Abstract
Benthic diatoms are being used as indicators to assess the biological quality of surface waters in Kosovo. The Klina River is the left tributary of the White Drin River Basin, with a length of 69 km. The study assessed the level of surface water quality in the Klina River using 12 diatomic indices calculated with the Omnidia program. For this purpose, three stations monitored the river Klina in the autumn of 2021 to conform to international standards. A total of 88 diatom taxa were identified, with the dominant species being Rhoicosphenia abbreviata (C. Agardh) Lange-Bertalot, Gyrosigma acuminatum (Kützing) Rabenhorst, Cocconeis placenula Ehrenberg, Gomphonema minutum (Ag.) Agardh f. minutum, Gomphonema clavatum Ehr, Meridion circulare (Greville) C.A. Agardh, Cocconeis pediculus Ehrenberg, Diatoma vulgaris Bory, and Nitzschia dissipata (Kützing) Grunow ssp. dissipata etc. This study assessed the surface water quality in the Klina River using diatom indices, indicating that the river is in good to moderate ecological condition. Environmental variables such as hydrogen ion concentration (pH) and dissolved oxygen (DO) had significant positive correlations (<0.01) with the biological diatom index (IBD), Descy’s pollution metric (Descy), Sladeček’s pollution metric (SLA), the European index (CEE), and Watanabe’s Index (WAT), while the total suspended solids (TSS) also showed a strong negative significant correlation (<0.01) with the generic diatom index (IDG), Indice Diatomique Artois Picardie (IDAP), the eutrophication pollution index (EPI-D), the trophic diatom index (TDI), the Pampean diatom index (IDP), and Steinberg and Schiefele’s index (SHE). Total phosphorus (TP), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), and chemical oxygen demand (COD) presented a significant negative correlation (<0.05) with the IBD, Descy, SLA, CEE, and WAT indices. Our findings provide insights for organizations dealing with the state of the environment and water protection in Kosovo, and these results can be used as a starting point for assessing the ecological quality of water and monitoring environmental pollution in the Kosovo region.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, the problem with water pollution and growing concern for water quality has been evident all over the globe [1,2,3,4]. Meanwhile, joint efforts by the scientific community and policy-makers continue to find and implement solutions for the conservation and protection of water resources [5,6]. Many studies have shown that the situation is alarming, resulting from the lack of water or the pollution of drinking water [7]. These are the main reasons for the spread of many diseases in less developed countries [8]. According to World Health Organization (WHO) data, every year, close to 500 million people get sick from waterborne diseases, and around 10 million people die from polluted water daily [9]. One can state with certainty that the main problem of human society nowadays is water [10].
Diatoms are widely used due to their high diversity and abundance compared to other groups; they are widespread in aquatic ecosystems and are of great importance due to their unique composition of the silica cell wall and the important applied aspects of their relationship with physicochemical parameters [11,12].
Recent research has proven that diatoms have crucial roles in the assessment of surface waters [13,14,15]. Biological assessment using diatoms is also a requirement of the European Water Framework Directive [16], as they are excellent indicators of water quality. Diatoms provide detailed insight into the health of aquatic ecosystems and respond quickly to environmental changes [17]. Due to their rapid response and sensitivity to the environment, diatoms serve as a valuable tool for monitoring and managing surface waters, including rivers and lakes, helping to preserve healthy and sustainable ecosystems, improve water resource management, and contribute to the development of policies for the protection and management of surface waters [15,18,19,20].
For biological assessment purposes, many European countries use diatom algae [21,22,23,24,25], where, according to some data, after benthic macroinvertebrates, which are the most applied in biological assessment, diatom algae are also included in proportions of up to 54% [19,26,27]. Even in Kosovo, according to research so far, the most applied species in biological assessment have been macroinvertebrates, followed by macrophytes, fish, and diatoms, which have been used in some rivers [1,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37].
Given the alarming pollution of river basins in recent years in Kosovo [1,38,39], river basin management plans have recently been approved, which also foresee biological monitoring based on the biological component, including diatom algae.
The Klina River is located in Kosovo and flows entirely through Kosovo’s territory. This river has several branches from forest streams and is influenced by anthropogenic activities, especially when it passes through the cities of Skenderaj and Klina. This study of the algae community, applying diatom indices, reflects the ecological condition of the Klina River and the impact of anthropogenic activities. In this study, based on the quality research data, we examined the applicability of 12 diatom indices to determine the ecological status and analyzed the correlation between diatom index values and environmental variables using Spearmen’s correlation. The objectives of this study were to identify the number of diatom algae species in the Klina River, assess the ecological quality of the Klina River based on diatom algae, and investigate the relationship between diatom indices and environmental variables.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Klina River is the left branch of the Drini i Bardhë River (Figure 1). It lies between coordinates 42°40′00″ and 42°50′00″ N and 20°30′00″ and 20°50′00″ E and has a catchment area of 477 km2 [40]. According to the “Report: The state of water in Kosovo 2020” [40,41], its average annual inflows are 2.8 m3s−1, its flow coefficient is 0.22, and its flow module is 4.92 dm3s−1km−2. According to the topographic map on a scale of 1:25,000 for the territory of Kosovo [40,42], the altitude of the watershed ranges from 375 m to 1751 m (Mount Radopole Neck). The minimum rainfall was 571.70 mm, 1081.90 mm, and 880.98 mm, while the average annual temperature was 10 °C [43]. Rock formations from the Paleozoic to the Quaternary take part in the geological construction of the Klinë river basin [42]. The area of the basin is covered with forests and bushes (60.20%), pastures, meadows, and plant areas (22.60%), and others (14.15%) [40] (Figure 1) and (Table 1).
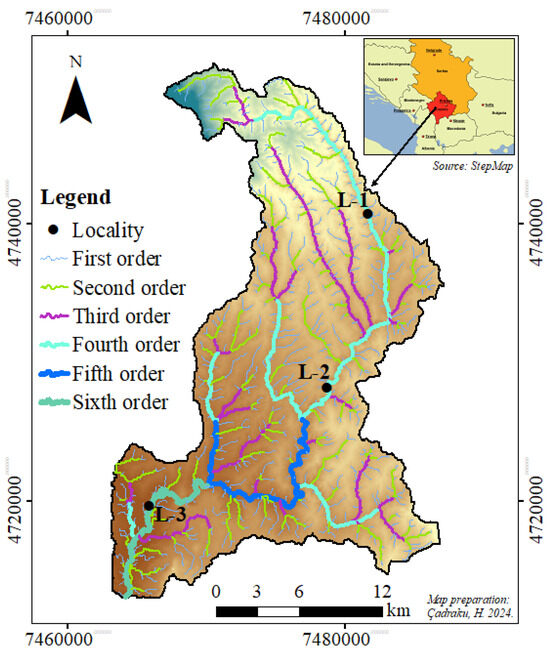
Figure 1.
Sampling locations and investigation areas.

Table 1.
The sampling sites with geographic coordinates and hydromorphological features.
To analyze and determine diatoms, samples were collected from three different sampling locations along the Klina River in 2021. Samples were taken in periphyton and on stones, tree branches, or other existing substrates in the Klina River basin, according to the standard [44].
