Bacterial, Archaeal, and Eukaryote Diversity in Planktonic and Sessile Communities Inside an Abandoned and Flooded Iron Mine (Quebec, Canada)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
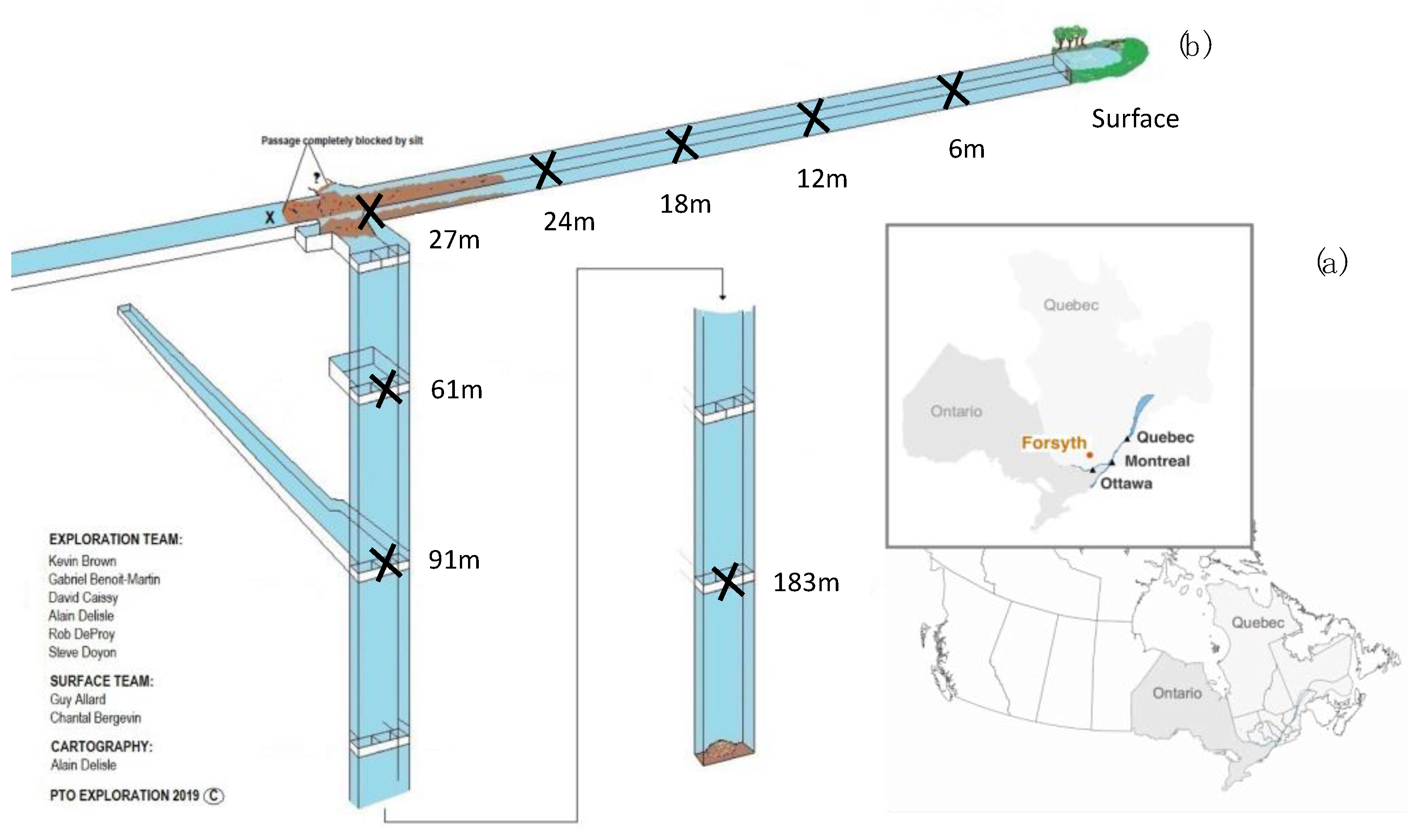
2.1. Site Description and Sample Collection
2.2. Physicochemical Analyses
2.3. DNA Extraction, 16S and 18S rRNA Gene Amplification, and Sequencing
2.4. Sequence Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Variables along the Depth Gradient
3.2. Alpha Diversity and Correlation with Environmental Variables
