IdentiFLY: The Development and Validation of a 15-Plex SNP Assay for Forensic Identification of UK Blowfly Species (Calliphoridae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Preliminary Identification
2.3. DNA Extraction and Quantification
2.4. Identification of Species-Specific SNPs
2.5. PCR Multiplex
2.6. SNaPshot™ Multiplex
2.7. Capillary Electrophoresis of SNaPshot™ Multiplex Products
2.8. SNaPshot™ Multiplex Validation
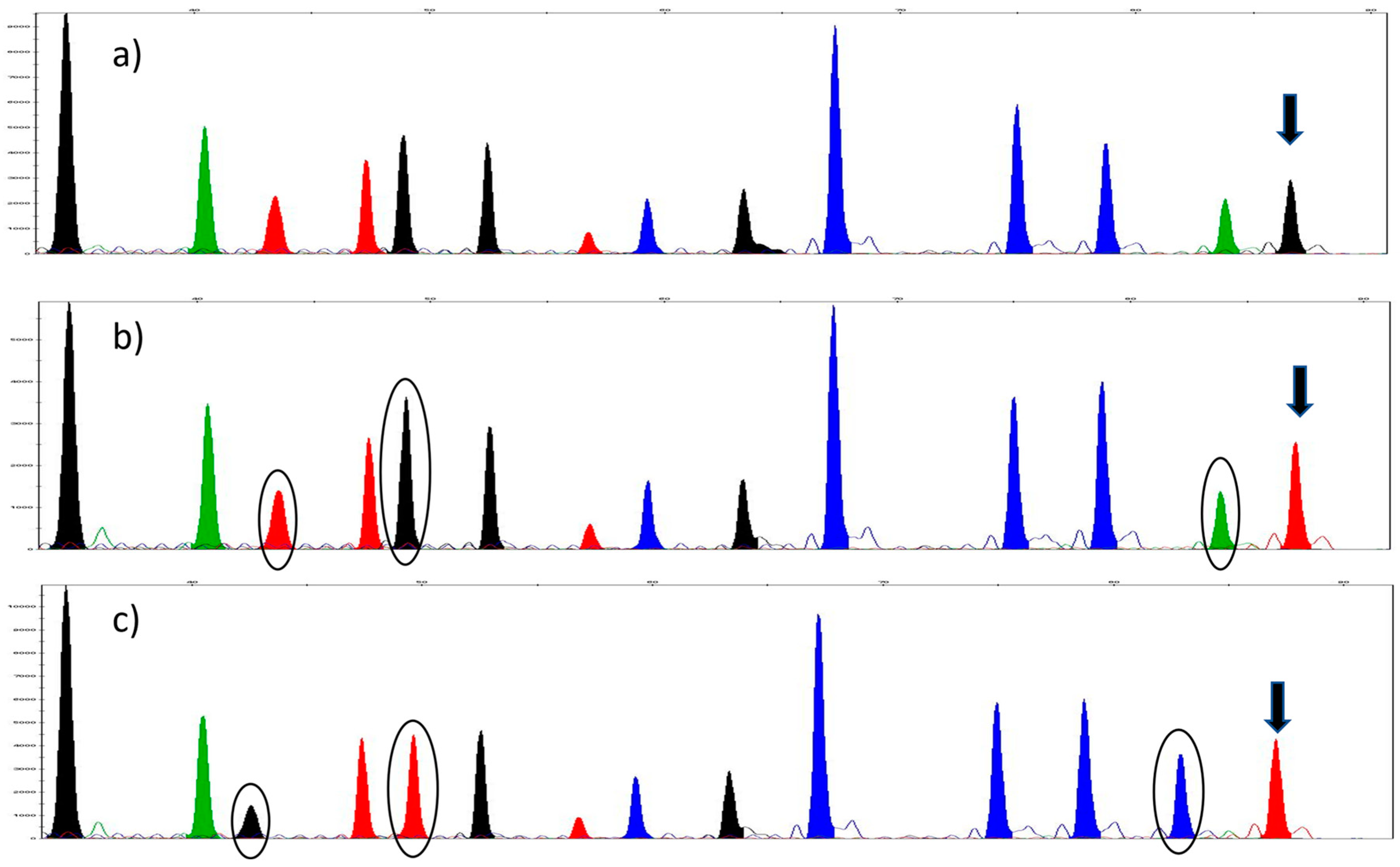
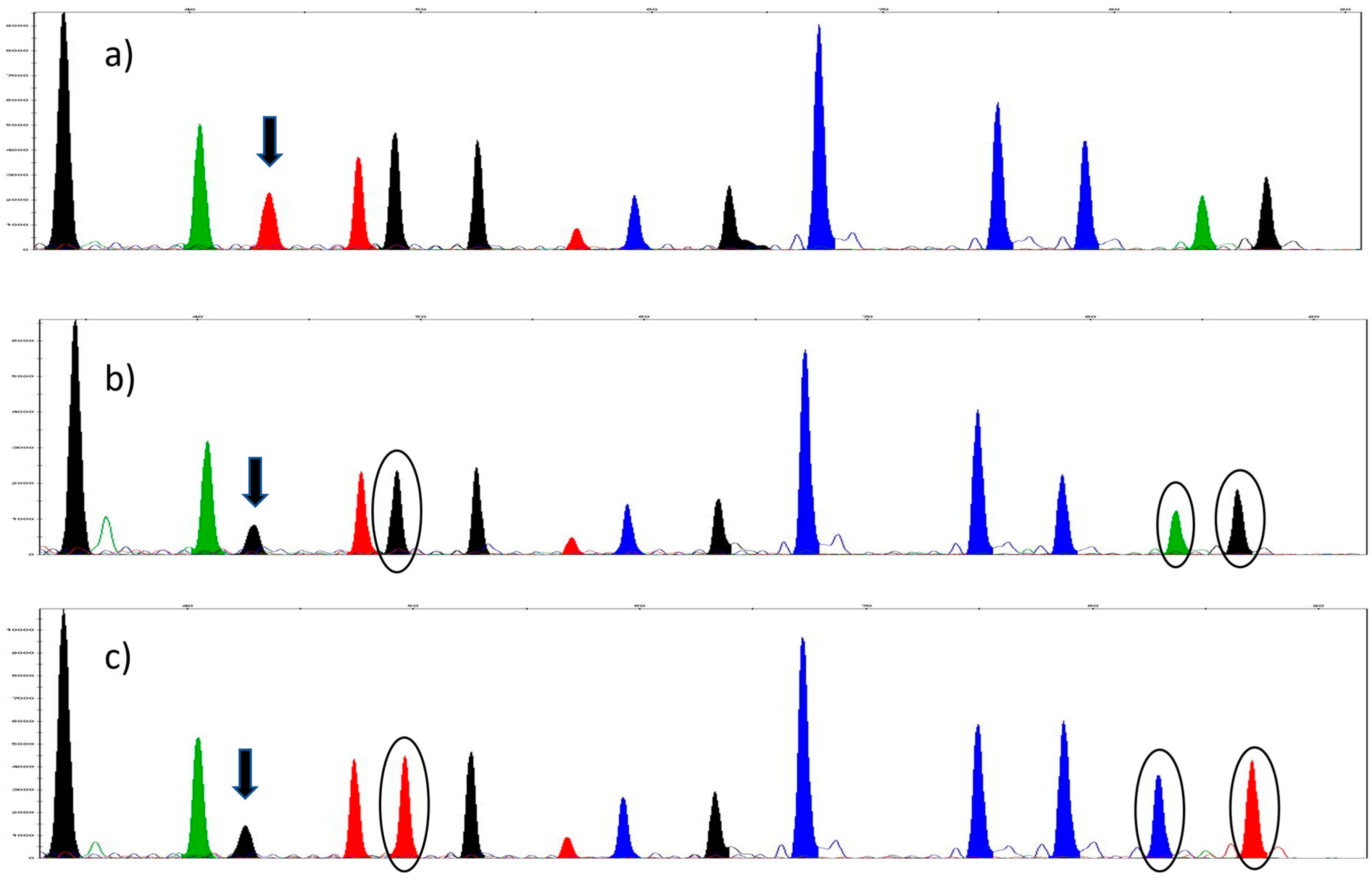
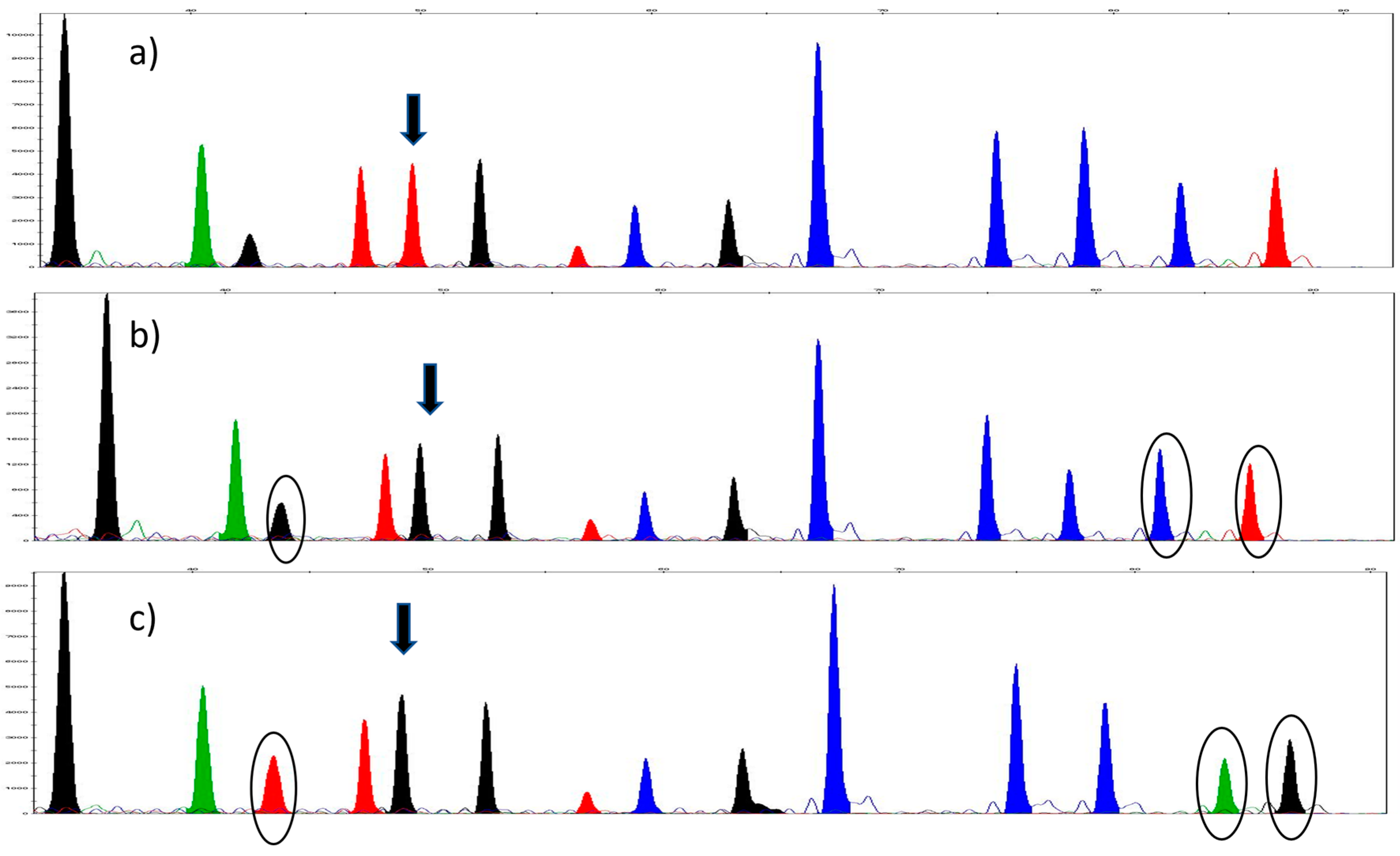
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing and the Selection of SNPs
3.2. SNaPshot™ Multiplex Assay
3.3. Validation of the SNaPshot™ Multiplex Assay
3.3.1. SNP Concordance Study
3.3.2. Reproducibility
3.3.3. Accuracy and Precision
3.3.4. Sensitivity
3.3.5. Specificity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
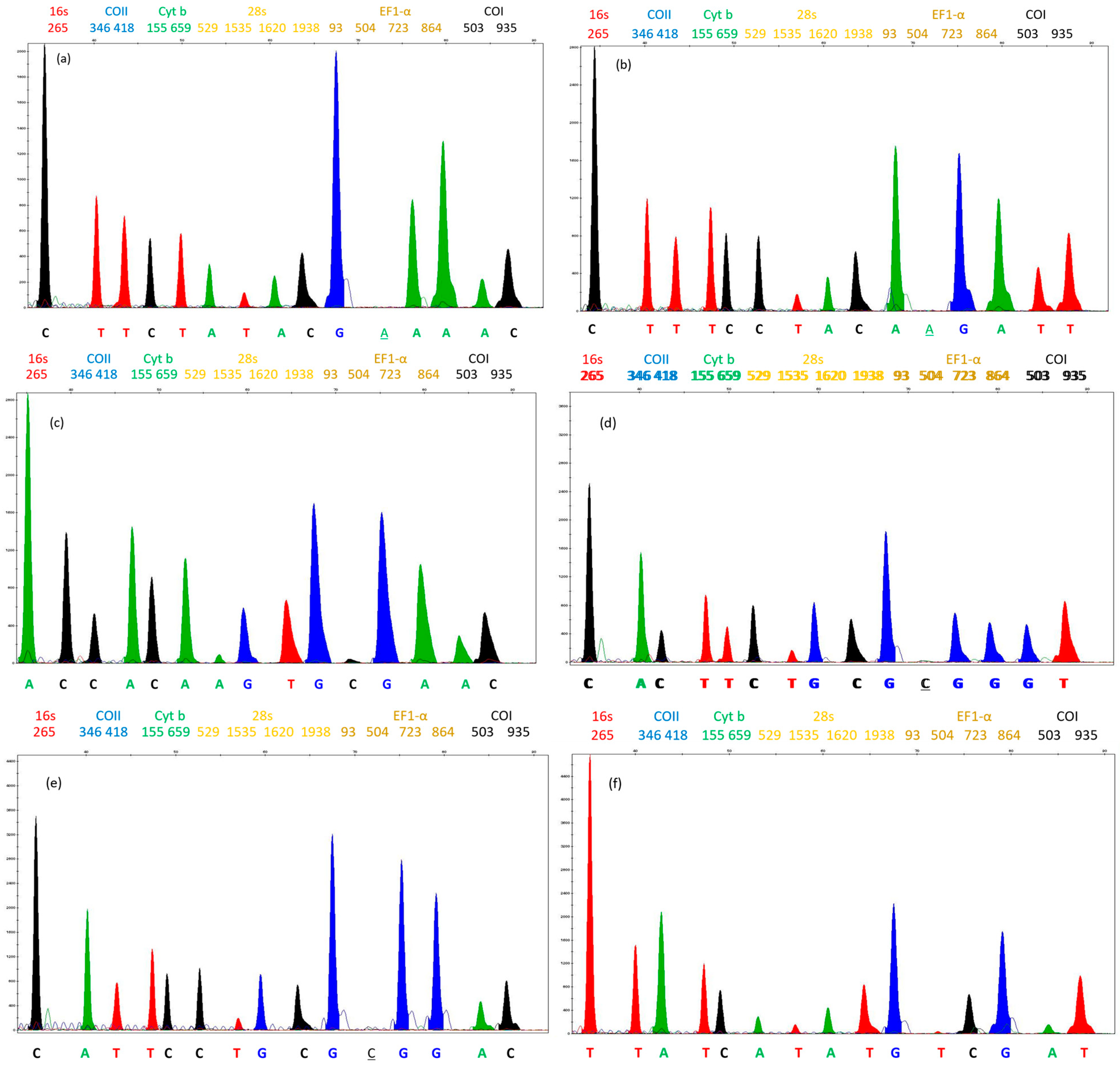
| Gene | 16S | COII | COII | Cytb | Cytb | 28S | 28S | 28S | 28S | EF1-a | EF1-a | EF1-a | EF1-a | COI | COI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP | 265 | 346 | 418 | 155 | 659 | 529 | 1535 | 1620 | 1938 | 93 | 504 | 723 | 864 | 503 | 935 |
| Expected size | 36 | 40 | 44 | 48 | 52 | 56 | 60 | 64 | 68 | 72 | 76 | 80 | 84 | 88 | 92 |
| Nucleotide | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | ||||
| Size range | 35.06–35.47 | 40.12–40.19 | 42.67–42.9 | 46.55–46.96 | 52.68–53.06 | 56.5–56.88 | 60.27–60.53 | 67.73–68.12 | 76.02–76.18 | 79.45–79.69 | 83.71–84.06 | ||||
| Average | 35.21 | 40.15 | 42.76 | 46.88 | 52.9 | 56.66 | 60.37 | 67.96 | 76.13 | 79.56 | 83.35 | ||||
| StdDev | 0.14 | 0.022 | 0.09 | 0.075 | 0.075 | 0.091 | 0.065 | 0.1 | 0.042 | 0.064 | 0.115 | ||||
| n | 25 | 37 | 10 | 25 | 53 | 23 | 66 | 25 | 12 | 32 | 96 | ||||
| Nucleotide | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | |||||
| Size range | 35.0–35.18 | 39.91–40.46 | 43.41–43.57 | 47.17–47.43 | 49.45–49.78 | 56.7–57.04 | 63.96–64.42 | 72.02–72.1 | 83.59–84.21 | 86.91–87.56 | |||||
| Average | 35.05 | 40.33 | 43.49 | 47.31 | 49.52 | 56.84 | 64.25 | 72.05 | 83.78 | 87.17 | |||||
| StdDev | 0.055 | 0.157 | 0.037 | 0.054 | 0.065 | 0.119 | 0.114 | 0.033 | 0.172 | 0.203 | |||||
| n | 10 | 64 | 82 | 77 | 31 | 102 | 33 | 7 | 30 | 40 | |||||
| Nucleotide | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | |||||
| Size range | 34.29–34.72 | 39.39–39.71 | 42.41–42.74 | 46.27–46.39 | 48.83–49.17 | 52.47–52.74 | 63.26–63.63 | 71.37–71.55 | 75.04–75.59 | 86.46–86.98 | |||||
| Average | 64.55 | 39.51 | 42.58 | 46.31 | 48.97 | 52.63 | 63.4 | 71.46 | 75.38 | 96.62 | |||||
| StdDev | 0.105 | 0.106 | 0.09 | 0.026 | 0.087 | 0.097 | 0.12 | 0.054 | 0.151 | 0.181 | |||||
| n | 103 | 25 | 29 | 30 | 85 | 55 | 93 | 18 | 10 | 86 | |||||
| Nucleotide | G | G | G | G | G | ||||||||||
| Size range | 59.14–59.54 | 67.13–67.55 | 74.94–75.27 | 78.8–79.17 | 83.19–83.26 | ||||||||||
| Average | 59.42 | 67.32 | 75.14 | 78.99 | 83.22 | ||||||||||
| StdDev | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.102 | 0.026 | ||||||||||
| n | 59 | 95 | 68 | 44 | 5 |
| Gene | 16S | COII | COII | Cytb | Cytb | 28S | 28S | 28S | 28S | EF1-a | EF1-a | EF1-a | EF1-a | COI | COI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP | 265 | 346 | 418 | 155 | 659 | 529 | 1535 | 1620 | 1938 | 93 | 504 | 723 | 864 | 503 | 935 |
| 50 ng | 2441 (666) | 971 (229) | 438 (115) | 1441 (367) | 849 (181) | 665 (159) | 191 (44) | 1110 (245) | 690 (168) | 1785 (414) | 110 (25) | 1308 (391) | 2057 (624) | 200 (45) | 559 (134) |
