Gene Therapy for Genetic Syndromes: Understanding the Current State to Guide Future Care
Abstract
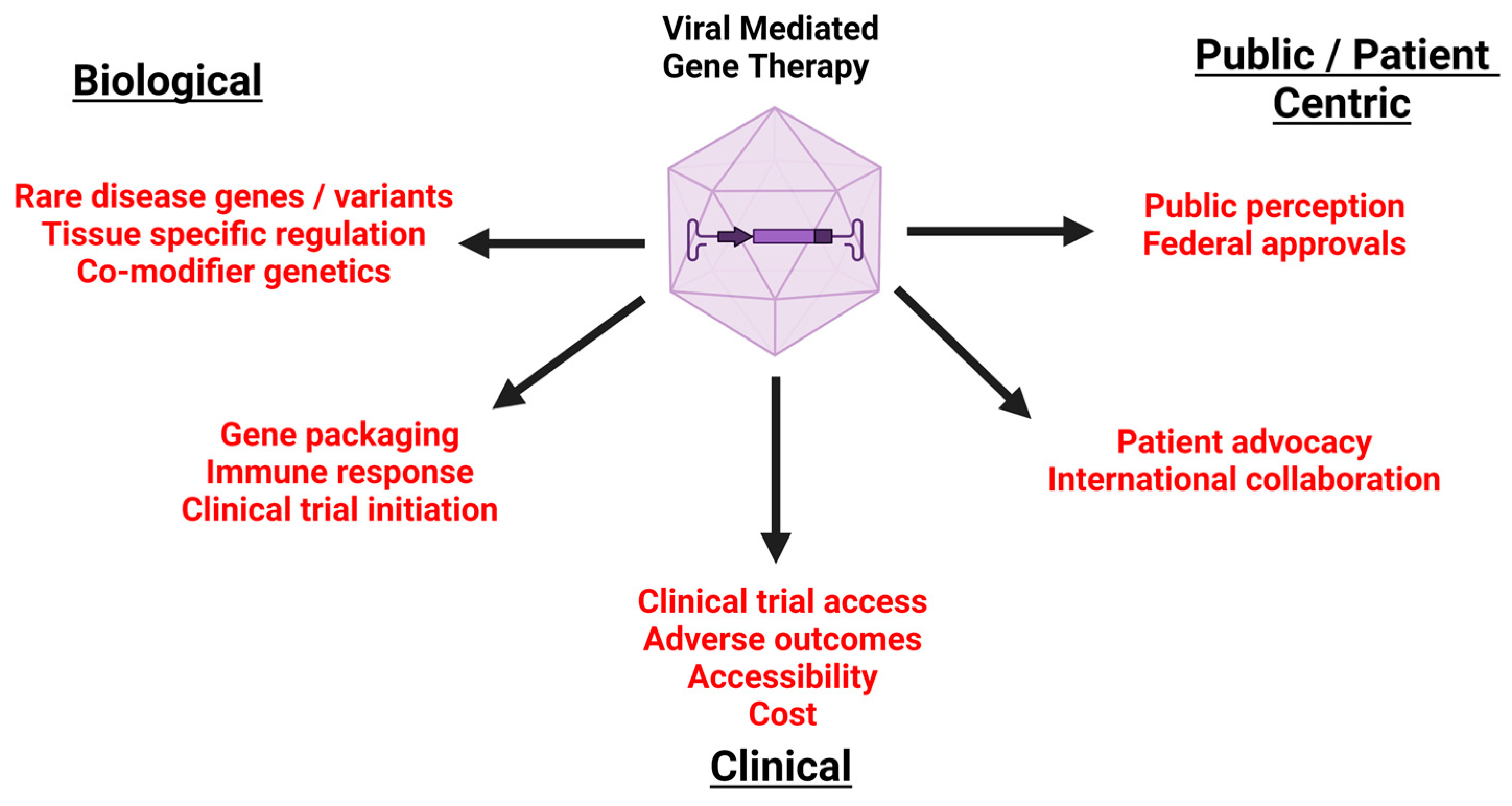
1. Introduction
2. Past and Current Work in Gene Therapy
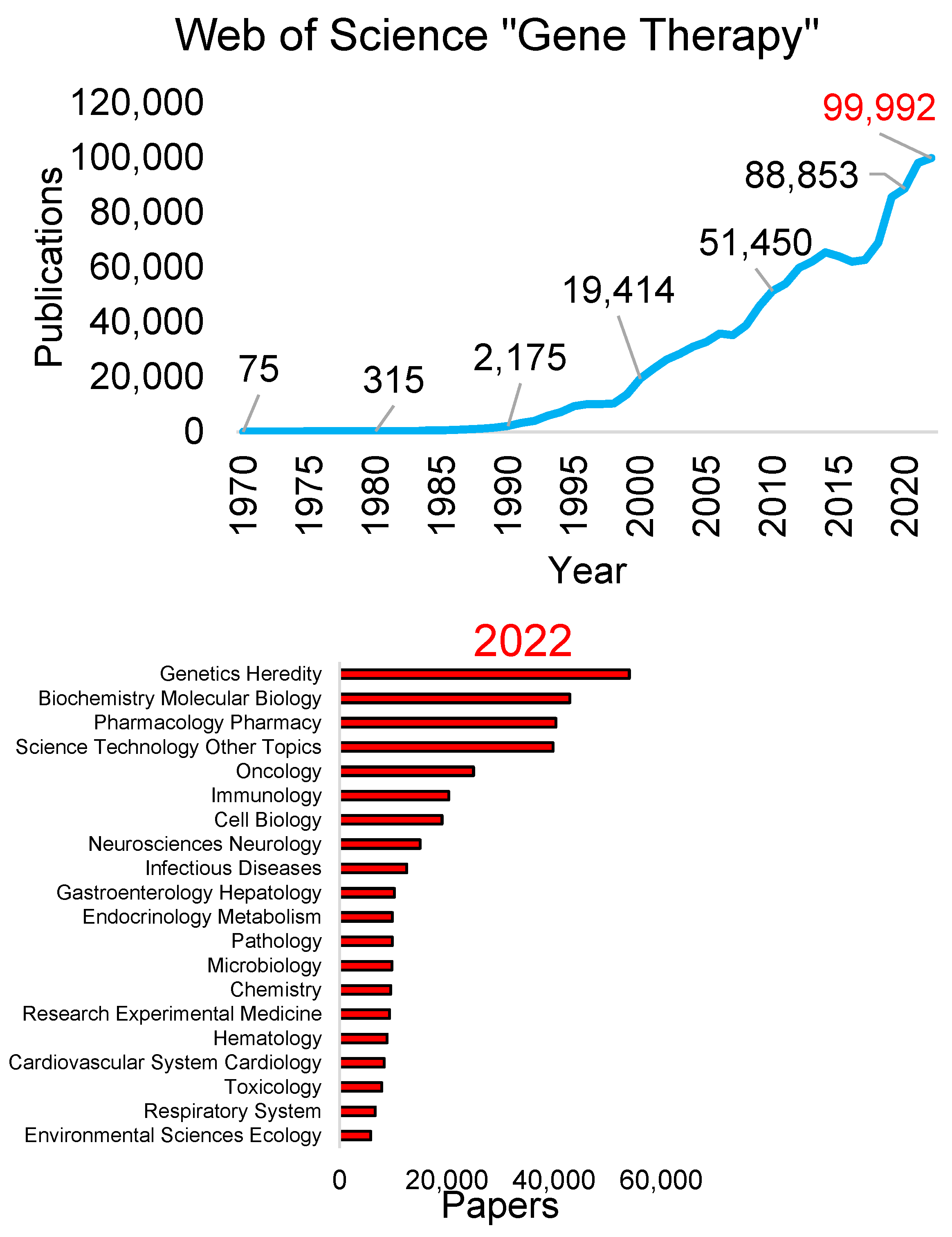
2.1. Publications
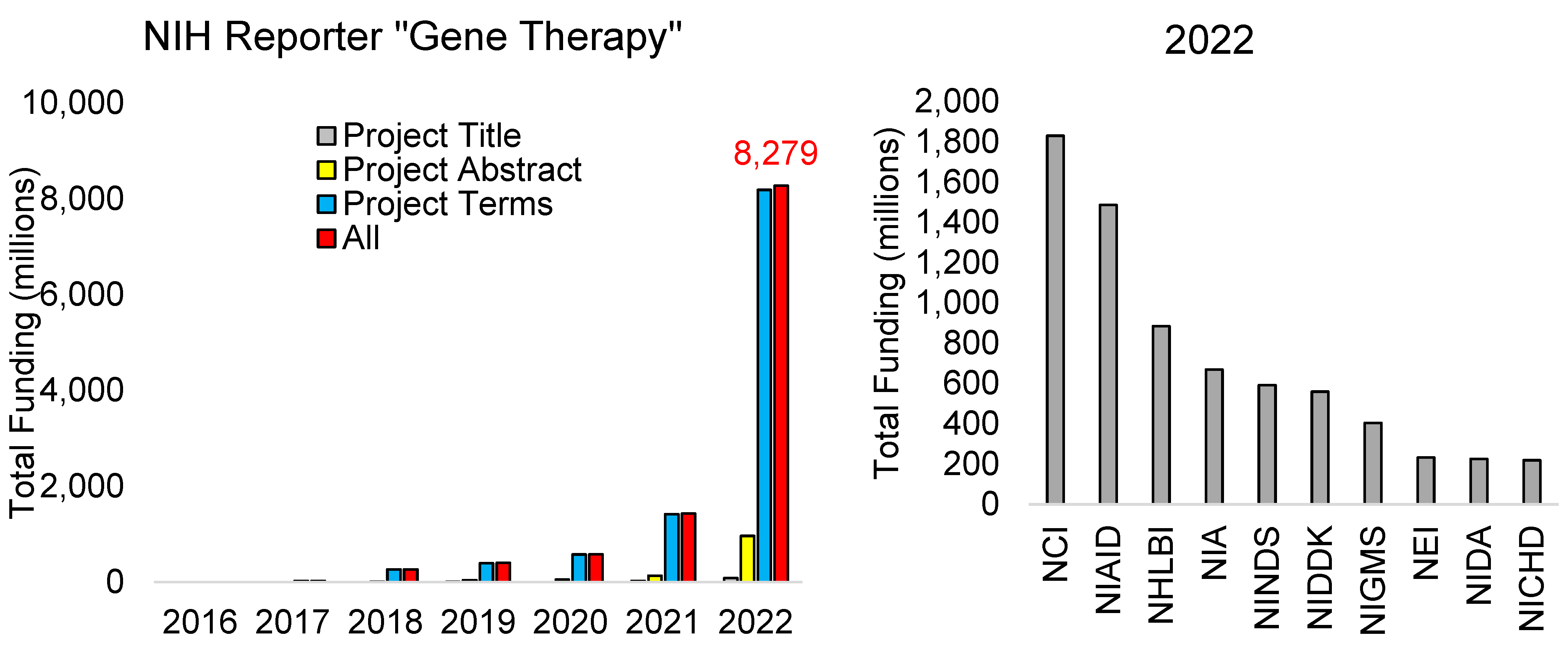
2.2. Funding
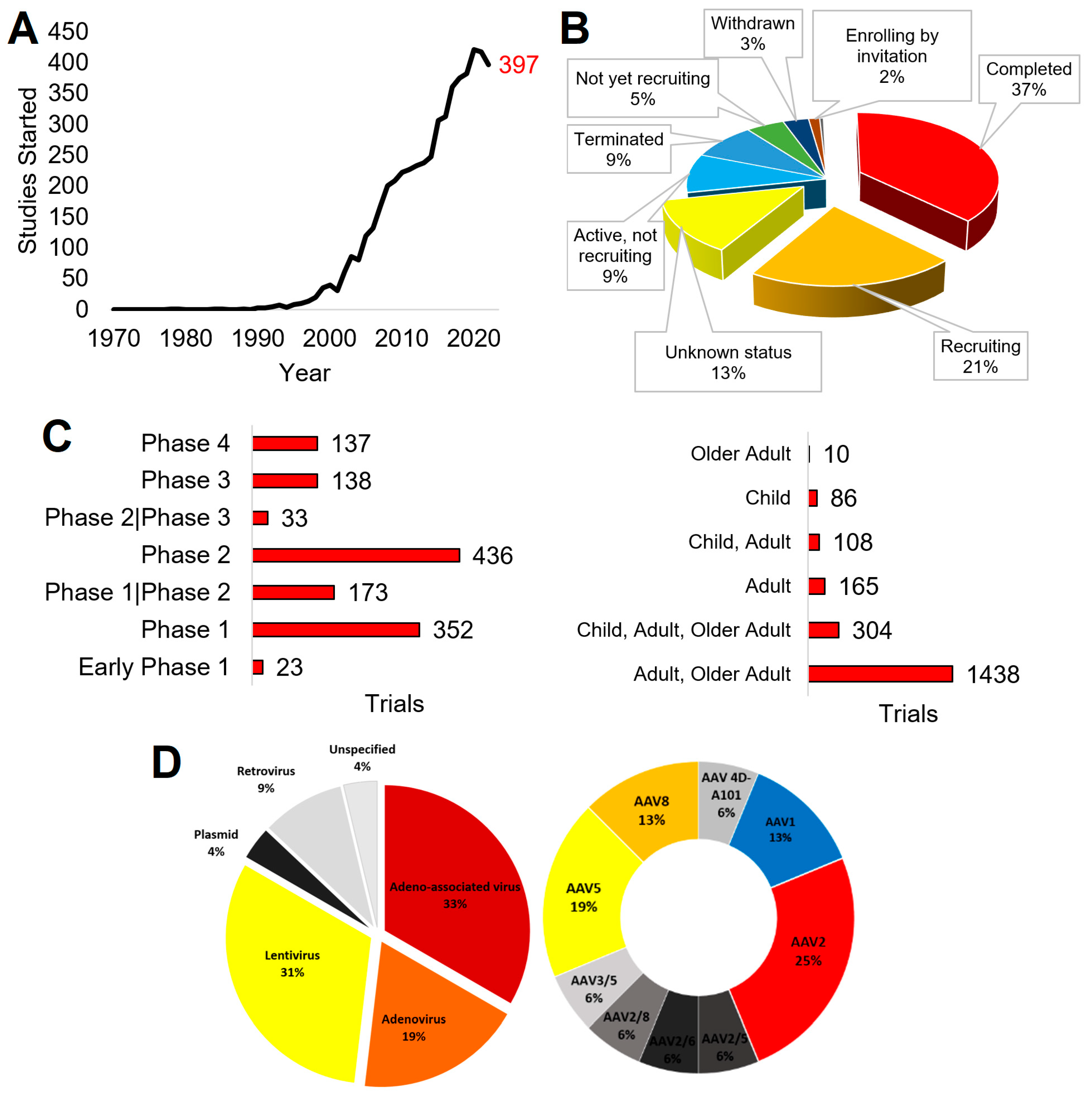
2.3. Clinical Trials
2.4. Approved Therapies
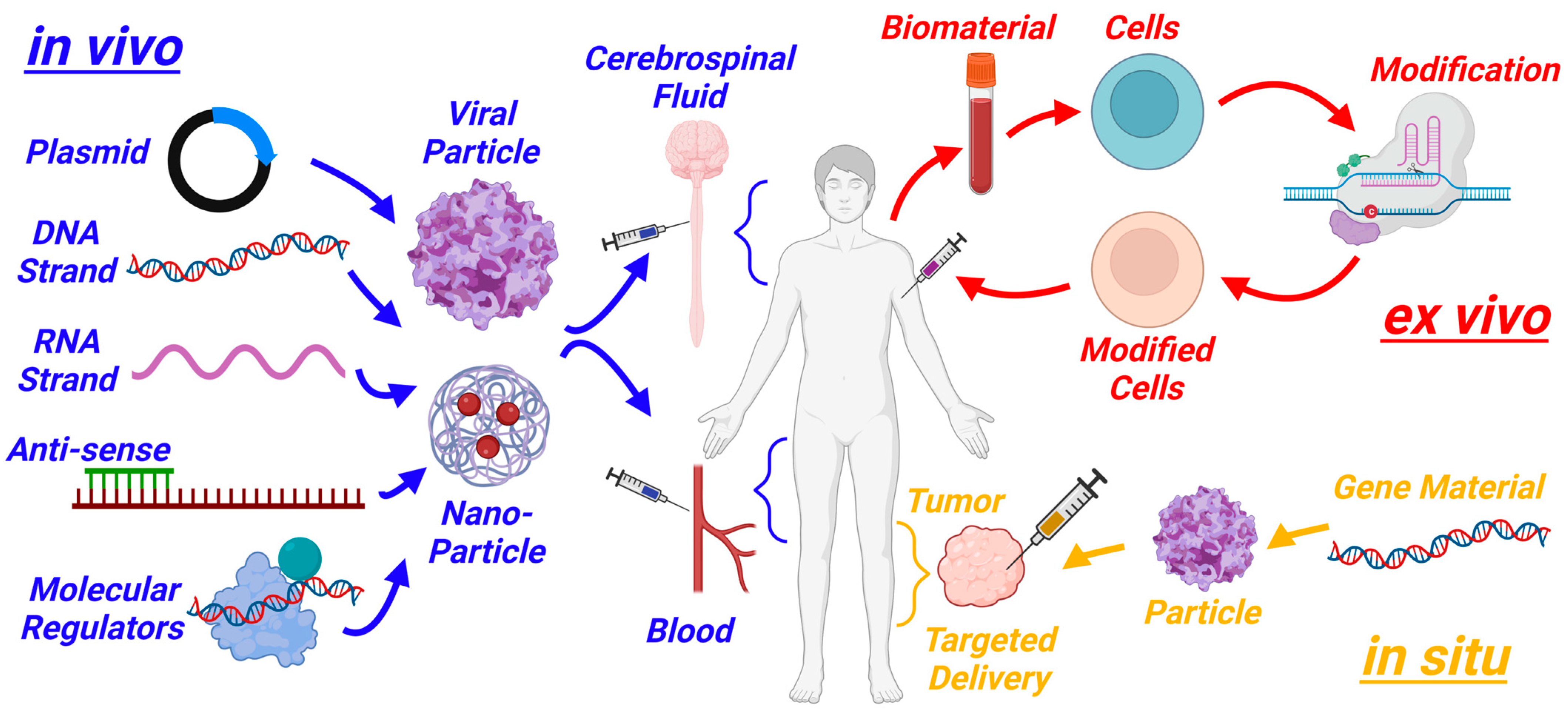
3. Biological Considerations
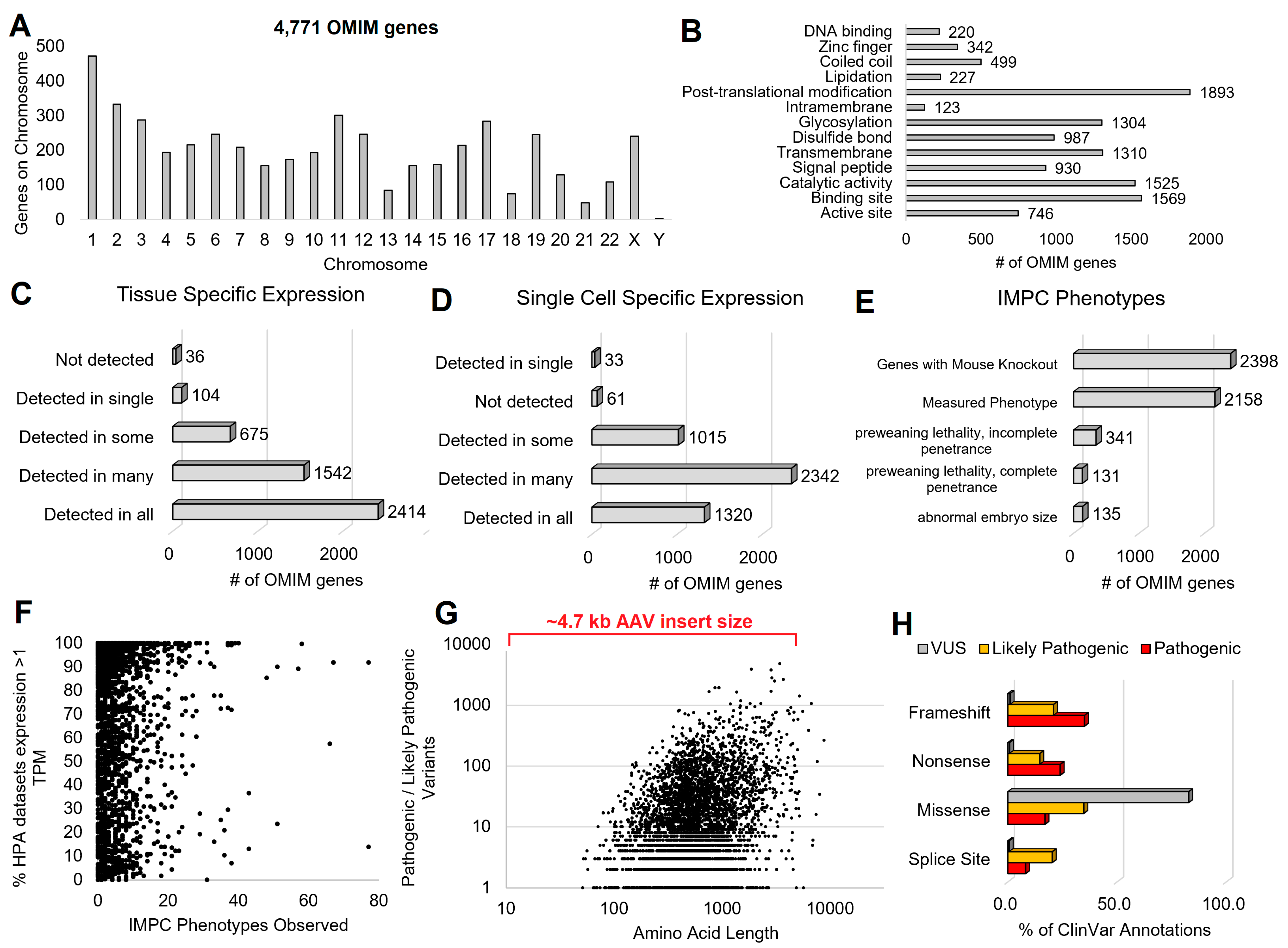
3.1. Genetic Syndromes
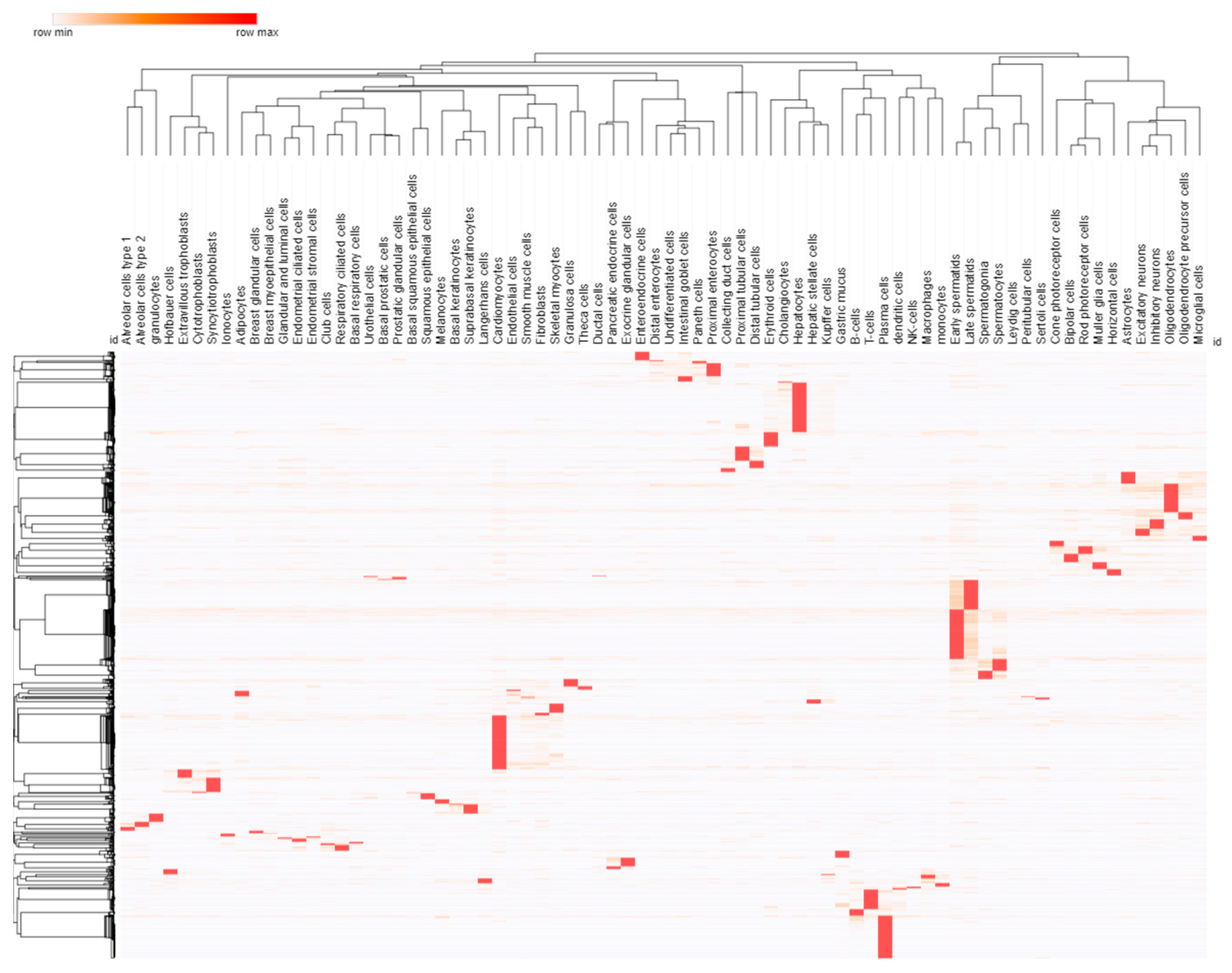
3.2. Cell and Promoter Specificity
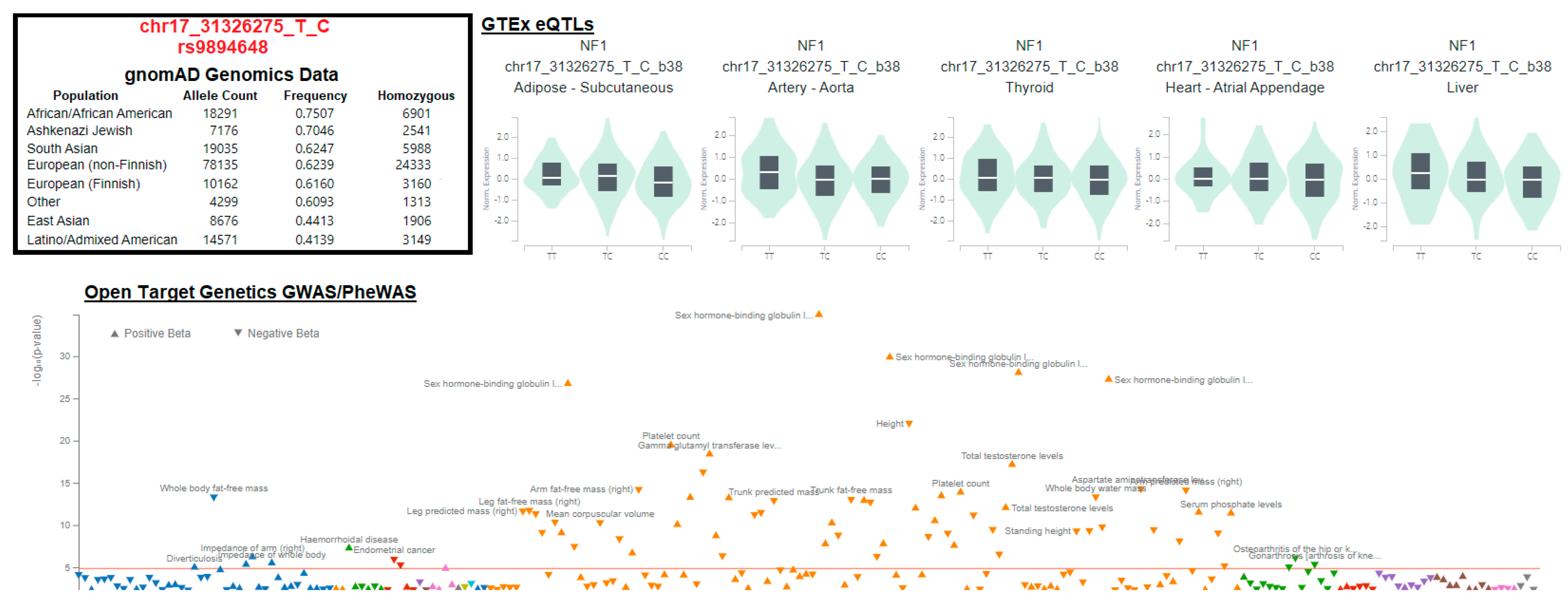
3.3. Variant Location within Proteins
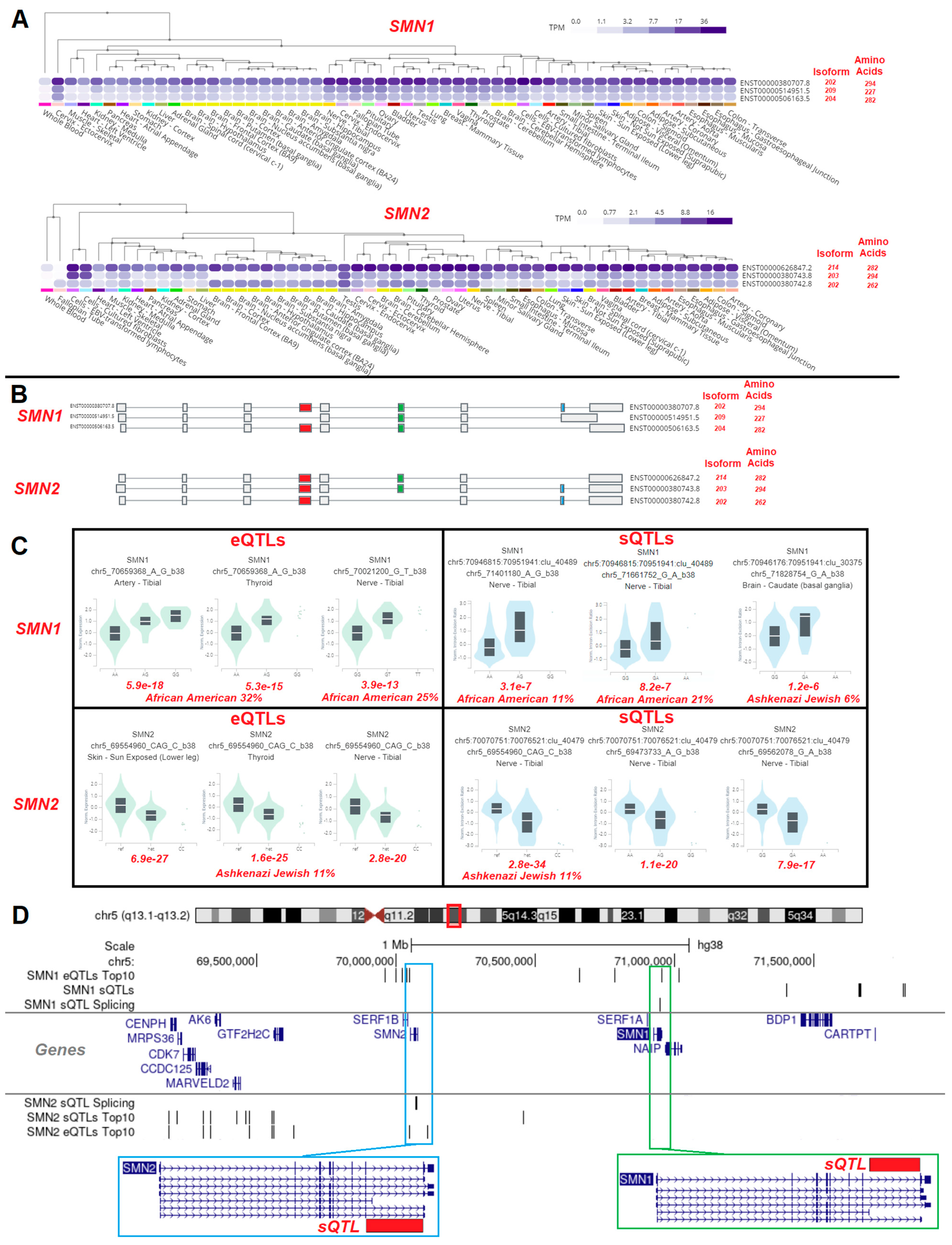
3.4. Gene Isoforms and Common Variants
3.5. Risk of Overexpression
3.6. Delivery Systems
4. Immune Response
5. Cost of Gene Therapy
6. Need for Increased Transparency
7. Ethical Considerations for Gene Therapy—Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Wirth, T.; Parker, N.; Ylä-Herttuala, S. History of Gene Therapy. Gene 2013, 525, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, C.E.; High, K.A.; Joung, J.K.; Kohn, D.B.; Ozawa, K.; Sadelain, M. Gene Therapy Comes of Age. Science 2018, 359, eaan4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermonat, P.L.; Quirk, J.G.; Bishop, B.M.; Han, L. The Packaging Capacity of Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) and the Potential for Wild-Type-Plus AAV Gene Therapy Vectors. FEBS Lett. 1997, 407, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraheem, D.; Elaissari, A.; Fessi, H. Gene Therapy and DNA Delivery Systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 459, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Aneed, A. An Overview of Current Delivery Systems in Cancer Gene Therapy. J. Control. Release 2004, 94, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tai, P.W.L.; Gao, G. Adeno-Associated Virus Vector as a Platform for Gene Therapy Delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 358–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, A.J. The Challenge of Gene Therapy and DNA Delivery. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W.F. Prospects for Human Gene Therapy. Science 1984, 226, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, S.A.; Aebersold, P.; Cornetta, K.; Kasid, A.; Morgan, R.A.; Moen, R.; Karson, E.M.; Lotze, M.T.; Yang, J.C.; Topalian, S.L. Gene Transfer into Humans—Immunotherapy of Patients with Advanced Melanoma, Using Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Modified by Retroviral Gene Transduction. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Cintina, I.; Pariser, A.; Oehrlein, E.; Sullivan, J.; Kennedy, A. The National Economic Burden of Rare Disease in the United States in 2019. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groft, S.C.; Posada, M.; Taruscio, D. Progress, Challenges and Global Approaches to Rare Diseases. Acta Paediatr. 2021, 110, 2711–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieppati, A.; Henter, J.-I.; Daina, E.; Aperia, A. Why Rare Diseases Are an Important Medical and Social Issue. Lancet 2008, 371, 2039–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, L.J.H.; Hegde, M.R. Gene Variant Databases and Sharing: Creating a Global Genomic Variant Database for Personalized Medicine. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boycott, K.M.; Rath, A.; Chong, J.X.; Hartley, T.; Alkuraya, F.S.; Baynam, G.; Brookes, A.J.; Brudno, M.; Carracedo, A.; den Dunnen, J.T.; et al. International Cooperation to Enable the Diagnosis of All Rare Genetic Diseases. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 100, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wain, K.E.; Palen, E.; Savatt, J.M.; Shuman, D.; Finucane, B.; Seeley, A.; Challman, T.D.; Myers, S.M.; Martin, C.L. The Value of Genomic Variant ClinVar Submissions from Clinical Providers: Beyond the Addition of Novel Variants. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 1660–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, C.P.; Cutillo, C.M.; Lau, L.P.L.; Jonker, A.H.; Rath, A.; Julkowska, D.; Thomson, D.; Terry, S.F.; de Montleau, B.; Ardigò, D.; et al. Future of Rare Diseases Research 2017-2027: An IRDiRC Perspective. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2018, 11, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochmüller, H.; Torrent I Farnell, J.; Le Cam, Y.; Jonker, A.H.; Lau, L.P.; Baynam, G.; Kaufmann, P.; Dawkins, H.J.; Lasko, P.; Austin, C.P.; et al. The International Rare Diseases Research Consortium: Policies and Guidelines to Maximize Impact. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 25, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julkowska, D.; Austin, C.P.; Cutillo, C.M.; Gancberg, D.; Hager, C.; Halftermeyer, J.; Jonker, A.H.; Lau, L.P.L.; Norstedt, I.; Rath, A.; et al. The Importance of International Collaboration for Rare Diseases Research: A European Perspective. Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, J.; Taruscio, D.; Llera, V.A.; Barrera, L.A.; Coté, T.R.; Edfjäll, C.; Gavhed, D.; Haffner, M.E.; Nishimura, Y.; Posada, M.; et al. The Need for Worldwide Policy and Action Plans for Rare Diseases. Acta Paediatr. 2012, 101, 805–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowling, K.M.; Thompson, M.L.; Finnila, C.R.; Hiatt, S.M.; Latner, D.R.; Amaral, M.D.; Lawlor, J.M.J.; East, K.M.; Cochran, M.E.; Greve, V.; et al. Genome Sequencing as a First-Line Diagnostic Test for Hospitalized Infants. Genet. Med. 2022, 24, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bupp, C.P.; Ames, E.G.; Arenchild, M.K.; Caylor, S.; Dimmock, D.P.; Fakhoury, J.D.; Karna, P.; Lehman, A.; Meghea, C.I.; Misra, V.; et al. Breaking Barriers to Rapid Whole Genome Sequencing in Pediatrics: Michigan’s Project Baby Deer. Children 2023, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokop, J.W.; May, T.; Strong, K.; Bilinovich, S.M.; Bupp, C.; Rajasekaran, S.; Worthey, E.A.; Lazar, J. Genome Sequencing in the Clinic: The Past, Present, and Future of Genomic Medicine. Physiol. Genom. 