Exploring the Potential of Epiregulin and Amphiregulin as Prognostic, Predictive, and Therapeutic Targets in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
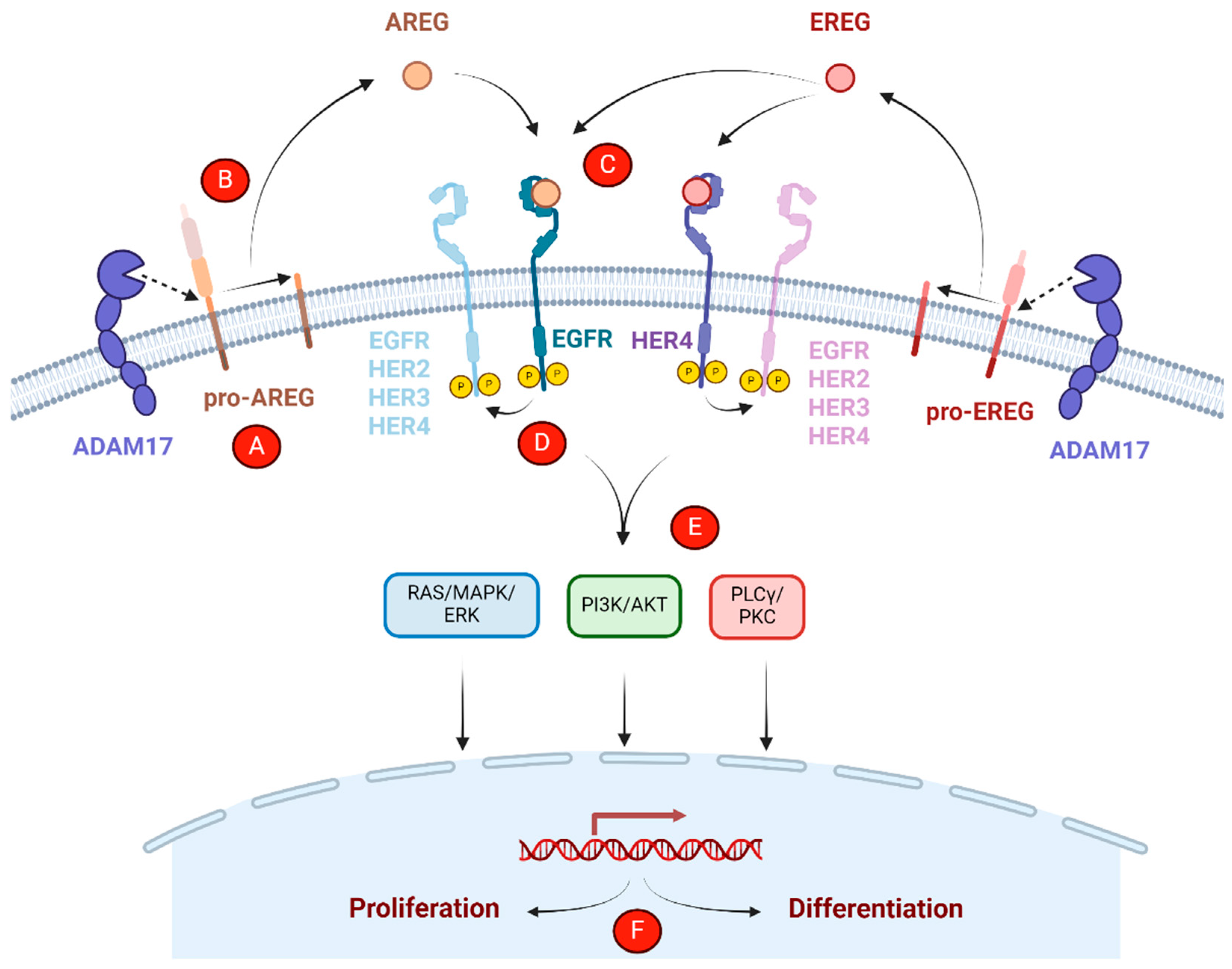
1.1. EGFR Signaling
1.2. EGFR in Colorectal Cancer
1.3. EGFR-Targeted Therapies
2. Epiregulin and Amphiregulin
2.1. Gene Regulation
2.2. Protein Structure
2.3. Processing and Post-Translational Modifications
2.4. EREG/AREG-Mediated Receptor Activation, Trafficking, and Downstream Signaling
3. Prognostic and Predictive Roles of Epiregulin and Amphiregulin in CRC
| Biomarker Type | Patient Population | Treatment | Finding | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive | Advanced CRC | Cetuximab or best supportive care | High EREG associated with cetuximab benefit in KRAS WT patients | [63] |
| Prognostic/Predictive | RAS WT mCRC | Cetuximab or panitumumab +/− FOLFOX or FOLFIRI | High EREG/AREG associated with improved survival across treatment regimens | [64] |
| Prognostic | mCRC | Chemotherapy (fluoropyrimidine-based, none, or unknown) | Low EREG associated with improved survival in KRAS WT patients | [67] |
| Prognostic | CRC | N/A | High AREG/vascular invasion associated with shorter disease- and hepatic metastasis-free survival | [68] |
| Predictive | mCRC | Cetuximab | High AREG associated with benefit in KRAS WT; high EREG associated with benefit, irrespective of KRAS mutational status | [69,79] |
| Predictive | mCRC | Cetuximab + irinotecan | High EREG/AREG associated with benefit in KRAS WT patients | [70] |
| Predictive | KRAS WT mCRC | Cetuximab | High EREG/AREG associated with benefit | [71] |
| Prognostic/Predictive | mCRC | Irinotecan +/− panitumumab | No association between EREG/AREG and survival with irinotecan alone High EREG/AREG associated with panitumumab benefit | [73,74,80] |
| Prognostic/Predictive | mCRC | Combination chemotherapy +/− cetuximab or bevacizumab | High AREG associated with survival benefit across treatment regimens High AREG associated with cetuximab benefit in KRAS WT patients | [75] |
| Predictive | mCRC | Cetuximab | High EREG/AREG associated with benefit | [76] |
| Predictive | mCRC | Cetuximab + irinotecan or oxaliplatin | High EREG/AREG associated with benefit | [77] |
| Predictive | KRAS WT mCRC | Anti-EGFR therapy + chemotherapy | High EREG/AREG associated with benefit | [78] |
4. The Roles of Epiregulin and Amphiregulin in EGFR-Targeted Therapy Resistance
4.1. Alterations in Ligand Expression
4.2. Paracrine Growth Factor Signaling
4.3. Growth Factor Secretion in the Tumor Microenvironment
5. Therapeutic Targeting of Epiregulin and Amphiregulin
5.1. Monoclonal Antibodies
5.2. Antibody–Drug Conjugates
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2024; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Cervantes, A.; Adam, R.; Roselló, S.; Arnold, D.; Normanno, N.; Taïeb, J.; Seligmann, J.; De Baere, T.; Osterlund, P.; Yoshino, T.; et al. Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2023, 34, 10–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ji, Q.; Li, Q. Resistance to Anti-EGFR Therapies in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Underlying Mechanisms and Reversal Strategies. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieduwilt, M.J.; Moasser, M.M. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Family: Biology Driving Targeted Therapeutics. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 1566–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarden, Y.; Pines, G. The ERBB Network: At Last, Cancer Therapy Meets Systems Biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga, C.L.; Engelman, J.A. ERBB Receptors: From Oncogene Discovery to Basic Science to Mechanism-Based Cancer Therapeutics. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 282–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graus-Porta, D.; Beerli, R.R.; Daly, J.M.; Hynes, N.E. ErbB-2, the Preferred Heterodimerization Partner of All ErbB Receptors, Is a Mediator of Lateral Signaling. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Carpenter, G.; Coffey, R.J. EGF Receptor Ligands: Recent Advances. F1000Research 2016, 5, F1000, Faculty Rev-2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.R.; Handsley, M.M.; Pennington, C.J. The ADAM Metalloproteinases. Mol. Asp. Med. 2008, 29, 258–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashiyama, S.; Nanba, D.; Nakayama, H.; Inoue, H.; Fukuda, S. Ectodomain Shedding and Remnant Peptide Signalling of EGFRs and Their Ligands. J. Biochem. 