Nanomarker for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease Combining Ab initio DFT Simulations and Molecular Docking Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Ligand Modeling and Preparation
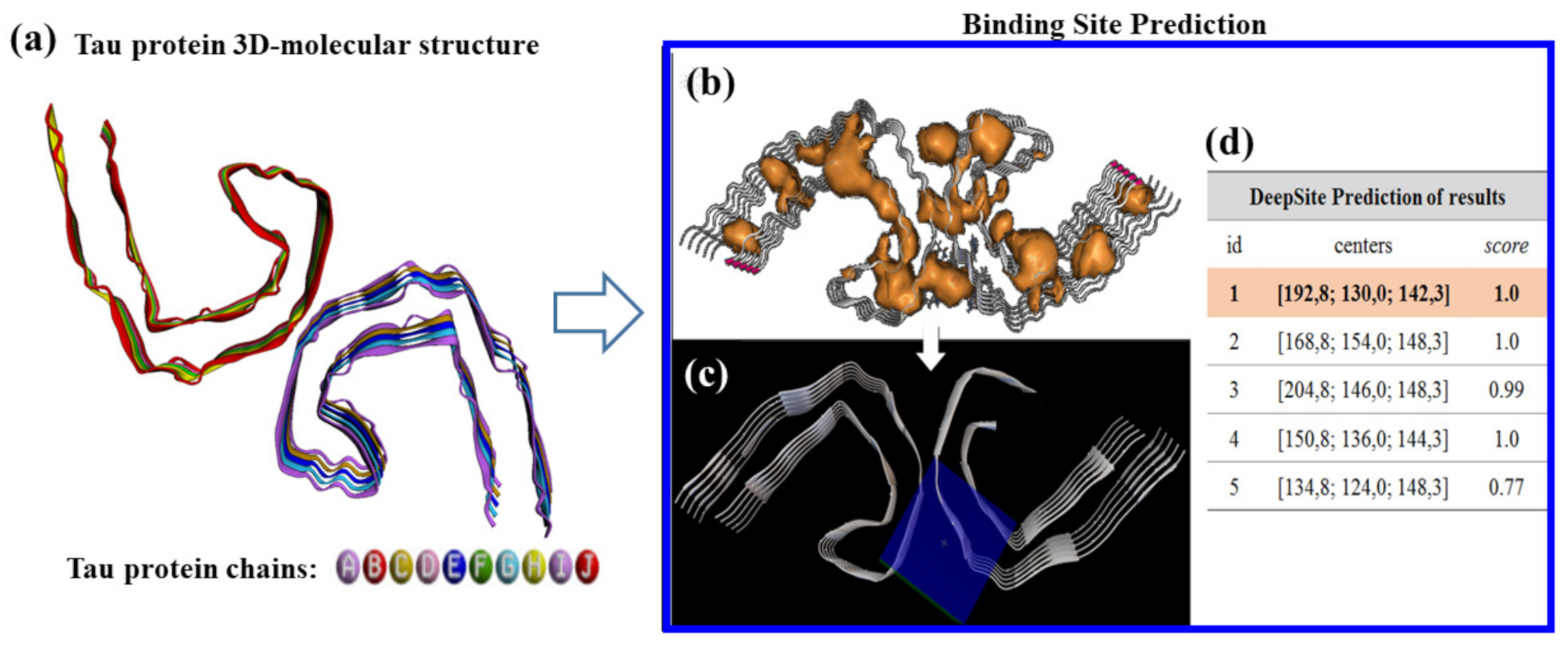
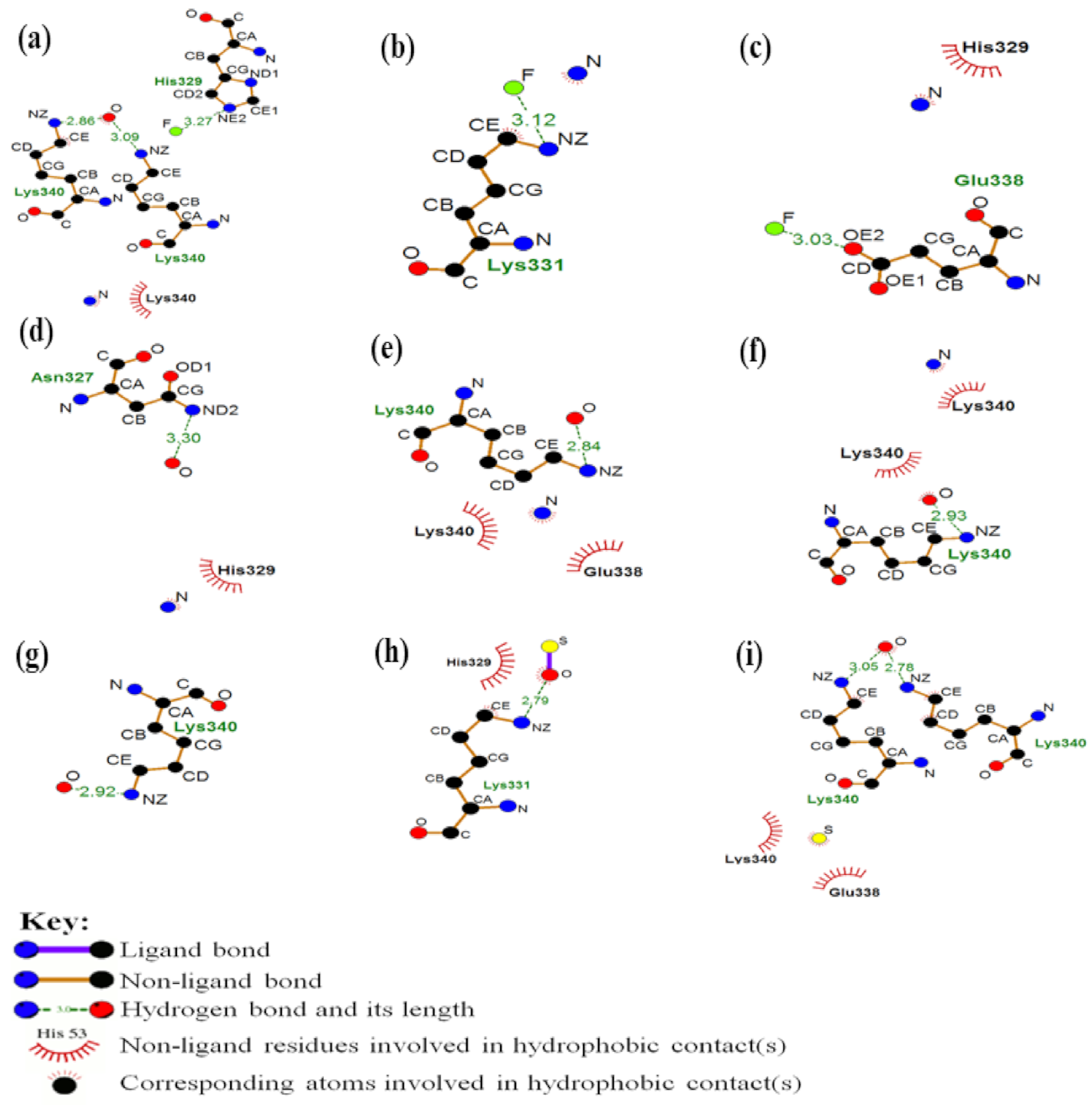
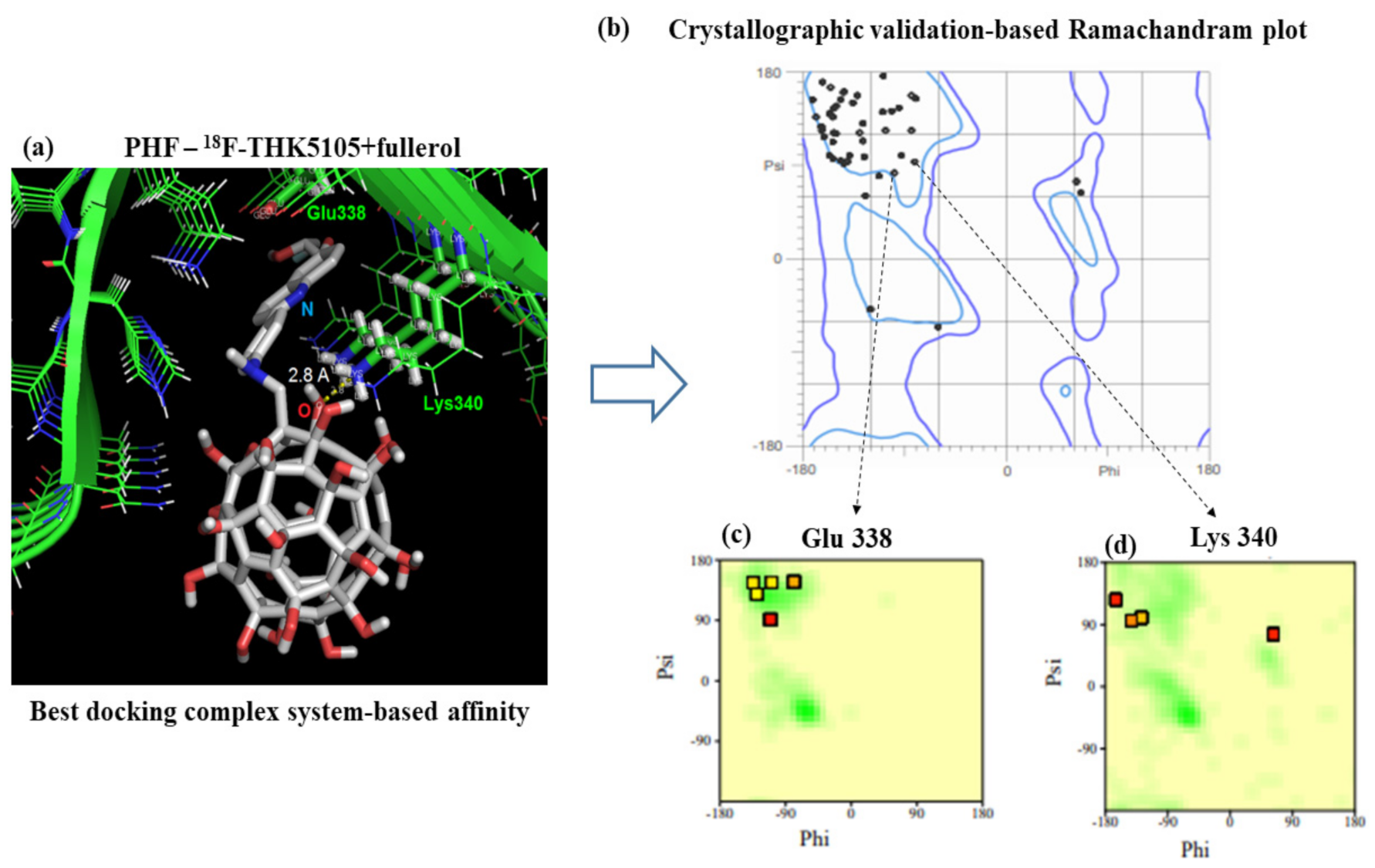
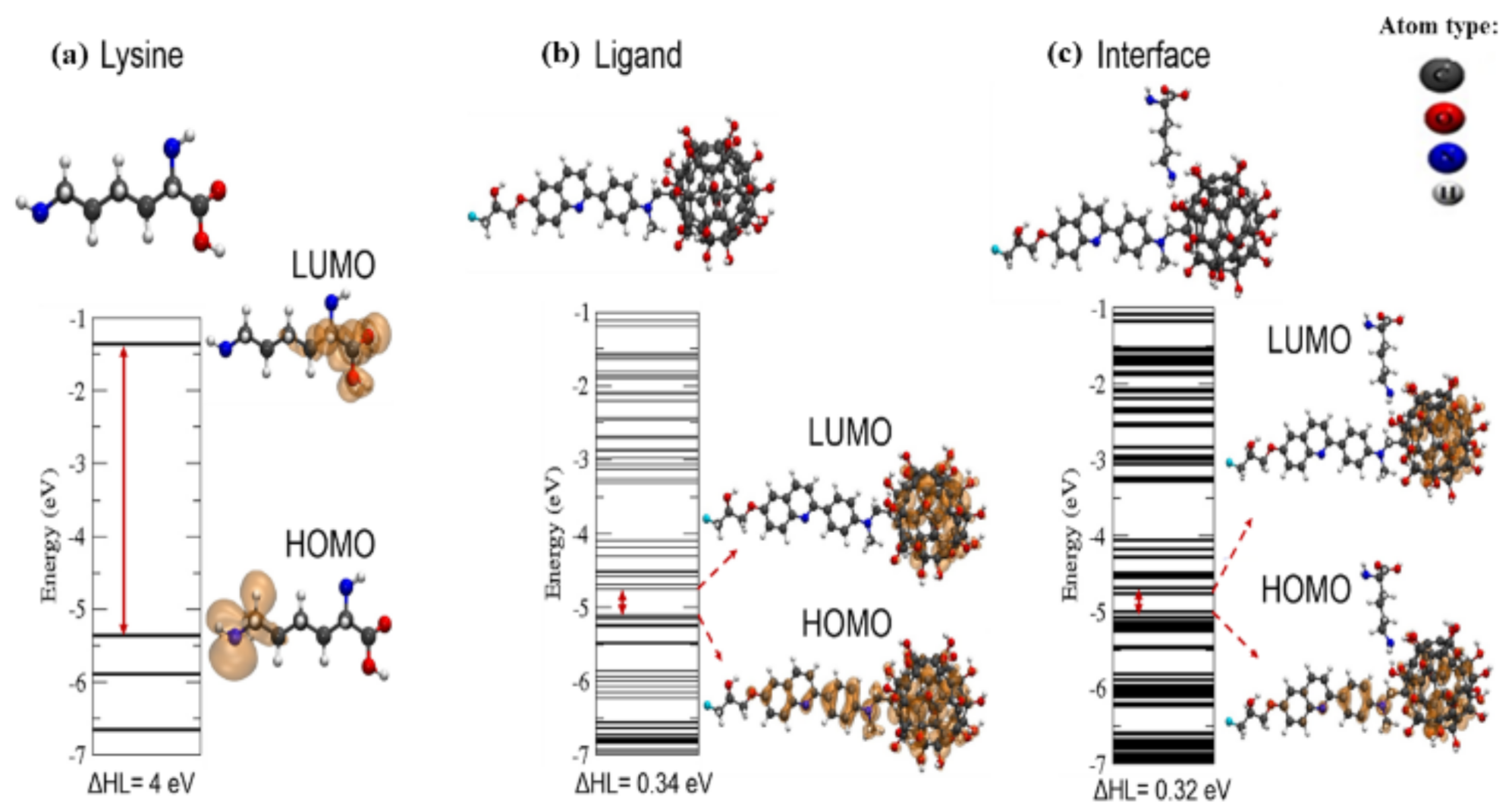
3.2. Modeling PHF-Tau Protein and Ligand Interactions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Afsahi, S.; Lerner, M.B.; Goldstein, J.M.; Lee, J.; Tang, X.; Bagarozzi, D.A., Jr.; Pan, D.; Locascio, L.; Walker, A.; Barron, F.; et al. Novel graphene-based biosensor for early detection of Zika virus infection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakry, R.; Vallant, R.M.; Najam-ul-Haq, M.; Rainer, M.; Szabo, Z.; Huck, C.W.; Bonn, G.K. Medicinal applications of fullerenes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 639–649. [Google Scholar]
- Benadiba, M.; Luurtsema, G.; Wichert-Ana, L.; Buchpigel, C.A. Novos alvos moleculares para tomografia por emissão de pósitrons (PET) e tomografia computadorizada por emissão de fóton único (SPECT) em doenças neurodegenerativas. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2012, 34, s125–s148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, P.; Leifer, M.D. Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Clinical and Economic Benefits. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2003, 51, 281–288. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunden, K.R.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M.Y. Advances in tau-focused drug discovery for Alzheimer’s disease and related tauopathies. Nat. Rev. 2009, 8, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceperley, D.M.; Alder, B.J. Ground state of the electron gas by a stochastic method. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1980, 45, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, D.T.; Szardenings, A.K.; Bahri, S.; Walsh, J.C.; Mu, F.; Xia, C.; Shankle, W.R.; Lerner, A.J.; Su, M.Y.; Elizarov, A.; et al. Early Clinical PET Imaging Results with the Novel PHF-Tau Radioligand [F18]-T808. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014, 38, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullum, B.M.; Vo-Dinh, T. The development of optical nanosensors for biological measurements. Trends Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Róz, A.L. Grandes Áreas da Nanociência, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2015; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Dugan, L.L.; Gabrielsen, J.K.; Shan, P.Y.; Lin, T.S.; Choi, D.W. Buckminsterfullerenol free radical scavengers reduce excitotoxic and apoptotic death of cultured cortical neurons. Neurobiol. Dis. 1996, 3, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Durruthy, M.; Werhli, A.V.; Seus, V.; Machado, K.S.; Pazos, A.; Munteanu, C.R.; González-Díaz, H.; Monserrat, J.M. Decrypting Strong and Weak Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Interactions with Mitochondrial Voltage-Dependent Anion Channels Using Molecular Docking and Perturbation Theory. Nat. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkekoglu, P.; Giray, B.K.; Basaran, N. 3R Principle and Alternative Toxicity Testing Methods. Fabad J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 36, 101–117. [Google Scholar]
