Arabian Partridge Abundance and Limiting Factors at the Northern Boundary of Its Range
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Species
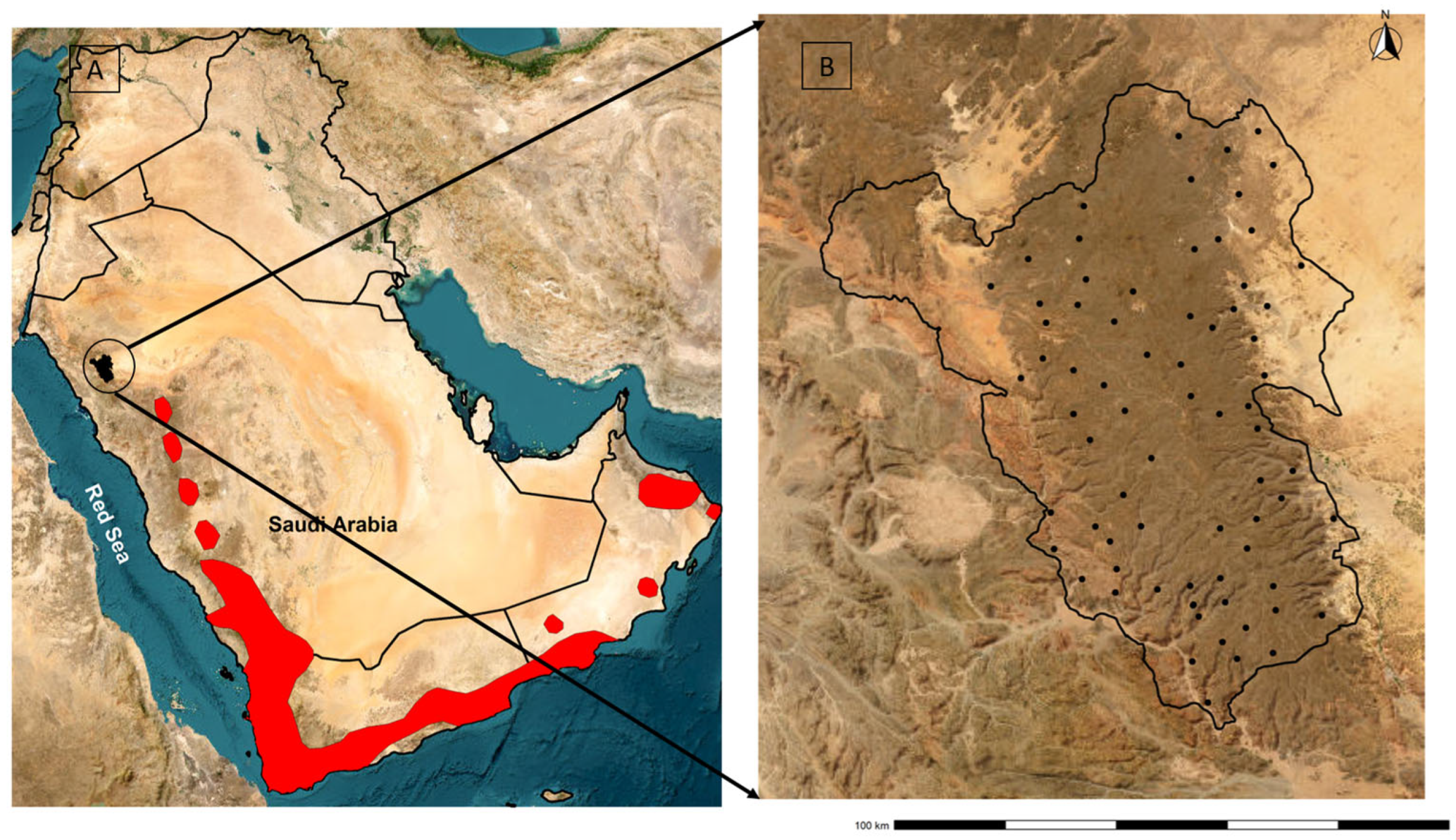
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Field Data Collection
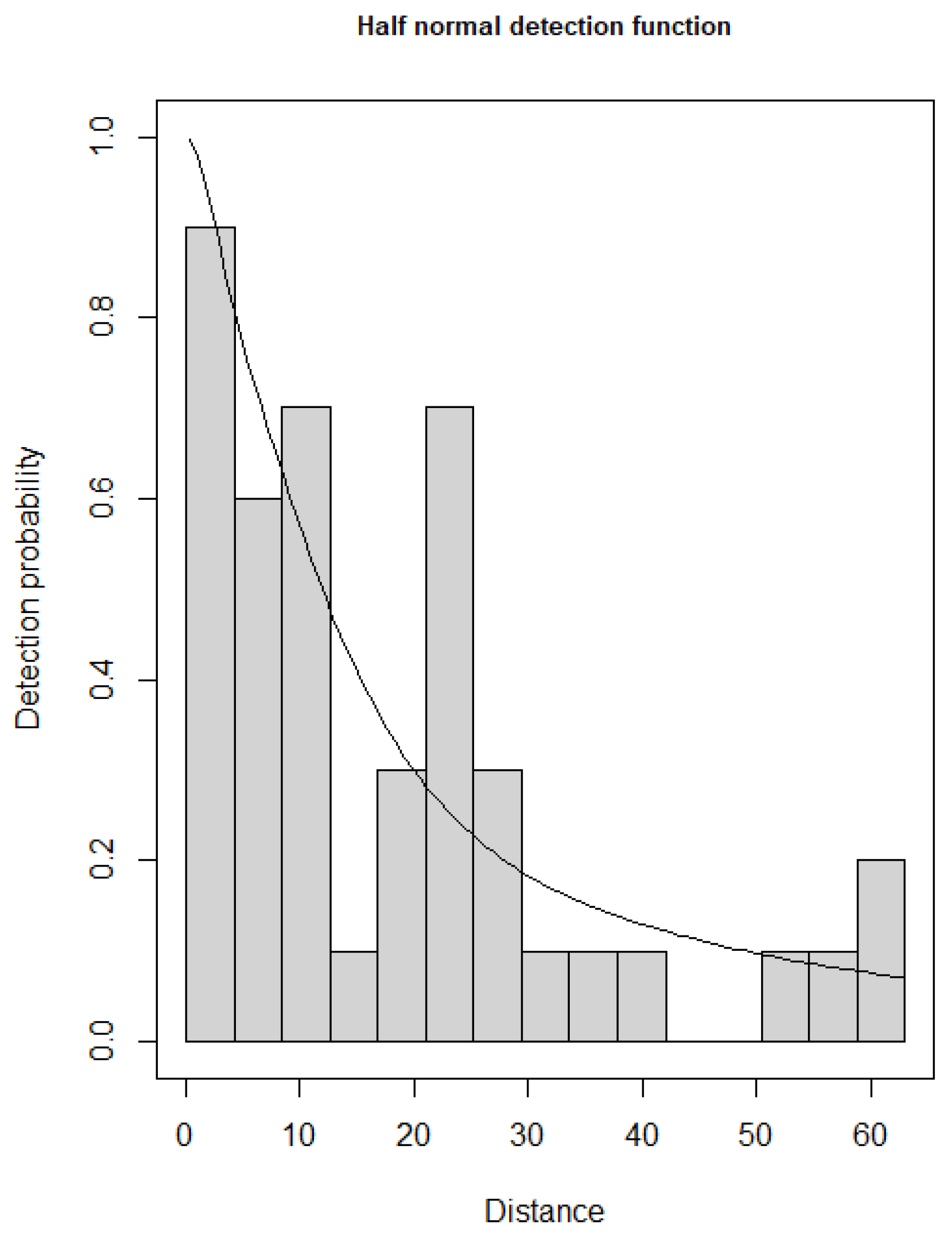
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alatawi, A.S. Conservation Action in Saudi Arabia: Challenges and Opportunities. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 3466–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metallinou, M.; Arnold, E.N.; Crochet, P.-A.; Geniez, P.; Brito, J.C.; Lymberakis, P.; Baha El Din, S.; Sindaco, R.; Robinson, M.; Carranza, S.; et al. Conquering the Sahara and Arabian Deserts: Systematics and Biogeography of Stenodactylus Geckos (Reptilia: Gekkonidae). BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbuZinada, A.H.; Robinson, E.R.; Nader, I.A.; Al Wetaid, Y.I. First Saudi Arabian National Report on the Convention on Biological Diversity; The National Commission for Wildlife Conservation and Development: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, P. Saudi Arabia: An Environmental Overview; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; ISBN 9780429216619. [Google Scholar]
- Soultan, A.; Wikelski, M.; Safi, K. Risk of Biodiversity Collapse under Climate Change in the Afro-Arabian Region. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, M.C. Atlas of the Breeding Birds of Arabia. Fauna Arab. 2010, 25, 1–751. [Google Scholar]
- BirdLife International Species Factsheet: Alectoris melanocephala. Available online: http://www.birdlife.org (accessed on 11 December 2022).
