Experimental Records from Blast Tests of Ten Reinforced Concrete Slabs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Concrete
2.2. Reinforcement
2.3. Field Measurements and Pre-Test Verification
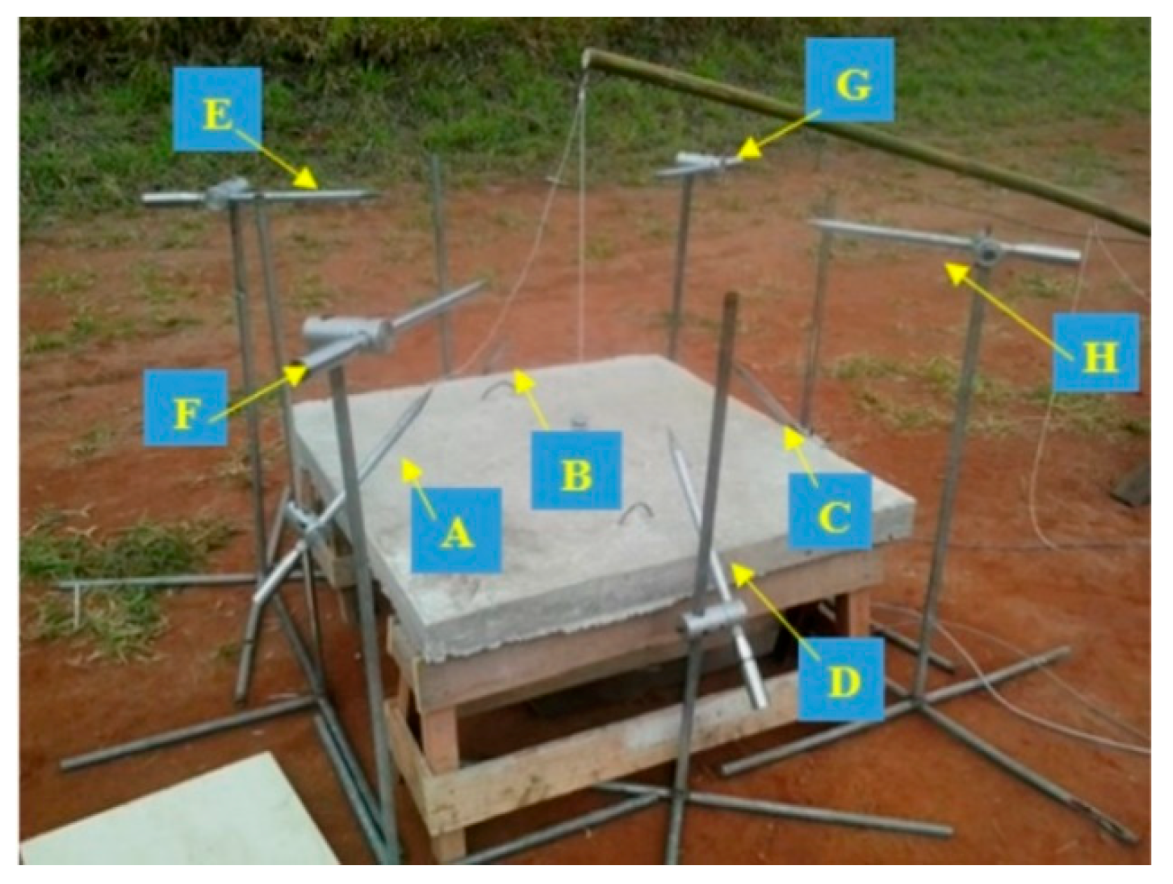
2.3.1. Accelerometers
