Development of a Prediction Method of Cell Density in Autotrophic/Heterotrophic Microorganism Mixtures by Machine Learning Using Absorbance Spectrum Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Growth Conditions
2.2. Cell Density Evaluation
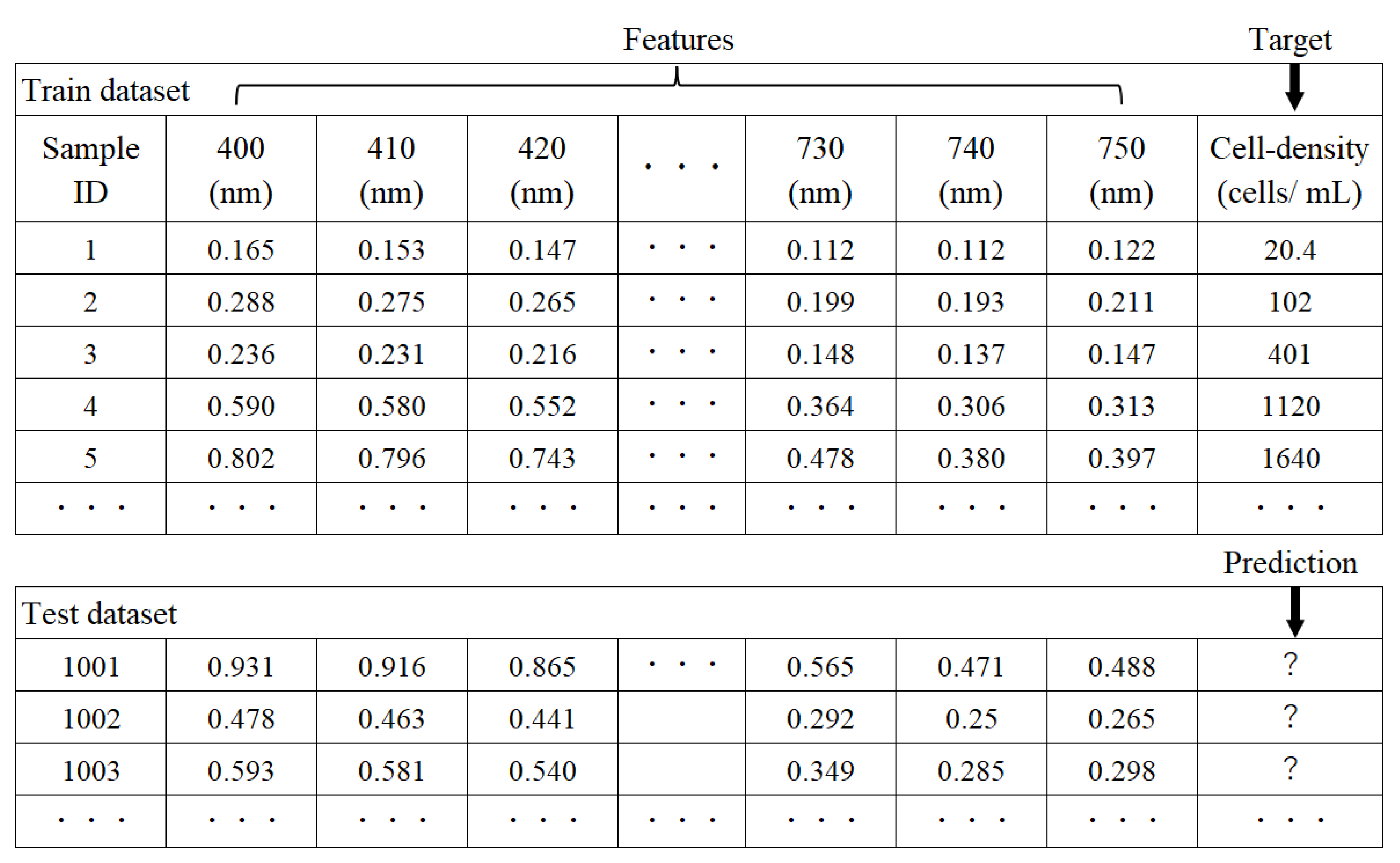
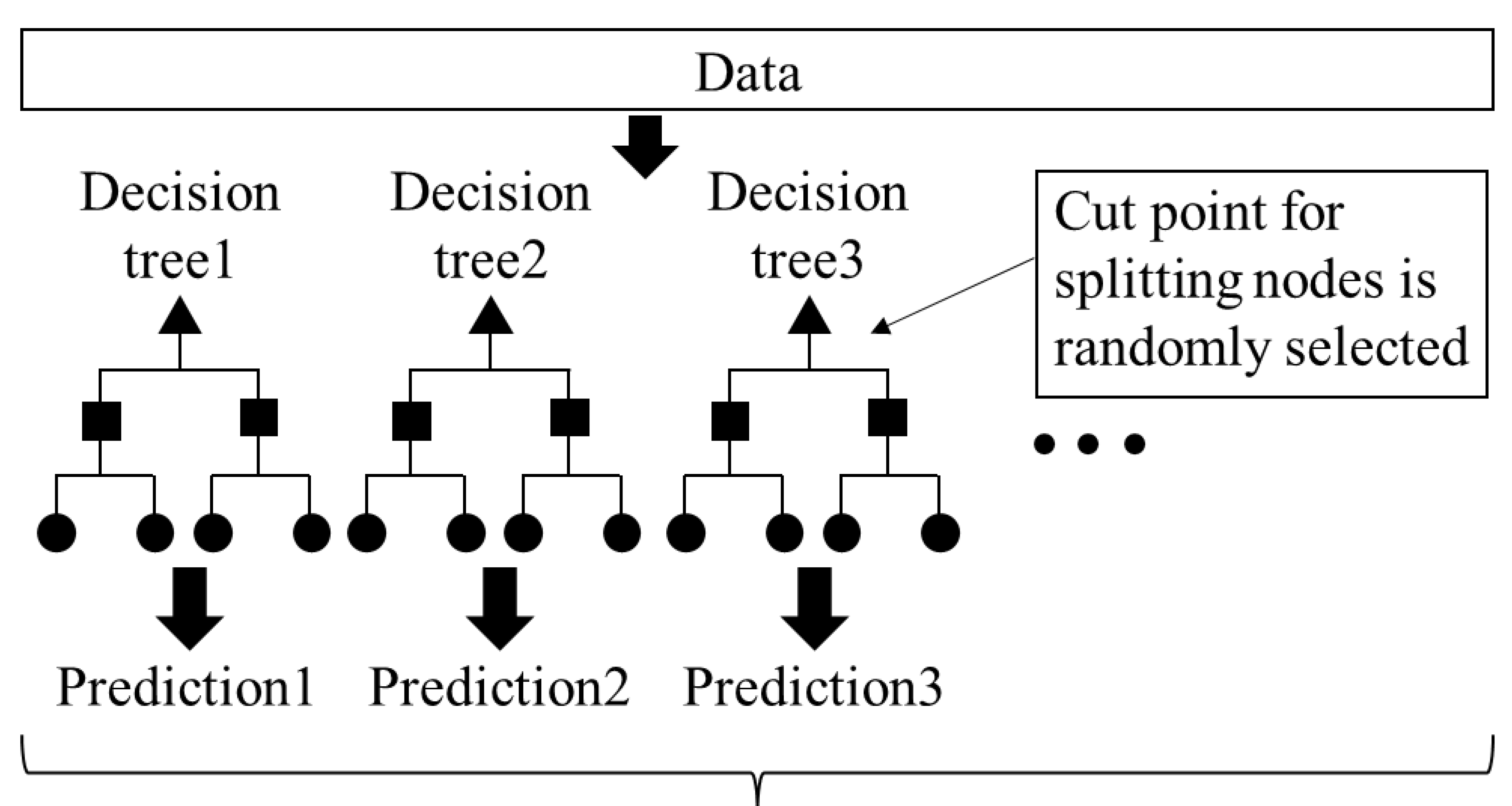
2.3. Cell Density Prediction by AI Analytics
2.4. Explanation of the Prediction Results
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of Absorbance Spectrum of Each Strain of S. cerevisiae and C. reinhardtii
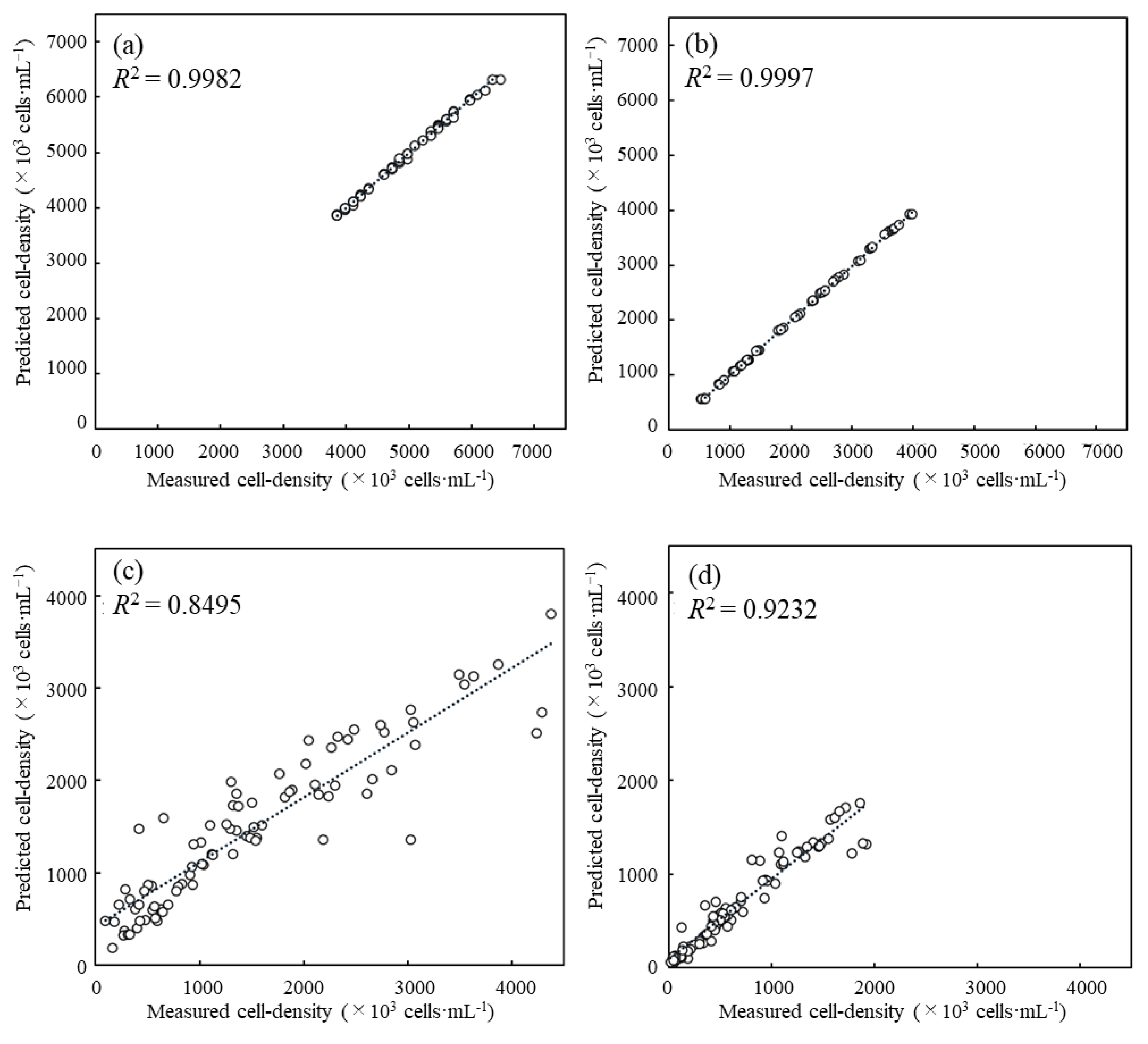
3.2. Evaluation of Predictive Performance for Cell Density Prediction with the Coefficient of Determination
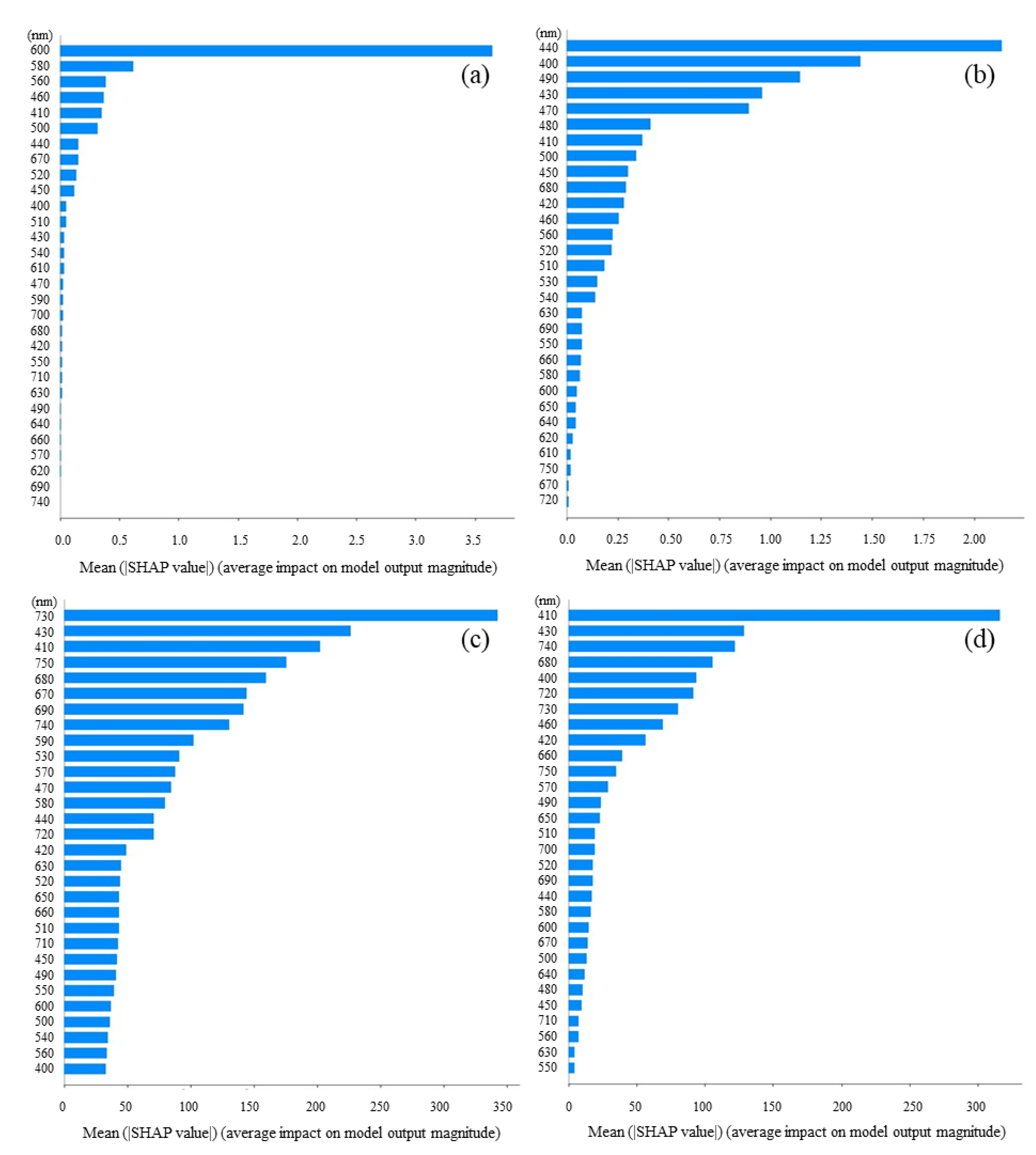
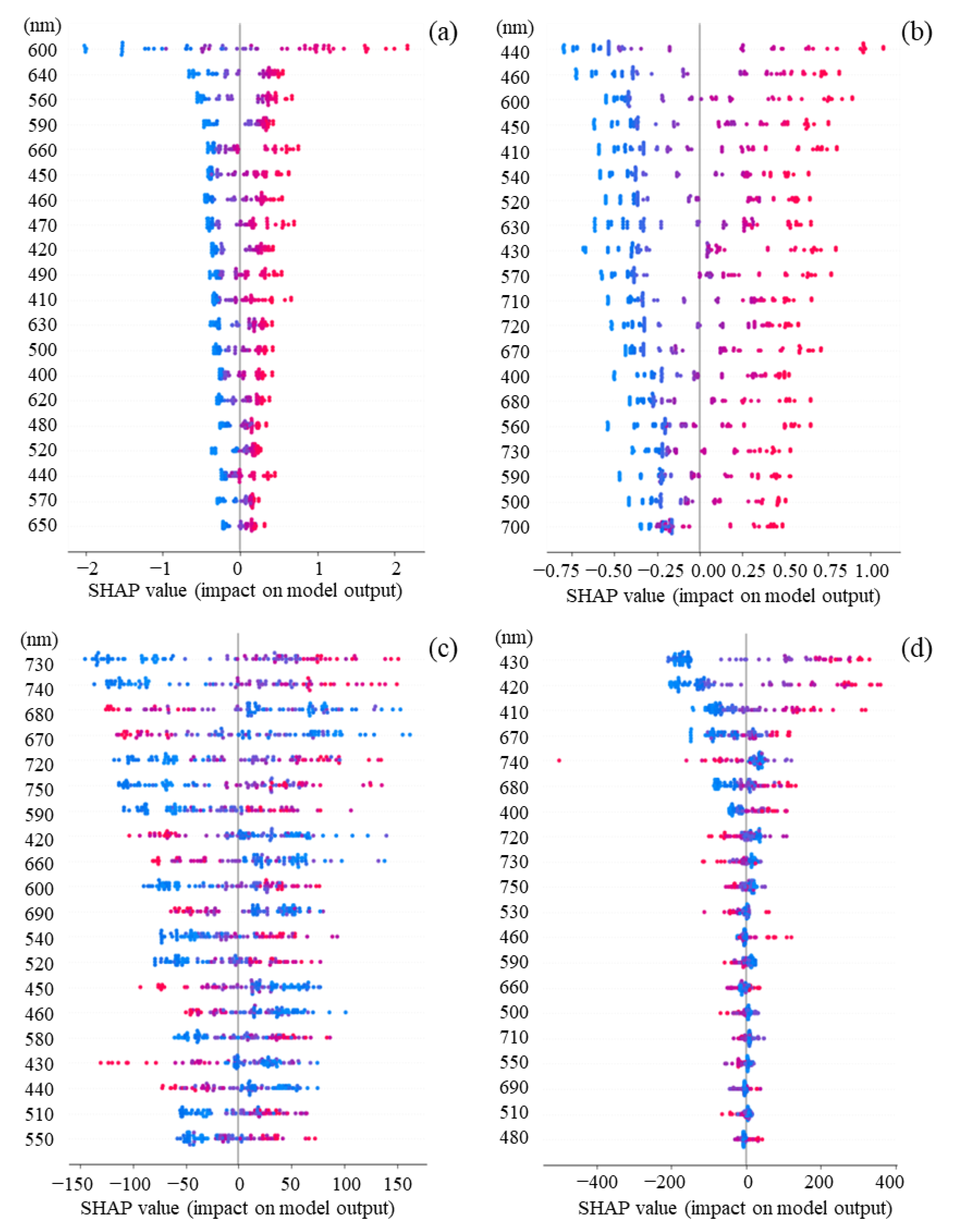
3.3. Feature Importance Based on SHAP Values
3.4. Contribution of Features for Each Sample Based on SHAP Values
3.5. Evaluation of Prediction Accuracy on Each Cell Density
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, J.; Jang, Y.-S.; Lee, S.Y. Metabolic engineering of microorganisms for the production of higher alcohols. MBio 2014, 5, e01524-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Tian, K.; Kumar, A.; Singh, S.; Prior, B.A.; Wang, Z. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli: A sustainable industrial platform for bio-based chemical production. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.W.; Park, J.M.; Chung, S.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Song, H. Microbial production of 2,3-butanediol for industrial applications. SIMB 2019, 46, 1583–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Shao, Z.; Zhao, H. Engineering microbial factories for synthesis of value-added products. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 38, 873–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzotto, E.; Weber, T. Omics and multi-omics approaches to study the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites in microorganisms. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 45, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wen, J. Recent progress in the application of omics technologies in the study of bio-mining microorganisms from extreme environments. Microb. Cell Factories 2021, 20, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodswen, S.J.; Barratt, J.L.N.; Kennedy, P.J.; Kaufer, A.; Calarco, L.; Ellis, J.T. Machine learning and applications in microbiology. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 45, fuab015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Luo, J.; Huang, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.D. Machine learning advances in microbiology: A review of methods and applications. Front Microbiol. 2022, 13, 925454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.-Y. Light: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dorogush, A.; Ershov, V.; Gulin, A. CatBoost: Gradient boosting with categorical features support. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Geurts, P.; Ernst, D.; Wehenkel, L. Extremely randomized trees. Mach. Learn. 2006, 63, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, A.B.; Díaz-Rodríguez, D.S.J.; Bennetot, A.; Tabik, S.; Barbado, A.; García, S.; Gil-López, S.; Molina, D.; Benjamins, R.; Chatila, R.; et al. Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI): Concepts taxonomies opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI. Inf. Fusion 2020, 58, 82–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Mit Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 30, pp. 4765–4774. [Google Scholar]
