Optimal Water Quality Simulation of the Proposed Water Distribution System for the University of Kashmir Using EPANET 2.2 and Leakage Modelling of the Network Using EPANET Extension—WaterNetGen †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodological Approach and Analysis
2.1. PDA of Water Quality of the Network Using EPANET 2.2
2.2. Leakage Modeling by EPANET Extension—WaterNetGen
2.3. Optimization of the Water Quality Model
3. Results and Discussion
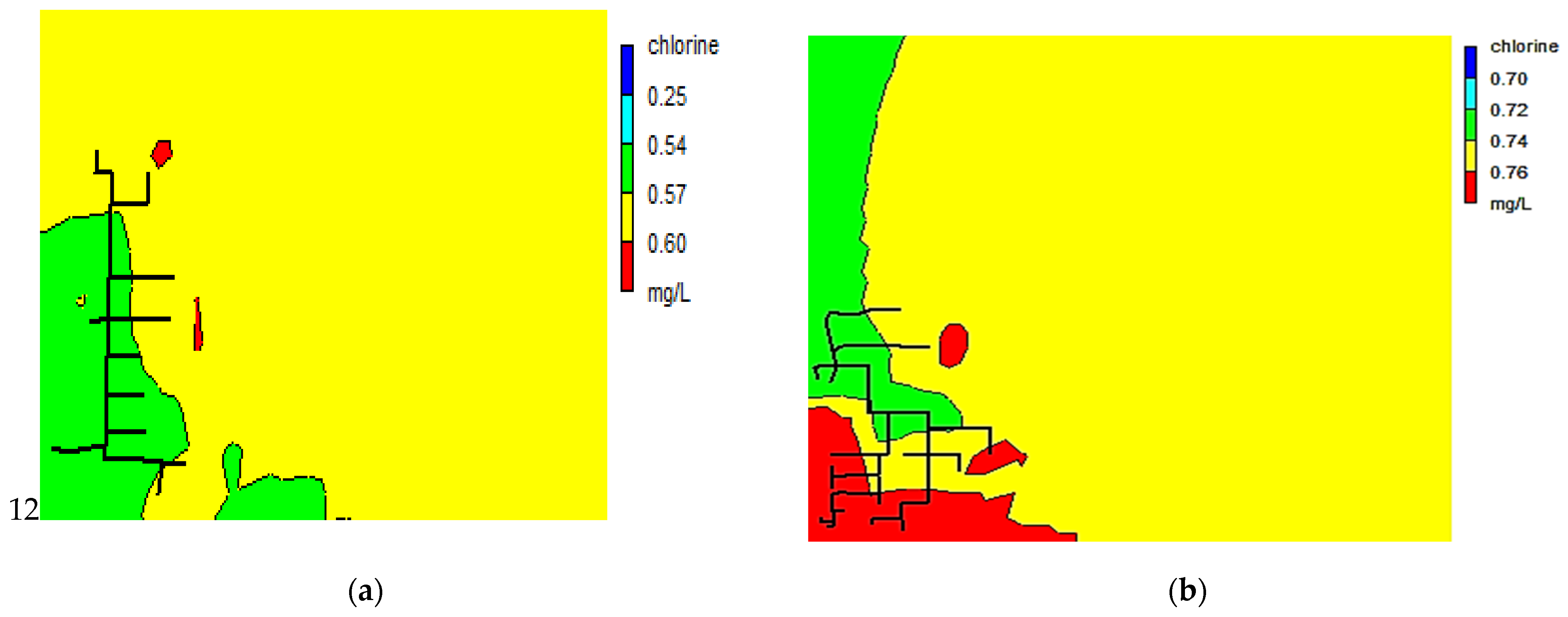
3.1. Chlorine Concentration at the Nodes
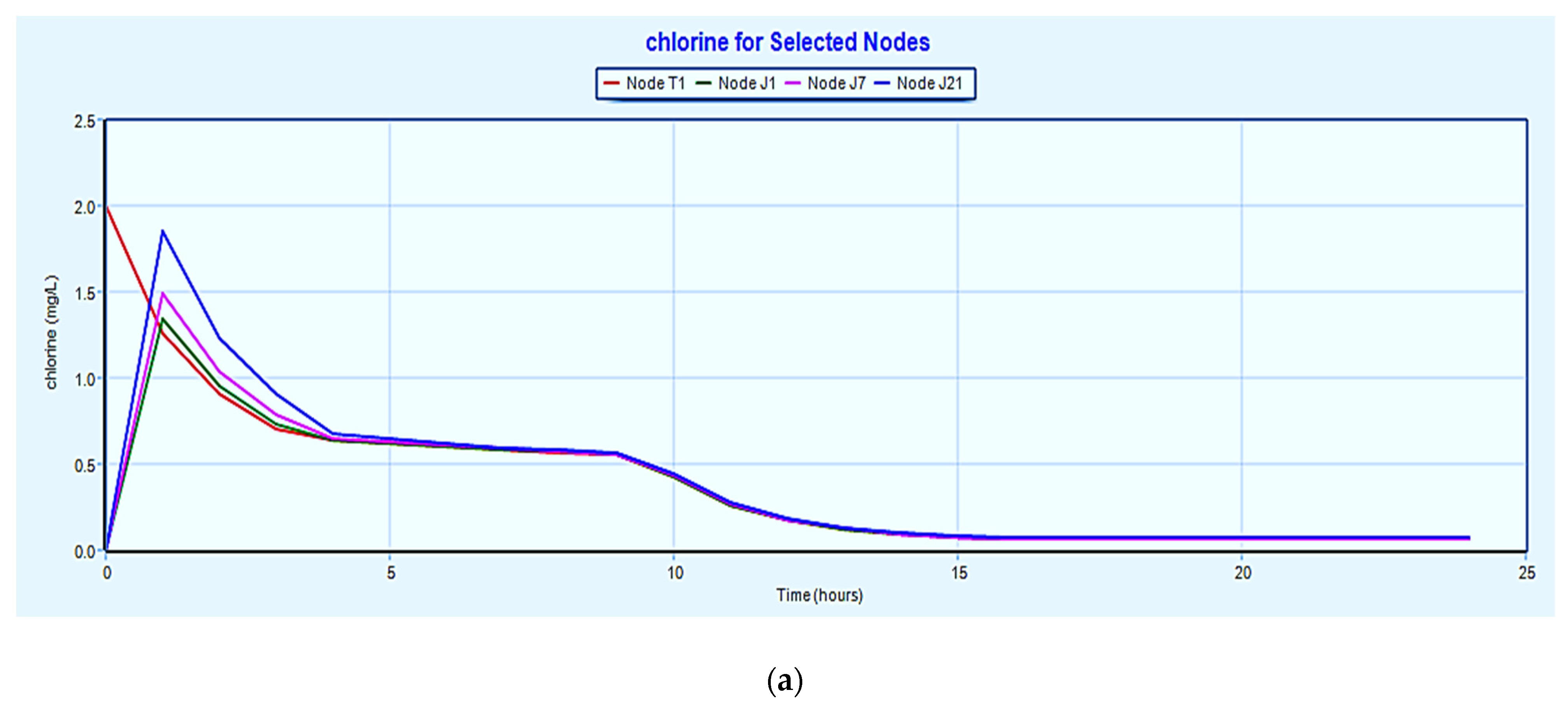
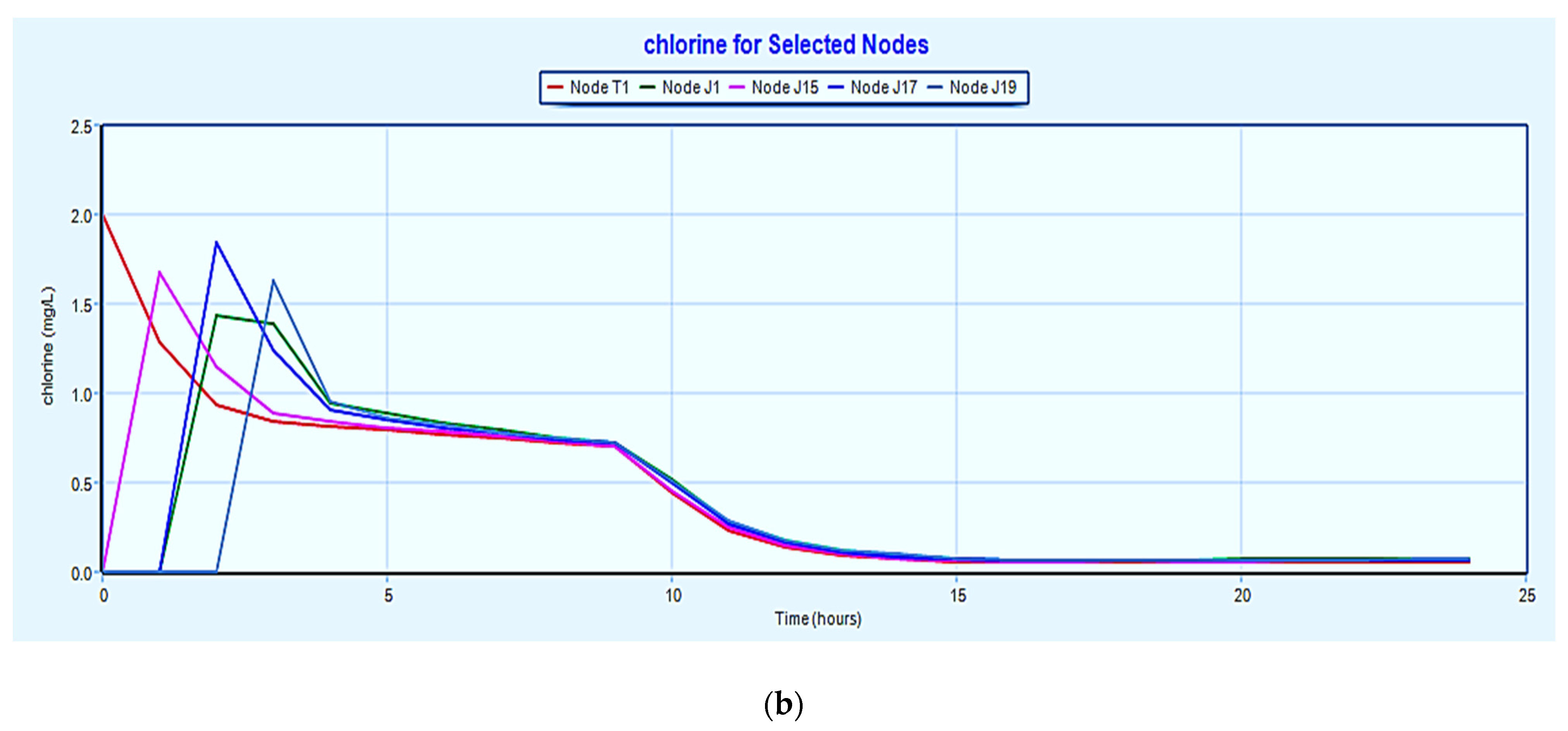
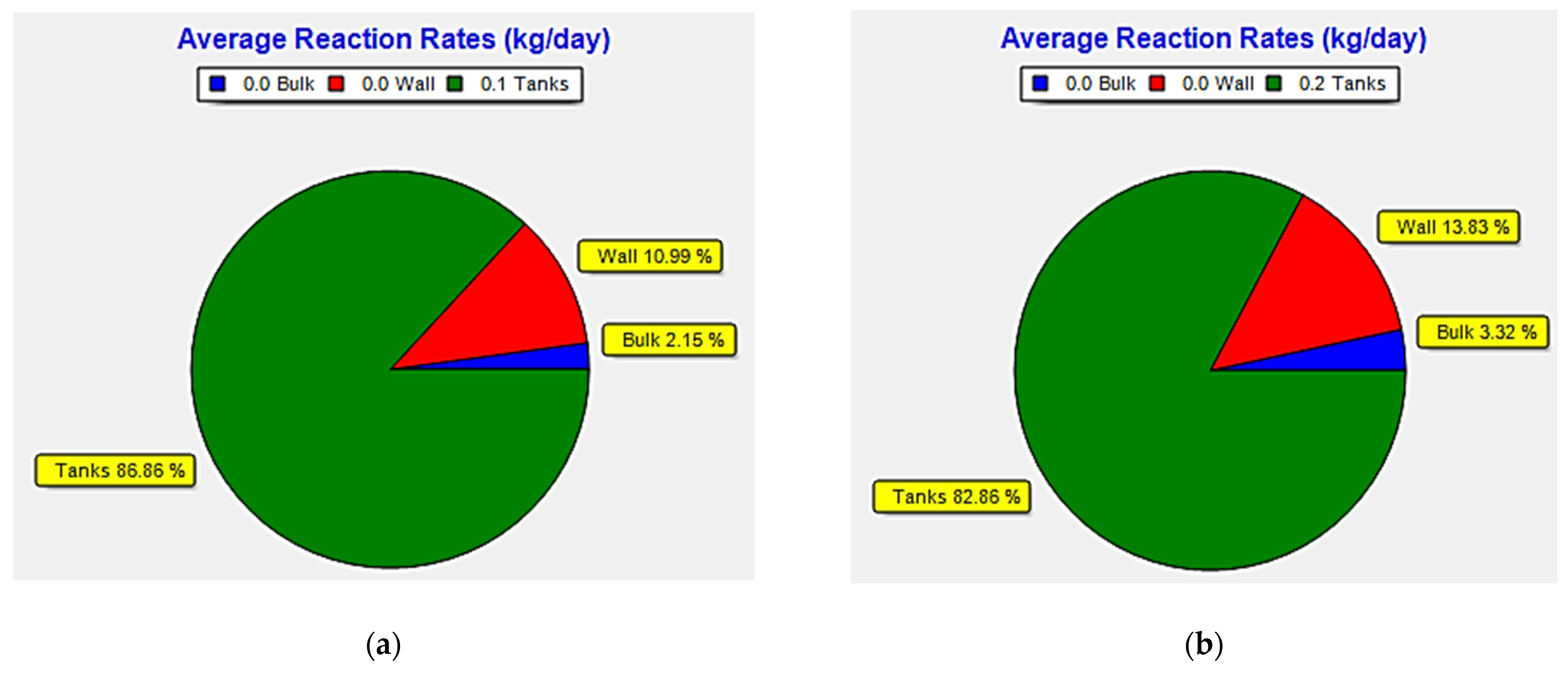
3.2. Decay of Chlorine in the System
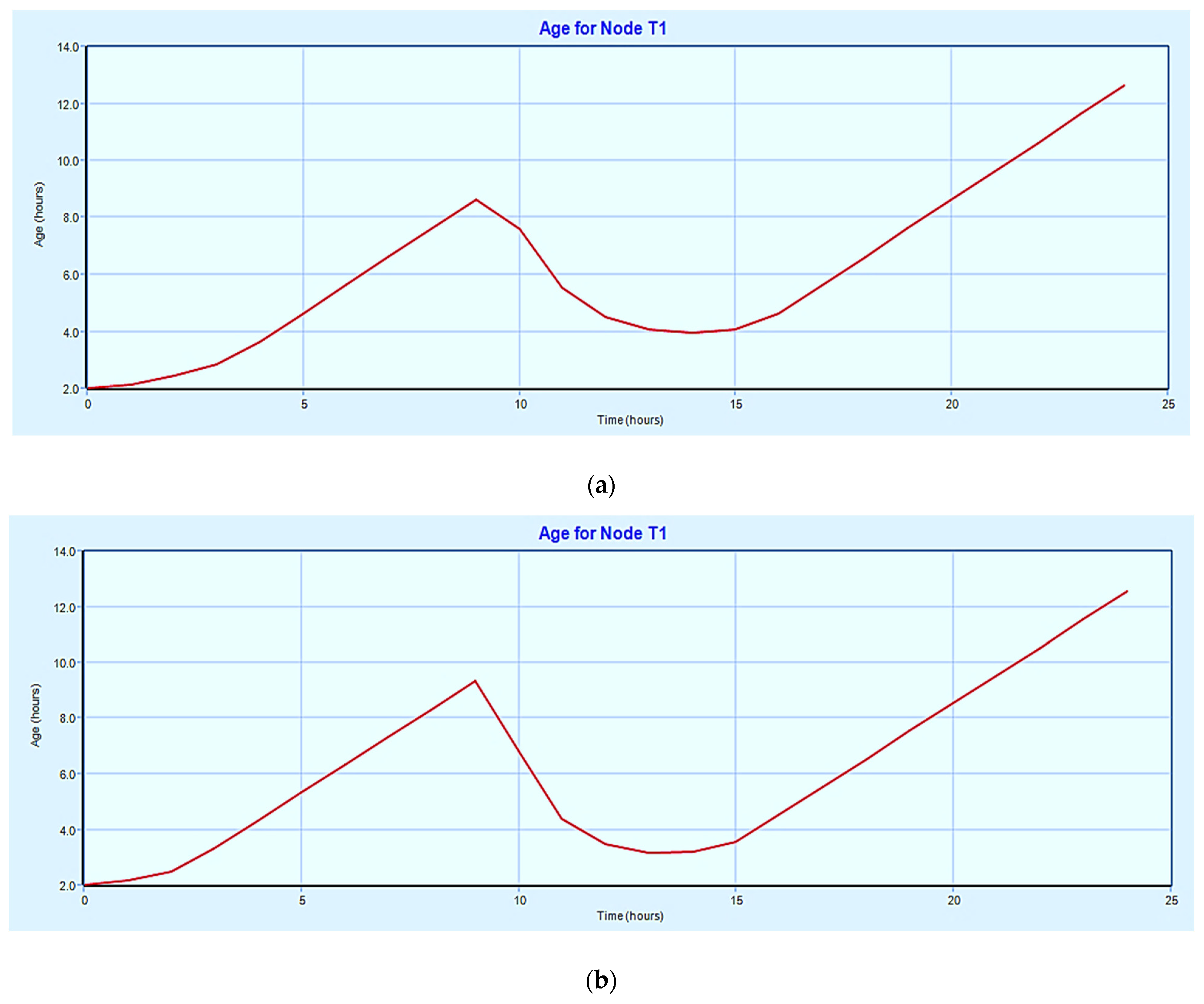
3.3. Time Series Graph for Age of Water in the Storage Tank
3.4. Leakage Modelling of the Network by EPANET Extension—WaterNetGen
4. Conclusions and Future Scope
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grayman, W.M. History of water quality modeling in distribution systems. In Proceedings of the 1st International WDSA/CCWI Joint Conference, Kingston, ON, Canada, 23–25 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lipiwattanakarn, S.; Kaewsang, S.; Makpiboon, C.; Changklom, J.; Pornprommin, A. Water quality audit in drinking water distribution networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2021, 