| 25 ng | 3108 (78) | 1152 (55) | 531 (25) | 1777 (81) | 860 (204) | 753 (105) | 224 (8) | 1413 (107) | 877 (36) | 2212 (178) | 136 (12) | 1757 (222) | 2855 (234) | 230 (13) | 676 (54) |
| 12.5 ng | 2254 (767) | 895 (281) | 402 (121) | 1326 (390) | 796 (236) | 681 (191) | 179 (50) | 1025 (349) | 678 (208) | 1706 (505) | 97 (36) | 1461 (347) | 2233 (698) | 172 (47) | 462 (141) |
| 6.25 ng | 2921 (684) | 1294 (126) | 568 (55) | 1699 (341) | 1002 (141) | 922 (149) | 237 (249) | 1538 (181) | 964 (116) | 2348 (199) | 129 (20) | 2008 (144) | 2926 (516) | 226 (43) | 695 (89) |
| 3.1 ng | 2909 (284) | 1196 (74) | 535 (34) | 1674 (100) | 834 (101) | 817 (71) | 217 (19) | 1447 (78) | 927 (30) | 2166 (64) | 116 (7) | 1810 (44) | 2707 (112) | 207 (7) | 652 (13) |
| 1.5 ng | 2545 (891) | 1096 (392) | 494 (156) | 1666 (474) | 1058 (215) | 920 (252) | 234 (63) | 1364 (561) | 847 (332) | 1908 (823) | 93 (42) | 1545 (614) | 2446 (960) | 227 (63) | 599 (237) |
| 0.75 ng | 2954 (106) | 1500 (152) | 650 (54) | 1909 (161) | 1292 (162) | 1120 (97) | 260 (29) | 1865 (247) | 1078 (108) | 2414 (318) | 108 (18) | 1836 (232) | 2671 (207) | 260 (29) | 812 (137) |
| 0.375 ng | 2692 (252) | 1156 (139) | 540 (63) | 1616 (113) | 833 (51) | 915 (33) | 223 (15) | 1471 (176) | 873 (85) | 1521 (215) | 66 (11) | 1333 (133) | 2054 (192) | 209 (14) | 589 (74) |
| 0.2 ng | 2295 (647) | 1107 (421) | 519 (173) | 1565 (487) | 983 (445) | 940 (338) | 219 (78) | 1450 (499) | 873 (273) | 1282 (440) | 47 (15) | 1121 (172) | 1768 (476) | 219 (77) | 605 (227) |
| 0.1 ng | 2847 (109) | 1408 (124) | 644 (54) | 1878 (59) | 1054 (63) | 1146 (65) | 262 (5) | 1837 (228) | 1040 (94) | 1346 (174) | 38 (5) | 868 (126) | 1565 (68) | 264 (23) | 756 (110) |
| 0.049 ng | 1880 (668) | 1115 (246) | 497 (97) | 1286 (402) | 920 (48) | 831 (15) | 185 (36) | 1326 (364) | 737 (227) | 943 (295) | 13 (10) | 561 (234) | 915 (432) | 187 (43) | 609 (110) |
| 0.024 ng | 1687 (736) | 1083 (198) | 506 (83) | 1134 (487) | 733 (179) | 720 (262) | 164 (48) | 1226 (288) | 727 (212) | 794 (167) | 0 | 468 (121) | 769 (339) | 168 (56) | 633 (51) |
| 0.012 ng | 2308 (366) | 1337 (208) | 613 (81) | 1691 (228) | 1017 (120) | 1172 (139) | 219 (30) | 1573 (321) | 916 (192) | 928 (186) | 0 | 447 (197) | 898 (288) | 247 (32) | 767 (108) |
| Gene | 16S | COII | COII | Cytb | Cytb | 28S | 28S | 28S | 28S | EF1-a | EF1-a | EF1-a | EF1-a | COI | COI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP | 265 | 346 | 418 | 155 | 659 | 529 | 1535 | 1620 | 1938 | 93 | 504 | 723 | 864 | 503 | 935 |
| L. ampullacae | A | A | T | T | C | C | T | G | C | G | G | A | G | A | T |
| C. loewi | C/T | T/A | T/A | T | C | C/A | T | G/A | C/T | G | x | x | x | A | C/T |
| C. uralensis | C/A | C/T | T/G | T | C | G/A | T | G/A | C/T | G | x | x | x | G | C/T |
| L. richardsi | T/A | C | T | A | T | A | A | G | T | G | C | G | A | G | T |
| P. angustgena | T | T/A | T | A | C | x | x | A | G | A | x | T | A | T | T |
| P. rudis | T/A | T/G | T/G | C | C | T | G/A | C | G/A | x | x | A | A | T | C/T |
| S. incisilobata | A | A | T | C | x | C | T | A | T | A | C | T | A | A | C |
| S. melanura | A | x | C | x | C | C | T | A | T | A | C | T | A | A | C/T |
| S. vagans | T/A | C/T | C/T | x | C/T | C | T | A | T | G/A | x | T | A | A | C |
| M. domestica | T | x | T | A | C | x | T | A | T | G | x | G/A | G/A | x | C/T |
