Phaseolus coccineus L. Landraces in Greece: Microsatellite Genotyping and Molecular Characterization for Landrace Authenticity and Discrimination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. DNA Extraction and EST-SSR/SSR Analysis
2.3. Capillary Electrophoresis Detection
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Population Structure
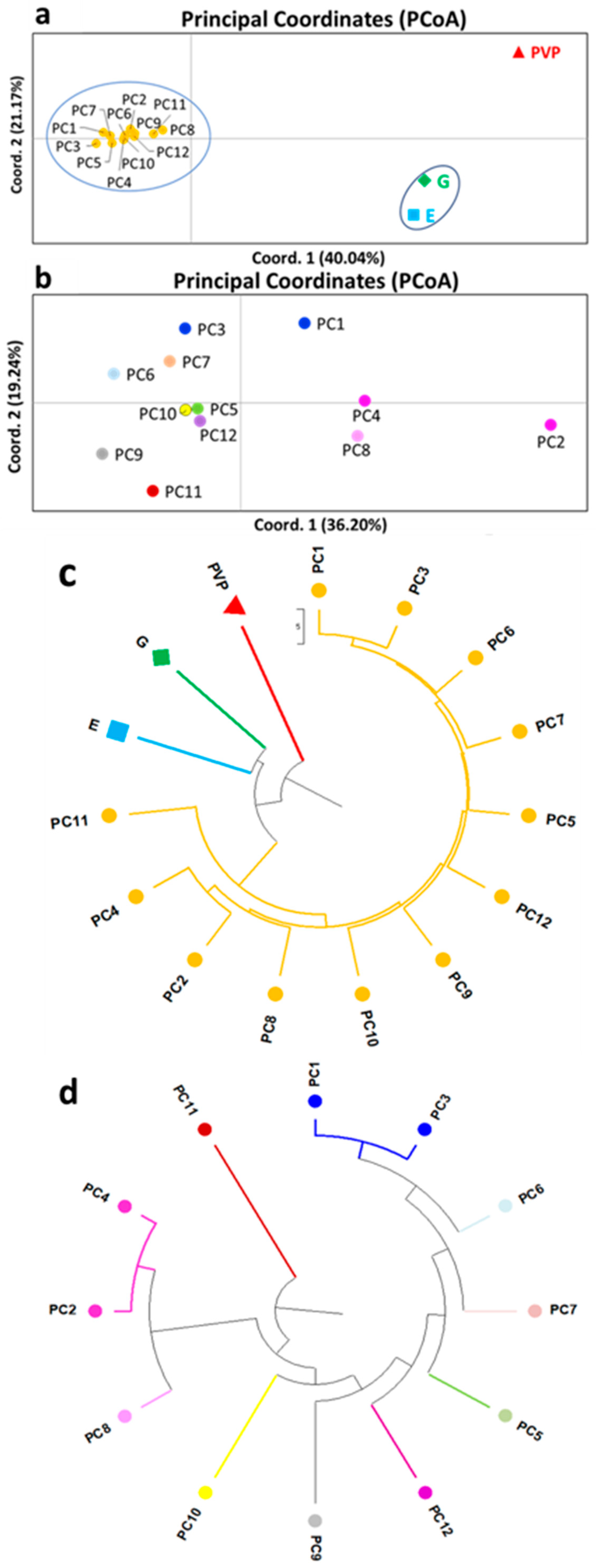
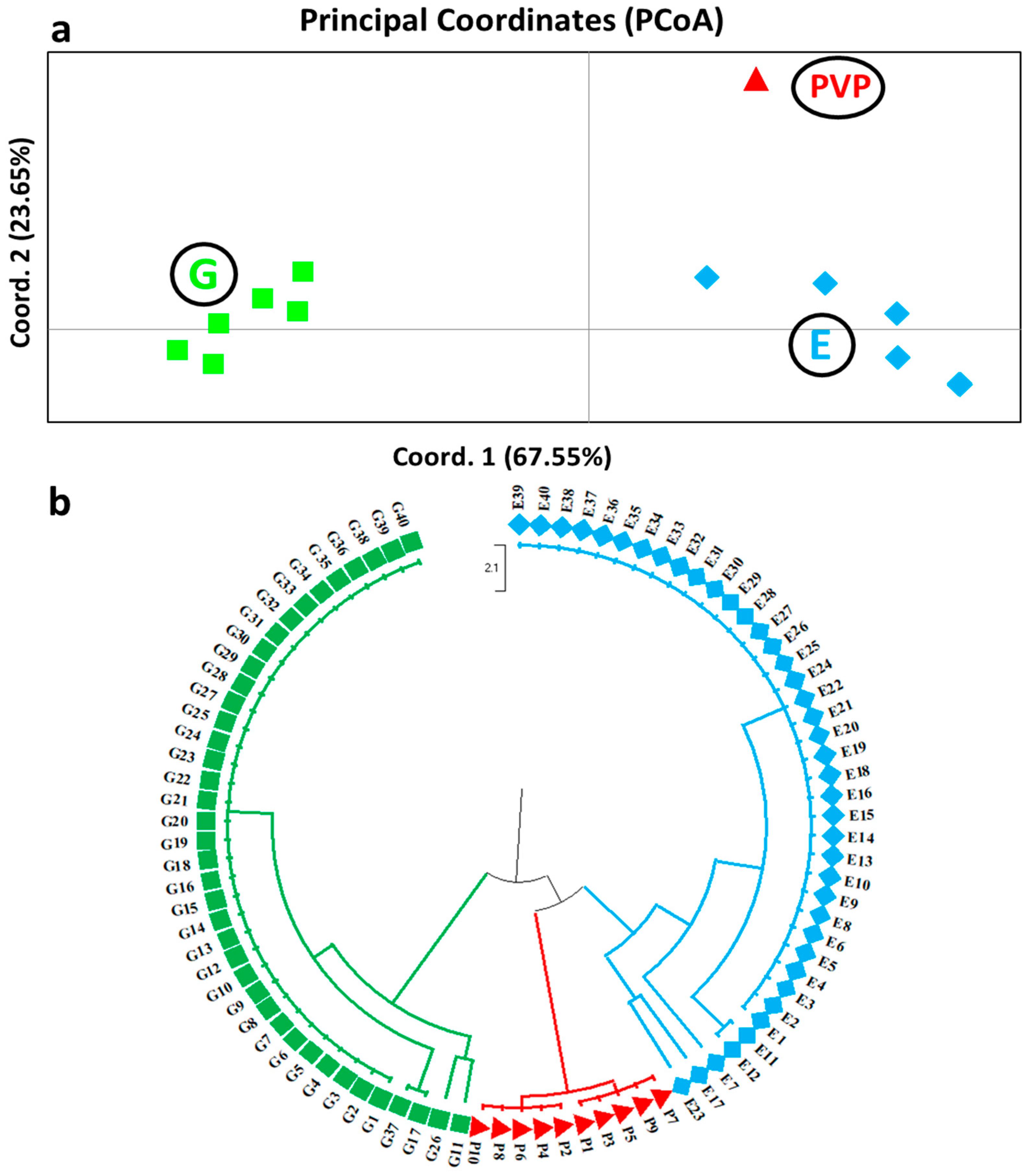
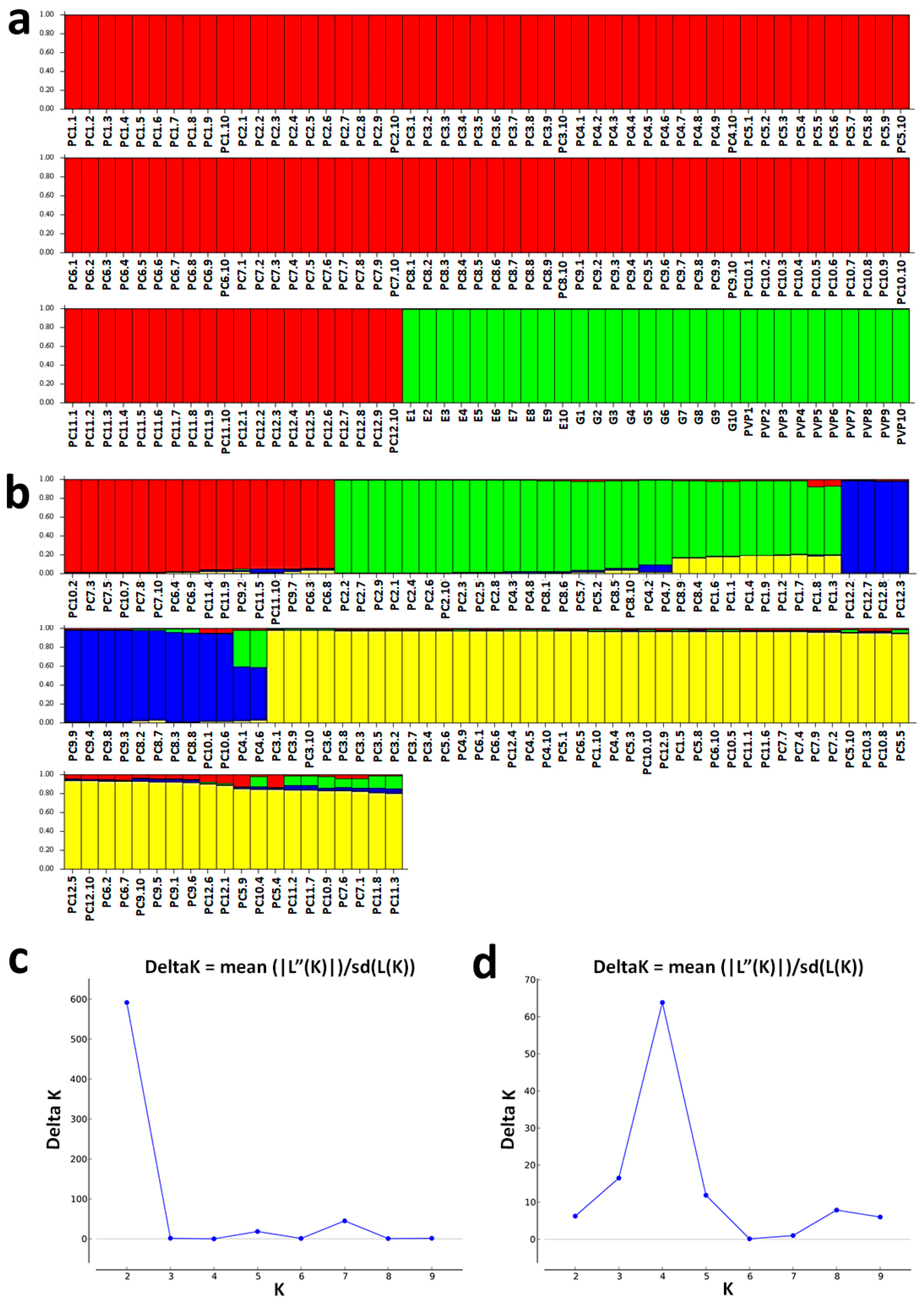
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Characterization of P. coccineus L. Landraces Based on SSR and EST-SSR Molecular Markers
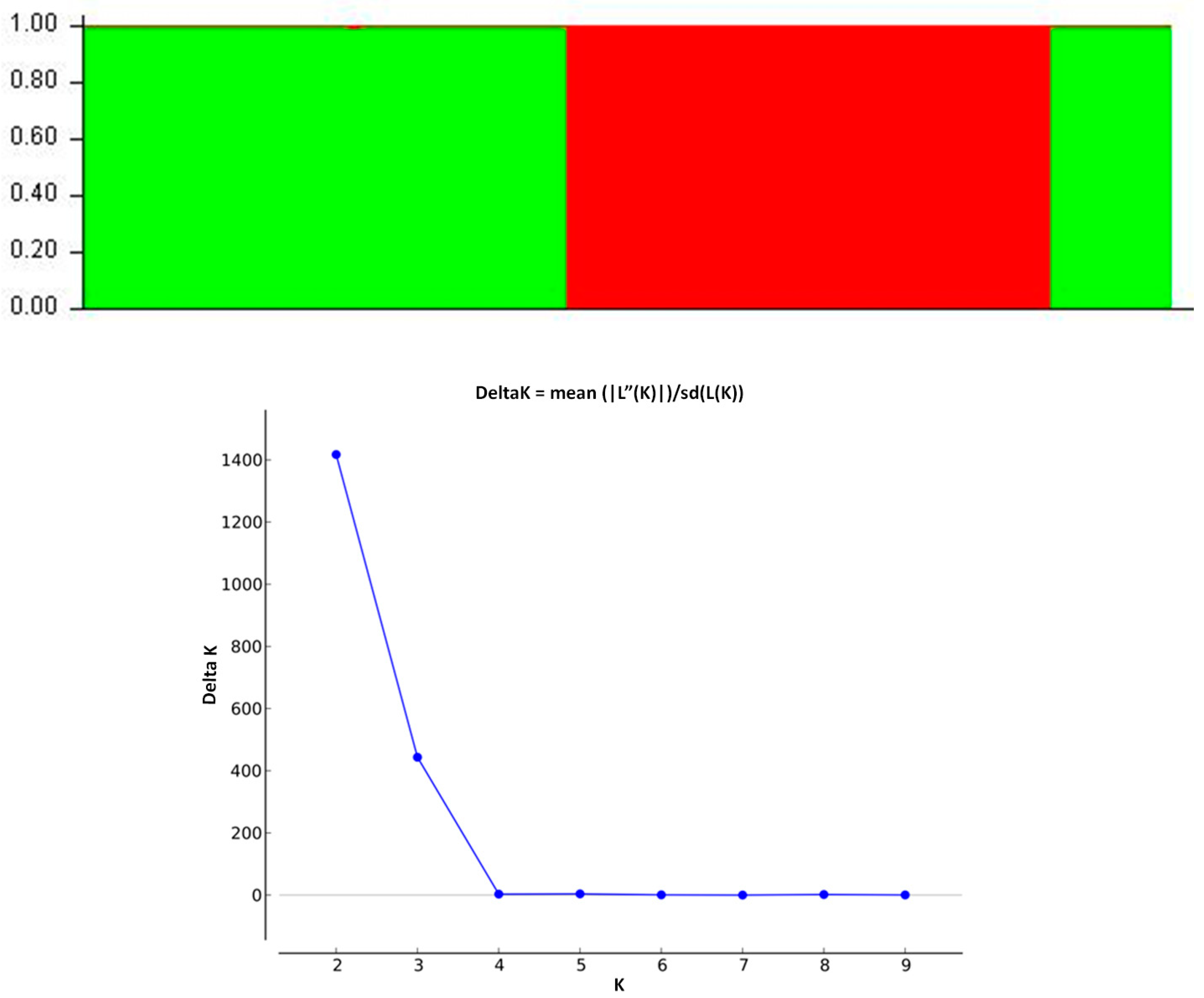
3.2. Model-Based Clustering Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwember, A.R.; Carrasco, B.; Gepts, P. Unraveling agronomic and genetic aspects of runner bean (Phaseolus coccineus L.). Field Crops Res. 2017, 206, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkovič, L.; Pipan, B.; Vasić, M.; Antić, M.; Todorović, V.; Ivanovska, S.; Brezeanu, C.; Šuštar-Vozlič, J.; Meglič, V. Morpho-Agronomic Characterisation of Runner Bean (Phaseolus coccineus L.) from South-Eastern Europe. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crivelli, A.J.; Catsadorakis, G.; Malakou, M.; Rosecchi, E. Fish and fisheries of the Prespa lakes. Hydrobiologia 1997, 351, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catsadorakis, G.; Malakou, M. Conservation and management issues of Prespa National Park. Hydrobiologia 1997, 351, 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulou, A.; Kissoudis, C.; Mellidou, I.; Manioudaki, M.; Bosmali, I.; Tsakonitis, V.; Kalivas, A.; Osathanunkul, M.; Tsaftaris, A.; Ganopoulos, I.; et al. Expanding Phaseolus coccineus Genomic Resources: De novo Transcriptome Assembly and Analysis of Landraces ‘Gigantes’ and ‘Elephantes’ Reveals Rich Functional Variation. Biochem. Genet. 2019, 57, 747–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hue, H.T.; Nghia, L.T.; Minh, H.T.; Anh, L.H.; Trang, L.T.T.; Khanh, T.D. Evaluation of Genetic Diversity of Local-Colored Rice Landraces Using SSR Markers. Int. Lett. Nat. Sci. 2018, 67, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Tan, W.