- Khan, H.A.; Arif, I.A.; Shobrak, M. DNA Barcodes of Arabian Partridge and Philby’s Rock Partridge: Implications for Phylogeny and Species Identification. Evol. Bioinforma. 2010, 2010, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, P.J.K.; Kirwan, G.M. Arabian Partridge (Alectoris melanocephala), version 1.0. In Birds of the World; del Hoyo, J., Elliott, A., Sargatal, J., Christie, D., de Juana, E., Eds.; Cornell Lab of Ornithology: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yom-Tov, Y.; Benjamini, Y.; Kark, S. Global Warming, Bergmann’s Rule and Body Mass–Are They Related? The Chukar Partridge (Alectoris chukar) Case. J. Zool. 2002, 257, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruychev, G.; Dyakov, N.; Dimitrov, D. Habitat Variables Influencing Chukar Partridge Decrease in Southeastern Bulgaria. Folia Zool. 2014, 63, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandercock, B.K.; Nilsen, E.B.; Brøseth, H.; Pedersen, H.C. Is Hunting Mortality Additive or Compensatory to Natural Mortality? Effects of Experimental Harvest on the Survival and Cause-Specific Mortality of Willow Ptarmigan. J. Anim. Ecol. 2011, 80, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO Harrat Uwayrid Biosphere Reserve-Saudi Arabia. Available online: https://www.unesco.org/archives/multimedia/document-5783 (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Hayes, L. Upland Game Birds: Their Breeding and Care; L.B. Hayes: Valley Center, CA, USA, 1995; ISBN 9780963319623. [Google Scholar]
- McGowan, P.; Madge, S.; D’Silva, C.; Cole, D.; Mead, D.; Cox, J.D.; Franklin, K.; Arlott, N.; Budden, R. Pheasants, Partridges & Grouse: Including Buttonquails, Sandgrouse and Allies; Helm Identification Guides; Bloomsbury Publishing: London, UK, 2010; ISBN 9781408135662. [Google Scholar]
- Obaid, W.A.; Boutraa, T.; Abdel-Hameed, U.K. Floristics and Soil Characteristics of Ohud Mountain, Al-Madinah Al-Munawarah, Western Saudi Arabia. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 2405–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Data. Available online: https://en.climate-data.org/ (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Sayed, O.H.; Masrahi, Y.S. Climatology and Phytogeography of Saudi Arabia. A Review. Arid L. Res. Manag. 2023, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataineh, A.L.; Oswald, B.P.; Bataineh, M.; Unger, D.; Hung, I.-K.; Scognamillo, D. Spatial Autocorrelation and Pseudoreplication in Fire Ecology. Fire Ecol. 2006, 2, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurlbert, S.H. Pseudoreplication and the Design of Ecological Field Experiments. Ecol. Monogr. 1984, 54, 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royle, J.A.; Dawson, D.K.; Bates, S. Modeling Abundance Eeffects in Distance Sampling. Ecology 2004, 85, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiske, I.; Chandler, R. Unmarked: An R Package for Fitting Hierarchical Models of Wildlife Occurrence and Abundance. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 43, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, R. Distance Sampling Analysis in Unmarked; USGS Patuxent Wildlife Research Center: Laurel, MD, USA, 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega-Álvarez, R.; Calderón-Parra, R.; Martínez Molina, U.; Martínez Molina, F.; Martínez Molina, G.; Martínez Molina, Y.; Martínez Villagrán, A.; Martínez Freire, J.D.; Vásquez Robles, R.; García Loaeza, D.; et al. How Many Are Left? Density and Population Size of the Endangered Sierra Madre Sparrow across Central Mexico. J. Ornithol. 2021, 162, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model Selection and Multimodel Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.L.; Rexstad, E.; Thomas, L.; Marshall, L.; Laake, J.L. Distance Sampling in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2019, 89, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckland, S.T.; Anderson, D.R.; Burnham, K.P.; Laake, J.L. Distance Sampling. In Encyclopedia of Biostatistics; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2016; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 11 December 2022).