The samples were placed in glass bottles, while their preservation and fixation were performed in 4% formalin [44]. The preparations were made in the laboratory according to the steps below. For diatom analysis, 5 mL of samples was placed in the test tubes. The supernatant water was removed from the algal material, which had settled on the bottom of the tubes (Figure 2). Then, 10 mL of H2O2 was added to all the samples in the test tubes, and the tubes were placed in a water bath at a temperature of 90 °C for 2–3 h. Then, 1M HCl 37% was added to the samples rich in organic matter to dissolve the carbonates [45,46,47]. After completing this stage, test tubes were placed in the centrifuge for 3–4 min, and the supernatant was removed. After this step, 4 mL of distilled water was added to the test tubes, and the samples were centrifuged 4 times with distilled water until they were thoroughly cleaned. Then, 1–2 drops of formalin were added to ensure preservation. Microscopic slides were made from the obtained material, and a thorough algological analysis of the samples was performed using an optical microscope (Figure 2). The determination of species was based on the keys provided in [48,49,50,51]. During the study, 200 to 400 individuals were counted at each sampling site, and the abundance of species was determined based on these counts. The OMNIDIA 5 program [52] was used to calculate twelve diatom-based indicators (Table 2), which are commonly used to analyze ecological conditions.
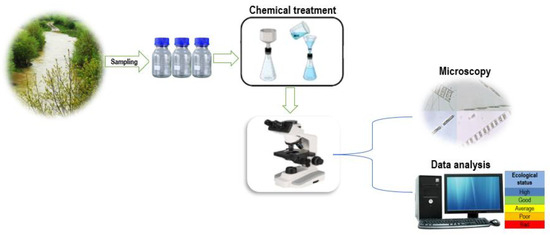
Figure 2.
The methodology of determination of diatom.

Table 2.
List of diatom indices calculated for the current investigation.
In addition to the samples for diatom analysis, samples were also taken for physical-chemical analysis of the water in the Klina River in the exact 3 locations. Samples were used to accurately assess the water quality and prove the correlations between the physicochemical and diatomic parameters.
Physicochemical parameter analyses were performed according to ISO 5667–6 [66]. Water samples for analysis were collected simultaneously with diatom samples. Environmental factors, including pH, water temperature, and dissolved oxygen (DO), were analyzed directly in the field and determined using the portable multiparameter meter HI98194. This multiprobe meter was calibrated before field sampling. Total phosphorus (TP), nitrite (NO2-), and total suspended solids (TSS) were determined using an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer, chemical oxygen demand (COD) was analyzed based on protocol NF T90-101, and biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5) was analyzed based on SS by the gravimetry (NF EN 872) parameter; all these were analyzed in the laboratory [66].
2.2. Statistical Analysis
Spearmen’s correlation analysis was used to analyze the correlation between various environmental factors and the assessment of the diatom index; PCA was also used to determine the relationship between environmental variables, while CCA was used to identify the main environmental factors that affect species abundance.
In this study, SPSS 24 was used to analyze Spearmen’s correlation. In contrast, PCA (principal component analysis) and CCA (canonical correlation analysis) were analyzed through the Past 5.0 program.
3. Results and Discussion
During this research, the state of water quality in the Klina River was assessed using diatoms in the three locations, L-1, L-2, and L-3; in addition to this, in these three locations, physicochemical parameters, such as temperature, total suspended solids, pH, dissolved oxygen, biochemical oxygen demand, chemical oxygen demand, total phosphorus, and nitrites, were analyzed to assess the quality of the water more accurately. The obtained results for diatoms and physicochemical parameters were compared with the values determined by the recommendations of international standards for monitoring surface waters.
Temperature is one of the most basic physical parameters and should always be measured. The development of aquatic life depends on oxygen. Since the oxygen concentration in water is temperature-dependent, a high water temperature lowers the oxygen solubility, thus limiting the development of the aquatic world. Slight differences in the temperature values were observed at locations L-1, L-2, and L-3. L-1 had a temperature of 13.1 °C, L-2 had a temperature of 16.3 °C, and L-3 had a temperature of 17.1 °C (Figure 3). Based on the temperature values, the water quality belongs to class I.
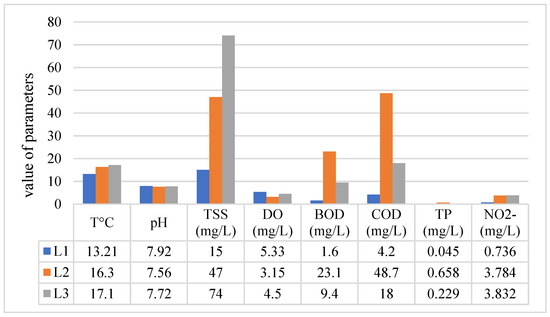
Figure 3.
Results of physicochemical analysis in Klina River.
Total suspended solids (TSS) refer to the concentration (mg/L) of inorganic and organic matter in waters of streams, rivers, lakes, etc. Total suspended solids usually consist of fine particles with a diameter of less than 62 µm [67]. The results of the Klina River analyses were as follows: L-1 had a concentration of total suspended solids of 15 mg/L, L-2 had 47 mg/L, and L-3 had 4 mg/L (Figure 3). According to the results, the first and second locations (L-1 and L-2)) were found to have a higher load of total suspended solids. As a result, damage to the biota can occur. Looking at macrophytes and algae, elevated values of the total suspended solids can reduce 3–13% of the primary productivity, and in phytoplankton, it reduces biomass production by up to 40% [67,68,69].
Dissolved oxygen is essential to sustaining higher forms of biological life. Fish of the Salmonidae family (trout, salmon) require O2 levels of at least 5 mg/L. Other fish will not survive at O2 levels lower than 2 mg/L. Based on the analysis of the Klina River, the following results were obtained: in L-1, the dissolved O2 was 5.35 mg/L; in L-2, it was 3.17 mg/L; and in L-3, it was 4.6 mg/L (Figure 3). The first location belongs to class III of water quality, and the second and third locations belong to class IV based on the classification standard [70]. The water quality based on dissolved oxygen is worse than in the [71] research in Morava e Binqes, while better water quality is reported than in the [72] research in some locations of the Sitnica River in Kosovo.
Chemical oxygen demand (COD) is the amount of oxygen spent oxidizing organic and inorganic substances expressed in mg/L. It measures the total amount of organic and inorganic pollution in polluted waters [73]. According to the Classification of the Environmental Quality of Freshwater in Norway, L-1 belongs to class I, L-2 belongs to class V, and L-3 belongs to class IV (Figure 3). The water quality values of the Klina River compared to previous research [71] are better, except for location 2, where industrial activity is evident, which affects the poor water quality.
The water pH level is one of the leading chemical parameters since many physicochemical reactions in water are controlled by pH. The pH of water affects both biological and chemical processes. pH values below 4.5 and above 9.5 are usually lethal to aquatic organisms. pH affects the solubility of organic compounds, metals, and salts. In highly acidic waters, certain minerals can dissolve and release metals and other chemicals into the water. Most organic pollutants are weak organic acids and are more likely to enter organisms at low pH. The pH values in the Klina River were 7.92 in L-1, 7.56 in L-2, and 7.72 in L-3 (Figure 3). These results conclude that the pH values are within the recommended values required according to Directive 75/440.
Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5) is one of the pollution indicators used to determine the impacts of wastewater on water quality. Microorganisms decompose organic matter in water, consuming oxygen. Variations in BOD5 in the Klina River were visible. L-1 had BOD5 values of 1.6 mg/L, L-2 showed 23.1 mg/L, and L-3 displayed 9.6 mg/L (Figure 3). Location L-1 has not been under anthropogenic industrial and urban influence and belongs to the first category [73]. In contrast, based on the above results, the other two locations (L-2 and L-3) have higher BOD5 values and belong to the V category. A similar situation regarding BOD and category V water quality is also presented in [74] research on the Topluha River branch, a branch of the same basin as the Klina River.
Phosphorus is a common constituent of agricultural manure, organic manure, and organic waste. Also, it can be found in higher concentrations in wastewater and industrial effluents [75]. It is an essential element for plant life, but when there is too much of it in water, it can accelerate eutrophication. The results of the analyses in the present research indicate high values of total phosphorus in the water. The total phosphorus concentration in the first location (L-1) was 0.047 mg/L, in L-2, it was 0.658 mg/L, and in L-3, it was 0.329 mg/L (Figure 3). The water taken from L-2 and L-3 can be classified as hypertrophic, while the water at L-1 is eutrophic [75,76] (Figure 3). Hypertrophic similarity of the water quality in locations L2 and L3 based on total phosphorus is also presented in the research of [36] in the Nerodime River.
From principal component analysis (PCA) (Figure 4) and the correlation coefficient between physical and chemical parameters (Table 3), it can be seen that there is a relationship between total phosphorus, biochemical and chemical oxygen demand, and total suspended solids (TSS). An increase in total suspended solids and a simultaneous increase in the number of total phosphorus particles can have an impact on the growth of phytoplankton, which causes an increase in the biochemical and chemical oxygen demand and a decrease in dissolved oxygen [77,78,79], while the total phosphorus suggests an increase in organic pollution, which increased the chemical expenditure of oxygen [77,80]. These parameters are closely related and can impact aquatic habitats, resulting in decreased water quality and potentially dangerous conditions for the living things that live there [81,82]. It has also been discovered that the oxygen concentration correlates negatively with the biochemical and chemical consumption of oxygen and total phosphorus. This results from microbial pollution caused by organic contamination, which influences the increase in biochemical oxygen demand and decrease in dissolved oxygen. Anthropogenic causes, including wastewater from residences, livestock, and industrial operations in the Klina River basin, cause this contamination. Similar findings were reported in [83,84,85] investigations in Europe and Asia.
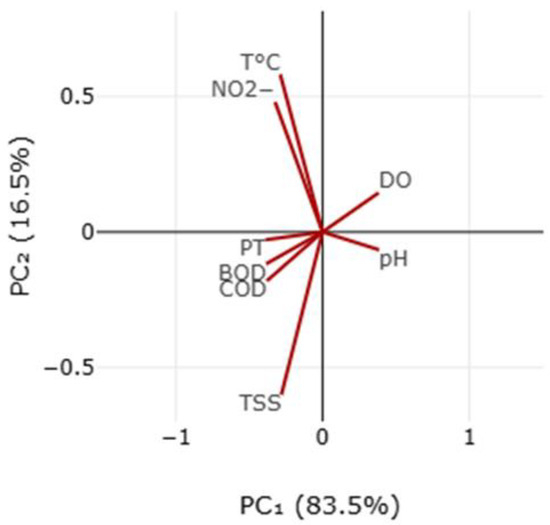
Figure 4.
Ordination plot of principal components analysis (PCA) of physicochemical parameters.

Table 3.
Determination of quality, ecological status, and trophic status based on diatom index values [86].
Figure 4 and Table 4 demonstrate a positive association between temperature and NO2−. NO2− levels drop with lower temperatures while increasing with higher temperatures. Higher water temperatures increase microbial activity and reduce nitrates (NO3−) to nitrites (NO2−), explaining the positive association. Higher temperatures accelerate the activity of microorganisms in the nitrogen cycle, leading to a rise in NO2− concentration in water [87].

Table 4.
Correlation between physicochemical parameters.
Table 5, Table 6 and Table 7 present the analysis of diatoms in three locations. Eighty-eight types of diatoms were identified during the research in the Klina River.

Table 5.
Results of diatoms at Kuçicë location (L-1).

Table 6.
Results of diatoms in the Tushilë location (L-2).

Table 7.
Results of diatoms at the Klinë location (L-3).
A total of 32 species of diatoms were identified in the Kuçicë location (L-1). The species with the highest abundance are Rhoicosphenia abbreviata (C. Agardh) Lange-Bertalot at 23.5%, Gyrosigma acuminatum (Kützing) Rabenhorst at 13.4%, Gomphonema minutum (Ag.) Agardh f. minutum at 9.6%, Meridion circulare (Greville) C.A.Agardh at 9.1%, Cocconeis pediculus Ehrenberg at 4.8%, and Gomphonema clavatum Ehr. At 3.2% (Table 5).
Based on the values of the IBD, IPS, IDG, Descy, IDAP, EPID, CEE, WAT, and SHE indices, the water quality is good and belongs to the second class (II) and the oligo-mesotroph trophic level (Table 8).

Table 8.
Values of diatoms indices in the Klina River.
However, according to the SLA, TDI, and PDI indices, the water quality is moderate and belongs to the third class (III) and the trophic-mesotrophic level. According to the Rott TI index, the water quality belongs to the fourth class, the bad category, and the eutrophic trophic level. Globally, the genus Rhoicosphenia is commonly reported in brackish freshwater and marine ecosystems and can be found on every continent [88].
A total of 37 species of diatoms were identified in the Tushilë location (L-2). The species with the highest abundance are Nitzschia dissipata (Kützing) Grunow ssp. dissipata at 5.8%, Gomphonema parvulum (Kützing) Kützing at 5.8%, Nitzschia palea (Kützing) W. Smith at 5.6%, Craticula ambigua (Ehrenberg) Mann at 4.7%, Gomphonema c.g. Ehrenberg at 4.7%, Rhoicosphenia abbreviata (C. Agardh) Lange-Bertalot at 5.0%, Gomphonema subclavatum Grunow at 3.8%, and Gomphonema clavatum Ehr. At 3.8% (Table 6).
According to the values of the IBDBDI, IPS, IDG, Sla, IDAP, CEE, WAT, IDP, and SHE indices, the water quality is moderate and belongs to the third class (III) and the mesotrophic trophic level (Table 7). Based on the Descy index, the water quality is good, belonging to the second class (II) and the oligo-mesotrophic trophic level.
According to the TDI index values, the water quality is poor and belongs to the fourth class (IV) and the trophic eutrophic level (Table 8).
