Simultaneous Detection of Foodborne Pathogens Using a Real-Time PCR Triplex High-Resolution Melt Assay
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. PCR Primers
2.3. PCR Reaction Conditions and HRM Analysis
3. Results
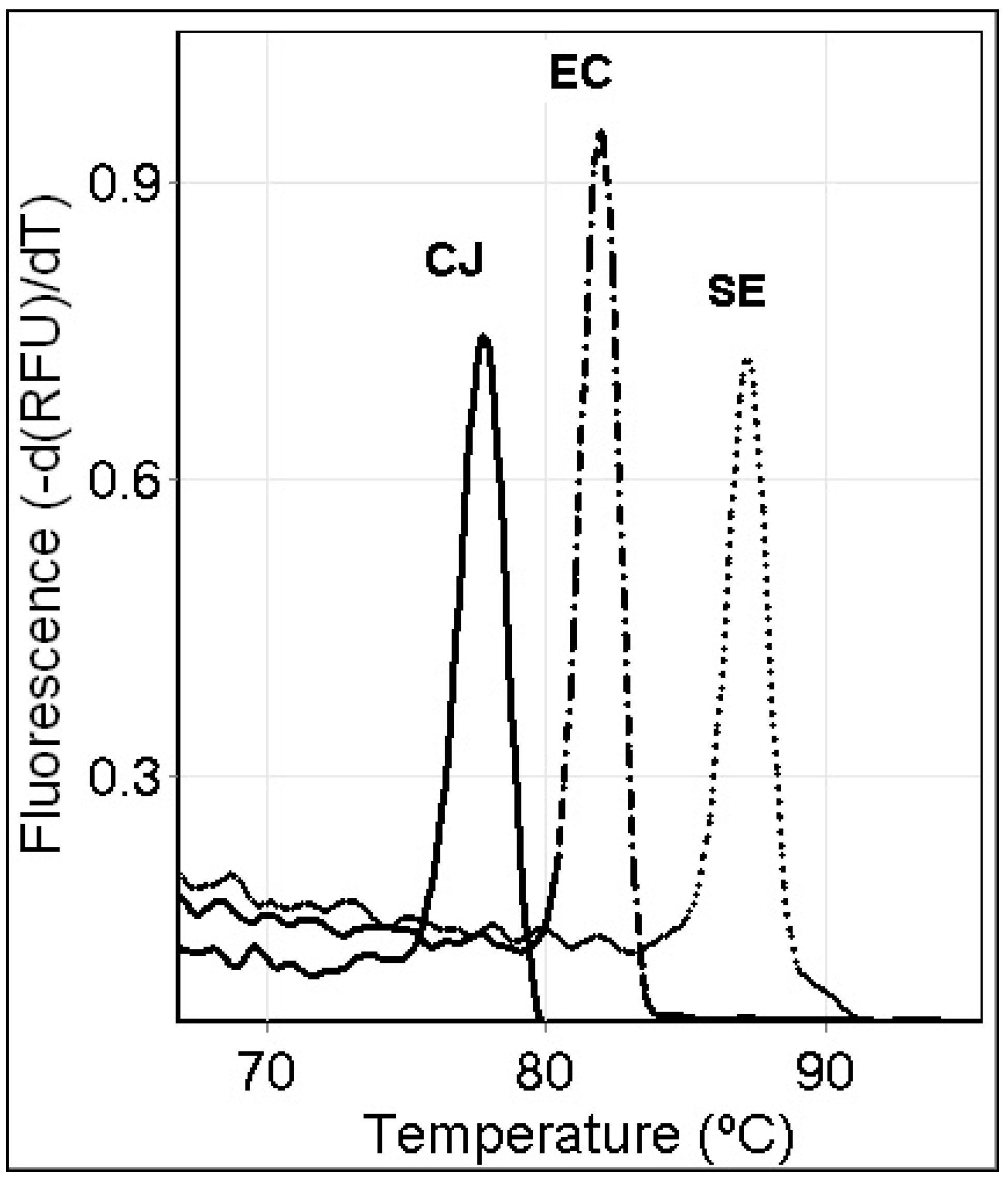
3.1. Results with Single-Specie PCR Melt Assays
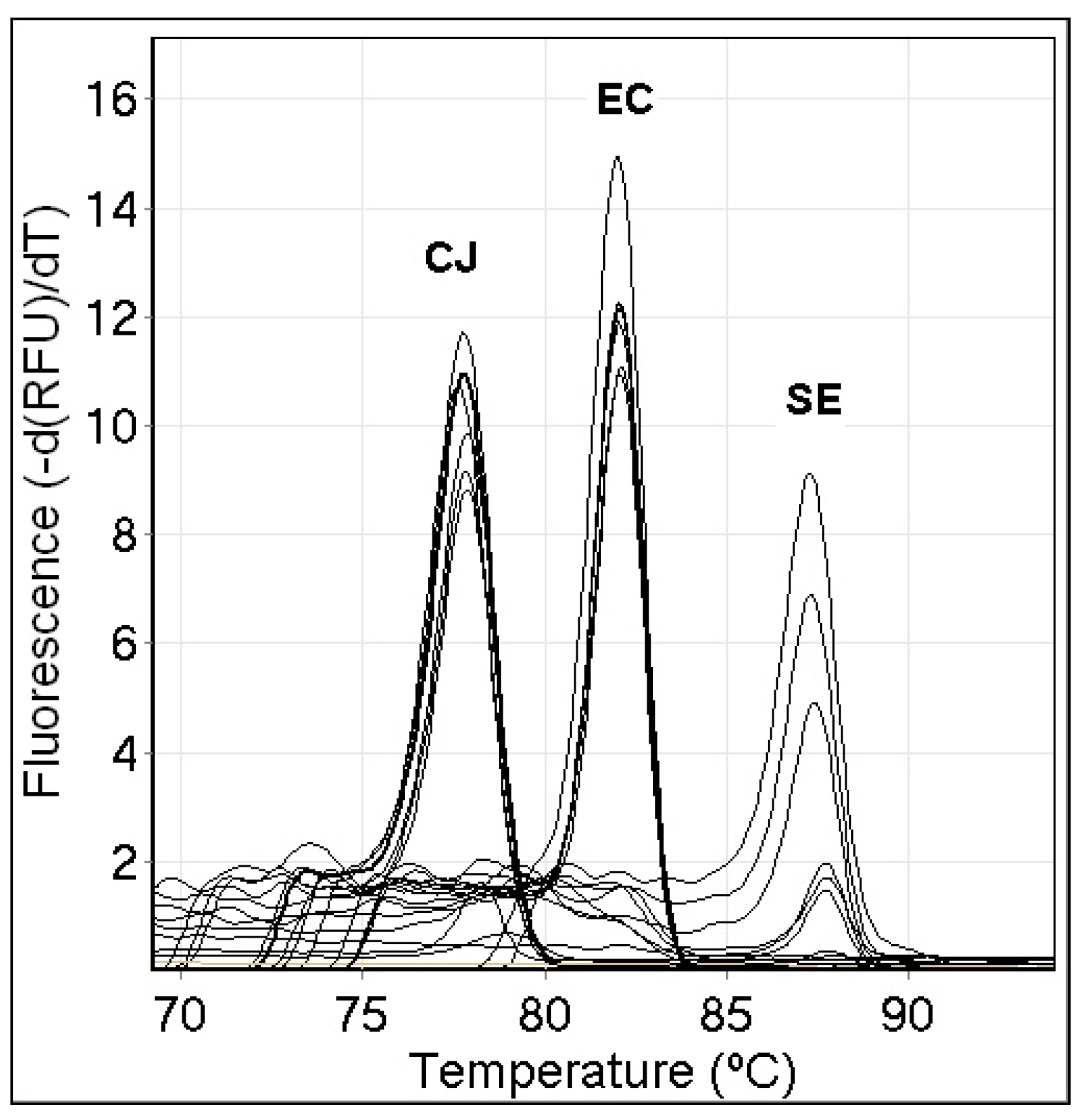
3.2. Sensitivity of the Single-Specie PCR Melt Assays
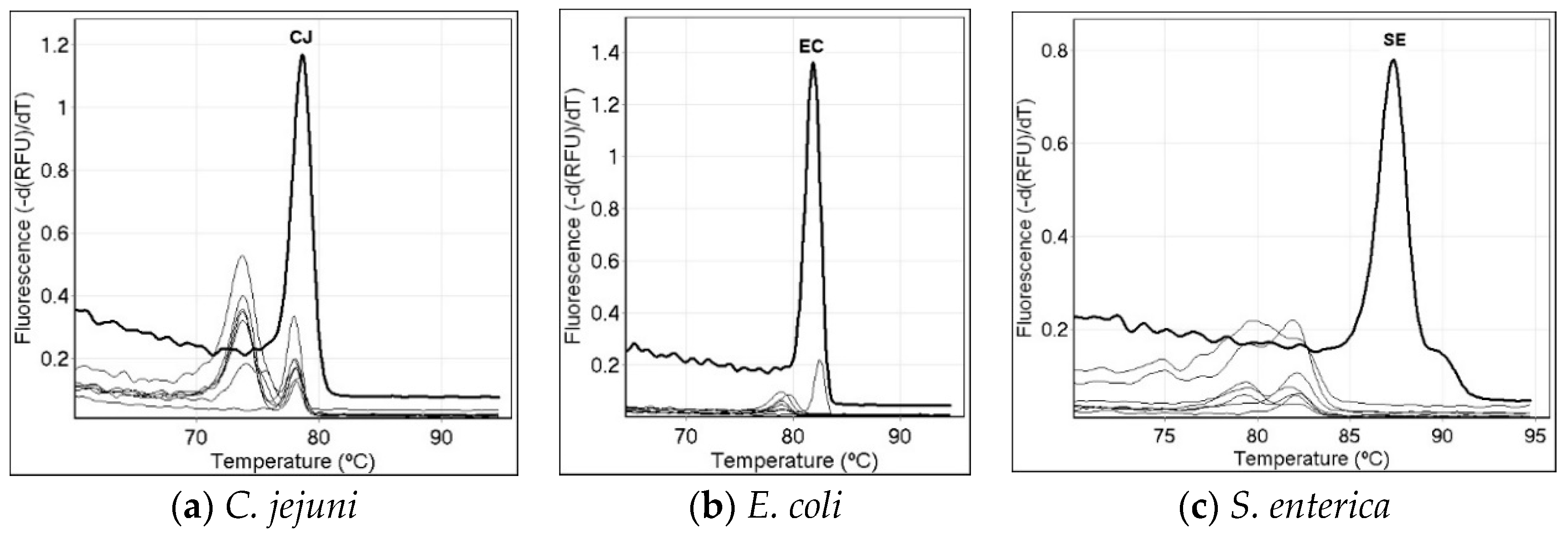
3.3. Specificity of the Single-Specie PCR Melt Assays
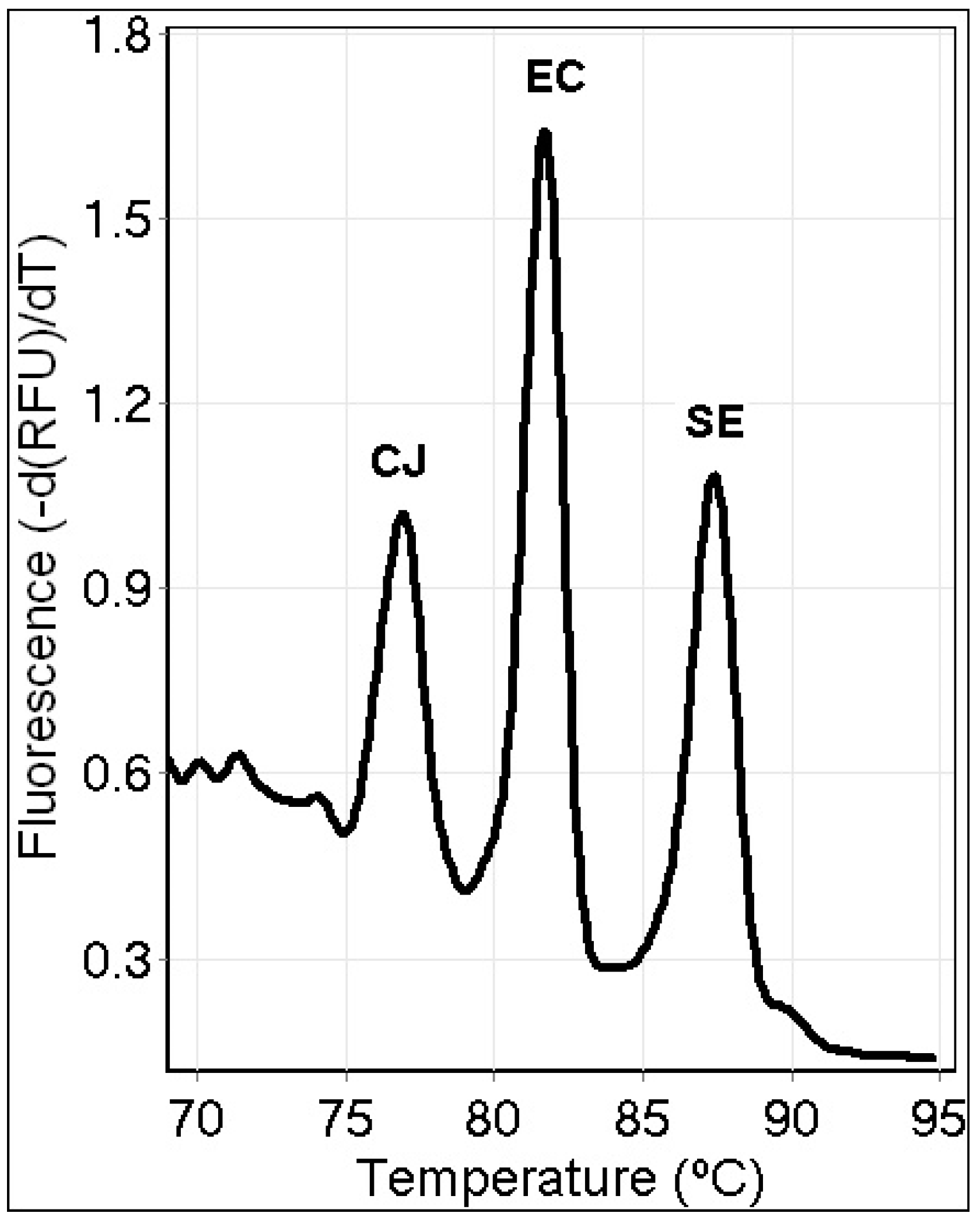
3.4. Triplex PCR Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Artenstein, A.W. Bioterrorism and Biodefense. Infect. Dis. 2017, 1, 670–679.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauxe, R.V. Emerging foodborne pathogens. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 78, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkins, K.; Bender, A. Foodborne Pathogens. Encyclopedia. 2020. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/512 (accessed on 4 July 2022).
- CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/csels/dsepd/ss1978/lesson1/section11.html (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/foodsafety/outbreaks/multistate-outbreaks/outbreaks-list.html (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- Török, T.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Wise, R.P.; Livengood, J.R.; Sokolow, R.; Mauvais, S.; Birkness, K.A.; Skeels, M.R.; Horan, J.M.; Foster, L.R. A Large Community Outbreak of Salmonellosis Caused by Intentional Contamination of Restaurant Salad Bars. JAMA 1997, 278, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolavic, S.A.; Kimura, A.; Simons, S.L.; Slutsker, L.; Barth, S.; Haley, C.E. Outbreak