Clinical Application of Next-Generation Sequencing in Recurrent Glioblastoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Information and Sample Collection
2.2. Strata Sequencing
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Sequencing Results and Outcomes
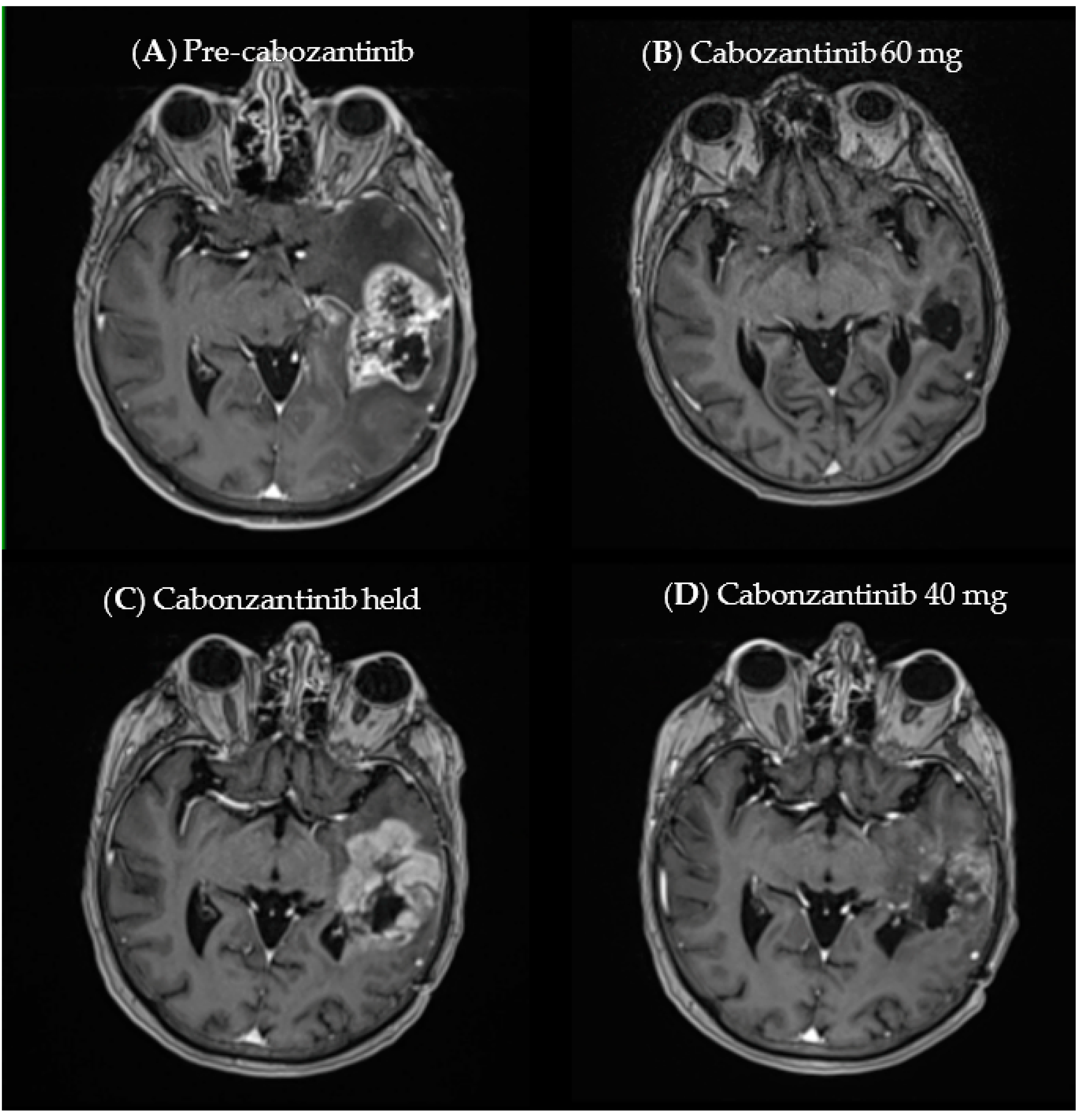
3.3. Case Example
4. Discussion
4.1. Future Directions
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Disclosures
References
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups; National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeman, N.I.; Cagle, P.T.; Beasley, M.B.; Chitale, D.A.; Dacic, S.; Giaccone, G.; Jenkins, R.B.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Saldivar, J.-S.; Squire, J.; et al. College of American Pathologists International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer and Association for Molecular Pathology Molecular testing guideline for selection of lung cancer patients for EGFR and ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Guideline from the College of American Pathologists, International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and Association for Molecular Pathology. J. Mol. Diagn. 2013, 15, 415–453. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, P.B.; Hauschild, A.; Robert, C.; Haanen, J.B.; Ascierto, P.; Larkin, J.; Dummer, R.; Garbe, C.; Testori, A.; Maio, M.; et al. BRIM-3 Study Group Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2507–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shabani Azim, F.; Houri, H.; Ghalavand, Z.; Nikmanesh, B. Next Generation Sequencing in Clinical Oncology: Applications, Challenges and Promises: A Review Article. Iran. J. Public Health 2018, 47, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.R.; Chitale, D.; Riely, G.J.; Pao, W.; Miller, V.A.; Zakowski, M.F.; Rusch, V.; Kris, M.G.; Ladanyi, M. EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinomas: Clinical testing experience and relationship to EGFR gene copy number and immunohistochemical expression. J. Mol. Diagn. 2008, 10, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Golding, B.; Luu, A.; Jones, R.; Viloria-Petit, A.M. The function and therapeutic targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katayama, R.; Lovly, C.M.; Shaw, A.T. Therapeutic targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in lung cancer: A paradigm for precision cancer medicine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, T.; Su, C.; Ren, S.; Cappuzzo, F.; Rocco, G.; Palmer, J.D.; van Zandwijk, N.; Blackhall, F.; Le, X.; Pennell, N.A.; et al. written on behalf of the AME Lung Cancer Collaborative Group A consensus on the role of osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer from the AME Lung Cancer Collaborative Group. J Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 3909–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboundji, K.; Auliac, J.-B.; Pérol, M.; François, G.; Janicot, H.; Marcq, M.; Dubos-Arvis, C.; Renault, A.; Guisier, F.; Odier, L.; et al. Efficacy of Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Leptomeningeal Metastases Pretreated with EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Target. Oncol. 