2018, 50, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokop, J.W.; Jdanov, V.; Savage, L.; Morris, M.; Lamb, N.; VanSickle, E.; Stenger, C.L.; Rajasekaran, S.; Bupp, C.P. Computational and Experimental Analysis of Genetic Variants. Compr. Physiol. 2022, 12, 3303–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokop, J.W.; Lazar, J.; Crapitto, G.; Smith, D.C.; Worthey, E.A.; Jacob, H.J. Molecular Modeling in the Age of Clinical Genomics, the Enterprise of the next Generation. J. Mol. Model. 2017, 23, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, S.; Bupp, C.P.; Leimanis-Laurens, M.; Shukla, A.; Russell, C.; Junewick, J.; Gleason, E.; VanSickle, E.A.; Edgerly, Y.; Wittmann, B.M.; et al. Repurposing Eflornithine to Treat a Patient with a Rare ODC1 Gain-of-Function Variant Disease. Elife 2021, 10, e67097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stainier, D.Y.R.; Raz, E.; Lawson, N.D.; Ekker, S.C.; Burdine, R.D.; Eisen, J.S.; Ingham, P.W.; Schulte-Merker, S.; Yelon, D.; Weinstein, B.M.; et al. Guidelines for Morpholino Use in Zebrafish. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1007000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heasman, J.; Holwill, S.; Wylie, C.C. Fertilization of Cultured Xenopus Oocytes and Use in Studies of Maternally Inherited Molecules. Methods Cell Biol. 1991, 36, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heasman, J. Morpholino Oligos: Making Sense of Antisense? Dev. Biol. 2002, 243, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasevicius, A.; Ekker, S.C. Effective Targeted Gene “knockdown” in Zebrafish. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bill, B.R.; Petzold, A.M.; Clark, K.J.; Schimmenti, L.A.; Ekker, S.C. A Primer for Morpholino Use in Zebrafish. Zebrafish 2009, 6, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robu, M.E.; Larson, J.D.; Nasevicius, A.; Beiraghi, S.; Brenner, C.; Farber, S.A.; Ekker, S.C. P53 Activation by Knockdown Technologies. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scacheri, P.C.; Rozenblatt-Rosen, O.; Caplen, N.J.; Wolfsberg, T.G.; Umayam, L.; Lee, J.C.; Hughes, C.M.; Shanmugam, K.S.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Meyerson, M.; et al. Short Interfering RNAs Can Induce Unexpected and Divergent Changes in the Levels of Untargeted Proteins in Mammalian Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1892–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerton, J.E. Morpholino, siRNA, and S-DNA Compared: Impact of Structure and Mechanism of Action on off-Target Effects and Sequence Specificity. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, J.S.; Smith, J.C. Controlling Morpholino Experiments: Don’t Stop Making Antisense. Development 2008, 135, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedell, V.M.; Westcot, S.E.; Ekker, S.C. Lessons from Morpholino-Based Screening in Zebrafish. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2011, 10, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokop, J.W.; Yeo, N.C.; Ottmann, C.; Chhetri, S.B.; Florus, K.L.; Ross, E.J.; Sosonkina, N.; Link, B.A.; Freedman, B.I.; Coppola, C.J.; et al. Characterization of Coding/Noncoding Variants for SHROOM3 in Patients with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte-Merker, S.; Stainier, D.Y.R. Out with the Old, in with the New: Reassessing Morpholino Knockdowns in Light of Genome Editing Technology. Development 2014, 141, 3103–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orloff, J.; Douglas, F.; Pinheiro, J.; Levinson, S.; Branson, M.; Chaturvedi, P.; Ette, E.; Gallo, P.; Hirsch, G.; Mehta, C.; et al. The Future of Drug Development: Advancing Clinical Trial Design. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, V.; Seoane-Vazquez, E.; Fawaz, S.; Brown, L.; Rodriguez-Monguio, R. The Landscape of Cellular and Gene Therapy Products: Authorization, Discontinuations, and Cost. Hum. Gene Ther. Clin. Dev. 2019, 30, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, B. An Update of the Mutation Spectrum of the Survival Motor Neuron Gene (SMN1) in Autosomal Recessive Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA). Hum. Mutat. 2000, 15, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, D.M.; Stevens, C.F.; Parker, A.; Saavedra-Matiz, C.A.; Sack, V.; Chung, W.K.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Engelstad, K.; Laureta, E.; Farooq, O.; et al. Implementation of Population-Based Newborn Screening Reveals Low Incidence of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Genet. Med. 2020, 22, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.W.; Finkel, R.S.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Connolly, A.M.; Crawford, T.O.; Darras, B.T.; Iannaccone, S.T.; Kuntz, N.L.; Peña, L.D.M.; Shieh, P.B.; et al. Onasemnogene Abeparvovec Gene Therapy for Symptomatic Infantile-Onset Spinal Muscular Atrophy in Patients with Two Copies of SMN2 (STR1VE): An Open-Label, Single-Arm, Multicentre, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, K.A.; Farrar, M.A.; Muntoni, F.; Saito, K.; Mendell, J.R.; Servais, L.; McMillan, H.J.; Finkel, R.S.; Swoboda, K.J.; Kwon, J.M.; et al. Onasemnogene Abeparvovec for Presymptomatic Infants with Two Copies of SMN2 at Risk for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type 1: The Phase III SPR1NT Trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.L. The Blunt End: Surgical Challenges of Gene Therapy for Inherited Retinal Diseases. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 196, xxv–xxix. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, F.; Duncan, C.; Musolino, P.L.; Orchard, P.J.; De Oliveira, S.; Thrasher, A.J.; Armant, M.; Dansereau, C.; Lund, T.C.; Miller, W.P.; et al. Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Gene Therapy for Cerebral Adrenoleukodystrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1630–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, F.; Thompson, A.A.; Kwiatkowski, J.L.; Porter, J.B.; Thrasher, A.J.; Hongeng, S.; Sauer, M.G.; Thuret, I.; Lal, A.; Algeri, M.; et al. Betibeglogene Autotemcel Gene Therapy for Non-Β0/Β0 Genotype β-Thalassemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, N.J.; Yu-Wai-Man, P.; Carelli, V.; Biousse, V.; Moster, M.L.; Vignal-Clermont, C.; Sergott, R.C.; Klopstock, T.; Sadun, A.A.; Girmens, J.-F.; et al. Intravitreal Gene Therapy vs. Natural History in Patients With Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy Carrying the m.11778G>A ND4 Mutation: Systematic Review and Indirect Comparison. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 662838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, M.L.; Moss, R.B.; Waltz, D.A.; Dovey, M.E.; Tonelli, M.R.; McNamara, S.C.; Gibson, R.L.; Ramsey, B.W.; Carter, B.J.; Reynolds, T.C. A Phase I Study of Aerosolized Administration of tgAAVCF to Cystic Fibrosis Subjects with Mild Lung Disease. Hum. Gene Ther. 2001, 12, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, R.B.; Rodman, D.; Spencer, L.T.; Aitken, M.L.; Zeitlin, P.L.; Waltz, D.; Milla, C.; Brody, A.S.; Clancy, J.P.; Ramsey, B.; et al. Repeated Adeno-Associated Virus Serotype 2 Aerosol-Mediated Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Regulator Gene Transfer to the Lungs of Patients with Cystic Fibrosis: A Multicenter, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Chest 2004, 125, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, R.B.; Milla, C.; Colombo, J.; Accurso, F.; Zeitlin, P.L.; Clancy, J.P.; Spencer, L.T.; Pilewski, J.; Waltz, D.A.; Dorkin, H.L.; et al. Repeated Aerosolized AAV-CFTR for Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Phase 2B Trial. Hum. Gene Ther. 2007, 18, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.; Bennett, J.; Wellman, J.A.; Chung, D.C.; Yu, Z.-F.; Tillman, A.; Wittes, J.; Pappas, J.; Elci, O.; McCague, S.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Voretigene Neparvovec (AAV2-hRPE65v2) in Patients with RPE65-Mediated Inherited Retinal Dystrophy: A Randomised, Controlled, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozelo, M.C.; Mahlangu, J.; Pasi, K.J.; Giermasz, A.; Leavitt, A.D.; Laffan, M.; Symington, E.; Quon, D.V.; Wang, J.-D.; Peerlinck, K.; et al. Valoctocogene Roxaparvovec Gene Therapy for Hemophilia A. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, V. Spinraza-a Rare Disease Success Story. Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercuri, E.; Darras, B.T.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Day, J.W.; Campbell, C.; Connolly, A.M.; Iannaccone, S.T.; Kirschner, J.; Kuntz, N.L.; Saito, K.; et al. Nusinersen versus Sham Control in Later-Onset Spinal Muscular Atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, P.G.; Mall, M.A.; Dřevínek, P.; Lands, L.C.; McKone, E.F.; Polineni, D.; Ramsey, B.W.; Taylor-Cousar, J.L.; Tullis, E.; Vermeulen, F.; et al. Elexacaftor-Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor for Cystic Fibrosis with a Single Phe508del Allele. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, P.J.; Mall, M.A.; Álvarez, A.; Colombo, C.; de Winter-de Groot, K.M.; Fajac, I.; McBennett, K.A.; McKone, E.F.; Ramsey, B.W.; Sutharsan, S.; et al. Triple Therapy for Cystic Fibrosis Phe508del-Gating and -Residual Function Genotypes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amberger, J.S.; Bocchini, C.A.; Schiettecatte, F.; Scott, A.F.; Hamosh, A. OMIM.Org: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM®), an Online Catalog of Human Genes and Genetic Disorders. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D789–D798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt Consortium UniProt: A Hub for Protein Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D204–D212. [CrossRef]
- Uhlen, M.; Oksvold, P.; Fagerberg, L.; Lundberg, E.; Jonasson, K.; Forsberg, M.; Zwahlen, M.; Kampf, C.; Wester, K.; Hober, S.; et al. Towards a Knowledge-Based Human Protein Atlas. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 1248–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehan, T.F.; Conte, N.; West, D.B.; Jacobsen, J.O.; Mason, J.; Warren, J.; Chen, C.-K.; Tudose, I.; Relac, M.; Matthews, P.; et al. Disease Model Discovery from 3,328 Gene Knockouts by The International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Benson, M.; Brown, G.; Chao, C.; Chitipiralla, S.; Gu, B.; Hart, J.; Hoffman, D.; Hoover, J.; et al. ClinVar: Public Archive of Interpretations of Clinically Relevant Variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D862–D868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, W.; Stein, U. Cell Type Specific and Inducible Promoters for Vectors in Gene Therapy as an Approach for Cell Targeting. J. Mol. Med. 1996, 74, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Douarin, N.M.; Creuzet, S.; Couly, G.; Dupin, E. Neural Crest Cell Plasticity and Its Limits. Development 2004, 131, 4637–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, P.R.; Murray, S.A.; Yang, T.; Eby, A.; Lai, A.; Lu, D.; Zieba, J.; Rajasekaran, S.; VanSickle, E.A.; Rossetti, L.Z.; et al. Autosomal Recessive LRP1-Related Syndrome Featuring Cardiopulmonary Dysfunction, Bone Dysmorphology, and Corneal Clouding. Cold Spring Harb. Mol. Case Stud. 2022, 8, a006169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Møller, R.S.; Weckhuysen, S.; Chipaux, M.; Marsan, E.; Taly, V.; Bebin, E.M.; Hiatt, S.M.; Prokop, J.W.; Bowling, K.M.; Mei, D.; et al. Germline and Somatic Mutations in the MTOR Gene in Focal Cortical Dysplasia and Epilepsy. Neurol. Genet. 