The Effects of Time-Restricted Eating and Alternate-Day Modified Fasting on Interferon-γ and Interleukin-10 Levels in Young Asian Women with Obesity: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Intermittent Fasting Protocol
2.4. Outcomes Measurement
2.4.1. Screening Measurements and Tools
2.4.2. Blood Sampling and Immunoassay Protocol
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Participant Characteristics
3.2. Dietary Intake and Physical Activity Compliance
3.3. Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Anthropometric Profile
3.4. Effects of Intermittent Fasting on IFN-γ Levels and IL-10 Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 10 September 2024).
- Lobstein, T.; Hannah Brinsden, M.N. World Obesity Federation. World Obesity Atlas. 2023. Available online: https://www.worldobesityday.org/assets/downloads/World_Obesity_Atlas_2022_WEB.pdf (accessed on 3 October 2024).
- Alam, M.R.; Begum, M.; Sharmin, R.; Naser, A.Z.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Hossain, M.A.; Tanveer, S.K.M.; Parves, M.M.; Ahmed, E.; Akter, T. Obesity in Southeast Asia: An Emerging Health Concern. Sch. J. Appl. Med. Sci. 2024, 12, 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, A.; Snehalatha, C. Rising Burden of Obesity in Asia. J. Obes. 2010, 2010, 868573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BKPK. Kemenkes RI Hasil Utama SKI. 2023. Available online: https://www.badankebijakan.kemkes.go.id/daftar-frequently-asked-question-seputar-hasil-utama-ski-2023/hasil-utama-ski-2023/ (accessed on 26 September 2024).
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global Epidemiology and Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, H. Obesity: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 706978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badan Pusat Statistik. Prevalensi Obesitas Pada Penduduk Umur > 18 Tahun Menurut Jenis Kelamin. 2018. Available online: https://www.bps.go.id/id/statistics-table/2/MTc4MSMy/prevalensi-obesitas-pada-penduduk-umur-18-tahun-menurut-jenis-kelamin.html?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Accardi, G.; Caruso, C. Immune-Inflammatory Responses in the Elderly: An Update. Immun. Ageing 2018, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turbitt, W.J.; Buchta Rosean, C.; Weber, K.S.; Norian, L.A. Obesity and CD8 T Cell Metabolism: Implications for Anti-Tumor Immunity and Cancer Immunotherapy Outcomes. Immunol. Rev. 2020, 295, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Qiu, T.; Li, L.; Yu, R.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Proud, C.G.; Jiang, T. Pathophysiology of Obesity and Its Associated Diseases. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2403–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Nikolajczyk, B.S. Tissue Immune Cells Fuel Obesity-Associated Inflammation in Adipose Tissue and Beyond. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in Inflammation and Metabolic Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wensveen, F.M.; Valentić, S.; Šestan, M.; Turk Wensveen, T.; Polić, B. The “Big Bang” in Obese Fat: Events Initiating Obesity-Induced Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 2446–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.Y.; Chiu, C.J.; Hsing, C.H.; Hsu, Y.H. Interferon Family Cytokines in Obesity and Insulin Sensitivity. Cells 2022, 11, 4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Wu, D.; Qiu, Y. Adipose Tissue Macrophage in Obesity-Associated Metabolic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 977485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D. The Roles of T Cells in Obese Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Adipocyte 2021, 10, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.X. A Detective Story of Intermittent Fasting Effect on Immunity. Immunology 2024, 173, 227–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marko, D.M.; Conn, M.O.; Schertzer, J.D. Intermittent Fasting Influences Immunity and Metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 35, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, D.; Shaw, R.J. AMPK: Mechanisms of Cellular Energy Sensing and Restoration of Metabolic Balance. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaix, A.; Manoogian, E.N.C.; Melkani, G.C.; Panda, S. Time-Restricted Eating to Prevent and Manage Chronic Metabolic Diseases. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2019, 39, 291–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Heddes, M.; Altaha, B.; Birkner, M.; Kleigrewe, K.; Meng, C.; Haller, D.; Kiessling, S. Targeting the Intestinal Circadian Clock by Meal Timing Ameliorates Gastrointestinal Inflammation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2024, 21, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeb, F.; Wu, X.; Fatima, S.; Zaman, M.H.; Khan, S.A.; Safdar, M.; Alam, I.; Feng, Q. Time-Restricted Feeding Regulates Molecular Mechanisms with Involvement of Circadian Rhythm to Prevent Metabolic Diseases. Nutrition 2021, 89, 111244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, F.; Gabel, K.; Cienfuegos, S.; Wiseman, E.; Ezpeleta, M.; Steward, M.; Pavlou, V.; Varady, K.A. Alternate Day Fasting Combined with a Low-Carbohydrate Diet for Weight Loss, Weight Maintenance, and Metabolic Disease Risk Reduction. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2019, 5, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshiar, S.H.; Yazdani, A.; Jafarnejad, S. Alternate-Day Modified Fasting Diet Improves Weight Loss, Subjective Sleep Quality and Daytime Dysfunction in Women with Obesity or Overweight: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1174293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepanowski, J.F.; Kroeger, C.M.; Barnosky, A.; Klempel, M.C.; Bhutani, S.; Hoddy, K.K.; Gabel, K.; Freels, S.; Rigdon, J.; Rood, J.; et al. Effect of Alternate-Day Fasting on Weight Loss, Weight Maintenance, and Cardioprotection among Metabolically Healthy Obese Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2017, 177, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gipson, L.; Deru, L.; Stevens, A.; Kemp, D.; Bailey, B.W. The Effects of Alternate Day Modified Fasting on Diet and Weight Loss: A Pilot Study. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2023, 55, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, V.; Marín, A.; Gihardo, D.; Maluenda, F.; Carrasco, F.; Chamorro, R. Intermittent Fasting and Human Metabolic Health. Rev. Med. Chil. 2023, 151, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attinà, A.; Leggeri, C.; Paroni, R.; Pivari, F.; Cas, M.D.; Mingione, A.; Dri, M.; Marchetti, M.; Di Renzo, L. Fasting: How to Guide. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Cabo, R.; Mattson, M.P. Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Health, Aging, and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2541–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilibio, B.L.E.; dos Reis, W.R.; Compagnon, L.; de Batista, D.G.; Sulzbacher, L.M.; Pinheiro, J.F.; Ludwig, M.S.; Frizzo, M.N.; Cruzat, V.; Heck, T.G. Effects of Alternate-Day Fasting and Time-Restricted Feeding in Obese Middle-Aged Female Rats. Nutrition 2023, 116, 112198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varady, K.A.; Bhutani, S.; Church, E.C.; Klempel, M.C. Short-Term Modified Alternate-Day Fasting: A Novel Dietary Strategy for Weight Loss and Cardioprotection in Obese Adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezpeleta, M.; Cienfuegos, S.; Lin, S.; Pavlou, V.; Gabel, K.; Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Varady, K.A. Time-Restricted Eating: Watching the Clock to Treat Obesity. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooshiar, S.H.; Yazdani, A.; Jafarnejad, S. Does an Alternate-Day Modified Fasting Diet Improve Premenstrual Syndrome Symptoms and Health-Related Quality of Life in Obese or Overweight Women with Premenstrual Syndrome? A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1298831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, E.F.; Beyl, R.; Early, K.S.; Cefalu, W.T.; Ravussin, E.; Peterson, C.M. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves Insulin Sensitivity, Blood Pressure, and Oxidative Stress Even without Weight Loss in Men with Prediabetes. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1212–1221.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horrigan, L.A.; Kelly, J.P.; Connor, T.J. Immunomodulatory Effects of Caffeine: Friend or Foe? Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 111, 877–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iris, M.; Tsou, P.S.; Sawalha, A.H. Caffeine Inhibits STAT1 Signaling and Downregulates Inflammatory Pathways Involved in Autoimmunity. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 192, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidou, E.; Papadopoulou, S.K.; Seroglou, K.; Giaginis, C. Revised Harris–Benedict Equation: New Human Resting Metabolic Rate Equation. Metabolites 2023, 13, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, A.; Bhattacharyya, S.P.; Ghosal, M.K. A Comparative Study of Total Body Fat Percentage, Visceral Fat Percentage and Whole Body Subcutaneous and Skeletal Fat Percentage between Patients with Depression and Normal Subjects. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2023, 11, 4125–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minshawi, F.; Lanvermann, S.; McKenzie, E.; Jeffery, R.; Couper, K.; Papoutsopoulou, S.; Roers, A.; Muller, W. The Generation of an Engineered Interleukin-10 Protein With Improved Stability and Biological Function. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altves, S.; Guclu, E.; Yetisgin, E.; Bilecen, K.; Vural, H. Upregulation of Immune Checkpoint PD-L1 in Colon Cancer Cell Lines and Activation of T Cells by Leuconostoc Mesenteroides. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioassay Technology Laboratory. Human Interferon Gamma, IFN-G ELISA Kit. Available online: https://www.bt-laboratory.com/index.php/Shop/Index/productShijiheDetail/p_id/265.html?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Gubari, M.I.M.; Norouzy, A.; Hosseini, M.; Hosseinzadeh-Attar, M.J. The Relationship between Serum Concentrations of Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines and Nutritional Status in Patients with Traumatic Head Injury in the Intensive Care Unit. Medicina 2019, 55, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioassay Technology Laboratory. Human Interleukin 10, IL-10 ELISA Kit. Available online: https://www.bt-laboratory.com/index.php/Shop/Index/productShijiheDetail/p_id/262/cate/kit.html?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Shin, P.; Park, S.; Kim, M.S.; Kwon, D.