Knockouts of Yeast Plasma Membrane Phosphate Transporters Alter Resistance to Heavy Metals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Yeast Strains and Cultivation
2.2. Sensitivity to Manganese and Vanadate Ions
2.3. The Treatment of the Cells with Ag+
2.4. Polyphosphate Assay
2.5. Manganese Assay
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. The Effect of Vanadate on Yeast Growth
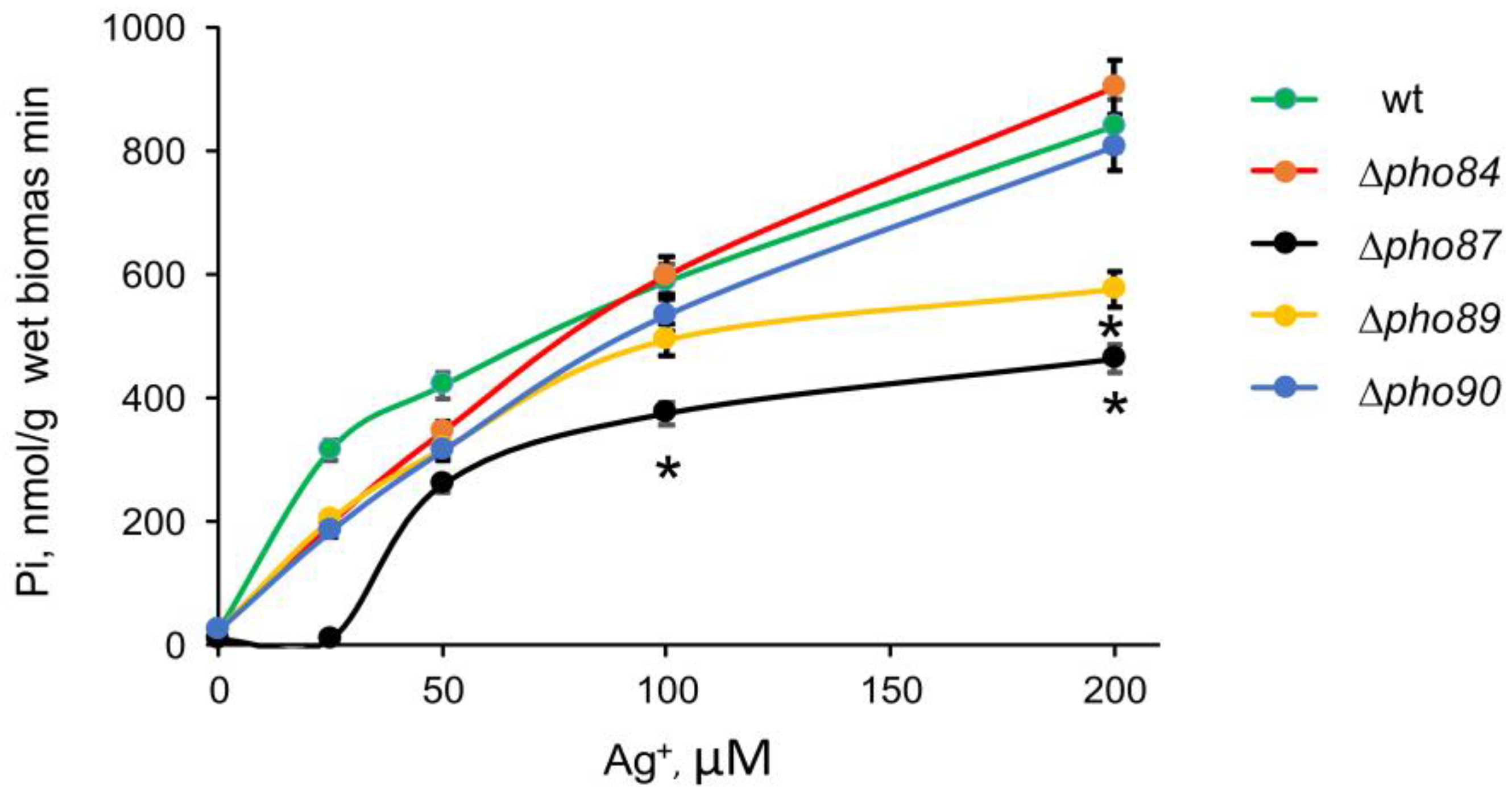
3.2. The Effect of Ag+ on Pi Release
3.3. The Effects of Mn2+ on Yeast Growth and polyP Content
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Pi | Orthophosphate |
| PolyP | Inorganic polyphosphate |
References
- Sobral, A.F.; Cunha, A.; Costa, I.; Silva-Carvalho, M.; Silva, R.; Barbosa, D.J. Environmental xenobiotics and epigenetic modifications: Implications for human health and disease. J. Xenobiotics 2025, 15, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sarker, A.; Masud, M.A.A.; Deepo, D.M.; Das, K.; Nandi, R.; Ansary, M.W.R.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Islam, T. Biological and green remediation of heavy metal contaminated water and soils: A state-of-the-art review. Chemosphere 2023, 332, 138861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iimaa, T.; Batmunkh, M.; Dulguun, B.; Dorjsuren, B.; Turmunkh, T.; Tserennadmid, E.; Surenjav, U.; Choidash, B.; Gereltuya, R. Bacterial heavy metal resistance in contaminated soil. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2025, 35, e2411073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C. Biosorption of heavy metals by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.; Chauhan, P.; Kaur, C.; Arora, P.K.; Garg, S.K.; Singh, V.P.; Singh, K.P.; Srivastava, A. Comprehensive heavy metal remediation mechanisms with insights into CRISPR-Cas9 and biochar innovations. Biodegradation 2025, 36, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, K.S.; Patel, K.M. Biosorption and bioremediation of heavy metal ions from wastewater using algae: A comprehensive review. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2025, 41, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavya, G.; De Britto, S.; Satapute, P.; Geetha, N.; Jogaiah, S. Biofabricated yeast: Super-soldier for detoxification of heavy metals. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aeini, K.; Zoghi, A.; Khosravi-Darani, K. Application of yeasts as pollutant adsorbents. Curr. Microbiol. 2025, 82, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.L.; Reynolds, E.E.; Belcher, A.M. Designing yeast as plant-like hyperaccumulators for heavy metals. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ruta, L.L.; Kissen, R.; Nicolau, I.; Neagoe, A.D.; Petrescu, A.J.; Bones, A.M.; Farcasanu, I.C. Heavy metal accumulation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells armed with metal binding hexapeptides targeted to the inner face of the plasma membrane. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 5749–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Xu, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, J.; Peng, Y.; Liao, J.; Qiao, Y.; Shang, C.; Guo, Z.; et al. A novel yeast strain Geotrichum sp. CS-67 capable of accumulating heavy metal ions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 236, 113497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankar, A.; Zinjarde, S.; Shinde, M.; Gopalghare, G.; Ravikumar, A. Heavy metal tolerance in marine strains of Yarrowia lipolytica. Extremophiles 2018, 22, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Chen, S.; Zhao, M.; Wen, D.; Peng, L.; Zou, L.; Han, J.; Li, Q. The adsorption capacity and genetic mechanism analysis of Yarrowia phangngaensis for multiple heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 494, 138756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreeva, N.; Ryazanova, L.; Dmitriev, V.; Kulakovskaya, T.; Kulaev, I. Cytoplasmic inorganic polyphosphate participates in the heavy metal tolerance of Cryptococcus humicola. Folia Microbiol. 