Assessing First and Multiple Reoperations in 23,301 Breast Reconstructions: Immediate Versus Delayed Reconstructions in Women with Breast Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
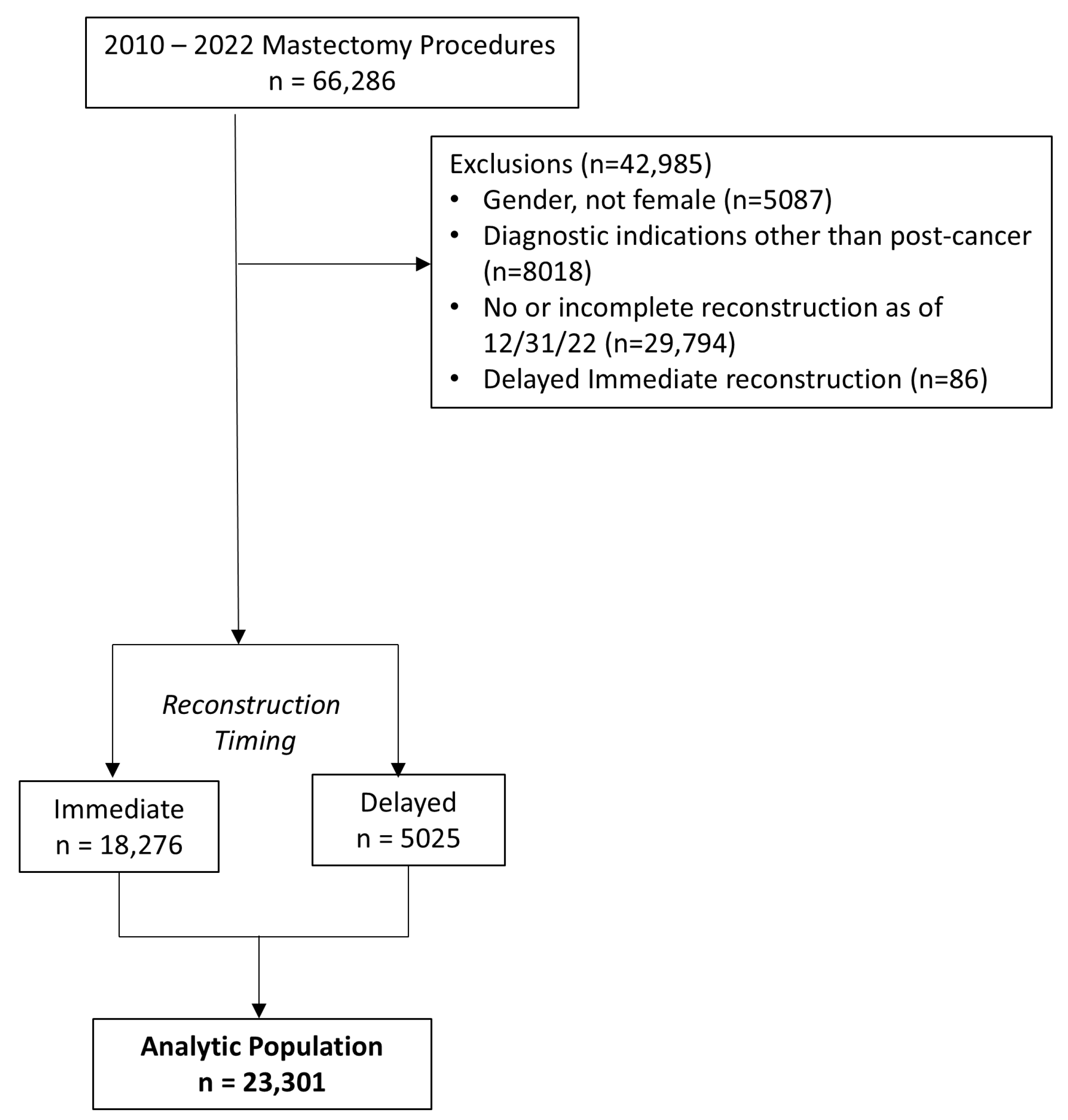
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Exposure of Interest
2.3. Outcome of Interest
2.4. Radiotherapy
2.5. Covariates of Interest
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Overall
3.2. Reoperation
3.3. Stratified Analysis by Reconstruction Type
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IBR | Immediate Breast Reconstruction |
| RORJ | Return to OR |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
References
- The American Cancer Society. Key Statistics for Breast Cancer: How Common Is Breast Cancer. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/breast-cancer/about/how-common-is-breast-cancer.html (accessed on 2 January 2023).
