Impact of Severe Salt Stress on Morphological, Physiological, and Biochemical Parameters in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
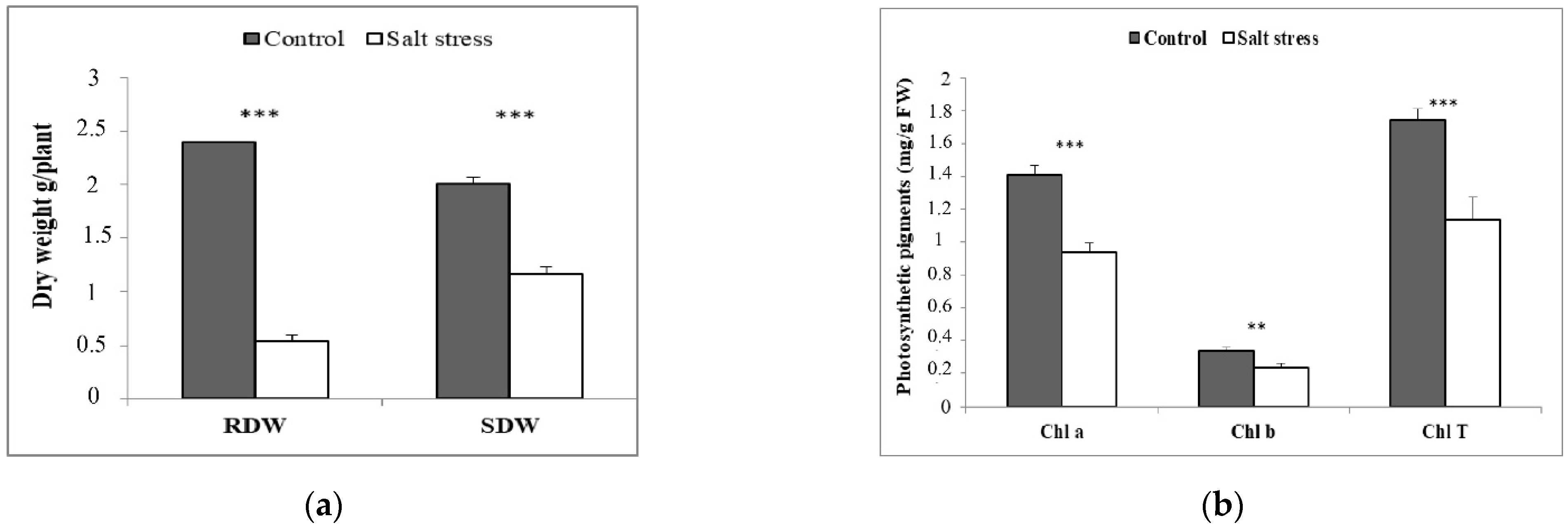
3. Results and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rengasamy, P. World salinization with emphasis on Australia. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Goumi, Y.; Fakiri, M.; Lamsaouri, O.; Benchekroun, M. Salt stress effect on seed germination and some physiological traits in three Moroccan barley (Hordeum vulgare L). cultivars. J. Mat. Env. Sci. 2014, 5, 625–632. [Google Scholar]
- Walia, H.; Wilson, C.; Wahid, A.; Condamine, P.; Cui, X.; Close, T.J. Expression analysis of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) during salinity stress. Funct. Integr. Genomics 2006, 6, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, J.; Laveday, J. Salinity in Irrigated Agriculture Riverside; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1990; pp. 1089–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Karoune, S.; Kechebar, M.S.A.; Halis, Y.; Djellouli, A.; Rahmoune, C. Effet du stress salin sur la morphologie, la physiologie et la biochimie de l’Acacia albida. J. Alg. Rég. Ar. 2017, 14, 60–73. [Google Scholar]
- Burnison, B.K. Modified dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) extraction for chlorophyll analysis of phytoplankton. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1980, 37, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erice, G.; Irigoyen, J.J.; Sánchez-Díaz, M.; Avice, J.C.; Ourry, A. Effect of drought, elevated CO2 and temperature on accumulation of N and vegetative storage proteins (VSP) in taproot of nodulated alfalfa before and after cutting. Pla. sci. 2007, 172, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, L.S.; Waldern, S.P.; Teare, I.D. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Rose, J.; Randall, A.J. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Bio. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, M.S.; El-Beshsbeshy, T.R.; Mahmoud, E.K.; Abdelkader, N.I.; Al-Shal, R.M.; Missaoui, A.M. Response of alfalfa under salt stress to the application of potassium sulfate nanoparticles. AJPS 2017, 8, 1751–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.S.; Han, J.G. Changes of proline content, activity, and active isoforms of antioxidative enzymes in two alfalfa cultivars under salt stress. JAS China 2009, 8, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.H.; Ha, C.V.; Nishiyama, R.; Watanabe, Y.; Leyva-González, M.A.; Fujita, Y.; Tran, U.T.; Li, W.; Tanaka, M.; Seki, M.; et al. Arabidopsis type B cytokinin response regulators ARR1, ARR10, and ARR12 negatively regulate plant responses to drought. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2016, 113, 3090–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashrafi, E.; Razmjoo, J.; Zahedi, M.; Pessarakli, M. Selecting alfalfa cultivars for salt tolerance based on some physiochemical traits. Agro. J. 2014, 106, 1758–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.A.D.C.; Suzuki, M.S.; Cunha, M.D.; Tullii, C.F. Effect of salt stress on nutrient concentration, photosynthetic pigments, proline and foliar morphology of Salvinia auriculata Aubl. Acta Limno Brasiliensia. 