Abstract
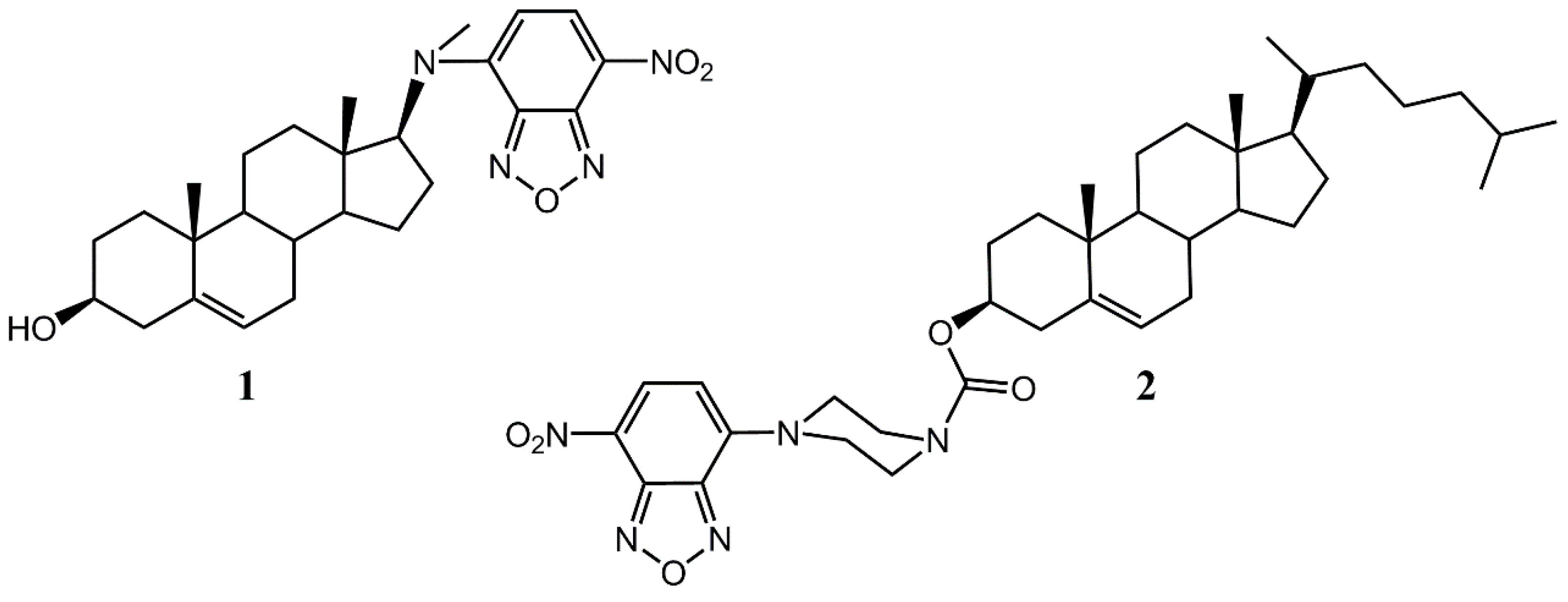
Two fluorescent sterol-like molecules have been synthesized, namely, a derivative of 7-nitrobenzofurazan (NBD) with 17-(methylamino)-androst-5-en-3beta-ol (DAM-NBD) and NBD-piperazine conjugate with cholesteryl chloroformate (NBD-pip-CCF). In silico docking and plasma membrane simulations have shown ability of the compounds to penetrate the lipid bilayer, as well as to bind affinely of the yellow fever mosquito SCP-2 protein structure (code PDB: 3BDQ; binding energy about −11.9 kcal/mol). Also docking with AlphaFOLD-predicted insect Neverland protein structure demonstrated DAM-NBD binding with a similar affinity. The theoretical results indicate perspectives of the fluorescent steroid usage to study insect protein-sterol interactions.
