Relationships in Diversity, Vegetation Indexes and Water Area in Terminal Lake of the Tarim River, Northwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
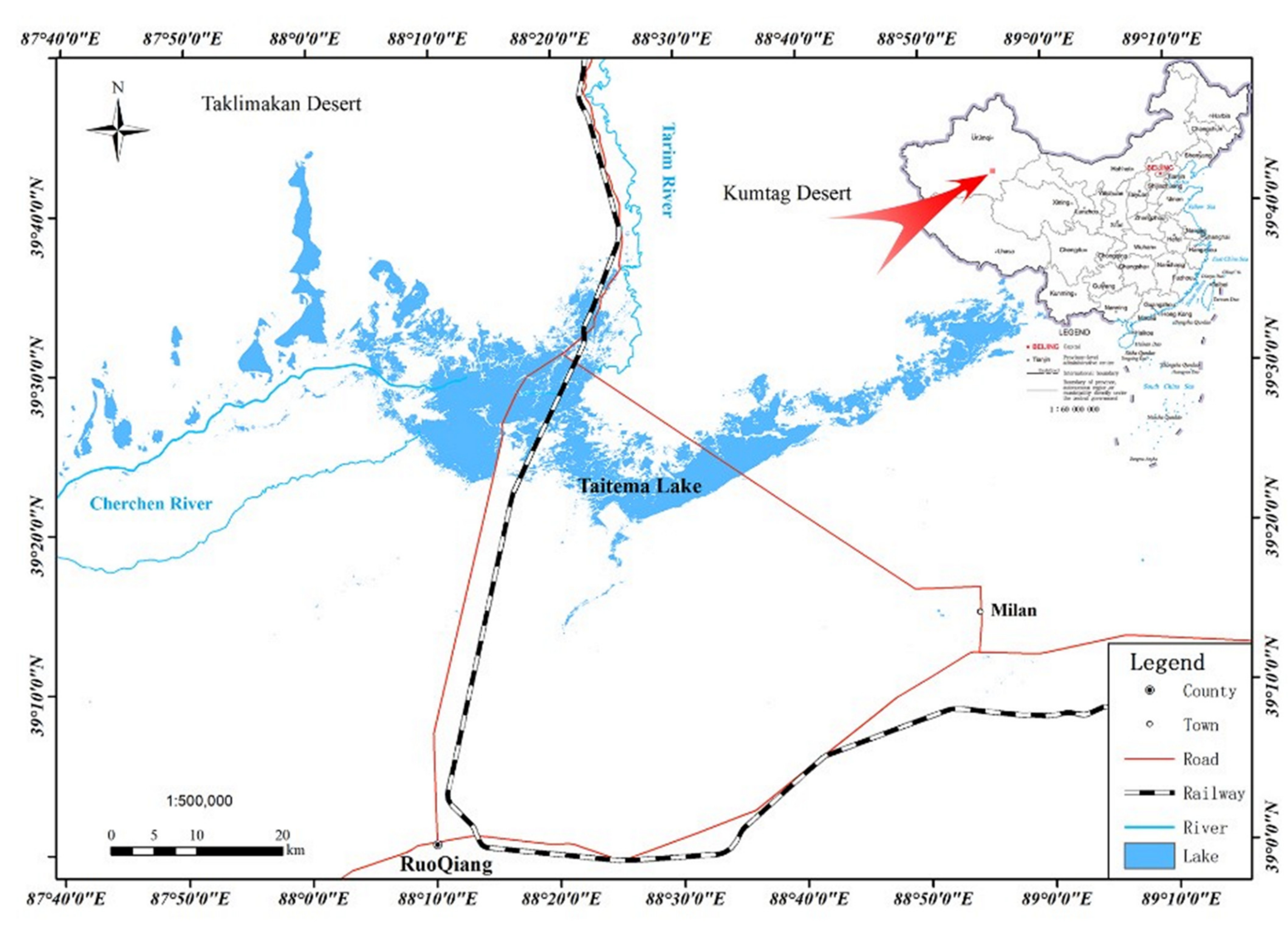
2.1. Overview of the Research Area
2.2. Sample Plot Distribution and Vegetation Investigation
2.2.1. Sample Plot Distribution
2.2.2. Vegetation Sampling
2.3. Measurement of Vegetation Area in Taitema Lake Zone
2.4. Interannual and Intra-Annual Data of Lake Area
2.4.1. Interannual Maximum Lake Area Date
2.4.2. Intra-Annual Measurement of Lake Area
2.4.3. Groundwater Level Date
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
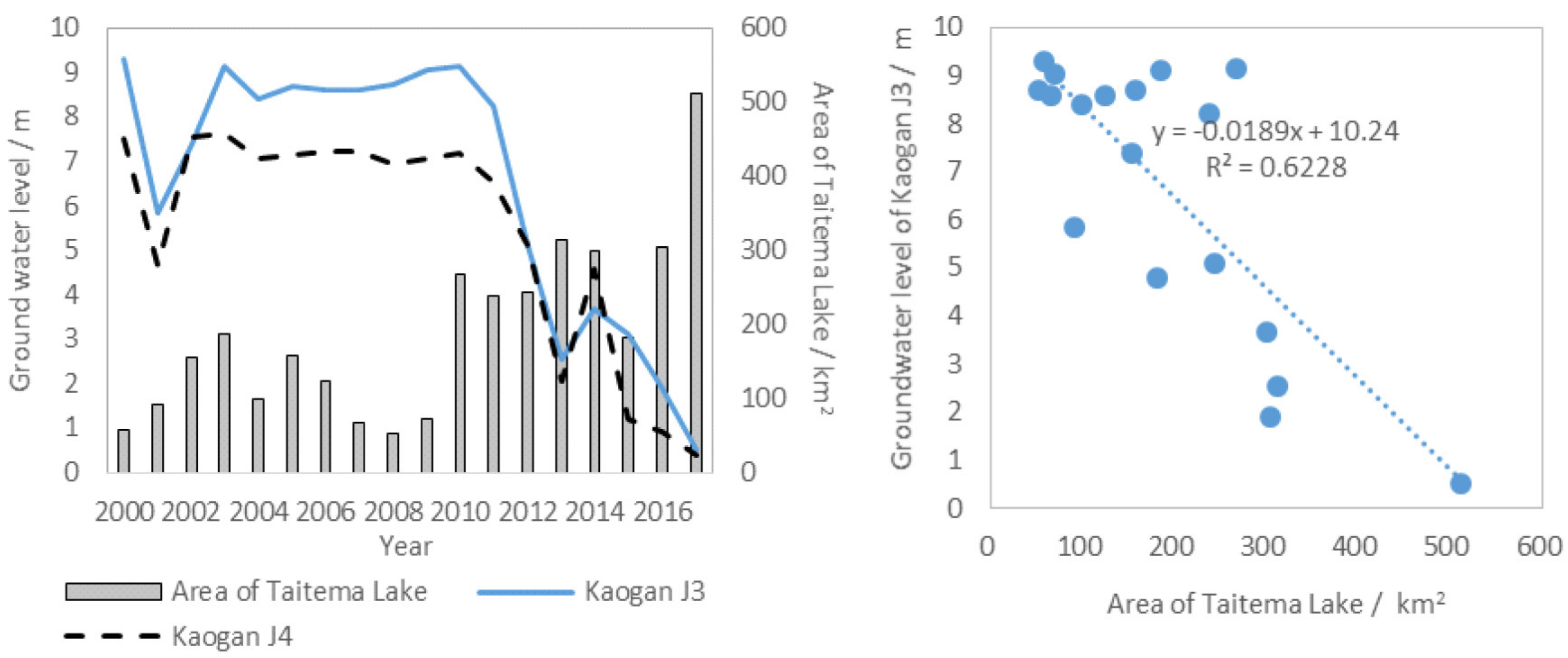
3.1. Lake Area and Water Volume Composed by Tarim River and Che’erchen River
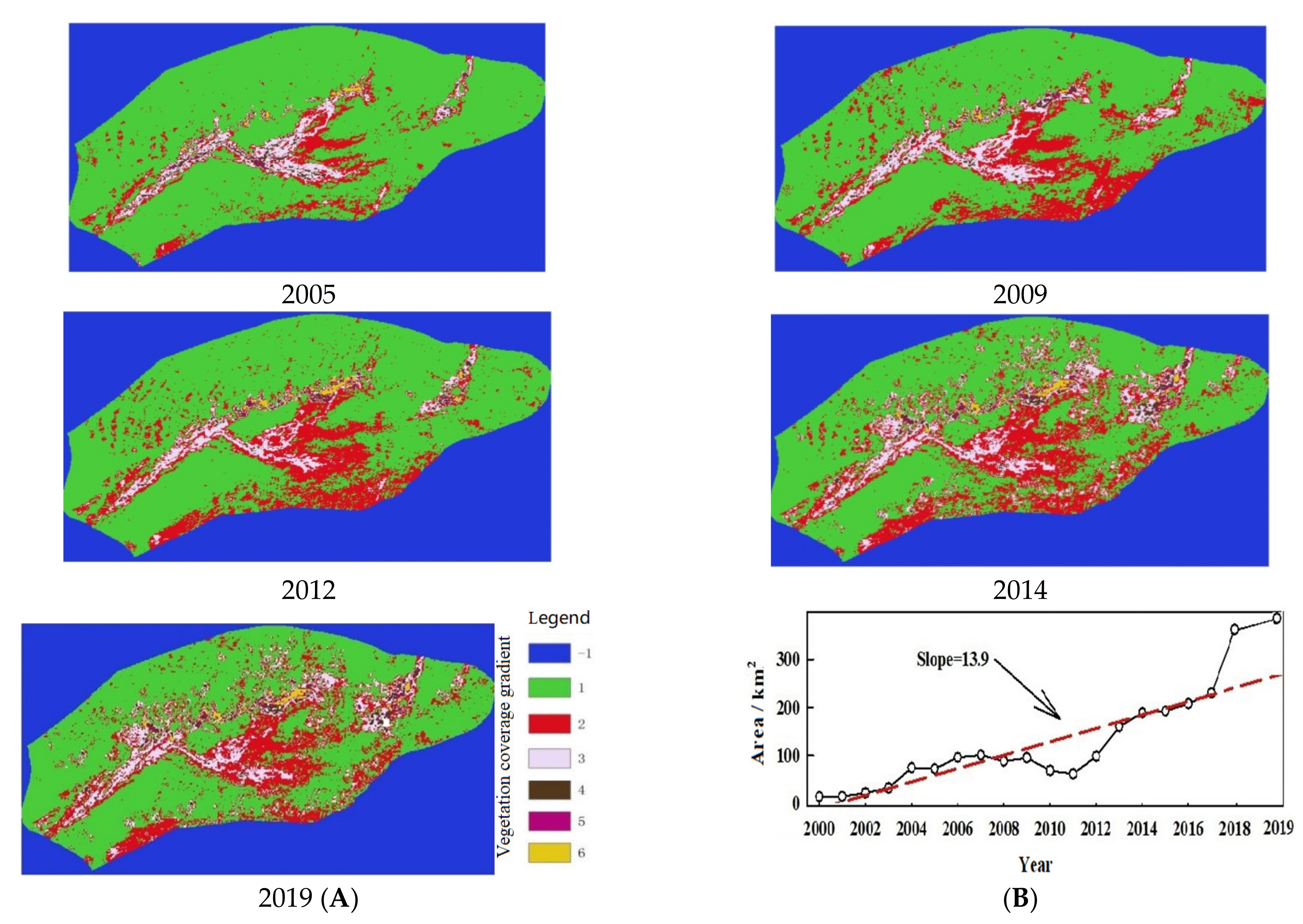
3.2. Variation in Vegetation Coverage
3.3. Response Characteristics of Groundwater Level in Lakeside Line
3.4. Intra-Annual Variation in Lake Area
4. Discussion
4.1. Change in Hydrological Elements
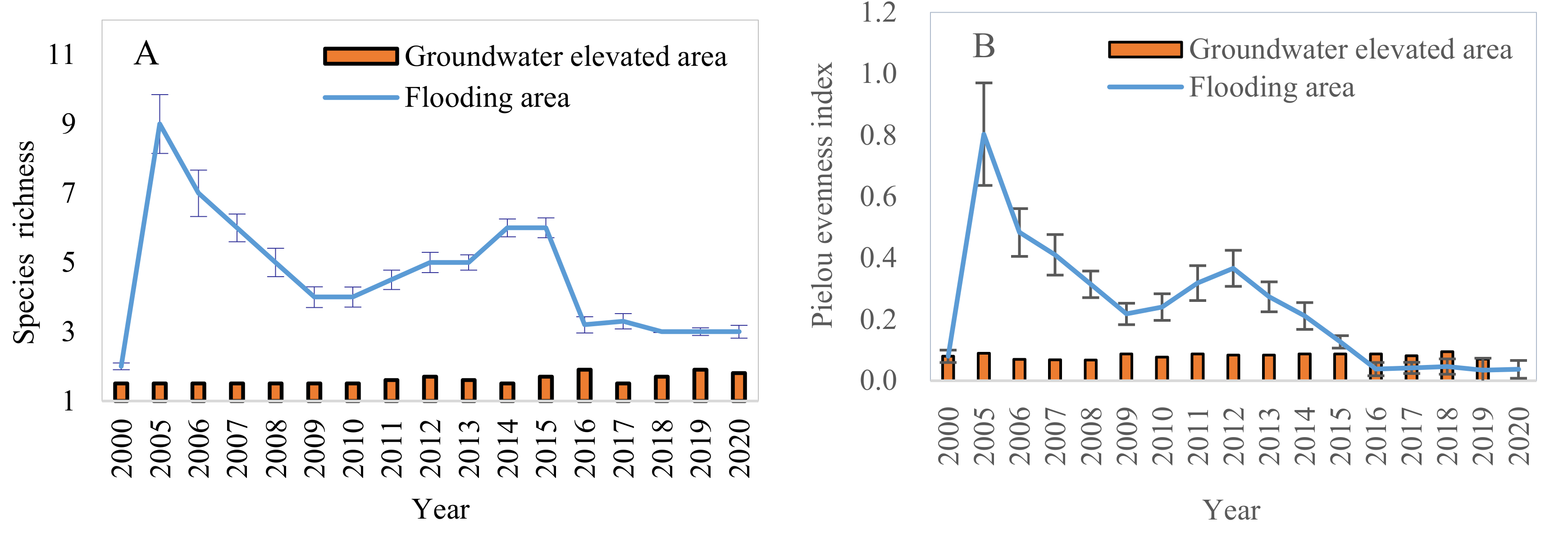
4.2. Response of Vegetation to the Enlarged Water Area
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turner, K.G.; Anderson, S.; Gonzales-Chang, M.; Costanza, R.; Wratten, S. A review of methods, data, and models to assess changes in the value of ecosystem services from land degradation and restoration. Ecol. Model. 2015, 319, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, R.J.; Boden, T.A.; Higdon, D.M. Gridded uncertainty in fossil fuel carbon dioxide emission maps, a CDIAC example. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 14979–14995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belmer, N.; Tippler, C.; Wright, I.A. Aquatic ecosystem degradation of high conservation value upland swamps, blue mountains australia. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestelmeyer, B.T.; Okin, G.S.; Duniway, M.C. Desertification, land use, and the transformation of global drylands. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 13, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Ye, M.; Xu, H.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhao, X.F. Effects of ecological water conveyance on the composition, diversity and stability of plant community in the lower reaches of Tarim River. Chin. J. Ecol. 2018, 37, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Deng, X.; Song, W.; Li, Z.; Chen, J. What is the main cause of grassland degradation? A case study of grassland ecosystem service in the middle-south Inner Mongolia. Catena 2017, 150, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Guo, Y.; Xu, H.; Ganjurjav, H.; Yue, L.; Wan, Y.; Qin, X.; Xin, M.; Liu, S. Climate change and its impacts on vegetation distribution and net primary productivity of the alpine ecosystem in the qinghai-tibetan plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 554–555, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, A.; Pfister, S.; Hellweg, S. Spatially Explicit Analysis of Biodiversity Loss Due to Global Agriculture, Pasture and Forest Land Use from a Producer and Consumer Perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3928–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.W.; Chun, X.; Liang, W.J.; Liu, J.Y. Review of lake evolution in arid and semi-arid area. Wetl. Sci. Manag. 2017, 13, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, D. Study on Ecological Reconstruction of Terminal Lakes of Arid Inland Rivers: A Comparison of Regional Practice; Lanzhou University: Lanzhou, China, 2016; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, C.S.; Cheng, X.H.; Ding, A.J. Study process of climate change, environment evolution and its driving mechanism in the last two centuries in the Alxa Desert. J. Desert Res. 2017, 37, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.L.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, X.F.; Lin, H.B. Effect of river-flooding on soil salinity in lower reaches of Tarim River. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mcdonald, T.; Jonson, J.; Dixon, K.W. National standards for the practice of ecological restoration in Australia. Restor. Ecol. 2016, 24, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S. Vegetation changes in recent large-scale ecological restoration projects and subsequent impact on water resources in china’s loess plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjaribe, C.; Frasier, C.L.; Rakouth, B.; Louis, E.E. Ecological restoration and reforestation of fragmented forests in Kianjavato, Madagascar. J. Ecol. 2013, 2013, 726275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancalion, P.H.S.; Cardozo, I.V.; Camatta, A.; Aronson, J.; Rodrigues, R.R. Cultural ecosystem services and popular perceptions of the benefits of an ecological restoration project in the Brazilian Atlantic forest. Restor. Ecol. 2014, 22, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudumijiti, A.B.L.K.M. The Temporal and Spatial Evolution of the Lake Pattern in the Lower Tarim River; Xinjiang Normal University: Xinjiang, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.F.; Guli, J.P.; Bao, A.M.; Meng, F.H.; Guo, H.; Luo, M.; Huang, X.R. Ecological effects evaluation for short term planning of the Tarim River. Arid Land Geogr. 