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, M.; Ren, R.; Ma, X.; Tang, X. Genetic relationships of 34 grapevine varieties and construction of molecular fingerprints by SSR markers. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.X.; Li, S.Y.; Guo, R.X.; Zeng, X.H.; Wen, J.; Ma, C.Z.; Yi, B. Construction of DNA fingerprinting for Brassica napus varieties based on SNP chip. Acta Agron. Sin. 2018, 44, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgante, M.; Olivieri, A.M. PCR-amplified microsatellites as markers in plant genetics. Plant J. 1993, 3, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, D.; Nanni, L.; Porfiri, O.; Bulfon, D.; Papa, R. Genetic diversity of Phaseolus vulgaris L. and Phaseolus coccineus L. landraces in central Italy. Plant Breed. 2005, 124, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spataro, G.; Tiranti, B.; Arcaleni, P.; Bellucci, E.; Attene, G.; Papa, R.; Zeuli, P.S.; Negri, V. Genetic diversity and structure of a worldwide collection of Phaseolus coccineus L. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 122, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercati, F.; Catarcione, G.; Paolacci, A.R.; Abenavoli, M.R.; Sunseri, F.; Ciaffi, M. Genetic diversity and population structure of an Italian landrace of runner bean (Phaseolus coccineus L.): Inferences for its safeguard and on-farm conservation. Genetica 2015, 143, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.; Smith, K.; MacKenzie, K.; Jorgenson, L.; Hackett, C.; Powell, W. The construction of a genetic linkage map of red raspberry (Rubus idaeus subsp. idaeus) based on AFLPs, genomic-SSR and EST-SSR markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Wang, H.; Xia, Z.; Zou, M.; Lu, C.; Wang, W. Developmenrt of EST-SSR and genomic-SSR markers to assess genetic diversity in Jatropha curcas L. BMC Res. Notes 2010, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, G.M.; Maguire, T.L.; Edwards, K.J.; Henry, R.J. Optimisation of a Microsatellite Enrichment Technique in Saccharum spp. Plant Mol. Biol. Report. 