of Shigella dysenteriae Type 2 among Laboratory Workers Due to Intentional Food Contamination. JAMA 1997, 278, 396–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, L.N.; Bej, A.K. Detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Shellfish by Use of Multiplexed Real-Time PCR with TaqMan Fluorescent Probes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2031–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elkins, K.M.; Perez, A.C.U.; Sweetin, K.C. Rapid and inexpensive species differentiation using a multiplex real-time polymerase chain reaction high-resolution melt assay. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 500, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Liu, H.; Wang, W. Multiplex real-time PCR assay for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and screening for non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing E. coli. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoseinpour, F.; Foroughi, A.; Nomanpour, B.; Nasab, R.S. Identification and differentiation of Campylobacter species by high-resolution melting curve analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 108, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omer, M.K.; Álvarez-Ordoñez, A.; Prieto, M.; Skjerve, E.; Asehun, T.; Alvseike, O.A. A Systematic Review of Bacterial Foodborne Outbreaks Related to Red Meat and Meat Products. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Singh, P.; Mustapha, A. High-resolution melt curve PCR assay for specific detection of E. coli O157:H7 in beef. Food Control 2018, 86, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candel-Pérez, C.; Ros-Berruezo, G.; Martínez-Graciá, C. A review of Clostridioides [Clostridium] difficile occurrence through the food chain. Food Microbiol. 