2017, 40, 156–164. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, M.J.; Zhou, H.Y.; Xu, H.L. Research on the ecological operation in the lower reaches of Tarim River based on water conveyance. Sci. Sin. 2016, 46, 864–876. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.L.; Tursun, K.S.M. Exploration and analysis of ecological environment change of Taitema lake before and after ecological water transfer. Ecol. Sci. 2020, 39, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, T.C.; Wei, Y.; Ma, X.F. A study of the variation and driving factors of the water area of the terminal lake of inland river: A case study of Taitema Lake region. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2020, 32, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.L.; Xu, H.L.; Fu, J.Y.; Ailixier, K.E.B.; Abudumijiti, A.B.L.K.M. Study on protection of wet land of Taitema lake. Quat. Sci. 2013, 33, 594–602. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.L.; Ye, M.; Song, Y.D. The dynamic variation of water resources and its tendency in the Tarim river basin. J. Geogr. Sci. 2005, 15, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzaz, F.A. Plant species diversity in old-field successional ecosystems in southern Illinois. Ecology 1975, 56, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.L.; Ye, M.; Song, Y.D. Relationship between climate changes and annual runoff of headstreams of Tarim River. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2007, 27, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Ma, Z.Y.; Jin, X.; He, J.S. Biodiversity and ecosystem multi functionality: Advances and perspectives. Biodivers. Sci. 2016, 24, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.L.; Xu, H.L.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, X.F.; Abudu, M.J.T.; Fu, J.Y. The Qarqan River in Xinjiang and its water resources utilization. Arid Zone Res. 2014, 31, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Holben, B.N. Characterization of maximum value composites from temporal AVHRR data. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandridis, T.K.; Ovakoglou, G.; Clevers, J.G. Relationship between MODIS EVI and LAI across time and space. Geocarto Int. 2020, 35, 1385–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomoaki, M.; Charlotte, Z.S.; Hiroki, Y. Validation and analysis of Terra and Aqua MODIS, and SNPP VIIRS vegetation indices under zero vegetation conditions: A case study using Railroad Valley Playa. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 257, 112344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedighifar, Z.; Motlagh, M.G.; Halimi, M. Investigating spatiotemporal relationship between EVI of the MODIS and climate variables in northern Iran. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xue, L.Q.; Wei, G.H. Assessing Vegetation Dynamics and Landscape Ecological Risk on the Mainstream of Tarim River, China. Water 2020, 12, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.L. Analysis of the relationship between the lake surface area of Taitema Lake and the main recharge water source. Water Conserv. Sci. Technol. Econ. 2016, 22, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.N.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhu, X.M. Analysis of the effect of ecological water in the lower reaches of Tarim River in Xinjiang. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2004, 34, 475–482. [Google Scholar]



| Plot | Size of Plot | Longitude | Latitude | Altitude (m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| overflow area | Plot 1 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°32′42.0″ | N37°34′7.9″ | 798.2 |
| Plot 2 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°22′23.9″ | N39°32′16.5″ | 793.4 | |
| Plot 3 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°21′22.8″ | N39°31′30.3″ | 793.3 | |
| Plot 4 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°17′03.0″ | N39°28′55.8″ | 796 | |
| Plot 5 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°15′43.4″ | N39°26′33.6″ | 799.5 | |
| Plot 6 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°11′53.5″ | N39°14′6.3″ | 801 | |
| Plot 7 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°23′23.7″ | N39°29′40.2″ | 802 | |
| Plot 8 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°22′51.5″ | N39°29′56.7″ | 791 | |
| Plot 9 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°22′23.1″ | N39°30′17″ | 786 | |
| Plot 10 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°22′15.9″ | N39°30′14.7″ | 794 | |
| Plot 11 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°22′06.8″ | N39°30′19.7″ | 794 | |
| Plot 12 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°21′56.3″ | N39°30′15.9″ | 794 | |
| Plot 13 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°23′41.3″ | N39°29′41.1″ | 791 | |
| Plot 14 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°23′53.5″ | N39°29′34.7″ | 794 | |
| Plot 15 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°24′12.7″ | N39°29′24.6″ | 795 | |