- D’Souza, N.; Darmanin, G.; Fedorowicz, Z. Immediate versus delayed reconstruction following surgery for breast cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 2011, Cd008674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, A.P.; Qi, J.; Brown, D.L.; Kim, H.M.; Hamill, J.B.; Erdmann-Sager, J.; Pusic, A.L.; Wilkins, E.G. Outcomes of immediate versus delayed breast reconstruction: Results of a multicenter prospective study. Breast 2018, 37, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albornoz, C.R.; Cordeiro, P.G.; Pusic, A.L.; McCarthy, C.M.; Mehrara, B.J.; Disa, J.J.; Matros, E. Diminishing relative contraindications for immediate breast reconstruction: A multicenter study. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2014, 219, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, A.; Hui, K.J.; Remington, A.C.; Liu, X.; Lee, G.K. Effects of A Novel Decision Aid for Breast Reconstruction: A Randomized Prospective Trial. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 76 (Suppl. S3), S249–S254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholas, Z.; Butow, P.; Tesson, S.; Boyle, F. A systematic review of decision aids for patients making a decision about treatment for early breast cancer. Breast 2016, 26, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.S.; Cantor, S.B.; Reece, G.P.; Fingeret, M.C.; Crosby, M.A.; Markey, M.K. Helping patients make choices about breast reconstruction: A decision analysis approach. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 134, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimes, A.S.; Stewen, K.; Hasenburg, A. Psychosocial Aspects of Immediate versus Delayed Breast Reconstruction. Breast Care 2017, 12, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, M.A.; Polo, K.; Pusic, A.L.; Cordeiro, P.G.; Hidalgo, D.A.; Mehrara, B.; Disa, J.J. Breast cancer local recurrence after mastectomy and TRAM flap reconstruction: Incidence and treatment options. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 117, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patani, N.; Devalia, H.; Anderson, A.; Mokbel, K. Oncological safety and patient satisfaction with skin-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 17, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, P.M.; Godfrey, N.V.; Romita, M.C. Immediate autogenous breast reconstruction in clinically advanced disease. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1995, 95, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, C.Z.; Wu, C.T.; Jiao, G.M.; Yan, F.; Zhu, H.C.; Zhang, X.P. Comparison of immediate breast reconstruction after mastectomy and mastectomy alone for breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 43, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieni, M.; Avram, R.; Dickson, L.; Farrokhyar, F.; Lovrics, P.; Faidi, S.; Sne, N. Local breast cancer recurrence after mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction for invasive cancer: A meta-analysis. Breast 2012, 21, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, J.S.; Kobayashi, M.R.; Paydar, K.; Wirth, G.A.; Evans, G.R. The number of operations required for completing breast reconstruction. Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Glob. Open 2014, 2, e242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticha, P.; Wu, M.; Mestak, O.; Sukop, A. Evaluation of the Number of Follow-up Surgical Procedures and Time Required for Delayed Breast Reconstruction by Clinical Risk Factors, Type of Oncological Therapy, and Reconstruction Approach. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2022, 46, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herly, M.; Ørholt, M.; Larsen, A.; Pipper, C.B.; Bredgaard, R.; Gramkow, C.S.; Katz, A.J.; Drzewiecki, K.T.; Vester-Glowinski, P.V. Efficacy of breast reconstruction with fat grafting: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. JPRAS 2018, 71, 1740–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losken, A.; Carlson, G.W.; Schoemann, M.B.; Jones, G.E.; Culbertson, J.H.; Hester, T.R. Factors that influence the completion of breast reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2004, 52, 258–261, discussion 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, J.A.; Voineskos, S.H.; Qi, J.; Kim, H.M.; Hamill, J.B.; Wilkins, E.G.; Pusic, A.L. Elective Revisions after Breast Reconstruction: Results from the Mastectomy Reconstruction Outcomes Consortium. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 144, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhadana, G.; Safran, T.; Al-Halabi, B.; Davison, P.G. Use of Decision Analysis and Economic Evaluation in Breast Reconstruction: A Systematic Review. Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Glob. Open 2020, 8, e2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenup, R.A.; Rushing, C.; Fish, L.; Campbell, B.M.; Tolnitch, L.; Hyslop, T.; Peppercorn, J.; Wheeler, S.B.; Zafar, S.Y.; Myers, E.R.; et al. Financial Costs and Burden Related to Decisions for Breast Cancer Surgery. J. Oncol. Pract. 