147, 04020113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siew, C.; Tanyimboh, T.T.; Seyoum, A.G. Penalty-Free Multi-Objective Evolutionary Approach to Optimization of Anytown Water Distribution Network. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 3671–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nono, D.; Odirile, P.T.; Basupi, I.; Parida, B.P. Assessment of probable causes of chlorine decay in water distribution systems of Gaborone city, Botswana. Water SA 2019, 45, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, N.G.; Matta, M.E.; Halim, H.A. Simulation of chlorine decay in water distribution networks using watercad—Case study. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2013, 60, 25–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kourbasis, N.; Patelis, M.; Tsitsifli, S.; Kanakoudis, V. Optimizing Water Age and Pressure in Drinking Water Distribution Networks. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2020, 2, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IS 10500. Indian Standard Drinking Water Specification. Bureau of Indian Standards: New Delhi, India, 2012.
- Cobacho, R.; Arregui, F.; Soriano, J.; Cabrera, E. Including leakage in network models: An application to calibrate leak valves in EPANET. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.—AQUA 2015, 64, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muranho, J.; Ferreira, A.; Sousa, J.; Gomes, A.; Sá Marques, A. WaterNetGen: An EPANET extension for automatic water distribution network models generation and pipe sizing João Muranho, Ana Ferreira, Joaquim Sousa, Abel Gomes. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2012, 12, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, L. EPANET 2.2 User Manual; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Muranho, J.; Ferreira, A.; Sousa, J.; Gomes, A.; Marques, A.S. Pressure dependent demand and leakage modelling with an EPANET Extension—WaterNetGen. Procedia Eng. 2014, 89, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avile, A.; Garcı, F. Pressure management for leakage reduction using pressure reducing valves. Case study in an Andean city. Alexendria Eng. J. 2019, 58, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Walski, T.; Researcher, I.; Weir, M.H. Modeling leakage reduction. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2006, 98, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Node | Pressure (m) | Emitter Flow (lps) | Node | Pressure (m) | Emitter Flow (lps) | Node | Pressure (m) | Emitter Flow (lps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Junc J1 | 34.39 | 0.00038 | Junc J11 | 24.79 | 0.00069 | Junc J21 | 28.64 | 0.00055 |