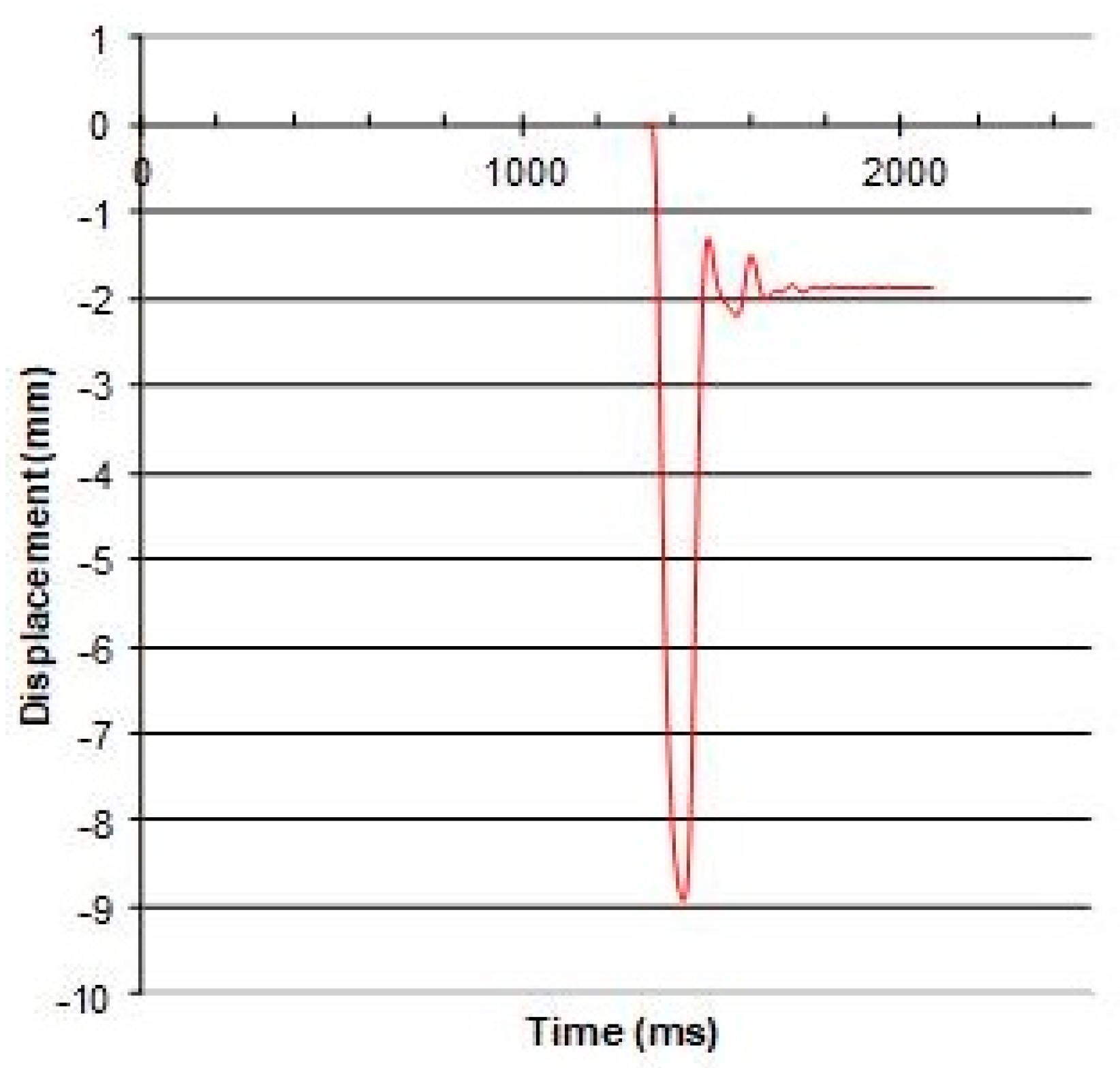
2.3.2. Displacement Meters
2.3.3. Strain Gages
2.3.4. Pressure Sensors