2019, 15, e666–e676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser Permanente Fast Facts: Our Company. Available online: https://about.kaiserpermanente.org/who-we-are/fast-facts (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Karter, A.J.; Ferrara, A.; Liu, J.Y.; Moffet, H.H.; Ackerson, L.M.; Selby, J.V. Ethnic disparities in diabetic complications in an insured population. JAMA 2002, 287, 2519–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koebnick, C.; Langer-Gould, A.M.; Gould, M.K.; Chao, C.R.; Iyer, R.L.; Smith, N.; Chen, W.; Jacobsen, S.J. Sociodemographic characteristics of members of a large, integrated health care system: Comparison with US Census Bureau data. Perm. J. 2012, 16, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, A.D.S., Jr. Assessment of operative times of multiple surgical specialties in a public university hospital. Einstein 2017, 15, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevray, P.M. Timing of breast reconstruction: Immediate versus delayed. Cancer J. 2008, 14, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanati-Mehrizy, P.; Massenburg, B.B.; Rozehnal, J.M.; Gupta, N.; Rosa, J.H.; Ingargiola, M.J.; Taub, P.J. A Comparison of Postoperative Outcomes in Immediate Versus Delayed Reconstruction After Mastectomy. Eplasty 2015, 15, e44. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, J.P.; Wes, A.M.; Tuggle, C.T.; Serletti, J.M.; Wu, L.C. Risk analysis and stratification of surgical morbidity after immediate breast reconstruction. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2013, 217, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.P.; Wes, A.M.; Tuggle, C.T.; Wu, L.C. Venous thromboembolism risk in mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction: Analysis of the 2005 to 2011 American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program data sets. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 133, 263e–273e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matar, D.Y.; Wu, M.; Haug, V.; Orgill, D.P.; Panayi, A.C. Surgical complications in immediate and delayed breast reconstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. JPRAS 2022, 75, 4085–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.A.; Allen, R.J.J.; Polanco, T.; Shamsunder, M.; Patel, A.R.; McCarthy, C.M.; Matros, E.; Dayan, J.H.; Disa, J.J.; Cordeiro, P.G.; et al. Long-term Patient-reported Outcomes Following Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction: An 8-year Examination of 3268 Patients. Ann. Surg. 2019, 270, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiboutot, E.; Craighead, P.; Webb, C.; Temple-Oberle, C. Patient-Reported Satisfaction Following Radiation of Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Surg. 2019, 27, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusic, A.L.; Klassen, A.F.; Snell, L.; Cano, S.J.; McCarthy, C.; Scott, A.; Cemal, Y.; Rubin, L.R.; Cordeiro, P.G. Measuring and managing patient expectations for breast reconstruction: Impact on quality of life and patient satisfaction. Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 2012, 12, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosa, K.B.; Qi, J.; Kim, H.M.; Hamill, J.B.; Wilkins, E.G.; Pusic, A.L. Long-term Patient-Reported Outcomes in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction. JAMA Surg. 2018, 153, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormand, E.L.; Banwell, P.E.; Goodacre, T.E. Radiotherapy and wound healing. Int. Wound J. 2005, 2, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, L.K.; Johnson, M.B.; Dedhia, R.D.; Niknam-Bienia, S.; Wong, A.K. Impaired wound healing after radiation therapy: A systematic review of pathogenesis and treatment. JPRAS Open 2017, 13, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnautovic, A.; Olafsson, S.; Wong, J.S.; Agarwal, S.; Broyles, J.M. Optimizing Breast Reconstruction through Integration of Plastic Surgery and Radiation Oncology. Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Glob. Open 2021, 9, e3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.P.; Shaw, J.; Pusic, A.; Wyld, L.; Morrow, M.; King, T.; Mátrai, Z.; Heil, J.; Fitzal, F.; Potter, S.; et al. Oncoplastic breast consortium recommendations for mastectomy and whole breast reconstruction in the setting of post-mastectomy radiation therapy. Breast 2022, 63, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, J.A.; Epstein, S.; Momoh, A.O.; Lin, S.J.; Singhal, D.; Lee, B.T. A meta-analysis of implant-based breast reconstruction and timing of adjuvant radiation therapy. J. Surg. Res. 2017, 218, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D. New Plastic Surgery Statistics and Breast Reconstruction Trends. Available online: https://www.plasticsurgery.org/news/blog/new-plastic-surgery-statistics-and-breast-reconstruction-trends (accessed on 2 January 2023).
