Non-Conventional Hybrid Microporous Layers for Enhanced Performance and Durability of PEM Fuel Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
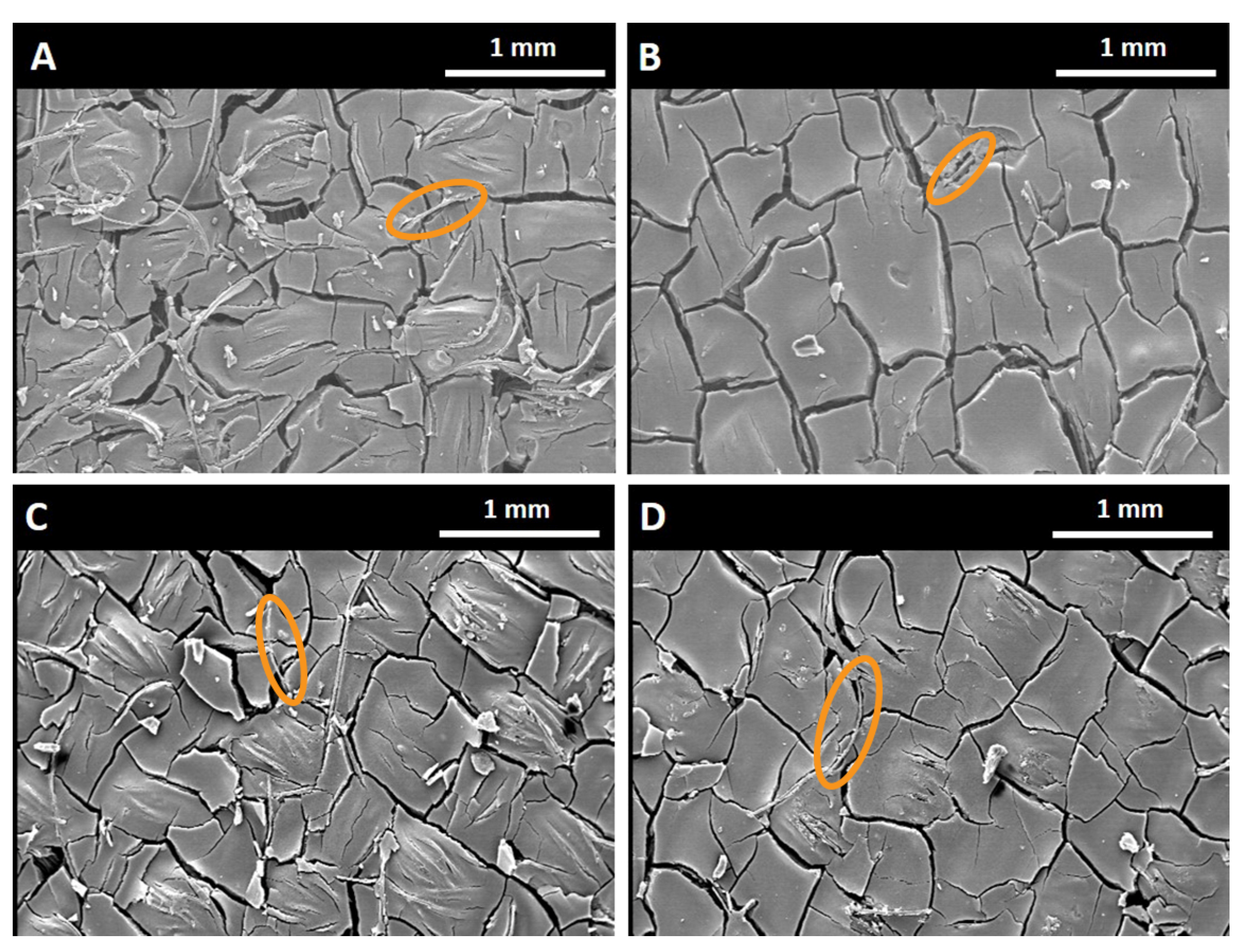
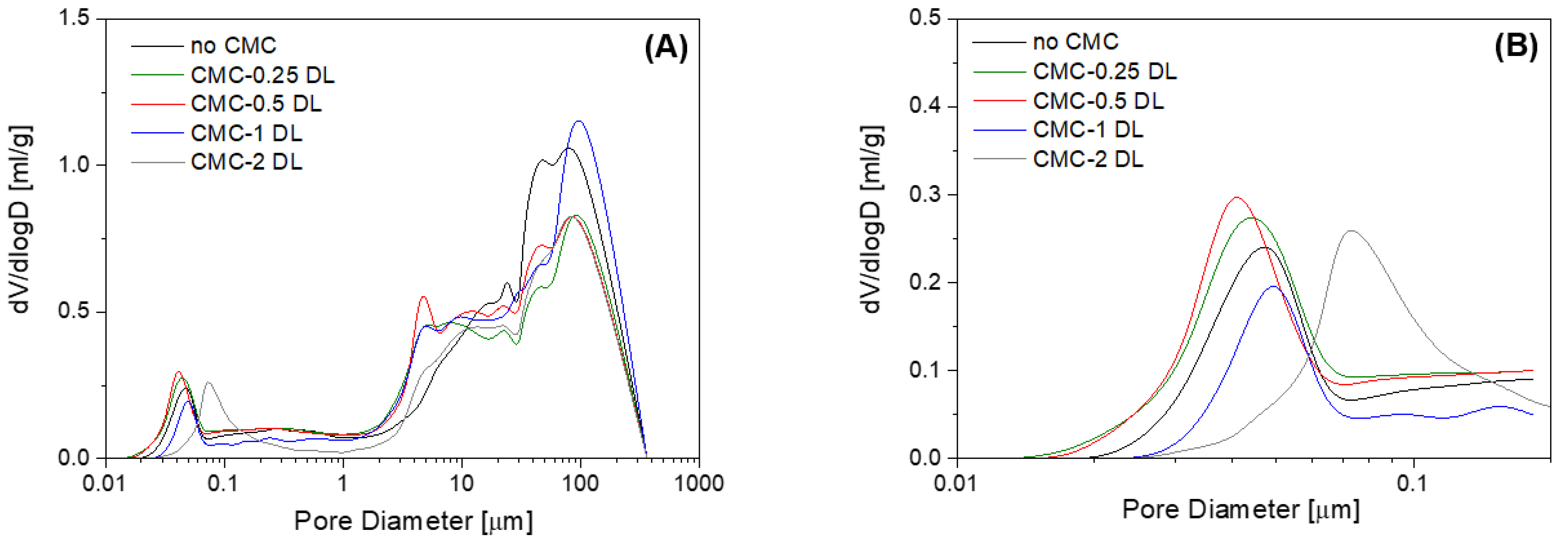
3.1. Morphology
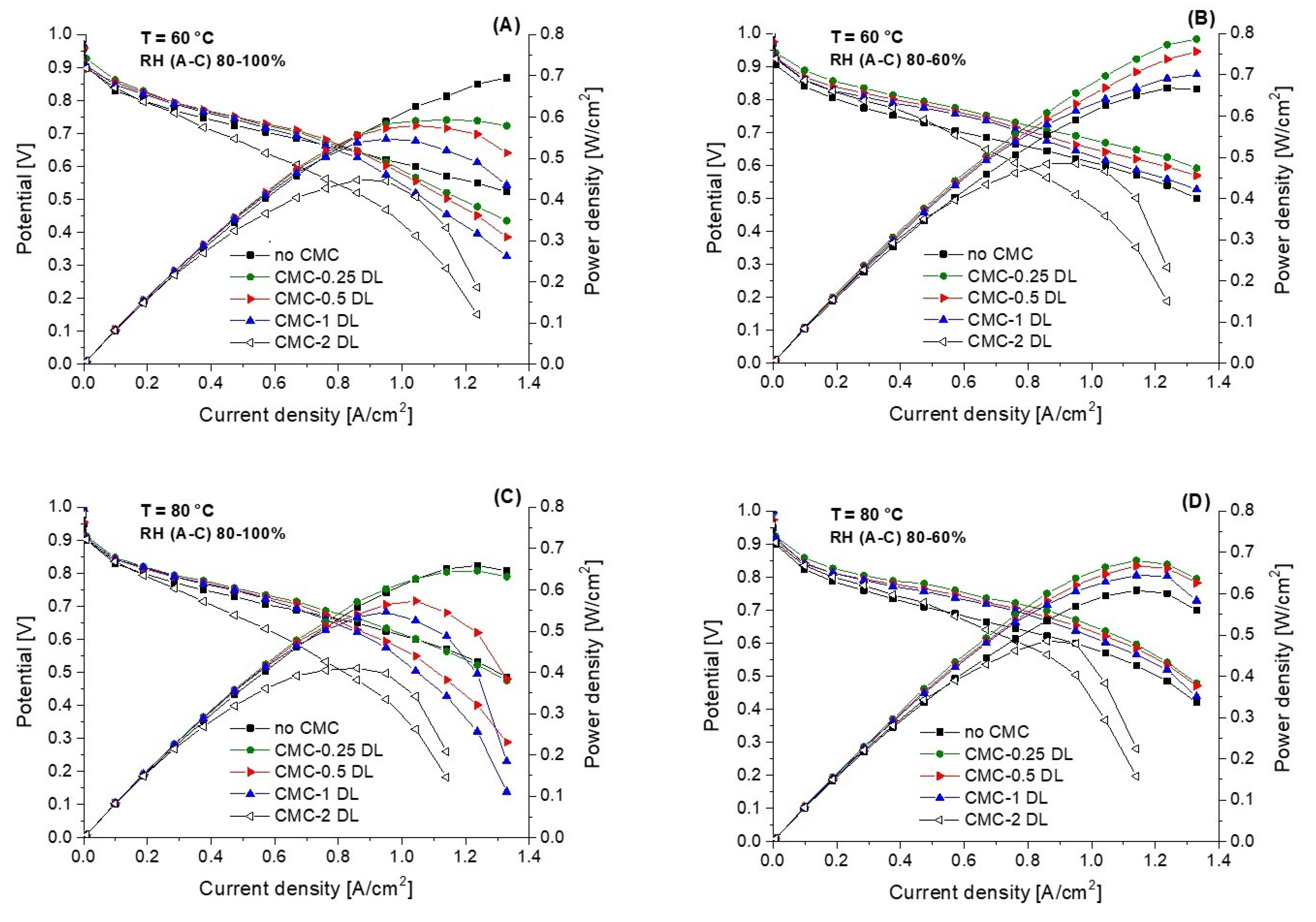
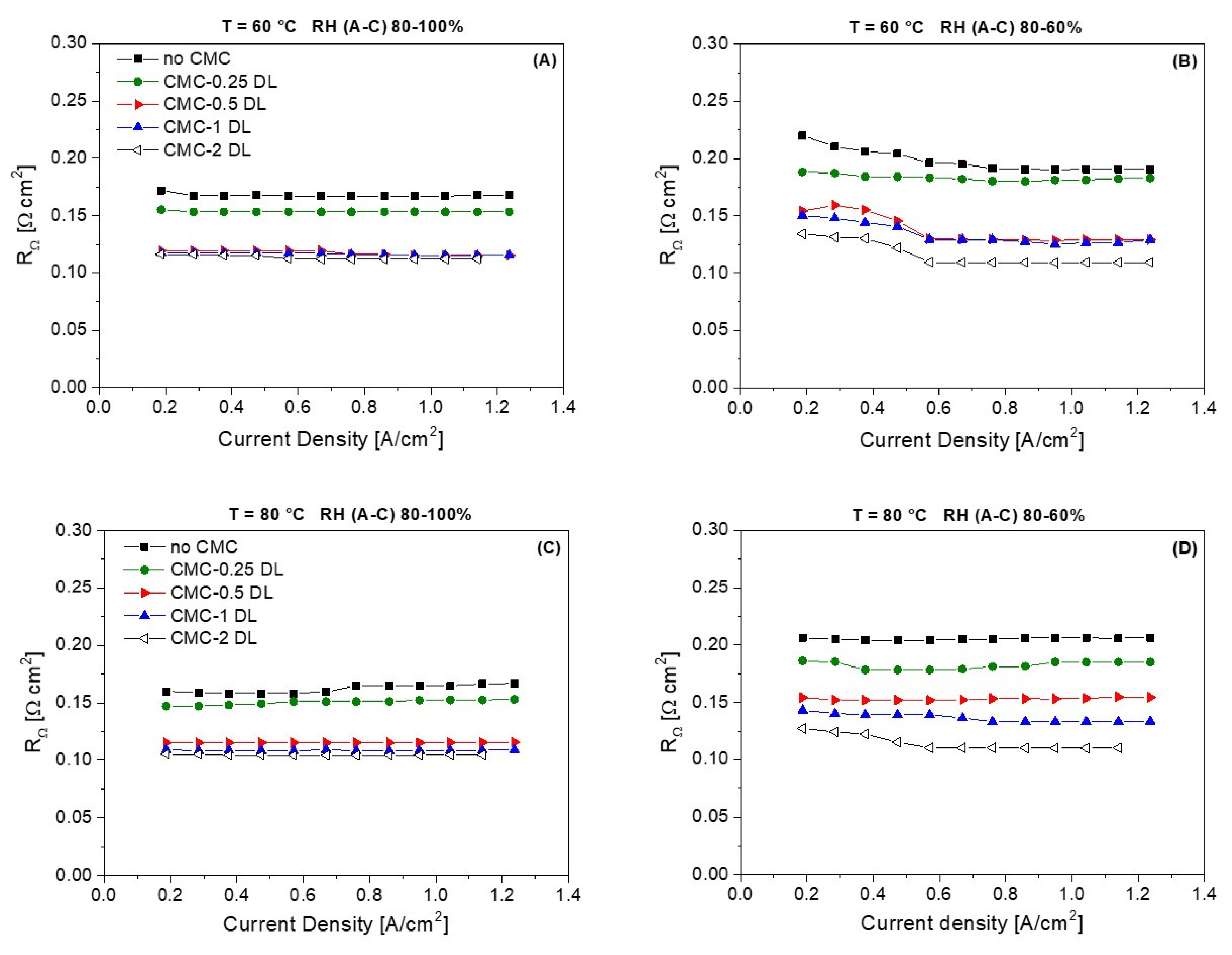
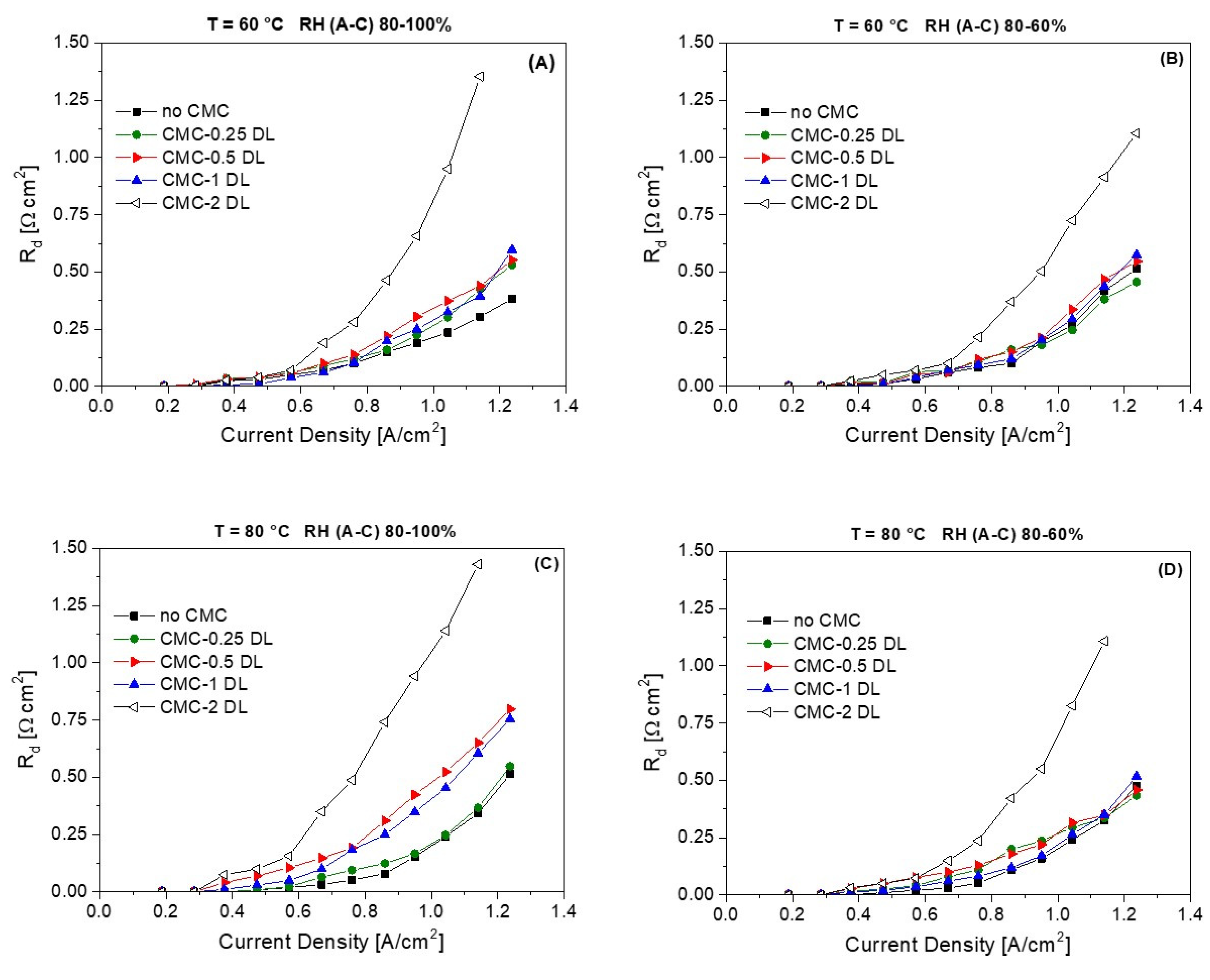
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization
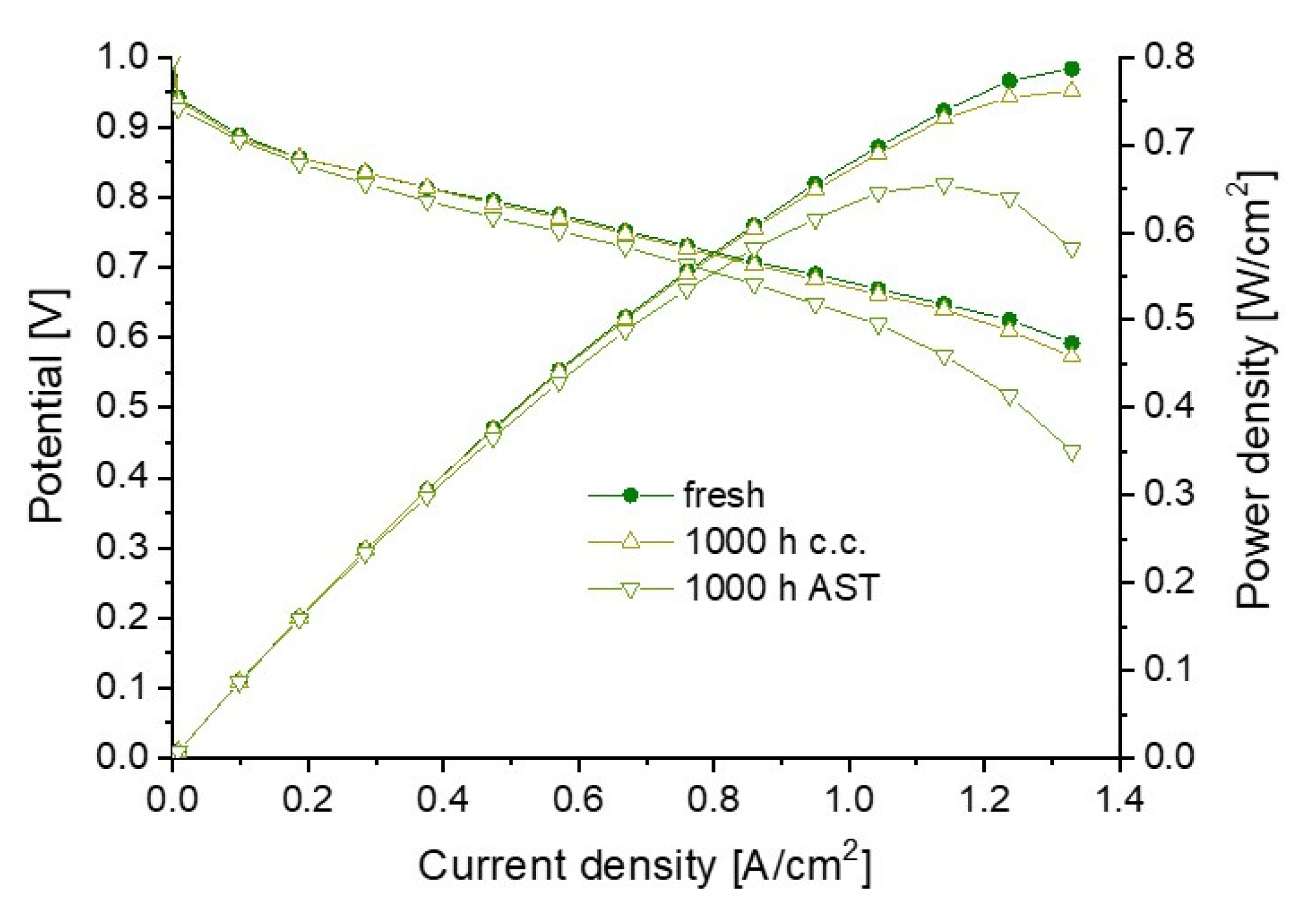
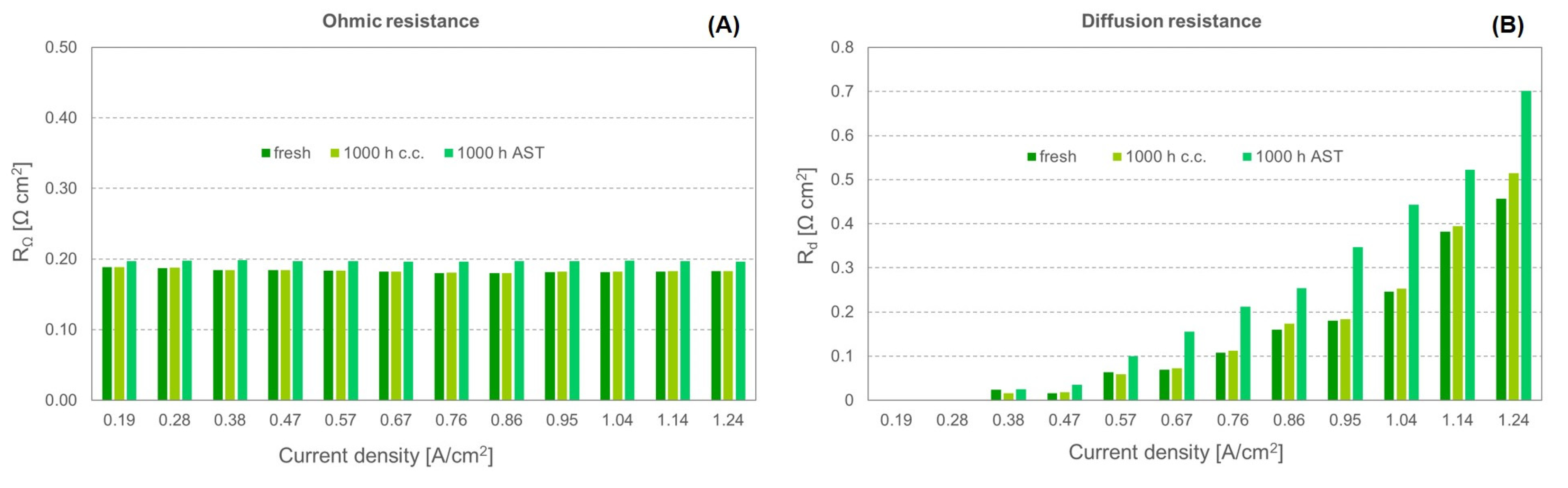
3.3. Durability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, C.; Negro, E.; Vezzù, K.; Pagot, G.; Cavinato, G.; Nale, A.; Herve, Y.; Di, V. Hybrid inorganic-organic proton-conducting membranes based on SPEEK doped with WO3 nanoparticles for application in vanadium redox flow batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 309, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbir, F. PEM Fuel Cells: Theory and Practice; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; ISBN 9780123877109. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Lee, J.-W.; Popov, B.N. A review of gas diffusion layer in PEM fuel cells: Materials and designs. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 5850–5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, B.N.; Park, S.; Lee, J.W. Effect of Gas Diffusion Layer Structure on the Performance of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell. In Electrocatalysts for Low Temperature Fuel Cells: Fundamentals and Recent Trends; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; p. 616. ISBN 9783527803873. [Google Scholar]
