In Silico Identification of Pathogenicity Effectors on Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vanillae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genome and Proteome Database
2.2. Synteny and SIX Gene Search in F. oxysporum Associated with Vanilla Root Rot
2.3. Identification and Comparison of Canonical Pathogenicity Effectors
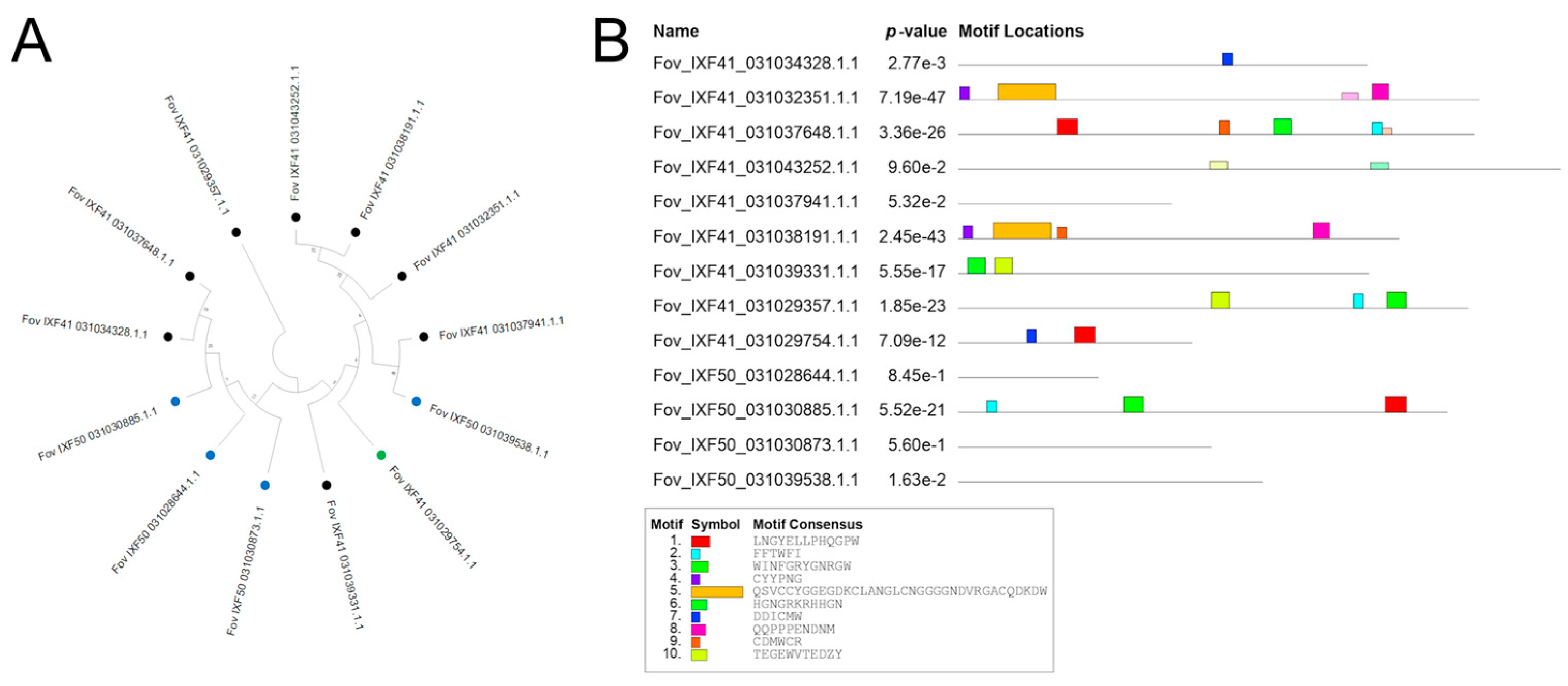
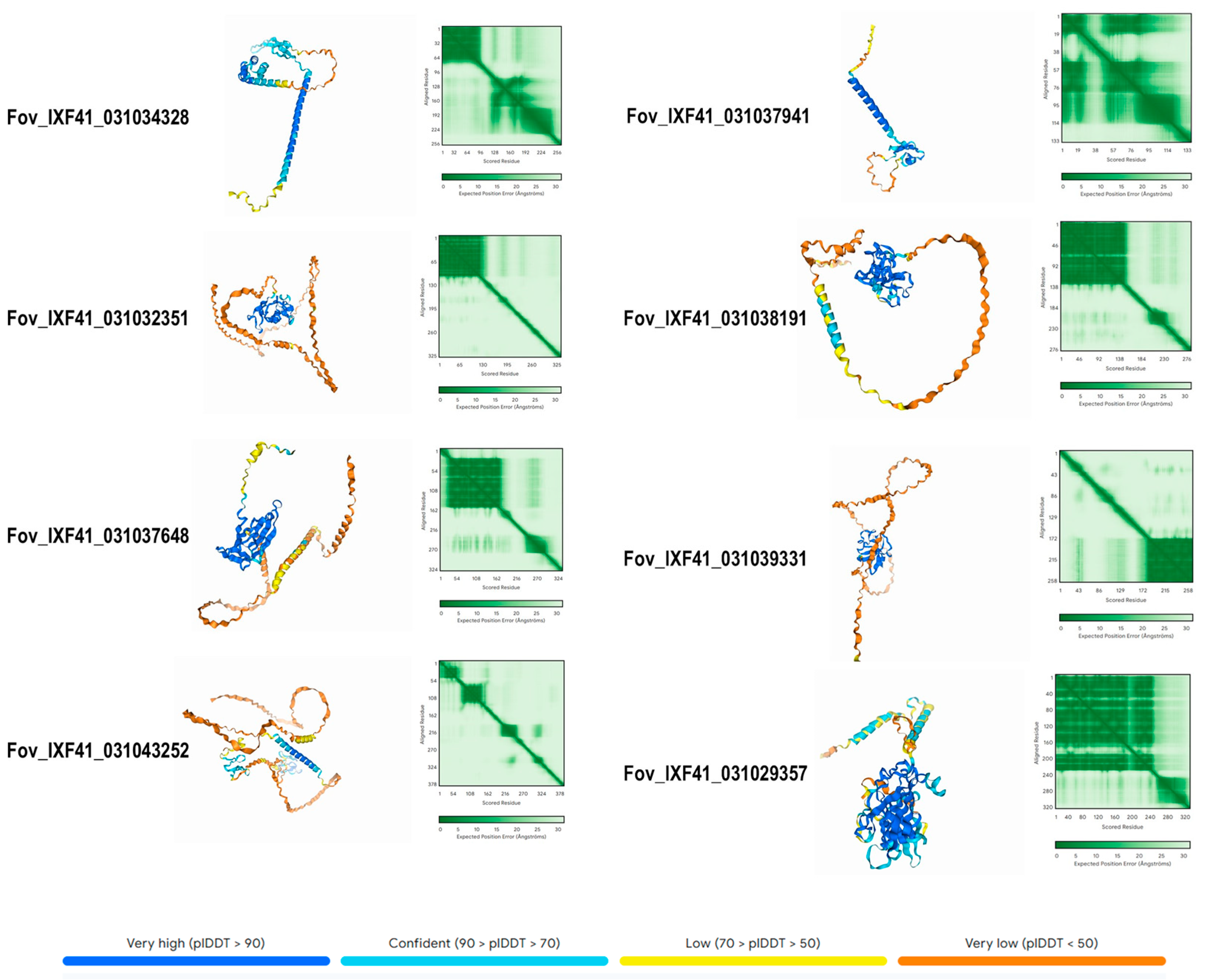
2.4. Alignment, Phylogenetic Analysis, and Structural Prediction of Pathogenicity Effectors
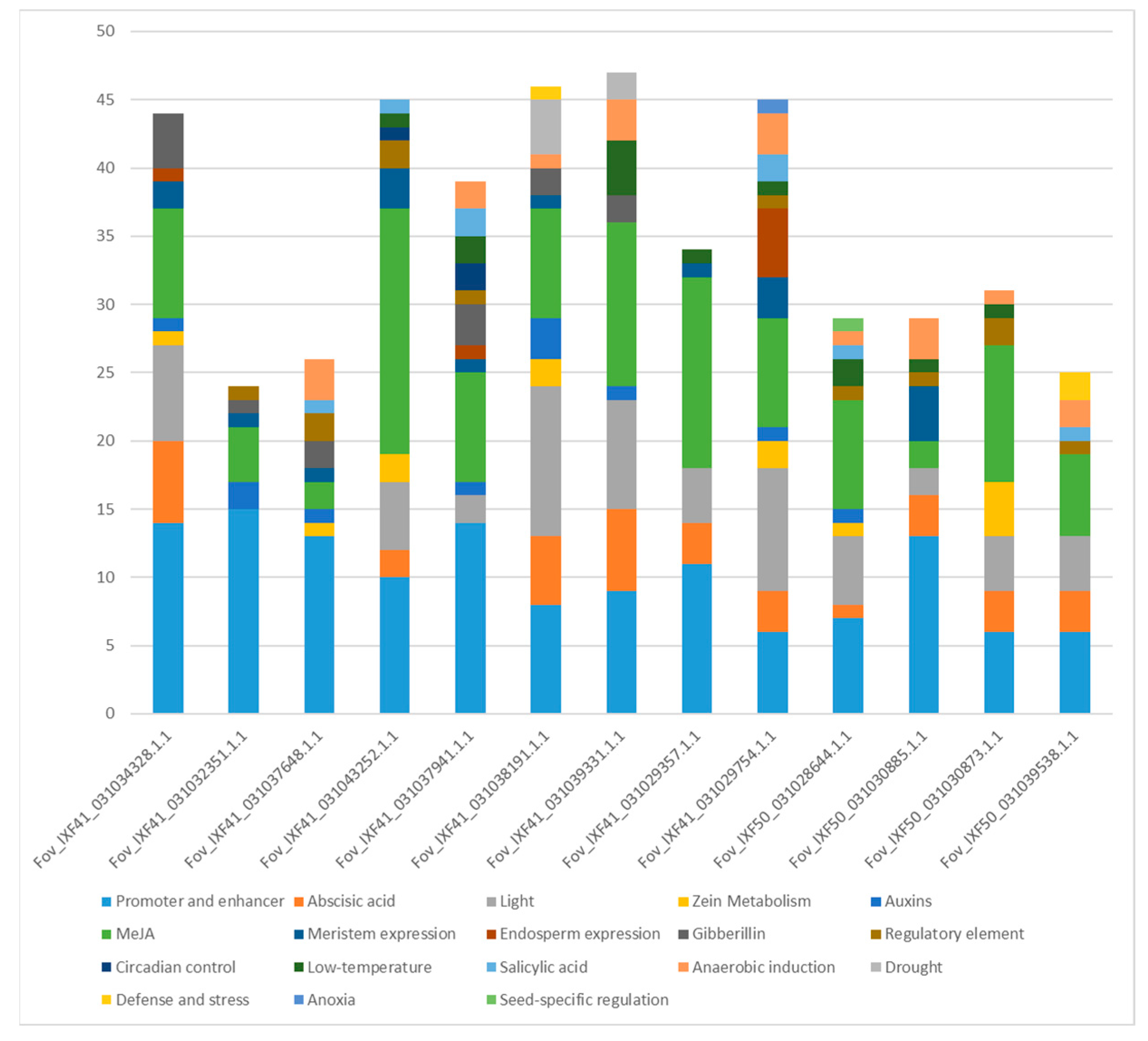
2.5. Identification of Cis-Regulatory Elements in the Promoter Regions of Identified Effectors
3. Results
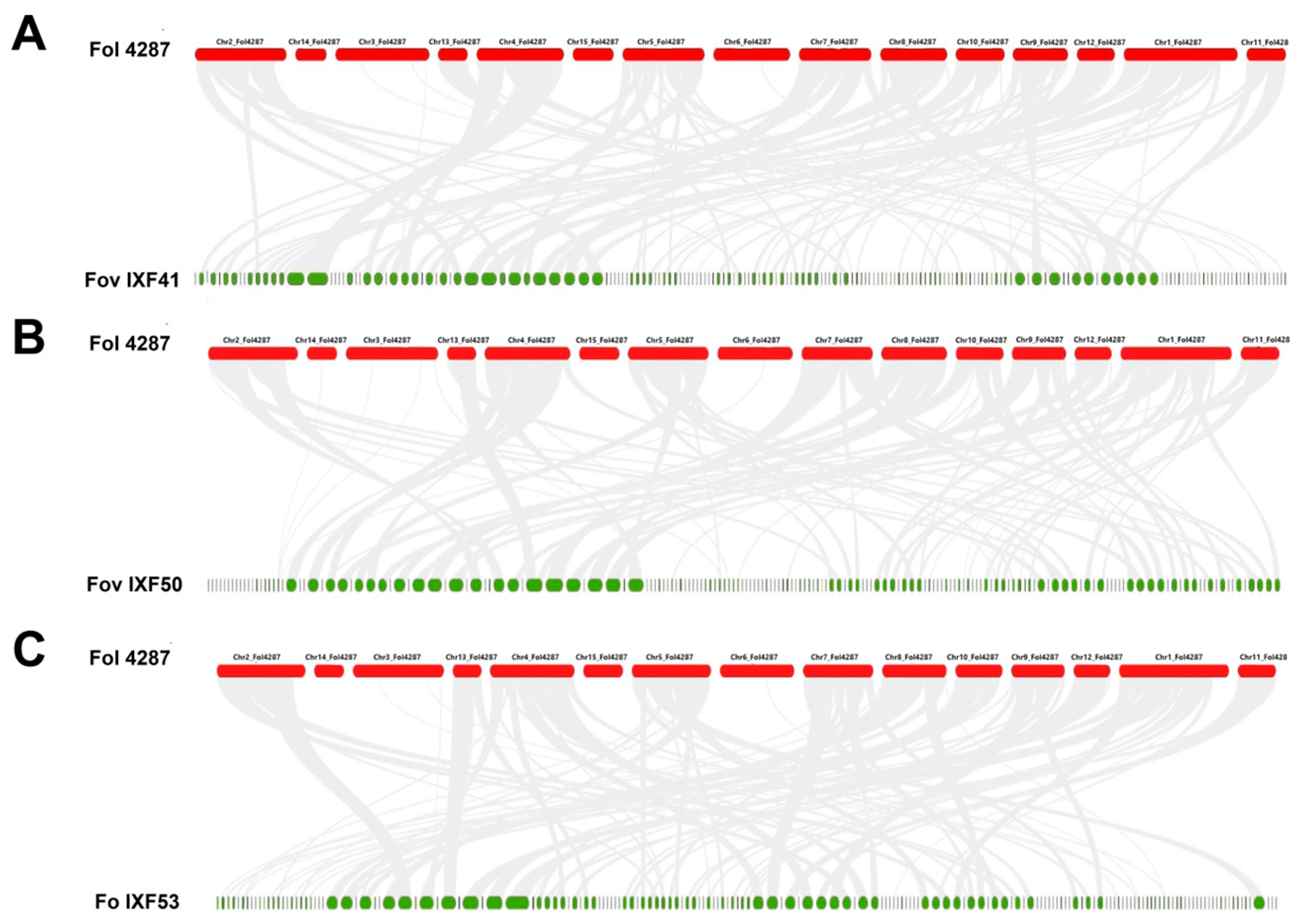
3.1. Identification of SIX Genes and Synteny
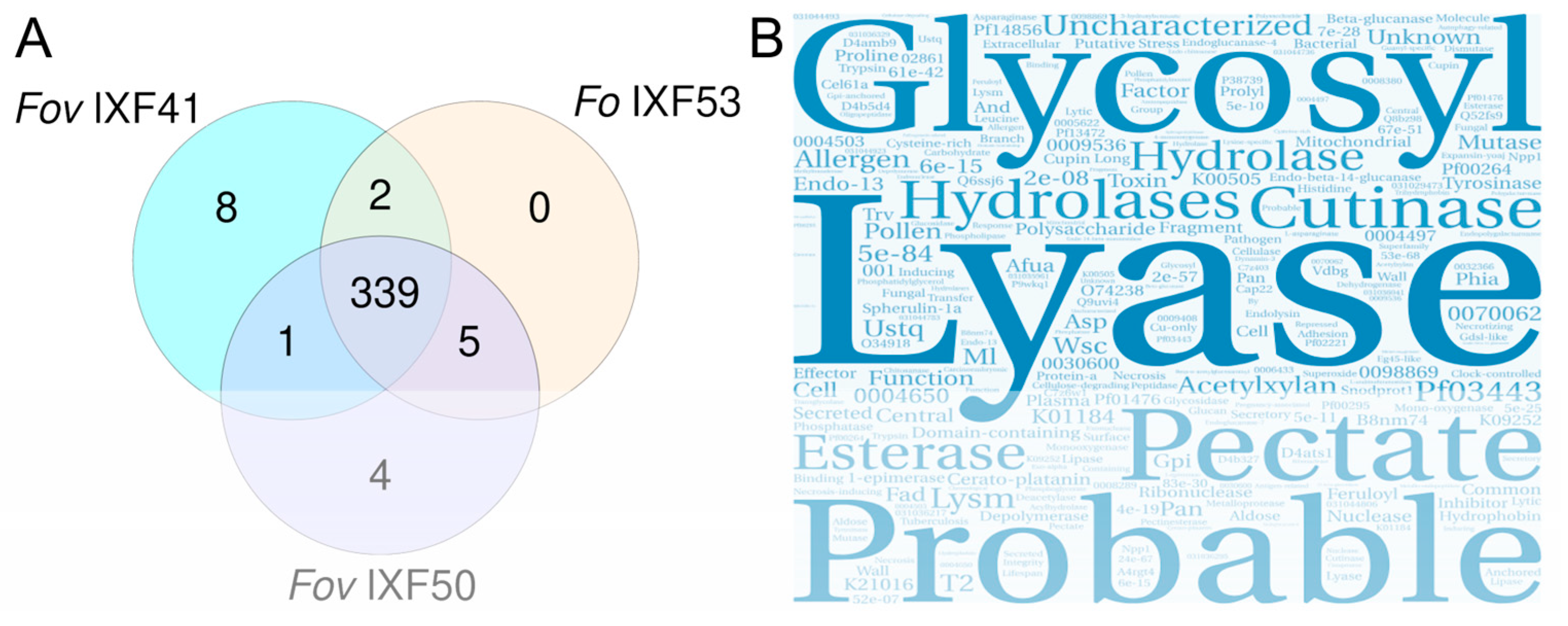
3.2. Identification of the Core Effectorome in F. oxysporum Associated with Vanilla Roots
3.3. Characterization of Putative Pathogenicity Effectors
3.4. Biochemical and Structural Prediction of Putative Effectors
3.5. Identification of Cis Elements in Promoter Region of Effectors
4. Discussion
4.1. The Pathogenic Ability of F. oxysporum f. sp. vanillae Toward Vanilla Is Independent of the SIX Effectors
4.2. Identification of the Core Effectorome in F. oxysporum Associated with Vanilla Root
4.3. Identification of Putative Pathogenic Effectors in F. oxysporum f. sp. vanillae
4.4. The Promoters of Putative Pathogenic Effectors Contain Cis Elements Responsive to Plant Hormones
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barragán-Ocaña, A.; Silva-Borjas, P.; Cecilio-Ayala, E. Vanilla production in the world and Mexico: Market value and technology. SSHO 2024, 10, e101076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdova-Nieto, C.; Flores-Estévez, N.; Iglesias-Andreu, L.G.; Rosas-Saito, G.H.; Alonso-López, A.; Noa-Carrazana, J.C. Identification of fungal disease in a Vanilla planifolia Jacks plantation in the central zone of the state of Veracruz, Mexico. Agroproductividad 2024, 17, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adame-García, J.; Rodríguez-Guerra, R.; Iglesias-Andreu, L.G.; Ramos-Prado, J.M.; Luna-Rodríguez, M. Molecular