In the location of Klina (L-3), there were 52 species of diatoms. The species with the highest abundance were Cocconeis placenula Ehrenberg at 9.0%, Diatoma vulgaris Bory at 7.4%, Cocconeis placenula Ehrenberg var. euglypta (Ehr.) Grunow at 7.4%, Rhoicosphenia abbreviata (C. Agardh) Lange-Bertalot at 6.8%, Amphora ovalis (Kützing) Kützing at 6.8%, and Gomphonema clavatum Ehr. at 3.9% (Table 6).
The water quality is good according to the indexed values of IBD, IPS, IDG, IDAP, EPI-D, CEE, WAT, and SHE. It belongs to the second class (II) and oligo-mesotrophic trophic level. According to the Descy index, the water quality is high, belonging to the first class (I) and the oligotrophic trophic level (Table 7).
According to the SLA index values, the water quality is moderate and belongs to the third class (III) and the trophic-mesotrophic level. However, according to the TDI index, the water analysis is poor and belongs to the fourth category (IV) and the trophic eutrophic level. (Table 7)
Species of the genera Nitzschia and Navicula predominated in three localities. They are cosmopolitan diatoms that prefer alkalophilic environments (pH > 7) and eutrophic waters. Navicula lanceolata prefers electrolyte waters. Regarding pH, the three localities of our research have shown basic pH values related to the preference of the genera Navicula and Nitzschia [89].
Other research in Kosovo used the same diatom indices and biological water quality assessment methods. In a previous study in Kosovo [13], which analyzed the water from the Lepence River basin based on the diatomic indices, the river was classified into good and moderate categories, similar to this research. While the results obtained in this research are comparable to the research of [28] in Kosovo’s Ibar River basin, the water quality based on diatom indices in their studies is high, good, and poor. In contrast, the results in the Klina River show no index falling in the category of poor water quality. Our results, compared to the macroinvertebrate indices from the study of [37] based on the biological assessment of water, show that the Kuçicë site has a similar good ecological status. Likewise, based on the macrophyte indices as bioindicators for ecological water assessments [29], similar results indicating a good ecological status were observed at the Kuçicë and Klina sites. The Klina River has 88 species in total, but the Llapi River has 52 species, according to previous [90] research. This is a good number of species, and according to this study, there are similarities because both water bodies fall into the second ecological category. A similar number of species was also presented in previous [91] research in the Nerodime River, where 70 species of diatoms exist. Still, compared to this river, the Klina River has better water quality. Also, comparing the Klina River flow with the main flow of the Drini Bardhe River, where 77 species are present [92]. It can be said that the Klina River, which is part of this basin, also has many species and similarities in the categorization of water quality. Compared to the flow of the Krena River, where, according to research [93], 28 species of diatoms dominate, the Klina River has a more significant number of species and better water quality. Compared to the countries in the region, like Albania, according to research by [94], the results of this research have similarities according to the Index of Pollution Sensitivity, where it has good and average ecological statuses. Also, compared to the Vjosa River in Albania [95], we have similarities in terms of ecological status. Similarities in the number of species and water quality are also found in research [96] on the Gjirokastra River in Albania. Compared to research in the neighboring country of Macedonia [97,98,99], research in Kosovo is more limited and scarce regarding the monitoring and diversity of diatom algae.
In recent years, much effort has been devoted to understanding ecosystem and species responses to environmental variability and its impact on ecosystem function [100,101,102].
The ordination of species in (Figure 5) showed that GMIN, CPED, RABB, and MCIR were mainly associated with Ph and dissolved oxygen (DO) and were more abundant in sites where Ph and Do were higher. Likewise, species such as NPAD, NDIS, GPAR, CEUG, ESBM, GOMP, and CAMB show a relationship with T°C, BOD, COD, PT, and NO2—the higher the value of the parameters, the greater the abundance of the species. Meanwhile, TSS presents a clear connection to the species CPLE, CPLA, APED, AOVA, TVUL, ESLE, and ADMI.
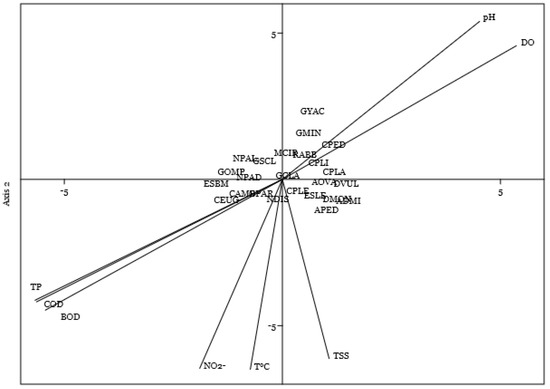
Figure 5.
Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) diagram showing environmental variables and the species of diatoms that were the most abundant.
Previous research indicated [103] that the correlation between diatom indices and environmental variables varies by region, possibly due to differences in the environmental parameters or nutrient gradients utilized to generate each index.
Table 9 shows Spearman’s correlation of the physicochemical parameters and diatomic indices of the river Klina. Total suspended solids (TSS) present a strong negative significant correlation (<0.01) with the IDG, IDAP, EPI-D, TDI, IDP, and SHE indices (Table 9). Because an increase in total suspended solids (TSS) contributes to the rise in eutrophication [104]. This study also finds a negative association between the TSS, IDG, IDAP, EPI-D, TDI, IDP, and SHE indexes (Table 9). The negative correlation between TSS and these indicators is because TSS obstructs light penetration in water, affecting photosynthesis [105] and resulting in poorer health of diatom algae. pH was significantly correlated (<0.01) with IBD, Descy, Sla, CEE, and Wat indices. Similar results regarding pH and the diatomic index are also presented in previous research [15]. Dissolved oxygen presents a significant positive correlation (<0.01) with the IBD, Descy, SLA, CEE, and WAT indexes (Table 9). A similar positive correlation between BOD and the IBD, Descy, SLA, CEE, and WAT indexes was also reported in previous research [103,106] in Turkey. Different countries use IDAP to evaluate the impacts of agriculture, industry, and urban development [64], and based on this context, the river Klina is polluted by urban pollution, which comes from the cities of Skenderaj and Klina and the industries and agricultural activities located in this region. Also, earlier research [29] on the Klina River, based on the assessment of macrophytes as bioindicators of organic pollution, reported the same situation in this river. The biochemical and chemical oxygen expenditures present a significant negative correlation with the indices IBD, Descy, Sla, CEE and Wat (Table 9), similar results were also reported in the research of [106] in Turkey. Since the IBD, Descy, Sla, CEE, and Wat indexes aim to measure the levels of general pollution, organic pollution, and eutrophication [58,63], the increase in biochemical costs indicates a high level of eutrophication; therefore, there was a negative correlation between BOD, COD, and the IBD, Descy, Sla, CEE, and Wat indexes, where the monitoring points that had higher values of biochemistry and oxygen expenditure had lower values in the IBD, Descy, Sla, CEE, and Wat indexes and average ecological status.

Table 9.
The Spearmen’s correlation between physicochemical parameters and diatoms indices.