2019, 77, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murasova, P.; Kovarova, A.; Kasparova, J.; Brozkova, I.; Hamiot, A.; Pekarkova, J.; Dupuy, B.; Drbohlavova, J.; Bilkova, Z.; Korecka, L. Direct culture-free electrochemical detection of Salmonella cells in milk based on quantum dots-modified nanostructured dendrons. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 863, 114051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Chica, J.; Correa, M.M.; Aceves-Diez, A.E.; Castañeda-Sandoval, L.M. A novel method for direct detection of Bacillus cereus toxin genes in powdered dairy products. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 103, 104625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, A.C.; Faulkner, J.A.; Tulimieri, K.; Boise, T.H.; Elkins, K.M. High Resolution Melt Assays to Detect and Identify Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Bacillus cereus, Escherichia coli, and Clostridioides difficile Bacteria. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campylobacter, Salmonella Led Bacterial Foodborne Illnesses in 2016. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2017/p0420-campylobacter-salmonella.html (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- CDC Salmonella Homepage. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/general/salmonella-symptoms.html (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- CDC E.coli Homepage. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/ecoli/ecoli-symptoms.html (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- CDC Campylobacter Homepage. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/campylobacter/symptoms.html (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- CDC Campylobacter Index. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/campylobacter/index.html (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- Tamburro, M.; Ripabelli, G. High Resolution Melting as a rapid, reliable, accurate and cost-effective emerging tool for genotyping pathogenic bacteria and enhancing molecular epidemiological surveillance: A comprehensive review of the literature. Ann. Ig. 2017, 29, 293–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tastanova, A.; Stoffel, C.I.; Dzung, A.; Cheng, P.F.; Bellini, E.; Johansen, P.; Duda, A.; Nobbe, S.; Lienhard, R.; Bosshard, P.P.; et al. A Comparative Study of Real-Time RT-PCR-Based SARS-CoV-2 Detection Methods and Its Application to Human-Derived and Surface Swabbed Material. J. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 23, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buss, J.E.; Cresse, M.; Doyle, S.; Buchan, B.W.; Craft, D.W.; Young, S. Campylobacter culture fails to correctly detect Campylobacter in 30% of positive patient stool specimens compared to non-cultural methods. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Druml, B.; Cichna-Markl, M. High resolution melting (HRM) analysis of DNA—Its role and potential in food analysis. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Bacterial Strain | Source |
|---|---|
| Bacillus cereus, str. NRRL B-568 | ATCC (10876D-5) |
| Bacillus subtilis, str. 168 | ATCC (23857D-5) |
| Bacillus thurigiensis, str. USDA H522 | ATCC (35646D-5) |
| Campylobacter jejuni, subsp. jejuni | ATCC (33560D-5) |
| Clostridium difficile, str. 90556-M6S | ATCC (9689D-5) |