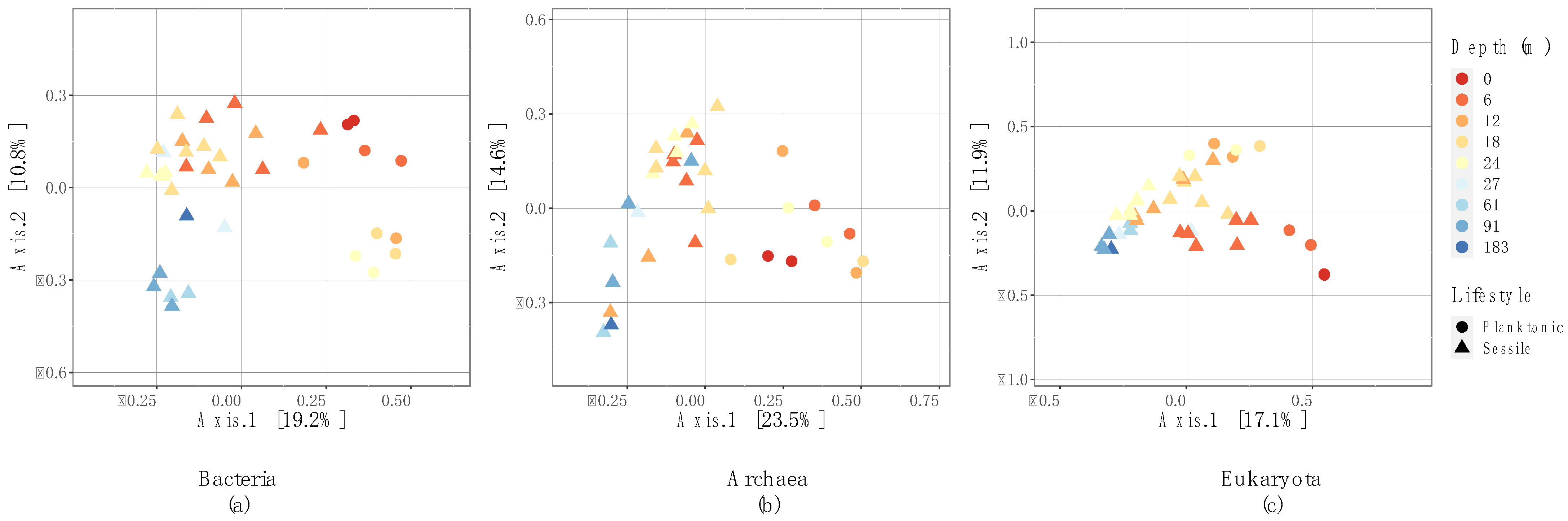
3.3. Microbial Community Structure
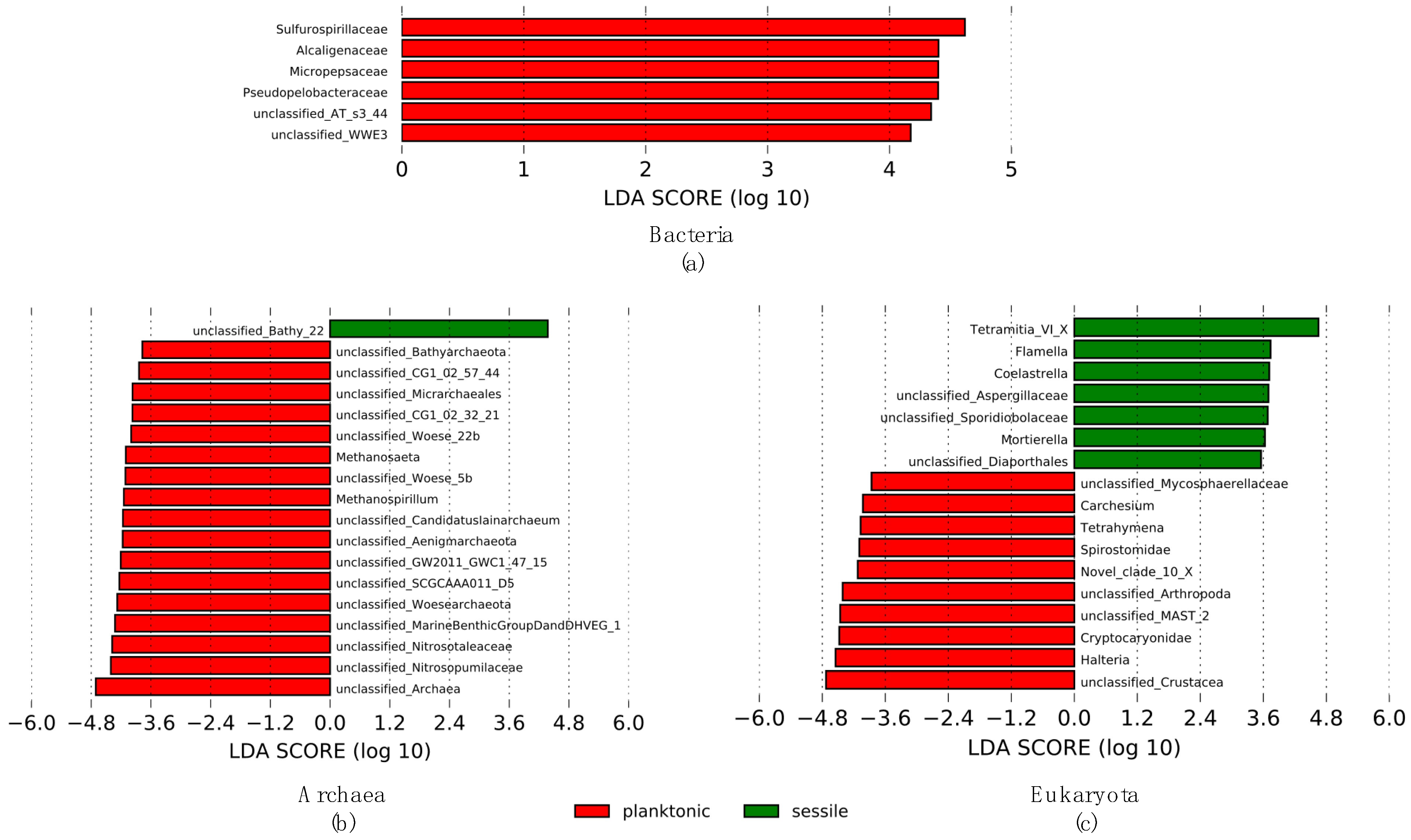
3.4. Discriminative Microorganism’s Taxa According to Lifestyle (LEfSe)
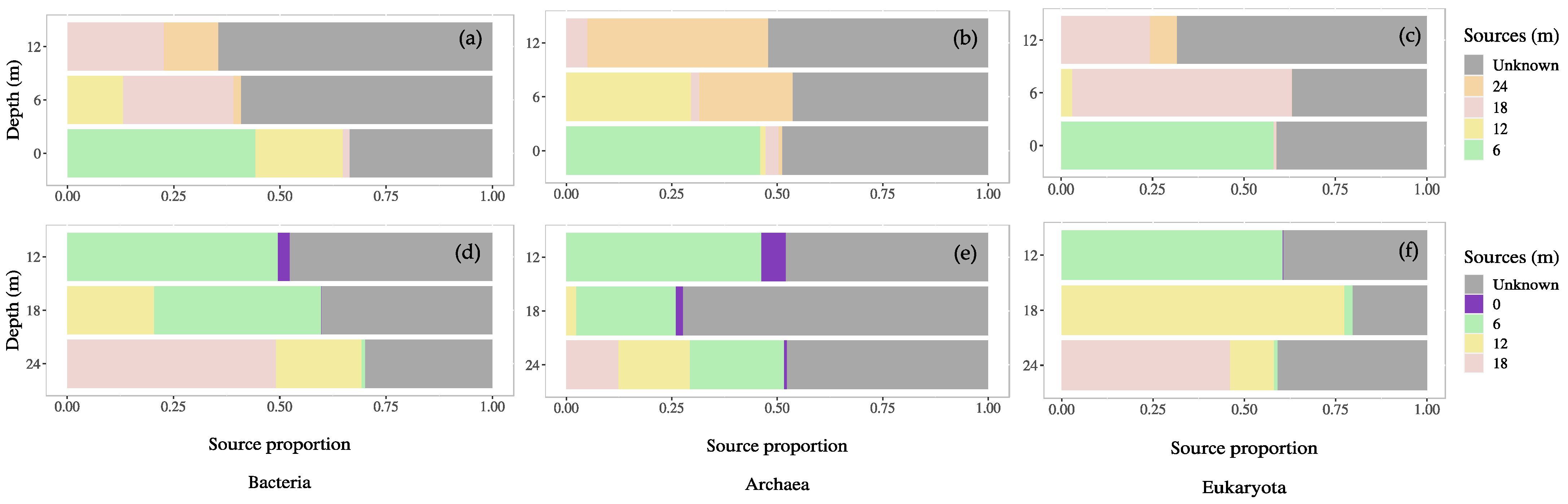
3.5. Microbial Source Tracking: Surface and Groundwater Contributions
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Depth on Environmental Variables and Microbial Communities
4.2. Sessile and Planktonic Microbial Communities: Differences between Lifestyles
4.2.1. Sessile Microbial Communities in the Forsyth Mine
4.2.2. Planktonic Microbial Communities in the Forsyth Mine
4.3. Connectivity of Surface and Mine Water and Impact on Microbial Communities
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mackasey, W.O. Abandoned Mines in Canada; WOM Geological Associates Inc.: Sudbury ON, Canada, 2000; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MERN. Restauration des Sites Miniers Sous la Responsabilité Réelle de l’Etat. Available online: https://mern.gouv.qc.ca/mines/restauration-miniere/restauration-des-sites-miniers-abandonnes/ (accessed on 4 January 2023).
