A Comparative Analysis of Analytical Hierarchy Process and Machine Learning Techniques to Determine the Fractional Importance of Various Moisture Sources for Iran’s Precipitation †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alijani, B. Iran Climatology, 5th ed.; Payam Nour Publication: Tehran, Iran, 2000; ISBN 978-964-455-621-0. [Google Scholar]
- Heydarizad, M. Meteoric Water Lines of Iran for Various Precipitation Sources; Shiraz University: Shiraz, Iran, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Modarres, R.; Sarhadi, A. Rainfall trends analysis of Iran in the last half of the twentieth century. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balling, R.C.; Sadegh Keikhosravi Kiany, M.; Roy, S.; Khoshhal, J. Trends in Extreme Precipitation Indices in Iran: 1951–2007. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimzadeh, F.; Asgari, A.; Fattahi, E. Variability of extreme temperature and precipitation in Iran during recent decades. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H.; Talaee, P.H. Temporal variability of precipitation over Iran: 1966–2005. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourasghar, F.; Tozuka, T.; Jahanbakhsh, S.; Sari Sarraf, B.; Ghaemi, H.; Yamagata, T. The interannual precipitation variability in the southern part of Iran as linked to large-scale climate modes. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 39, 2329–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydarizad, M.; Raeisi, E.; Sori, R.; Gimeno, L.; Nieto, R.; Heydarizad, M.; Raeisi, E.; Sori, R.; Gimeno, L.; Nieto, R. The Role of Moisture Sources and Climatic Teleconnections in Northeastern and South-Central Iran’s Hydro-Climatology. Water 2018, 10, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydarizad, M.; Raeisi, E.; Sori, R.; Gimeno, L. The Identification of Iran’s Moisture Sources Using a Lagrangian Particle Dispersion Model. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; James, P. A Lagrangian Analysis of the Atmospheric Branch of the Global Water Cycle. Part II: Moisture Transports between Earth’s Ocean Basins and River Catchments. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 961–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; James, P. Lagrangian Analysis of the Atmospheric Branch of the Global Water Cycle. Part I: Method Description, Validation, and Demonstration for the August 2002 Flooding in Central Europe. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 656–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numaguti, A. Origin and recycling processes of precipitating water over the Eurasian continent: Experiments using an atmospheric general circulation model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 1957–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, R.; Bagheri, F.; Karami, G.H.; Jafari, H. Chemo-isotopes (18O & 2H) signatures and HYSPLIT model application: Clues to the atmospheric moisture and air mass origins. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 215, 116892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drumond, A.; Taboada, E.; Nieto, R.; Gimeno, L.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Ignacio López-Moreno, J. Lagrangian analysis of the present-day sources of moisture for major ice-core sites. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2016, 7, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Farajzadeh, M. Spatial and Temporal distribution of Iran’s precipitation moisture. J. Geogr. Sci. Stud. 2011, 19, 109–127. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, R.W. The analytic hierarchy process—What it is and how it is used. Math. Model. 1987, 9, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
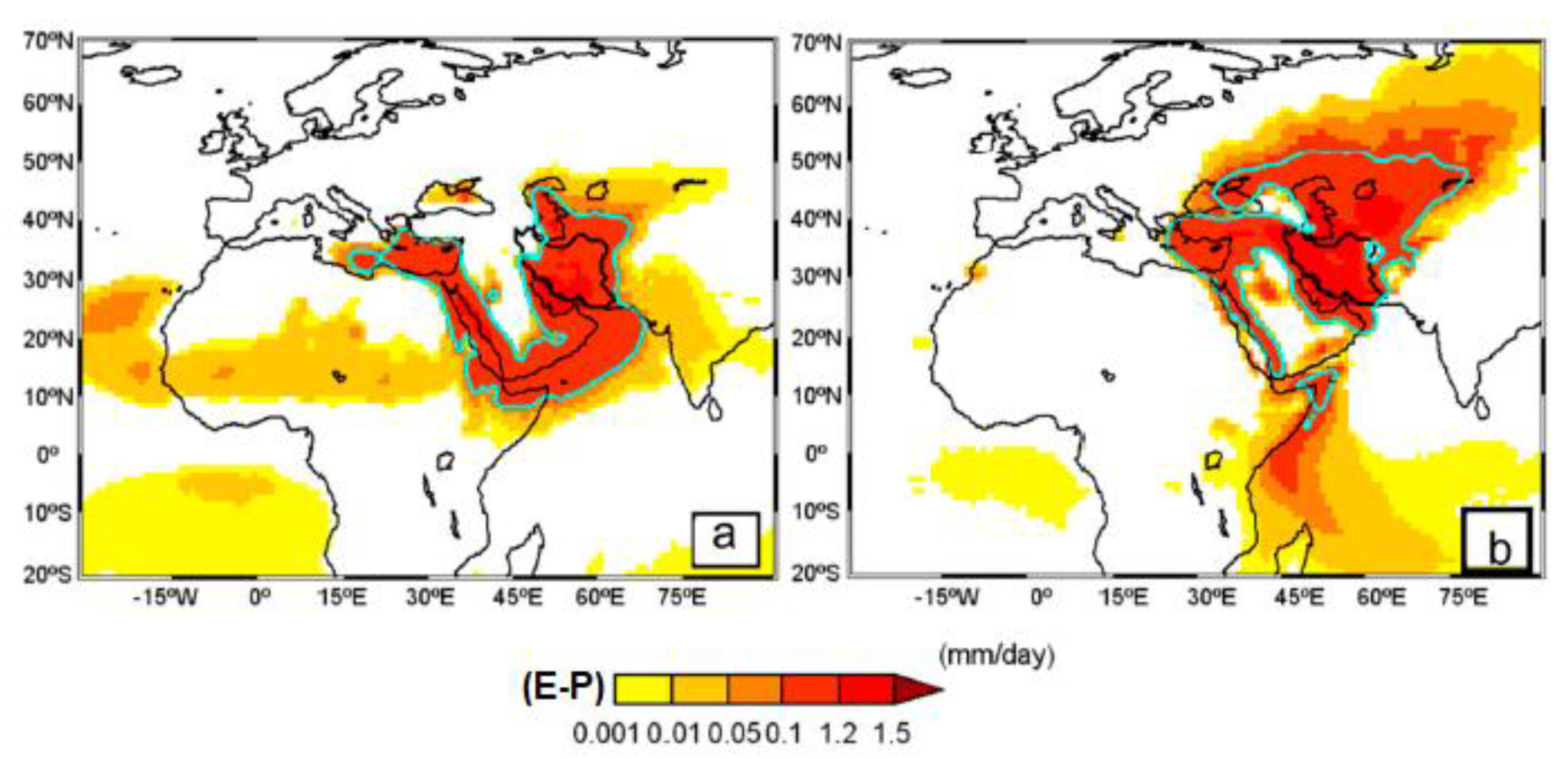
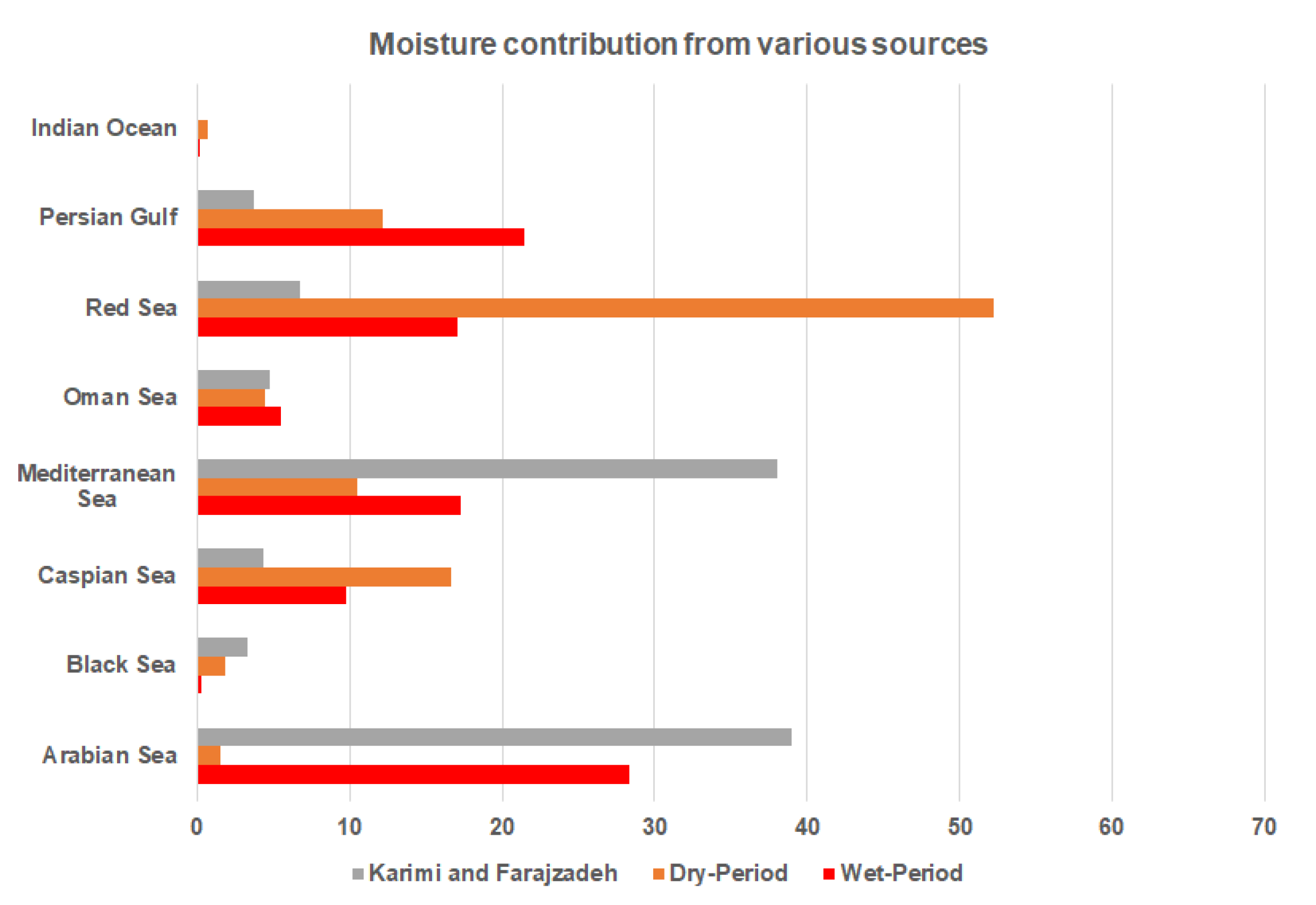