- Shapley, L. A value for n-person games. In Contributions to the Theory of Games (AM-28); Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1953; Volume II, pp. 307–317. [Google Scholar]
- Vilne, B.; Meistere, I.; Grantiņa-Ieviņa, L.; Ķibilds, J. Machine learning approaches for epidemiological investigations of food-borne disease outbreaks. Front Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culley, C.; Vijayakumar, S.; Zampieri, G.; Angione, C. A mechanism-aware and multiomic machine-learning pipeline characterizes yeast cell growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 18869–18879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielinski, B.; Plichta, A.; Misztal, K.; Spurek, P.; Brzychczy-Włoch, M.; Ochońska, D. Deep learning approach to bacterial colony classification. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, M.B.; Li, H. A GLM-based latent variable ordination method for microbiome samples. Biometrics 2018, 74, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brachmann, C.B.; Davies, A.; Cost, G.J.; Caputo, E.; Li, J.; Hieter, P.; Boeke, J.D. Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: A useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast 1998, 14, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterbury, J.B.; Stanier, R.Y. Isolation and growth of cyanobacteria from marine and hypersaline environments. Prokaryotes 1981, 7, 221–223. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M. 2020, Pycaret. Available online: https://pycaret.readthedocs.io/en/stable/index.html (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Gergstra, J.; Bengio, Y. Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2021, 13, 281–305. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Erion, G.G.; Lee, S.I. Consistent individualized feature attribution for tree ensembles. In Proceedings of the 2017 ICML Workshop on Human Interpretability in Machine Learning (WHI 2017), Sydney, Australia, 10 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Soret, J.L. “Analyse spectrale: Sur le spectre d’absorption du sang dans la partie violette et ultra-violette” (French). Comptes Rendus De L’académie Des Sci. 1883, 97, 1269–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Scotter, M.J.; Castle, L.; Roberts, D. Method development and HPLC analysis of retail foods and beverages for copper chlorophyll (E141[i]) and chlorophyllin (E141[ii]) food colouring materials. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakanishi, A.; Fukunishi, H.; Matsumoto, R.; Eguchi, F. Development of a Prediction Method of Cell Density in Autotrophic/Heterotrophic Microorganism Mixtures by Machine Learning Using Absorbance Spectrum Data. BioTech 2022, 11, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech11040046
Nakanishi A, Fukunishi H, Matsumoto R, Eguchi F. Development of a Prediction Method of Cell Density in Autotrophic/Heterotrophic Microorganism Mixtures by Machine Learning Using Absorbance Spectrum Data. BioTech. 2022; 11(4):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech11040046
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakanishi, Akihito, Hiroaki Fukunishi, Riri Matsumoto, and Fumihito Eguchi. 2022. "Development of a Prediction Method of Cell Density in Autotrophic/Heterotrophic Microorganism Mixtures by Machine Learning Using Absorbance Spectrum Data" BioTech 11, no. 4: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech11040046
APA StyleNakanishi, A., Fukunishi, H., Matsumoto, R., & Eguchi, F. (2022). Development of a Prediction Method of Cell Density in Autotrophic/Heterotrophic Microorganism Mixtures by Machine Learning Using Absorbance Spectrum Data. BioTech, 11(4), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech11040046