1. Introduction
Insects are unable to synthesize cholesterol de novo, but for most of them it is necessary for as a component of cell membranes and a precursor for the synthesis of the hormone ecdysone. The organisms are able to modify others sterols, e.g., beta-sitosterol, to cholesterol for their normal development [1]. It is important to note that in the biosynthesis of ecdysone, the oxidation of cholesterol is carried out by Neverland Rieske monooxygenase [2] and little-studied “black box” enzymes [3]. Intracellular transport of cholesterol and other steroids in insects is also important for survival, as illustrated for the case of the steroid transfer protein SCP-2 [4]. Fluorescent sterol-like molecules are used to study the distribution and metabolism of cholesterol widely, but not too much researches are devoted to insect proteins and cells. For instance, such studies were carried out only for a pair of SCP-2 with commercial 22-NBD-cholesterol [4,5]. Thus, in this work we performed calculations in silico for synthesized by our group fluorescent 7-nitrobenzoxadiazole (NBD) derivatives codenamed DAM-NBD (Figure 1, 1) and NBD-pip-CCF (Figure 1, 2) with some SCP-2 experiment-based PDB structures as well as predicted Neverland structure.
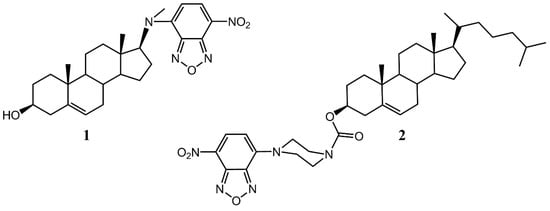
Figure 1.
Structural formulas of fluorescent sterol-like molecules 1 and 2.
2. Materials and Methods
The following reagents were used: 7-nitrobenzoxadiazol-4-yl chloride (NBD chloride), dehydroepiandrosterone, CH3NH2·HCl, NaBH3CN, Na2CO3, cholesterol chloroformate, piperazine, acetonitrile, CH3CO2H, triethylamine, butanol-1. Reagents and solvents had the qualification “grade” and “p.a.”. The assessment of the uniqueness of the obtained substances and the observation of the course of the ongoing reactions was carried out by TLC on Sorbfil plates. Benzene and ethanol, acetonitrile and methanol in various ratios were used as eluent. Steroidal molecules were specifically stained on TLC plates using known 40% H2SO4 spaying and heating procedure for additional confirmation of the compound’s nature. Molecular weights of the compounds were estimated using mass-spectrometry: LCMS2020 (Shimadzu) equipment, positive ion electrospray ionization mode, nitrogen as both drying and nebulizing gas; samples were injected as methanolic solutions.
Cholest-5-en-3-yl-4-(7-nitrobenzoxo[c][1,2,5]oxadiazol-4-yl)piperazine-1-carboxylate (NBD-pip-CCF): A weighed portion of NBD-Cl was dissolved in methanol containing additional sodium bicarbonate. A solution of piperazine in methanol was added dropwise to the resulting solution with stirring. The resulting mixture was kept for 1 h. The completeness of the conversion was assessed by TLC. The product was purified by column chromatography using the eluent mentioned above. A compound codenamed NBD-piperazine was obtained and then it was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran containing pyridine as a base, and a solution of cholesterol chloroformate in tetrahydrofuran was added dropwise [6]. The completeness of the conversion was assessed by TLC. The product was purified by column chromatography as described above. The yield was 70%. TLC (methanol): Rf = 0.95 for NBD-pip-CCF vs. Rf = 0.1 for NBD-piperazine; m/z = 662 for [M+H]+ ions (C38H56N5O5+), 1H-NMR (CDCl3; δ, ppm) 8.5 (d), 7.3 (s), 5.44 (s), 4.63 (s), 3.54 (s), 2.48–2.34 (m) [7].