2016, 2, e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtz, A.M.; VanCoillie, R.; Vansickle, E.A.; Carere, D.A.; Withrow, K.; Torti, E.; Juusola, J.; Millan, F.; Person, R.; Guillen Sacoto, M.J.; et al. Heterozygous Variants in MYH10 Associated with Neurodevelopmental Disorders and Congenital Anomalies with Evidence for Primary Cilia-Dependent Defects in Hedgehog Signaling. Genet. Med. 2022, 24, 2065–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, L.; Adams, S.D.; James, K.; Chowdhury, S.; Rajasekaran, S.; Prokop, J.W.; Bupp, C. Rapid Whole-Genome Sequencing Identifies a Homozygous Novel Variant, His540Arg, in HSD17B4 Resulting in D-Bifunctional Protein Deficiency Disorder Diagnosis. Cold Spring Harb. Mol. Case Stud. 2020, 6, a005496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, T.W.; Wilstermann, A.M.; Mitchell, J.T.; Arnold, N.E.; Rajasekaran, S.; Bupp, C.P.; Prokop, J.W. Understanding Insulin in the Age of Precision Medicine and Big Data: Under-Explored Nature of Genomics. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, A.; Prokop, J.W.; Underwood, A.; Uhl, K.L.; VanSickle, E.A.; Baruwal, R.; Wajda, M.; Rajasekaran, S.; Bupp, C. NAA10 Variant in 38-Week-Gestation Male Patient: A Case Study. Cold Spring Harb. Mol. Case Stud. 2020, 6, a005868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, A.; Rasicci, D.T.; Hinds, D.; Mitchell, J.T.; Zieba, J.K.; Mills, J.; Arnold, N.E.; Cook, T.W.; Moustaqil, M.; Gambin, Y.; et al. Evolutionary Landscape of SOX Genes to Inform Genotype-to-Phenotype Relationships. Genes 2023, 14, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijders Blok, L.; Hiatt, S.M.; Bowling, K.M.; Prokop, J.W.; Engel, K.L.; Cochran, J.N.; Bebin, E.M.; Bijlsma, E.K.; Ruivenkamp, C.A.L.; Terhal, P.; et al. De Novo Mutations in MED13, a Component of the Mediator Complex, Are Associated with a Novel Neurodevelopmental Disorder. Hum. Genet. 2018, 137, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GTEx Consortium. The GTEx Consortium Atlas of Genetic Regulatory Effects across Human Tissues. Science 2020, 369, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.S.; Sherry, E.C.; Vaughan, R.M.; Henderson, M.L.; Zieba, J.; Uhl, K.L.; Koehn, O.; Bupp, C.P.; Rajasekaran, S.; Li, X.; et al. The Complex, Dynamic SpliceOme of the Small GTPase Transcripts Altered by Technique, Sex, Genetics, Tissue Specificity, and RNA Base Editing. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1033695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehm, H.L.; Berg, J.S.; Brooks, L.D.; Bustamante, C.D.; Evans, J.P.; Landrum, M.J.; Ledbetter, D.H.; Maglott, D.R.; Martin, C.L.; Nussbaum, R.L.; et al. ClinGen—The Clinical Genome Resource. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2235–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, R.-Y.; Esposito, D.; Tam, A.J.; McCormick, F.; Riggins, G.J.; Wade Clapp, D.; Staedtke, V. Feasibility of Using NF1-GRD and AAV for Gene Replacement Therapy in NF1-Associated Tumors. Gene Ther. 2019, 26, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho-Silva, D.; Pierleoni, A.; Pignatelli, M.; Ong, C.; Fumis, L.; Karamanis, N.; Carmona, M.; Faulconbridge, A.; Hercules, A.; McAuley, E.; et al. Open Targets Platform: New Developments and Updates Two Years On. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1056–D1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayerossadat, N.; Maedeh, T.; Ali, P.A. Viral and Nonviral Delivery Systems for Gene Delivery. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2012, 1, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Tang, L.; Yang, L. Nonviral Delivery Systems of mRNA Vaccines for Cancer Gene Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchin, R.; Troyer, Z.; Witwer, K.; Morris, K.V. Extracellular Vesicles: The next Generation in Gene Therapy Delivery. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, N.; Allawadhi, P.; Khurana, A.; Singh, V.; Navik, U.; Pasumarthi, S.K.; Khurana, I.; Banothu, A.K.; Weiskirchen, R.; Bharani, K.K. Gene Therapy: Comprehensive Overview and Therapeutic Applications. Life Sci. 2022, 294, 120375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucchiarini, M. Human Gene Therapy: Novel Approaches to Improve the Current Gene Delivery Systems. Discov. Med. 2016, 21, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanders, M.; Lawlor, J.M.J.; Li, X.; Schuen, J.N.; Millard, S.L.; Zhang, X.; Buck, L.; Grysko, B.; Uhl, K.L.; Hinds, D.; et al. Genomic, Transcriptomic, and Protein Landscape Profile of CFTR and Cystic Fibrosis. Hum. Genet. 2021, 140, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keswani, S.G.; Balaji, S.; Le, L.; Leung, A.; Katz, A.B.; Lim, F.-Y.; Habli, M.; Jones, H.N.; Wilson, J.M.; Crombleholme, T.M. Pseudotyped AAV Vector-Mediated Gene Transfer in a Human Fetal Trachea Xenograft Model: Implications for in Utero Gene Therapy for Cystic Fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limberis, M.P.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Zhang, L.; Pickles, R.J.; Wilson, J.M. Transduction Efficiencies of Novel AAV Vectors in Mouse Airway Epithelium In Vivo and Human Ciliated Airway Epithelium In Vitro. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bals, R.; Xiao, W.; Sang, N.; Weiner, D.J.; Meegalla, R.L.; Wilson, J.M. Transduction of Well-Differentiated Airway Epithelium by Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Is Limited by Vector Entry. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 6085–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirninger, J.; Muller, C.; Braag, S.; Tang, Q.; Yue, H.; Detrisac, C.; Ferkol, T.; Guggino, W.B.; Flotte, T.R. Functional Characterization of a Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus 5-Pseudotyped Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Vector. Hum. Gene Ther. 2004, 15, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabner, J.; Seiler, M.; Walters, R.; Kotin, R.M.; Fulgeras, W.; Davidson, B.L.; Chiorini, J.A. Adeno-Associated Virus Type 5 (AAV5) but Not AAV2 Binds to the Apical Surfaces of Airway Epithelia and Facilitates Gene Transfer. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 3852–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.C.; Smith, C.I.; Cebotaru, L.; Zhang, X.; Askin, F.B.; Wright, J.; Guggino, S.E.; Adams, R.J.; Flotte, T.; Guggino, W.B. Expression of a Truncated Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator with an AAV5-Pseudotyped Vector in Primates. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Lou, H.H.; Boyer, J.L.; Limberis, M.P.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Hackett, N.R.; Leopold, P.L.; Wilson, J.M.; Crystal, R.G. Functional Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Expression in Cystic Fibrosis Airway Epithelial Cells by AAV6.2-Mediated Segmental Trans-Splicing. Hum. Gene Ther. 2009, 20, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffon, K.J.D.A.; Koerber, J.T.; Dickey, D.D.; Murtha, M.; Keshavjee, S.; Kaspar, B.K.; Zabner, J.; Schaffer, D.V. Directed Evolution of Adeno-Associated Virus to an Infectious Respiratory Virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3865–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Johnson, J.S.; Zhijian, W.; Grieger, J.C.; Ping-Jie, X.; Drouin, L.M.; Agbandje-McKenna, M.; Pickles, R.J.; Samulski, R.J. Generation of Novel AAV Variants by Directed Evolution for Improved CFTR Delivery to Human Ciliated Airway Epithelium. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 2067–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paunovska, K.; Loughrey, D.; Dahlman, J.E. Drug Delivery Systems for RNA Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasbrouck, N.C.; High, K.A. AAV-Mediated Gene Transfer for the Treatment of Hemophilia B: Problems and Prospects. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muruve, D.A.; Barnes, M.J.; Stillman, I.E.; Libermann, T.A. Adenoviral Gene Therapy Leads to Rapid Induction of Multiple Chemokines and Acute Neutrophil-Dependent Hepatic Injury In Vivo. Hum. Gene Ther. 1999, 10, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, P.; Lai, H.; Zhong, W.; Feng, N.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; et al. AAV Induces Hepatic Necroptosis and Carcinoma in Diabetic and Obese Mice Dependent on Pebp1 Pathway. EMBO Mol. Med. 2023, 15, e17230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deverman, B.E.; Ravina, B.M.; Bankiewicz, K.S.; Paul, S.M.; Sah, D.W.Y. Gene Therapy for Neurological Disorders: Progress and Prospects. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.R.; Markusic, D.M.; Biswas, M.; High, K.A.; Herzog, R.W. Clinical Development of Gene Therapy: Results and Lessons from Recent Successes. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2016, 3, 16034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Lourenço, S.P.; Hidalgo, I.J. Development of Gene Therapy Vectors: Remaining Challenges. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.E.; Ehrhardt, A.; Kay, M.A. Progress and Problems with the Use of Viral Vectors for Gene Therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2003, 4, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, J.L.; de Jong, Y.P.; Terhorst, C.; Herzog, R.W. Immune Responses to Viral Gene Therapy Vectors. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, T.K.; Samulski, R.J. Addressing High Dose AAV Toxicity—“One and Done” or “Slower and Lower”? Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2022, 22, 1067–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehrman, S. Virus Treatment Questioned after Gene Therapy Death. Nature 1999, 401, 517–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somanathan, S.; Calcedo, R.; Wilson, J.M. Adenovirus-Antibody Complexes Contributed to Lethal Systemic Inflammation in a Gene Therapy Trial. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.M.; Flotte, T.R. Moving Forward After Two Deaths in a Gene Therapy Trial of Myotubular Myopathy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2020, 31, 695–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendell, J.R.; Connolly, A.M.; Lehman, K.J.; Griffin, D.A.; Khan, S.Z.; Dharia, S.D.; Quintana-Gallardo, L.; Rodino-Klapac, L.R. Testing Preexisting Antibodies Prior to AAV Gene Transfer Therapy: Rationale, Lessons and Future Considerations. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2022, 25, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowitz, J.; Chan, Y.K.; Samulski, R.J. Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) versus Immune Response. Viruses 2019, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mennechet, F.J.D.; Paris, O.; Ouoba, A.R.; Salazar Arenas, S.; Sirima, S.B.; Takoudjou Dzomo, G.R.; Diarra, A.; Traore, I.T.; Kania, D.; Eichholz, K.; et al. A Review of 65 Years of Human Adenovirus Seroprevalence. Expert. Rev. Vaccines 2019, 18, 597–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri, A.; Shelke, R.; Guan, S.; Somanathan, S. Higher Seroprevalence of Anti-Adeno-Associated Viral Vector Neutralizing Antibodies Among Racial Minorities in the United States. Hum. Gene Ther. 2022, 33, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, B.C.; Donohoe, C.; Akmaev, V.R.; Sugarman, E.A.; Labrousse, P.; Boguslavskiy, L.; Flynn, K.; Rohlfs, E.M.; Walker, A.; Allitto, B.; et al. Differences in SMN1 Allele Frequencies among Ethnic Groups within North America. J. Med. Genet. 