Croton macrostachyus Bark Extract-Assisted Sustainable Synthesis of CuO Nanomaterials for 4-Nitrophenol Catalytic Reduction and Antibacterial Applications †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Chemicals and Procedures
2.1. Sample Collection
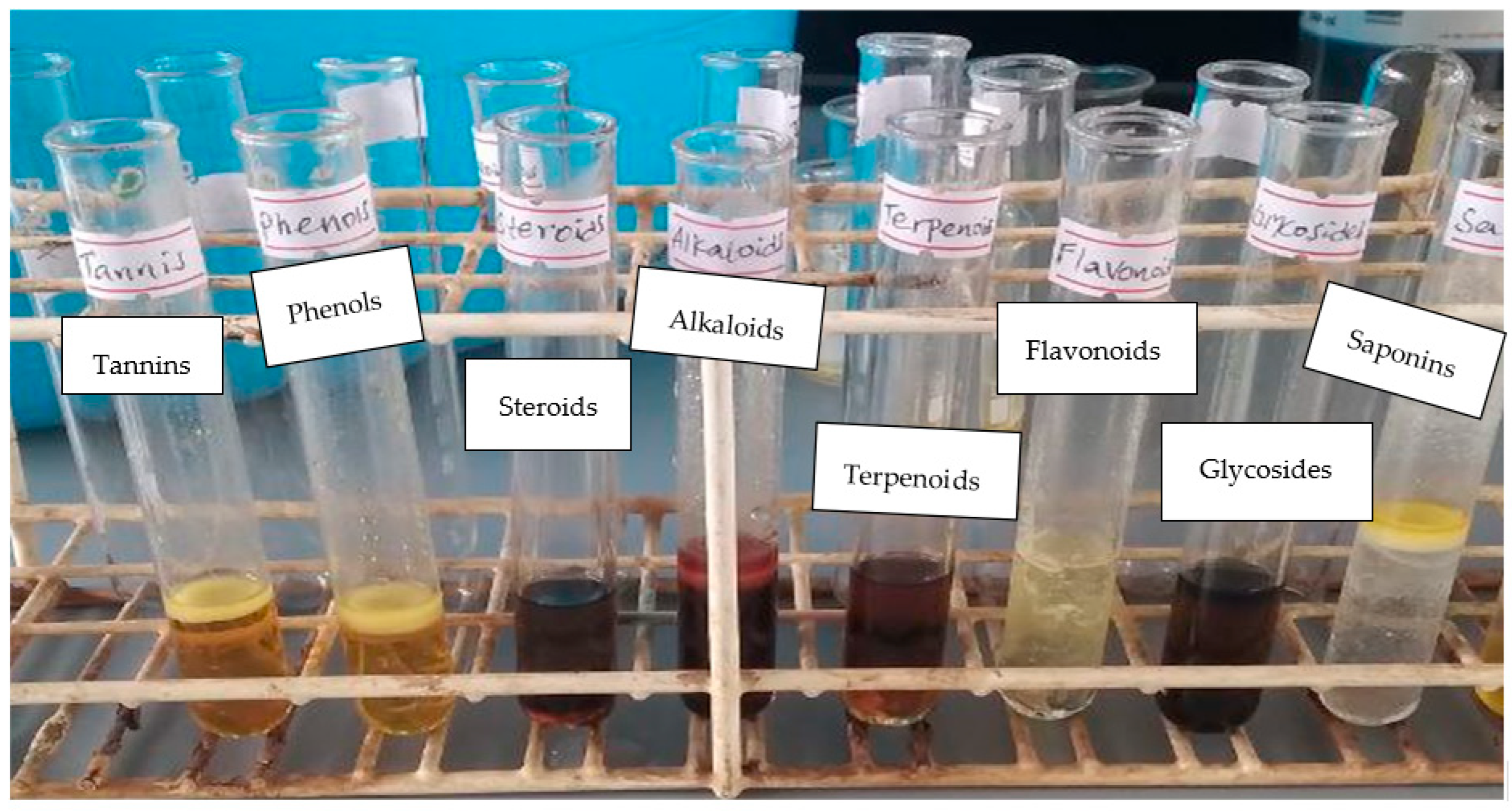
2.2. Phytochemical Screening
2.3. CuO Nanomaterials Synthesis
2.4. Characterization of CuO Nanomaterial
2.5. Evaluation of Catalytic Performance
2.6. Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phytochemical Analysis
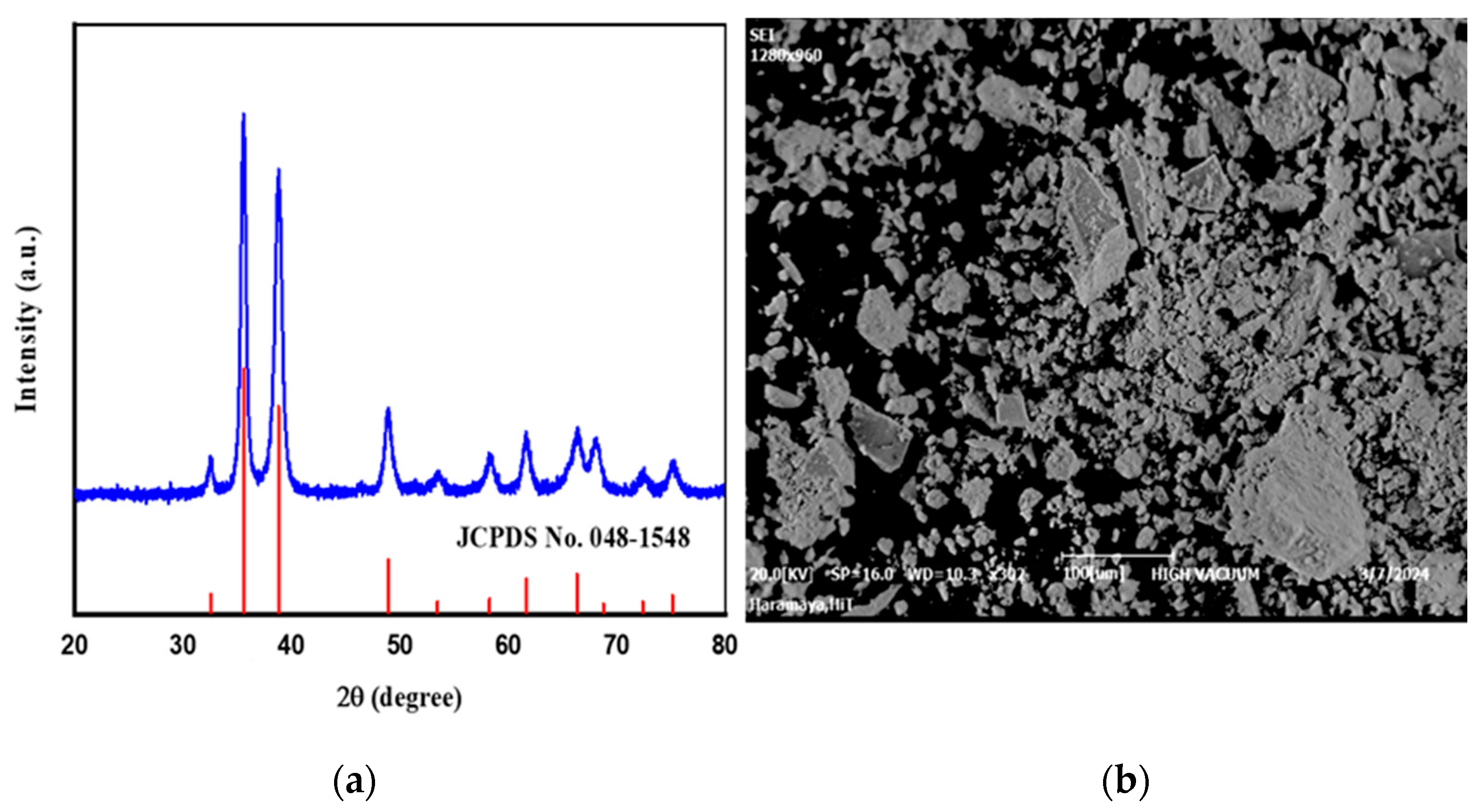
3.2. Characterization Studies: XRD Patterns, FTIR Spectra, and Morphology
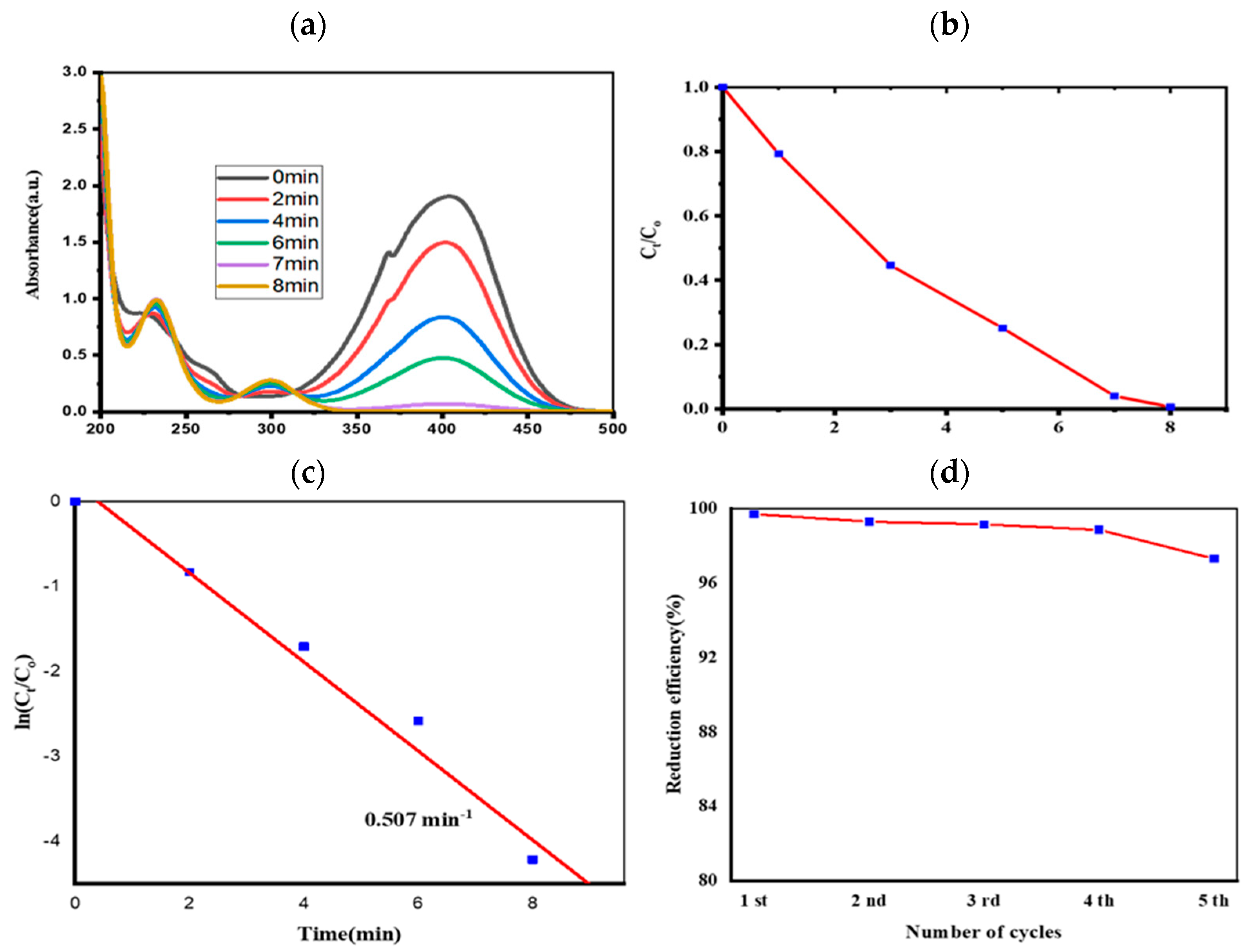
3.3. 4-NP Reduction
3.4. Antibacterial Activity Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- du Plessis, A. Persistent degradation: Global water quality challenges and required actions. One Earth 2022, 5, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Chen, W.; Lai, C.; Liu, S.; Fu, Y.; Yan, H.; Xu, F.; Ma, D.; Duan, A.; Deng, H. Highly efficient reduction of nitrophenols by Fe-NC single-atom catalyst: Performance and mechanism insights. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, S.; Ishaq, A.; Intisar, A.; Mahmood, T.; Din, M.I.; Ahmed, E.; Tariq, M.R.; Abid, M.A. Predictive modeling for the adsorptive and photocatalytic removal of phenolic contaminants from water using artificial neural networks. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.; Boora, A.; Thakur, A.; Gupta, T.K. Green and sustainable synthesis of nanomaterials: Recent advancements and limitations. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, S.; Gul, A.; Zia, M.; Javed, R. Synthesis, biomedical applications, and toxicity of CuO nanoparticles. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 1039–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance and the United Nations Sustainable Development Cooperation Framework: Guidance for United Nations Country Teams; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Stankic, S.; Suman, S.; Haque, F.; Vidic, J. Pure and multi metal oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, antibacterial and cytotoxic properties. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 14, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulta, K.; Koşarsoy Ağçeli, G.; Chauhan, P.; Jasrotia, R.; Chauhan, P.; Ighalo, J.O. Multifunctional CuO nanoparticles with enhanced photocatalytic dye degradation and antibacterial activity. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2022, 32, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davari, A.; Hakimzadeh, V.; Mahdian, E.; Shahidi-Noghabi, M. Synthesis and characterization of copper oxide nanoparticles using aqueous extract of iranian violaceae flower. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 15, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.; Jewena, N.; Shahabuddin, A.K.M.; Das, S.K.; Khandaker, J.I. Hydrothermal synthesis of CuO nanoparticles and a study on property variation with synthesis temperature. J. Appl. Fundam. Sci. 2020, 6, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, K.; Sajid, M.; Bakar, S.A.; Younus, A.; Ali, H.; Rashid, M.Z. Synthesis of copper oxide (CuO) via coprecipitation method: Tailoring structural and optical properties of CuO nanoparticles for optoelectronic device applications. Hybrid Adv. 2024, 6, 100250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, B.; Rahman, M.Z.; Fatimah, I.; Lett, J.A.; Annaraj, J.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Al-Anber, M.A.; Sagadevan, S. Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles for biological applications. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 155, 111088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Azadi, E.; Hussain, C.M. Environmentally benign production of cupric oxide nanoparticles and various utilizations of their polymeric hybrids in different technologies. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 419, 213378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzilu, D.M.; Madivoli, E.S.; Makhanu, D.S.; Wanakai, S.I.; Kiprono, G.K.; Kareru, P.G. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its efficiency in degradation of rifampicin antibiotic. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhalili, Z. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles CuO NPs from Eucalyptus Globoulus leaf extract: Adsorption and design of experiments. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javid-Naderi, M.J.; Sabouri, Z.; Jalili, A.; Zarrinfar, H.; Samarghandian, S.; Darroudi, M. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) fruit extract and assessment of their cytotoxicity and photocatalytic applications. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thandapani, G.; Arthi, K.; Pazhanisamy, P.; John, J.J.; Vinothini, C.; Rekha, V.; Santhanalakshmi, K.; Sekar, V. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Spinacia oleracea leaf extract and evaluation of biological applications: Antioxidant, antibacterial, larvicidal and biosafety assay. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroyi, A. Ethnopharmacological uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacological properties of Croton macrostachyus Hochst. Ex Delile: A comprehensive review. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 1694671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabessa Masho, T.; Thillai Arasu, P.; Feyisa Bogale, R.; Amare Zerrefa, E.; Ramamurthy, S. Green Synthesis, Characterization of Ag2O/CuO/ZnO Nano Composites Using Aqueous Extract of Croton Macrostachyus Leaf for Photo Degradation, Anti-Microbial and Antioxidant Activities. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masho, T.; Arasu, P.T.; Bogale, R.F.; Abebe, A. Anti-oxidant studies on phyto mediated synthesis and characterization of ZnO Nanoparticles using Croton macrostachyus Leaf Extract. J. Sci. Technol. Arts Res. 2024, 13, 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Bassa, A.B.; Zelekew, O.A.; Meresa, T.A.; Berhe, T.A. Croton macrostachyus leaf-mediated biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for enhanced catalytic reduction of organic dyes. Mater. Res. Express 2024, 11, 085001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejen, K.D.; Kibret, D.Y.; Mengesha, T.H.; Bekele, E.T.; Tedla, A.; Bafa, T.A.; Derib, F.T. Green synthesis and characterisation of silver nanoparticles from leaf and bark extract of Croton macrostachyus for antibacterial activity. Mater. Technol. 2023, 38, 2164647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, F.W.; Zeleke, T.D. Green synthesis of silver and cobalt oxide nanoparticles using Croton macrostachyus plant extract and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. Nanomed. J. 2024, 11, 80. [Google Scholar]
- Aroob, S.; Carabineiro, S.A.; Taj, M.B.; Bibi, I.; Raheel, A.; Javed, T.; Yahya, R.; Alelwani, W.; Verpoort, F.; Kamwilaisak, K. Green synthesis and photocatalytic dye degradation activity of CuO nanoparticles. Catalysts 2023, 13, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubale, S.; Kebebe, D.; Zeynudin, A.; Abdissa, N.; Suleman, S. Phytochemical screening and antimicrobial activity evaluation of selected medicinal plants in Ethiopia. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2023, 15, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, B.; Nawaz, K.; Munazir, M. Phytochemical Analysis and Antibacterial Activity of Tannins Extracted from Salix alba L. Against Different Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacterial Strains. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Sci. 2020, 44, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longbap, B.; Ushie, O.; Ogah, E.; Kendenson, A.; Nyikyaa, J. Phytochemical Screening and Quantitative Determination of Phytochemicals in Leaf Extracts of Hannoa Undulata. Int. J. Med. Plants Nat. Prod. 2018, 4, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Singh, A.; Patnaik, R.S.; Bhardwaj, S. Phytochemical analysis of bioactive components of medicinal plants. J. Pharm. Negat. Results 2022, 13, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Morsy, N. Cardiac Glycosides in Medicinal Plants. Aromatic and Medicinal Plants–Back to Nature; Intechopen: London, UK, 2017; pp. 29–45. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.; Krishnan, R.R.; Chandran, S.R.; Prema, K.H. Green Mediated Sol-Gel Synthesis of Copper Oxide Nanoparticle: An Efficient Candidate for Waste Water Treatment and Antibacterial Agent. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2023, 107, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirsaheb, M.; Gholami, T.; Seifi, H.; Dawi, E.A.; Said, E.A.; Hamoody, A.-H.M.; Altimari, U.S.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Green Synthesis of Nanomaterials by Using Plant Extracts as Reducing and Capping Agents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 24768–24787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.N.; Esakkiraja, A.; Asan, S.M. Green synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized using catharanthus roseus leaf extract. J. Appl. Sci. Comput. 2019, 6, 3228–3240. [Google Scholar]
- Bin Mobarak, M.; Hossain, M.S.; Chowdhury, F.; Ahmed, S. Synthesis and Characterization of CuO Nanoparticles Utilizing Waste Fish Scale and Exploitation of XRD Peak Profile Analysis for Approximating the Structural Parameters. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakruthi, R.; Deepakumari, H.N. CuO nanoparticles: Green combustion synthesis, applications to antioxidant, photocatalytic and sensor studies. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 28703–28715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklu, B.; Kadiri, S.K.; Vidavalur, S. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Balanites aegyptiaca stem bark extract and investigation of antibacterial activity. Results Chem. 2023, 6, 101152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedefoglu, N.; Er, S.; Veryer, K.; Zalaoglu, Y.; Bozok, F. Green synthesized CuO nanoparticles using macrofungi extracts: Characterization, nanofertilizer and antibacterial effects. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 309, 128393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.K.; Das, N.C. Advances on catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol by nanostructured materials as benchmark reaction. Int. Nano Lett. 2022, 12, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, A.A.