| Model | Wet Periods | Dry Periods | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSE | R2 | MSE | R2 | |||||
| Training | Test | Training | Test | Training | Test | Training | Test | |
| ANN | 469 | 519 | 0.67 | 0.63 | 126 | 251 | 0.16 | 0.03 |
| DNN | 546 | 694 | 0.67 | 0.48 | 107 | 228 | 0.11 | 0.11 |
| Decision tree | 870 | 959 | 0.41 | 0.26 | _ | _ | _ | _ |
| Random forest | 517 | 889 | 0.43 | 0.28 | 244 | 412 | 0.12 | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heydarizad, M.; Pumijumnong, N.; Gimeno, L. A Comparative Analysis of Analytical Hierarchy Process and Machine Learning Techniques to Determine the Fractional Importance of Various Moisture Sources for Iran’s Precipitation. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 19, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2022-12839
Heydarizad M, Pumijumnong N, Gimeno L. A Comparative Analysis of Analytical Hierarchy Process and Machine Learning Techniques to Determine the Fractional Importance of Various Moisture Sources for Iran’s Precipitation. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2022; 19(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2022-12839
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeydarizad, Mojtaba, Nathsuda Pumijumnong, and Luis Gimeno. 2022. "A Comparative Analysis of Analytical Hierarchy Process and Machine Learning Techniques to Determine the Fractional Importance of Various Moisture Sources for Iran’s Precipitation" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 19, no. 1: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2022-12839
APA StyleHeydarizad, M., Pumijumnong, N., & Gimeno, L. (2022). A Comparative Analysis of Analytical Hierarchy Process and Machine Learning Techniques to Determine the Fractional Importance of Various Moisture Sources for Iran’s Precipitation. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 19(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2022-12839