| E. cyanella | x | T | A | x | x | x | T | G | T | A | x | A | A | x | T |
| Tachinidae sp. | T | x | x | C/T | C/T | x | x | A | C | A | x | A | G/A | A | T |
References
- Goff, M.L. Estimation of postmortem interval using arthropod development and successional patterns. Forensic Sci. Rev. 1993, 5, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Byrd, J.H.; Castner, J.L. Forensic Entomology: The Utility of Arthropods in Legal Investigations; CRC Press: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, J.; Wall, R. Genetic variation in populations of the blowflies Lucilia cuprina and Lucilia sericata (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis and mitochondrial DNA sequences. Biochem. Sys. Ecol. 1997, 25, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benecke, M. Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) typing of necrophageous insects (diptera, coleoptera) in criminal forensic studies: Validation and use in practice. Forensic Sci. Int. 1998, 98, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Wang, S.; Miao, X.; Wu, H.; Huang, Y. Identification of necrophagous fly species using ISSR and SCAR markers. Forensic Sci. Int. 2007, 168, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallman, J.F.; Adams, M. The Forensic Application of Allozyme Electrophoresis to the Identification of Blowfly Larvae (Diptera: Calliphoridae) in Southern Australia. J. Forensic Sci. 2001, 46, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florin, A.B.; Gyllenstrand, N. Isolation and characterisation of polymorphic microsatellite markers in the blowflies Lucilia illustris and Lucilia sericata. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2002, 2, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.A.; de Azeredo-Espin, A.M.L.; Torres, T.T. Microsatellite markers for population genetic studies of the blowfly Chrysomya putoria (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2009, 104, 1047–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, H.; Klotzbach, H.; Elias, S.; Augustin, C.; Pueschel, K. Use of PCR-RFLP for differentiation of calliphorid larvae (Diptera, Calliphoridae) on human corpses. Forensic Sci. Int. 2003, 132, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliffe, S.T.; Webb, D.W.; Weinzievr, R.A.; Robertson, H.M. PCR-RFLP identification of Diptera (Calliphoridae, Muscidae and Sarcophagidae)—A generally applicable method. J. Forensic Sci. 2003, 48, 783–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, L.A.; Wallman, J.F.; Dowton, M.M. Identification of forensically important Chrysomya (Diptera: Calliphoridae) species using the second ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS2). Forensic Sci. Int. 2008, 177, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, C.J.; Wells, J.D. A Test for Carrion Fly Full Siblings: A Tool for Detecting Postmortem Relocation of a Corpse. J. Forensic Sci. 2012, 57, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malewski, T.; Draber-Mónko, A.; Pomorski, J.; Loś, M.; Bogdanowicz, W. Identification of forensically important blowfly species (Diptera: Calliphoridae) by high resolution melting PCR analysis. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2010, 124, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, L.; Thornton, C.; Wallman, J.F.; Stevens, J.R. Development of an antigen-based rapid diagnostic test for the identification of blowfly (Calliphoridae) species of forensic significance. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2009, 3, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, F.A.; Anderson, G.S.; Hickey, D.A. A DNA-based approach to the identification of insect species used for postmortem interval estimation. J. Forensic Sci. 1994, 39, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, J.; Wall, R. Genetic relationships between blowflies (Calliphoridae) of forensic importance. Forensic Sci. Int. 2001, 120, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, F.; Wei, S.J.; Shi, M.; Chen, X.X. Utility of multi-gene loci for forensic species diagnosis of blowflies. J. Insect Sci. 2011, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessandrini, F.; Mazzanti, M.; Onofri, V.; Turchi, C.; Tagliabracci, A. MtDNA analysis for genetic identification of forensically important insects. Forensic Sci. Int. Gene. 2008, 1, 584–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.; Wall, R.; Wells, J.D. Paraphyly in Hawaiian hybrid blowfly populations and the evolutionary. Insect Mol. Biol. 2002, 11, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, J.D.; Lunt, N.; Villet, M.H. Recent African derivation of Chrysomya putoria from C.chloropyga and mitochondrial DNA paraphyly of cytochrome oxidase subunit one in blowflies of forensic importance. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2004, 18, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Hung, T.H.; Shiao, S.F. Molecular identification of forensically important blow fly species (Diptera: Calliphoridae) in Taiwan. J. Med. Entomol. 2004, 41, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallman, J.F.; Adams, M. Molecular Systematics of Australian Carrion-breeding Blowflies of the Genus Calliphora (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Aust. J. Zoo. 1997, 45, 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reibe, S.; Schmitz, J.; Madea, B. Molecular identification of forensically important blowfly species (Diptera: Calliphoridae) from Germany. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 160, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.H.; Aris, E.M.; Surin, J.; Omar, B.; Kurahashi, H.; Mohamed, Z. Sequence variation in the cytochrome oxidase subunit I and II genes of two commonly found blow fly species, Chrysomya megacephala (Fabricius) and Chrysomya rufifacies (Macquart) (Diptera: Calliphoridae) in Malaysia. Trop. Biomed. 2009, 26, 173–181. [Google Scholar]
- Caine, L.M.; Real, F.C.; Salona-Bordas, M.I.; de Pancorbo, M.M.; Lima, G.; Magalhaes, T.; Pinheiro, F. DNA typing of Diptera collected from human corpses in Portugal. Forensic Sci. Int. 2009, 184, e21–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.B.; Ting, L.T.; Hong, F. The application of mitochondrial DNA cytochrome oxidase II gene for the identification of forensically important blowflies in western China. Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 2007, 28, 308–313. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, M.L.; Gaudieri, S.; Villet, M.H.; Dadour, I.R. A global study of forensically significant calliphorids: Implications for identification. Forensic Sci. Int. 2008, 177, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, M.L.; Dadour, I.R.; Gaudieri, S. Mitochondrial DNA cytochrome oxidase I gene: Potential for distinction between immature stages of some forensically important fly species (Diptera) in western Australia. Forensic Sci. Int. 2003, 131, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saigusa, K.; Takamiya, M.; Aoki, Y. Species