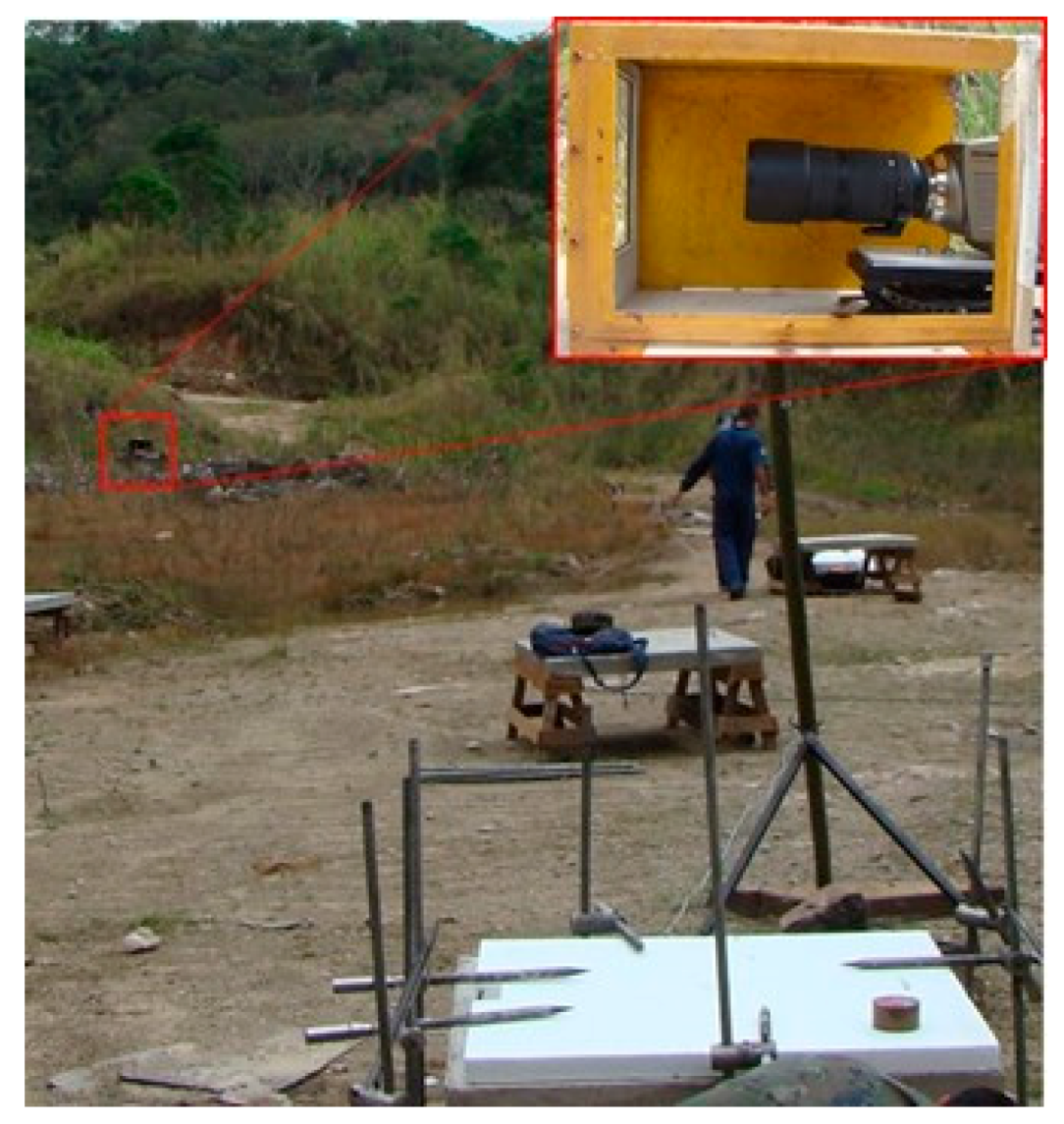
2.3.5. Imaging
2.3.6. Verification of Measurement Sensors
2.4. Finite Element Analysis