- Ijaodola, O.S.; El- Hassan, Z.; Ogungbemi, E.; Khatib, F.N.; Wilberforce, T.; Thompson, J.; Olabi, A.G. Energy efficiency improvements by investigating the water flooding management on proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC). Energy 2019, 179, 246–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majlan, E.H.; Rohendi, D.; Daud, W.R.W.; Husaini, T.; Haque, M.A. Electrode for proton exchange membrane fuel cells: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 89, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cindrella, L.; Kannan, A.M.; Lin, J.F.; Saminathan, K.; Ho, Y.; Lin, C.W.; Wertz, J. Gas diffusion layer for proton exchange membrane fuel cells-A review. J. Power Sources 2009, 194, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Matsuura, T.; Hori, M. Novel gas diffusion layer with water management function for PEMFC. J. Power Sources 2004, 131, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Dong, E.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Tao, W.-Q. Effects of Cathode Gas Diffusion Layer Configuration on the Performance of Open Cathode Air-Cooled Polymer Electrolyte. Energies 2022, 15, 6262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitahara, T.; Konomi, T.; Nakajima, H. Microporous layer coated gas diffusion layers for enhanced performance of polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2010, 95, 2202–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Lee, S.; Park, H. A study of water transport as a function of the micro-porous layer arrangement in PEMFCs. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 8631–8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Liao, Q.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H. Liquid and oxygen transport through bilayer gas diffusion materials of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 6363–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.H.; Jo, D.H.; Kim, S.G.; Park, S.H.