2011, 23, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattarai, S.; Biswas, D.; Fu, Y.B.; Biligetu, B. Morphological, physiological, and genetic responses to salt stress in alfalfa. Agronomy 2020, 10, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fougere, F.; Le Rudulier, D.; Streeter, J.G. Effects of salt stress on amino acid, organic acid, and carbohydrate composition of roots, bacteroids, and cytosol of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant physiology. 1991, 96, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torabi, M.; Halim, M.R.A. Variation of root and shoot growth and free proline accumulation in Iranian alfalfa ecotypes under salt stress. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2010, 8, 323–327. [Google Scholar]
- Balnška, F.; Ovecka, M.; Hirt, H. Salt stress induces changes in amounts and localization of the mitogen-activated protein kinase SIMK in alfalfa roots. Protoplasma 2000, 212, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wanga, Y.; Xionga, H.; Zhanga, H.; et al. OsERF71 confers drought tolerance via modulating ABA signaling and proline biosynthesis. Plant Sci. 2018, 270, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Q.; Tian, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M. Proteomic analysis of early salt stress responsive proteins in alfalfa roots and shoots. Proteome Sci. 2017, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bertrand, A.; Dhont, C.; Bipfubusa, M.; Chalifour, F.P.; Drouin, P.; Beauchamp, C.J. Improving salt stress responses of the symbiosis in alfalfa using salt-tolerant cultivar and rhizobial strain. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 87, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Source | Df | Proline | TSS | Proteins |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of plant (pp) | 1 | 0.89142 * | 29.8207 *** | 246.385 *** |
| Treatment (trt) | 1 | 5.38135 *** | 64.6927 *** | 399.661 *** |
| Replicates | 2 | 0.05616 | 0.2490 | 1.208 |
| pp*trt | 1 | 0.74541 * | 6.4557 ** | 20.663 * |
| Error | 6 | 0.08834 | 0.4190 | 1.759 |
| Total | 11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Srhiouar, N.; Ferioun, M.; Bouhraoua, S.; Hammani, K.; Louahlia, S. Impact of Severe Salt Stress on Morphological, Physiological, and Biochemical Parameters in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 16, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022016027
Srhiouar N, Ferioun M, Bouhraoua S, Hammani K, Louahlia S. Impact of Severe Salt Stress on Morphological, Physiological, and Biochemical Parameters in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2022; 16(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022016027
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrhiouar, Nassira, Mohamed Ferioun, Said Bouhraoua, Khalil Hammani, and Said Louahlia. 2022. "Impact of Severe Salt Stress on Morphological, Physiological, and Biochemical Parameters in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.)" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 16, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022016027
APA StyleSrhiouar, N., Ferioun, M., Bouhraoua, S., Hammani, K., & Louahlia, S. (2022). Impact of Severe Salt Stress on Morphological, Physiological, and Biochemical Parameters in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 16(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022016027