2011, 150, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlessinger, J.; Lemmon, M.A. SH2 and PTB Domains in Tyrosine Kinase Signaling. Sci. STKE 2003, 2003, RE12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarden, Y.; Sliwkowski, M.X. Untangling the ErbB Signalling Network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olayioye, M.A.; Graus-Porta, D.; Beerli, R.R.; Rohrer, J.; Gay, B.; Hynes, N.E. ErbB-1 and ErbB-2 Acquire Distinct Signaling Properties Dependent upon Their Dimerization Partner. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 5042–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.J.; Mill, C.; Lambert, S.; Buchman, J.; Wilson, T.R.; Hernandez-Gordillo, V.; Gallo, R.M.; Ades, L.M.C.; Settleman, J.; Riese, D.J., II. EGFR Ligands Exhibit Functional Differences in Models of Paracrine and Autocrine Signaling. Growth Factors 2012, 30, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, D.M.; Bessman, N.J.; Kiyatkin, A.; Salazar-Cavazos, E.; Byrne, P.O.; Moore, J.O.; Valley, C.C.; Ferguson, K.M.; Leahy, D.J.; Lidke, D.S.; et al. EGFR Ligands Differentially Stabilize Receptor Dimers to Specify Signaling Kinetics. Cell 2017, 171, 683–695.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roepstorff, K.; Grandal, M.V.; Henriksen, L.; Knudsen, S.L.J.; Lerdrup, M.; Grøvdal, L.; Willumsen, B.M.; van Deurs, B. Differential Effects of EGFR Ligands on Endocytic Sorting of the Receptor. Traffic 2009, 10, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, S.; Martini, G.; Ciardiello, D.; Del Tufo, S.; Martinelli, E.; Troiani, T.; Ciardiello, F. Targeting the EGFR Signalling Pathway in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, A.; Singh, V.; Liu, X.; McGregor, D.H.; Hall, S. Correlation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor with Morphological Features of Colorectal Advanced Adenomas: A Pilot Correlative Case Series. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2010, 340, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williet, N.; Petcu, C.A.; Rinaldi, L.; Cottier, M.; Del Tedesco, E.; Clavel, L.; Dumas, O.; Jarlot, C.; Bouarioua, N.; Roblin, X.; et al. The Level of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors Expression Is Correlated with the Advancement of Colorectal Adenoma: Validation of a Surface Biomarker. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 16507–16517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.; Anami, Y.; High, P.; Liang, Z.; Subramanian, S.; Ghosh, S.C.; AghaAmiri, S.; Guernsey, C.; Tran, H.; Liu, Q.J.; et al. Antibody-Drug Conjugates Targeting EGFR Ligand Epiregulin Inhibit Colorectal Tumor Growth Irrespective of RAS Mutational Status. bioRxiv 2024. bioRxiv:2024.02.20.581056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardiello, F.; Kim, N.; Saeki, T.; Dono, R.; Persico, M.G.; Plowman, G.D.; Garrigues, J.; Radke, S.; Todaro, G.J.; Salomon, D.S. Differential Expression of Epidermal Growth Factor-Related Proteins in Human Colorectal Tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 7792–7796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasi, P.M.; Afable, M.G.; Herting, C.; Lukanowski, M.; Jin, Z. Anti-EGFR Antibodies in the Management of Advanced Colorectal Cancer. Oncologist 2023, 28, 1034–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.-Q.; Zeng, L.-S.; Wang, L.-F.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Cheng, J.-T.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Z.-W.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, S.-L.; Wang, X.-W.; et al. The Latest Battles between EGFR Monoclonal Antibodies and Resistant Tumor Cells. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Song, Y.; Tian, W. How to Select IgG Subclasses in Developing Anti-Tumor Therapeutic Antibodies. J. Hematol. 2020, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, M.; Hsieh, M.; Park, J.-Y.; Su, Y.-Q. Role of the Epidermal Growth Factor Network in Ovarian Follicles. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.-L.; Feng, P.-H.; Lee, K.-Y.; Chen, K.-Y.; Sun, W.-L.; Van Hiep, N.; Luo, C.-S.; Wu, S.-M. The Role of EREG/EGFR Pathway in Tumor Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.S.; Chauhan, S.B.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Engwerda, C.R.; Sundar, S.; Kumar, R. Amphiregulin in Cellular Physiology, Health, and Disease: Potential Use as a Biomarker and Therapeutic Target. J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avraham, R.; Yarden, Y. Feedback Regulation of EGFR Signalling: Decision Making by Early and Delayed Loops. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolitho, C.; Moscova, M.; Baxter, R.C.; Marsh, D.J. Amphiregulin Increases Migration and Proliferation of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cells by Inducing Its Own Expression via PI3-Kinase Signaling. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2021, 533, 111338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Sun, Y.-P.; Cheng, J.-C. The Role of Amphiregulin in Ovarian Function and Disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2023, 80, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveras-Ferraros, C.; Cufí, S.; Queralt, B.; Vazquez-Martin, A.; Martin-Castillo, B.; de Llorens, R.; Bosch-Barrera, J.; Brunet, J.; Menendez, J.A. Cross-Suppression of EGFR Ligands Amphiregulin and Epiregulin and de-Repression of FGFR3 Signalling Contribute to Cetuximab Resistance in Wild-Type KRAS Tumour Cells. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, B.L.; Liu, J.; Qi, L.; Wang, C.; O’Connor, K.L. Integrin A6β4 Upregulates Amphiregulin and Epiregulin through Base Excision Repair-Mediated DNA Demethylation and Promotes Genome-Wide DNA Hypomethylation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.S.; McGuffey, E.J.; Morris, J.S.; Manyam, G.; Baladandayuthapani, V.; Wei, W.; Morris, V.K.; Overman, M.J.; Maru, D.M.; Jiang, Z.-Q.; et al. Association of CpG Island Methylator Phenotype and EREG/AREG Methylation and Expression in Colorectal Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 1352–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormann, F.; Stinzing, S.; Tierling, S.; Morkel, M.; Markelova, M.R.; Walter, J.; Weichert, W.; Roßner, F.; Kuhn, N.; Perner, J.; et al. Epigenetic Regulation of Amphiregulin and Epiregulin in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodland, K.D.; Bollinger, N.; Ippolito, D.; Opresko, L.K.; Coffey, R.J.; Zangar, R.; Wiley, H.S. Multiple Mechanisms Are Responsible for Transactivation of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Mammary Epithelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 31477–31487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.S.; Cheng, X.; Pawlowski, J.E.; Wallace, A.R.; Ferrer, P.; Molloy, C.J. Epiregulin Is a Potent Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell-Derived Mitogen Induced by Angiotensin II, Endothelin-1, and Thrombin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, S.; Xu, R.; Tang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Wei, J.; Yao, R.; Zhao, X.; Wei, Q.; et al. Mechanisms of Estradiol-Induced EGF-like Factor Expression and Oocyte Maturation via G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqaa190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsu, H.; Dempsey, P.J.; Eguchi, S. ADAMs as Mediators of EGF Receptor Transactivation by G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2006, 291, C1–C10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massip-Copiz, M.; Clauzure, M.; Valdivieso, Á.G.; Santa-Coloma, T.A. Epiregulin (EREG) Is Upregulated through an IL-1β Autocrine Loop in Caco-2 Epithelial Cells with Reduced CFTR Function. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 2911–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riese, D.J., 2nd; Cullum, R.L. Epiregulin: Roles in Normal Physiology and Cancer. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 28, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.R.; Wolf, E. The Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Ligands at a Glance. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 218, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, I.; Shirasawa, S.; Iwamoto, R.; Okumura, K.; Tsunoda, T.; Nishioka, M.; Fukuyama, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Mekada, E.; Sasazuki, T. Involvement of Deregulated Epiregulin Expression in Tumorigenesis In Vivo through Activated Ki-Ras Signaling Pathway in Human Colon Cancer Cells1. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 6886–6889. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.L.; Meise, K.S.; Plowman, G.D.; Coffey, R.J.; Dempsey, P.J. Cell Surface Ectodomain Cleavage of Human Amphiregulin Precursor Is Sensitive to a Metalloprotease Inhibitor: Release of a Predominant n-Glycosylated 43-kda Soluble Form. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 17258–17268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willmarth, N.E.; Ethier, S.P. Autocrine and Juxtacrine Effects of Amphiregulin on the Proliferative, Invasive, and Migratory Properties of Normal and Neoplastic Human Mammary Epithelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 37728–37737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Han, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, W.; Duan, S.; Deng, J.; et al. Stabilization of EREG via STT3B-Mediated N-Glycosylation Is Critical for PDL1 Upregulation and Immune Evasion in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2024, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, U.; Weskamp, G.; Kelly, K.; Zhou, H.