1999, 17, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acampora, A.; Ciaffi, M.; De Pace, C.; Paolacci, A.R.; Tanzarella, O.A. Pattern of variation for seed size traits and molecular markers in Italian germplasm of Phaseolus coccineus L. Euphytica 2007, 157, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.; Rau, D.; Angioi, S.A.; Bellucci, E.; Bitocchi, E.; Nanni, L.; Knüpffer, H.; Negri, V.; Papa, R.; Attene, G. European Phaseolus coccineus L. landraces: Population Structure and Adaptation, as Revealed by cpSSRs and Phenotypic Analyses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendón-Anaya, M.; Montero-Vargas, J.M.; Saburido-Álvarez, S.; Vlasova, A.; Capella-Gutierrez, S.; Ordaz-Ortiz, J.J.; Aguilar, O.M.; Vianello-Brondani, R.P.; Santalla, M.; Delaye, L.; et al. Genomic history of the origin and domestication of common bean unveils its closest sister species. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.J.; Nguyen, T.M.; Waterman, A.; McMichael, G.L.; Chalmers, K.J. Application of multiplex-ready PCR for fluorescence-based SSR genotyping in barley and wheat. Mol. Breed. 2002, 21, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Wan, T.; Xu, S.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Feng, Y.; Cai, Y. Molecular identification and genetic analysis of cherry cultivars using capillary electrophoresis with fluorescence-labeled SSR markers. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.; Grisham, M.P.; Pan, Y.B. Allelic divergence and cultivar-specific SSR alleles revealed by capillary electrophoresis using fluorescence-labeled SSR markers in sugarcane. Genome 2014, 57, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—An update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M.; Li, W.H. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 5269–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Using Maximum Likelihood, Evolutionary Distance, and Maximum Parsimony Methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Smouse, P.E.; Quattro, J.M. Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: Application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 1992, 131, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneath, P.H.A.; Sokal, R.R. Numerical Taxonomy. The Principles and Practice of Numerical Classification; W. H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Orlóci, L. Multivariate Analysis in Vegetation Research; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of Population Structure Using Multilocus Genotype Data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software structure: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, D.A.; von Holdt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2014, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omari, S.; Kamenir, Y.; Benichou, J.I.C.; Pariente, S.; Sela, H.; Perl-Treves, R. Landraces of snake melon, an ancient Middle Eastern crop, reveal extensive morphological and DNA diversity for potential genetic improvement. BMC Genet. 2018, 19, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, N.P.S.; Singh, J.; Fergany, M.; Monforte, A.J.; Sureja, A.K. Phenotypic and molecular diversity among landraces of snapmelon (Cucumis melo var. momordica) adapted to the hot and humid tropics of eastern India. Plant Genet. Resour. Characterisation Util. 2009, 7, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, D.; Rubio, F.; Ruiz, J.J.; Rao, R.; Corrado, G. Morphological and genetic diversity among and within common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) landraces from the Campania region (Southern Italy). Sci. Hortic. 2014, 180, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-García, A.; Suárez-Atilano, M.; Mastretta-Yanes, A.; Delgado-Salinas, A.; Piñero, D. Domestication genomics of the open-pollinated scarlet runner bean (Phaseolus coccineus L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Blair, M.W.; Wang, S. Genetic diversity of Chinese common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) landraces assessed with simple sequence repeat markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 117, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desiderio, F.; Bitocchi, E.; Bellucci, E.; Rau, D.; Rodriguez, M.; Attene, G.; Papa, R.; Nanni, L. Chloroplast microsatellite diversity in Phaseolus vulgaris. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 3, 39686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.; Gepts, P. Structure of genetic diversity in the two major gene pools of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.; Fabaceae). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 118, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, M.W.; Galeano, C.H.; Tovar, E.; Torres, M.C.M.; Castrillón, A.V.; Beebe, S.E.; Rao, I.M. Development of a Mesoamerican intra-genepool genetic map for quantitative trait loci detection in a drought tolerant × susceptible common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cross. Mol. Breed. 2012, 29, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegay, S.; Geleta, M.; Bryngelsson, T.; Gustavsson, L.; Hovmalm, H.P.; Ortiz, R. Comparing genetic diversity and population structure of common beans grown in Kyrgyzstan using microsatellites. Sci. J. Crop Sci. 2012, 1, 63–75. [Google Scholar]
- Escalante, A.M.; Coello, G.; Eguiarte, L.E.; Piñero, D. Genetic structure and mating systems in wild and cultivated populations of Phaseolus coccineus and P. vulgaris (Fabaceae). Am. J. Bot. 1994, 81, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Métais, I.; Aubry, C.; Hamon, B.; Jalouzot, R.; Peltier, D. Description and analysis of genetic diversity between commercial bean lines (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2000, 101, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavromatis, A.G.; Arvanitoyannis, I.S.; Chatzitheodorou, V.; Kaltsa, A.; Patsiaoura, I.; Nakas, C.T. A comparative study among landraces of Phaseolus vulgaris L. and Phaseolus coccineus L. based on molecular, physicochemical and sensory analysis for authenticity purposes. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 144, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
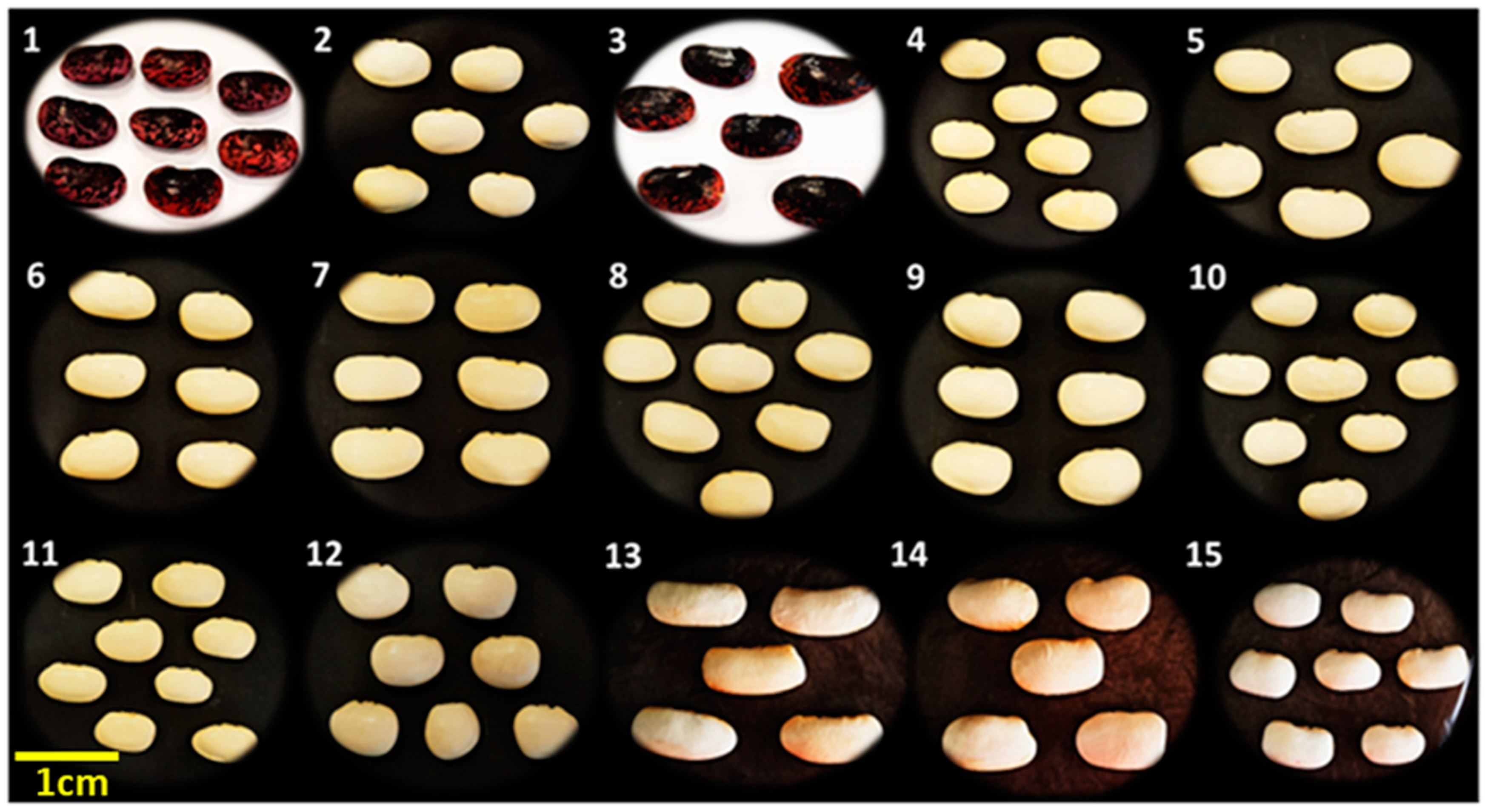

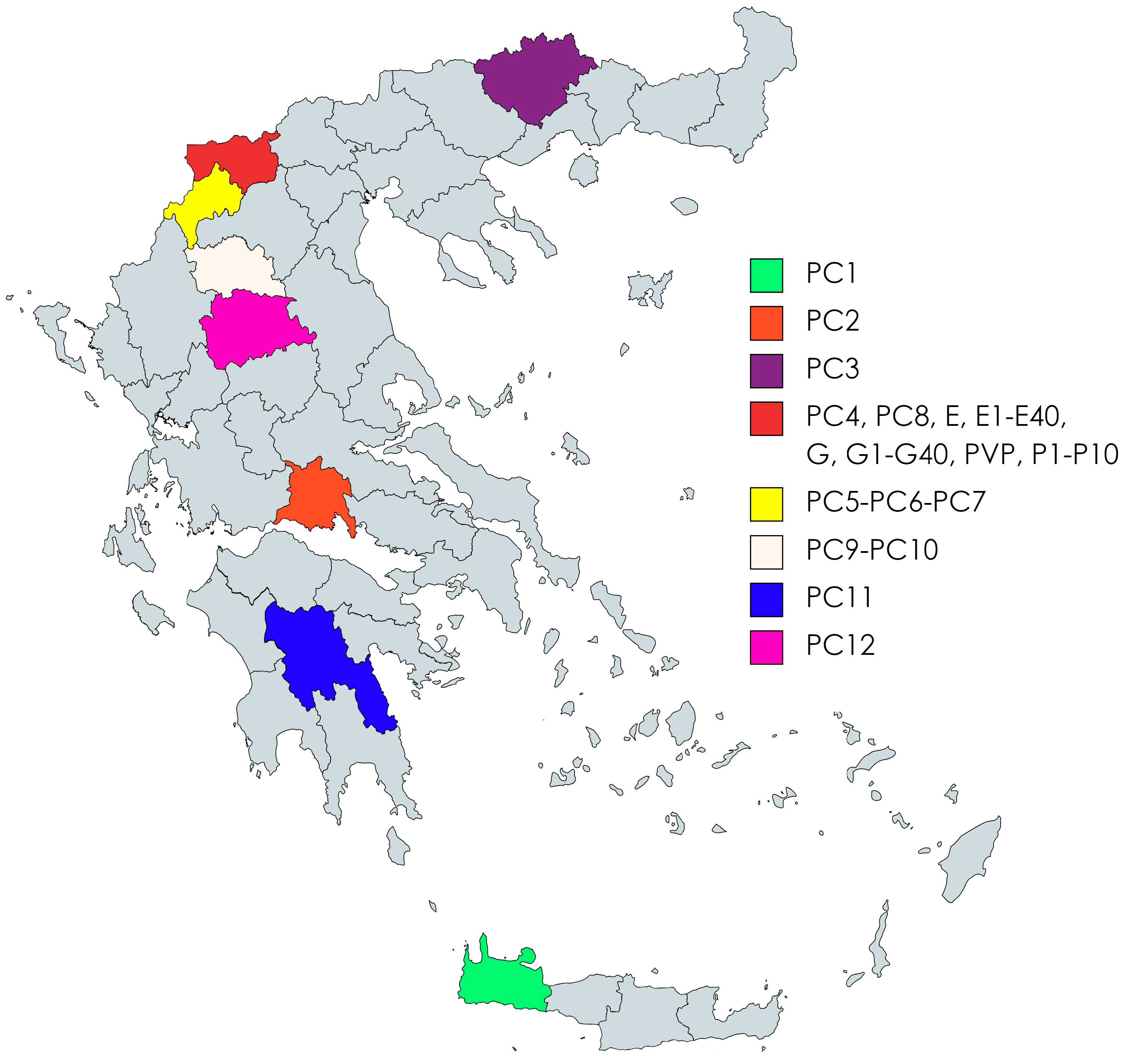
| Code | Runner Bean | Species | Local Name * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PC1 | Red Gigantes | P. coccineus L. | Chania-Voutas |
| 2 | PC2 | Gigantes | P. coccineus L. | Fokida-Artotina |
| 3 | PC3 | Red Gigantes | P. coccineus L. | Drama-Peliti |
| 4 | PC4 | Gigantes | P. coccineus L. | Agios Germanos |
| 5 | PC5 | Gigantes | P. coccineus L. | Kastoria-Korestia |