2014, 59, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhi, R.; Dehghani, M.H.; Nabizadeh, R.; Mahvi, A.H.; Naddafi, K.; Ahmadikia, K. Developing and optimizing a Saccharomyces cerevisiae-based cytotoxicity bioassay for toxicity assessment of contaminated waters. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 299, 118407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, A.J.; Wilson, S. Zinc homeostasis in the secretory pathway in yeast. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2020, 55, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Robinson, J.R.; Isikhuemhen, O.S.; Anike, F.N. Fungal–metal interactions: A review of toxicity and homeostasis. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xue, P.; Hu, G.; Jung, W.H.; Kronstad, J.W. Metals and the cell surface of Cryptococcus neoformans. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2023, 74, 102331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Auesukaree, C.; Homma, T.; Tochio, H.; Shirakawa, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Harashima, S. Intracellular phosphate serves as a signal for the regulation of the PHO pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 17289–17294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouillon, J.M.; Persson, B.L. New aspects on phosphate sensing and signalling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res. 2006, 6, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samyn, D.R.; Persson, B.L. Inorganic phosphate and sulfate transport in S. cerevisiae. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 892, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Rajagopa, L.A.; Xu, Y.F.; Rabinowitz, J.D.; O’Shea, E.K. A systematic genetic screen for genes involved in sensing inorganic phosphate availability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskes, E.; Deprez, M.A.; Wilms, T.; Winderickx, J. pH homeostasis in yeast; the phosphate perspective. Curr. Genet. 2018, 64, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddi, A.R.; Jensen, L.T.; Culotta, V.C. Manganese homeostasis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4722–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kulakovskaya, T. Inorganic polyphosphates and heavy metal resistance in microorganisms. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auesukaree, C.; Homma, T.; Kaneko, Y.; Harashima, S. Transcriptional regulation of phosphate-responsive genes in low-affinity phosphate-transporter-defective mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 306, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bun-Ya, M.; Nishimura, M.; Harashima, S.; Oshima, Y. The PHO84 Gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes an inorganic phosphate transporter. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 3229–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, L.T.; Ajua-Alemanji, M.; Culotta, V.C. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae high affinity phosphate transporter encoded by PHO84 also functions in manganese homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 42036–42040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.W.; Shah, D.; Chen, W.; Da Silva, N. Enhanced arsenate uptake in Saccharomyces cerevisiae overexpressing the Pho84 phosphate transporter. Biotechnol. Prog. 2012, 28, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culotta, V.C.; Daly, M.J. Manganese complexes: Diverse metabolic routes to oxidative stress resistance in prokaryotes and yeast. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzicalupo, A.L.; Kahn, P.C.; Ao, E.; Campbell, J.; Otto, S.P. Evolution of cross-tolerance to metals in yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2505337122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghillebert, R.; Swinnen, E.; De Snijder, P.; Smets, B.; Winderickx, J. Differential roles for the low-affinity phosphate transporters Pho87 and Pho90 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. BioChem. J. 2011, 434, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, G.M. The nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5.8 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 1973, 11, 3860–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeva, N.; Ledova, L.; Ryazanova, L.; Tomashevsky, A.; Kulakovskaya, T.; Eldarov, M. Ppn2 endopolyphosphatase overexpressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Comparison with Ppn1, Ppx1, and Ddp1 polyphosphatases. Biochimie 2019, 163, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldarov, M.A.; Baranov, M.V.; Dumina, M.V.; Shgun, A.A.; Andreeva, N.A.; Trilisenko, L.V.; Kulakovskaya, T.V.; Ryasanova, L.P.; Kulaev, I.S. Polyphosphates and exopolyphosphatase activities in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae under overexpression of homologous and heterologous PPN1 genes. Biochemistry 2013, 78, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, G.; Evans, I.H.; Bruce, I.J. The effects of vanadate on the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1989, 55, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho-Silva, J.M.; Vilela Teixeira, A.B.; Schiavon, M.A.; Dos Reis, A.C. Antimicrobial gel with silver vanadate and silver nanoparticles: Antifungal and physicochemical evaluation. Future Microbiol. 2024, 19, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ambesi, A.; Miranda, M.; Petrov, V.V.; Slayman, C.W. Biogenesis and function of the yeast plasma-membrane H(+)-ATPase. J. Exp. Biol. 2000, 203 Pt 1, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, B.J. Vanadate uptake in Neurospora crassa occurs via phosphate transport system II. J. Bacteriol. 1983, 153, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Karginov, A.V.; Fokina, A.V.; Kang, H.A.; Kalebina, T.S.; Sabirzyanova, T.A.; Ter-Avanesyan, M.D.; Agaphonov, M.O. Dissection of differential vanadate sensitivity in two Ogataea species links protein glycosylation and phosphate transport regulation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Żyro, D.; Sikora, J.; Szynkowska-Jóźwik, M.I.; Ochocki, J. Silver, its salts and application in medicine and pharmacy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nie, P.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H. Synthesis, applications, toxicity and toxicity mechanisms of silver nanoparticles: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 253, 114636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagabov, V.M.; Ivanov, A.Y.; Kulakovskaya, T.V.; Kulakovskaya, E.V.; Petrov, V.V.; Kulaev, I.S. Efflux of potassium ions from cells and spheroplasts of Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast treated with silver and copper ions. Biochemistry 2008, 73, 1224–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trilisenko, L.; Valiakhmetov, A.; Kulakovskaya, T. Phosphate efflux as a test of plasma membrane leakage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. Can. J. Microbiol. 