- Giordano, S.; Harkkila, S.; Oranges, C.M.; di Summa, P.G.; Koskivuo, I. Immediate versus Delayed Contralateral Breast Symmetrisation in Breast Reconstruction with Latissimus dorsi Flap: A Comparative Study. Breast Care 2019, 14, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.L.; Clarke-Pearson, E.M.; Vornovitsky, M.; Dayan, J.H.; Samson, W.; Sultan, M.R. The efficacy of simultaneous breast reconstruction and contralateral balancing procedures in reducing the need for second stage operations. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2014, 41, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracon, S.; Renzi, N.; Manara, M.; Ramella, V.; Papa, G.; Arnež, Z.M. Patient Satisfaction after Breast Reconstruction: Implants vs. Autologous Tissues. Acta Chir. Plast. 2018, 59, 120–128. [Google Scholar]
- Pirro, O.; Mestak, O.; Vindigni, V.; Sukop, A.; Hromadkova, V.; Nguyenova, A.; Vitova, L.; Bassetto, F. Comparison of Patient-reported Outcomes after Implant Versus Autologous Tissue Breast Reconstruction Using the BREAST-Q. Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Glob. Open 2017, 5, e1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, S.M.; Lester, M.E.; Fontenot, B.; Allen, R.J., Sr. Perforator flap breast reconstruction after unsatisfactory implant reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2011, 66, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Immediate Breast Reconstruction | Delayed Breast Reconstruction | SMD 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 18,276 | 78.4% | n = 5025 | 21.6% | ||
| Patient Characteristics | |||||
| Age, Percentiles (25th 50th 75th) | 43, 50, 59 | 45, 53, 61 | −0.1889 | ||
| Race/Ethnicity | |||||
| Non-Hispanic White | 10,236 | 56.0% | 2855 | 56.8% | |
| Black | 1485 | 8.1% | 372 | 7.4% | |
| Hispanic | 3518 | 19.3% | 1165 | 23.2% | |
| Asian | 2780 | 15.2% | 565 | 11.2% | |
| Missing/Other | 257 | 1.4% | 68 | 1.4% | |
| BMI, in kg/m2 (category) | −0.2560 | ||||
| <18.5 | 202 | 1.1% | 43 | 0.9% | |
| 18.5–24.4 | 7114 | 38.9% | 1404 | 27.9% | |
| 25.0–29.4 | 6279 | 34.4% | 1814 | 36.1% | |