| Escherichia coli, str. MG1655 | ATCC (700926D-5) |
| Listeria monocytogenes, str. EGDe | ATCC (BAA-679D-5) |
| Salmonella enterica, subsp. enterica | ATCC (700720) |
| Shigella flexneri type 2, str. 24570 | ATCC (29903D-5) |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus, str. EB101 | ATCC (17802D-5) |
| Specie | Gene Target | Forward Primer (5′ to 3′) | Reverse Primer (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | yedN | TCCTGGATTGAGGTGCTTTATC | CTACGGAGACCTGGGTAATTCC |
| Campylobacter jejuni | cadF | TGCTATTAAAGGTATTGATGTAGGTGA | CAGCATTTGAAAAATCCTCAT |
| Salmonella enterica | hilA | CAGGGCTATCGGTTTAATCGTCC | GCAGACTCTCGGATTGAACCTG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reese, K.R.; Elkins, K.M. Simultaneous Detection of Foodborne Pathogens Using a Real-Time PCR Triplex High-Resolution Melt Assay. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 2, 453-459. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol2030034
Reese KR, Elkins KM. Simultaneous Detection of Foodborne Pathogens Using a Real-Time PCR Triplex High-Resolution Melt Assay. Applied Microbiology. 2022; 2(3):453-459. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol2030034
Chicago/Turabian StyleReese, Kashiya R., and Kelly M. Elkins. 2022. "Simultaneous Detection of Foodborne Pathogens Using a Real-Time PCR Triplex High-Resolution Melt Assay" Applied Microbiology 2, no. 3: 453-459. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol2030034
APA StyleReese, K. R., & Elkins, K. M. (2022). Simultaneous Detection of Foodborne Pathogens Using a Real-Time PCR Triplex High-Resolution Melt Assay. Applied Microbiology, 2(3), 453-459. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmicrobiol2030034