identification and pathogenic variation of Fusarium species isolated from Vanilla planifolia in Papantla Mexico. Bot. Sci. 2015, 93, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyyappurath, S.; Atuahiva, T.; Le Guen, R.; Batina, H.; Le Squin, S.; Gautheron, N.; Hermann, V.E.; Peribe, J.; Jahiel, M.; Steinberg, C.; et al. Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. radicis-vanillae is the causal agent of root and stem rot of vanilla. Plant Pathol. 2015, 65, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-de la Rosa, F.R.; De Luna, E.; Adame-García, J.; Iglesias-Andreu, L.G.; Luna-Rodríguez, M. Phylogenetic position and nucleotide diversity of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vanillae worldwide based on translation elongation factor 1α sequences. Plant Pathol. 2018, 67, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Galindo, L.S.; Mosquera-Espinosa, A.T. Biocontrol against Fusarium spp. in vanilla crop: A new study model. Temas Agrarios 2023, 28, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinaria, A.G.; Liew, E.C.Y.; Burgess, L.W. Fusarium species associated with vanilla stem rot in Indonesia. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2010, 39, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangir, P.; Mehra, N.; Sharma, K.; Singh, N.; Rani, M.; Kapoor, R. Secreted in Xylem genes: Drivers of host adaptation in Fusarium oxysporum. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, e628611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fokkens, L.; Conneely, L.J.; Rep, M. Partial pathogenicity chromosomes in Fusarium oxysporum are sufficient to cause disease and can be horizontally transferred. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 14, 4985–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimkovicová, M.; Kramer, G.; Rep, M.; Takken, F.L.W. Tomato R-gene-mediated resistance against Fusarium wilt originates in roots and extends to shoots via xylem to limit pathogen colonization. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, e1384431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano-de la Cruz, M.T.; Escobar-Hernández, E.E.; Arciniega-González, J.A.; Rueda-Zozaya, R.P.; Adame-García, J.; Luna-Rodríguez, M. Bioinformatic analysis deciphers the molecular toolbox in the endophytic/pathogenic behavior in F. oxysporum f. sp. vanillae—V. planifolia Jacks interaction. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, K.; Krasileva, K.V. Prediction of effector protein structures from fungal phytopathogens enables evolutionary analyses. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Feng, Q.; Ruan, J.; Wang, G.L.; You, X.; Ning, Y. Targeting conserved secreted effectors to control rice blast. Trends Plant Sci. 2025, 30, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreón-Anguiano, K.G.; Islas-Flores, I.; Vega-Arreguín, J.; Sáenz-Carbonell, L.; Canto-Canché, B. EffHunter: A Tool for Prediction of Effector Protein Candidates in Fungal Proteomic Databases. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longsaward, R.; Viboonjun, U.; Wen, Z.; Asiegbu, F.O. In silico analysis of secreted effectorome of the rubber tree pathogen Rigidoporus microporus highlights its potential virulence proteins. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, e1439454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovelace, A.H.; Dorhmi, S.; Hulin, M.T.; Li, Y.; Mansfield, J.W.; Ma, W. Effector identification in plant pathogens. Phytopathology 2023, 113, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillán-Mendoza, R.; Estrella-Maldonado, H.J.; Matilde-Hernández, C.; Luna-Rodríguez, M.; Rodríguez-Quibrera, C.G.; González-Cruz, C.; Torres-Olaya, M.; Flores-de la Rosa, F.R. Genome Sequence Resource of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vanillae IXF41 and IXF50 Alongside the Endophyte F. oxysporum IXF53, Isolated from Vanilla Root Rot. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 899–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.J.; van der Does, H.C.; Borkovich, K.A.; Coleman, J.J.; Daboussi, M.J.; Di Pietro, A.; Dufresne, M.; Freitag, M.; Grabherr, M.; Henrissat, B.; et al. Comparative genomics reveals mobile pathogenicity chromosomes in Fusarium. Nature 2010, 464, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rombauts, S.; Rouzé, P. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batson, A.M.; Fokkens, L.; Rep, M.; du Toit, L.J. Putative effector genes distinguish two pathogenicity groups of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. spinaciae. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2020, 34, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaliapan, K.; Mazlin, S.N.A.; Chua, K.O.; Rejab, N.A.; Mohd-Yusuf, Y. Secreted in Xylem (SIX) genes in Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense (Foc) unravels the potential biomarkers for early detection of Fusarium wilt disease. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, e271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobe, T.O.; Urner, M.; Ulloa, M.; Broders, K.; Hutmacher, R.B.; Ellis, M.L. Secreted in Xylem (SIX) gene SIX9 is highly conserved in Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vasinfectum race 4 isolates from cotton in the United States. Phytofrontiers 2024, 4, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, S.; Taylor, A.; Jackson, A.C.; Armitage, A.D.; Bates, H.J.; Mead, A.; Harrison, R.J.; Clarkson, J.P. Identification and expression of Secreted In Xylem pathogenicity genes in Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. pisi. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, e593140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakane, K.; Akiyama, M.; Jogaiah, S.; Ito, S.; Sasaki, K. Pathogenicity chromosome of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cepae. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2024, 170, 103860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, H.J.; Pike, J.; Price, R.J.; Jenkins, S.; Connell, J.; Legg, A.; Armitage, A.; Harrison, R.J.; Clarkson, J.P. Comparative genomics and transcriptomics reveal differences in effector complement and expression between races of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lactucae. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, e1415534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yu, H.; Ma, L.J. Accessory chromosomes in Fusarium oxysporum. Phytopathology 2020, 110, 1488–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.S.; Outram, M.A.; Smith, A.; McCombe, C.L.; Khambalkar, P.B.; Rima, S.A.; Sun, X.; Ma, L.; Ericsson, D.J.; Jones, D.A.; et al. The structural repertoire of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici effectors revealed by experimental and computational studies. eLife 2024, 12, RP89280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, O.; Purugganan, M.D. Domestication and the evolution of crops: Variable syndromes, complex genetic architectures, and ecological entanglements. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 1227–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, F.; Jourda, C.; Grisoni, M.; Piet, Q.; Rivallan, R.; Dijoux, J.B.; Hascoat, J.; Lepers-Andrzejewski, S.; Besse, P.; Charron, C. A genome-wide assessment of the genetic diversity, evolution and relationships with allied species of the clonally propagated crop Vanilla planifolia Jacks. ex Andrews. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2022, 69, 2125–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbyshire, M.C. Bioinformatic detection of positive selection pressure in plant pathogens: The neutral theory of molecular sequence evolution in action. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, e644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anna-Todd, J.W.; Carreón-Anguiano, K.G.; Islas-Flores, I.; Canto-Canché, B. Microbial effectors: Key determinants in plant health and disease. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perincherry, L.; Ajmi, C.; Oueslati, S.; Waskiewicz, A.; Stepien, L. Induction of Fusarium lytic enzymes by extracts from resistant and susceptible cultivars of pea (Pisum sativum L.). Pathogens 2020, 9, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistu, A.A. Endophytes: Colonization, behaviour, and their role in defense mechanism. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, e6927219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, Z.; Duan, Z.; Zhu, L.; Di, R.; Bao, Y.; Powell, C.A.; Hu, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhang, M.; et al. Pectate lyase from Fusarium sacchari induces plant immune responses and contributes to virulence. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e00165-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, E.L.; Ökmen, B.; Doehlmann, G.; Henrissat, B.; Bradshaw, R.E.; Mesarich, C.H. Secreted glycoside hydrolase proteins as effectors and invasion patterns of plant-associated fungi and oomycetes. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, e853106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhon, E.; Chau, M.Q.; Hoang, C.V.; Chandrasekharan, N.; Bhaskar, C.; Ma, L.M. Fungal cell wall-associated effectors: Sensing, integration, suppression, and protection. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2024, 37, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smigielski, L.; Aguilar, G.B.; Kwaaitaal, M.; Zhang, W.J.; Thordal-Christensen, H. The isoelectric point of proteins influences their translocation to the extrahaustorial matrix of the barley powdery mildew fungus. Cell. Microbiol. 2019, 21, e13091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavya, N.; Prasannakumar, M.K.; Venkateshbabu, G.; Niranjan, V.; Uttarkar, A.; Buela Parivallal, P.; Banakar, S.N.; Mahesh, H.B.; Devanna, P.; Manasa, K.G.; et al. Insights on novel effectors and characterization of metacaspase (RS107_6) as a potential cell death-inducing protein in Rhizoctonia solani. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, F.; Gallei, M.; Kornienko, A.E.; Saado, I.; Khan, M.; Chia, K.S.; Darino, M.A.; Bindics, J.; Djamei, A. TOPLESS promotes plant immunity by repressing auxin signaling and is targeted by the fungal effector Naked1. Plant Commun. 2021, 3, 100269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindics, J.; Khan, M.; Uhse, S.; Kogelmann, B.; Baggely, L.; Reumann, D.; Ingole, K.D.; Stirnberg, A.; Rybecky, A.; Darino, M.; et al. Many ways to TOPLESS—Manipulation of plant auxin signalling by a cluster of fungal effectors. New Phytol. 