Jakarta’s 2020 New Year Flood Assessment with a Rainfall–Runoff–Inundation (RRI) Model †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
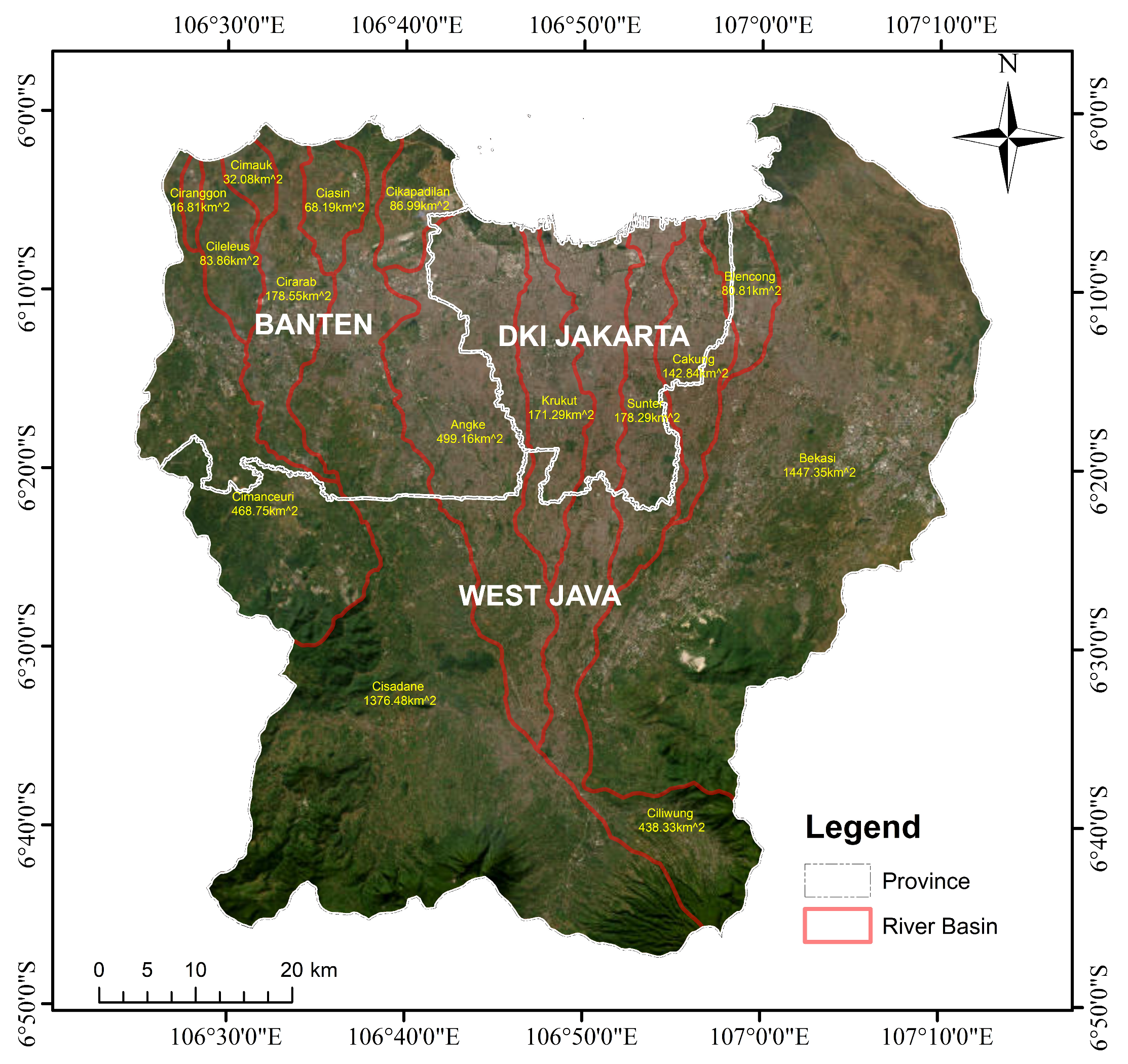
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Precipitation Data
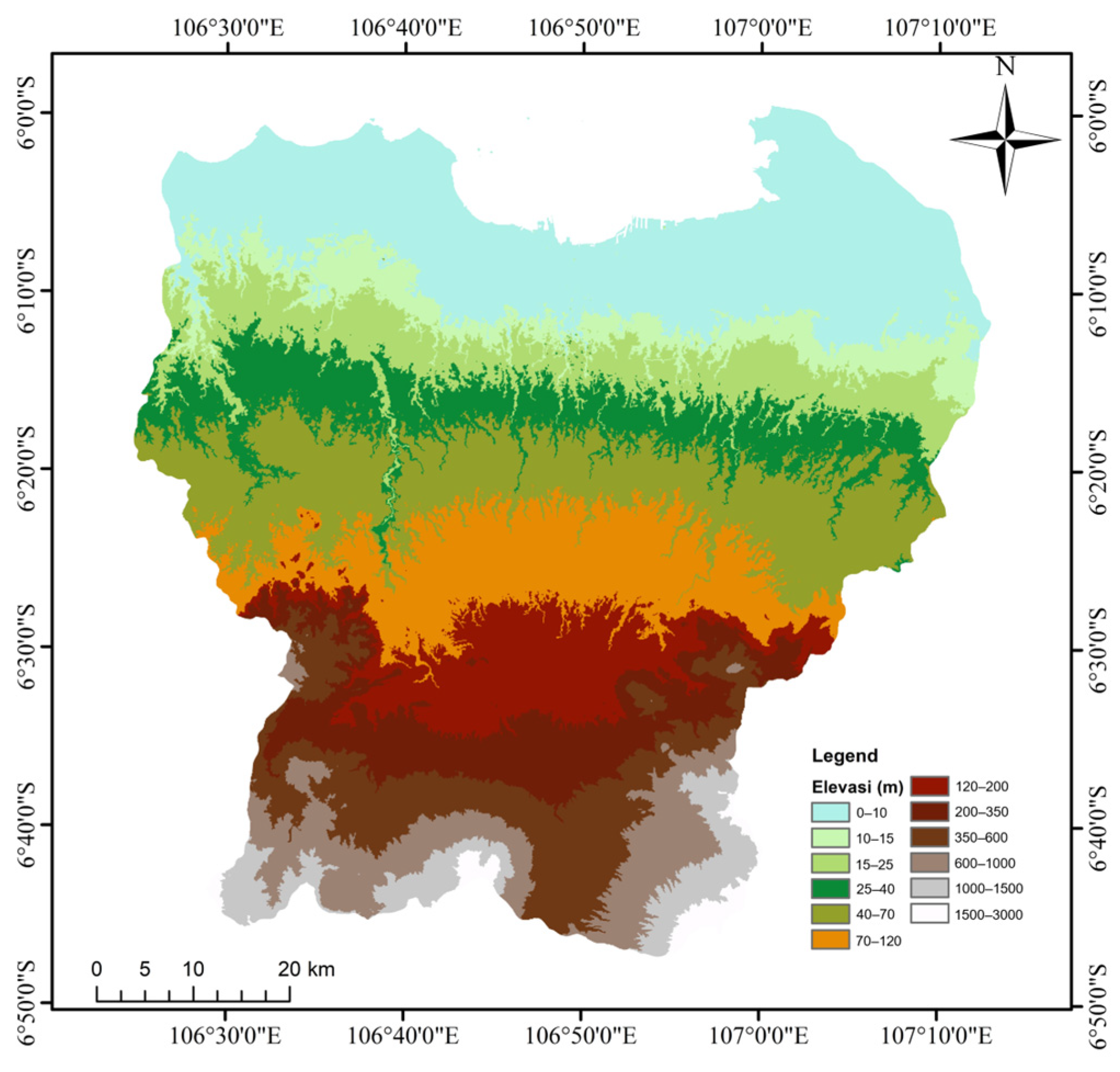
2.2.2. Topography
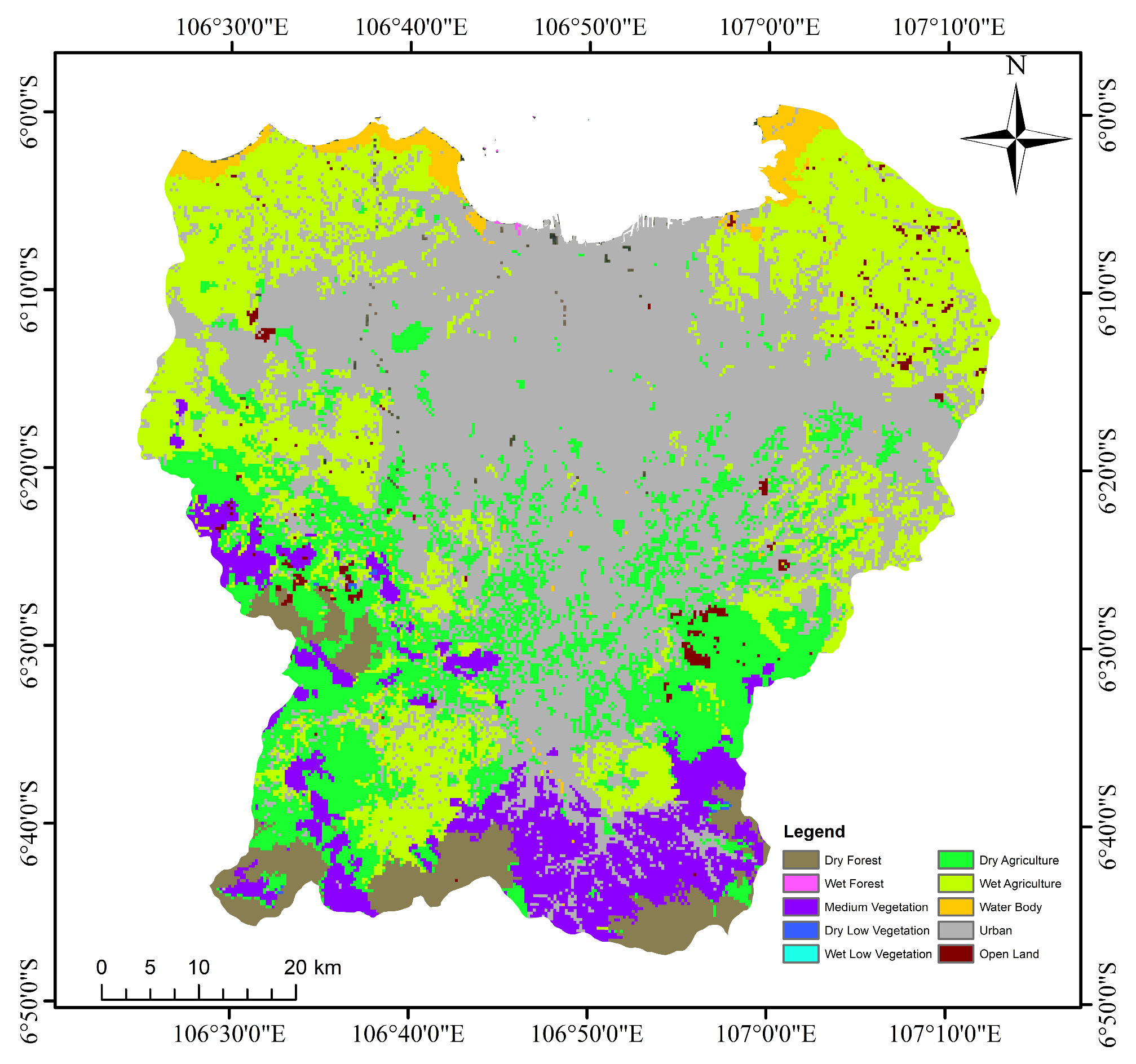
2.2.3. Land Cover
2.3. Rainfall–Runoff–Inundation (RRI) Model
3. Results and Discussion
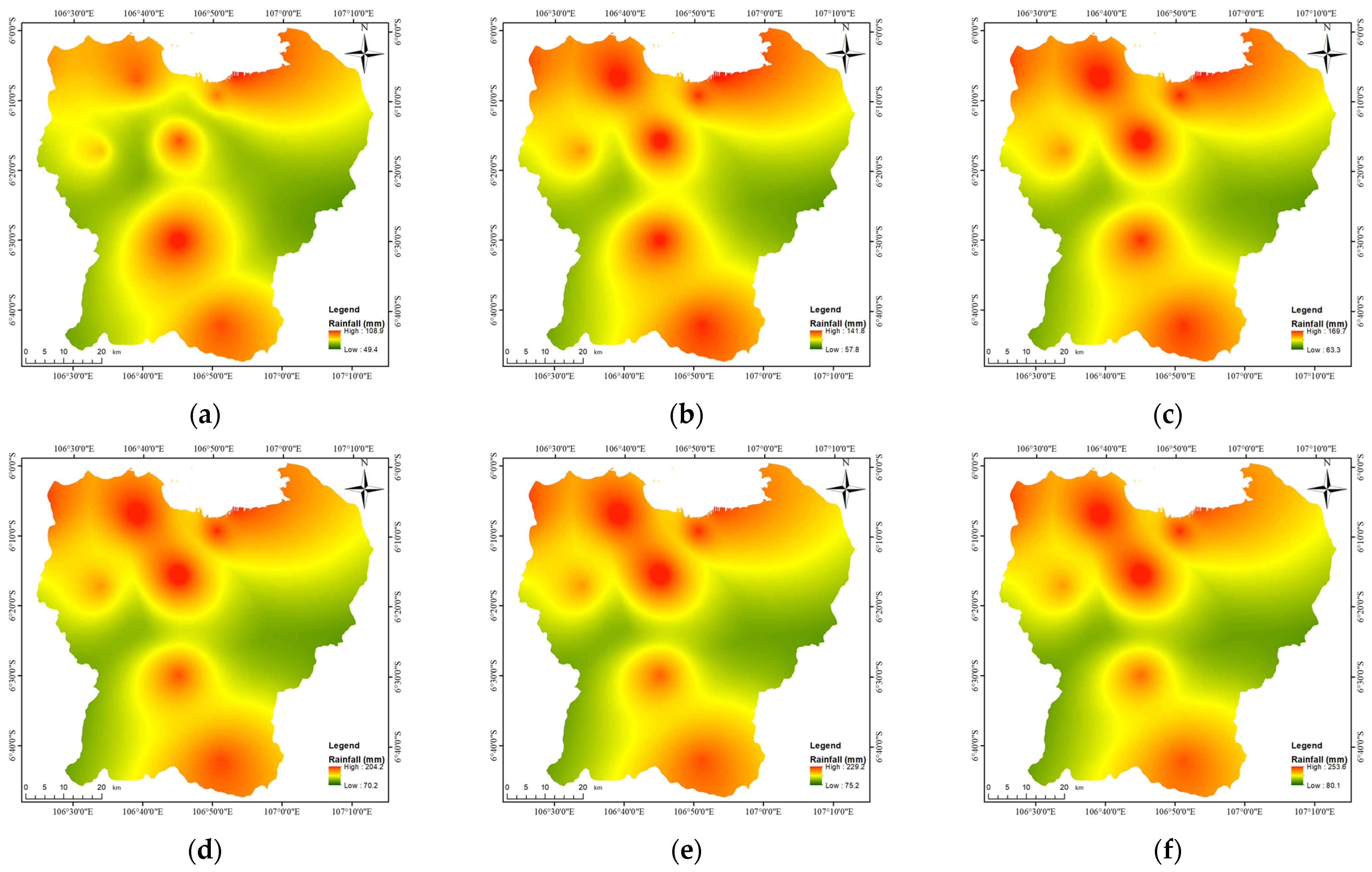
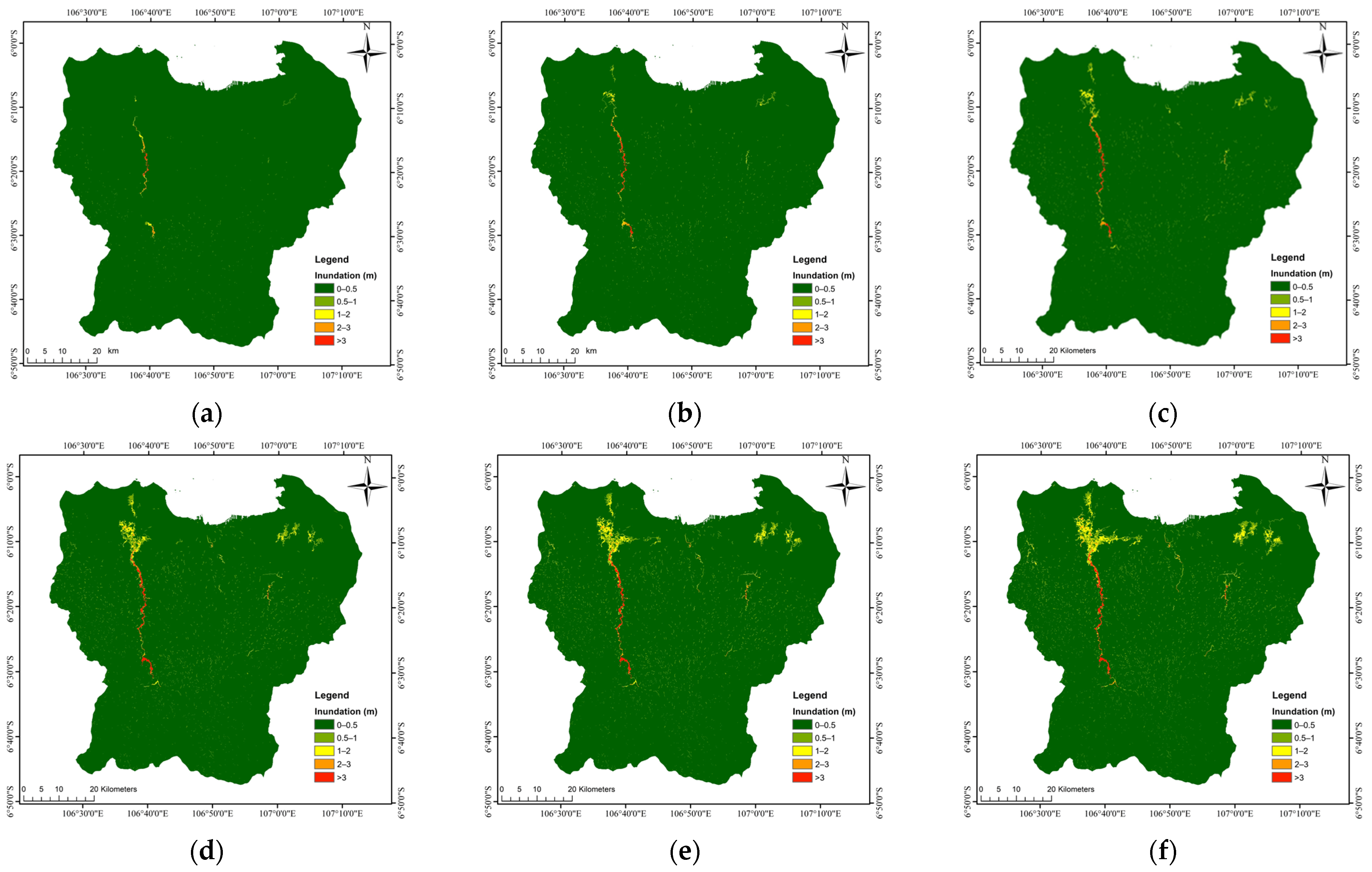
3.1. Model Calibration
3.2. Model Application
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chow, V.T.; Maidment, D.R.; Mays, L.W. Applied Hydrology; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1988; Available online: https://ponce.sdsu.edu/Applied_Hydrology_Chow_1988.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Penning-Rowsell, E.C.; Ward, R. Floods: A Geographical Perspective. Geogr. J. 1980, 146, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, T.L.; Forbes, D.L.; Dickie, S.; Shreenan, R. Using topographic lidar to map flood risk from storm-surge events for Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, Canada. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 30, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, B.; Hall, A.J.; Disse, M.; Schumann, A.H. Fluvial flood risk management in a changing world. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 509–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Mikkelsen, P.S.; Halsnæs, K.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K. Framework for economic pluvial flood risk assessment considering climate change effects and adaptation benefits. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414–415, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguli, P.; Merz, B. Extreme Coastal Water Levels Exacerbate Fluvial Flood Hazards in Northwestern Europe. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Ghimire, R. Forest cover, socioeconomics, and reported flood frequency in developing countries. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W08529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y. Evolvement rules of basin flood risk under low-carbon mode. Part I: Response of soil organic carbon to land use change and its influence on land use planning in the Haihe basin. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, J.; Molombe, J.M.; Mertens, K.; Parra, C.; Poesen, J.; Che, V.B.; Kervyn, M. Socio-political drivers and consequences of landslide and flood risk zonation: A case study of Limbe city, Cameroon. Environ. Plan. C Politics Space 2019, 37, 707–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, S.H.; Gan, T.Y. Urbanization and climate change implications in flood risk management: Developing an efficient decision support system for flood susceptibility mapping. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, T.; Zehe, E.; Bronstert, A. Rainfall—Runoff response, event-based runoff coefficients and hydrograph separation. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2007, 52, 843–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, V.R.; Pickup, G. Flood geomorphology of the Katherine Gorge, Northern Territory, Australia. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1987, 98, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, B.O.; Baker, V.R.; Kochel, R.C.; Patton, P.C. Flood Geomorphology. Geogr. Rev. 1990, 80, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texier, P. Floods in Jakarta: When the extreme reveals daily structural constraints and mismanagement. Disaster Prev. Manag. 