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, K.; Chun, S.; Lee, H.; Choi, S. A Traditional Korean Diet with a Low Dietary Inflammatory Index Increases Anti-Inflammatory IL-10 and Decreases Pro-Inflammatory NF-κB in a Small Dietary Intervention Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.; Pabla, P.; Mallinson, J.; Nixon, A.; Taylor, T.; Bennett, A.; Tsintzas, K. Two Weeks of Early Time-Restricted Feeding (ETRF) Improves Skeletal Muscle Insulin and Anabolic Sensitivity in Healthy Men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeneessier, A.S.; BaHammam, A.A.; Alzoghaibi, M.; Olaish, A.H.; Nashwan, S.Z.; BaHammam, A.S. The Effects of Diurnal Intermittent Fasting on Proinflammatory Cytokine Levels While Controlling for Sleep/Wake Pattern, Meal Composition and Energy Expenditure. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faris, M.A.I.E.; Jahrami, H.A.; Obaideen, A.A.; Madkour, M.I. Impact of Diurnal Intermittent Fasting during Ramadan on Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Markers in Healthy People: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Nutr. Intermed. Metab. 2019, 15, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faris, M.A.I.E.; Kacimi, S.; Al-Kurd, R.A.; Fararjeh, M.A.; Bustanji, Y.K.; Mohammad, M.K.; Salem, M.L. Intermittent Fasting during Ramadan Attenuates Proinflammatory Cytokines and Immune Cells in Healthy Subjects. Nutr. Res. 2012, 32, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.Y.; Piccio, L.; Childress, P.; Bollman, B.; Ghosh, A.; Brandhorst, S.; Suarez, J.; Michalsen, A.; Cross, A.H.; Morgan, T.E.; et al. A Diet Mimicking Fasting Promotes Regeneration and Reduces Autoimmunity and Multiple Sclerosis Symptoms. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 2136–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, S.R.; Ghaemi, A.; Alizadeh, A.; Fatemeh, S.; Tabriz, H.M.; Togha, M. Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Experimental Autoimune Encephalomyelitis in C57BL/6 Mice. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016, 15, 212–219. [Google Scholar]
- Cignarella, F.; Cantoni, C.; Ghezzi, L.; Salter, A.; Dorsett, Y.; Chen, L.; Phillips, D.; Weinstock, G.M.; Fontana, L.; Cross, A.H.; et al. Intermittent Fasting Confers Protection in CNS Autoimmunity by Altering the Gut Microbiota. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1222–1235.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procaccini, C.; de Candia, P.; Russo, C.; De Rosa, G.; Lepore, M.T.; Colamatteo, A.; Matarese, G. Caloric Restriction for the Immunometabolic Control of Human Health. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 2787–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okawa, T.; Nagai, M.; Hase, K. Dietary Intervention Impacts Immune Cell Functions and Dynamics by Inducing Metabolic Rewiring. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 623989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, A.K.; Lichtman, A.H.; Pillai, S. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 10th ed.; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; ISBN 978-0323-75748-5. [Google Scholar]
- Anft, M.; Netter, P.; Urlaub, D.; Prager, I.; Schaffner, S.; Watzl, C. NK Cell Detachment from Target Cells Is Regulated by Successful Cytotoxicity and Influences Cytokine Production. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasmi, M.; Sellami, M.; Denham, J.; Padulo, J.; Kuvacic, G.; Selmi, W.; Khalifa, R. Time-Restricted Feeding Influences Immune Responses without Compromising Muscle Performance in Older Men. Nutrition 2018, 51–52, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, S.D.; Moehl, K.; Donahoo, W.T.; Marosi, K.; Lee, S.A.; Mainous, A.G.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Mattson, M.P. Flipping the Metabolic Switch: Understanding and Applying Health Benefits of Fasting. Obesity 2018, 26, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, N.; Zhang, Q.; Sung, H.K. From Fasting to Fat Reshaping: Exploring the Molecular Pathways of Intermittent Fasting-Induced Adipose Tissue Remodeling. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 27, 13062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeb, F.; Wu, X.; Chen, L.; Fatima, S.; Haq, I.U.; Chen, A.; Li, M.; Feng, Q. Effect of Time-Restricted Feeding on Metabolic Risk and Circadian Rhythm Associated with Gut Microbiome in Healthy Males. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 123, 1216–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhag, M.R.A.; Abu-Median, A.-B.; Da Boit, M.; Haris, P.I.; Madkour, M.I.; Alkawamleh, D.H.; Faris, M.E. Transforming Gut Health through Ramadan Intermittent Fasting: A Review on Metabolic and Microbiomic Insights. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2025, 69, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, R.E.; Sears, D.D. Metabolic Effects of Intermittent Fasting. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2017, 37, 371–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Simmons, N.; Awan, S.; Chamari, K.; Ahmed, I. Intermittent Fasting: Eating by the Clock for Health and Exercise Performance. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2022, 8, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, M.I.; Islam, M.T.; Tippetts, T.S.; Chowdhury, K.H.; Lesniewski, L.A.; Summers, S.A.; Zeb, F.; Abdelrahim, D.N.; AlKurd, R.; Khraiwesh, H.M.; et al. Ramadan Intermittent Fasting Is Associated with Ameliorated Inflammatory Markers and Improved Plasma Sphingolipids/Ceramides in Subjects with Obesity: Lipidomics Analysis. Science 2023, 13, 22671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Adipocytokines: Mediators Linking Adipose Tissue, Inflammation and Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, R.A.; Tsutsumi, N.; Su, L.L.; Abhiraman, G.C.; Mohan, K.; Henneberg, L.T.; Aduri, N.G.; Gati, C.; Garcia, K.C. Structure-Based Decoupling of the Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Functions of Interleukin-10. Science 2021, 371, eabc8433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faris, M.A.I.E.; Madkour, M.I.; Obaideen, A.K.; Dalah, E.Z.; Hasan, H.A.; Radwan, H.; Jahrami, H.A.; Hamdy, O.; Mohammad, M.G. Effect of Ramadan Diurnal Fasting on Visceral Adiposity and Serum Adipokines in Overweight and Obese Individuals. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 153, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, R.D.S.; Maria, C.; Silva, D.S.; Fratelli, C.F.; De Lima, L.R.; Stival, M.M.; Funghetto, S.S.; Cristina, I. IL-10 and IL-1β Serum Levels, Genetic Variants, and Metabolic Syndrome: Insights into Older Adults’ Clinical Characteristics. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Hutchison, A.T.; Thompson, C.H.; Lange, K.; Heilbronn, L.K. Markers of Adipose Tissue Inflammation Are Transiently Elevated during Intermittent Fasting in Women Who Are Overweight or Obese. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 13, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, J.R.; Tavira, B.; Douagi, I.; Kulyté, A.; Arner, P.; Rydén, M.; Laurencikiene, J. Human-Specific Function of IL-10 in Adipose Tissue Linked to Insulin Resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 4552–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
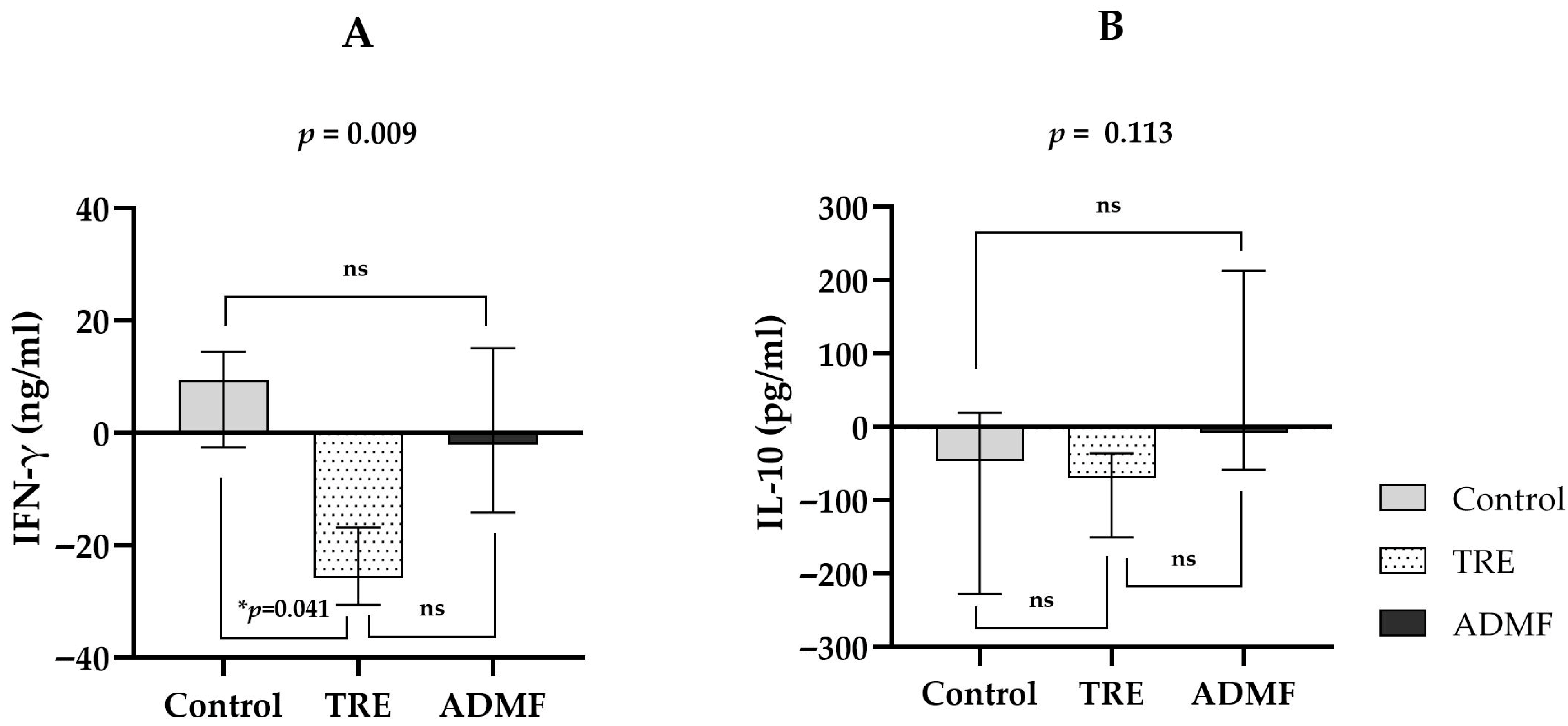
| Parameter | Control (n = 8) | TRE (n = 8) | ADMF (n = 7) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years a | 21.00 ± 1.69 | 22.00 ± 1.85 | 21.14 ± 1.95 | 0.513 |
| Blood pressure, mmHg | ||||
| Systolic a | 111.25 ± 9.37 | 117.50 ± 13.33 | 110.42 ± 7.16 | 0.362 |
| Diastolic a | 81.12 ± 6.64 | 80.62 ± 10.44 | 78.42 ± 4.03 | 0.775 |