2021, 67, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreeva, N.; Ryazanova, L.; Ledova, L.; Trilisenko, L.; Kulakovskaya, T. Stress resistance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains overexpressing yeast polyphosphatases. Stresses 2022, 2, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomashevsky, A.; Kulakovskaya, E.; Trilisenko, L.; Kulakovskiy, I.V.; Kulakovskaya, T.; Fedorov, A.; Eldarov, M. VTC4 polyphosphate polymerase knockout increases stress resistance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. Biology 2021, 10, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trilisenko, L.V.; Ledova, L.A.; Ryazanova, L.P.; Kulakovskaya, E.V.; Tomashevsky, A.A.; Kulakovskaya, T.V. Polyphosphates, polyphosphatase activity and stress resistance of knockout mutants in the PPN1 and PPN2 genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ppn1 and Ppn2. Biol. Biotechnol. 2024, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofiteru, A.M.; Ruta, L.L.; Rotaru, C.; Dumitru, I.; Ene, C.D.; Neagoe, A.; Farcasanu, I.C. Overexpression of the PHO84 gene causes heavy metal accumulation and induces Ire1p-dependent unfolded protein response in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 94, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hürlimann, H.C.; Pinson, B.; Stadler-Waibel, M.; Zeeman, S.C.; Freimoser, F.M. The SPX domain of the yeast low-affinity phosphate transporter Pho90 regulates transport activity. EMBO Rep. 2009, 10, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Kühlbrandt, W.; Yildiz, Ö. Complementary structures of the yeast phosphate transporter Pho90 provide insights into its transport mechanism. Structure 2024, 32, 979–988.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; da Costa Gonzales, L.J.; Bowler-Barnett, E.H.; Rice, D.L.; Kim, M.; Wijerathne, S.; Luciani, A.; Kandasaamy, S.; Luo, J.; Watkins, X.; et al. UniProt Consortium The UniProt website API: Facilitating programmatic access to protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, gkaf394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, E.W.; Bandeira, N.; Perez-Riverol, Y.; Sharma, V.; Carver, J.J.; Mendoza, L.; Kundu, D.J.; Wang, S.; Bandla, C.; Kamatchinathan, S.; et al. The ProteomeXchange consortium at 10 years: 2023 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1539–D1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Trilisenko, L.; Zvonarev, A.; Valiakhmetov, A.; Penin, A.A.; Eliseeva, I.A.; Ostroumov, V.; Kulakovskiy, I.V.; Kulakovskaya, T. The reduced level of inorganic polyphosphate mobilizes antioxidant and manganese-resistance systems in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cells 2019, 8, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ledova, L.; Ryazanova, L.; Trilisenko, L.; Ostroumov, V.; Kulakovskaya, T. Knockouts of Yeast Plasma Membrane Phosphate Transporters Alter Resistance to Heavy Metals. Appl. Microbiol. 2025, 5, 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5040109
Ledova L, Ryazanova L, Trilisenko L, Ostroumov V, Kulakovskaya T. Knockouts of Yeast Plasma Membrane Phosphate Transporters Alter Resistance to Heavy Metals. Applied Microbiology. 2025; 5(4):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5040109
Chicago/Turabian StyleLedova, Larisa, Lubov Ryazanova, Ludmila Trilisenko, Vladimir Ostroumov, and Tatiana Kulakovskaya. 2025. "Knockouts of Yeast Plasma Membrane Phosphate Transporters Alter Resistance to Heavy Metals" Applied Microbiology 5, no. 4: 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5040109
APA StyleLedova, L., Ryazanova, L., Trilisenko, L., Ostroumov, V., & Kulakovskaya, T. (2025). Knockouts of Yeast Plasma Membrane Phosphate Transporters Alter Resistance to Heavy Metals. Applied Microbiology, 5(4), 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol5040109