2008, 17, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Bae, D.-H. Climate Change Impact Assessment on Green and Blue Water over Asian Monsoon Region. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 2407–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, V.R. Stream-Channel Response to Floods, with Examples from Central Texas. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1977, 88, 1057–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasanto, B.D.; Pramudya, B.; Boer, R.; Suharnoto, Y. Effects of Forest Cover Change on Flood Characteristics in the Upper Citarum Watershed. J. Manaj. Hutan Trop. (J. Trop. For. Manag.) 2014, 20, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M.; Mano, A.; Udo, K. Modeling flood runoff response to land cover change with rainfall spatial distribution in urbanized catchment. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. B1 (Hydraul. Eng.) 2011, 67, I_19–I_24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, R.; Rulli, M.C. An integrated simulation method for flash-flood risk assessment: 2. Effects of changes in land-use under a historical perspective. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, S.N.; Reid, S.C.; Tayefi, V.; Yu, D.; Hardy, R.J. Reconceptualising coarse sediment delivery problems in rivers as catchment-scale and diffuse. Geomorphology 2008, 98, 227–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizaldi, A.; Moe, I.R.; Farid, M.; Aribawa, T.M.; Bayuadji, G.; Sugiharto, T. Study of flood characteristic in Cikalumpang River by using 2D flood model. MATEC Web Conf. 2019, 270, 04010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghloul, M.S.; Ghaderpour, E.; Dastour, H.; Farjad, B.; Gupta, A.; Eum, H.; Achari, G.; Hassan, Q.K. Long