- Randi, E. A Mitochondrial Cytochrome B Phylogeny of the Alectoris Partridges. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1996, 6, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, M.; Degen, A.A.; Nagy, K.A. Seasonal Energy, Water, and Food Consumption of Negev Chukars and Sand Partridges. Ecology 1987, 68, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.G.; Possingham, H.P. Predicting the Impact of Livestock Grazing on Birds Using Foraging Height Data. J. Appl. Ecol. 2005, 42, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.H.; Rosamond, K.M.; Goded, S.; Soultan, A.; Glass, A.; Kim, D.H.; Arcilla, N. Bobolink (Dolichonyx oryzivorus) Declines Follow Bison (Bison bison) Reintroduction on Private Conservation Grasslands. Animals 2021, 11, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzan, F.R.; Bellis, L.M.; Dardanelli, S. Livestock Grazing Constrains Bird Abundance and Species Richness: A Global Meta-Analysis. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2021, 56, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Lu, S.; Song, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, J. Effects of Livestock Grazing on Spatio-Temporal Patterns and Behaviour of Reeves’s Pheasant Syrmaticus Reevesii. Animals 2022, 12, 2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadey, M. Livestock Indirectly Decrease Nest Abundance of Two Shrub-Nesting Species in Patagonian Monte Desert. Rangel. J. 2020, 42, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, E.J.; Ramp, D.; Middleton, O.S.; Wooster, E.I.F.; Kusch, E.; Balisi, M.; Ripple, W.J.; Hasselerharm, C.D.; Sanchez, J.N.; Mills, M.; et al. A Novel Trophic Cascade between Cougars and Feral Donkeys Shapes Desert Wetlands. J. Anim. Ecol. 2022, 91, 2348–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beschta, R.L.; Donahue, D.L.; DellaSala, D.A.; Rhodes, J.J.; Karr, J.R.; O’Brien, M.H.; Fleischner, T.L.; Deacon Williams, C. Adapting to Climate Change on Western Public Lands: Addressing the Ecological Effects of Domestic, Wild, and Feral Ungulates. Environ. Manag. 2013, 51, 474–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danvir, R.E. Multiple-Use Management of Western U.S. Rangelands: Wild Horses, Wildlife, and Livestock. Hum.–Wildl. Interact. 2018, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beever, E.A.; Aldridge, C.L. Influences of Free-Roaming Equids on Sagebrush Ecosystems, with a Focus on Greater Sage-Grouse. In Greater Sage-GrouseEcology and Conservation of a Landscape Species and Its Habitats; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2011; pp. 272–290. [Google Scholar]
- Attum, O.; El Noby, S.K.; Hassan, I.N. The Influence of Landscape Characteristics and Anthropogenic Factors on Waterhole Use by Vulnerable Nubian Ibex Capra Nubiana. Oryx 2009, 43, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.K.; Olson, K.A.; Reading, R.P.; Amgalanbaatar, S.; Berger, J. Is Wildlife Going to the Dogs? Impacts of Feral and Free-Roaming Dogs on Wildlife Populations. Bioscience 2011, 61, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenth, B.E.; Knight, R.L.; Brennan, M.E. The Effects of Dogs on Wildlife Communities. Nat. Areas J. 2008, 28, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manor, R.; Saltz, D. The Impact of Free-Roaming Dogs on Gazelle Kid/Female Ratio in a Fragmented Area. Biol. Conserv. 2004, 119, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soultan, A.; Attum, O.; Lahue, W. The Relationship between Landscape Features and Domestic Species on the Occupancy of Native Mammals in Urban Forests. Urban Ecosyst. 