2018, 13, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.O.; Koyama, T.; Rhrissorrakrai, K.; Robine, N.; Utro, F.; Emde, A.-K.; Chen, B.-J.; Arora, K.; Shah, M.; Geiger, H.; et al. Sequencing and curation strategies for identifying candidate glioblastoma treatments. Bmc Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchanan, J.; Wordsworth, S.; Schuh, A. Issues surrounding the health economic evaluation of genomic technologies. Pharmacogenomics 2013, 14, 1833–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ballester, L.Y.; Olar, A.; Roy-Chowdhuri, S. Next-generation sequencing of central nervous systems tumors: The future of personalized patient management. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, 308–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.M.; Datto, M.; Duncavage, E.J.; Kulkarni, S.; Lindeman, N.I.; Roy, S.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; Vnencak-Jones, C.L.; Wolff, D.J.; Younes, A.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation and Reporting of Sequence Variants in Cancer: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the Association for Molecular Pathology, American Society of Clinical Oncology, and College of American Pathologists. J. Mol. Diagn 2017, 19, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blandin, A.-F.; Durand, A.; Litzler, M.; Tripp, A.; Guérin, É.; Ruhland, E.; Obrecht, A.; Keime, C.; Fuchs, Q.; Reita, D.; et al. Hypoxic Environment and Paired Hierarchical 3D and 2D Models of Pediatric H3.3-Mutated Gliomas Recreate the Patient Tumor Complexity. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Escudier, B.; Powles, T.; Tannir, N.M.; Mainwaring, P.N.; Rini, B.I.; Hammers, H.J.; Donskov, F.; Roth, B.J.; Peltola, K.; et al. METEOR investigators Cabozantinib versus everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma (METEOR): Final results from a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mateo, J.; Porta, N.; Bianchini, D.; McGovern, U.; Elliott, T.; Jones, R.; Syndikus, I.; Ralph, C.; Jain, S.; Varughese, M.; et al. Olaparib in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer with DNA repair gene aberrations (TOPARP-B): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesueur, P.; Lequesne, J.; Grellard, J.-M.; Dugué, A.; Coquan, E.; Brachet, P.-E.; Geffrelot, J.; Kao, W.; Emery, E.; Berro, D.H.; et al. Phase I/IIa study of concomitant radiotherapy with olaparib and temozolomide in unresectable or partially resectable glioblastoma: OLA-TMZ-RTE-01 trial protocol. Bmc. Cancer 2019, 19, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.Y.; Drappatz, J.; de Groot, J.; Prados, M.D.; Reardon, D.A.; Schiff, D.; Chamberlain, M.; Mikkelsen, T.; Desjardins, A.; Holland, J.; et al. Phase II study of cabozantinib in patients with progressive glioblastoma: Subset analysis of patients naive to antiangiogenic therapy. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Guo, D. MET in glioma: Signaling pathways and targeted therapies. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woo, P.Y.M.; Lam, T.-C.; Pu, J.K.S.; Li, L.-F.; Leung, R.C.Y.; Ho, J.M.K.; Zhung, J.T.F.; Wong, B.; Chan, T.S.K.; Loong, H.H.F.; et al. Regression of BRAFV600E mutant adult glioblastoma after primary combined BRAF-MEK inhibitor targeted therapy: A report of two cases. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 3818–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- International Cancer Genome Consortium PedBrain Tumor Project Recurrent MET fusion genes represent a drug target in pediatric glioblastoma. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1314–1320. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.K.; Smith, E.J.; Mladek, A.C.; Tian, S.; Decker, P.A.; Kizilbash, S.H.; Kitange, G.J.; Sarkaria, J.N. PARP Inhibitors for Sensitization of Alkylation Chemotherapy in Glioblastoma: Impact of Blood-Brain Barrier and Molecular Heterogeneity. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ameratunga, M.; McArthur, G.; Gan, H.; Cher, L. Prolonged disease control with MEK inhibitor in neurofibromatosis type I-associated glioblastoma. J. Clin. Pharm. 2016, 41, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romo, C.G.; Slobogean, B.L.; Blair, L.K.; Blakeley, J.O. Trametinib for aggressive gliomas in adults with neurofibromatosis type 1. JCO 2019, 37, e13562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocco, E.; Scaltriti, M.; Drilon, A. NTRK fusion-positive cancers and TRK inhibitor therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 731–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drilon, A.; Laetsch, T.W.; Kummar, S.; DuBois, S.G.; Lassen, U.N.; Demetri, G.D.; Nathenson, M.; Doebele, R.C.; Farago, A.F.; Pappo, A.S.; et al. Efficacy of Larotrectinib in TRK Fusion-Positive Cancers in Adults and Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doebele, R.C.; Drilon, A.; Paz-Ares, L.; Siena, S.; Shaw, A.T.; Farago, A.F.; Blakely, C.M.; Seto, T.; Cho, B.C.; Tosi, D.; et al. Trial investigators Entrectinib in patients with advanced or metastatic NTRK fusion-positive solid tumours: Integrated analysis of three phase 1-2 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Shi, L.; Shan, Q.; Cao, Q.; Yue, C.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Gao, S.; et al. The third-generation EGFR inhibitor AZD9291 overcomes primary resistance by continuously blocking ERK signaling in glioblastoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Lim, S.H.; An, H.J.; Kim, K.H.; Park, K.U.; Kang, E.J.; Choi, Y.H.; Ahn, M.S.; Lee, M.H.; Sun, J.-M.; et al. Osimertinib for Patients With Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Uncommon EGFR Mutations: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Phase II Trial (KCSG-LU15-09). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frattini, V.; Trifonov, V.; Chan, J.M.; Castano, A.; Lia, M.; Abate, F.; Keir, S.T.; Ji, A.X.; Zoppoli, P.; Niola, F.; et al. The integrated landscape of driver genomic alterations in glioblastoma. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bahleda, R.; Italiano, A.; Hierro, C.; Mita, A.; Cervantes, A.; Chan, N.; Awad, M.; Calvo, E.; Moreno, V.; Govindan, R.; et al. Multicenter Phase I Study of Erdafitinib (JNJ-42756493), Oral Pan-Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced or Refractory Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4888–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenting, K.; van den Heuvel, C.N.A.M.; van Ewijk, A.; ElMelik, D.; de Boer, R.; Tindall, E.; Wei, G.; Kusters, B.; te Dorsthorst, M.; ter Laan, M.; et al. Mapping actionable pathways and mutations in brain tumours using targeted RNA next generation sequencing. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, C.; Guo, Y.; Shao, G.; Yang, Z.; Qiu, S.; Ma, K. RET fusion in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and response to cabozantinib: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019, 98, e14120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natsume, A.; Wakabayashi, T.; Miyakita, Y.; Narita, Y.; Mineharu, Y.; Arakawa, Y.; Yamasaki, F.; Sugiyama, K.; Hata, N.; Muragaki, Y.; et al. Phase I study of a brain penetrant mutant IDH1 inhibitor DS-1001b in patients with recurrent or progressive IDH1mutant gliomas. JCO 2019, 37, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shen, L.; Ding, D.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Lu, S. Efficacy of Crizotinib among Different Types of ROS1 Fusion Partners in Patients with ROS1-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davare, M.A.; Henderson, J.J.; Agarwal, A.; Wagner, J.P.; Iyer, S.R.; Shah, N.; Woltjer, R.; Somwar, R.; Gilheeney, S.W.; DeCarvalo, A.; et al. Rare but Recurrent ROS1 Fusions Resulting From Chromosome 6q22 Microdeletions are Targetable Oncogenes in Glioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6471–6482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stein, E.M.; Fathi, A.T.; DiNardo, C.D.; Pollyea, D.A.; Roboz, G.J.; Collins, R.; Sekeres, M.A.; Stone, R.M.; Attar, E.C.; Frattini, M.G.; et al. Enasidenib in patients with mutant IDH2 myelodysplastic syndromes: A phase 1 subgroup analysis of the multicentre, AG221-C-001 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e309–e319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Niu, M.; Xie, P.; Yue, C.; Liu, N.; Qi, Z.; Gao, S.; Liu, H.; Shi, Q.; Yu, R.; et al. Smoothened is a poor prognosis factor and a potential therapeutic target in glioma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassler, M.R.; Vedadinejad, M.; Flechl, B.; Haberler, C.; Preusser, M.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Wöhrer, A.; Dieckmann, K.U.; Rössler, K.; Kast, R.; et al. Response to imatinib as a function of target kinase expression in recurrent glioblastoma. Springerplus 2014, 3, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chukwueke, U.N.; Wen, P.Y. Use of the Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (RANO) criteria in clinical trials and clinical practice. Cns. Oncol. 2019, 8, CNS28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhodes, D.; Hovelson, D.H.; Suga, J.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Dees, E.C.; Koh, H.A.; Burkard, M.E.; Khatri, J.; Safa, M.M.; Matrana, M.R.; et al. PCR-based comprehensive genomic profiling (PCR-CGP): Feasibility from >20,000 tumor tissue specimens (TTS) and predicted impact on actionable biomarker identification versus hybrid capture (H)-CGP and plasma (P)-CGP. JCO 2020, 38, 3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- STRATA NGS Gene List. Available online: https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5eb03a8225db790ffcb446cf/t/5feb8848e1363469ebed413f/1609271368995/Gene_List_SO-SPEC-003-4.pdf (accessed on 4 August 2021).