17-(4-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazol-7-yl)amino)androst-5-en-3β-ol (DAM-NBD): A weighed portion of dehydroepiandrosterone was dissolved in 1-butanol. To the resulting solution was added an excess of CH3NH2·HCl, an excess of NaBH3CN as a reducing agent, and an excess of Na2CO3 as a base. The resulting mixture was kept for 48 h with stirring. The completeness of the conversion was assessed by TLC. The product was purified by column chromatography using a gradient of acetonitrile and methanol as eluent. A compound was obtained under the code name DAM. DAM was dissolved in methanol containing triethylamine as base, and a solution of 7-nitrobenzoxadiazol-4-yl chloride in acetonitrile was added dropwise with stirring. The completeness of the transformation was assessed by TLC. A compound was obtained under the code name DAM-NBD. The product was purified by column chromatography using a gradient of benzene and ethanol as the eluent. The yield was 65%. TLC (chloroform): Rf = 0.33 for DAM-NBD vs. Rf = 0.05 for DAM; for DAM-NBD m/z = 467 for [M+H]+ ions (C26H35N4O4+); 1H-NMR (CDCl3; δ, ppm): 8.45 ppm (d), 6.3 (d), 5.3 (s), 3.4 (m), 2.2–0.8 (m).
Calculations and analysis of the docking simulations results were carried out using the Autodock Vina [8,9] and FYTDock [10] programs. From the Internet resource Protein Data Bank (PDB, https://www.rcsb.org/, accessed on 1 September 2022), structures of the SCP-2 proteins of the yellow fever mosquito (codes 3BKS, 3BDQ, 2KSH) were selected, and the structure of the AlphaFold algorithm-predicted structure of enzyme sterol 7, 8-Neverland dehydrogenase code A0A0K2UIY3) was download from the corresponding internet resource (https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk, accessed on 9 September 2022). ChemBioDraw and Avogadro programs were used to prepare ligand structures, OpenBabel was used to convert the ligand format, and MGL Tools was used to analyze the results. The binding efficiency was evaluated by the interaction energy parameter automatically calculated by the Autodock Vina program (docking score, binding energy, Ebind). Graphical data processing was done using BioVia software. Analysis of the permeability of compounds through phospholipid membranes in silico was calculated on the PerMM server according to the method [7].
3. Results and Discussion
To consider the biological properties of compounds 1 and 2, an in silico assessment was made of the penetration of the studied substances into the cell by the mechanism of passive diffusion through the lipid bilayer using the PerMM (Permeability of Molecules across Membranes) service [7]. The main results of this test are given in Table 1.

Table 1.
Theoretically calculated values for free energy of binding with a membrane, Logs of permeability coefficients of different membranes for 1 and 2 *.
The logarithms of permeability coefficients for models of three different membranes have values exceeding −4.35; therefore, compounds 1–3 are able to penetrate through phospholipid membranes [7]. So, they are potentially useful for intracellular metabolism and traffic studies.
At the moment, for a preliminary assessment of the effectiveness and spatial features of the interactions of low molecular weight compounds with proteins, the most modern is computer modeling of protein-ligand interactions (molecular docking) [8,9].