- Tremblay, G.A.; Hogan, C. Managing Orphaned and Abandoned Mines—A Canadian Perspective. In Proceedings of the Dealing with Derelict Mines Summit Organized by CRC-Care, Singleton, Australia, 4–6 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Xie, X.; Wang, P.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Heavy metal pollution caused by small-scale metal ore mining activities: A case study from a polymetallic mine in South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epelde, L.; Lanzén, A.; Blanco, F.; Urich, T.; Garbisu, C. Adaptation of soil microbial community structure and function to chronic metal contamination at an abandoned Pb-Zn mine. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Routh, J.; Jacks, G.; Bhattacharya, P.; Mörth, M. Environmental assessment of abandoned mine tailings in Adak, Västerbotten district (northern Sweden). Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 1760–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chételat, J.; Cott, P.A.; Rosabal, M.; Houben, A.; McClelland, C.; Rose, E.B.; Amyot, M. Arsenic bioaccumulation in subarctic fishes of a mine-impacted bay on Great Slave Lake, Northwest Territories, Canada. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concas, A.; Ardau, C.; Cristini, A.; Zuddas, P.; Cao, G. Mobility of heavy metals from tailings to stream waters in a mining activity contaminated site. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, M.; Wu, X. Investigations of groundwater bursting into coal mine seam floors from fault zones. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2004, 41, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanacković, N.; Dragišić, V.; Stojković, J.; Papić, P.; Živanović, V. Hydrochemical characteristics of mine waters from abandoned mining sites in Serbia and their impact on surface water quality. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7615–7626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoire, P.; Fardeau, M.; Guasco, S.; Bouanane, A.; Michotey, V.; Bonin, P.; Dubourg, K.; Cambar, J.; Ollivier, B. Les Micro-Organismes de L’Extrême. Presse Therm. Clim. 2009, 146, 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, P.Q.; Bachand, S.C.; McIntyre, P.B.; Kraemer, B.M.; Vadeboncoeur, Y.; Kimirei, I.A.; Tamatamah, R.; McMahon, K.D.; Anantharaman, K. Depth-discrete metagenomics reveals the roles of microbes in biogeochemical cycling in the tropical freshwater Lake Tanganyika. ISME J. 2021, 15, 1971–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshri, J.; Mankazana, B.B.J.; Momba, M.N.B. Profile of bacterial communities in South African mine-water samples using Illumina next-generation sequencing platform. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 3233–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-x.; Huang, L.-n.; Méndez-García, C.; Kuang, J.-l.; Hua, Z.-s.; Liu, J.; Shu, W.S. Microbial communities, processes and functions in acid mine drainage ecosystems. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 38, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, J.L.; Huang, L.N.; Chen, L.X.; Hua, Z.S.; Li, S.J.; Hu, M.; Li, J.T.; Shu, W.S. Contemporary environmental variation determines microbial diversity patterns in acid mine drainage. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drewniak, L.; Krawczyk, P.S.; Mielnicki, S.; Adamska, D.; Sobczak, A.; Lipinski, L.; Burec-Drewniak, W.; Sklodowska, A. Physiological and metagenomic analyses of microbial mats involved in self-purification of mine waters contaminated with heavy metals. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Xie, X.; Xiao, S.; Liu, J.; Qiu, G. Microbial diversity of mine water at Zhong Tiaoshan copper mine, China. J. Basic Microbiol. 2007, 47, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamika, I.; Momba, M.N.B. Microbial Diversity of Emalahleni Mine Water in South Africa and Tolerance Ability of the Predominant Organism to Vanadium and Nickel. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Culley, D.E.; Nie, L.; Scholten, J.C.M. Comparative transcriptome analysis of Desulfovibrio vulgaris grown in planktonic culture and mature biofilm on a steel surface. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 76, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenova, V.V.; Gladkikh, A.S.; Belykh, O.I. Comparative analysis of biodiversity in the planktonic and biofilm bacterial communities in Lake Baikal. Microbiology 2013, 82, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Kino, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Kamei, S.; Mori, H.; Kurokawa, K.; Nakashima, N. Establishment of a multi-species biofilm model and metatranscriptomic analysis of biofilm and planktonic cell communities. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 7263–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; He, J. Biofilms: The microbial “protective clothing” in extreme environments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, K.C. Planktonic Versus Sessile Life of Prokaryotes. In The Prokaryotes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K. A Deep Diver’s Becoming. 2020. Available online: http://oatd.org/oatd/record?record=handle%5C:10393%5C%2F40424&q=%28%28EnvironmentORSustainabilityORGreenORCarbonFootprint%29AND%28SportANDMega-EventOROlympicOROlympicsORWorldCup%29%29 (accessed on 4 January 2023).
- Patton, C.; Kryskalla, J. Evaluation of Alkaline Persulfate Digestion as an Alternative to Kjeldahl Digestion for Determination of Total and Dissolved Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Water; U.S. Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 2003.
