Study of Black Carbon (BC) Mass Concentration Variation at a Coastal Region (Surat) †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Study Region
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Data
3. Results and Discussion
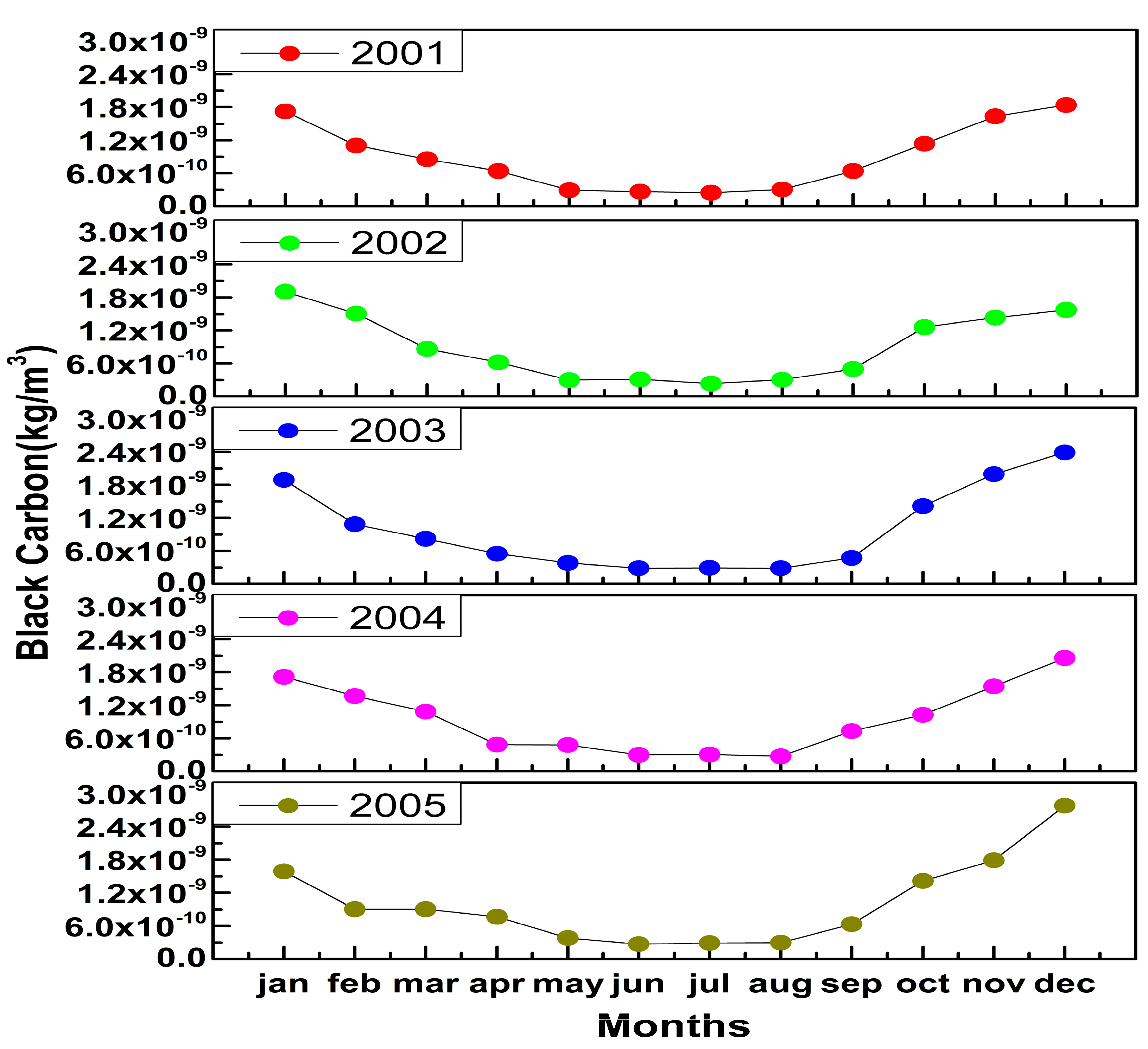
3.1. Annual Variations of Aerosol Black Carbon Mass Concentration
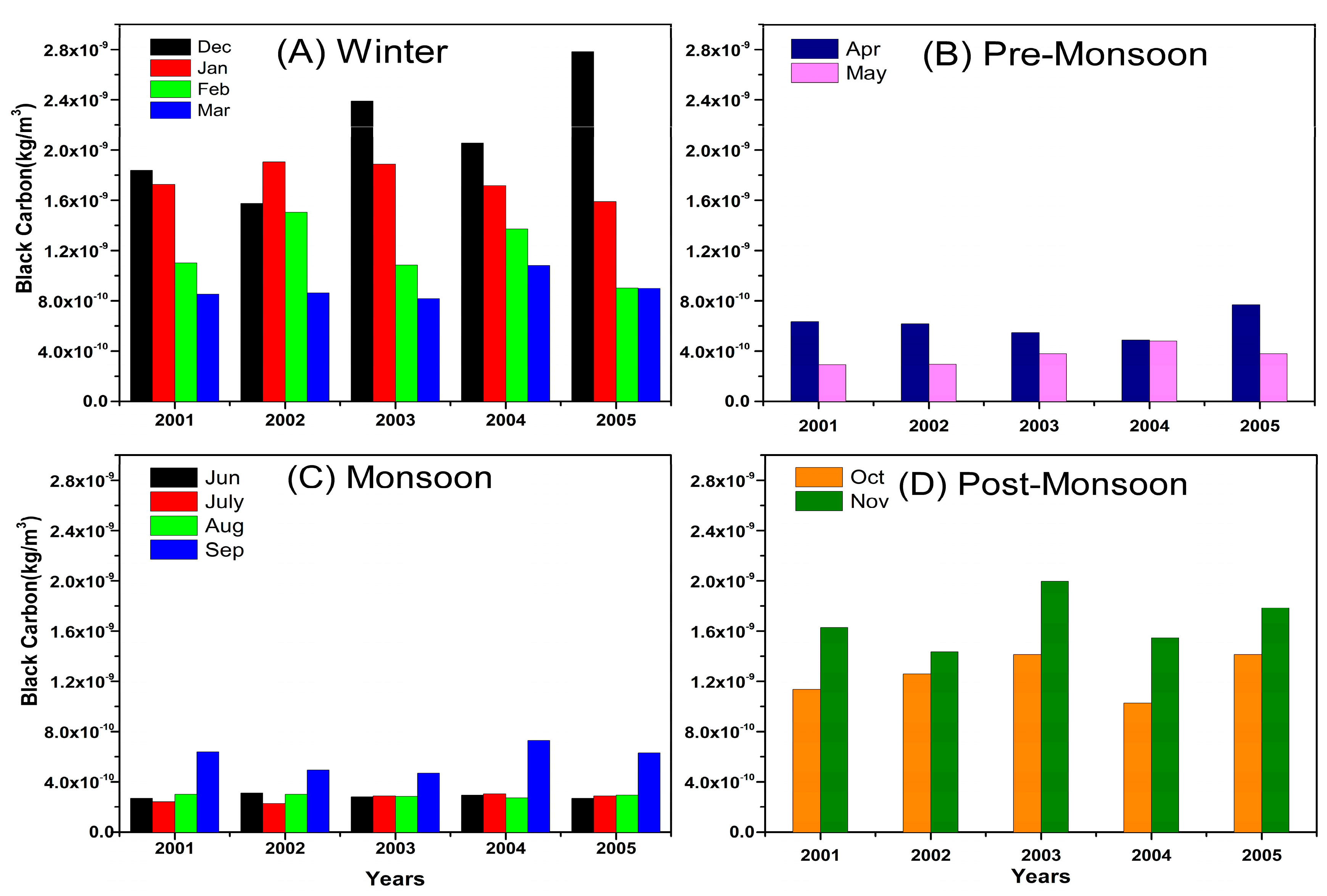
3.2. Seasonal Variation of Black Carbon
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bond, T.C.; Sun, H. Can reducing black carbon emissions counteract global warming? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5921–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, V.; Feng, Y. Air pollution, greenhouse gases and climate change: Global and regional perspectives. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, J.M.; Shine, K.P. Multi-spectral Calculations of the Radiative Forcing of Tropospheric Sulphate and Soot Aerosols Using a Column Model. Q.J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 123, 1907–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Climate response of fossil fuel and biofuel soot, accounting for soot’s feedback to snow and sea ice albedo and emissivity. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D21201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Carmichael, G. Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, S.; Wiscombe, W. A model for the spectral albedo of Snow. II: Snow containing atmospheric aerosols. J. Atmos. Sci. 1980, 37, 2734–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanner, M.G.; Zender, C.S.; Hess, P.G.; Mahowald, N.M.; Painter, T.H.; Ramanathan, V.; Rasch, P.J. Springtime warming and reduced snow cover from carbonaceous particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2481–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindell, D.; Faluvegi, G. Climate response to regional radiative forcing during the twentieth century. Nature Geosci. 2009, 2, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, J.M.; Roberts, D.L.; Slingo, A.; Edwards, J.M.; Shine, K.P. General circulation model calculations of the direct radiative forcing by anthropogenic sulphate and fossil-fuel soot aerosol. J. Clim. 1997, 10, 1562–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Control of fossil-fuel particulate black carbon and organic matter, possibly the most effective method of slowing global warming. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, 4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G.; Stordal, F.; Restad, K.; Isaksen, I.S.A. Estimation of the Direct Radiative Forcing Due to Sulfate and Soot Aerosols. Tellus 1998, 50, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change). The Scientific Basis, in: Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquir, M., Averyt, K.B., Tignor, M., Miller, H.L., Eds.; Cambridge Univ. Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols. Nature 2001, 409, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, N.; Kondo, Y.; Moteki, N.; Takegawa, N.; Koike, M.; Kita, K.; Matsui, H.; Kajino, M.; Nakamura, H.; Jung, J.S.; et al. Wet removal of black carbon in Asian outflow: Aerosol Radiative Forcing in East Asia (A-FORCE) aircraft campaign. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D03204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASAEarth Data Giovanni Webpage. Available online: https://giovanni.gsfc.nasa.gov/giovanni/ (accessed on 14 November 2020).
- Ganesh, K.E.; Dhanya, G.; Shivkumar, M.; Pranesha, T.S. A study on long term variation in particulate matter and black carbon aerosol optical thickness over mysuru, india: A satellite data approach. Mausam 2018, 69, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solanki, R.; Pathak, K.N. Study of Black Carbon (BC) Mass Concentration Variation at a Coastal Region (Surat). Environ. Sci. Proc. 2021, 4, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2020-08146
Solanki R, Pathak KN. Study of Black Carbon (BC) Mass Concentration Variation at a Coastal Region (Surat). Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2021; 4(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2020-08146
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolanki, Ranjitkumar, and Kamlesh N. Pathak. 2021. "Study of Black Carbon (BC) Mass Concentration Variation at a Coastal Region (Surat)" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 4, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2020-08146
APA StyleSolanki, R., & Pathak, K. N. (2021). Study of Black Carbon (BC) Mass Concentration Variation at a Coastal Region (Surat). Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 4(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2020-08146