Total phosphorus presents a significant negative correlation (<0.05) with the IBD, Descy, Sla, CEE, and Wat indexes (Table 9), similar correlation values were also presented in previous authors’ research [106,107,108]. High levels of total phosphorus affect the growth of biomass of algae, including other types of algae, which can affect the development of diatoms, oxygen reductions and increases in biochemical and chemical oxygen consumption, which can also affect the eutrophication of waters and their acidification [109,110,111]. Therefore, the negative correlation of this parameter should be of great concern as it also shows the high presence of organic pollution from the activities carried out around the Klina River.
Environmental stresses that affect the diatom community and water quality indices of diatom algae in the Klinë River include industrial activities along the river’s course, sewage discharge, anthropogenic pollution, and agricultural activities. Various studies [112] report similar stressors, including climate change, and recommend continuing international efforts to develop more effective tools and strategies for biomonitoring based on biological components, including diatom metrics, in the context of environmental variables.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we investigated the water quality in the Klina River based on the composition of diatoms in 2020. We selected twelve diatom indices, IBD, IPS, IDG, Descy, SLA, IDAP, EPI-D, CEE, WAT, TDI, IDP, and SHE, to observe the quality and ecological status in the Klina River.
This study found that diatom indices were related to environmental factors. pH and DO show strong positive relationships (p < 0.01) with IBD, Descy, SLA, CEE, and WAT indices. TSS had a high negative connection (p < 0.01) with IDG, IDAP, EPI-D, TDI, IDP, and SHE indexes. TP, BOD, and COD had a significant negative correlation (p < 0.05) with the IBD, Deascy, Sla, CEE, and Wat indices.
Based on the results, the Klina River belongs to the second- and third-class water quality categories and falls in the good and moderate ecological categories based on diatomic indices.
Also, based on the physical and chemical parameters, the first location (L-1) had higher water quality, with lower levels of total suspended solids (TSS), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), and total phosphorus. In contrast, the second (L-2) and third (L-3) locations showed greater pollution levels, most likely due to industrial and urban discharges, pollution from agriculture, improper waste management, and household wastewater flows, as seen by the heightened TSS, BOD, and TP concentrations. These results indicate the necessity of initiatives that should be undertaken to preserve surface water ecosystems, especially in areas with high levels of pollution, to protect and improve the ecological integrity of the Klina River. To ensure sustainable management of this surface water resource, future research should focus on long-term monitoring and the application and setting of reference values for biological water monitoring to address the identified sources of pollution.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, O.F., R.K. and A.S.; methodology, O.F. and A.S.; software, D.N., F.S. and P.B.; validation, P.B., B.Đ., R.H. and D.N.; formal analysis, R.K. and F.S.; investigation, O.F. and D.D.; resources, P.B.; data curation, O.F., D.D. and B.Đ.; writing—original draft preparation, O.F., A.S., P.B., R.K. and D.D.; writing—review and editing, O.F. and A.B.; visualization, D.D., U.R. and R.H.; supervision, U.R. and B.Đ. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All data available upon the reasonable request from the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors also thank University North, Croatia, for helping with the scientific project, “Hydrological and geodetic analysis of the watercourse”, from 2024.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bytyqi, P.; Czikkely, M.; Shala-Abazi, A.; Fetoshi, O.; Ismaili, M.; Hyseni-Spahiu, M.; Ymeri, P.; Kabashi-Kastrati, E.; Millaku, F. Macrophytes as Biological Indicators of Organic Pollution in the Lepenci River Basin in Kosovo. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2020, 35, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetoshi, O.; Koto, R.; Sallaku, F.; Çadraku, H.; Rizani, S.; Bytyçi, P.; Nuha, D.; Đurin, B.; Durmishi, B.; Haziri, V.; et al. Assessments of Heavy Metal Contaminants in the Drenica River and Bioremediation by Typha Angustifolia. Hydrology 2024, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yang, H.; Xu, X. Effects of Water Pollution on Human Health and Disease Heterogeneity: A Review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 880246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ding, Z.; Wei, G.; Zhao, H.; Huang, T. Sources of Water Pollution and Evolution of Water Quality in the Wuwei Basin of Shiyang River, Northwest China. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Pan, X.; Fang, Z.; Li, J.; Bryan, B.A. Future Global Urban Water Scarcity and Potential Solutions. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nura, A.; Hasalliu, R.; Bytyçi, P.; Durmishi, B.; Haziri, S.S.; Ajazi, F.; Haziri, V. Application of Water Quality Index for Assessment of Surface Water, Dukagjini Region, Kosovo. Ecol. Balk. 2023, 15, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Adelodun, B.; Ajibade, F.O.; Ighalo, J.O.; Odey, G.; Ibrahim, R.G.; Kareem, K.Y.; Bakare, H.O.; Tiamiyu, A.O.; Ajibade, T.F.; Abdulkadir, T.S.; et al. Assessment of Socioeconomic Inequality Based on Virus-Contaminated Water Usage in Developing Countries: A Review. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashbolt, N.J. Microbial Contamination of Drinking Water and Disease Outcomes in Developing Regions. Toxicology 2004, 198, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizullah, A.; Khattak, M.N.K.; Richter, P.; Häder, D.-P. Water Pollution in Pakistan and Its Impact on Public Health—A Review. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehnder, A.J.B.; Yang, H.; Schertenleib, R. Water Issues: The Need for Action at Different Levels. Aquat. Sci. 2003, 65, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; Saxena, A.; Kapoor, N.; Singh, K.J.; Saldarriaga-Hernández, S.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Therapeutic Attributes and Applied Aspects of Biological Macromolecules (Polypeptides, Fucoxanthin, Sterols, Fatty Acids, Polysaccharides, and Polyphenols) from Diatoms—A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 171, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, A.; Tiwari, A.; Kaushik, R.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Diatoms Recovery from Wastewater: Overview from an Ecological and Economic Perspective. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 39, 101705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bytyçi, P.; Ymeri, P.; Czikkely, M.; Fetoshi, O.; Shala-Abazi, A.; Ismaili, M.; Ramshaj, Q.; Millaku, F. The Application of Benthic Diatoms in Water Quality Assessment in Lepenci River Basin, Kosovo. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelekli, A.; Lekesiz, H.; Yavuzatmaca, M. Bioassessment of Water Quality of Surface Waters Using Diatom Metrics. Turk. J. Bot. 2021, 45, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Burford, M.A.; Sheldon, F.; Bunn, S.E. Benthic Diatom Based Indices for Water Quality Assessment in Two Subtropical Streams. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 204645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Directive—2000/60—EN—Water Framework Directive—EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2000/60/oj (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Çelekli, A.; Kapı, E. Ecoregion Approach in the Assessment of Aquatic Ecosystems in the West of Gaziantep (Turkey): Application of Diatom Metrics. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 103, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, E.A.; Heinrich, C.G.; Schuch, M.; Wetzel, C.E.; Ector, L. Diatoms as Bioindicators in Rivers. In River Algae; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 245–271. ISBN 978-3-319-31984-1. [Google Scholar]