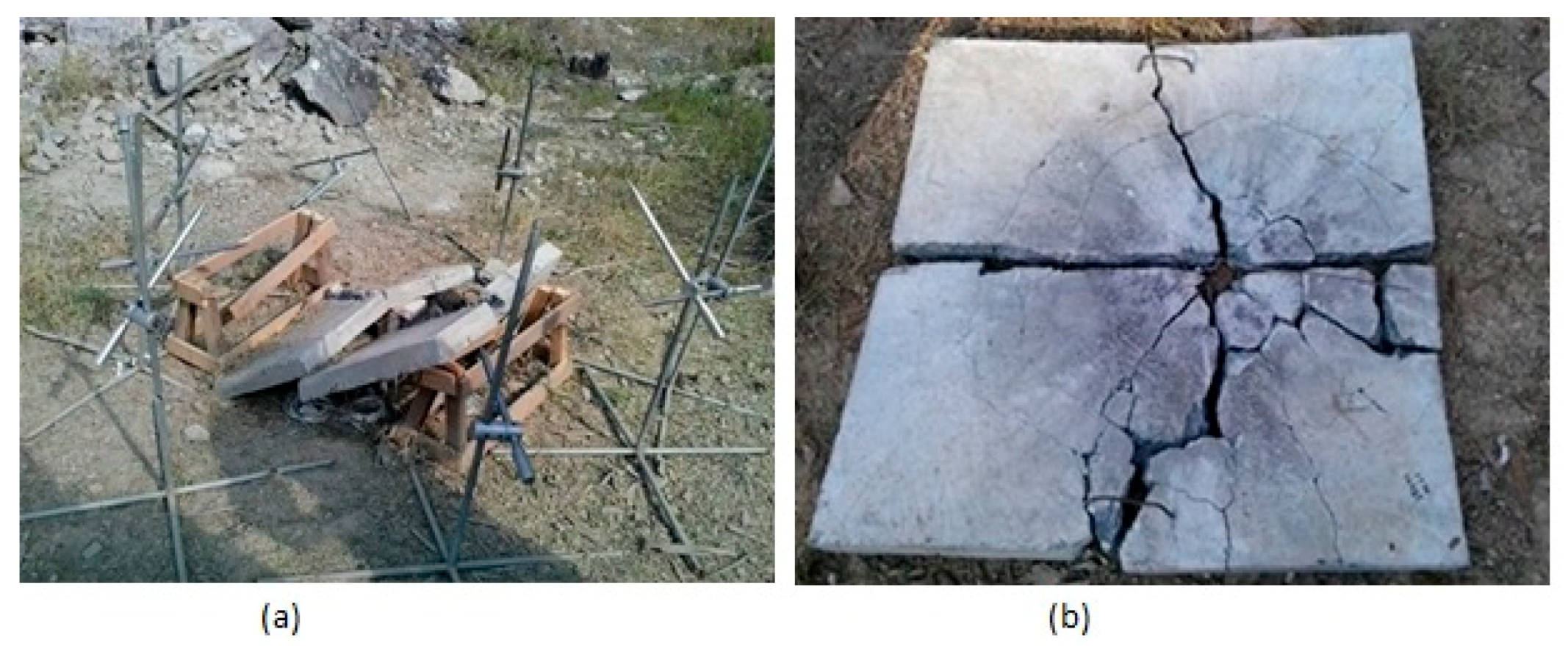
3. Experimental Results
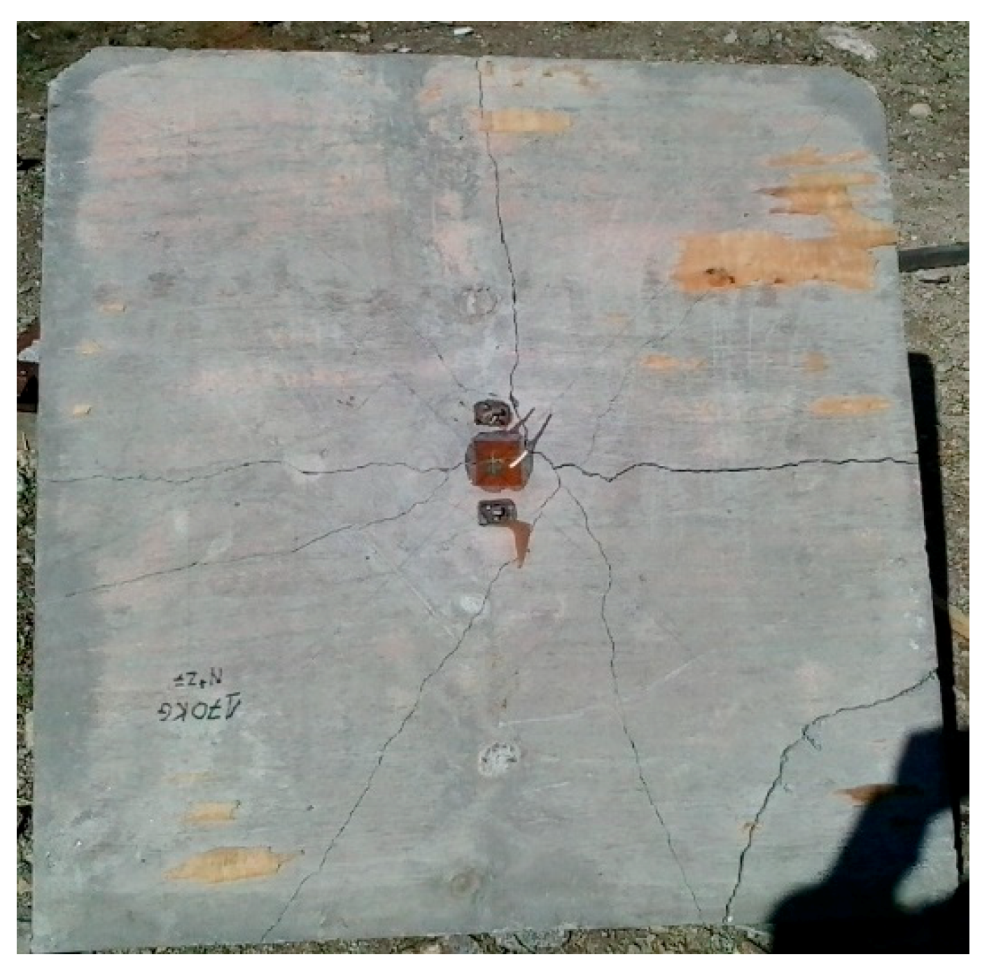
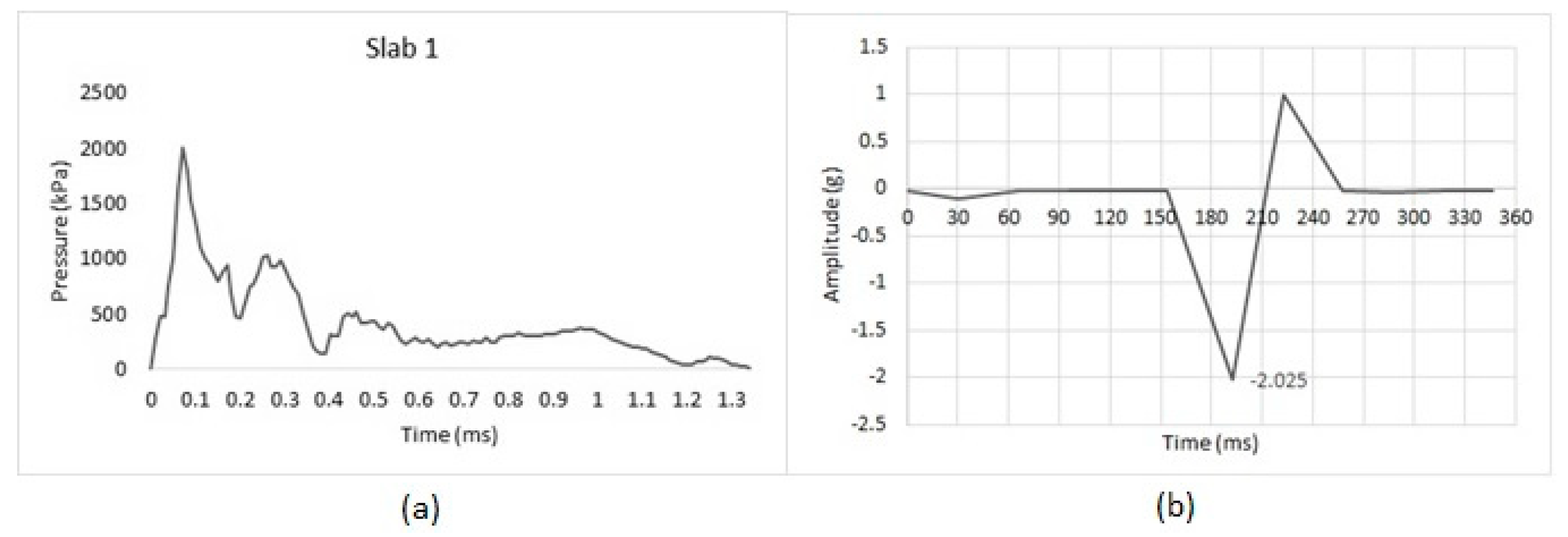