- Gasser, A.L.; Salamin, V.; Zumbach, S. Late life depression or prodromal Alzheimer’s disease: Which tools for the differential diagnosis? Encephale 2017, 44, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, C.R.W. As múltiplas Contribuições para a Complexação Proteína-Ligante: Consequências em Drug Design. Rev. Virtual Química 2012, 4, 348–364. [Google Scholar]
- Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, B864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD—Visual Molecular Dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Albert, M.S.; Knopman, D.S.; McKhann, G.M.; Sperling, R.A.; Carrillo, M.C.; Thies, B.; Phelps, C.H. Introduction to the recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, J.; Doerr, S.; Martínez-Rosell, G.; Rose, A.S.; De Fabritiis, G. DeepSite: Protein-binding site predictor using 3D-convulation neural networks. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3036–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple ligand-protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, L.C. Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Rev. 2015, 1, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, A.; Yoneda, M. Dementia due to Endocrine Diseases. Brain Nerve 2016, 68, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Passini, E.; Britton, O.J.; Lu, H.R.; Rohrbacher, J.; Hermans, A.N.; Gallacher, D.J.; Greig, R.J.; Bueno-Orovio, A.; Rodriguez, B. Human In Silico Drug Trials Demonstrate Higher Accuracy than Animal Models in Predicting Clinical Pro-Arrhythmic Cardiotoxicity. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, M.; Bryce, R.; Ferri, C. World Alzheimer Report 2011: The Benefits of Early Diagnosis and Intervention; Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2011; Available online: https://www.alz.co.uk/research/WorldAlzheimerReport2011.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2017).
- Prince, M.; Bryce, R.; Ferri, C. The Global Impact of Dementia: An Analysis of Prevalence, Incidence, Cost and Trends; Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2015; Available online: http://www.worldalzreport2015.org/downloads/world-alzheimer-report-2015.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2017).