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; Fouad, D.M.; Ibrahim, S.A. Catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol using copper terephthalate frameworks and CuO@ C composite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Fang, X.; Kang, X.; Yang, M.; Wei, Y.; Xu, X. A study on the high efficiency reduction of p-nitrophenol (4-NP) by a Fe(OH)3/Fe2O3@ Au composite catalyst. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 26502–26508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, G.; Chauhan, S.; Soni, S.; Kumar, A.; Negi, D.S.; Bahadur, I. Catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol using synthesized and characterized CoS@ MorphcdtH/CoS@ 4-MPipzcdtH nanoparticles. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2023, 70, 879–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekru, A.G.; Zelekew, O.A.; Andoshe, D.M.; Sabir, F.K.; Eswaramoorthy, R. Microwave-assisted synthesis of CuO nanoparticles using Cordia africana Lam. leaf extract for 4-nitrophenol reduction. J. Nanotechnol. 2021, 2021, 5581621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbayoumy, E.; Ibrahim, E.M.; El-Bindary, A.; Nakano, T.; Aboelnga, M.M. Revealing an efficient copper oxide nanoparticle catalyst for the reduction of the hazardous nitrophenol: Experimental and DFT studies. Mater. Adv. 2025, 6, 6291–6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian-Robinson, S.; Kong, F.; Easton, E.B.; Kerton, F.M. Modification of calcium carbonate from blue mussel shells with copper oxide nanoparticles. RSC Sustain. 2025, 3, 3009–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, T.; Amin, D.H.; Salama, H.M.; Elkholy, I.M.A.; Elnakib, M.; Gebreel, H.M.; Sayed, H.A.E. Antibacterial activity of green synthesized copper oxide nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmin, S.; Rahaman, M.M.; Sarkar, C.; Atolani, O.; Islam, M.T.; Adeyemi, O.S. Nanoparticles as antimicrobial and antiviral agents: A literature-based perspective study. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabila, M.I.; Kannabiran, K. Biosynthesis, Characterization and Antibacterial Activity of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles (CuO NPs) from Actinomycetes. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 15, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masho, T.J.; Arasu, P.T.; Bogale, R.F.; Gendo, K.M.; Deressa, D.A. Biosynthesis of CuO/ZnO nanocomposites using leaf extract of croton macrostachyus: Characterization, photodegradation, and biological activities. Chem. Afr. 2025, 8, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, R.B.; Delgado-Beleño, Y.; Martinez-Nuñez, C.; Cortez-Valadez, M.; Flores-Acosta, M. Biosynthesis and antibacterial activity of Cu and CuO nanoparticles against pathogenic microorganisms. In Copper Nanostructures: Next-Generation of Agrochemicals for Sustainable Agroecosystems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 417–452. [Google Scholar]

| Catalyst | Time (min) | Mass of Catalyst (mg) | Apparent Rate Constant (min−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuO/poly(DVB) | 6 | 20 | 0.45 | [42] |
| Soft calcite/Cu2O/CuO | 20 | 1.5 | 0.0747 | [43] |
| CuO@C composite | 3 | 50.00 | 6.0 × 10−3 | [38] |
| CuO | 12 | 5 | 0.379 | [44] |
| CuO | 8 | 10 | 0.507 | This study |
| Sample Type | Concentration (mg/mL) | S. aureus (mm) | E. coli (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcined CuO NPs | 200 | 20 ± 1.1 | 10 ± 0.6 |
| 100 | 18 ± 0.6 | – | |
| 50 | 16 ± 0.8 | – | |
| 25 | 14 ± 1.5 | – | |
| Uncalcined CuO NPs | 200 | 22 ± 1.3 | 11 ± 0.7 |
| 100 | 19 ± 0.95 | 8 ± 1.3 | |
| 50 | 17 ± 0.1 | 5 ± 1.1 | |
| 25 | 16 ± 0.5 | – | |
| Chloramphenicol | 0.05 | 24 ± 1.63 | 20 ± 0.94 |
| DMSO (1%) | — | – | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bassa, A.B.; Adula, S.H.; Bassa, M.B.; Berhe, T.A. Croton macrostachyus Bark Extract-Assisted Sustainable Synthesis of CuO Nanomaterials for 4-Nitrophenol Catalytic Reduction and Antibacterial Applications. Chem. Proc. 2025, 17, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2025017011
Bassa AB, Adula SH, Bassa MB, Berhe TA. Croton macrostachyus Bark Extract-Assisted Sustainable Synthesis of CuO Nanomaterials for 4-Nitrophenol Catalytic Reduction and Antibacterial Applications. Chemistry Proceedings. 2025; 17(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2025017011
Chicago/Turabian StyleBassa, Atinafu Bergene, Shemelis Hailu Adula, Muluken Bergene Bassa, and Taame Abraha Berhe. 2025. "Croton macrostachyus Bark Extract-Assisted Sustainable Synthesis of CuO Nanomaterials for 4-Nitrophenol Catalytic Reduction and Antibacterial Applications" Chemistry Proceedings 17, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2025017011
APA StyleBassa, A. B., Adula, S. H., Bassa, M. B., & Berhe, T. A. (2025). Croton macrostachyus Bark Extract-Assisted Sustainable Synthesis of CuO Nanomaterials for 4-Nitrophenol Catalytic Reduction and Antibacterial Applications. Chemistry Proceedings, 17(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemproc2025017011