identification of forensically important flies in Iwate prefecture, Japan based mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase gene subunit I (COI) sequences. Leg. Med. 2005, 7, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallman, J.F.; Donnellan, S.C. The utility of mitochondrial DNA sequences for the identification of forensically important blowflies (Diptera: Calliphoridae) in southeastern Australia. Forensic Sci. Int. 2001, 120, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Wang, X.; Liang, G. Species identification of some common necrophagous flies in Guangdong province, southern China based on the rDNA internal transcribed spacer 2 (ITS2). Forensic Sci. Int. 2008, 175, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Ren, L.; Wang, Z.; Deng, J.; Guo, Y.; Chen, C.; Finkelbergs, D.J. Cai Identification of forensically important blowflies (Diptera: Calliphoridae) in China based on COI. J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, M.; Singh, B. DNA based identification of forensically important blowflies (Diptera: Calliphoridae) from India. J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBry, R.W.; Timm, A.; Wong, E.S.; Stamper, T.; Dahlem, C.C.G.A. DNA based identification of forensically important Lucilia (Diptera: Calliphoridae) in the continental United States. J. Forensic Sci. 2013, 58, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shayya, S.; Debruyne, R.; Nel, A.; Azar, D. Forensically relevant blowflies in Lebanon survey and identification using molecular markers. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thipphet, K.; Horpaopan, S.; Jaturas, N.; Thanchomnang, T.; Moophayak, K.; Chaiwong, T.; Hongsrichan, N.; Nakhonkam, W.; Phuwanatsurunya, P.; Dumidae, A.; et al. Molecular identification and genetic variation of forensically important fly specues (Order: Diptera) in Thailand using DNA barcoding. Acta Trop. 2024, 258, 107366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusseff-Vanegas, S.Z.; Agnarsson, I. DNA barcoding of forensically important blow flies (Diptera: Calliphoridae) in the Caribbean region. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, T.; Kulenkampff, K.; Hayns, M.; Heathfield, L.J. DNA barcoding of forensically important flies in the Western Cape, South Africa. Genome 2018, 12, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, A.M.; Adham, F.K.; Picard, C.J. Survey of the genetica diversity of forensically important Chrysomya (Diptera: Calliphoridae) from Egypt. J. Med. Entomol. 2015, 52, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, R.; Tan, T.C.; Lee, H.L.; Nazni, W.A.; Sofian-Azirum, M. DNA typing of Calliphorids collected from human corpses in Malaysia. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 30, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. Barcoding: BOLD: The Barcode of Life Data System. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonet, G.; Jordaens, K.; Braet, Y.; Bourguignon, L.; Dupont, E.; Backeljau, T.; De Meyer, M.; Desmyter, S. Utility of GenBank and the Barcode of Life Data Systems (BOLD) for the identification of forensically important Diptera from Belgium and France. Zookeys 2013, 365, 307–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ames, C.; Turner, B.; Daniel, B. The use of mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I gene (COI) to differentiate two UK blowfly species—Calliphora vicina and Calliphora vomitoria. Forensic Sci. Int. 2006, 164, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.A.; Baker, N.C. Molecular genetic identification of forensically important flies in the UK. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2008, 1, 620–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, L.M.; Stevens, J.R. The molecular systematics of blowflies and screwworm flies (Diptera: Calliphoridae) using 28S rRNA, COX1 and EF-1α: Insights into the evolution of dipteran parasitism. Parasitology 2011, 138, 1760–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erzinçlioğlu, Z. Naturalists Handbooks 23: Blowflies; The Richmond Publishing Co., Ltd.: Slough, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Rognes, K. Blowflies (Diptera Calliphoridae) of Fennoscandia and Denmark; Fauna Entomologica Scandinavica 24; Scandinavian Science Press Ltd.: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Linacre, A.; Gusmão, L.; Hecht, W.; Hellmann, A.P.; Mayr, W.R.; Parson, W.; Prinz, M.; Schneider, P.M.; Morling, N. ISFG: Recommendations regarding the use of non-human (animal) DNA in forensic genetic investigations. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2011, 5, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintáns, B.; Álvarez-Iglesias, V.; Salas, A.; Philips, C.; Lareu, M.V.; Carracedo, A. Typing of mitochondrial DNA coding region SNPs of forensic and anthropological interest using SNaPshot minisequencing. Forensic Sci. Int. 2004, 140, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, S.C.; Sanfor, M.R.; Donley, M.; Welch, K.; Khan, R. Simplified COI barcoding of blow, flesh and scuttle flies encountered in medicolegal investigations. For. Sci. Med. Path. 2023, 20, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amat, E.; Gómez, G.F.; López-Rubio, A.; Gómez-Piñerez, L.M.; Rafael, J.A. A short fragment of mitochondrial DNA for taxonomic identification of blow flies (Diptera: Calliphoridae) in northwestern South America. J. Med. Ento. 2023, 60, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonet, G.; Jordaens, K.; Braet, Y.; Desmyter, S. Why is the molecular identification of the forensically important blowfly species Lucilia caesar and L. illustris (family Calliphoridae) so problematic? Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 223, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GilArriotua, M.; Bordas, M.I.S.; Khönemann, S.; Pfeiffer, H.; de Pancrobo, M.M. Molecular differentiation of Central European blowfly species (Diptera, Calliphoridae) using mitochondrial and nuclear genetic markers. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 242, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoofs, K.R.; Ahmadzai, U.K.; Goodwin, W. Analysis of the complete mitochondrial genomes of two forensically important blowfly species: Lucilia caesar and Lucilia illustris Mito. DNA Part. B Resour. 2018, 3, 1114–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, J.P.; Diaz, J.A.P.; López-Rubio, A.; Gómez-Piñerez, L.M.; Rúa-Uribe, G.; Márquez, E.J. Evidence of two mitochondrial lineages and genetic variability in forensically important Lucilia eximia (Diptera: Calliphoridae) in Colombia. J. Med. Ento. 2023, 60, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.P.; Danforth, B.N. How do insect nuclear and mitochondrial gene substitution patterns differ? Insights from Bayesian analyses of combined datasets. Mol. Phylogenetic Evol. 2004, 30, 