| 30.0–39.4 | 4380 | 24.0% | 1632 | 32.5% | |
| ≥39.5 | 298 | 1.6% | 124 | 2.4% | |
| Unknown | 3 | 0.0% | 8 | 0.2% | |
| Smoking | 0.2522 | ||||
| Never | 13,452 | 73.6% | 3393 | 67.5% | |
| Yes | 217 | 1.2% | 39 | 0.8% | |
| Quit | 4524 | 24.8% | 1569 | 31.2% | |
| Other/Missing | 83 | 0.4% | 24 | 0.5% | |
| Hospital Characteristics | 0.1219 | ||||
| Hospital Region | |||||
| Hawaii | 516 | 2.8% | 256 | 5.1% | |
| Northern California | 7727 | 42.3% | 1971 | 39.2% | |
| Northwest | 1188 | 6.5% | 231 | 4.6% | |
| Southern California | 8845 | 48.4% | 2567 | 51.1% | |
| Bilateral Same-Day Surgery (yes) | 12,512 | 68.5% | 2393 | 47.6% | 0.4162 |
| Year of Mastectomy 3 | 0.3944 | ||||
| 2010 | 830 | 61.7% | 515 | 38.3% | |
| 2011 | 997 | 65.6% | 524 | 34.5% | |
| 2012 | 1104 | 69.7% | 479 | 30.3% | |
| 2013 | 1302 | 72.9% | 484 | 27.1% | |
| 2014 | 1353 | 75.0% | 450 | 25.0% | |
| 2015 | 1586 | 78.7% | 430 | 21.3% | |
| 2016 | 1495 | 78.2% | 417 | 21.8% | |
| 2017 | 1540 | 80.7% | 369 | 19.3% | |
| 2018 | 1691 | 81.9% | 375 | 18.2% | |
| 2019 | 1663 | 83.3% | 334 | 16.7% | |
| 2020 | 1418 | 82.2% | 308 | 17.8% | |
| 2021 | 1799 | 87.8% | 250 | 12.2% | |
| 2022 | 1498 | 94.3% | 90 | 5.7% | |
| ASA Classification | −0.1524 | ||||
| 1–2 | 15,347 | 84.2% | 4092 | 81.4% | |
| 3–5 | 2682 | 14.5% | 838 | 16.7% | |
| Missing | 247 | 1.3% | 95 | 1.9% | |
| Length of Stay (days) (mean, std) | 1.3, 1.5 | 1.2, 2.1 | 0.0150 | ||
| Radiotherapy (yes) | 6425 | 35.2% | 1881 | 37.4% | −0.0455 |
| Reconstruction Type 4 | |||||
| Expander with or without Additional Reconstruction (yes) | 13,204 | 72.3% | 2561 | 51.0% | 0.4485 |
| Expander with no Additional Reconstruction (yes) | 1198 | 6.6% | 199 | 4.0% | 0.1165 |
| Single-Stage Reconstruction Procedure 4 | |||||
| Flap (yes) | 2179 | 11.9% | 1520 | 30.3% | −0.4610 |
| Direct-to-Implant Reconstruction (yes) | 2893 | 15.8% | 944 | 18.8% | −0.0782 |
| Flap plus Implant (yes) | 2168 | 11.9% | 641 | 12.8% | −0.0272 |
| Two-Stage Reconstruction | |||||
| Expander-to-Flap Reconstruction (yes) | 1004 | 5.5% | 148 | 3.0% | 0.1270 |
| Expander-to-Implant Reconstruction (yes) | 11,002 | 60.2% | 2214 | 44.1% | 0.3274 |