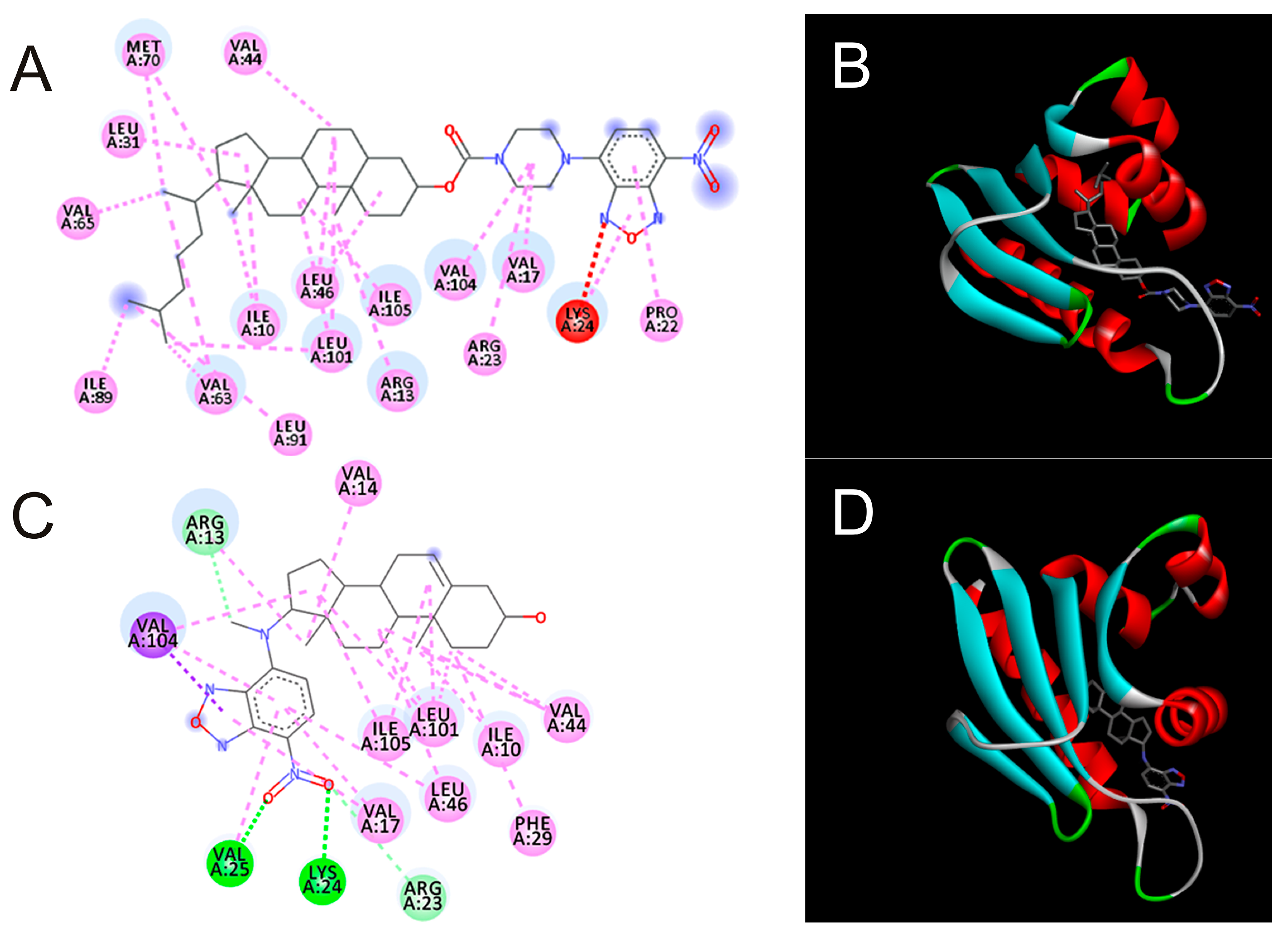
To address new interaction modeling with insect proteins of the compounds we conducted docking simulations with SCP-2 structures as well as a Neverland model structure (Table 2, Figure 2).

Table 2.
Ebind values, amino acid environment, and 3-OH group orientation for SCP-2 protein structures and the Neverland model structure (NVLD).
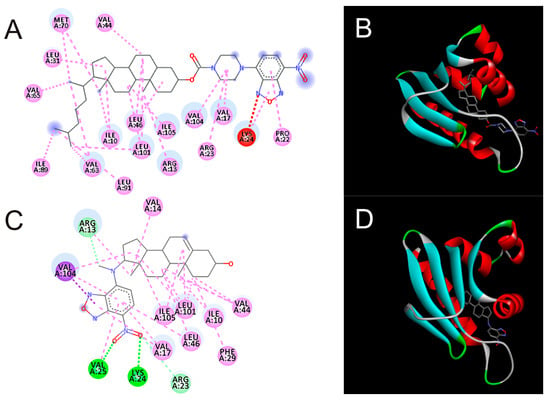
Figure 2.