| Plot 16 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°21′30.2″ | N39°30′15.8″ | 806.4 | |
| Plot 17 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°20′45.5″ | N39°30′9.6″ | 806.5 | |
| Plot 18 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°21′46.0″ | N39°30′14.4″ | 807.5 | |
| Plot 19 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°16′28.1″ | N39°26′37.7″ | 795.3 | |
| Plot 20 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°16′13.5″ | N39°26′36.3″ | 798.5 | |
| Plot 21 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°21′23.0″ | N39°31′18.6″ | 808.9 | |
| non-overflow area | Plot 1 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°20′41.0″ | N39°30′59.0″ | 807.5 |
| Plot 2 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°20′45.9″ | N39°30′54.0″ | 807.9 | |
| Plot 3 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°20′56.3″ | N39°30′51.4″ | 807.8 | |
| Plot 4 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°21′56.8″ | N39°30′12.2″ | 807.7 | |
| Plot 5 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°23′28.6″ | N39°29′41.2″ | 808 | |
| Plot 6 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°23′43.4″ | N39°29′50.6″ | 807.9 | |
| Plot 7 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°23′39.8″ | N39°30′7.9″ | 807.5 | |
| Plot 8 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°23′25.8″ | N39°29′40.9″ | 807.9 | |
| Plot 9 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°23′15.7″ | N39°29′24.3″ | 806.5 | |
| Plot 10 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°23′27.6″ | N39°29′26.5″ | 807.1 | |
| Plot 11 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°25′20.6″ | N39°36′23.8″ | 812.7 | |
| Plot 12 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°25′20.6″ | N39°36′24.1″ | 811.8 | |
| Plot 13 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°9′22.7″ | N39°26′36.9″ | 810.6 | |
| Plot 14 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°11′13.9″ | N39°17′20.4″ | 812.1 | |
| Plot 15 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°12′25.9″ | N39°16′50.5″ | 810.8 | |
| Plot 16 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°12′10.4″ | N39°15′45.3″ | 812.1 | |
| Plot 17 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°14′8.1″ | N39°18′46.0″ | 810.4 | |
| Plot 18 | 50 × 50 m2 | E88°15′22.3″ | N39°19′28.2″ | 809.5 |
| Species | 20 | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 00 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | ||