| Elixhauser Comorbidities | Immediate Breast Reconstruction (IBR) | Delayed Reconstruction | SMD * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 17,643 | 78.3% | n = 4889 | 21.7% | ||
| No. of comorbidities | 0.082 | ||||
| 0 | 5787 | 32.8% | 1379 | 28.2% | |
| 1 | 5328 | 30.2% | 1594 | 32.6% | |
| 2 | 3599 | 20.4% | 1002 | 20.5% | |
| 3 | 1553 | 8.8% | 533 | 10.9% | |
| 4 | 829 | 4.7% | 249 | 5.1% | |
| 5 or more | 547 | 3.1% | 132 | 2.7% | |
| Alcohol Abuse | 194 | 1.1% | 73 | 1.5% | 0.040 |
| Anemia | 1535 | 8.7% | 381 | 7.8% | 0.038 |
| Congestive Heart Failure | 159 | 0.9% | 15 | 0.3% | 0.081 |
| Depression | 1606 | 9.1% | 455 | 9.3% | 0.010 |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 2329 | 13.2% | 694 | 14.2% | 0.047 |
| Electrolyte/Fluid Disorder | 582 | 3.3% | 132 | 2.7% | 0.036 |
| Peptic Ulcer Disease | 35 | 0.2% | 0 | 0.0% | 0.055 |
| PVD | 776 | 4.4% | 156 | 3.2% | 0.058 |
| PCD | 71 | 0.4% | 10 | 0.2% | 0.028 |
| Psychosis | 1006 | 5.7% | 352 | 7.2% | 0.071 |
| Renal Insufficiency | 582 | 3.3% | 93 | 1.9% | 0.090 |
| Valvular Disease | 300 | 1.7% | 54 | 1.1% | 0.047 |
| Breast Reconstruction Type | Adjusted HR (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Immediate | Delayed (Ref) | ||
| 1st Reoperation | Cumulative Incidence (95% CI) | ||
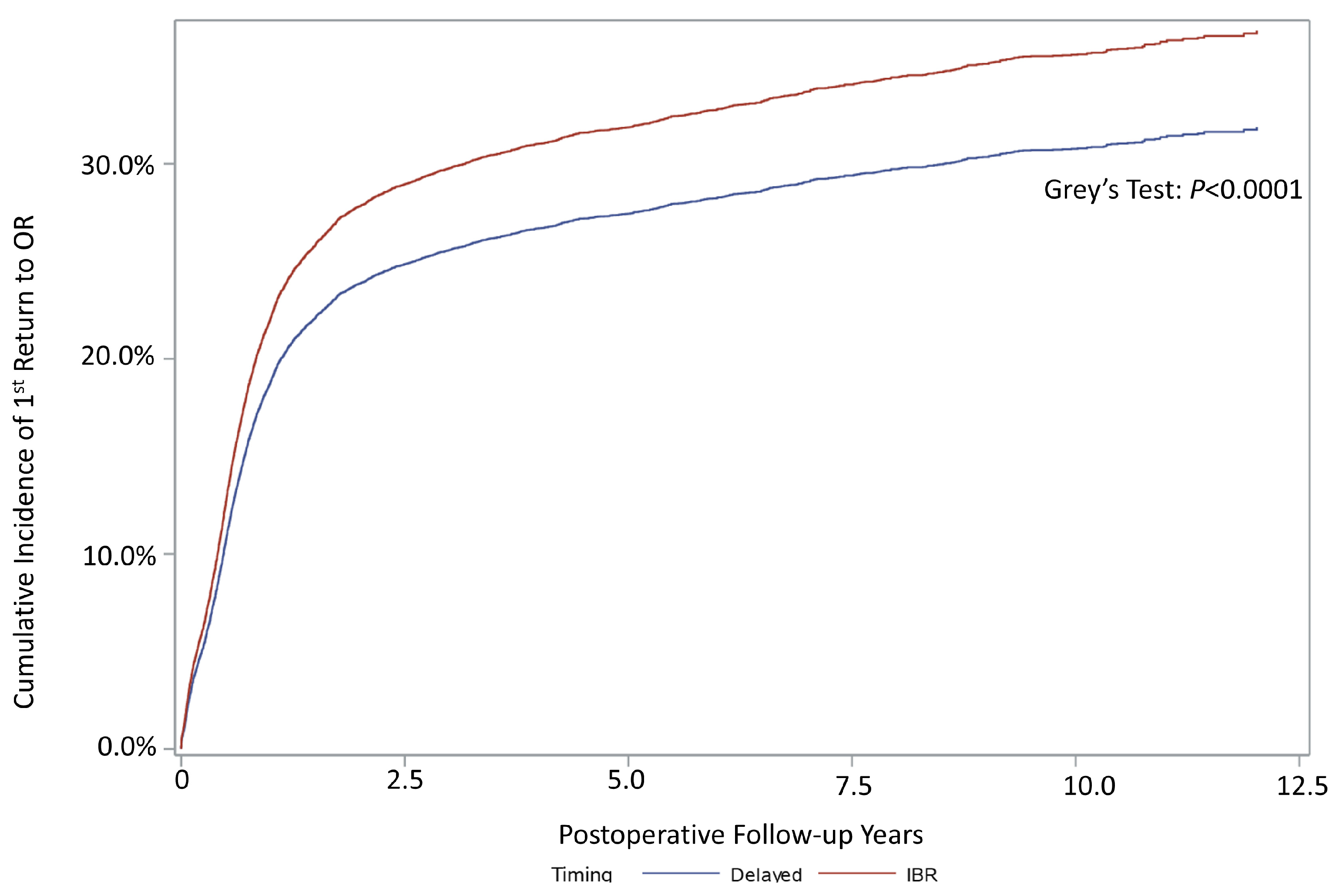
| Overall %, (95% CI) | 33.04% (32.36–33.73) | 31.72% (30.44–33.03) | 1.18 (1.12–1.25) 1 |
| 1 year | 21.29% (20.69–21.90) | 21.89% (20.77–23.07) | |
| 3 years | 29.27% (28.58–29.97) | 28.30% (27.06–29.58) | |
| 5 years | 31.67% (30.95–32.41) | 29.89% (28.61–31.21) | |
| 10 years | 36.37% (35.48–37.29) | 33.15% (31.72–34.61) | |
| All Reoperations 3 | 1.00 (0.95–1.04) 2,3 | ||
| Breast Reconstruction Type | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immediate | Delayed (Ref) | |||||||
| n= | Reoperations | n= | Reoperations | 1st Reoperation | All Reoperations | |||
| 1st (%) | Mean (±SD) | 1st (%) | Mean (±SD) | HR 1 (95% CI) | HR 2,3 (95% CI) | |||
| Incomplete Reconstruction with Expander | ||||||||