- Masouras, A.; Karaouzas, I.; Dimitriou, E.; Tsirtsis, G.; Smeti, E. Benthic Diatoms in River Biomonitoring—Present and Future Perspectives within the Water Framework Directive. Water 2021, 13, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taurozzi, D.; Cesarini, G.; Scalici, M. Diatoms as Bioindicators for Health Assessments of Ephemeral Freshwater Ecosystems: A Comprehensive Review. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, D.F.; Kelly, M.G.; Stevenson, R.J.; Poikane, S.; Theroux, S.; Zgrundo, A.; Cantonati, M. Benthic Algae Assessments in the EU and the US: Striving for Consistency in the Face of Great Ecological Diversity. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidlerová, D.; Hlúbiková, D. Relationships between Benthic Diatom Assemblages’ Structure and Selected Environmental Parameters in Slovak Water Reservoirs (Slovakia, Europe). Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2016, 27, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasprica, N.; Hafner, D. Taxonomic Composition and Seasonality of Diatoms in Three Dinaric Karstic Lakes in Croatia. Limnologica 2005, 35, 304–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Poikane, S.; Kelly, M.; Cantonati, M. Benthic Algal Assessment of Ecological Status in European Lakes and Rivers: Challenges and Opportunities. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelnik, I.; Balanč, T.; Toman, M.J. Diversity and Structure of the Tychoplankton Diatom Community in the Limnocrene Spring Zelenci (Slovenia) in Relation to Environmental Factors. Water 2018, 10, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springe, G.; Sandin, L.; Briede, A.; Skuja, A. Biological Quality Metrics: Their Variability and Appropriate Scale for Assessing Streams. In The Ecological Status of European Rivers: Evaluation and Intercalibration of Assessment Methods; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 153–172. ISBN 978-1-4020-5493-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, N.; Thodsen, H.; Andersen, H.E.; Tornbjerg, H.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A.; Riis, T. Flow Regimes Filter Species Traits of Benthic Diatom Communities and Modify the Functional Features of Lowland Streams—A Nationwide Scale Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buçinca, A.; Bilalli, A.; Ibrahimi, H.; Slavevska-Stamenković, V.; Mitić-Kopanja, D.; Hinić, J.; Grapci-Kotori, L. Water Quality Assessment in the Ibër River Basin (Kosovo) Using Macroinvertebrate and Benthic Diatom Indices. J. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 25, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bytyçi, P.; Shala-Abazi, A.; Zhushi-Etemi, F.; Bonifazi, G.; Hyseni-Spahiu, M.; Fetoshi, O.; Çadraku, H.; Feka, F.; Millaku, F. The Macrophyte Indices for Rivers to Assess the Ecological Conditions in the Klina River in the Republic of Kosovo. Plants 2022, 11, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etemi, F.Z.; Bytyçi, P.; Ismaili, M.; Fetoshi, O.; Ymeri, P.; Shala–Abazi, A.; Muja-Bajraktari, N.; Czikkely, M. The Use of Macroinvertebrate Based Biotic Indices and Diversity Indices to Evaluate the Water Quality of Lepenci River Basin in Kosovo. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2020, 55, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grapci-Kotori, L.; Ibrahimi, B.; Bilalli, A.; Ibrahimi, H.; Musliu, M. The Composition, Distribution and Abundance of Fish Species According to the Effects of Water Physicochemical Parameters in the Livoq Lake, Kosovo. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grapci-Kotori, L.; Vavalidis, T.; Zogaris, D.; Šanda, R.; Vukić, J.; Geci, D.; Ibrahimi, H.; Bilalli, A.; Zogaris, S. Fish Distribution Patterns in the White Drin (Drini i Bardhë) River, Kosovo. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2020, 29, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahimi, H.; Kučinić, M.; Gashi, A.; Grapci Kotori, L. The Caddisfly Fauna (Insecta, Trichoptera) of the Rivers of the Black Sea Basin in Kosovo with Distributional Data for Some Rare Species. ZooKeys 2012, 182, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahimi, H.; Kučinić, M.; Gashi, A.; Grapci-Kotori, L. Trichoptera Biodiversity of the Aegean and Adriatic Sea Basins in the Republic of Kosovo. J. Insect Sci. 2014, 14, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashtanjeva, A.; Vehapi, I.; Kurteshi, K.; Paçarizi, M.; Berisha, A.; Morina, R. Assessment of Physico-Chemical, Microbiological Parameters and Diatom Algae of Badovc Lake, Kosovo. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 32, 2155–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bytyçi, P.S.; Zhushi Etemi, F.N.; Ismaili, M.A.; Shala, S.A.; Serbinovski, M.S.; Çadraku, H.S.; Fetoshi, O.B. Biomonitoring of Water Quality of River Nerodime Based on Physicochemical Parameters and Macroinvertebrates. Rasayan J. Chem. 2018, 11, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhushi Etemi, F.; Çadraku, H.; Bytyçi, A.; Kuçi, T.; Desku, A.; Ymeri, P.; Bytyçi, P. Correlation between Physical and Chemical Parameters of Water and Biotic Indices: The Case Study the White Drin River Basin, Kosovo. J. Water Land Dev. 2020, 46, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asllani, F.H.; Schürz, M.; Bresgen, N.; Eckl, P.M.; Alija, A.J. Genotoxicity Risk Assessment in Fish (Rutilus rutilus) from Two Contaminated Rivers in the Kosovo. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zogaris, S.; Grapci-Kotori, L.; Geci, D.; Ibrahimi, H.; Zogaris, D.; Bilalli, A.; Buçinca, A.; Vlachopoulos, K.; Vavalidis, T. River Degradation Impacts Fish Assemblages in Kosovo’s Ibër Basin. Ecol. Montenegrina 2024, 75, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çadraku, H.; Hasa, X. Morphometric Analysis of Klina River Basin Using Geospatial Technology and Open Access Datasets. J. Water Land Dev. 2023, 58, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MESPI and KEPA (10.10.2024) Report: The State of Water in Kosovo 2020. Ministry of Environment, Spatial Planning and Infrastructure, Kosovo Environmental Protection Agency: Pristina. Available online: https://ammk-rks.net/assets/cms/uploads/files/dokumente/ANGLISHT_WEB_uji.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2022).
- The Independent Commission for Mines and Minerals. Geological Map of Kosovo (1:200,000). 2006. Available online: https://www.kosovo-mining.org/gdk/login (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Instituti Hidrometeorologjik i Kosovës. Të Dhënat Meteorologjike, Mesatare Mujore 2001–2019 [Hydrometeorological Yearbook of Kosovo, 2001–2019]. 2022. Available online: https://ihmk-rks.net/?page=1,89,14 (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- EN 13946:2003; Water Quality—Guidance Standard for the Routine Sampling and Pretreatment of Benthic Diatoms from Rivers. ECS (European Committee for Standardization): Brussels, Belgium, 2003.