- Coplen, T.B. New guidelines for reporting stable hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen isotope-ratio data. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 3359–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, A.J.; Raskin, L. PCR biases distort bacterial and archaeal community structure in pyrosequencing datasets. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van De Peer, Y.; De Rijk, P.; Wuyts, J.; Winkelmans, T.; De Wachter, R. The European Small Subunit Ribosomal RNA database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gast, R.J.; Dennett, M.R.; Caron, D.A. Characterization of protistan assemblages in the ross sea, antarctica, by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. Dada2 : High resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, M.; Castelle, C.J.; Probst, A.J.; Zhou, Z.; Pan, J.; Liu, Y.; Banfield, J.F.; Gu, J.D. Insights into the ecology, evolution, and metabolism of the widespread Woesearchaeotal lineages. Microbiome 2018, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Pan, J.; Wang, F.; Gu, J.D.; Li, M. Bathyarchaeota: Globally distributed metabolic generalists in anoxic environments. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, N.M.; Proctor, D.M.; Holmes, S.P.; Relman, D.A.; Callahan, B.J. Simple statistical identification and removal of contaminant sequences in marker-gene and metagenomics data. Microbiome 2018, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, A.J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Mcglinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; Hara, R.B.O.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Package ‘Vegan’: Community Ecology Package. Encycl. Food Agric. Ethics 2019, 2395–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, K.; Yu, T.; Wu, H. Accurate feature selection improves single-cell RNA-seq cell clustering. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenhav, L.; Thompson, M.; Joseph, T.A.; Briscoe, L.; Furman, O.; Bogumil, D.; Mizrahi, I.; Pe’er, I.; Halperin, E. FEAST: Fast expectation-maximization for microbial source tracking. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, M.P.; Staehr, P.A.; Barbosa, F.A.R.; Chartone-Souza, E.; Nascimento, A.M.A. Seasonality of freshwater bacterioplankton diversity in two tropical shallow lakes from the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Sharp, J.O.; Saikaly, P.E.; Ali, S.; Alidina, M.; Alarawi, M.S.; Keller, S.; Hoppe-Jones, C.; Drewes, J.E. Dissolved organic carbon influences microbial community composition and diversity in managed aquifer recharge systems. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 6819–6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, O.J.; Chen, J.M.; Huang, L.; Buglass, R.L. Sulfate-reducing bacteria. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 26, 155–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, W.A. The Sulphate-Reducing Bacteria. Br. Corros. J. 1984, 19, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias-Hünefeldt, S.P.; Wing, S.R.; Espinel-Velasco, N.; Baltar, F.; Morales, S.E. Depth and location influence prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbial community structure in New Zealand fjords. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, M.; Schwab, C.; Borg Jensen, B.; Engberg, R.M.; Spang, A.; Canibe, N.; Højberg, O.; Milinovich, G.; Fragner, L.; Schleper, C.; et al. Methylotrophic methanogenic Thermoplasmata implicated in reduced methane emissions from bovine rumen. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iino, T.; Tamaki, H.; Tamazawa, S.; Ueno, Y.; Ohkuma, M.; Suzuki, K.I.; Igarashi, Y.; Haruta, S. Candidatus methanogranum caenicola: A novel methanogen from the anaerobic digested sludge, and proposal of Methanomassiliicoccaceae fam. nov. and Methanomassiliicoccales ord. nov., for a methanogenic lineage of the class Thermoplasmata. Microbes Environ. 2013, 28, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welte, C.U.; Rasigraf, O.; Vaksmaa, A.; Versantvoort, W.; Arshad, A.; Op den Camp, H.J.M.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Lüke, C.; Reimann, J. Nitrate- and nitrite-dependent anaerobic oxidation of methane. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2016, 8, 941–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, M.; Ozaki, H.; Hiraoka, S.; Kamagata, Y.; Sakata, S.; Yoshioka, H.; Iwasaki, W. Possible cross-feeding pathway of facultative methylotroph Methyloceanibacter caenitepidi Gela4 on methanotroph Methylocaldum marinum S8. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjöberg, S.; Stairs, C.W.; Allard, B.; Homa, F.; Martin, T.; Sjöberg, V.; Ettema, T.J.G.; Dupraz, C. Microbiomes in a manganese oxide producing ecosystem in the Ytterby mine, Sweden: Impact on metal mobility. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begmatov, S.; Savvichev, A.S.; Kadnikov, V.V.; Beletsky, A.V.; Rusanov, I.I.; Klyuvitkin, A.A.; Novichkova, E.A.; Mardanov, A.V.; Pimenov, N.V.; Ravin, N.V. Microbial communities involved in methane, sulfur, and nitrogen cycling in the sediments of the barents sea. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, J.M.; Beetz, N.; Günther, P.M.; Möller, F.; Cao, J. Extremophiles in soil communities of former copper mining sites of the east harz region (Germany) reflected by re-analyzed 16s rrna data. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Koo, T.; Yulisa, A.; Hwang, S. Magnetite as an enhancer in methanogenic degradation of volatile fatty acids under ammonia-stressed condition. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 241, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, R.M.; Melick, M.; O’Neill, K.; Quintero, E. Hyphomonas adhaerens sp. nov., Hyphomonas johnsonii sp. nov. and Hyphomonas rosenbergii sp. nov., marine budding and prosthecate bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Jimenez, K.; Wurzbacher, C.; Bourne, E.C.; Chiuchiolo, A.; Priscu, J.C.; Grossart, H.P. Early diverging lineages within Cryptomycota and Chytridiomycota dominate the fungal communities in ice-covered lakes of the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nercessian, O.; Noyes, E.; Kalyuzhnaya, M.G.; Lidstrom, M.E.; Chistoserdova, L. Bacterial populations active in metabolism of C1 compounds in the sediment of Lake Washington, a freshwater lake. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 6885–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maus, I.; Rumming, M.; Bergmann, I.; Heeg, K.; Pohl, M.; Nettmann, E.; Jaenicke, S.; Blom, J.; Pühler, A.; Schlüter, A.; et al. Characterization of Bathyarchaeota genomes assembled from metagenomes of biofilms residing in mesophilic and thermophilic biogas reactors. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compte-Port, S.; Fillol, M.; Gich, F.; Borrego, C.M. Metabolic versatility of freshwater sedimentary archaea feeding on different organic carbon sources. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Zubin, R.; Wang, F. Core Metabolic Features and Hot Origin of Bathyarchaeota. Engineering 2019, 5, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compte-Port, S.; Subirats, J.; Fillol, M.; Sànchez-Melsió, A.; Marcé, R.; Rivas-Ruiz, P.; Rosell-Melé, A.; Borrego, C.M. Abundance and Co-Distribution of Widespread Marine Archaeal Lineages in Surface Sediments of Freshwater Water Bodies across the Iberian Peninsula. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 74, 776–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonne-Hansen, J.; Ahring, B.K. Thermodesulfobacterium hveragerdense sp. nov., and Thermodesulfovibrio islandicus sp. nov., two thermophilic sulfate reducing bacteria isolated from a Icelandic hot spring. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 22, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, Y.; Muramatsu, M.; Imachi, H.; Narihiro, T.; Ohashi, A.; Harada, H.; Hanada, S.; Kamagata, Y. Thermodesulfovibrio aggregans sp. nov. and Thermodesulfovibrio thiophilus sp. nov., anaerobic, thermophilic, sulfate-reducing bacteria isolated from thermophilic methanogenic sludge, and emended description of the genus Thermodesulfovibrio. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 2541–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.J.; Lazar, C.S.; Teske, A.P.; Dick, G.J. Genomic resolution of linkages in carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur cycling among widespread estuary sediment bacteria. Microbiome 2015, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, Y.A.; Kadnikov, V.V.; Lukina, A.P.; Banks, D.; Beletsky, A.V.; Mardanov, A.V.; Sen’kina, E.I.; Avakyan, M.R.; Karnachuk, O.V.; Ravin, N.V. Characterization and genome analysis of the first facultatively alkaliphilic Thermodesulfovibrio isolated from the deep terrestrial subsurface. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konno, U.; Kouduka, M.; Komatsu, D.D.; Ishii, K.; Fukuda, A.; Tsunogai, U.; Ito, K.; Suzuki, Y. Novel Microbial Populations in Deep Granitic Groundwater from Grimsel Test Site, Switzerland. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardanov, A.V.; Gumerov, V.M.; Beletsky, A.V.; Perevalova, A.A.; Karpov, G.A.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A.; Ravin, N.V. Uncultured archaea dominate in the thermal groundwater of Uzon Caldera, Kamchatka. Extremophiles 2011, 15, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, S. Detection of Euryarchaeota and Crenarchaeota in an oxic basalt aquifer. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2003, 1489, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, G.; O’Connor, L.; Mahony, T.; Gieseke, A.; De Beer, D.; O’Flaherty, V. Distribution, localization, and phylogeny of abundant populations of Crenarchaeota in anaerobic granular sludge. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 7523–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesa, V.; Gallego, J.L.R.; González-Gil, R.; Lauga, B.; Sánchez, J.; Méndez-García, C.; Peláez, A.I. Bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic diversity across distinct microhabitats in an acid mine drainage. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunoura, T.; Hirayama, H.; Takami, H.; Oida, H.; Nishi, S.; Shimamura, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Inagaki, F.; Takai, K.; Nealson, K.H.; et al. Genetic and functional properties of uncultivated thermophilic crenarchaeotes from a subsurface gold mine as revealed by analysis of genome fragments. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1967–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gough, H.L.; Stahl, D.A. Microbial community structures in anoxic freshwater lake sediment along a metal contamination gradient. ISME J. 2011, 5, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandaa, R.A.; Enger, Ø.; Torsvik, V. Abundance and diversity of Archaea in heavy-metal-contaminated soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 3293–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAteer, P.G.; Christine Trego, A.; Thorn, C.; Mahony, T.; Abram, F.; O’Flaherty, V. Reactor configuration influences microbial community structure during high-rate, low-temperature anaerobic treatment of dairy wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 123221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaden, P.J.; Seed, R. An Introduction to Coastal Ecology; Limnology Oceanography: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 1987; Volume 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaro, M.A.; Hummon, W.D. An overview and a dichotomous key to genera of the phylum Gastrotricha. Meiofauna Mar. 2008, 16, 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, J.E.; Dismukes, W.E.; Duma, R.J.; Gerald, M.; Sand, M.A.; Gallis, H.; Leonard, J.; Fields, B.T.; Bradshaw, M.; Haywood, H.; et al. A comparison of amphotericin B alone and combined with flucytosine in the treatment of cryptoccal meningitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983, 308, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisendle-Flöckner, U.; Hilberg, S. Hard rock aquifers and free-living nematodes—An interdisciplinary approach based on two widely neglected components in groundwater research. Ecohydrology 2015, 8, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, B.W.; Salomon, C.E.; Blanchette, R.A. Diverse subterranean fungi of an underground iron ore mine. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilhen, C.; Charbonnel, N.; Parisot, N.; Gueguen, N.; Iltis, A.; Forestier, C.; Balestrino, D. Transcriptional profiling of Klebsiella pneumoniae defines signatures for planktonic, sessile and biofilm-dispersed cells. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luef, B.; Frischkorn, K.R.; Wrighton, K.C.; Holman, H.Y.N.; Birarda, G.; Thomas, B.C.; Singh, A.; Williams, K.H.; Siegerist, C.E.; Tringe, S.G.; et al. Diverse uncultivated ultra-small bacterial cells in groundwater. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Ning, D.; He, Z.; Zhang, P.; Spencer, S.J.; Gao, S.; Shi, W.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Small and mighty: Adaptation of superphylum Patescibacteria to groundwater environment drives their genome simplicity. Microbiome 2020, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, L.N.; Medeiros, J.D.; Dini-Andreote, F.; Fernandes, G.R.; Varani, A.M.; Oliveira, G.; Pylro, V.S. Genomic signatures and co-occurrence patterns of the ultra-small Saccharimonadia (phylum CPR/Patescibacteria) suggest a symbiotic lifestyle. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 4259–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.R.; Colquhoun, D.R.; Halden, R.U. Identification of wastewater bacteria involved in the degradation of triclocarban and its non-chlorinated congener. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesbahi-Nowrouzi, M.; Mollania, N.; Khajeh, K. Chromium bioremediation by Alcaligenes sp. strain newly isolated from chromite mine of Sabzevar. J. Adv. Environ. Health Res. 2017, 5, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrae, J.D.; Lavine, I.N.; Mccaffery, K.A.; Ricupero, K. Sulfurospirillum, from Maine Groundwater. J. Environ. Eng. 2007, 133, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garris, H.W.; Baldwin, S.A.; Van Hamme, J.D.; Gardner, W.C.; Fraser, L.H. Genomics to assist mine reclamation: A review. Restor. Ecol. 2016, 24, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Keren, R.; Whittaker, M.L.; Farag, I.F.; Doudna, J.A.; Cate, J.H.D.; Banfield, J.F. Genome-resolved metagenomics reveals site-specific diversity of episymbiotic CPR bacteria and DPANN archaea in groundwater ecosystems. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, G.M.; López-García, P.; Moreira, D.; Alric, B.; Deschamps, P.; Bertolino, P.; Restoux, G.; Rochelle-Newall, E.; Thébault, E.; Simon, M.; et al. Small freshwater ecosystems with dissimilar microbial communities exhibit similar temporal patterns. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 2162–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurch, L.; Giannone, R.J.; Belisle, B.S.; Swift, C.; Utturkar, S.; Hettich, R.L.; Reysenbach, A.L.; Podar, M. Genomics-informed isolation and characterization of a symbiotic Nanoarchaeota system from a terrestrial geothermal environment. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarett, J.K.; Nayfach, S.; Podar, M.; Inskeep, W.; Ivanova, N.N.; Munson-Mcgee, J.; Schulz, F.; Young, M.; Jay, Z.J.; Beam, J.P.; et al. Single-cell genomics of co-sorted Nanoarchaeota suggests novel putative host associations and diversification of proteins involved in symbiosis. Microbiome 2018, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelle, C.J.; Brown, C.T.; Anantharaman, K.; Probst, A.J.; Huang, R.H.; Banfield, J.F. Biosynthetic capacity, metabolic variety and unusual biology in the CPR and DPANN radiations. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, N.H.; Rinke, C.; Stepanauskas, R.; Farag, I.; Woyke, T.; Elshahed, M.S. Insights into the metabolism, lifestyle and putative evolutionary history of the novel archaeal phylum “Diapherotrites”. ISME J. 2015, 9, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weig, A.R.; Löder, M.G.J.; Ramsperger, A.F.R.M.; Laforsch, C. In situ Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Communities on Microplastic Particles in a Small Headwater Stream in Germany. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-García, C.; Peláez, A.I.; Mesa, V.; Sánchez, J.; Golyshina, O.V.; Ferrer, M. Microbial diversity and metabolic networks in acid mine drainage habitats. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirnstein, I.; Arnold, T.; Krawczyk-Bärsch, E.; Jenk, U.; Bernhard, G.; Röske, I. Eukaryotic life in biofilms formed in a uranium mine. Microbiologyopen 2012, 1, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisse, T. Functional diversity of aquatic ciliates. Eur. J. Protistol. 2017, 61, 331–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardillier, L.; Bettarel, Y.; Richardot, M.; Bardot, C.; Amblard, C.; Sime-Ngando, T.; Debroas, D. Effects of viruses and predators on prokaryotic community composition. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 50, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernthaler, J. Predation on prokaryotes in the water column and its ecological implications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, L.M.; Alvarez, P.J.; McLean, R.J.C. Bacterial Signaling Ecology and Potential Applications during Aquatic Biofilm Construction. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 68, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, J.B. Biofilm Dispersal: Mechanisms, Clinical Implications, and Potential Therapeutic Uses. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Bacteria | Archaea | Eukaryota | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dF | Sumof Sqs | R2 | F | Pr (>F) | dF | Sumof Sqs | R2 | F | Pr (>F) | dF | Sumof Sqs | R2 | F | Pr (>F) | |
| Depth | 1 | 0.959 | 0.08 | 3.812 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.794 | 0.094 | 4.292 | 0.001 | 1 | 1.23 | 0.091 | 4.469 | 0.001 |
| Lifestyle | 1 | 1.755 | 0.146 | 6.98 | 0.001 | 1 | 1.464 | 0.174 | 7.919 | 0.001 | 1 | 1.337 | 0.099 | 4.859 | 0.001 |
| Residual | 33 | 8.297 | 0.692 | 30 | 5.548 | 0.659 | 36 | 9.905 | 0.73 | ||||||
| Depth | 1 | 0.959 | 0.08 | 4.187 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.794 | 0.094 | 4.703 | 0.001 | 1 | 1.23 | 0.091 | 4.434 | 0.001 |
| Substrate | 4 | 2.894 | 0.241 | 3.161 | 0.001 | 4 | 2.424 | 2.288 | 3.591 | 0.001 | 4 | 2.31 | 0.17 | 2.082 | 0.001 |
| Residual | 27 | 0.515 | 0.515 | 24 | 4.051 | 0.481 | 30 | 8.321 | 0.613 | ||||||
| Total | 36 | 11.996 | 1 | 33 | 8.418 | 1 | 39 | 13.565 | 1 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lhoste, E.; Comte, F.; Brown, K.; Delisle, A.; Jaclin, D.; Ponsin, V.; Rosabal, M.; Lazar, C.S. Bacterial, Archaeal, and Eukaryote Diversity in Planktonic and Sessile Communities Inside an Abandoned and Flooded Iron Mine (Quebec, Canada). Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 3, 45-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol3010004
Lhoste E, Comte F, Brown K, Delisle A, Jaclin D, Ponsin V, Rosabal M, Lazar CS. Bacterial, Archaeal, and Eukaryote Diversity in Planktonic and Sessile Communities Inside an Abandoned and Flooded Iron Mine (Quebec, Canada). Applied Microbiology. 2023; 3(1):45-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol3010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleLhoste, Elise, Francis Comte, Kevin Brown, Alain Delisle, David Jaclin, Violaine Ponsin, Maikel Rosabal, and Cassandre Sara Lazar. 2023. "Bacterial, Archaeal, and Eukaryote Diversity in Planktonic and Sessile Communities Inside an Abandoned and Flooded Iron Mine (Quebec, Canada)" Applied Microbiology 3, no. 1: 45-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol3010004
APA StyleLhoste, E., Comte, F., Brown, K., Delisle, A., Jaclin, D., Ponsin, V., Rosabal, M., & Lazar, C. S. (2023). Bacterial, Archaeal, and Eukaryote Diversity in Planktonic and Sessile Communities Inside an Abandoned and Flooded Iron Mine (Quebec, Canada). Applied Microbiology, 3(1), 45-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol3010004