- Aykan, N.F.; Özatlı, T. Objective response rate assessment in oncology: Current situation and future expectations. World, J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 11, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.-B.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Ye, Y.; Bekaii-Saab, T.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y. A Rare EGFR-SEPT14 Fusion in a Patient with Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Responding to Erlotinib. Oncologist 2020, 25, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reardon, D.A.; Nabors, L.B.; Mason, W.P.; Perry, J.R.; Shapiro, W.; Kavan, P.; Mathieu, D.; Phuphanich, S.; Cseh, A.; Fu, Y.; et al. BI 1200 36 Trial Group and the Canadian Brain Tumour Consortium Phase I/randomized phase II study of afatinib, an irreversible ErbB family blocker, with or without protracted temozolomide in adults with recurrent glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2015, 17, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wirth, L.J.; Sherman, E.; Robinson, B.; Solomon, B.; Kang, H.; Lorch, J.; Worden, F.; Brose, M.; Patel, J.; Leboulleux, S.; et al. Efficacy of Selpercatinib in RET-Altered Thyroid Cancers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drilon, A.; Oxnard, G.R.; Tan, D.S.W.; Loong, H.H.F.; Johnson, M.; Gainor, J.; McCoach, C.E.; Gautschi, O.; Besse, B.; Cho, B.C.; et al. Efficacy of Selpercatinib in RET Fusion-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, H.-N.; Liu, P. Targeting MET in cancer therapy. Chronic. Dis. Transl. Med. 2017, 3, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, R.; Kobayashi, Y.; Friboulet, L.; Lockerman, E.L.; Koike, S.; Shaw, A.T.; Engelman, J.A.; Fujita, N. Cabozantinib overcomes crizotinib resistance in ROS1 fusion-positive cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; Von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weller, M.; Pfister, S.M.; Wick, W.; Hegi, M.E.; Reifenberger, G.; Stupp, R. Molecular neuro-oncology in clinical practice: A new horizon. Lancet. Oncol. 2013, 14, e370–e379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegel, C.; Aboud, O.; Brown, M.; Chung, H.-J.; Raffeld, M.; Crandon, S.; Ji, M.; Levine, J.; Vera, E.; Patel, S.; et al. Utilizing next generation sequencing reports in clinical decision making: Report from the national institutes of health (nih) neuro-oncology branch (nob) natural history study (nhs) primary brain tumor panel (pbtp). Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, vi170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Trial Endpoints for the Approval of Cancer Drugs and Biologics. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/71195/download (accessed on 12 September 2020).
- Gatalica, Z.; Xiu, J.; Swensen, J.; Vranic, S. Molecular characterization of cancers with NTRK gene fusions. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Highlights of Prescribing Information Vitrakvi®. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/211710s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2020).