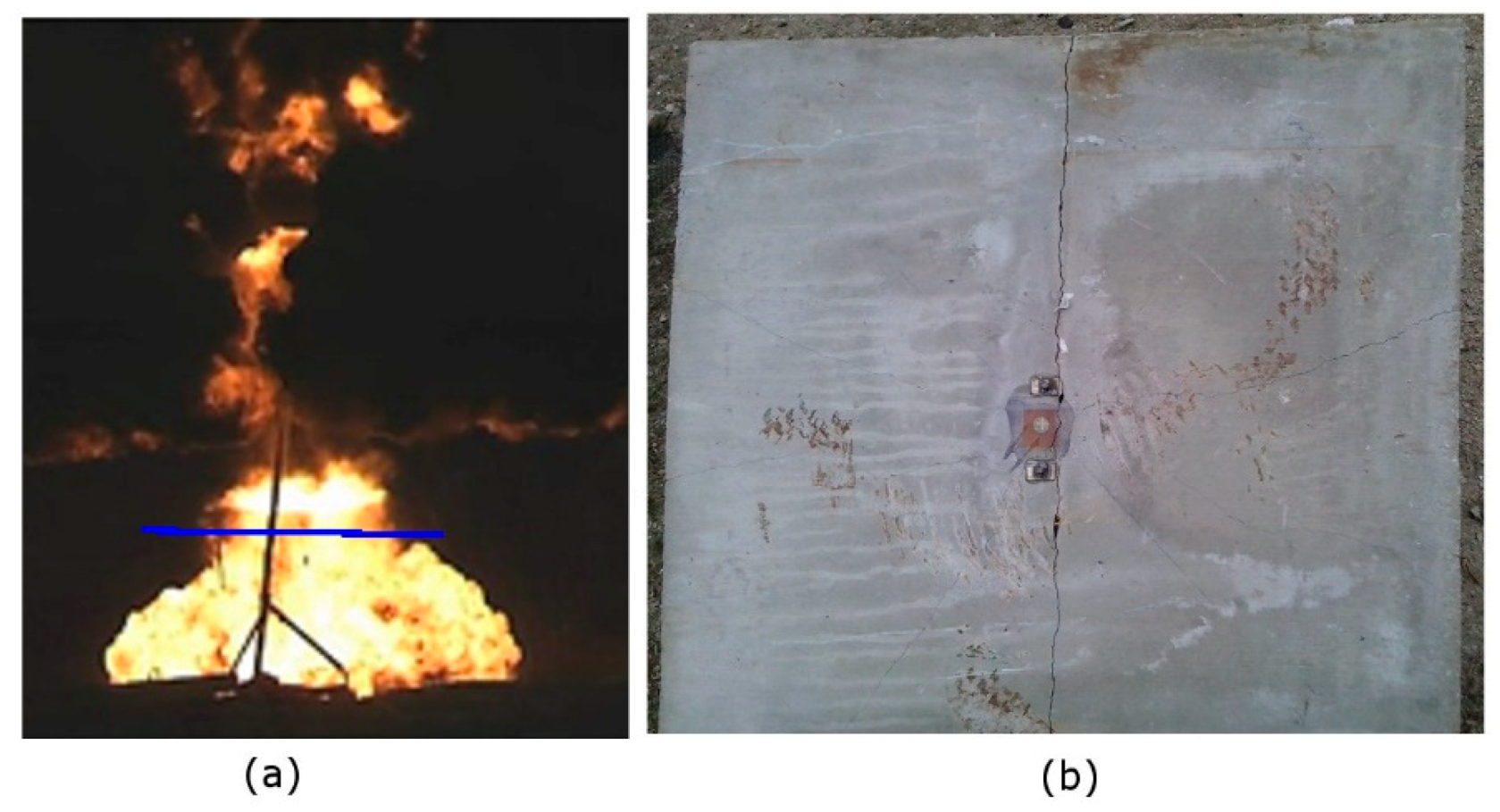
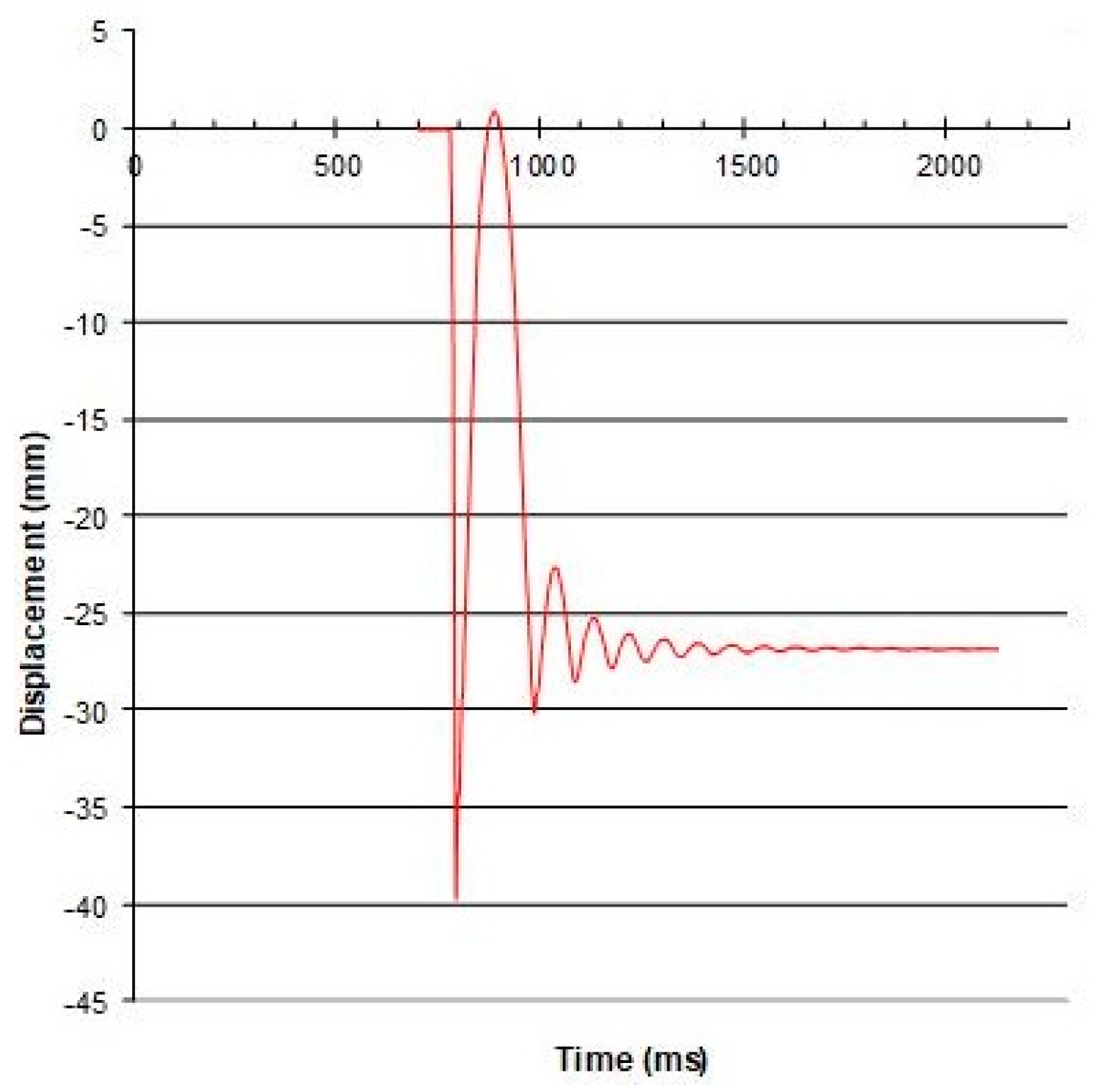
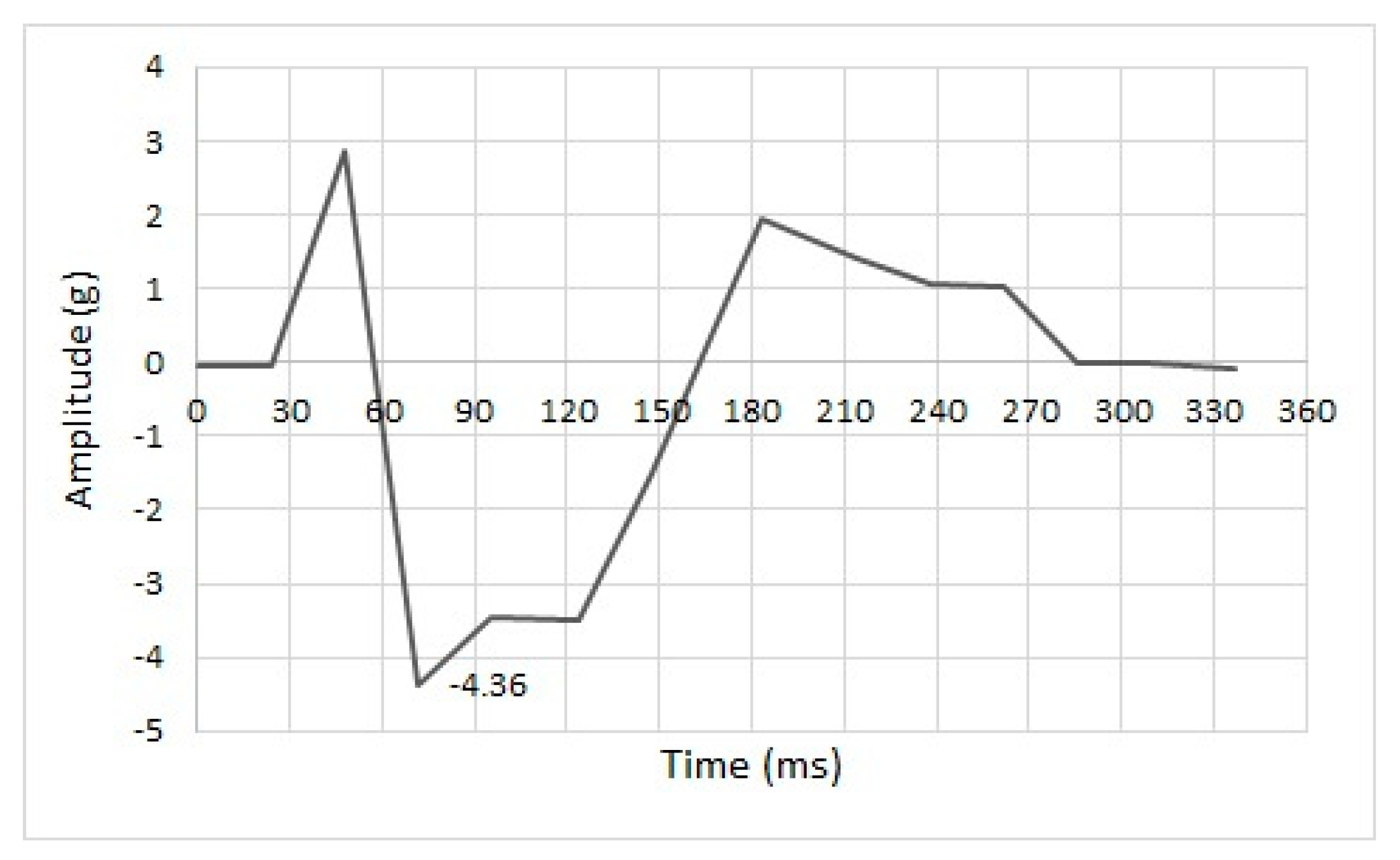