2022, 236, 1455–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, N.; Khan, M.; Djamei, A. Manipulation of auxin signaling by smut fungi during plant colonization. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, S.; Jin, L.; Yu, X.; Yang, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Ma, F. Silencing of early auxin responsive genes MdGH3-2/12 reduces the resistance to Fusarium solani in apple. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, 3012–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Macareno, L.C.; Iglesias-Andreu, L.G.; Luna-Rodríguez, M.; Noa-Carrazana, J.C. Resistance induction in Vanilla planifolia Jacks. by foliar spray of salicylic acid (SA) against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vanillae. Vegetos 2023, 37, 2002–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievens, L.; Pollier, J.; Goossens, A.; Beyaert, R.; Staal, J. Abscisic acid as pathogen effector and immune regulator. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macioszek, V.K.; Jęcz, T.; Ciereszko, I.; Kononowicz, A.K. Jasmonic acid as a mediator in plant response to necrotrophic fungi. Cells 2023, 12, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Weng, G.; Zhu, M.; Yan, K. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the fatty acid desaturase gene family in Vanilla planifolia. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 150, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Protein | aa 1 | MW 2 | pI 3 | II 4 | AI 5 | GRAVY 6 | Effector Type 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fov_IXF41_031034328.1.1 | 257 | 27,552.25 | 7.94 | 35.50 | 67.90 | −0.342 | Cytoplasmic |
| Fov_IXF41_031032351.1.1 | 327 | 34,886.48 | 5.29 | 41.17 | 52.02 | −0.633 | Cytoplasmic |
| Fov_IXF41_031037648.1.1 | 324 | 35,352.66 | 5.92 | 25.69 | 88.43 | −0.186 | Apoplastic |
| Fov_IXF41_031043252.1.1 | 378 | 40,439.83 | 9.01 | 45.85 | 49.92 | −0.683 | Cytoplasmic |
| Fov_IXF41_031037941.1.1 | 134 | 14,782.06 | 9.24 | 43.94 | 63.36 | −0.265 | Cytoplasmic |
| Fov_IXF41_031038191.1.1 | 277 | 29,170.01 | 4.70 | 47.74 | 52.53 | −0.482 | Apoplastic |