| A | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alterations | Type | Tier | Grade | Alterations | Type | Tier | Grade |
| ALK [14] | Fusion | II | D | MET [15] | CNV | II | C |
| ATM [16,17] | Hotspot | II | C | MET [18,19] | Hotspot | II | C |
| BRAF V600E [20] | Hotspot | II | D | MET [15,21] | Fusion | II | C |
| BRCA1 [22] | Hotspot | II | D | NF1 [23,24] | Fusion | II | C |
| BRCA2 [22] | Hotspot | II | D | NTRK1 [25,26,27] | Fusion | I | A |
| EGFR [28,29] | Hotspot | II | C | NTRK2 [25,26,27] | Fusion | I | A |
| EGFR-SEPT14 [30] | Fusion | II | C | NTRK3 [25,26,27] | Fusion | I | A |
| FGFR1 [31] | Hotspot | II | C | PTPRZ-MET [15,21] | Fusion | II | C |
| FGFR2 [31] | Hotspot | II | C | RET [32] | Hotspot | II | D |
| FGFR3 [31] | Hotspot | II | C | RET [33] | Fusion | II | D |
| IDH1 [34] | Hotspot | II | C | ROS1 [35,36] | Fusion | II | D |
| IDH2 [37] | Hotspot | II | C | SMO [38] | Hotspot | II | D |
| KIT [39] | Hotspot | II | C | ||||
| B | |||||||
| Tier | Grade | ||||||
| I | A | FDA-approved therapy for disease in question | |||||
| B | Large studies, not yet approved | ||||||
| II | C | Approved in other diseases, some studies in disease in question | |||||
| D | Pre-clinical data, case reports | ||||||
| III | VUS, not clear association with cancer | ||||||
| IV | Benign variant | ||||||
| Variable | ||
|---|---|---|
| Age | Mean (sd) | 56 (14.9) |
| Age | <55 | 6 (43%) |
| ≥55 | 8 (57%) | |
| Gender | Female | 3 (21%) |
| Male | 11 (79%) | |
| Surgical Status | biopsy | 4 (29%) |
| STR 1 | 4 (29%) | |
| GTR 2 | 6 (42%) | |
| Ki67 3 | <30 | 2 (14%) |
| ≥30 | 10 (72%) | |
| Unknown | 2 (14%) | |
| TERT 4 | Mutant | 11 (79%) |
| Wildtype | 3 (21%) | |
| MGMT 5 | Methylated | 8 (57%) |
| Unmethylated | 6 (43%) |
| Alteration | Treatment | Response % | Time to Achieve Best Response in Weeks |
|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR-SEPT14 fusion EGFR amp EGFR vIII deletion | Afatinib | 100 | 55.5 |
| MET exon 14 deletion MET amp | Cabozantinib | 100 | 25.4 |
| RET amp | Selpercatinib | 100 | 5.0 |
| BRAFV600E | Dabrafenib/trametinib | 72 | 4.3 |
| EGFR amp | Osimertinib | 53 | 18.9 |
| NF1 exon 23 splice donor site mutation | Trametinib | 52 | 2.4 |
| EGFR p.A289T | Afatinib 1 | 46 | 55.6 |
| MET amp | Crizotinib | 45 | 8.4 |
| PDGFR amp, KIT amp | Imatinib | 41 | 4.0 |
| EGFR-SEPT14 fusion EGFR amp | Osimertinib | 39 | 5.4 |
| SQSTM1-NTRK2 Fusion | Larotrectinib | 26 | 7.9 |
| TPM1-ALK fusion | Alectinib | 25 | 5.6 |
| EGFR vIII deletion EGFR amp | Osimertinib | 23 | 2.6 |
| BRAFV600E | Dabrafenib/trametinib | 4 | 4.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeitouni, D.; Catalino, M.P.; Wise, J.; McCabe, S.; Pietrosimone, K.; Rashid, N.; Khagi, S. Clinical Application of Next-Generation Sequencing in Recurrent Glioblastoma. Onco 2021, 1, 38-48. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco1010005
Zeitouni D, Catalino MP, Wise J, McCabe S, Pietrosimone K, Rashid N, Khagi S. Clinical Application of Next-Generation Sequencing in Recurrent Glioblastoma. Onco. 2021; 1(1):38-48. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco1010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeitouni, Daniel, Michael P. Catalino, Jordan Wise, Sean McCabe, Kathryn Pietrosimone, Naim Rashid, and Simon Khagi. 2021. "Clinical Application of Next-Generation Sequencing in Recurrent Glioblastoma" Onco 1, no. 1: 38-48. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco1010005
APA StyleZeitouni, D., Catalino, M. P., Wise, J., McCabe, S., Pietrosimone, K., Rashid, N., & Khagi, S. (2021). Clinical Application of Next-Generation Sequencing in Recurrent Glioblastoma. Onco, 1(1), 38-48. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco1010005