| 1 | Tamarix sp. | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| 2 | Halostachys caspica | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| 3 | Halocnemum strobilaceum | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 4 | Phragmites australis | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| 5 | Karelinia caspia | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| 6 | Lycium ruthenicum | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||||||
| 7 | Alhagi sparsifolia | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||||
| 8 | Hexinia polydichotoma | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||||||
| 9 | Glycyrrhiza inflata | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||
| 10 | Halogeton glomeratus | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||
| 11 | Poacynum hendersonii | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||
| 12 | Salsola pellucida | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||
| 13 | Salicornia europaea | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||||
| 14 | Scirpus strobilinus | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||||||
| 15 | Cynodon dactylon | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| 16 | Crypsis schoenoides | √ | √ | |||||||||||||||
| 17 | Inula salsoloides | √ | ||||||||||||||||
| 18 | Kalidium foliatum | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||||||
| 19 | Aeluropus pungens | √ | ||||||||||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Lin, T.; Xu, H.; Aili, A.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Y. Relationships in Diversity, Vegetation Indexes and Water Area in Terminal Lake of the Tarim River, Northwest China. Ecologies 2021, 2, 332-344. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies2040019
Zhao X, Lin T, Xu H, Aili A, Zhao W, Yang Y. Relationships in Diversity, Vegetation Indexes and Water Area in Terminal Lake of the Tarim River, Northwest China. Ecologies. 2021; 2(4):332-344. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies2040019
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xinfeng, Tao Lin, Hailiang Xu, Aishajiang Aili, Wanyu Zhao, and Yongqiang Yang. 2021. "Relationships in Diversity, Vegetation Indexes and Water Area in Terminal Lake of the Tarim River, Northwest China" Ecologies 2, no. 4: 332-344. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies2040019
APA StyleZhao, X., Lin, T., Xu, H., Aili, A., Zhao, W., & Yang, Y. (2021). Relationships in Diversity, Vegetation Indexes and Water Area in Terminal Lake of the Tarim River, Northwest China. Ecologies, 2(4), 332-344. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies2040019