- Afanasyev, S.; Lyashenko, A. Development of Standard Procedures for Ecological Monitoring of Danube River Basin Water Bodies in Ukraine. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/238071399_Development_of_standard_procedures_for_ecological_monitoring_of_Danube_River_Basin_water_bodies_in_Ukraine (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- Janauer, G.; Dokulil, M. Macrophytes and Algae in Running Waters. In Biological Monitoring of Rivers: Applications and Perspectives; Ziglio, G., Siligardi, M., Flaim, G., Eds.; Wiley Online Library: Hudson County, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Manual for Biological Monitoring of Rivers and Lakes/Reservoirs in B&H | PDF | Aquatic Ecosystem | Water. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/106794091/Bio-Manual (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- Cantonati, M.; Kelly, M.G.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Freshwater Benthic Diatoms of Central Europe: Over 800 Common Species Used in Ecological Assessment English Edition with Updated Taxonomy and Added Species; Koeltz Botanical Books: Oberreifenberg, Germany, 2017; ISBN 978-3-946583-06-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Bertalot, H. Navicula Sensu Stricto, 10 Genera Separated from Navicula Sensu Lato, Frustulia. In Diatoms of Europe: Diatoms of the European Inland Waters and Comparable Habitats; Koeltz Botanical Books: Oberreifenberg, Germany, 2001; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K. Cymbella. In Diatoms of Europe; A.R.G. Gantner Verlag K.G: Ruggell, Liechtenstein, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Bertalot, H. Diatomeen Im Süßwasser-Benthos von Mitteleuropa: Bestimmungsflora Kieselalgen Für Die Ökologische Praxis: Über 700 Der Häufigsten Arten Und Ihre Ökologie; 2. Korrigierte Aufl.; Koeltz Scientific Books: Königstein, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lecointe, C.; Coste, M.; Prygiel, J. “Omnidia”: Software for Taxonomy, Calculation of Diatom Indices and Inventories Management. Hydrobiologia 1993, 269, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, A.; Coste, M. Development of a Practical Diatom Index of Overall Water Quality Applicable to the French National Water Board Network. In Use of Algae for Monitoring Rivers II; Universität Innsbruck: Innsbruck, Austria, 1996; pp. 29–45. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, S. What Do Diatom Indices Indicate? Modeling the Specific Pollution Sensitivity Index. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 29449–29459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cemagref. Etude des Methodes Biologiques Quantitatives d’Appreciation de la Qualite des Eaux; Agence de l’eau Rhône Méditerranée Corse: Lyon, France, 1982; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- Coste, M.; Ayphassorho, H. Etude de La Qualité Des Eaux Du Bassin Artois-Picardie à l’aide Des Communautés de Diatomées Benthiques: Application Des Indices Diatomiques; CEMAGREF: Douai, France, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Descy, J.P. A New Approach to Water Quality Estimation Using Diatoms. Nova Hedwig. Beih. 1979, 64, 305–323. [Google Scholar]
- Sládeček, V. Diatoms as Indicators of Organic Pollution. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 1986, 14, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prygiel, J.; Coste, M. Progress in the Use of Diatoms for Monitoring Rivers in France. In Use of Algae for Monitoring Rivers III; Agence de l’eau Artois-Picardie: Douai, France, 1999; p. 165. [Google Scholar]
- Dell’uomo, A. Assessment of Water Quality of an Apennine River as a Pilot Study for Diatom-Based Monitoring of Italian Watercourses. In Use of Algae for Monitoring Rivers II; Universität Innsbruck: Innsbruck, Austria, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Descy, J.-P.; Coste, M. A Test of Methods for Assessing Water Quality Based on Diatoms. SIL Proc. 1922–2010 1991, 24, 2112–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Asai, K.; Houki, A. Numerical Estimation to Organic Pollution of Flowing Water by Using the Epilithic Diatom Assemblage Diatom Assemblage Index (DAIpo). Sci. Total Environ. 1986, 55, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.G.; Whitton, B.A. The Trophic Diatom Index: A New Index for Monitoring Eutrophication in Rivers. J. Appl. Phycol. 1995, 7, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, N.; Licursi, M. The Pampean Diatom Index (IDP) for Assessment of Rivers and Streams in Argentina. Aquat. Ecol. 2001, 35, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.C.; Kahlert, M.; Kelly, M.G. Interactions between pH and Nutrients on Benthic Algae in Streams and Consequences for Ecological Status Assessment and Species Richness Patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 444, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- ISO 5667-6:2014; Water Quality—Sampling—Part 6: Guidance on Sampling of Rivers and Streams. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. Available online: https://webstore.ansi.org/standards/iso/iso56672014?gad_source=1&gclid=Cj0KCQiAi_G5BhDXARIsAN5SX7q6TMQbVsE0FWH-lbyITsvwrNHbqQFKrmU4YgpV2zcEOG7InxMLy80aAqf1EALw_wcB (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- Bilotta, G.S.; Brazier, R.E. Understanding the Influence of Suspended Solids on Water Quality and Aquatic Biota. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2849–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Council of the European Communities. Council Directive 75/440/EEC of 16 June 1975 Concerning the Quality Required of Surface Water Intended for the Abstraction of Drinking Water in the Member States. Off. J. Eur. Communities 1975, 194, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, D.S. Turbidity as a Water Quality Standard for Salmonid Habitats in Alaska. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1987, 7, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratli, J.L. Classification of the Environmental Quality of Freshwater in Norway. In Water Quality Measurements Series; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 331–343. ISBN 978-0-470-51112-1. [Google Scholar]
- Musliu, M.; Bilalli, A.; Durmishi, B.; Isamili, M.; Ibrahimi, H. Water Quality Assessment of the Morava e Binçës River Based on the Physicochemical Parameters and Water Quality Index. J. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 19, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shala, A.; Sallaku, F.; Shala, A.; Ukaj, S. The Effects of Industrial and Agricultural Activity on the Water Quality of the Sitnica River (Kosovo). Geoadria 2014, 20, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galinha, C.F.; Sanches, S.; Crespo, J.G. Chapter 6—Membrane Bioreactors. In Fundamental Modelling of Membrane Systems; Luis, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 209–249. ISBN 978-0-12-813483-2. [Google Scholar]
- Shehu, I. Water and Sediment Quality Status of the Toplluha River in Kosovo. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngatia, L.; Taylor, R. Phosphorus Eutrophication and Mitigation Strategies. In Phosphorus—Recovery and Recycling; Zhang, T., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-1-83881-021-4. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Wu, X.; Hao, H.; He, Z. Mechanisms and Assessment of Water Eutrophication. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2008, 9, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badamasi, H.; Yaro, M.N.; Ibrahim, A.; Bashir, I.A. Impacts of Phosphates on Water Quality and Aquatic Life. Chem. Res. J. 2019, 4, 124–133. [Google Scholar]