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, S.H. Improvement of the mechanical durability of micro porous layer in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell by elimination of surface cracks. Renew. Energy 2012, 48, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Alcántara, A.; González-Morán, L.; Pino, J.; Guerra, J. Effect of the Gas Diffusion Layer Design on the Water Management and Cell Performance of a PEM Fuel Cell. Processes 2022, 10, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, J.; Kang, M.; Min, K. Effects of basic gas diffusion layer components on PEMFC performance with capillary pressure gradient. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 27731–27748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.B.; Kim, S.; Park, Y.; Oh, M. Fabrication of GDL microporous layer using PVDF for PEMFCs Fabrication of GDL microporous layer using PVDF for PEMFCs. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 165, 012046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzarotti, R.; Latorrata, S.; Stampino, P.G.; Cristiani, C.; Dotelli, G. Development and characterization of non-conventional micro-porous layers for PEM fuel cells. Energies 2015, 8, 7070–7083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, E.M.; Mufundirwa, A.; Wang, P.; Iwasaki, S.; Kitahara, T.; Nakajima, H. Superhydrophobic fluorinated carbon powders for improved water management in hydrogen fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2022, 548, 232098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.C.; Ismail, M.S.; Ingham, D.B.; Hughes, K.J.; Ma, L.; Lyth, S.M.; Pourkashanian, M. Alternative architectures and materials for PEMFC gas diffusion layers: A review and outlook. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 166, 112640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.; Latorrata, S.; Patrignani, S.; Gallo Stampino, P.; Dotelli, G. Characterization of novel graphene-based microporous layers for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells operating under low humidity and high temperature. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 7046–7058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garsany, Y.; Bancroft, C.H.; Atkinson, R.W.; Bethune, K.; Gould, B.D.; Swider-lyons, K.E. Effect of GDM Pairing on PEMFC Performance in Flow-Through and Dead-Ended Anode Mode. Molecules 2020, 25, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitahara, T.; Nakajima, H. Microporous layer-coated gas diffusion layer to reduce oxygen transport resistance in a polymer electrolyte fuel cell under high humidity conditions. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 9547–9555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peighambardoust, S.J.; Rowshanzamir, S.; Amjadi, M. Review of the proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 9349–9384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitahara, T.; Nakajima, H.; Okamura, K. Gas diffusion layers coated with a microporous layer containing hydrophilic carbon nanotubes for performance enhancement of polymer electrolyte fuel cells under both low and high humidity conditions. J. Power Sources 2015, 283, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorrata, S.; Stampino, P.G.; Amici, E.; Pelosato, R.; Cristiani, C.; Dotelli, G. Effect of rheology controller agent addition to Micro-Porous Layers on PEMFC performances. Solid State Ion. 2012, 216, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorrata, S.; Stampino, P.G.; Cristiani, C.; Dotelli, G. Preparation, ex situ and in situ Characterization of Gas Diffusion Media Containing and Non-Containing Carboxymethylcellulose for PEM Fuel Cells. Fuel Cells 2015, 15, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracton, A.A. Coatings Technology: Fundamentals, Testing, and Processing Techniques; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; ISBN 9781420044089. [Google Scholar]