Molecular docking poses of NBD-pip-CCF (A,B) and DAM-NBD (C,D) (A,C—in 2D view; B,D—in 3D view) of structure of SCP-2 of the yellow fever mosquito (PDB 3BDQ). The sub-pictures were build using BioVia software using default settings.
Computer modeling revealed the possibility and high, relative to the natural ligand, binding affinity of synthetic DAM-NBD and CCF-pip-NBD with respect to the SCP-2 structure. DAM-NBD demonstrated also high affinity to Neverland enzyme.
Thus, according to our in silico tests, the synthetic fluorescent sterol-like compounds might be usefull to study SCP-2-related intracellular processes in cells of insects.
4. Conclusions
Two new fluorescent derivatives of NBD with cholesterol residues and piperazine formyl cholesterol (compounds 1 and 2, respectively) were synthesized. Calculation-theoretical methods have shown their ability to penetrate through the lipid bilayer, as well as bind affinity to SCP-2 protein of the yellow fever mosquito. DAM-NBD demonstrated very good affinity to modeled Neverland structure. The obtained computational data, together with literature data on the essentiality of sterol uptake and the “black boxes” of metabolic pathways, open up prospects for using the obtained substances in vitro to search for mechanisms to control the viability of insects and further in vitro studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.F.; writing—original draft preparation, H.P. and A.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.F.; supervision, V.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was supported governmental grants of republic of Belarus No. of registration 20210560.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ciufo, L.F.; Murray, P.A.; Thompson, A.; Rigden, D.J.; Rees, H.H. Characterisation of a Desmosterol Reductase Involved in Phytosterol Dealkylation in the Silkworm, Bombyx mori. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiyama-Yanagawa, T.; Enya, S.; Shimada-Niwa, Y.; Yaguchi, S.; Haramoto, Y.; Matsuya, T.; Shiomi, K.; Sasakura, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Asashima, M.; et al. The Conserved Rieske Oxygenase DAF-36/Neverland Is a Novel Cholesterol-metabolizing Enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 29, 25756–25762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoko, H.-S.; Takashi, S. Cell surface control of the layer specific targeting in the Drosophila visual system. Genes Genet. Syst. 2014, 1, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Ma, Y.; Liu, X.; Dyer, D.H.; Xu, P.; Liu, K.; Lan, Q.; Hong, H.; Peng, J.; Peng, R. NMR structure and function of Helicoverpa armigera sterol carrier protein-2, an important insecticidal target from the cotton bollworm. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minsik, K.; Vilena, W.; Que, L. Identification of mosquito sterol carrier protein-2 inhibitors. Nat. Lib. Med. 2005, 46, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faletrov, Y.V.; Pozniak, H.I.; Yakovets, P.S.; Frolova, N.S.; Shkumatov, V.M. New lipophilic conjugates of fluorescent NBD-piperazine: Synthesis, in silico interactions with lipid bilayer and cytochromes P450. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. Belarus Chem. Ser. 2022, 58, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomize, A.L.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Mosberg, H.I. Anisotropic solvent model of the lipid bilayer. 2. Energetics of insertion of small molecules, peptides, and proteins in membranes. J. Chem. Inform. Mod. 2011, 51, 930–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faletrov, Y.V.; Gilep, K.A.; Falchevskaya, A.S.; Horetski, M.S.; Panada, J.V.; Andrievskaya, E.V.; Rudaya, E.V.; Frolova, N.S.; Brzostek, A.; Plocinska, R.; et al. In silico modeling of izoniazid steroid conjugates interactions with cytochromes P450 of mycobacteria and their bioconversion in vitro by the cells. Biomed. Khimiya 2020, 66, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faletrov, Y.V.; Staravoitava, V.A.; Dudko, A.R.; Shkumatov, V.M. Application of docking-based inverse high throughput virtual screening to found phytochemical covalent inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease, NSP12 and NSP16. Res. Square 2022, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).