- Heikal, G.; El Shahawy, A. Biosorption of Phosphorus, Total Suspended and Dissolved Solids by Dried Phragmites Australis: Isotherm, Kinetic and Interactive Response Surface Methodology (IRSM) in Oil and Soap-Derivatives Industrial Wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 137, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uusitalo, R.; Yli-Halla, M.; Turtola, E. Suspended Soil as a Source of Potentially Bioavailable Phosphorus in Surface Runoff Waters from Clay Soils. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2477–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, X.; Lv, X.; Xu, X.; Weng, Q.; Lei, K. Exploration of the Factors That Influence Total Phosphorus in Surface Water and an Evaluation of Surface Water Vulnerability Based on an Advanced Algorithm and Traditional Index Method. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinnawo, S.O. Eutrophication: Causes, Consequences, Physical, Chemical and Biological Techniques for Mitigation Strategies. Environ. Chall. 2023, 12, 100733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damseth, S.; Thakur, K.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, S.; Mahajan, D.; Kumari, H.; Sharma, D.; Sharma, A.K. Assessing the Impacts of River Bed Mining on Aquatic Ecosystems: A Critical Review of Effects on Water Quality and Biodiversity. HydroResearch 2024, 7, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, F.G.A.; Fernández-Sevilla, J.M.; Moya, B.L.; Grima, E.M. Chapter 6—Microalgae Production Systems. In Handbook of Microalgae-Based Processes and Products; Jacob-Lopes, E., Maroneze, M.M., Queiroz, M.I., Zepka, L.Q., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 127–163. ISBN 978-0-12-818536-0. [Google Scholar]
- Vigiak, O.; Grizzetti, B.; Udias-Moinelo, A.; Zanni, M.; Dorati, C.; Bouraoui, F.; Pistocchi, A. Predicting Biochemical Oxygen Demand in European Freshwater Bodies. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 1089–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, M.; Liu, S.; Li, K.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, T.; Tang, G. Modeling Spatial Patterns of Dissolved Oxygen and the Impact Mechanisms in a Cascade River. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 781646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloranta, P.; Soininen, J. Ecological Status of Some Finnish Rivers Evaluated Using Benthic Diatom Communities. J. Appl. Phycol. 2002, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Suo, L.; Liu, R.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, L.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Z. Influence of Temperature on Denitrification and Microbial Community Structure and Diversity: A Laboratory Study on Nitrate Removal from Groundwater. Water 2022, 14, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, E.W.; Kociolek, J.P.; Karthick, B. Four New Rhoicosphenia Species from Fossil Deposits in India and North America. Diatom Res. 2015, 30, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noga, T.; Stanek-Tarkowska, J.; Peszek, Ł.; Pajączek, A.; Kowalska, S. Use of Diatoms to Asses Water Quality of Anthropogenically Modified Matysówka Stream. J. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurteshi, K.; Vehapi, I.; Letaj, K.; Amiti, S.; Ismajli, M.; Haziri, A.; Salihu, D. Saprobiological Analysis of Llap Water (Kosovo). Ann. Ser. Hist. Nat. 2009, 19, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Kurteshi, K.; Vehapi, I.; Ismaili, M.; Vllasaku, I. Algological Investigation in River Nerodime During the Summer Season 2011. New Knowl. J. Sci. 2013, 2, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Kurteshi, K.; Vehapi, I.; Vllasaku, I. Determination of Pollution in River Drini Bardhë During the Summer Season 2010 Through the Algal Bioindicators. New Knowl. J. Sci. 2013, 2, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Ramshaj, Q.; Kurteshi, K.; Ramadani, I. Algological Analysis of River Krena (Gjakova, Kosovo) during Spring Season 2015. J. Mt. Agric. Balk. 2017, 20, 379–385. Available online: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.5555/20183199930 (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- Salca, A.; Kupe, L.; Miho, A. Data on Diatoms (Bacillariophyceae) and the Biological Quality of Rivers (Osumi, Devolli and Semani) in Berati Area (South-Central Albania). J. Nat. Tech. Sci. 2023, XXVIII, 69–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kupe, L.; Alikaj, M.; Bahiti, E.; Imeri, A.; Duka, I. The Development of Epiphytic Diatoms in the Vjosa River and Their Impact on Water Quality Based on the IPS Index. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Interdiscip. Sci. 2023, 6, 1186–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikaj, M.; Brahushi, F. Ecological Status Assessment Using Diatom Indices of Water Ecosystems in Gjirokastra District, Albania. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2019, 28, 899–904. [Google Scholar]
- Cvetkoska, A.; Pavlov, A.; Jovanovska, E.; Tofilovska, S.; Blanco, S.; Ector, L.; Wagner-Cremer, F.; Levkov, Z. Spatial Patterns of Diatom Diversity and Community Structure in Ancient Lake Ohrid. Hydrobiologia 2018, 819, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levkov, Z.; Krstic, S.; Nakov, T.; Melovski, L. Diatom Assemblages on Shara and Nidze Mountains, Macedonia. Nova Hedwig. 2005, 81, 501–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Reed, J.; Wagner, B.; Francke, A.; Levkov, Z. Lateglacial and Holocene Climate and Environmental Change in the Northeastern Mediterranean Region: Diatom Evidence from Lake Dojran (Republic of Macedonia/Greece). Quat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 103, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meron, E. Pattern Formation—A Missing Link in the Study of Ecosystem Response to Environmental Changes. Math. Biosci. 2016, 271, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meron, E. Pattern-Formation Approach to Modelling Spatially Extended Ecosystems. Ecol. Model. 2012, 234, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, A.M.; Lopes, L.F. Revisiting Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning through the Lens of Complex Adaptive Systems. Diversity 2023, 15, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Meng, F.; Xu, M. Exploration of Applicability of Diatom Indices to Evaluate Water Ecosystem Quality in Tangwang River in Northeast China. Water 2023, 15, 3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, G.J.; Couperthwaite, S.J.; Moodliar, C.D. Strategies for the Management and Treatment of Coal Seam Gas Associated Water. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 669–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammaa, Y.; Zhu, D.Z. Techniques for Controlling Total Suspended Solids in Stormwater Runoff. Can. Water Resour. J./Rev. Can. Ressour. Hydr. 2001, 26, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solak, C.N.; Peszek, Ł.; Yilmaz, E.; Ergül, H.A.; Kayal, M.; Ekmekçi, F.; Várbíró, G.; Yüce, A.M.; Canli, O.; Binici, M.S.; et al. Use of Diatoms in Monitoring the Sakarya River Basin, Turkey. Water 2020, 12, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslennikova, A.V.; Gulakov, V.O. Application of European Diatom Indices for Paleolimnological Reconstructions of Lake Tavatui (Middle Urals, Russia) Ecosystem Changes. Limnol. Freshw. Biol. 2022, 1492–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulíčková, A.; Duchoslav, M.; Dokulil, M. Littoral Diatom Assemblages as Bioindicators of Lake Trophic Status: A Case Study from Perialpine Lakes in Austria. Eur. J. Phycol. 2004, 39, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagowati, B.; Ahamad, K.U. A Review on Lake Eutrophication Dynamics and Recent Developments in Lake Modeling. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2019, 19, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Dodds, W.K. Nutrients, Eutrophication and Harmful Algal Blooms along the Freshwater to Marine Continuum. WIREs Water 2019, 6, e1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, E.; Su, Y.; Deng, S.; Kontopyrgou, M.; Zhang, D. Significant Influence of Phosphorus Resources on the Growth and Alkaline Phosphatase Activities of Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrego-Ramos, M.; Rimet, F.; Bécares, E.; Blanco, S. Environmental Drivers of Genetic Variability in Common Diatom Genera: Implications for Shallow Lake Biomonitoring. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).