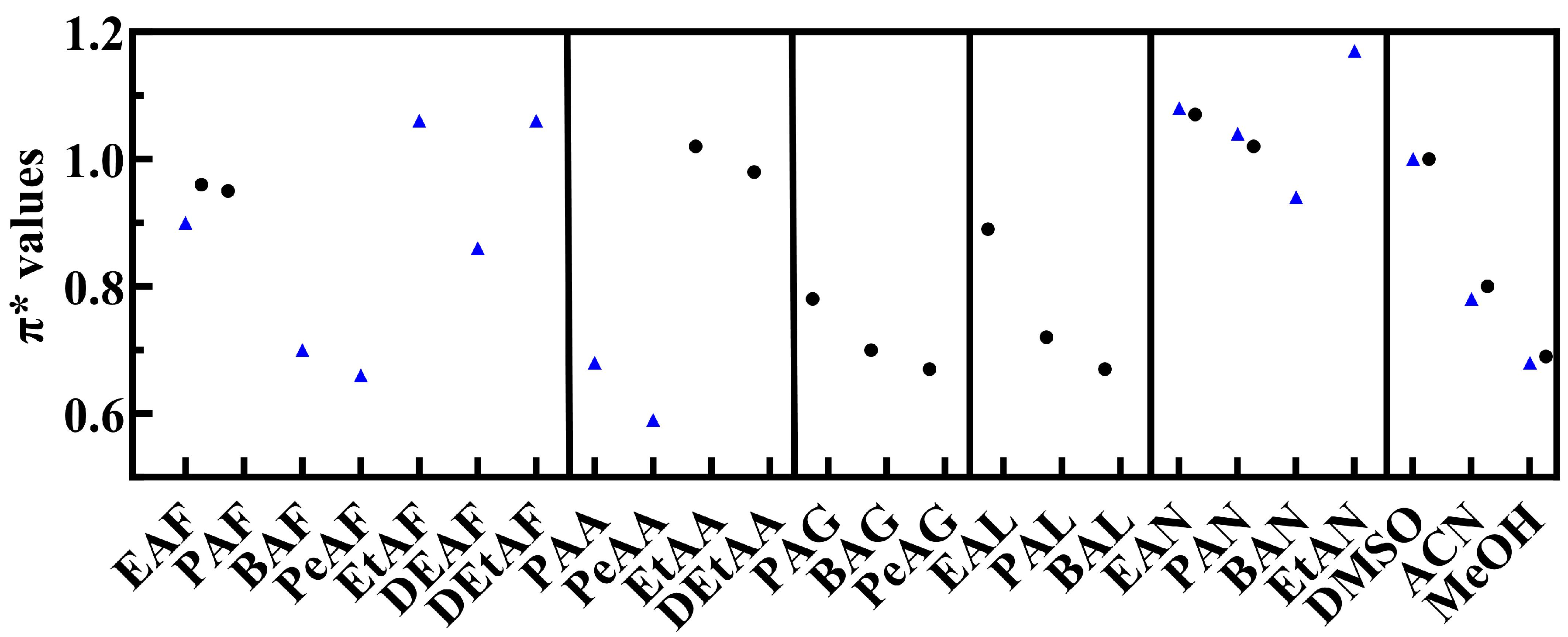
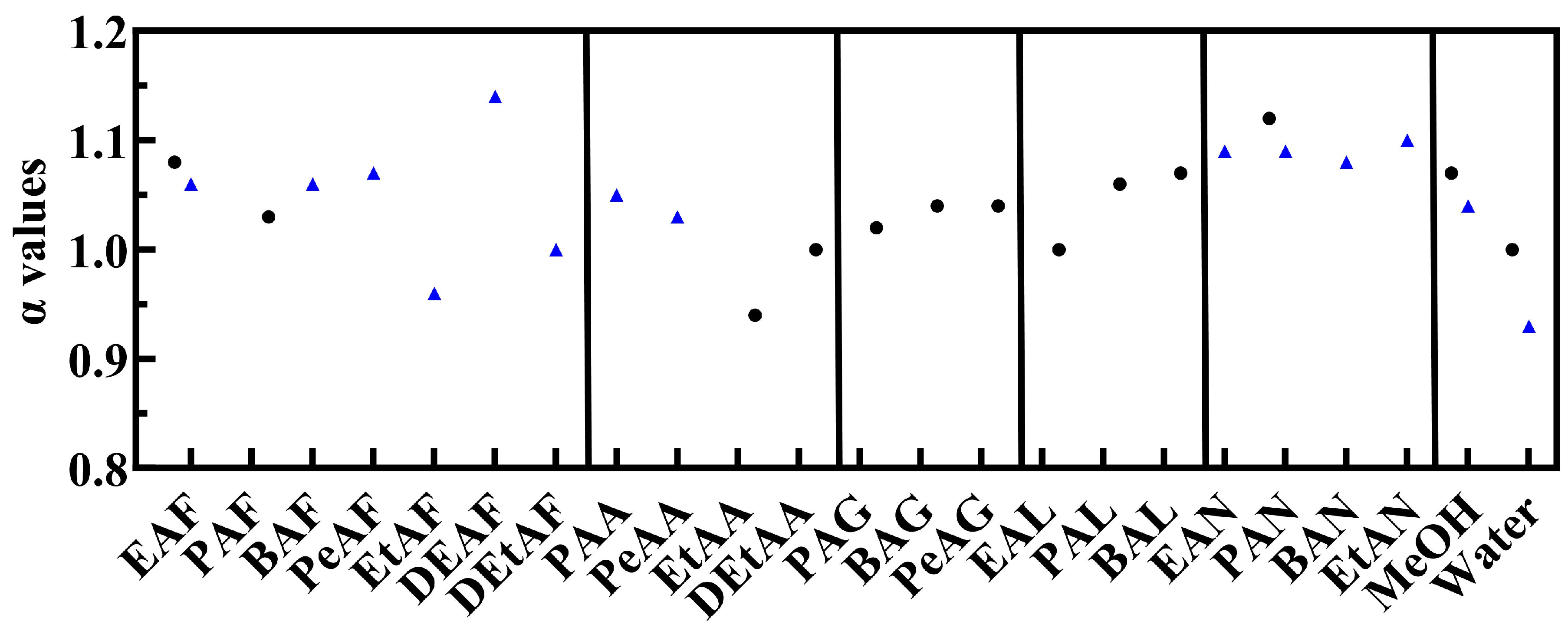
3.1. KAT Parameter Characterisation of PILs
| Max Absorbance Wavelength (nm) | π* (±0.01) | α (±0.03) | β (±0.03) | ET(30) (±0.3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE4A (±1) | 4NA (±1) | RD(33) (±1) | ||||||
| Novel | PAF | 410 | 385 | 426 | 0.95 | 1.03 | 0.68 | 57.6 |
| PAG | 401 | 383 | 440 | 0.78 | 1.02 | 0.84 | 55.6 | |
| BAG | 397 | 382 | 444 | 0.70 | 1.04 | 0.90 | 55.1 | |
| PeAG | 395 | 382 | 447 | 0.67 | 1.04 | 0.95 | 54.7 | |
| EAL | 407 | 385 | 433 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 0.75 | 56.6 | |
| PAL | 398 | 383 | 440 | 0.72 | 1.06 | 0.91 | 55.6 | |
| BAL | 395 | 383 | 443 | 0.67 | 1.07 | 0.98 | 55.2 | |
| EtAA | 414 | 388 | 430 | 1.02 | 0.94 | 0.67 | 57.0 | |
| DEtAA | 412 | 385 | 426 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.64 | 57.6 | |
| Control | DMSO | 413 | 390 | 529 | 1.00 | 0.19 | 0.74 | 45.30 |
| acetonitrile | 402 | 368 | - | 0.80 | - | 0.43 | - | |
| methanol | 396 | 370 | 442 | 0.69 | 1.07 | 0.62 | 55.34 | |
| water | 429 | 377 | 406 | 1.27 | 1.00 | 0.09 | 60.76 | |
| EAN | 417 | 380 | - | 1.07 | - | 0.41 | - | |
| PAN | 414 | 383 | 411 | 1.02 | 1.13 | 0.55 | 59.95 | |
| EAF | 411 | 385 | 423 | 0.96 | 1.05 | 0.66 | 58.09 | |
3.1.1. ET(30) Scale
3.1.2. π* (Polarizability)
3.1.3. α H-Bond Acidity
3.1.4. β H-Bond Basicity
3.2. Radial Distribution Functions of PILs
3.2.1. The Effect of Cation Structure
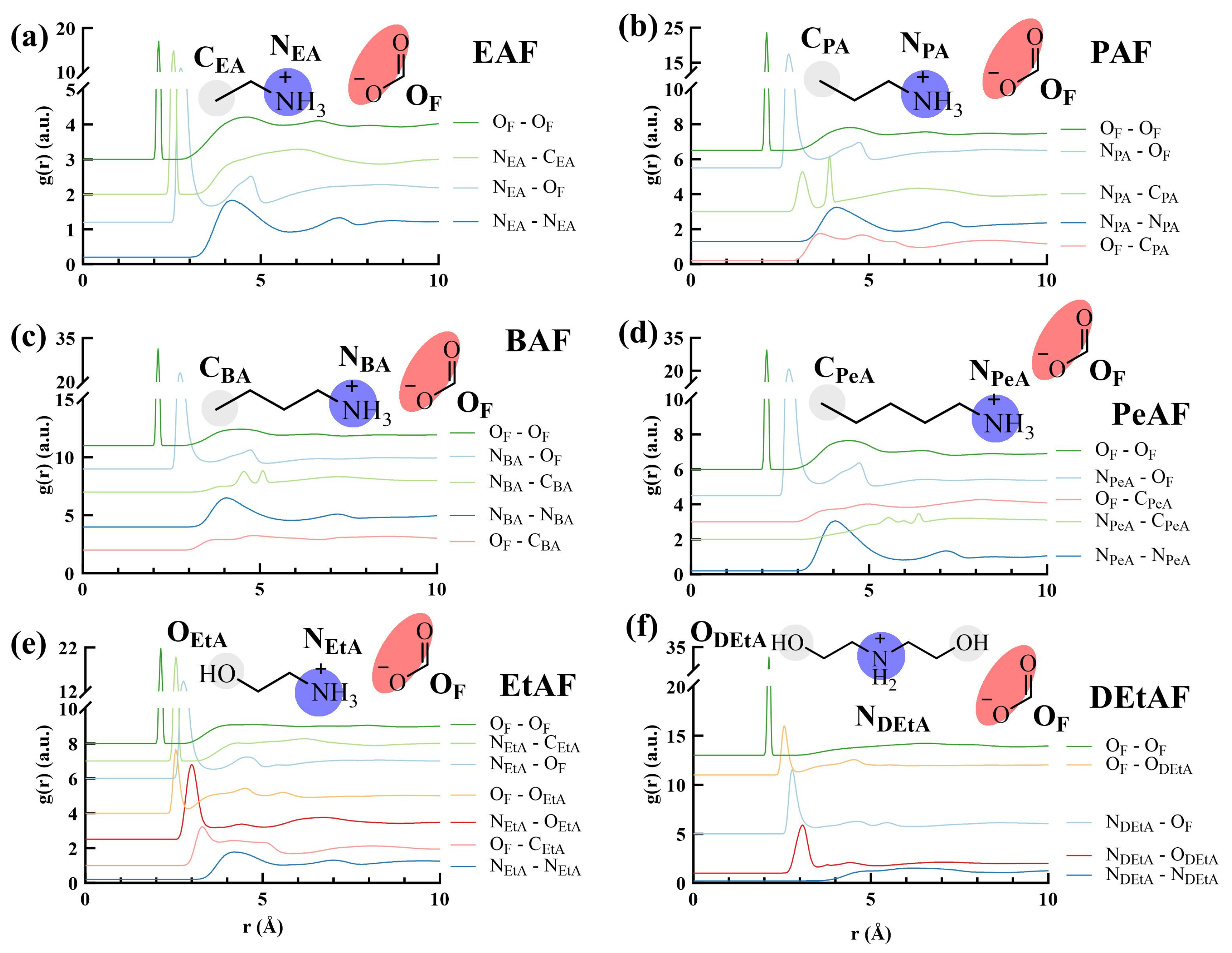
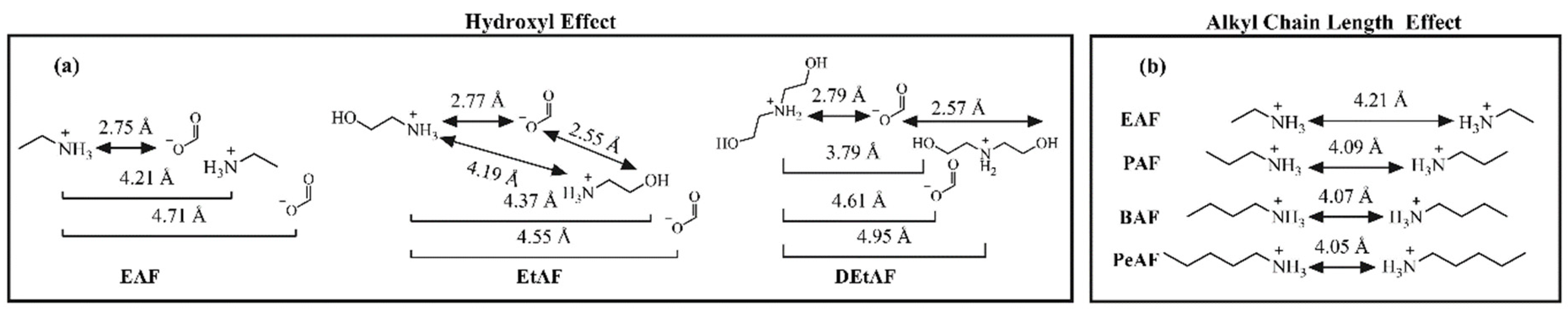
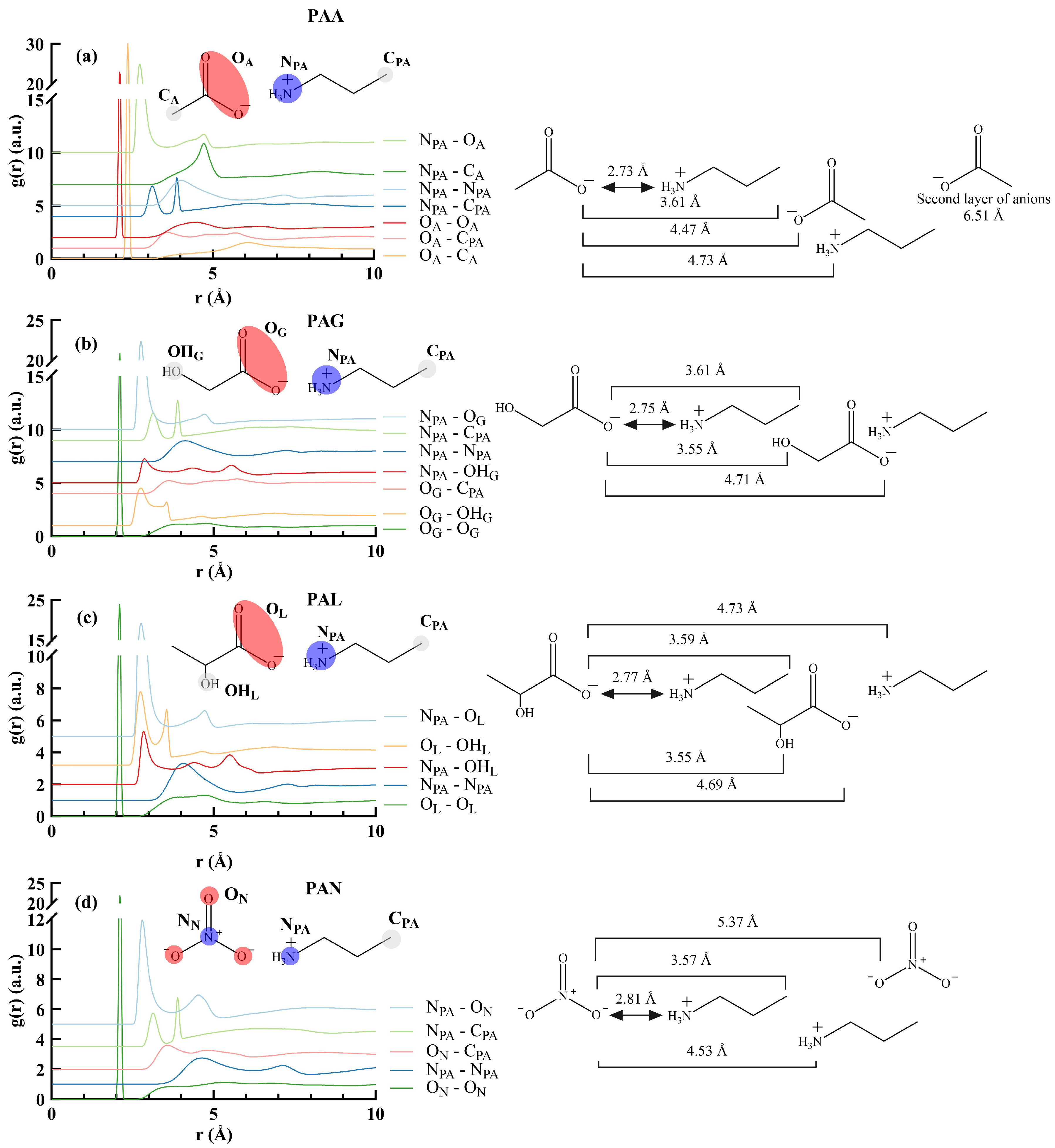
3.2.2. The Effect of Anion Structure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greaves, T.L.; Drummond, C.J. Protic Ionic Liquids: Properties and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 206–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaves, T.L.; Drummond, C.J. Solvent nanostructure, the solvophobic effect and amphiphile self-assembly in ionic liquids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 1096–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, R.; Warr, G.G.; Atkin, R. Structure and Nanostructure in Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 6357–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Chong, A.L.; Forsyth, M.; Kar, M.