| Expander | 1198 | 652 (52.42) | 0.80 ± 0.91 | 199 | 70 (35.18) | 0.47 ± 0.77 | 1.82 (1.43–2.34) | 1.69 (1.36–2.10) |
| Single-Stage Reconstruction | ||||||||
| Autologous | 2179 | 995 (45.66) | 0.81 ± 0.93 | 1520 | 639 (42.02) | 0.82 ± 0.99 | 1.19 (1.07–1.31) | 1.09 (1.07–1.18) |
| Direct-to-Implant | 2893 | 823 (28.45) | 0.60 ± 0.94 | 944 | 228 (24.15) | 0.44 ± 0.77 | 1.47 (1.27–1.71) | 1.66 (1.49–1.86) |
| Two-Stage Reconstruction | ||||||||
| Expander–Flap | 1004 | 439 (43.73) | 0.20 ± 0.49 | 148 | 67 (45.27) | 0.15 ± 0.47 | 0.94 (0.72–1.23) | 0.85 (0.69–11.04) |
| Expander–Implant | 11,002 | 3130 (28.45) | 0.10 ± 0.40 | 2214 | 590 (26.65) | 0.07 ± 0.32 | 1.12 (1.02–1.23) | 1.02 (0.99–1.17) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Royse, K.E.; Smith, T.M.; Tan, C.M.; Lin, E.Y.; Neumann, R.G.; Harris, J.E.; Paxton, E.W.; Tong, W.M. Assessing First and Multiple Reoperations in 23,301 Breast Reconstructions: Immediate Versus Delayed Reconstructions in Women with Breast Cancer. Onco 2025, 5, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco5020015
Royse KE, Smith TM, Tan CM, Lin EY, Neumann RG, Harris JE, Paxton EW, Tong WM. Assessing First and Multiple Reoperations in 23,301 Breast Reconstructions: Immediate Versus Delayed Reconstructions in Women with Breast Cancer. Onco. 2025; 5(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco5020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoyse, Kathryn E., Tina M. Smith, Cissy M. Tan, Eric Y. Lin, Robert G. Neumann, Jessica E. Harris, Elizabeth W. Paxton, and Winnie M. Tong. 2025. "Assessing First and Multiple Reoperations in 23,301 Breast Reconstructions: Immediate Versus Delayed Reconstructions in Women with Breast Cancer" Onco 5, no. 2: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco5020015
APA StyleRoyse, K. E., Smith, T. M., Tan, C. M., Lin, E. Y., Neumann, R. G., Harris, J. E., Paxton, E. W., & Tong, W. M. (2025). Assessing First and Multiple Reoperations in 23,301 Breast Reconstructions: Immediate Versus Delayed Reconstructions in Women with Breast Cancer. Onco, 5(2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco5020015