-M.; Higashiyama, S.; Peschon, J.; Hartmann, D.; Saftig, P.; Blobel, C.P. Distinct Roles for ADAM10 and ADAM17 in Ectodomain Shedding of Six EGFR Ligands. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 164, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, K.; Le Gall, S.; Schulte, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Reiss, K.; Murphy, G.; Toyama, Y.; Hartmann, D.; Saftig, P.; Blobel, C.P. Substrate Selectivity of Epidermal Growth Factor-Receptor Ligand Sheddases and Their Regulation by Phorbol Esters and Calcium Influx. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosur, V.; Farley, M.L.; Burzenski, L.M.; Shultz, L.D.; Wiles, M.V. ADAM17 Is Essential for Ectodomain Shedding of the EGF-Receptor Ligand Amphiregulin. FEBS Open Bio 2018, 8, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternlicht, M.D.; Sunnarborg, S.W.; Kouros-Mehr, H.; Yu, Y.; Lee, D.C.; Werb, Z. Mammary Ductal Morphogenesis Requires Paracrine Activation of Stromal EGFR via ADAM17-Dependent Shedding of Epithelial Amphiregulin. Development 2005, 132, 3923–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkle, C.L.; Sunnarborg, S.W.; Loiselle, D.; Parker, C.E.; Stevenson, M.; Russell, W.E.; Lee, D.C. Selective Roles for Tumor Necrosis Factor α-Converting Enzyme/ADAM17 in the Shedding of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Ligand Family: The Juxtamembrane Stalk Determines Cleavage Efficiency. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 24179–24188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, S.M.; Bobé, P.; Reiss, K.; Horiuchi, K.; Niu, X.-D.; Lundell, D.; Gibb, D.R.; Conrad, D.; Saftig, P.; Blobel, C.P. ADAMs 10 and 17 Represent Differentially Regulated Components of a General Shedding Machinery for Membrane Proteins Such as Transforming Growth Factor α, L-Selectin, and Tumor Necrosis Factor α. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komurasaki, T.; Toyoda, H.; Uchida, D.; Morimoto, S. Epiregulin Binds to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and ErbB-4 and Induces Tryosine Phosphorylation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor, ErbB-2, ErbB-3 and ErbB-4. Oncogene 1997, 15, 2841–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riese, D.J.; Kim, E.D.; Elenius, K.; Buckley, S.; Klagsbrun, M.; Plowman, G.D.; Stern, D.F. The Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Couples Transforming Growth Factor-α, Heparin-Binding Epidermal Growth Factor-like Factor, and Amphiregulin to Neu, ErbB-3, and ErbB-4. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 20047–20052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yotsumoto, F.; Fukami, T.; Yagi, H.; Funakoshi, A.; Yoshizato, T.; Kuroki, M.; Miyamoto, S. Amphiregulin Regulates the Activation of ERK and Akt through Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and HER3 Signals Involved in the Progression of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 2351–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussinov, R.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Jang, H. Mitogen Signaling Strength and Duration Can Control Cell Cycle Decisions. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadm9211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, M.; Pittarella, P.; Sabbatini, M.; Renò, F. Epiregulin Induces Human SK-N-BE Cell Differentiation through ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway. Growth Factors 2013, 31, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Hirayama, D.; Maryu, G.; Matsuda, K.; Hino, N.; Deguchi, E.; Aoki, K.; Iwamoto, R.; Terai, K.; Matsuda, M. Redundant Roles of EGFR Ligands in the ERK Activation Waves during Collective Cell Migration. Life Sci. Alliance 2022, 5, e202101206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliardi, P.A.; Dobrzyński, M.; Jacques, M.-A.; Dessauges, C.; Ender, P.; Blum, Y.; Hughes, R.M.; Cohen, A.R.; Pertz, O. Collective ERK/Akt Activity Waves Orchestrate Epithelial Homeostasis by Driving Apoptosis-Induced Survival. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 1712–1726.