686–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, J.F.; Guo, Y.D.; Wu, K.L.; Wang, J.F.; Liu, Q.L.; Wang, X.H.; Chang, Y.F.; Yang, L.; Lan, L.M.; et al. The availability of 16s rDNA gene for identifying forensically important blowflies in China. Rom. J. Leg. Med. 2010, 1, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor, S.; Young, N.D.; Yang, Y.T.; Batterham, P.; Gasser, R.B.; Bowles, V.M.; Anstead, C.A.; Perry, T. Mitochondrial genomic investigation reveals a clear association between species and genotypes of Lucilia and geographical origin in Australia. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietjen, M.; Arp, A.P.; Lohmeyer, K.H. Development of a diagnostic single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) panel for identifying geographical origins of Cochliomyia hominivorax, the New Worldscrewworm. Vet. Parasitol. 2023, 315, 109884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Shin, S.E.; Ko, K.S.; Park, S.W. Identification of forensically important Calliphoridae and Sarcophagidae species collected in Korea using SNaPshot multiplex system targeting the Cytochrome c Oxidase Subunit 1 gene. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 2953892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Shin, S.E.; Ko, K.S.; Park, S.H. SNP typing using multiplex real-time PCR assay for species identification of forensically important blowflies and fleshflies collected in South Korea (Diptera: Calliphoridae and Sarchophagidae). Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 6762517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.A.; Villet, M.H. Ancient and modern hybridization between Lucila sericata and L. cuprina (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2013, 110, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, L.; Matheson, P.; Flemming, C.; Butterworth, N.J.; McGaughran, A. Population structure and interspecific hybridization of two invasive blowflies (Diptera: Calliphoridae) following replicated incursions into New Zealand. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e10832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitpipit, T.; Thingjued, K.; Penchart, K.; Ouithavon, K.; Chotgeat, W. Mini-SNaPshot multiplex asses authenticate elephant ivory and simultaneously identify the species origin. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2017, 27, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, H.H.; Li, B.; Ma, Y.; Bai, S.Y.; Dahmer, T.D.; Linacre, A.; Xu, Y.C. Forensic validation of a panel of 12 SNPs for identification of Mongolian wolf and dog. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13249. [Google Scholar]
| Gene (SNP Position) | PCR Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Product Size (bp) | Concentration (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16S (265) | FOR: AAAAGACGAGAAGACCCTATAAATC REV: AAAAATTACGCTGTTATCCYTAAA | 206 | 0.4 |
| COII (346/418) | FOR: GGTWGATGAAATTAATGAACCTTC REV: GGATAGTTCAWGAATGAATYACATC | 239 | 0.5 |
| Cyt b (155) | FOR: TTCWGCTWGATGAAATTTYGGA REV: GCWCCATTAGCAWGYATAGTTCG | 180 | 0.3 |
| Cyt b (659) | FOR: GGYCCWATAGGATTAAATTCWAATATTG REV: GGAAYTATCATTCTGGTTGRATATG | 201 | 0.4 |
| COI (503) | FOR: GCMGGAATYTCWTCAATTTTAGG REV: AATAGCDCCWGCTAATACTGGTAA | 162 | 0.3 |
| COI (935) | FOR: GGATTAGCTATTGGAYTAYTAGGA REV: GCCRTAAAGAGTTGCTARTCAAC | 160 | 0.3 |
| 28S (529) | FOR: GTTAAGCCCGATGAACCTGA REV: TCAACRCTTTATCAAATCAAAAGMA | 218 | 0.4 |
| 28S (1535/1620) | FOR: AATGGATGGCGCTTAAGTTG REV: GTCCTCCAAGGTCTCATTCG | 209 | 0.1 |