| FBG, mg/dL a | 99.75 ± 8.03 | 100.12 ± 14.87 | 101.85 ± 13.74 | 0.943 |
| Hemoglobin, mg/dL a | 13.01 ± 1.52 | 12.71 ± 1.63 | 12.75 ± 2.12 | 0.936 |
| Weight, kg a | 71.92 ± 11.69 | 78.59 ± 8.88 | 74.95 ± 9.94 | 0.443 |
| Height, cm a | 157.93 ± 5.51 | 159.37 ± 4.54 | 155.50 ± 5.67 | 0.375 |
| BMI, kg/m2 b | 27.60 (25.75–29.90) | 31.35 (28.07–32.57) | 31.40 (28.00–33.20) | 0.184 |
| Fat Mass, % b | 36.40 (33.30–38.17) | 38.05 (34.85–39.42) | 38.90 (36.70–39.60) | 0.457 |
| Visceral Fat, level a | 10.43 ± 3.74 | 10.87 ± 2.91 | 11.64 ± 2.74 | 0.765 |
| Resting Metabolic Rate, Kcal a | 1433.75 ± 163.59 | 1525.12 ± 126.74 | 1484.14 ± 128.23 | 0.446 |
| IFN-γ, ng/mL b | 82.89 (76.31–92.62) | 106.46 (86.57–137.17) | 91.53 (79.50–116.37) | 0.181 |
| IL-10, pg/mL b | 386.77 (338.52–530.18) | 357.27 (316.77–502.64) | 347.07 (298.04–563.12) | 0.841 |
| Parameters | Group | Pre-Test | Post-Test | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI, kg/m2 b | Control (n = 8) | 27.60 (25.75–29.90) | 28.05 (26.05–29.70) | 0.622 |
| TRE (n = 8) | 31.35 (28.07–32.57) | 31.40 (28.35–33.05) | 0.833 | |
| ADMF (n = 7) | 31.40 (28.00–33.20) | 31.30 (27.70–32.50) | 0.445 | |
| Fat Mass, % b | Control (n = 8) | 36.40 (33.30–38.17) | 35.65 (33.00–39.10) | 0.735 |
| TRE (n = 8) | 38.05 (34.85–39.42) | 38.65 (35.70–39.07) | 0.140 | |
| ADMF (n = 7) | 38.90 (36.70–39.60) | 37.40 (35.00–39.20) | 0.735 | |
| Visceral Fat, level a | Control (n = 8) | 10.43 ± 3.74 | 10.50 ± 3.67 | 0.763 |
| TRE (n = 8) | 10.87 ± 2.91 | 10.81 ± 2.91 | 0.785 | |
| ADMF (n = 7) | 11.64 ± 2.74 | 10.78 ± 3.40 | 0.111 |
| Variable | Group | Pre-Test | Post-Test | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFN-γ levels, ng/mL | Control (n = 8) | 82.89 (76.31–92.62) | 88,80 (80.08–99.07) | 0.123 |
| TRE (n = 8) | 106.46 (86.57–137.17) | 87.89 (67.44–109.25) | 0.025 * | |
| ADMF (n = 7) | 91.53 (79.50–116.37) | 94.58 (78.52–117.74) | 0.866 | |
| IL-10 levels, pg/mL | Control (n = 8) | 386.77 (338.52–530.18) | 306.03 (262.58–380.25) | 0.123 |
| TRE (n = 8) | 357.27 (316.77–502.64) | 321.13 (250.29–434.04) | 0.069 | |
| ADMF (n = 7) | 347.07 (298.04–563.12) | 289.37 (265.28–776.45) | 1.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Permataputri, C.D.A.; Rejeki, P.S.; Argarini, R.; Halim, S.; Purnomo, S.P.; Rachmayanti, D.A. The Effects of Time-Restricted Eating and Alternate-Day Modified Fasting on Interferon-γ and Interleukin-10 Levels in Young Asian Women with Obesity: A Quasi-Experimental Study. Immuno 2025, 5, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5030039
Permataputri CDA, Rejeki PS, Argarini R, Halim S, Purnomo SP, Rachmayanti DA. The Effects of Time-Restricted Eating and Alternate-Day Modified Fasting on Interferon-γ and Interleukin-10 Levels in Young Asian Women with Obesity: A Quasi-Experimental Study. Immuno. 2025; 5(3):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5030039
Chicago/Turabian StylePermataputri, Chy’as Diuranil Astrid, Purwo Sri Rejeki, Raden Argarini, Shariff Halim, Sheeny Priska Purnomo, and Dian Aristia Rachmayanti. 2025. "The Effects of Time-Restricted Eating and Alternate-Day Modified Fasting on Interferon-γ and Interleukin-10 Levels in Young Asian Women with Obesity: A Quasi-Experimental Study" Immuno 5, no. 3: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5030039
APA StylePermataputri, C. D. A., Rejeki, P. S., Argarini, R., Halim, S., Purnomo, S. P., & Rachmayanti, D. A. (2025). The Effects of Time-Restricted Eating and Alternate-Day Modified Fasting on Interferon-γ and Interleukin-10 Levels in Young Asian Women with Obesity: A Quasi-Experimental Study. Immuno, 5(3), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5030039