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponsioen, B.; Post, J.B.; Buissant des Amorie, J.R.; Laskaris, D.; van Ineveld, R.L.; Kersten, S.; Bertotti, A.; Sassi, F.; Sipieter, F.; Cappe, B.; et al. Quantifying Single-Cell ERK Dynamics in Colorectal Cancer Organoids Reveals EGFR as an Amplifier of Oncogenic MAPK Pathway Signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2021, 23, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, J.A.Q.A.; de Andrade, C.; Goes, A.M.; Rodrigues, M.A.; Gomes, D.A. Effects of Different Ligands on Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Nuclear Translocation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Sandmann, T.; Frierson, H.; Fu, L.; Fuentes, E.; Walter, K.; Okrah, K.; Rumpel, C.; Moskaluk, C.; Lu, S.; et al. Integrated Genomic Analysis of Colorectal Cancer Progression Reveals Activation of EGFR through Demethylation of the EREG Promoter. Oncogene 2016, 35, 6403–6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, D.J.; Karapetis, C.S.; Harbison, C.; O’Callaghan, C.J.; Tu, D.; Simes, R.J.; Malone, D.P.; Langer, C.; Tebbutt, N.; Price, T.J.; et al. Epiregulin Gene Expression as a Biomarker of Benefit from Cetuximab in the Treatment of Advanced Colorectal Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.J.M.; Elliott, F.; Sapanara, N.; Aghaei, F.; Zhang, L.; Muranyi, A.; Yan, D.; Bai, I.; Zhao, Z.; Shires, M.; et al. Associations between AI-Assisted Tumor Amphiregulin and Epiregulin IHC and Outcomes from Anti-EGFR Therapy in the Routine Management of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 4153–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-D.; Miao, S.-Y.; Wang, G.-L.; Yang, L.; Shu, Y.-Q.; Yin, Y.-M. Amphiregulin and Epiregulin Expression in Colorectal Carcinoma and the Correlation with Clinicopathological Characteristics. Onkologie 2010, 33, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Kobunai, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kanazawa, T.; Konishi, T.; Tanaka, T.; Matsuda, K.; Ishihara, S.; Nozawa, K.; Eshima, K.; et al. Prediction of Liver Metastasis after Colorectal Cancer Using Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis of 10 Genes. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramochi, H.; Nakajima, G.; Kaneko, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Inoue, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Hayashi, K. Amphiregulin and Epiregulin mRNA Expression in Primary Colorectal Cancer and Corresponding Liver Metastases. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Ichikawa, Y.; Yamagishi, S.; Momiyama, N.; Ota, M.; Fujii, S.; Tanaka, K.; Togo, S.; Ohki, S.; Shimada, H. Amphiregulin Is a Promising Prognostic Marker for Liver Metastases of Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2351–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pentheroudakis, G.; Kotoula, V.; De Roock, W.; Kouvatseas, G.; Papakostas, P.; Makatsoris, T.; Papamichael, D.; Xanthakis, I.; Sgouros, J.; Televantou, D.; et al. Biomarkers of Benefit from Cetuximab-Based Therapy in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Interaction of EGFR Ligand Expression with RAS/RAF, PIK3CA Genotypes. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, B.; De Roock, W.; Piessevaux, H.; Van Oirbeek, R.; Biesmans, B.; De Schutter, J.; Fieuws, S.; Vandesompele, J.; Peeters, M.; Van Laethem, J.-L.; et al. Amphiregulin and Epiregulin mRNA Expression in Primary Tumors Predicts Outcome in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Treated With Cetuximab. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5068–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.B.; Dutta, D.; Watson, D.; Maddala, T.; Munneke, B.M.; Shak, S.; Rowinsky, E.K.; Xu, L.-A.; Harbison, C.T.; Clark, E.A.; et al. Tumour Gene Expression Predicts Response to Cetuximab in Patients with KRAS Wild-Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, S.M.; Jiang, C.; Hatch, A.J.; Shterev, I.; Sibley, A.B.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Venook, A.P.; Owzar, K.; Hurwitz, H.I.; Nixon, A.B. Gene Expression Markers of Efficacy and Resistance to Cetuximab Treatment in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Results from CALGB 80203 (Alliance). Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seligmann, J.F.; Elliott, F.; Richman, S.D.; Jacobs, B.; Hemmings, G.; Brown, S.; Barrett, J.H.; Tejpar, S.; Quirke, P.; Seymour, M.T. Combined Epiregulin and Amphiregulin Expression Levels as a Predictive Biomarker for Panitumumab Therapy Benefit or Lack of Benefit in Patients with RAS Wild-Type Advanced Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.J.M.; Seligmann, J.F.; Elliott, F.; Shires, M.; Richman, S.D.; Brown, S.; Zhang, L.; Singh, S.; Pugh, J.; Xu, X.-M.; et al. Artificial Intelligence–Assisted Amphiregulin and Epiregulin IHC Predicts Panitumumab Benefit in RAS Wild-Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3422–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahler, A.; Stintzing, S.; Modest, D.P.; Ricard, I.; Giessen-Jung, C.; Kapaun, C.; Ivanova, B.; Kaiser, F.; Fischer von Weikersthal, L.; Moosmann, N.; et al. Amphiregulin Expression Is a Predictive Biomarker for EGFR Inhibition in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Combined Analysis of Three Randomized Trials. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 6559–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khambata-Ford, S.; Garrett, C.R.; Meropol, N.J.; Basik, M.; Harbison, C.T.; Wu, S.; Wong, T.W.; Huang, X.; Takimoto, C.H.; Godwin, A.K.; et al. Expression of Epiregulin and Amphiregulin and K-Ras Mutation Status Predict Disease Control in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients Treated with Cetuximab. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 3230–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saridaki, Z.; Tzardi, M.; Papadaki, C.; Sfakianaki, M.; Pega, F.; Kalikaki, A.; Tsakalaki, E.; Trypaki, M.; Messaritakis, I.; Stathopoulos, E.; et al. Impact of KRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA Mutations, PTEN, AREG, EREG Expression and Skin Rash in ≥ 2 Line Cetuximab-Based Therapy of Colorectal Cancer Patients. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, P.; Sastre, J.; Ortega, J.S.; Bando, I.; Ferrer, M.; García-Alfonso, P.; Donnay, O.; Carrato, A.; Jiménez, A.; Aranda, E.; et al. Prognostic Value of BRAF, PI3K, PTEN, EGFR Copy Number, Amphiregulin and Epiregulin Status in Patients with KRAS Codon 12 Wild-Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Receiving First-Line Chemotherapy with Anti-EGFR Therapy. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2015, 19, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strimpakos, A.; Pentheroudakis, G.; Kotoula, V.; De Roock, W.; Kouvatseas, G.; Papakostas, P.; Makatsoris, T.; Papamichael, D.; Andreadou, A.; Sgouros, J.; et al. The Prognostic Role of Ephrin A2 and Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor Pathway Mediators in Patients with Advanced Colorectal Cancer Treated with Cetuximab. Clin. Color. Cancer 2013, 12, 267–274.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seligmann, J.F.; Elliott, F.; Richman, S.; Hemmings, G.; Brown, S.; Jacobs, B.; Williams, C.; Tejpar, S.; Barrett, J.H.; Quirke, P.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Characteristics and Treatment Outcomes of Advanced Right-Colon, Left-Colon and Rectal Cancers: Data from 1180 Patients in a Phase III Trial of Panitumumab with an Extended Biomarker Panel. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, C.-S.; Sun, E.-G.; Choi, J.-N.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Ryu, K.-H.; Shim, H.-J.; Hwang, J.-E.; Bae, W.-K.; Kim, H.-R.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 4 Increases Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Signaling by Inducing Amphiregulin Expression and Attenuates Response to EGFR Inhibitors in Colon Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 3268–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobor, S.; Van Emburgh, B.O.; Crowley, E.; Misale, S.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Bardelli, A. TGFα and Amphiregulin Paracrine Network Promotes Resistance to EGFR Blockade in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6429–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luraghi, P.; Bigatto, V.; Cipriano, E.; Reato, G.; Orzan, F.; Sassi, F.; De Bacco, F.; Isella, C.; Bellomo, S.E.; Medico, E.; et al. A Molecularly Annotated Model of Patient-Derived Colon Cancer Stem–Like Cells to Assess Genetic and Nongenetic Mechanisms of Resistance to Anti-EGFR Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Hoyo, A.; Monzonís, X.; Vidal, J.; Linares, J.; Montagut, C. Unveiling Acquired Resistance to Anti-EGFR Therapies in Colorectal Cancer: A Long and Winding Road. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1398419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higginbotham, J.N.; Demory Beckler, M.; Gephart, J.D.; Franklin, J.L.; Bogatcheva, G.; Kremers, G.-J.; Piston, D.W.; Ayers, G.D.; McConnell, R.E.; Tyska, M.J.; et al. Amphiregulin Exosomes Increase Cancer Cell Invasion. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Kroeger, B.; Marie, P.P.; Bridges, E.M.; Mason, J.D.; McCormick, K.; Zois, C.E.; Sheldon, H.; Khalid Alham, N.; Johnson, E.; et al. Glutamine Deprivation Alters the Origin and Function of Cancer Cell Exosomes. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e103009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, J.D.; Marks, E.; Fan, S.-J.; McCormick, K.; Wilson, C.; Harris, A.L.; Hamdy, F.C.; Cunningham, C.; Goberdhan, D.C.I. Stress-Induced Rab11a-Exosomes Induce Amphiregulin-Mediated Cetuximab Resistance in Colorectal Cancer. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolston, A.; Khan, K.; Spain, G.; Barber, L.J.; Griffiths, B.; Gonzalez-Exposito, R.; Hornsteiner, L.; Punta, M.; Patil, Y.; Newey, A.; et al. Genomic and Transcriptomic Determinants of Therapy Resistance and Immune Landscape Evolution during Anti-EGFR Treatment in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 35–50.