| Junc J2 | 29.66 | 0.00033 | Junc J12 | 24.58 | 0.0002 | Junc J22 | 27.17 | 0.00018 |
| Junc J3 | 27.41 | 0.00016 | Junc J13 | 25.36 | 0.00036 | Junc J23 | 27.78 | 0.00019 |
| Junc J4 | 31.62 | 0.00041 | Junc J14 | 25.43 | 0.0005 | Junc J24 | 25.07 | 0.00015 |
| Junc J5 | 29.43 | 0.0004 | Junc J15 | 25.02 | 0.00039 | Junc J25 | 26.27 | 0.00049 |
| Junc J6 | 32.83 | 0.00036 | Junc J16 | 25.87 | 0.00011 | Junc J26 | 24.14 | 0.00014 |
| Junc J7 | 31.28 | 0.00026 | Junc J17 | 25.55 | 0.00042 | Junc J27 | 23.93 | 0.00036 |
| Junc J8 | 28.75 | 0.00073 | Junc J18 | 25.81 | 0.00041 | Junc J28 | 34.09 | 0.00041 |
| Junc J9 | 25.86 | 0.00024 | Junc J19 | 25.44 | 0.00037 | Junc J29 | 27.4 | 0.00073 |
| Junc J10 | 26.5 | 0.00113 | Junc J20 | 25.36 | 0.00005 | Junc J30 | 30.19 | 0.00031 |
| total | 0.013 |
| Node | Pressure (m) | Emitter Flow (lps) | Node | Pressure (m) | Emitter Flow (lps) | Node | Pressure (m) | Emitter Flow (lps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Junc J1 | 27.73 | 0.00012 | Junc J19 | 23.57 | 0.00043 | Junc J37 | 24.61 | 0.00036 |
| Junc J2 | 27.99 | 0.00039 | Junc J20 | 23.65 | 0.00084 | Junc J38 | 24.05 | 0.00014 |
| Junc J3 | 28.66 | 0.00021 | Junc J21 | 24.65 | 0.00023 | Junc J39 | 24.77 | 0.0001 |
| Junc J4 | 29.07 | 0.00017 | Junc J22 | 25.4 | 0.00021 | Junc J40 | 23.9 | 0.00031 |