- Prince, M.; Comas-Herrera, A.; Knapp, M.; Guerchet, M.; Karagiannidou, M. Improving Healthcare for People Living with Dementia: Coverage, Quality and Costs Now and In the Future; Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2016; Available online: https://www.alz.co.uk/research/WorldAlzheimerReport2016.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2017).
- Santos, L.J.D.; Rocha, G.P.; Alves, R.B.; Freitas, R.P.D. Fulereno [C60]: Química e aplicações. Química Nova 2010, 33, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2016, 388, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloane, P.D.; Zimmerman, S.; Suchindran, C.; Reed, P.; Wang, L.; Boustani, M.; Sudha, S. The public health impact of Alzheimer’s disease, 2000-2050: Potential implication of treatment advances. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2002, 23, 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, J.M.; Artacho, E.; Gale, J.D.; García, A.; Junquera, J.; Ordejón, P.; Sánchez-Portal, D. The SIESTA method for ab initio order-N materials simulation. Chem. Rev. 2002, 14, 2745–2779. [Google Scholar]
- Touhami, A. Biosensors and Nanobiosensors: Design and Applications. Nanomedicine 2015, 15, 374–400. [Google Scholar]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. Autodock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. J. Comp. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilela Neto, O.P.; Pacheco, M.A.C. Nanotecnologia Computacional Inteligente: Concebendo a Engenharia em Nanotecnologia, 1st ed.; Interciência: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Villemagne, V.L.; Fodero-Tavoletti, M.T.; Masters, C.L.; Rowe, C.C. Tau imaging: Early progress and future directions. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bryant, S.H.; Cheng, T.; Wang, J.; Gindulyte, A.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; He, S.; Zhang, J. Pubchem BioAssay: 2017 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Q. Aptamer-functionalized carbon nanomaterials electrochemical sensors for detecting cancer relevant biomolecules. Carbon 2018, 129, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
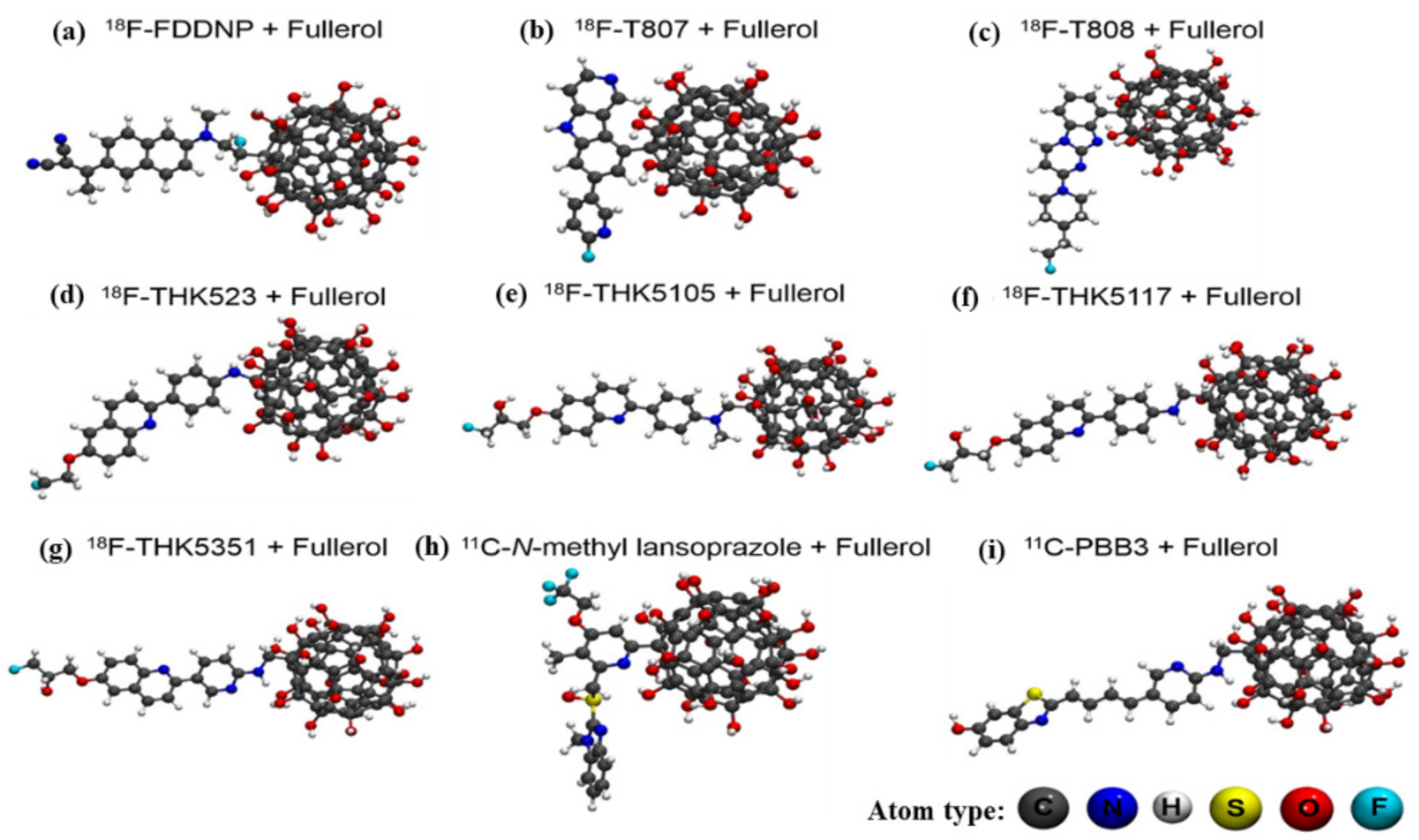
