Diabetic Ketoacidosis as a Debut and Immune-Mediated Complication Caused by Pembrolizumab: Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
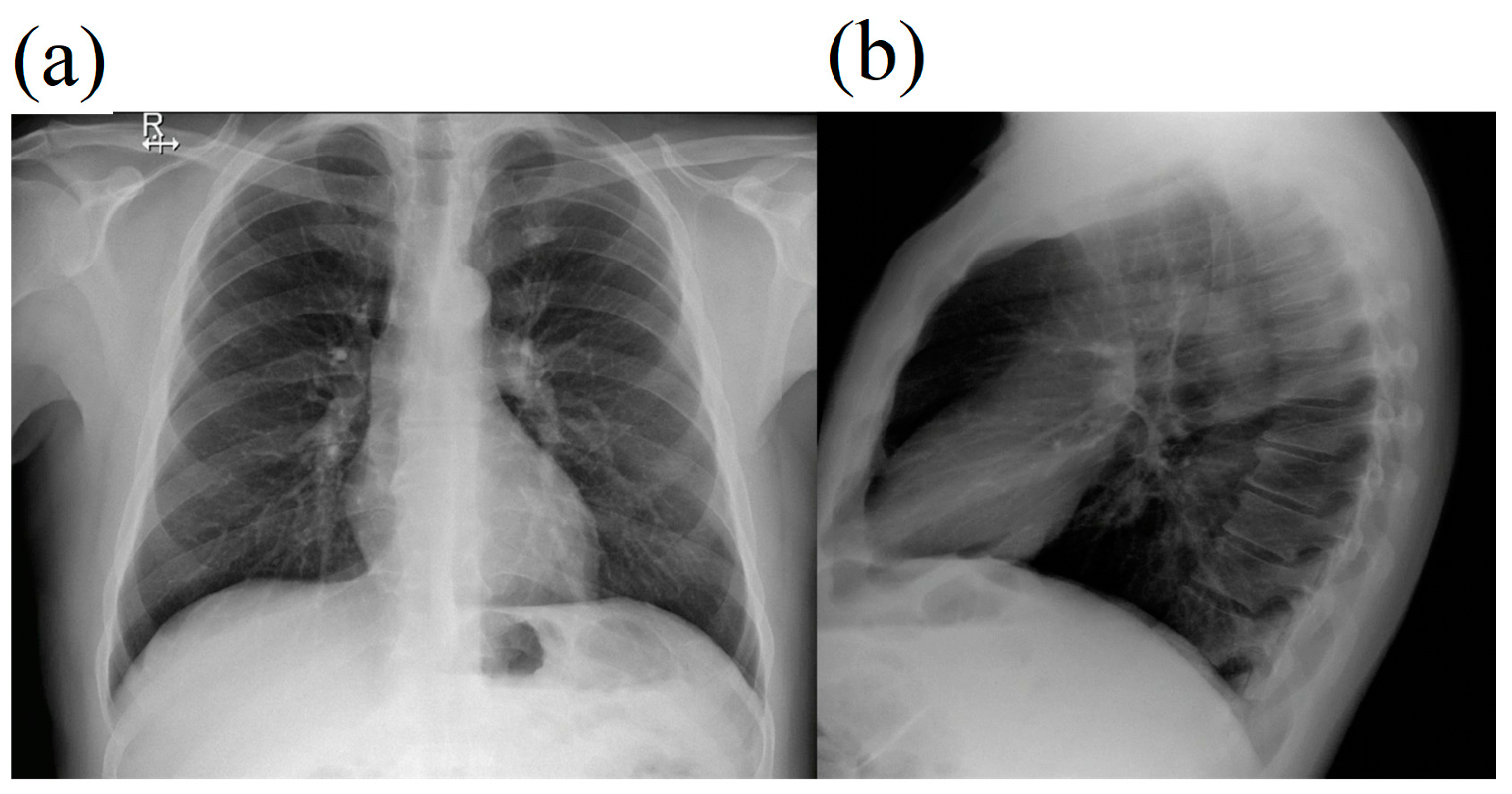
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DKA | diabetic ketoacidosis |
| ICI | immune checkpoint inhibitors |
| BRAF | v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 |
| anti-CTLA4 | antibodies against cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 |
| anti-PD-1 | antibodies against programmed cell death receptor 1 |
| anti-PD-L1 | antibodies against programmed cell death receptor ligand 1 |
| PET-CT | positron emission tomography |
| KDIGO | kidney disease: improving global outcomes |
| HbA1C | glycosylated hemoglobin |
| TSH | thyroid stimulating hormone |
| T4L | free thyroxine |
| FSH | follicle stimulating hormone |
| LH | luteinizing hormone |
| PTHS | sex hormone transport protein |
| IGF-1 | insulin-like growth factor 1 |
| iSGLT2 | sodium-glucose cotransporter type 2 inhibitors |
| ICI-T1DM | ICI-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| irAEs | immune-related adverse events |
References
- Azoury, S.C.; Straughan, D.M.; Shukla, V. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy: Clinical Efficacy and Safety. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2015, 15, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiravand, Y.; Khodadadi, F.; Kashani, S.M.A.; Hosseini-Fard, S.R.; Hosseini, S.; Sadeghirad, H.; Ladwa, R.; O’Byrne, K.; Kulasinghe, A. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 3044–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlino, M.S.; Larkin, J.; Long, G.V. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in melanoma. Lancet 2021, 398, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Tykodi, S.S.; Chow, L.Q.; Hwu, W.J.; Topalian, S.L.; Hwu, P.; Drake, C.G.; Camacho, L.H.; Kauh, J.; Odunsi, K.; et al. Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with advanced cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postow, M.A.; Sidlow, R.; Hellmann, M.D. Immune-Related Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Blockade. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggermont, A.M.M.; Blank, C.U.; Mandala, M.; Long, G.V.; Atkinson, V.; Dalle, S.; Haydon, A.; Lichinitser, M.; Khattak, A.; Carlino, M.S.; et al. Adjuvant Pembrolizumab versus Placebo in Resected Stage III Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1789–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuratomi Nakamura, K.; Paredes, A.; Passos-Rangel, X.; Ocampo Posada, M. Diabetic ketoacidosis, a common metabolic emergency. Interdiscip. J. Epidemiol. Public Health 2023, 5, e-9955. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, P.T.F.M.; Cazzoletti, G.; Passos, J.R.C.; Silva, R.R.C.; Rodrigues, L.A.P.; Nogueira, J.C.; Duarte, A.L.D.; Amaral, M.P.R. Cetoacidose Diabética: Fisiopatologia, diagnóstico e abordagem terapêutica. Braz. J. Dev. 2023, 9, 26370–26378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clotman, K.; Janssens, K.; Specenier, P.; Weets, I.; De Block, C.E.M. Programmed Cell Death-1 Inhibitor-Induced Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 3144–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatouli, A.M.; Quandt, Z.; Perdigoto, A.L.; Clark, P.L.; Kluger, H.; Weiss, S.A.; Gettinger, S.; Sznol, M.; Young, A.; Rushakoff, R.; et al. Collateral Damage: Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Induced With Checkpoint Inhibitors. Diabetes 2018, 67, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delivanis, D.A.; Gustafson, M.P.; Bornschlegl, S.; Merten, M.M.; Kottschade, L.; Withers, S.; Dietz, A.B.; Ryder, M. Pembrolizumab-Induced Thyroiditis: Comprehensive Clinical Review and Insights into Underlying Involved Mechanisms. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 2770–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso-Sousa, R.; Barry, W.T.; Garrido-Castro, A.C.; Hodi, F.S.; Min, L.; Krop, I.E.; Tolaney, S.M. Incidence of Endocrine Dysfunction Following the Use of Different Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Regimens: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longoria, T.C.; Tewari, K.S. Evaluation of the pharmacokinetics and metabolism of pembrolizumab in the treatment of melanoma. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2016, 12, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, E.S.; Liu, P.; Baleeiro, R.; Lemoine, N.R.; Yuan, M.; Wang, Y.H. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer therapy. J. Biomed. Res. 2018, 32, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seth, R.; Agarwala, S.S.; Messersmith, H.; Alluri, K.C.; Ascierto, P.A.; Atkins, M.B.; Bollin, K.; Chacon, M.; Davis, N.; Faries, M.B.; et al. Systemic Therapy for Melanoma: ASCO Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 4794–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggermont, A.M.M.; Kicinski, M.; Blank, C.U.; Mandala, M.; Long, G.V.; Atkinson, V.; Dalle, S.; Haydon, A.; Meshcheryakov, A.; Khattak, A.; et al. Five-year analysis of adjuvant pembrolizumab or placebo in stage III melanoma. NEJM Evid. 2022, 1, EVIDoa2200214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, J.J.; Rutkowski, P.; Queirolo, P.; Del Vecchio, M.; Mackiewicz, J.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Merino, L.d.l.C.; A Khattak, M.; Schadendorf, D.; Long, G.V.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus placebo as adjuvant therapy in completely resected stage IIB or IIC melanoma (KEYNOTE-716): A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2022, 399, 1718–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, J.; Del Vecchio, M.; Mandalá, M.; Gogas, H.; Fernandez, A.M.A.; Dalle, S.; Cowey, C.L.; Schenker, M.; Grob, J.-J.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; et al. Adjuvant nivolumab versus ipilimumab in resected stage III/IV melanoma: 5-year efficacy and biomarker results from CheckMate 238. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 3352–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkwood, J.M.; Del Vecchio, M.; Weber, J.; Hoeller, C.; Grob, J.J.; Mohr, P.; Loquai, C.; Dutriaux, C.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Mackiewicz, J.; et al. Adjuvant nivolumab in resected stage IIB/C melanoma: Primary results from the randomized, phase 3 CheckMate 76K trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2835–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dummer, R.; Hauschild, A.; Santinami, M.; Atkinson, V.; Mandalà, M.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Sileni, V.C.; Larkin, J.; Nyakas, M.; Dutriaux, C.; et al. Five-year analysis of adjuvant dabrafenib plus trametinib in stage III melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, C.D.; Khushalani, N.I.; Angeles, C.; Petrella, T.M. Current State of Adjuvant Therapy for Melanoma: Less Is More, or More Is Better? Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2022, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouri Rouzbahani, F.; Shirkhoda, M.; Memari, F.; Dana, H.; Mahmoodi Chalbatani, G.; Mahmoodzadeh, H.; Samarghandi, N.; Gharagozlou, E.; Mohammadi Hadloo, M.H.; Maleki, A.R.; et al. Immunotherapy a New Hope for Cancer Treatment: A Review. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 21, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidel, J.A.; Otsuka, A.; Kabashima, K. Anti-PD-1 and Anti-CTLA-4 Therapies in Cancer: Mechanisms of Action, Efficacy, and Limitations. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salangsang, J.; Sapkota, S.; Kharel, S.; Gupta, P.; Kalla, A. A Case of Pembrolizumab-Induced Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperthyroidism in a Patient with Recurrent Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Cureus 2023, 15, e35276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, A.; Soares, D.M.; Azevedo, S.; Pereira, T.; Amaral, C. Pembrolizumab-induced type 1 diabetes. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2024, 10781552241255699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, K.; Macfarlane, M.; Cooper, O.; Falk, J. Pembrolizumab-Induced Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Review of Critical Care Case. Cureus 2021, 13, e18983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, Y.K.; Chiec, L.; Mohindra, N.; Gentzler, R.; Patel, J.; Giles, F. A case of pembrolizumab-induced type-1 diabetes mellitus and discussion of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced type 1 diabetes. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sznol, M.; Postow, M.A.; Davies, M.J.; Pavlick, A.C.; Plimack, E.R.; Shaheen, M.; Veloski, C.; Robert, C. Endocrine-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade and expert insights on their management. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 58, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, C.A.; Menzies, A.M.; Clifton-Bligh, R.; Tsang VH, M. Thyroid Toxicity Following Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment in Advanced Cancer. Thyroid. Off. J. Am. Thyroid. Assoc. 2020, 30, 1458–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaker, L.; Cooper, D.S.; Walsh, J.P.; Peeters, R.P. Hyperthyroidism. Lancet 2024, 403, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotwal, A.; Haddox, C.; Block, M.; Kudva, Y.C. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: An emerging cause of insulin-dependent diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2019, 7, e000591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdigoto, A.L.; Quandt, Z.; Anderson, M.; Herold, K.C. Checkpoint inhibitor-induced insulin-dependent diabetes: An emerging syndrome. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 421–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akturk, H.K.; Kahramangil, D.; Sarwal, A.; Hoffecker, L.; Murad, M.H.; Michels, A.W. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced Type 1 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabet. Med. A J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 2019, 36, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barski, L.; Golbets, E.; Jotkowitz, A.; Schwarzfuchs, D. Management of diabetic ketoacidosis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 117, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Chen, D.; Zhao, R.; Zheng, X.; Gu, Y.; Yang, T.; Shi, Y. Real-world adherence to toxicity management guidelines for immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1213225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haanen, J.; Ernstoff, M.S.; Wang, Y.; Menzies, A.M.; Puzanov, I.; Grivas, P.; Larkin, J.; Peters, S.; Thompson, J.A.; Obeid, M. Autoimmune diseases and immune-checkpoint inhibitors for cancer therapy: Review of the literature and personalized risk-based prevention strategy. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2020, 31, 724–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahab, N.; Shah, M.; Suarez-Almazor, M.E. Adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade in patients with cancer: A systematic review of case reports. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, Y.; Kim, I.Y.; Sun, J.-M.; Lee, J.; Cha, H.-S.; Koh, E.-M.; Kim, H.; Lee, J. Risk factors for immune-related adverse events associated with anti-PD-1 pembrolizumab. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chennamadhavuni, A.; Abushahin, L.; Jin, N.; Presley, C.J.; Manne, A. Risk Factors and Biomarkers for Immune-Related Adverse Events: A Practical Guide to Identifying High-Risk Patients and Rechallenging Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 779691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardarli, I.; Tan, S.; Brandenburg, T.; Weidemann, F.; Görges, R.; Herrmann, K.; Führer, D. Risk and Incidence of Endocrine Immune-Related Adverse Effects under Checkpoint Inhibitor Mono- or Combination Therapy in Solid Tumors: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 1132–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Laboratory Test | Result | Reference Range |
|---|---|---|
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) | WBC 15.69 × 103/µL | 4–10 × 103/µL |
| ANC 13.34 × 103/µL | 1.8–7 × 103/µL | |
| Hb 17.4 g/dL | 13–16 g/dL | |
| Hct 58.2% | 40–48% | |
| Platelets 441 × 103/µL | 150–450 × 103/µL | |
| Creatinine | 1.82 mg/dL | 0.7–1.3 mg/dL |
| Blood Urea Nitrogen | 39 mg/dL | 9–23 mg/dL |
| Sodium | 132 mEq/L | 135–145 mEq/L |
| Potassium | 5.51 mEq/L | 3.5–4.5 mEq/L |
| Lactic Acid | 0.94 mmol/L | <2 mmol/L |
| Glucose | 764 mg/dL | 70–130 mg/dL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pacichana, J.A.; Osorio, L.M.; Restrepo, K.; García, A.F.; Rivas, G.; Liscano, Y. Diabetic Ketoacidosis as a Debut and Immune-Mediated Complication Caused by Pembrolizumab: Case Report. Diabetology 2024, 5, 600-607. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology5060043
Pacichana JA, Osorio LM, Restrepo K, García AF, Rivas G, Liscano Y. Diabetic Ketoacidosis as a Debut and Immune-Mediated Complication Caused by Pembrolizumab: Case Report. Diabetology. 2024; 5(6):600-607. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology5060043
Chicago/Turabian StylePacichana, Julian Andrés, Luis Miguel Osorio, Katherine Restrepo, Andres Felipe García, Giovanna Rivas, and Yamil Liscano. 2024. "Diabetic Ketoacidosis as a Debut and Immune-Mediated Complication Caused by Pembrolizumab: Case Report" Diabetology 5, no. 6: 600-607. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology5060043
APA StylePacichana, J. A., Osorio, L. M., Restrepo, K., García, A. F., Rivas, G., & Liscano, Y. (2024). Diabetic Ketoacidosis as a Debut and Immune-Mediated Complication Caused by Pembrolizumab: Case Report. Diabetology, 5(6), 600-607. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology5060043