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Somers, A.; Pringle, J.M. New dimensions in salt–solvent mixtures: A 4th evolution of ionic liquids. Faraday Discuss. 2018, 206, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welton, T. Room-temperature ionic liquids. Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2071–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsyth, S.A.; Pringle, J.M.; MacFarlane, D.R. Ionic Liquids; An Overview. Aust. J. Chem. 2004, 57, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandi, K. A Review of Ionic Liquids, Their Limits and Applications. Green Sustain. Chem. 2014, 4, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, T.L.; Drummond, C.J. Protic Ionic Liquids: Evolving Structure–Property Relationships and Expanding Applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11379–11448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, H.; Yoshizawa-Fujita, M.; Kohno, Y. Functional Design of Ionic Liquids: Unprecedented Liquids that Contribute to Energy Technology, Bioscience, and Materials Sciences. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 92, 852–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, T.L.; Schaffarczyk McHale, K.S.; Burkart-Radke, R.F.; Harper, J.B.; Le, T.C. Machine learning approaches to understand and predict rate constants for organic processes in mixtures containing ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 2742–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids: Solvents for Synthesis and Catalysis. 2. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3508–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedov, I.A.; Magsumov, T.I.; Salikov, T.M.; Solomonov, B.N. Solvation of apolar compounds in protic ionic liquids: The non-synergistic effect of electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonds. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 25352–25359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, C.L.; Agranat, I.; Bagno, A.; Braslavsky, S.E.; Fernandes, P.A.; Gal, J.