| Docking System ID | Docking Systems | Affinity (kcal/mol) | RMSD (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PHF—18F-FDDNP + fullerol | −5.9 | 1.356 |
| 2 | PHF—18F-T807 + fullerol | −6.0 | 1.617 |
| 3 | PHF—18F-T808 + fullerol | −5.7 | 1.344 |
| 4 | PHF—18F-THK523 + fullerol | −5.6 | 1.598 |
| 5 * | PHF—18F-THK5105 + fullerol | −7.0 | 1.491 |
| 6 | PHF—18F-THK5117 + fullerol | −6.8 | 1.628 |
| 7 | PHF—18F-THK5351 + fullerol | −6.6 | 1.360 |
| 8 | PHF—11C-N-methyl lansoprazole + fullerol | −6.6 | 1.394 |
| 9 | PHF—11C-PBB3 + fullerol | −6.3 | 1.050 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Initial distance | 2.83Å |
| Final distance | 2.80 Å |
| Binding energy | −0.9 eV |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira Schopf, P.; Zanella, I.; D. S. Cordeiro, M.N.; Ruso, J.M.; González-Durruthy, M.; Ortiz Martins, M. Nanomarker for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease Combining Ab initio DFT Simulations and Molecular Docking Approach. Biophysica 2021, 1, 76-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica1020007
Ferreira Schopf P, Zanella I, D. S. Cordeiro MN, Ruso JM, González-Durruthy M, Ortiz Martins M. Nanomarker for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease Combining Ab initio DFT Simulations and Molecular Docking Approach. Biophysica. 2021; 1(2):76-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica1020007
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira Schopf, Patricia, Ivana Zanella, M. Natália D. S. Cordeiro, Juan M. Ruso, Michael González-Durruthy, and Mirkos Ortiz Martins. 2021. "Nanomarker for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease Combining Ab initio DFT Simulations and Molecular Docking Approach" Biophysica 1, no. 2: 76-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica1020007
APA StyleFerreira Schopf, P., Zanella, I., D. S. Cordeiro, M. N., Ruso, J. M., González-Durruthy, M., & Ortiz Martins, M. (2021). Nanomarker for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease Combining Ab initio DFT Simulations and Molecular Docking Approach. Biophysica, 1(2), 76-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica1020007