Term Trend Analysis of River Flow and Climate in Northern Canada. Hydrology 2022, 9, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.F.; Mimura, N. Impacts of climate change and sea-level rise on cyclonic storm surge floods in Bangladesh. Glob. Environ. Change 2008, 18, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegatte, S.; Ranger, N.; Mestre, O.; Dumas, P.; Corfee-Morlot, J.; Herweijer, C.; Wood, R.M. Assessing climate change impacts, sea level rise and storm surge risk in port cities: A case study on Copenhagen. Clim. Change 2010, 104, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darsan, J.; Asmath, H.; Jehu, A. Flood-risk mapping for storm surge and tsunami at Cocos Bay (Manzanilla), Trinidad. J. Coast. Conserv. 2013, 17, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, M.K.; Kopp, R.E.; Oppenheimer, M.; Tebaldi, C. Allowances for evolving coastal flood risk under uncertain local sea-level rise. Clim. Change 2016, 137, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Qian, L.; Rui, H.; Zuo, T.; Zheng, D.; Xu, Y.; Xu, C.-Y. Assessing the effects of urbanization on annual runoff and flood events using an integrated hydrological modeling system for Qinhuai River basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 464–465, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aich, V.; Liersch, S.; Vetter, T.; Fournet, S.; Andersson, J.C.; Calmanti, S.; van Weert, F.H.; Hattermann, F.F.; Paton, E.N. Flood projections within the Niger River Basin under future land use and climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BNPB Editorial. Hujan Ekstrem Penyebab Banjir Jakarta. Available online: https://bnpb.go.id/berita/hujan-ekstrem-penyebab-banjir-jakarta (accessed on 16 May 2020).