| Junc J5 | 34.61 | 0.00025 | Junc J23 | 25.01 | 0.0002 | Junc J41 | 23.69 | 0.00031 |
| Junc J6 | 34.84 | 0.00067 | Junc J24 | 24.76 | 0.00011 | Junc J42 | 25.04 | 0.00097 |
| Junc J7 | 34.61 | 0.00088 | Junc J25 | 24.29 | 0.00019 | Junc J43 | 24.78 | 0.0001 |
| Junc J8 | 33.36 | 0.00072 | Junc J26 | 24.04 | 0.00019 | Junc J44 | 31.08 | 0.00037 |
| Junc J9 | 31.97 | 0.00021 | Junc J27 | 23.86 | 0.0002 | Junc J45 | 30.87 | 0.00029 |
| Junc J10 | 31.53 | 0.00027 | Junc J28 | 23.53 | 0.00031 | Junc J46 | 25.26 | 0.00014 |
| Junc J11 | 30.75 | 0.0002 | Junc J29 | 23.49 | 0.0001 | Junc J47 | 25.39 | 0.00008 |
| Junc J12 | 31.57 | 0.00065 | Junc J30 | 25.15 | 0.00058 | Junc J48 | 24.63 | 0.00022 |
| Junc J13 | 30.98 | 0.00057 | Junc J31 | 24.81 | 0.00035 | Junc J49 | 27.28 | 0.00052 |
| Junc J14 | 31.62 | 0.00028 | Junc J32 | 24.74 | 0.00017 | Junc J50 | 29.22 | 0.00131 |
| Junc J15 | 29.13 | 0.00089 | Junc J33 | 24.65 | 0.00024 | Junc J51 | 27.77 | 0.0009 |
| Junc J16 | 23.89 | 0.00036 | Junc J34 | 23.48 | 0.00011 | Junc J52 | 26.07 | 0.00094 |
| Junc J17 | 23.64 | 0.00048 | Junc J35 | 24.53 | 0.00035 | Junc J53 | 25.78 | 0.00111 |
| Junc J18 | 23.52 | 0.0004 | Junc J36 | 25.43 | 0.00009 | Junc J54 | 25.08 | 0.0001 |
| total | 0.029 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ajaz, M.; Ahmad, D. Optimal Water Quality Simulation of the Proposed Water Distribution System for the University of Kashmir Using EPANET 2.2 and Leakage Modelling of the Network Using EPANET Extension—WaterNetGen. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 25, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14251
Ajaz M, Ahmad D. Optimal Water Quality Simulation of the Proposed Water Distribution System for the University of Kashmir Using EPANET 2.2 and Leakage Modelling of the Network Using EPANET Extension—WaterNetGen. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2023; 25(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14251
Chicago/Turabian StyleAjaz, Mominah, and Danish Ahmad. 2023. "Optimal Water Quality Simulation of the Proposed Water Distribution System for the University of Kashmir Using EPANET 2.2 and Leakage Modelling of the Network Using EPANET Extension—WaterNetGen" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 25, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14251
APA StyleAjaz, M., & Ahmad, D. (2023). Optimal Water Quality Simulation of the Proposed Water Distribution System for the University of Kashmir Using EPANET 2.2 and Leakage Modelling of the Network Using EPANET Extension—WaterNetGen. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 25(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14251