| 6 | PC6 | Gigantes | P. coccineus L. | Kastoria-Melas |
| 7 | PC7 | Elephantes | P. coccineus L. | Kastoria-Ano Melas |
| 8 | PC8 | Gigantes | P. coccineus L. | Lechovo |
| 9 | PC9 | Gigantes | P. coccineus L. | Grevena-Monaxiti |
| 10 | PC10 | Gigantes | P. coccineus L. | Grevena-Spileo |
| 11 | PC11 | Gigantes | P. coccineus L. | Arkadia-Kato Dadia |
| 12 | PC12 | Gigantes | P. coccineus L. | Trikala-Xrysomhlia |
| 13 | E | Elephantes | P. coccineus L. | Prespon |
| 14 | G | Gigantes | P. coccineus L. | Prespon |
| 15 | PVP | Plake | P. vulgaris L. | Prespon-Laimos |
| Individual | Genotype | Species | Local Name | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | G1–G10 | 6G | P. coccineus L. | Gigantes Prespon |
| 2 | G11–G20 | 5G | P. coccineus L. | |
| 3 | G21–G30 | 13G | P. coccineus L. | |
| 4 | G31–G40 | 16G | P. coccineus L. | |
| 5 | E1–E10 | 1E | P. coccineus L. | Elephantes Prespon |
| 6 | E11–E20 | 4E | P. coccineus L. | |
| 7 | E21–E30 | 9E | P. coccineus L. | |
| 8 | E31–E40 | 27E | P. coccineus L. | |
| 9 | P1–P10 | Plake | P. vulgaris L. | Plake Prespon |
| Primer Name | Sequence | Ta (°C) | Predicted Size (bp) | Molecular Marker | Fluore -Scence Dye | Fst | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AY298744 | F | 5′-CATAACATCGAAGCCTCACAGT-3′ | 47 | 140–175 | SSR | ROX | 0.518 |
| R | 3′-ACGTGCGTACGAATACTCAGTC-5′ | ||||||
| AZ301561 | F | 5′-CAGTAAATATTGGCGTGGATGA-3′ | 47 | 200–230 | SSR | ROX | 0.487 |
| R | 3′-TGAAAGTGCAGAGTGGTGGA-5′ | ||||||
| X80051 | F | 5′-AGTTAAATTATACGAGGTTAGCCTAAATC-3′ | 49 | 220–240 | SSR | HEX | 0.362 |
| R | 3′-CATTCCCTTCACACATTCACCG-5′ | ||||||
| X79722 | F | 5′-CCAACCACATTCTTCCCTACGTC-3′ | 49 | 143–173 | SSR | FAM | 0.421 |
| R | 3′-GCGGAGGCAGTTATCTTTAGGAGTG-5′ | ||||||
| X04660 | F | 5′-TTGATGACGTGGATGCATTGC-3′ | 47 | 190–220 | SSR | HEX | 0.857 |
| R | 3′-AAAGGGCTAGGGAGAGTAAGTTGG-5′ | ||||||
| J01263 | F | 5′-ATGCATGTTCCAACCACCTTCTC-3′ | 49 | 220–240 | SSR | TAM | 0.766 |
| R | 3′-GGAGTGGAACCCTTGCCTCTCATC-5′ | ||||||
| AZ044945 | F | 5′-CATCAACAAGGACAGCCTCA-3′ | 47 | 140–175 | SSR | TAM | 0.461 |
| R | 3′-GCAGCTGGCGGGTAAAACAG-5′ | ||||||
| endo | F | 5′-TCGAGTCACCATATGCCAGA-3′ | 49 | 220–250 | EST-SSR | FAM | 0.138 |