2009, 46, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, R.W.; Biswas, M. Neutralizing the Neutralizers in AAV Gene Therapy. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 1741–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leborgne, C.; Barbon, E.; Alexander, J.M.; Hanby, H.; Delignat, S.; Cohen, D.M.; Collaud, F.; Muraleetharan, S.; Lupo, D.; Silverberg, J.; et al. IgG-Cleaving Endopeptidase Enables In Vivo Gene Therapy in the Presence of Anti-AAV Neutralizing Antibodies. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampson, G.; Towse, A.; Pearson, S.D.; Dreitlein, W.B.; Henshall, C. Gene Therapy: Evidence, Value and Affordability in the US Health Care System. J. Comp. Eff. Res. 2018, 7, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chand, D.; Mohr, F.; McMillan, H.; Tukov, F.F.; Montgomery, K.; Kleyn, A.; Sun, R.; Tauscher-Wisniewski, S.; Kaufmann, P.; Kullak-Ublick, G. Hepatotoxicity Following Administration of Onasemnogene Abeparvovec (AVXS-101) for the Treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landfeldt, E. Gene Therapy for Neuromuscular Diseases: Health Economic Challenges and Future Perspectives. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2022, 9, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, R.; Jensen, I.; Cyr, P.; Miller, B.; Maru, B.; Sproule, D.M.; Feltner, D.E.; Wiesner, T.; Malone, D.C.; Bischof, M.; et al. An Updated Cost-Utility Model for Onasemnogene Abeparvovec (Zolgensma®) in Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type 1 Patients and Comparison with Evaluation by the Institute for Clinical and Effectiveness Review (ICER). J. Mark. Access Health Policy 2021, 9, 1889841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broekhoff, T.F.; Sweegers, C.C.G.; Krijkamp, E.M.; Mantel-Teeuwisse, A.K.; Leufkens, H.G.M.; Goettsch, W.G.; Vreman, R.A. Early Cost-Effectiveness of Onasemnogene Abeparvovec-Xioi (Zolgensma) and Nusinersen (Spinraza) Treatment for Spinal Muscular Atrophy I in The Netherlands With Relapse Scenarios. Value Health 2021, 24, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.M. Gene Therapy for Neuromuscular Disorders: Prospects and Ethics. Arch. Dis. Child. 2022, 107, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, R.; Cook, F.; Hunt, T.; Malech, H.L.; Reilly, P.; Foss-Campbell, B.; Barrett, D. Addressing the Value of Gene Therapy and Enhancing Patient Access to Transformative Treatments. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 2717–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, M.G.; Pawlik, T.M.; Fader, A.N.; Esnaola, N.F.; Makary, M.A. The Orphan Drug Act: Restoring the Mission to Rare Diseases. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 39, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockdale, A. Waiting for the Cure: Mapping the Social Relations of Human Gene Therapy Research. Sociol. Health Illn. 1999, 21, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, G. Gene Therapy Is in Danger of Being Overhyped, Expert Says. BMJ 2008, 336, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhove, J.; Osenk, I.; Prichard, I.; Donnelley, M. Public Acceptability of Gene Therapy and Gene Editing for Human Use: A Systematic Review. Hum. Gene Ther. 2020, 31, 20–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, W. A Rare Disease Patient/Caregiver Perspective on Fair Pricing and Access to Gene-Based Therapies. Gene Ther. 2019, 27, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addison, C.; Lassen, J. “My Whole Life Is Ethics!” Ordinary Ethics and Gene Therapy Clinical Trials. Med. Anthropol. 2017, 36, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sioutis, S.; Reppas, L.; Bekos, A.; Limneos, P.; Saranteas, T.; Mavrogenis, A.F. The Hippocratic Oath: Analysis and Contemporary Meaning. Orthopedics 2021, 44, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharrer, G.T. Personalized Medicine: Ethical Aspects. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1606, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deakin, C.T.; Alexander, I.E.; Kerridge, I. Accepting Risk in Clinical Research: Is the Gene Therapy Field Becoming Too Risk-Averse? Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 1842–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAERS Reporting by Patient Outcomes by Year; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2019. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/questions-and-answers-fdas-adverse-event-reporting-system-faers/faers-reporting-patient-outcomes-year. (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- The New York Times. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/topic/person/jesse-gelsinger. (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Pattee, S.R. Protections for Participants in Gene Therapy Trials: A Patient’s Perspective. Hum. Gene Ther. 2008, 19, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braveman, P. Health Disparities and Health Equity: Concepts and Measurement. Annu. Rev. Public. Health 2006, 27, 167–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Application ID | Project Number | Total Cost I.C. | Administering I.C. | Organization Name | Project Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10695742 | 1ZIATR000437-01 | USD 77,500,000 | NCATS | National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences | Antiviral Program for Pandemics (App) and Ncats: Accelerating Antiviral Development |
| 10514264 | 1U19AI171421-01 | USD 69,058,677 | NIAID | Stanford University | Development of Outpatient Antiviral Cocktails Against SARS-CoV-2 and Other Potential Pandemic Rna Viruses. |