-F.; Lloyd-Jones, G.C.; Mayr, H.; Murdoch, J.R.; Nudelman, N.S.; et al. Glossary of terms used in physical organic chemistry (IUPAC Recommendations 2021). Pure Appl. Chem. 2022, 94, 353–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Chang, N.; Yang, L.; Bu, X.; Wei, J.; Liu, Q. Determination and Prediction for the Polarity of Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2017, 62, 2610–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deye, J.F.; Berger, T.A.; Anderson, A.G. Nile Red as a solvatochromic dye for measuring solvent strength in normal liquids and mixtures of normal liquids with supercritical and near critical fluids. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, M.A.; Morris, B.C.; Edwards, W.D.; Blumenfeld, A.; Zhao, X.; McHale, J.L. Thermosolvatochromism of Phenol Blue in Polar and Nonpolar Solvents. J. Phys. Chem. A 2004, 108, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cave, R.J.; Castner, E.W. Time-Dependent Density Functional Theory Investigation of the Ground and Excited States of Coumarins 102, 152, 153, and 343. J. Phys. Chem. A 2002, 106, 12117–12123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Homma, Y.; Hiruta, Y.; Citterio, D.; Suzuki, K. Structural characteristics and optical properties of a series of solvatochromic fluorescent dyes displaying long-wavelength emission. Dye. Pigment. 2009, 83, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Baker, G.A.; Arzhantsev, S.; Dong, J.; Maroncelli, M. Solvation and Rotational Dynamics of Coumarin 153 in Ionic Liquids: Comparisons to Conventional Solvents. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 7291–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, P.H.; Youngberg, P.J.; Kersten, B.R.; Poole, C.F. Solvent properties of liquid organic salts used as mobile phases in microcolumn reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1987, 411, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, S.K.; Shetty, P.H.; Poole, C.F. Chromatographic and spectroscopic studies of the solvent properties of a new series of room-temperature liquid tetraalkylammonium sulfonates. Anal. Chim. Acta 1989, 218, 241–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.L.; Ding, J.; Welton, T.; Armstrong, D.W. Characterizing Ionic Liquids on the Basis of Multiple Solvation Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 14247–14254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bini, R.; Chiappe, C.; Mestre, V.L.; Pomelli, C.S.; Welton, T. A rationalization of the solvent effect on the Diels–Alder reaction in ionic liquids using multiparameter linear solvation energy relationships. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008, 6, 2522–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeličić, A.; García, N.; Löhmannsröben, H.-G.; Beuermann, S. Prediction of the Ionic Liquid Influence on Propagation Rate Coefficients in Methyl Methacrylate Radical Polymerizations Based on Kamlet−Taft Solvatochromic Parameters. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 8801–8808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowhurst, L.; Falcone, R.; Lancaster, N.L.; Llopis-Mestre, V.; Welton, T. Using Kamlet−Taft Solvent Descriptors To Explain the Reactivity of Anionic Nucleophiles in Ionic Liquids. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 8847–8853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranieri, G.; Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Nucleophilic Reactions at Cationic Centers in Ionic Liquids and Molecular Solvents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawker, R.R.; Haines, R.S.; Harper, J.B. The effect of varying the anion of an ionic liquid on the solvent effects on a nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 3453–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, B.J.; Harper, J.B. The effect of the structure of the anion of an ionic liquid on the rate of reaction at a phosphorus centre. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2019, 32, e3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, C. Polarity of ionic liquids determined empirically by means of solvatochromic pyridinium N-phenolate betaine dyes. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappe, C.; Pomelli, C.S.; Rajamani, S. Influence of Structural Variations in Cationic and Anionic Moieties on the Polarity of Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 9653–9661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Rani, M.A.; Brant, A.; Crowhurst, L.; Dolan, A.; Lui, M.; Hassan, N.H.; Hallett, J.P.; Hunt, P.A.; Niedermeyer, H.; Perez-Arlandis, J.M.; et al. Understanding the polarity of ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 16831–16840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spange, S.; Lungwitz, R.; Schade, A. Correlation of molecular structure and polarity of ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 192, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamlet, M.J.; Taft, R.W. The solvatochromic comparison method. I. The β-scale of solvent hydrogen-bond acceptor (HBA) basicities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taft, R.W.; Kamlet, M.J. The solvatochromic comparison method. 2. The α-scale of solvent hydrogen-bond donor (HBD) acidities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 2886–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, T.; Taft, R.W.; Kamlet, M.J. The solvatochromic comparison method. 3. Hydrogen bonding by some 2-nitroaniline derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 3233–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamlet, M.J.; Abboud, J.L.; Taft, R.W. The solvatochromic comparison method. 6. The π * scale of solvent polarities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977, 99, 6027–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minesinger, R.R.; Jones, M.E.; Taft, R.W.; Kamlet, M.J. The solvatochromic comparison method. 5. Spectral effects and relative strengths of the first and second hydrogen bonds by 4-nitroaniline to hydrogen bond acceptor solvents. J. Org. Chem. 1977, 42, 1929–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, D.; Drummond, C.J.; Greaves, T.L. Solvation properties of protic ionic liquids and molecular solvents. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, C. Pyridinium N-phenolate betaine dyes as empirical indicators of solvent polarity: Some new findings. Pure Appl. Chem. 2004, 76, 1903–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, R.; Zayat, M.; Levy, D. ET(33) dye as a tool for polarity determinations: Application to porous hybrid silica thin-films. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2010, 210, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; El Mohamad, M.; Brown, S.; Zhai, J.; Rosado, C.; Shen, Y.; Blanch, E.W.; Drummond, C.J.; Greaves, T.L. Small angle X-ray scattering investigation of ionic liquid effect on the aggregation behavior of globular proteins. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 648, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Binns, J.; Zhai, J.; Guo, X.; Ryan, T.M.; Drummond, C.J.; Greaves, T.L. Insights on lysozyme aggregation in protic ionic liquid solvents by using small angle X-ray scattering and high throughput screening. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 345, 117816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Brown, S.J.; Drummond, C.J.; Greaves, T.L. Protein aggregation and crystallization with ionic liquids: Insights into the influence of solvent properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 1173–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Smith, K.M.; Darmanin, C.; Ryan, T.M.; Drummond, C.J.; Greaves, T.L. Lysozyme conformational changes with ionic liquids: Spectroscopic, small angle X-ray scattering and crystallographic study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 585, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Ryan, T.M.; Rosado, C.J.; Drummond, C.J.; Greaves, T.L. Effect of ionic liquids on the fluorescence properties and aggregation of superfolder green fluorescence protein. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 591, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, C.F. Chromatographic and spectroscopic methods for the determination of solvent properties of room temperature ionic liquids. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1037, 49–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, S.; Imberti, S.; Atkin, R.; Warr, G. Nanostructure in amino acid ionic molecular hybrid solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 351, 118599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyckens, D.J.; Demir, B.; Walsh, T.R.; Welton, T.; Henderson, L.C. Determination of Kamlet–Taft parameters for selected solvate ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 13153–13157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauber, D.; Philippi, F.; Becker, J.; Zapp, J.; Morgenstern, B.; Kuttich, B.; Kraus, T.; Hempelmann, R.; Hunt, P.; Welton, T.; et al. Anion and ether group influence in protic guanidinium ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 6436–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.J.; Yalcin, D.; Pandiancherri, S.; Le, T.C.; Orhan, I.; Hearn, K.; Han, Q.; Drummond, C.J.; Greaves, T.L. Characterising a protic ionic liquid library with applied machine learning algorithms. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 367, 120453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.; Andrade, R.; Birgin, E.G.; Martínez, J.M. PACKMOL: A package for building initial configurations for molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16 Rev. C.01; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, D.A.; Aktulga, H.M.; Belfon, K.; Ben-Shalom, I.Y.; Brozell, S.R.; Cerutti, D.S.; Cheatham, I.T.E.; Cisneros, G.A.; Cruzeiro, V.W.D.; Darden, T.A.; et al. Amber 2021; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa da Silva, A.W.; Vranken, W.F. ACPYPE—AnteChamber PYthon Parser interfacE. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, D.; Christofferson, A.J.; Drummond, C.J.; Greaves, T.L. Solvation properties of protic ionic liquid–molecular solvent mixtures. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 10995–11011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcin, D.; Drummond, C.J.; Greaves, T.L. High throughput approach to investigating ternary solvents of aqueous non-stoichiometric protic ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 6810–6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumino, K.; Wulf, A.; Ludwig, R. Hydrogen Bonding in Protic Ionic Liquids: Reminiscent of Water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 3184–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.F.; Chen, S.-H.; Schriver, G.W.; Arnett, E.M. Thermodynamics of solution of nonpolar gases in a fused salt. Hydrophobic bonding behavior in a nonaqueous system. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 481–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, T.L.; Kennedy, D.F.; Mudie, S.T.; Drummond, C.J. Diversity Observed in the Nanostructure of Protic Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 10022–10031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M.; Izgorodina, E.I.; Abbott, A.P.; Annat, G.; Fraser, K. On the concept of ionicity in ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 4962–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.J.; Ryan, T.M.; Drummond, C.J.; Greaves, T.L.; Han, Q. Lysozyme aggregation and unfolding in ionic liquid solvents: Insights from small angle X-ray scattering and high throughput screening. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 655, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Wang, X.; Bynre, N. Utilizing Water Activity as a Simple Measure to Understand Hydrophobicity in Ionic Liquids. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Wang, X.; Byrne, N. Understanding the Influence of Key Ionic Liquid Properties on the Hydrolytic Activity of Thermomyces lanuginosus Lipase. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Su, Y.; Smith, K.M.; Binns, J.; Drummond, C.J.; Darmanin, C.; Greaves, T.L. Probing ion-binding at a protein interface: Modulation of protein properties by ionic liquids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 650, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brown, S.J.; Christofferson, A.J.; Drummond, C.J.; Han, Q.; Greaves, T.L. Exploring Solvation Properties of Protic Ionic Liquids by Employing Solvatochromic Dyes and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Analysis. Liquids 2024, 4, 288-304. https://doi.org/10.3390/liquids4010014
Brown SJ, Christofferson AJ, Drummond CJ, Han Q, Greaves TL. Exploring Solvation Properties of Protic Ionic Liquids by Employing Solvatochromic Dyes and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Analysis. Liquids. 2024; 4(1):288-304. https://doi.org/10.3390/liquids4010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrown, Stuart J., Andrew J. Christofferson, Calum J. Drummond, Qi Han, and Tamar L. Greaves. 2024. "Exploring Solvation Properties of Protic Ionic Liquids by Employing Solvatochromic Dyes and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Analysis" Liquids 4, no. 1: 288-304. https://doi.org/10.3390/liquids4010014
APA StyleBrown, S. J., Christofferson, A. J., Drummond, C. J., Han, Q., & Greaves, T. L. (2024). Exploring Solvation Properties of Protic Ionic Liquids by Employing Solvatochromic Dyes and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Analysis. Liquids, 4(1), 288-304. https://doi.org/10.3390/liquids4010014