- Latorrata, S.; Stampino, P.G.; Cristiani, C.; Dotelli, G. Development of an optimal gas diffusion medium for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells and assessment of its degradation mechani. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 14596–14608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitahara, T.; Nakajima, H.; Mori, K. Hydrophilic and hydrophobic double microporous layer coated gas diffusion layer for enhancing performance of polymer electrolyte fuel cells under no-humidification at the cathode. J. Power Sources 2012, 199, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, P.; Banerjee, R.; Lee, J.; Ge, N.; Muirhead, D.; Liu, H.; Kai, A.; Wong, C.; Ouellette, D.; Zhao, B.; et al. Hydrophilic microporous layer coatings for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells operating without anode humidification. J. Power Sources 2018, 402, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Negro, E.; Nale, A.; Pagot, G.; Vezzù, K.; Zawodzinski, T.A.; Meda, L.; Gambaro, C.; Di, V. An efficient barrier toward vanadium crossover in redox flow batteries: The bilayer [Nafion/(WO3) x] hybrid inorganic-organic membrane. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 378, 138133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorrata, S.; Stampino, P.G.; Cristiani, C.; Dotelli, G. Performance evaluation and durability enhancement of FEP-based gas diffusion media for PEM fuel cells. Energies 2017, 10, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorrata, S.; Pelosato, R.; Stampino, P.G.; Cristiani, C.; Dotelli, G. Use of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for the evaluation of performance of PEM fuel cells based on carbon cloth gas diffusion electrodes. J. Spectrosc. 2018, 3254375, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, X. A review of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell durability for vehicular applications: Degradation modes and experimental techniques. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 199, 112022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guo, L.; Liu, H. Performance Degradation of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Caused by an Accelerated Stress Test. Fuel Cells 2019, 19, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.; Latorrata, S.; Gallo Stampino, P.; Dotelli, G. Evaluation of Graphene Nanoplatelets as a Microporous Layer Material for PEMFC: Performance and Durability Analysis. Fuel Cells 2019, 19, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorrata, S.; Sansotera, M.; Gola, M.; Stampino, P.G.; Navarrini, W.; Dotelli, G. Innovative Perfluoropolyether-Functionalized Gas Diffusion Layers with Enhanced Performance in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Fuel Cells 2020, 20, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetenko, T.; Ben, B.L. Electrochimica Acta Impact of a gas diffusion layer’ s structural and textural properties on oxygen mass transport resistance in the cathode and performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 371, 137752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasaki, G.; Wang, Q.; Shi, X.; Chauhan, N.; Vimala, V. Design and development of gas diffusion layers with pore forming agent for proton exchange membrane fuel cells at various relative humidity conditions. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 46, 6835–6844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahiri, B.; Felix, R.M.; Hill, A.; Kung, C.H.; Sharma, T.; Real, J.D.; Mérida, W. Applied Surface Science Through-plane wettability tuning of fi brous carbon layers via O2 plasma treatment for enhanced water management. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 458, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nguyen, T.; Ahosseini, A.; Wang, X.; Yarlagadda, V.; Kwong, A.; Weber, A.Z.; Deevanhxay, P.; Tsushima, S. Hydrophobic Gas-Diffusion Media for Polymer-Electrolyte Fuel Cells by Direct Fluorination. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, F1451–F1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorrata, S.; Balzarotti, R.; Gallo Stampino, P.; Cristiani, C.; Dotelli, G.; Guilizzoni, M. Design of properties and performances of innovative gas diffusion media for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 78, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, S.; Ying, Z.; Lin, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Q.; Li, J. Novel scalable freezing-pore-forming strategy for constructing hierarchically porous carbon materials for supercapacitors. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 846, 156235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, H. A novel hydrophilic-modified gas diffusion layer for proton exchange membrane fuel cells operating in low humidification. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 16874–16883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwan, J.; Tae, K.; Hyun, D.; Young, J.; Gon, S.; Hee, S.; Sook, E.; Jyoung, J.; Hyun, S. Development of a novel hydrophobic / hydrophilic double micro porous layer for use in a cathode gas diffusion layer in PEMFC. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 8422–8428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.; Cho, Y.; Cho, Y.; Kim, J.; Jung, N.; Sung, Y. Influence of hydrophilicity in micro-porous layer for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 2450–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ink | C-Phase 1/H2O [w/w] | FEP/C-Phase [w/w] | IPA/C-Phase [w/w] | CMC/H2O [w/w] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| no CMC | 0.13 | 0.12 | 5.6 | 0 |
| CMC-0.25 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 5.6 | 0.25 |