| R | 3′-CAAAGATTGATCCCGAGTGG-5′ | ||||||
| transmemb | F | 5′-CAAACCCCAATGACACATGA-3′ | 48 | 220–230 | EST-SSR | TAM | 0.121 |
| R | 3′-TGCTAGAGTGGCTTGGTTCA-5′ | ||||||
| catalase | F | 5′-CTTTCCCTGTCGAAGTTTGC-3′ | 48 | 220–250 | EST-SSR | HEX | 0.153 |
| R | 3′-CATCAACCGCCTTCAATTCT-5′ | ||||||
| hyp | F | 5′-TGGCTAGTGGTAGCCTTTGG-3′ | 47 | 310–320 | EST-SSR | FAM | 0.825 |
| R | 3′-CTGAACGTGCCTGCAGATAA-5′ | ||||||
| Ser | F | 5′-ACGAAATGGAGCTGGGATTA-3′ | 49 | 230–250 | EST-SSR | TAM | 0.139 |
| R | 3′-CCCAGGACTGCACTTCGTAT-5′ | ||||||
| Sial | F | 5′-TTTTTGCTTTCAGTGCCAGA-3′ | 48 | 220–240 | EST-SSR | HEX | 0.110 |
| R | 3′-CCAGCTCTCTTGGACCAAAC-5′ | ||||||
| bHLH | F | 5′-CCATGACTGGCATCATCATC-3′ | 49 | 220–280 | EST-SSR | ROX | 0.268 |
| R | 3′-GGCCTTTTCTCCAACAACAA-5′ | ||||||
| Landrace/ Variety | N | Na | Ne | Ho | He | P (%) | I | Fst |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 10 | 1.667 | 1.456 | 0.403 | 0.253 | 66.67 | 0.372 | 0.453 |
| PC2 | 10 | 1.667 | 1.542 | 0.520 | 0.292 | 66.67 | 0.418 | |
| PC3 | 10 | 1.667 | 1.549 | 0.520 | 0.284 | 60.00 | 0.407 | |
| PC4 | 10 | 2.000 | 1.685 | 0.440 | 0.367 | 86.67 | 0.548 | |
| PC5 | 10 | 2.067 | 1.685 | 0.507 | 0.348 | 80.00 | 0.539 | |
| PC6 | 10 | 1.867 | 1.652 | 0.480 | 0.324 | 73.33 | 0.485 | |
| PC7 | 10 | 1.933 | 1.691 | 0.467 | 0.332 | 73.33 | 0.507 | |
| PC8 | 10 | 2.133 | 1.881 | 0.578 | 0.391 | 80.00 | 0.606 | |
| PC9 | 10 | 1.933 | 1.759 | 0.587 | 0.377 | 80.00 | 0.556 | |
| PC10 | 10 | 2.000 | 1.752 | 0.440 | 0.354 | 73.33 | 0.545 | |
| PC11 | 10 | 2.133 | 1.899 | 0.556 | 0.407 | 80.00 | 0.625 | |
| PC12 | 10 | 1.933 | 1.806 | 0.483 | 0.384 | 80.00 | 0.567 | |
| E | 10 | 1.400 | 1.357 | 0.343 | 0.186 | 40.00 | 0.262 | |
| G | 10 | 1.333 | 1.323 | 0.307 | 0.164 | 33.33 | 0.228 | |
| PVP | 10 | 1.000 | 0.957 | 0.173 | 0.103 | 20.00 | 0.156 | |
| Mean | 10 | 1.782 | 1.600 | 0.454 | 0.304 | 66.22 | 0.455 |
| Landrace/ Variety | N | Na | Ne | Ho | He | P (%) | I | Fst |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | 10 | 1.143 | 1.143 | 0.143 | 0.071 | 14.29 | 0.099 | 0.802 |
| G | 10 | 1.429 | 1.429 | 0.429 | 0.214 | 42.86 | 0.297 | |