| 28S (1938) | FOR: ATATGGRCCTTGTGCTCATC REV: TTTCAAGGTCCGAGGAGAAA | 189 | 0.1 |
| EF1-α (93) | FOR: CCATCGATATTGCTTTGTGG REV: GATACCRGCTTCGAATTCAC | 167 | 0.5 |
| EF1-α (504) | FOR: GARGCTTCCACCAACATGC REV: GGGTACTGTGCCGATACCMC | 183 | 0.5 |
| EF1-α (723/864) | FOR: CYCCCGCTAACATCACCACT REV: GGGRGTGTAACCGTTGGAGA | 236 | 0.6 |
| Gene (SNP) | Single-Base Extension Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | SBE Primer Length (bp) | Concentration (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16S (265) | (A)11TTTTAATATCACCCCAATAAAATAT | 36 | 0.4 |
| COII (346) | (A)15CTACWAAYGAATTATCAATTGATAG | 40 | 0.7 |
| COII (418) | (A)21CAARTYCGAATTTTAGTRACWGC | 44 | 0.5 |
| Cyt b (155) | (A)23AAATTTTAACTGGWYTATTTTTAGC | 48 | 0.6 |
| Cyt b (659) | (A)27CWAATATTGATAAAATTCCATT | 52 | 1.0 |
| COI (503) | (A)29CAAGCAAAAATAATTTGAATAAACWTA | 88 | 1.0 |
| COI (935) | (A)36TACTCASTAAAGKTTCAAAGTTTA | 92 | 0.2 |
| 28S (529) | (A)44AACTACTACCACCAAGATCTGT | 56 | 0.2 |
| 28S (1535) | (A)46AAGAAAAGAAAACTCTTCCGATA | 60 | 0.3 |
| 28S (1620) | (A)52ATTGATGAAATCTCTSTGACC | 64 | 1.0 |
| 28S (1938) | (A)57AMGGTAAGACCYTCATCGA | 68 | 1.0 |
| EF1-α (93) | (A)63CCAACGTTGTCACCGGG | 72 | 1.0 |
| EF1-α (504) | (A)65ACCGTTGGAGATTTGACC | 76 | 1.0 |
| EF1-α (723) | (A)65AAGTHATTAATATACGATCWACAGG | 80 | 0.6 |
| EF1-α (864) | (A)68AGAGTTGCTARTCAACTAAAAAT | 84 | 0.5 |
| COI | COII | Cyt b | 16SrRNA | EF-1α | 28SrRNA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intraspecific variation | 0–1.2% | 0–0.8% | 0–1.5% | 0–0.9% | 0–1.0% | 0–0.4% |
| Interspecific variation | 2.2–10.2% | 1.7–9.9% | 3.0–11.5% | 0–3.2% | 0–5.0% | 0–3.0% |
| Number of species specific SNPs | 128 | 37 | 71 | 11 | 28 | 23 |
| Locus | 16S | COII | Cyt b | 28S | EF1-α | COI | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP | 265 | 346 | 418 | 155 | 659 | 529 | 1535 | 1620 | 1938 | 93 | 504 | 723 | 864 | 503 | 935 |
| C. vicina | C | T | T | C | T | A | T | A | C | G | A | A | A | A | C |
| C. vomitoria | C | T | T | T | C | C | T | A | C | A | A | G | A | T | T |
| L. sericata | A | C | C | A | C | A | A | G | T | G | C | G | A | A | C |
| L. illustris | C | A | C | T | T | C | T | G | C | G | C | G | G | G | T |
| L. caesar | C | A | T | T | C | C | T | G | C | G | C | G | G | A | C |
| P. terraenovae | T | T | A | T | C | A | T | A | T | G | T | C | G | A | T |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Godfrey, H.; Smith, J.A. IdentiFLY: The Development and Validation of a 15-Plex SNP Assay for Forensic Identification of UK Blowfly Species (Calliphoridae). Taxonomy 2024, 4, 680-695. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy4040035
Godfrey H, Smith JA. IdentiFLY: The Development and Validation of a 15-Plex SNP Assay for Forensic Identification of UK Blowfly Species (Calliphoridae). Taxonomy. 2024; 4(4):680-695. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy4040035
Chicago/Turabian StyleGodfrey, Helen, and Judith A. Smith. 2024. "IdentiFLY: The Development and Validation of a 15-Plex SNP Assay for Forensic Identification of UK Blowfly Species (Calliphoridae)" Taxonomy 4, no. 4: 680-695. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy4040035
APA StyleGodfrey, H., & Smith, J. A. (2024). IdentiFLY: The Development and Validation of a 15-Plex SNP Assay for Forensic Identification of UK Blowfly Species (Calliphoridae). Taxonomy, 4(4), 680-695. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy4040035