2021, 24, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloufi, A.; Eid, E. Conservation Perspectives of Illegal Animal Trade at Markets in Tabuk, Saudi Arabia. Traffic Bull. 2014, 26, 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Cybertracker. Available online: https://cybertracker.org/ (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- SMART. Available online: https://smartconservationtools.org/ (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Kingsford, R.T.; West, R.S.; Pedler, R.D.; Keith, D.A.; Moseby, K.E.; Read, J.L.; Letnic, M.; Leggett, K.E.A.; Ryall, S.R. Strategic Adaptive Management Planning—Restoring a Desert Ecosystem by Managing Introduced Species and Native Herbivores and Reintroducing Mammals. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2021, 3, e268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.J.H. Feral Animals and the Restoration of Nature. Between Species Online J. Study Philos. Anim. 2009, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummer, T.D.; Degange, A.R.; Pank, L.L.; McDonald, L.L. Adjusting for Group Size Influence in Line Transect Sampling. J. Wildl. Manag. 1990, 54, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummer, T.D.; McDonald, L.L. Size Bias in Line Transect Sampling. Biometrics 1987, 43, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soultan, A.; Pavón-Jordán, D.; Bradter, U.; Sandercock, B.K.; Hochachka, W.M.; Johnston, A.; Brommer, J.; Gaget, E.; Keller, V.; Knaus, P.; et al. The Future Distribution of Wetland Birds Breeding in Europe Validated against Observed Changes in Distribution. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 024025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virkkala, R.; Lehikoinen, A. Patterns of Climate-Induced Density Shifts of Species: Poleward Shifts Faster in Northern Boreal Birds than in Southern Birds. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2995–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovick, T.J.; Allred, B.W.; McGranahan, D.A.; Palmer, M.W.; Dwayne Elmore, R.; Fuhlendorf, S.D. Informing Conservation by Identifying Range Shift Patterns across Breeding Habitats and Migration Strategies. Biodivers. Conserv. 2016, 25, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Estimate | SE | Z Value | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density model | (Intercept) | 4.492 | 0.801 | 5.607 | 0.001 |
| Wadi width | −0.085 | 0.377 | −0.227 | 0.820 | |
| Wadi width (quadratic term) | 0.032 | 0.275 | 0.117 | 0.906 | |
| Tree cover | 0.004 | 0.216 | 0.018 | 0.985 | |
| Disturbance | −0.519 | 0.229 | −2.269 | 0.023 | |
| Distance to hillside | 1.849 | 0.979 | 1.887 | 0.059 | |
| Interaction between disturbance and distance to hillside | −0.532 | 0.286 | −1.86 | 0.062 | |
| Detection probability model | (Intercept) | 1.797 | 0.482 | 3.726 | 0.001 |
| Covey size | 0.727 | 0.217 | 3.354 | 0.001 | |
| Second observer | 0.024 | 0.257 | 0.096 | 0.923 | |
| Third observer | 0.224 | 0.321 | 0.699 | 0.484 | |
| Medium vegetation cover | 0.992 | 0.449 | 2.21 | 0.027 | |
| High vegetation cover | 0.437 | 0.455 | 0.962 | 0.336 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soultan, A.; Shah, M.S.; Almalki, A.M.; Browne, S.; Arcilla, N. Arabian Partridge Abundance and Limiting Factors at the Northern Boundary of Its Range. Birds 2023, 4, 179-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/birds4020015
Soultan A, Shah MS, Almalki AM, Browne S, Arcilla N. Arabian Partridge Abundance and Limiting Factors at the Northern Boundary of Its Range. Birds. 2023; 4(2):179-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/birds4020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoultan, Alaaeldin, Moayyed Sher Shah, Ahmed Mohammed Almalki, Stephen Browne, and Nico Arcilla. 2023. "Arabian Partridge Abundance and Limiting Factors at the Northern Boundary of Its Range" Birds 4, no. 2: 179-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/birds4020015
APA StyleSoultan, A., Shah, M. S., Almalki, A. M., Browne, S., & Arcilla, N. (2023). Arabian Partridge Abundance and Limiting Factors at the Northern Boundary of Its Range. Birds, 4(2), 179-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/birds4020015