| 10514317 | 1U19AI171443-01 | USD 67,624,156 | NIAID | Scripps Research Institute, The | Center For Antiviral Medicines and Pandemic Preparedness (Campp) |
| 10512617 | 1U19AI171110-01 | USD 67,452,049 | NIAID | University of California, San Francisco | Qcrg Pandemic Response Program |
| 10522804 | 1U19AI171954-01 | USD 66,431,207 | NIAID | University of Minnesota | Midwest Avidd Center |
| 10513679 | 1U19AI171292-01 | USD 65,483,194 | NIAID | Univ of North Carolina Chapel Hill | Rapidly Emerging Antiviral Drug Development Initiative—Avidd Center (Readdi-Ac) |
| 10513935 | 1U19AI171403-01 | USD 51,914,880 | NIAID | Emory University | Antiviral Countermeasures Development Center (Ac/Dc) |
| 10716676 | 75N91019D00024-0-759102200019-1 | USD 22,364,766 | NCI | Leidos Biomedical Research, Inc. | Discovery and Development of Cancer Therapeutics for Next Program |
| 10446989 | 5U01AG059798-03 | USD 20,263,304 | NIA | Washington University | Dian-Tu Primary Prevention Trial |
| 10649756 | 1UF1NS131791-01 | USD 18,136,504 | NINDS | Massachusetts General Hospital | An Expanded Access Protocol of Intravenous Trehalose Injection 90 mg/mL Treatment of Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis |
| 10693707 | 1ZIAHD002400-31 | USD 17,942,380 | NICHD | Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development | The Role of Subclinical Infection and Cytokines in Preterm Parturition |
| 10452692 | 5R01AG068319-03 | USD 16,720,909 | NIA | Washington University | Dian-Tu: Tau Next Generation Prevention Trial |
| 9457012 | 1U24CA224319-01 | USD 13,559,983 | NCI | Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai | High-Dimensional Immune Monitoring of Nci-Supported Immunotherapy Trials |
| 10266149 | 5U19NS120384-02 | USD 13,212,214 | NINDS | University Of California at Davis | The Clinical Significance of Incidental White Matter Lesions on Mri Amongst a Diverse Population with Cognitive Complaints (Indeed) |
| Disorder | Trials | Total Enrollment | Trials with under 18 | Phase I | Phase I |Phase II | Phase II | Phase II |Phase III | Phase III | FDA-Authorized Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cystic Fibrosis | 43 | 4080 | 27 | 7 | 3 | 15 | 2 | 10 | Elexacaftor–Tezacaftor–Ivacaftor * |
| Hemophilia B | 26 | 666 | 2 | 5 | 11 | 4 | 0 | 3 | Hemgenix |
| Retinal Dystrophy | 2 | 35 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Luxturna |
| Cerebral Adrenoleukodystrophy | 2 | 67 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Skysona |
| Spinal Muscular Atrophy | 14 | 713 | 13 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 8 | Zolgensma |
| β-Thalassemia | 25 | 604 | 17 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 2 | Zynteglo |
| Muscular Dystrophy | 42 | 1837 | 37 | 9 | 12 | 12 | 0 | 7 | Elevidys |
| Hemophilia A | 22 | 678 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 5 | Roctavian |
| Epidermolysis Bullosa | 18 | 228 | 15 | 0 | 12 | 2 | 0 | 2 | Vyjuvek |
| Fabry Disease | 12 | 377 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 1 | - |
| Sickle Cell Anemia | 5 | 245 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | - |
| Mucopolysaccharidosis | 17 | 186 | 17 | 1 | 13 | 0 | 2 | 0 | - |
| Gaucher Disease | 13 | 366 | 8 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 5 | - |
| Retinitis Pigmentosa | 27 | 1713 | 13 | 1 | 14 | 3 | 3 | 3 | - |
| Leber Congenital Amaurosis | 11 | 178 | 11 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 1 | - |
| Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis | 5 | 308 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | - |
| Severe Combined Immunodeficiency | 19 | 181 | 19 | 3 | 11 | 1 | 1 | 0 | - |
| Fanconi Anemia | 14 | 82 | 14 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | 4 | 43 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Trial | Status | Phases | Start Date | Completion Date | Age | Enrollment # | Conditions | Interventions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02292537 | Completed | Phase III | 24 November 2014 | 20 February 2017 | 2–12 years | 126 | Spinal Muscular Atrophy | Nusinersen (Spinraza) |
| NCT03306277 | Completed | Phase III | 24 October 2017 | 12 November 2019 | up to 180 Days | 22 | Spinal Muscular Atrophy | Biological: Onasemnogene Abeparvovec |
| NCT03461289 | Completed | Phase III | 16 August 2018 | 11 September 2020 | up to 6 Months | 33 | Spinal Muscular Atrophy | Biological: Onasemnogene Abeparvovec |
| NCT03496012 | Completed | Phase III | 11 December 2017 | 1 December 2020 | 18 Years and older | 170 | Choroideremia | Genetic: BIIB111 |
| NCT01896102 | Completed | Phase III Phase III | 21 August 2013 | 26 March 2021 | up to 17 Years | 32 | Cerebral Adrenoleukodystrophy (CALD) | Genetic: Lenti-D Drug Product |
| NCT03505099 | Completed | Phase III | 2 April 2018 | 15 June 2021 | up to 42 Days | 30 | Spinal Muscular Atrophy | Biological: Onasemnogene Abeparvovec |
| NCT03837184 | Completed | Phase III | 31 May 2019 | 29 June 2021 | 0 Days to 6 Months | 2 | Spinal Muscular Atrophy | Biological: Onasemnogene Abeparvovec |
| NCT02906202 | Completed | Phase III | 1 July 2016 | 31 March 2022 | 0 Years to 50 Years | 23 | β-Thalassemia | Genetic: LentiGlobin BB305 |
| NCT03406104 | Completed | Phase III | 9 January 2018 | 4 July 2022 | 15 Years and older | 61 | Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy | Genetic: GS010 |
| NCT03207009 | Completed | Phase III | 8 June 2017 | 15 November 2022 | 0 Years to 50 Years | 18 | β-Thalassemia | Genetic: LentiGlobin BB305 |
| NCT00999609 | Active, not recruiting | Phase III | 1 October 12 | - | 3 Years and older | 31 | Inherited Retinal Dystrophy | Biological: AAV2-hRPE65v2 |