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, C.M.; Lau, R.; Sanchez, A.; Sun, R.X.; Fong, E.J.; Doche, M.E.; Chen, O.; Jusuf, A.; Lenz, H.-J.; Larson, B.; et al. Anti-EGFR Therapy Induces EGF Secretion by Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts to Confer Colorectal Cancer Chemoresistance. Cancers 2020, 12, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufert, C.; Becker, C.; Türeci, Ö.; Waldner, M.J.; Backert, I.; Floh, K.; Atreya, I.; Leppkes, M.; Jefremow, A.; Vieth, M.; et al. Tumor Fibroblast–Derived Epiregulin Promotes Growth of Colitis-Associated Neoplasms through ERK. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1428–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jing, Y.; Ding, L.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, X.; Huang, X.; Pu, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Epiregulin Reprograms Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Facilitates Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Invasion via JAK2-STAT3 Pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.Y.; Cho, K.H.; Jeong, K.J.; Cho, S.J.; Won, M.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, N.H.; Hur, G.M.; Yoon, S.-H.; Park, H.-W.; et al. Lysophosphatidic Acid-Induced Amphiregulin Secretion by Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Augments Cancer Cell Invasion. Cancer Lett. 2022, 551, 215946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westendorp, F.; Karpus, O.N.; Koelink, P.J.; Vermeulen, J.L.M.; Meisner, S.; Koster, J.; Büller, N.V.J.A.; Wildenberg, M.E.; Muncan, V.; van den Brink, G.R. Epithelium-Derived Indian Hedgehog Restricts Stromal Expression of ErbB Family Members That Drive Colonic Tumor Cell Proliferation. Oncogene 2021, 40, 1628–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Long, Q.; Fu, Q.; Xu, Q.; Fu, D.; Li, Y.; Gao, L.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; Lam, E.W.-F.; et al. Targeting Epiregulin in the Treatment-Damaged Tumor Microenvironment Restrains Therapeutic Resistance. Oncogene 2022, 41, 4941–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parseghian, C.; Eluri, M.; Kopetz, S.; Raghav, K. Mechanisms of Resistance to EGFR-Targeted Therapies in Colorectal Cancer: More than Just Genetics. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1176657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.; Venè, R.; Benelli, R.; Romairone, E.; Scabini, S.; Catellani, S.; Rebesco, B.; Mastracci, L.; Grillo, F.; Minghelli, S.; et al. Targeting the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Can Counteract the Inhibition of Natural Killer Cell Function Exerted by Colorectal Tumor-Associated Fibroblasts. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, L.; Ren, Y.; Dai, W.; Chen, T.; Luo, L.; Zeng, J.; Mi, K.; Lang, J.; Cao, B. Epiregulin Confers EGFR-TKI Resistance via EGFR/ErbB2 Heterodimer in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 2596–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindzen, M.; Ghosh, S.; Noronha, A.; Drago, D.; Nataraj, N.B.; Leitner, O.; Carvalho, S.; Zmora, E.; Sapoznik, S.; Shany, K.B.; et al. Targeting Autocrine Amphiregulin Robustly and Reproducibly Inhibits Ovarian Cancer in a Syngeneic Model: Roles for Wildtype P53. Oncogene 2021, 40, 3665–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, S.; Lindzen, M.; Lauriola, M.; Shirazi, N.; Sinha, S.; Abdul-Hai, A.; Levanon, K.; Korach, J.; Barshack, I.; Cohen, Y.; et al. An Antibody to Amphiregulin, an Abundant Growth Factor in Patients’ Fluids, Inhibits Ovarian Tumors. Oncogene 2016, 35, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Long, Q.; Zhu, D.; Fu, D.; Zhang, B.; Han, L.; Qian, M.; Guo, J.; Xu, J.; Cao, L.; et al. Targeting Amphiregulin (AREG) Derived from Senescent Stromal Cells Diminishes Cancer Resistance and Averts Programmed Cell Death 1 Ligand (PD-L1)-Mediated Immunosuppression. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofgren, K.A.; Sreekumar, S.; Jenkins, E.C., Jr.; Ernzen, K.J.; Kenny, P.A. Anti-Tumor Efficacy of an MMAE-Conjugated Antibody Targeting Cell Surface TACE/ADAM17-Cleaved Amphiregulin in Breast Cancer. Antib. Ther. 2021, 4, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Iijima, M.; Kado, Y.; Mizohata, E.; Inoue, T.; Sugiyama, A.; Doi, H.; Shibasaki, Y.; Kodama, T. Construction and Characterization of Functional Anti-Epiregulin Humanized Monoclonal Antibodies. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kado, Y.; Mizohata, E.; Nagatoishi, S.; Iijima, M.; Shinoda, K.; Miyafusa, T.; Nakayama, T.; Yoshizumi, T.; Sugiyama, A.; Kawamura, T.; et al. Epiregulin Recognition Mechanisms by Anti-Epiregulin Antibody 9E5: Structural, Functional, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Analyses. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 2319–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, M.; Anai, M.; Kodama, T.; Shibasaki, Y. Epiregulin-Blocking Antibody Inhibits Epiregulin-Dependent EGFR Signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 489, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Yamada-Okabe, H.; Suzuki, M.; Natori, O.; Kato, A.; Matsubara, K.; Jau Chen, Y.; Yamazaki, M.; Funahashi, S.; Yoshida, K.; et al. LGR5-Positive Colon Cancer Stem Cells Interconvert with Drug-Resistant LGR5-Negative Cells and Are Capable of Tumor Reconstitution. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 2631–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High, P.; Guernsey, C.; Subramanian, S.; Jacob, J.; Carmon, K.S. The Evolving Paradigm of Antibody-Drug Conjugates Targeting the ErbB/HER Family of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.Y.; Anami, Y.; Yamazaki, C.M.; Xiong, W.; Haase, C.M.; Olson, S.D.; Lee, J.; Ueno, N.T.; Zhang, N.; An, Z. An Enzymatically Cleavable Tripeptide Linker for Maximizing the Therapeutic Index of Antibody–Drug Conjugates. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 1449–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, L.F.; Schuster, H.J.; Schmuck, K.; Schuberth, I.; Alves, F. Duocarmycin-Based Prodrugs for Cancer Prodrug Monotherapy. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 6312–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.; Emmerson, J.; Beggs, A.D.; West, N.; Bridgewater, J.A.; Graham, J.; Seymour, M.T.; Hemmings, G.; Dimbleby, C.; Murden, G.A.; et al. A Biomarker Enrichment Trial of Anti-EGFR Agents in Right Primary Tumor Location (rPTL), RAS Wild-Type (RAS-Wt) Advanced Colorectal Cancer (aCRC): ARIEL (ISRCTN11061442). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, TPS3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randon, G.; Pietrantonio, F. Towards Multiomics-Based Dissection of Anti-EGFR Sensitivity in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 4021–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calligaris, M.; Cuffaro, D.; Bonelli, S.; Spanò, D.P.; Rossello, A.; Nuti, E.; Scilabra, S.D. Strategies to Target ADAM17 in Disease: From Its Discovery to the iRhom Revolution. Molecules 2021, 26, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-X.; Fang, J.-Y. Comprehensive Review of Targeted Therapy for Colorectal Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Agent Name | Target | Modality | Cancer Type | In Vivo Dosing | Safety | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR37 | AREG | mAb | Ovarian | 0.2 mg twice weekly | No effect on body weight or overall appearance | [98] |
| AR30 | AREG | mAb | Ovarian | 200 μg twice weekly | N/A | [99] |
| N/A | AREG | mAb | Prostate, Breast | 10.0 mg/kg biweekly | No effect on body weight | [100] |
| GMF-1A3-MMAE | AREG | ADC | Breast | 5 mg/kg every 4 days | No effect on body weight or overall appearance | [101] |
| 9E5 | EREG | mAb | CRC | N/A | N/A | [102,103,104] |
| HM1 | EREG | mAb | CRC | N/A | N/A | [102] |
| N/A | EREG | mAb | CRC | N/A | N/A | [105] |
| N/A | EREG | mAb | Prostate, Breast | 10.0 mg/kg biweekly | No effect on body weight, kidney and liver enzymes, or blood cell counts | [94] |
| H231-VC-cDuoDM | EREG | ADC | CRC | 5–10 mg/kg weekly | No effect on body weight, kidney and liver enzymes, or blood cell counts | [21] |
| H231-EGC-cDuoDM | ||||||
| H231-EGC-qDMDM gluc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guernsey-Biddle, C.; High, P.; Carmon, K.S. Exploring the Potential of Epiregulin and Amphiregulin as Prognostic, Predictive, and Therapeutic Targets in Colorectal Cancer. Onco 2024, 4, 257-274. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco4040019
Guernsey-Biddle C, High P, Carmon KS. Exploring the Potential of Epiregulin and Amphiregulin as Prognostic, Predictive, and Therapeutic Targets in Colorectal Cancer. Onco. 2024; 4(4):257-274. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco4040019
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuernsey-Biddle, Cara, Peyton High, and Kendra S. Carmon. 2024. "Exploring the Potential of Epiregulin and Amphiregulin as Prognostic, Predictive, and Therapeutic Targets in Colorectal Cancer" Onco 4, no. 4: 257-274. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco4040019
APA StyleGuernsey-Biddle, C., High, P., & Carmon, K. S. (2024). Exploring the Potential of Epiregulin and Amphiregulin as Prognostic, Predictive, and Therapeutic Targets in Colorectal Cancer. Onco, 4(4), 257-274. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco4040019