- Biro Komunikasi Publik Kementrian PUPR. Menteri Basuki Siapkan Langkah Penanganan Banjir di Jakarta dan Sekitarnya. Available online: https://pu.go.id/berita/view/17794/menteri-basuki-siapkan-langkah-penanganan-banjir-di-jakarta-dan-sekitarnya (accessed on 16 May 2020).
- Caljouw, M.; Nas, P.J.; Pratiwo, M. Flooding in Jakarta: Towards a blue city with improved water management. J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Southeast Asia 2009, 161, 454–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, B.E.; Corps, M. Adapting cities to climate variability and change: Balance between community engagement and supporting facilitation roles of the local government to reduce the impact of climate change. In Proceedings of the Human(e) Settlements: The Urban Challenge Conference, Johannesburg, South Africa, 17–21 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Octavianti, T.; Charles, K. The evolution of Jakarta’s flood policy over the past 400 years: The lock-in of infrastructural solutions. Environ. Plan. C Politics Space 2019, 37, 1102–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, R.; Sotgiu, I.; Settanni, M. Disaster preparedness and perception of flood risk: A study in an alpine valley in Italy. J. Environ. Psychol. 2008, 28, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petry, B. Keynote Lecture: Coping with Floods: Complementarity of Structural and Non-Structural Measures. In Flood Defence; Science Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 60–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hadihardaja, I.K.; Kuntoro, A.A.; Farid, M. Flood Resilience for Risk Management: Case Study of River Basin in Indonesia. Glob. Asp. 2013, 3, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Budiyono, Y.; Aerts, J.C.J.H.; Tollenaar, D.; Ward, P.J. River flood risk in Jakarta under scenarios of future change. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 757–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.K.; Emam, A.R.; Masago, Y.; Kumar, P.; Regmi, R.K.; Fukushi, K. Assessment of future flood inundations under climate and land use change scenarios in the Ciliwung River Basin, Jakarta. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2017, 11, S1105–S1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, I.R.; Kure, S.; Januriyadi, N.F.; Farid, M.; Udo, K.; Kazama, S.; Koshimura, S. Effect of land subsidence on flood inundation in Jakarta, Indonesia. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. G (Environ. Res.) 2016, 72, I_283–I_289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, I.R.; Kure, S.; Januriyadi, N.F.; Farid, M.; Udo, K.; Kazama, S.; Koshimura, S. Future projection of flood inundation considering land-use changes and land subsidence in Jakarta, Indonesia. Hydrol. Res. Lett. 2017, 11, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, A.R.; Mishra, B.K.; Kumar, P.; Masago, Y.; Fukushi, K. Impact Assessment of Climate and Land-Use Changes on Flooding Behavior in the Upper Ciliwung River, Jakarta, Indonesia. Water 2016, 8, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januriyadi, N.F.; Kazama, S.; Moe, I.R.; Kure, S. Evaluation of future flood risk in Asian megacities: A case study of Jakarta. Hydrol. Res. Lett. 2018, 12, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, I.R.; Rizaldi, A.; Farid, M.; Moerwanto, A.S.; Kuntoro, A.A. The use of rapid assessment for flood hazard map development in upper citarum river basin. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 229, 04011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronowicka-Mielniczuk, U.; Mielniczuk, J.; Obroślak, R.; Przystupa, W. A Comparison of Some Interpolation Techniques for Determining Spatial Distribution of Nitrogen Compounds in Groundwater. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2019, 13, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Doan, C.D.; Liong, S.-Y.; Sanders, R.; Dao, A.T.; Fewtrell, T. Regional frequency analysis of extreme rainfall events in Jakarta. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 1075–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, A.; Rubiano, J.; Nelson, A.; Farrow, A.; Mulligan, M. Practical Use of SRTM Data in the Tropics—Comparisons with Digital Elevation Models Generated from Cartographic Data; Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical (CIAT): Cali, Colombia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Saifullah, M.; Li, Q.; Li, X. Impact of DEM Resolution and Spatial Scale: Analysis of Influence Factors and Parameters on Physically Based Distributed Model. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 8582041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayama, T.; Ozawa, G.; Kawakami, T.; Nabesaka, S.; Fukami, K. Rainfall–runoff–inundation analysis of the 2010 Pakistan flood in the Kabul River basin. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2012, 57, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, M.; Pelich, R.; Pulvirenti, L.; Pierdicca, N.; Hostache, R.; Matgen, P. Sentinel-1 InSAR Coherence to Detect Floodwater in Urban Areas: Houston and Hurricane Harvey as a Test Case. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, F.L.; Sharif, H.O.; Senarath, S.U.S.; Smith, J.A.; Baeck, M.L.; Richardson, J.R. Hydrologic analysis of the Fort Collins, Colorado, flash flood of 1997. J. Hydrol. 2000, 228, 82–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, P.; Bouvier, C.; Cisneros, L.; Dominguez, R. Influence of rainfall spatial variability on flood prediction. J. Hydrol. 2002, 260, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
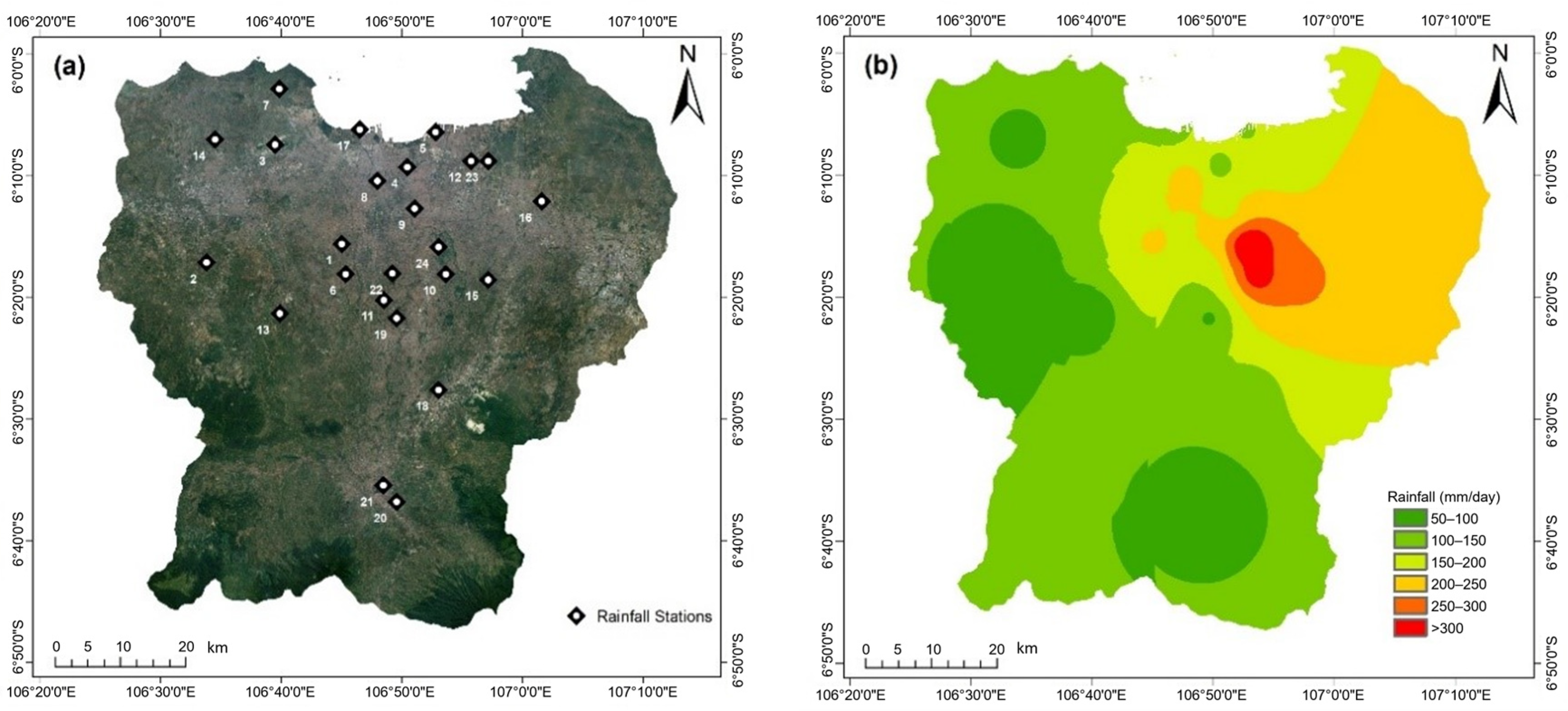
| No. | Rainfall Station | No. | Rainfall Station |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Stasiun Klimatologi Tanggerang Selatan | 13 | AWS Puspitek |
| 2 | Stasiun Meteorologi Curug | 14 | ARG Sepatan |
| 3 | Stasiun Meteorologi Cengkareng | 15 | ARG Jatiasih |
| 4 | Stasiun Meteorologi Kemayoran | 16 | ARG Teluk Pucung |
| 5 | Stasiun Maritim Tanjung Priok | 17 | ARG Muara |
| 6 | Pos Hujan Bd Ciputat | 18 | ARG Jagorawi |
| 7 | Pos Hujan Teluk Naga | 19 | AWS UI |
| 8 | ARG Tomang | 20 | ARG Katulampa |
| 9 | ARG Manggarai | 21 | AWS IPB |
| 10 | AWW TMII | 22 | Pos Hujan Ragunan |
| 11 | ARG Ciganjur | 23 | Pos Hujan Rorotan |
| 12 | ARG Sukapura | 24 | TNI AU Halim |
| Parameter | Land Cover | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Clay | Loam | Sandy Clay Loam | |
| Soil Depth (m) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Porosity (-) | 0.475 | 0.463 | 0.398 |
| kv (m/s) | 0–8.33 × 10−8 | 0–9.44 × 10−7 | 0–4.17 × 10−7 |
| Sf | 0.361 | 0.089 | 0.219 |