| NCT03370913 | Active, not recruiting | Phase III | 19 December 2017 | - | 18 Years and older | 134 | Hemophilia A | Biological: valoctocogene roxaparvovec |
| NCT03293524 | Active, not recruiting | Phase III | 12 March 2018 | - | 15 Years and older | 90 | Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy | Genetic: GS010 |
| NCT03392974 | Active, not recruiting | Phase III | 14 March 2018 | - | 18 Years and older | 1 | Hemophilia A | Biological: Valoctocogene Roxaparvovec |
| NCT03569891 | Active, not recruiting | Phase III | 27 June 2018 | - | 18 Years and older | 67 | Hemophilia B | Genetic: AAV5-hFIXco-Padua (Hemgenix) |
| NCT03837483 | Active, not recruiting | Phase III | 21 January 2019 | - | up to 65 Years | 10 | Wiskott–Aldrich Syndrome | Genetic: OTL-103 |
| NCT03852498 | Active, not recruiting | Phase III | 24 January 2019 | - | up to 17 Years | 35 | Cerebral Adrenoleukodystrophy (CALD) | Genetic: Lenti-D |
| NCT04042025 | Active, not recruiting | Phase III | 10 February 2020 | - | Child, Adult, Older Adult | 85 | Spinal Muscular Atrophy | Biological: Onasemnogene Abeparvovec |
| NCT04323098 | Active, not recruiting | Phase III | 10 November 2020 | - | 18 Years and older | 22 | Hemophilia A | Biological: valoctocogene roxaparvovec |
| NCT04516369 | Active, not recruiting | Phase III | 24 November 2020 | - | 4 Years and older | 4 | Retinal Dystrophy | Genetic: voretigene neparvovec (LUXTURNA) |
| NCT04851873 | Active, not recruiting | Phase III | 8 September 2021 | - | up to 17 Years | 24 | Spinal Muscular Atrophy | Genetic: OAV101 |
| NCT05096221 | Active, not recruiting | Phase III | 27 October 2021 | - | 4 Years to 7 Years | 126 | Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy | Genetic: SRP-9001 |
| NCT05139316 | Active, not recruiting | Phase III | 8 November 2021 | - | 8 Years and older | 50 | Glycogen Storage Disease Type IA | Genetic: DTX401 |
| NCT03566043 | Recruiting | Phase II| Phase III | 27 September 2018 | - | 4 Months to 5 Years | 48 | Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II (MPS II) | Genetic: RGX-121 |
| NCT03861273 | Recruiting | Phase III | 29 July 2019 | - | 18 Years to 65 Years | 55 | Hemophilia B | Biological: fidanacogene elaparvovec |
| NCT04293185 | Recruiting | Phase III | 14 February 2020 | - | 2 Years to 50 Years | 35 | Sickle Cell Disease | Genetic: bb1111 |
| NCT04370054 | Recruiting | Phase III | 18 August 2020 | - | 18 Years to 64 Years | 63 | Hemophilia A | Biological: PF-07055480 |
| NCT04281485 | Recruiting | Phase III | 5 November 2020 | - | 4 Years to 7 Years | 99 | Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy | Genetic: PF-06939926 |
| NCT04704921 | Recruiting | Phase II| Phase III | 29 December 2020 | - | 50 Years to 89 Years | 300 | Age-related Macular Degeneration | Genetic: RGX-314 |
| NCT04671433 | Recruiting | Phase III | 16 March 2021 | - | 3 Years and older | 96 | X-Linked Retinitis Pigmentosa | Genetic: AAV5-RPGR |
| NCT04794101 | Recruiting | Phase III | 16 March 2021 | - | 3 Years and older | 96 | X-Linked Retinitis Pigmentosa | Genetic: AAV5-RPGR |
| NCT05407636 | Recruiting | Phase III | 28 December 2021 | - | 50 Years to 89 Years | 465 | Age-related Macular Degeneration | Genetic: RGX-314 |
| NCT05089656 | Recruiting | Phase III | 12 January 2022 | - | 2 Years to 17 Years | 125 | Spinal Muscular Atrophy | Genetic: OAV101 |
| NCT04283227 | Recruiting | Phase III | 17 January 2022 | - | Child, Adult, Older Adult | 6 | Lysosomal Storage Diseases | Genetic: OTL-200 |
| NCT05345171 | Recruiting | Phase III | 18 October 2022 | - | 12 Years and older | 50 | OTC Deficiency | Genetic: DTX301 |
| NCT05335876 | Recruiting | Phase III | 19 December 2022 | - | Child, Adult, Older Adult | 260 | Spinal Muscular Atrophy | Biological: onasemnogene abeparvovec |
| NCT05386680 | Recruiting | Phase III | 12 January 2023 | - | 2 Years to 12 Years | 28 | Spinal Muscular Atrophy | Genetic: OAV101 |
| NCT05689164 | Not yet recruiting | Phase III | 14 April 2023 | - | 0 Years and older | 250 | Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy | Biological: fordadistrogene movaparvovec |
| NCT05815004 | Not yet recruiting | Phase II| Phase III | 1 October 2023 | - | 2 Years to 25 Years | 40 | Gaucher Disease, Type 3 | Drug: Gene therapy |
| NCT00073463 | Terminated | Phase II| Phase III | 1 June 2003 | - | 12 Years and older | 100 | Cystic Fibrosis | Genetic: tgAAVCF |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henderson, M.L.; Zieba, J.K.; Li, X.; Campbell, D.B.; Williams, M.R.; Vogt, D.L.; Bupp, C.P.; Edgerly, Y.M.; Rajasekaran, S.; Hartog, N.L.; et al. Gene Therapy for Genetic Syndromes: Understanding the Current State to Guide Future Care. BioTech 2024, 13, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech13010001
Henderson ML, Zieba JK, Li X, Campbell DB, Williams MR, Vogt DL, Bupp CP, Edgerly YM, Rajasekaran S, Hartog NL, et al. Gene Therapy for Genetic Syndromes: Understanding the Current State to Guide Future Care. BioTech. 2024; 13(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech13010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenderson, Marian L., Jacob K. Zieba, Xiaopeng Li, Daniel B. Campbell, Michael R. Williams, Daniel L. Vogt, Caleb P. Bupp, Yvonne M. Edgerly, Surender Rajasekaran, Nicholas L. Hartog, and et al. 2024. "Gene Therapy for Genetic Syndromes: Understanding the Current State to Guide Future Care" BioTech 13, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech13010001
APA StyleHenderson, M. L., Zieba, J. K., Li, X., Campbell, D. B., Williams, M. R., Vogt, D. L., Bupp, C. P., Edgerly, Y. M., Rajasekaran, S., Hartog, N. L., Prokop, J. W., & Krueger, J. M. (2024). Gene Therapy for Genetic Syndromes: Understanding the Current State to Guide Future Care. BioTech, 13(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech13010001