| Fov_IXF41_031039331.1.1 | 258 | 27,552.76 | 5.54 | 50.08 | 54.11 | −0.795 | Cytoplasmic |
| Fov_IXF41_031029357.1.1 | 320 | 35,667.71 | 5.39 | 22.42 | 69.78 | −0.707 | Cytoplasmic |
| Fov_IXF41_031029754.1.1 | 147 | 16,372.57 | 6.31 | 51.77 | 83.40 | −0.418 | Cytoplasmic |
| Fov_IXF50_031028644.1.1 | 88 | 9924.11 | 6.44 | 32.21 | 42.05 | −1.034 | Cytoplasmic |
| Fov_IXF50_031030885.1.1 | 307 | 33,405.00 | 6.31 | 23.31 | 79.48 | −0.171 | Apoplastic |
| Fov_IXF50_031030873.1.1 | 159 | 18,385.14 | 8.77 | 30.39 | 30.63 | −1.597 | Cytoplasmic |
| Fov_IXF50_031039538.1.1 | 191 | 26,121.29 | 9.86 | 42.77 | 98.64 | 0.468 | Apoplastic |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flores-de la Rosa, F.R.; Matilde-Hernández, C.; González-Oviedo, N.A.; Estrella-Maldonado, H.J.; Saucedo-Picazo, L.E.; Santillán-Mendoza, R. In Silico Identification of Pathogenicity Effectors on Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vanillae. BioTech 2025, 14, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14030050
Flores-de la Rosa FR, Matilde-Hernández C, González-Oviedo NA, Estrella-Maldonado HJ, Saucedo-Picazo LE, Santillán-Mendoza R. In Silico Identification of Pathogenicity Effectors on Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vanillae. BioTech. 2025; 14(3):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14030050
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlores-de la Rosa, Felipe Roberto, Cristian Matilde-Hernández, Nelly Abigail González-Oviedo, Humberto José Estrella-Maldonado, Liliana Eunice Saucedo-Picazo, and Ricardo Santillán-Mendoza. 2025. "In Silico Identification of Pathogenicity Effectors on Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vanillae" BioTech 14, no. 3: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14030050
APA StyleFlores-de la Rosa, F. R., Matilde-Hernández, C., González-Oviedo, N. A., Estrella-Maldonado, H. J., Saucedo-Picazo, L. E., & Santillán-Mendoza, R. (2025). In Silico Identification of Pathogenicity Effectors on Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vanillae. BioTech, 14(3), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14030050