| ka (m/s) | 0–0.3 | 0–0.3 | 0–0.3 |
| Unsat. Porosity (-) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Beta | 8 | 8 | 8 |
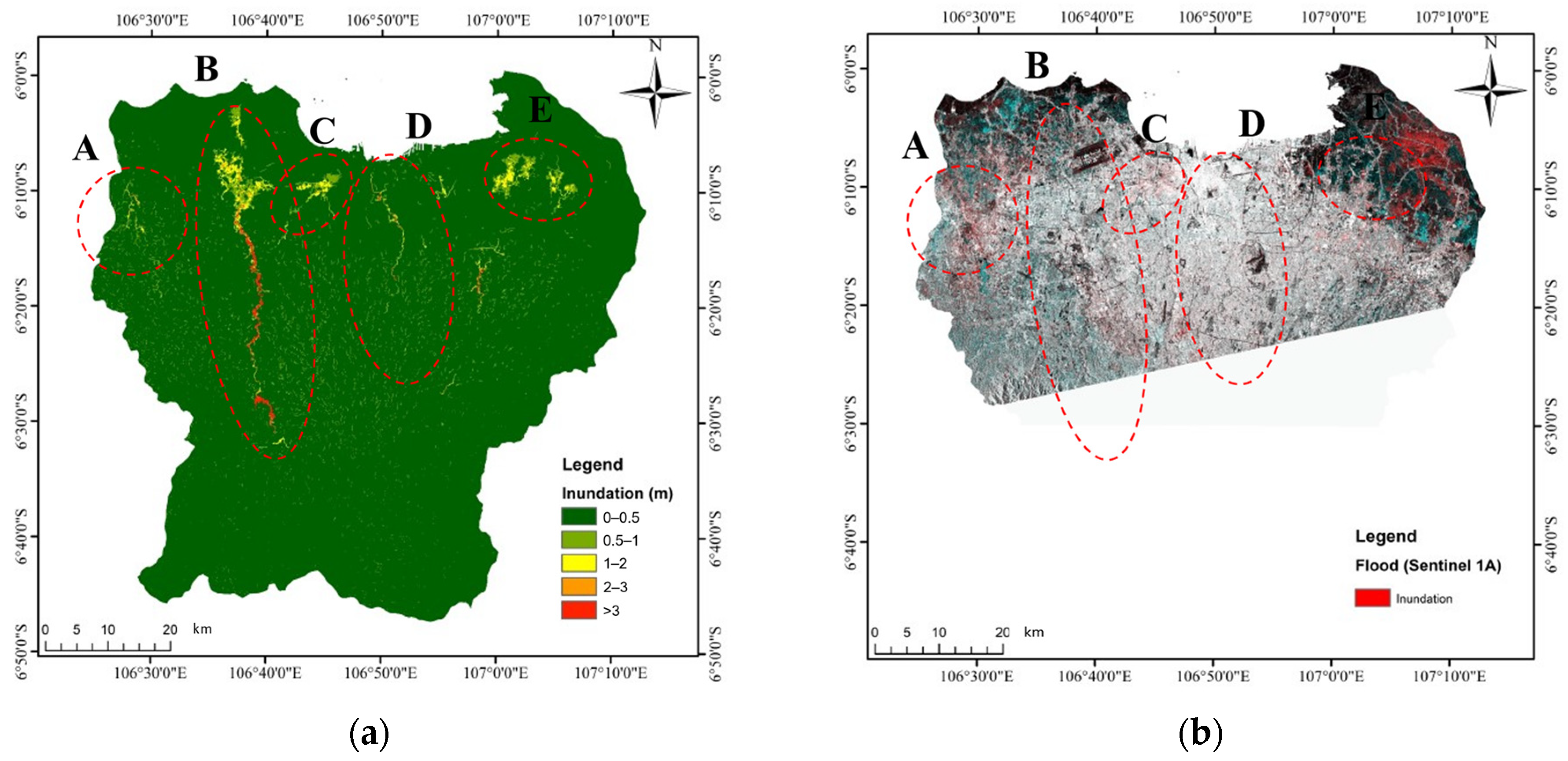
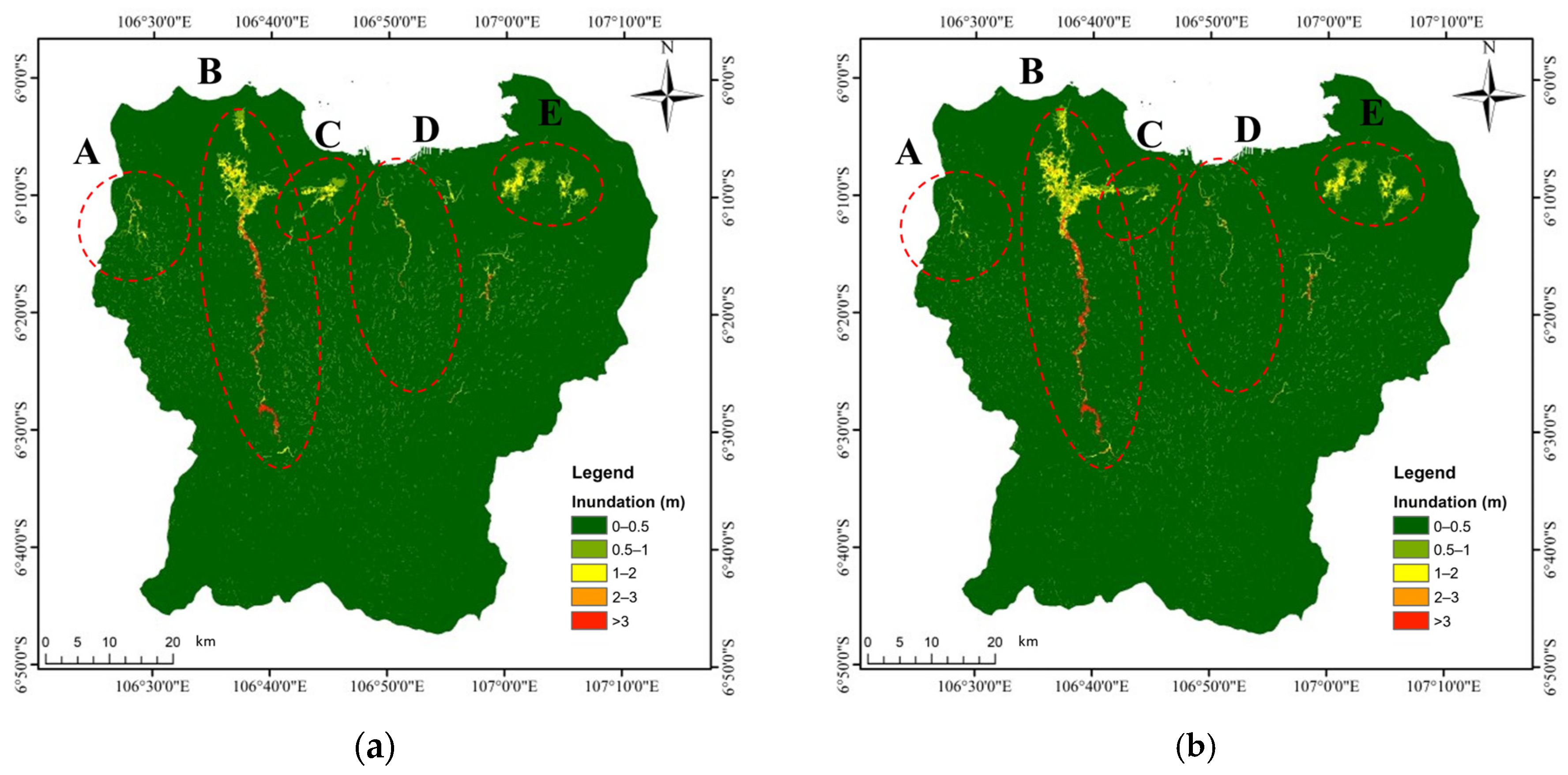
| Location | River Basin | Inundation Area (km2) | Affected City(ies) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Cimanceuri | 6.3 | Tanggerang |
| B | Cisadane | 51.05 | Tanggerang |
| C | Angke | 11.9 | West Jakarta |
| D | Ciliwung | 5.03 | East Jakarta, South Jakarta, Central Jakarta |
| E | Bekasi | 32.26 | Bekasi |
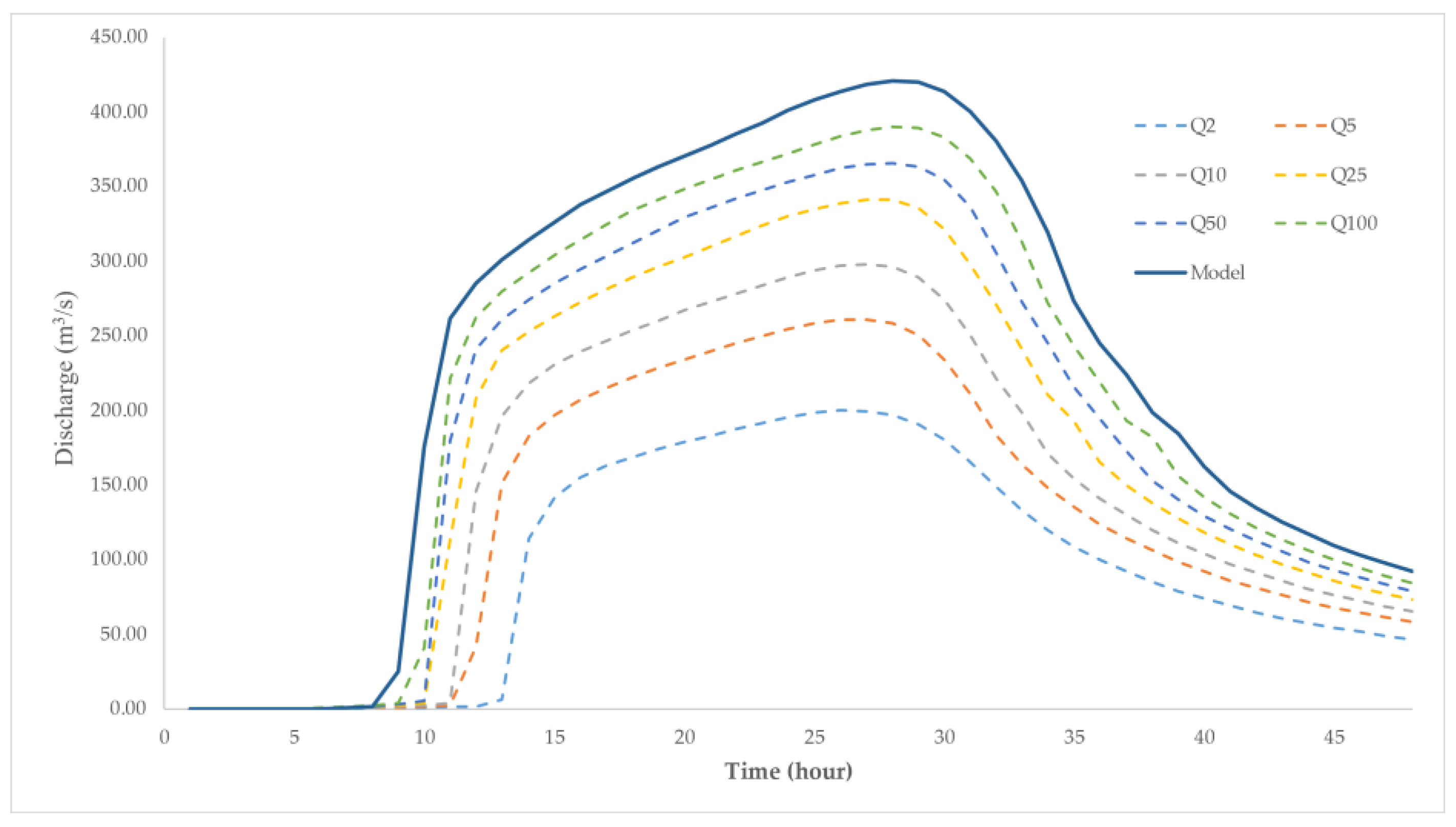
| Flood Simulation | Volume (1000 m3) | Max. Discharge (m3/s) |
|---|---|---|
| Return Period of 2 Years | 16,475 | 199.75 |
| Return Period of 5 Years | 22,059 | 260.88 |
| Return Period of 10 Years | 25,797 | 297.85 |
| Return Period of 25 Years | 30,397 | 340.95 |
| Return Period of 50 Years | 33,450 | 365.67 |
| Return Period of 100 Years | 36,355 | 389.97 |
| Jakarta Flood | 40,204 | 420.76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sihombing, Y.I.; Rizaldi, A.; Farid, M.; Januriyadi, N.F.; Moe, I.R. Jakarta’s 2020 New Year Flood Assessment with a Rainfall–Runoff–Inundation (RRI) Model. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 25, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14317
Sihombing YI, Rizaldi A, Farid M, Januriyadi NF, Moe IR. Jakarta’s 2020 New Year Flood Assessment with a Rainfall–Runoff–Inundation (RRI) Model. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2023; 25(1):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14317
Chicago/Turabian StyleSihombing, Yeremia Immanuel, Akbar Rizaldi, Mohammad Farid, N. Fajar Januriyadi, and Idham Riyando Moe. 2023. "Jakarta’s 2020 New Year Flood Assessment with a Rainfall–Runoff–Inundation (RRI) Model" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 25, no. 1: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14317
APA StyleSihombing, Y. I., Rizaldi, A., Farid, M., Januriyadi, N. F., & Moe, I. R. (2023). Jakarta’s 2020 New Year Flood Assessment with a Rainfall–Runoff–Inundation (RRI) Model. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 25(1), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14317