| PVP | 10 | 1.143 | 1.095 | 0.143 | 0.089 | 14.29 | 0.149 | |
| Mean | 10 | 1.238 | 1.222 | 0.238 | 0.125 | 23.81 | 0.182 |
| df | SS | MS | Est.var | PV | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) SV (P. coccineus L.) | ||||||
| Among Pops | 14 | 1113.573 | 79.541 | 7.549 | 65% | 0.607 |
| Within Pops | 135 | 546.400 | 4.047 | 4.047 | 35% | 0.001 |
| Total | 149 | 1659.973 | 11.597 | 100% | ||
| (b) SV (P. coccineus L.) | ||||||
| Among Pops | 11 | 317.433 | 28.858 | 2.406 | 33% | 0.284 |
| Within Pops | 108 | 518.400 | 4.800 | 4.800 | 67% | 0.001 |
| Total | 119 | 835.833 | 7.206 | 100% | ||
| (c) SV (Gigantes-Elephantes-Plake Prespon) | ||||||
| Among Pops | 2 | 506.797 | 253.399 | 9.477 | 93% | 0.934 |
| Within Pops | 87 | 58.225 | 0.669 | 0.669 | 7% | 0.001 |
| Total | 89 | 565.022 | 10.147 | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bosmali, I.; Lagiotis, G.; Ganopoulos, I.; Stefanidou, E.; Madesis, P.; Biliaderis, C.G. Phaseolus coccineus L. Landraces in Greece: Microsatellite Genotyping and Molecular Characterization for Landrace Authenticity and Discrimination. BioTech 2024, 13, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech13020018
Bosmali I, Lagiotis G, Ganopoulos I, Stefanidou E, Madesis P, Biliaderis CG. Phaseolus coccineus L. Landraces in Greece: Microsatellite Genotyping and Molecular Characterization for Landrace Authenticity and Discrimination. BioTech. 2024; 13(2):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech13020018
Chicago/Turabian StyleBosmali, Irene, Georgios Lagiotis, Ioannis Ganopoulos, Eleni Stefanidou, Panagiotis Madesis, and Costas G. Biliaderis. 2024. "Phaseolus coccineus L. Landraces in Greece: Microsatellite Genotyping and Molecular Characterization for Landrace Authenticity and Discrimination" BioTech 13, no. 2: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech13020018
APA StyleBosmali, I., Lagiotis, G., Ganopoulos, I., Stefanidou, E., Madesis, P., & Biliaderis, C. G. (2024). Phaseolus coccineus L. Landraces in Greece: Microsatellite Genotyping and Molecular Characterization for Landrace Authenticity and Discrimination. BioTech, 13(2), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech13020018