| CMC-0.5 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 5.6 | 0.5 |
| CMC-1 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 5.6 | 1 |
| CMC-2 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 5.6 | 2 |
| Sample | Average Thickness [µm] | Static Contact Angle [°] | Average Pore Diameter [nm] | Dynamic Viscosity at 100 s−1 [Pa s] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| no CMC 1 | 50 | 158 ± 3 | 45 | 0.176 |
| CMC-0.25 DL | 51 | 144 ± 8 | 40 | 0.179 |
| CMC-0.5 DL | 52 | 137 ± 6 | 44 | 0.359 |
| CMC-1 DL | 49 | 134 ± 5 | 49 | 0.522 |
| CMC-2 DL | 51 | 129 ± 3 | 72 | 0.975 |
| Sample | ΔPAST [%] | Δηgc [%] |
|---|---|---|
| no CMC 1 | 21.8 | 4.7 |
| CMC-0.25 DL | 16.8 | 2.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Latorrata, S.; Mariani, M.; Basso Peressut, A.; Balzarotti, R.; Dotelli, G. Non-Conventional Hybrid Microporous Layers for Enhanced Performance and Durability of PEM Fuel Cells. Physchem 2023, 3, 78-91. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem3010007
Latorrata S, Mariani M, Basso Peressut A, Balzarotti R, Dotelli G. Non-Conventional Hybrid Microporous Layers for Enhanced Performance and Durability of PEM Fuel Cells. Physchem. 2023; 3(1):78-91. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem3010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleLatorrata, Saverio, Marco Mariani, Andrea Basso Peressut, Riccardo Balzarotti, and Giovanni Dotelli. 2023. "Non-Conventional Hybrid Microporous Layers for Enhanced Performance and Durability of PEM Fuel Cells" Physchem 3, no. 1: 78-91. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem3010007
APA StyleLatorrata, S., Mariani, M., Basso Peressut, A., Balzarotti, R., & Dotelli, G. (2023). Non-Conventional Hybrid Microporous Layers for Enhanced Performance and Durability of PEM Fuel Cells. Physchem, 3(1), 78-91. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem3010007