3.1. Slab 1 Results
3.2. Slab 2 Results
3.3. Slab 3 Results
3.4. Slab 4 Results
3.5. Slab 5 Results
3.6. Slab 6 Results
3.7. Slab 7 Results
3.8. Slab 8 Results
3.9. Slab 9 Results
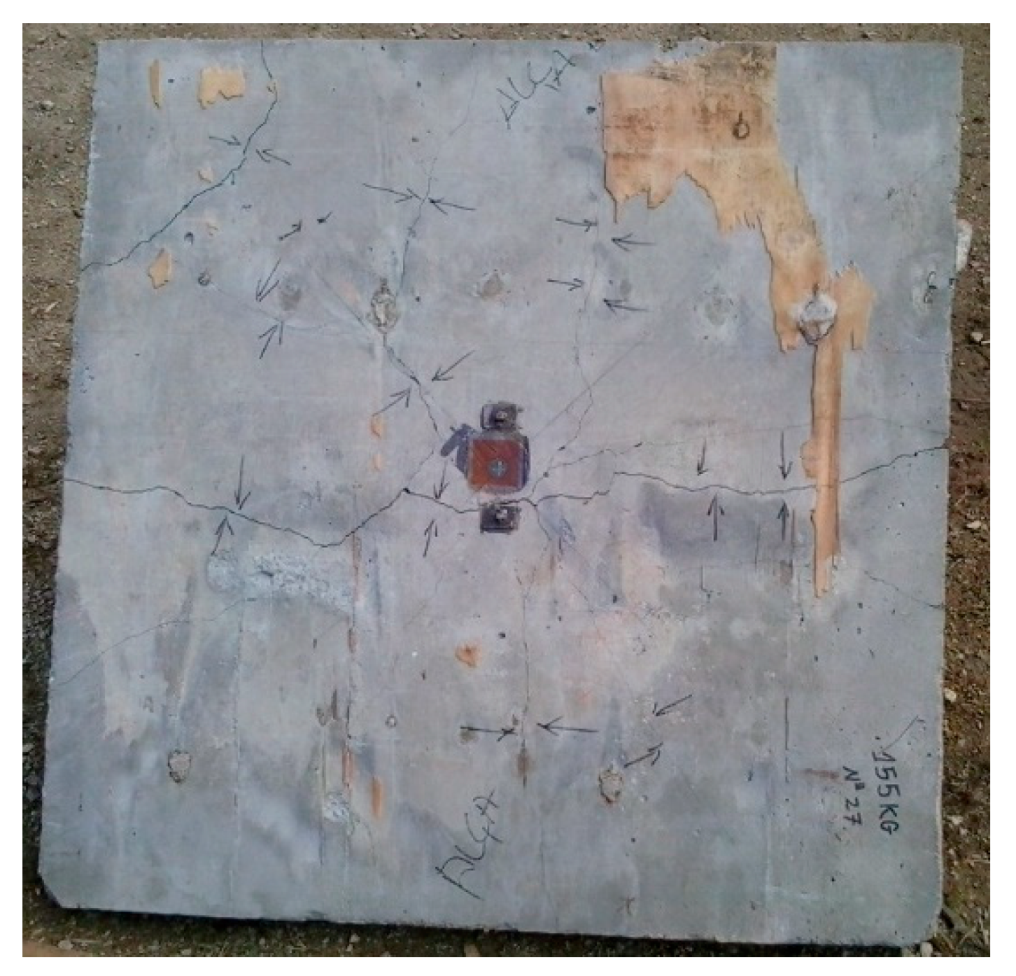
3.10. Slab 10 Results
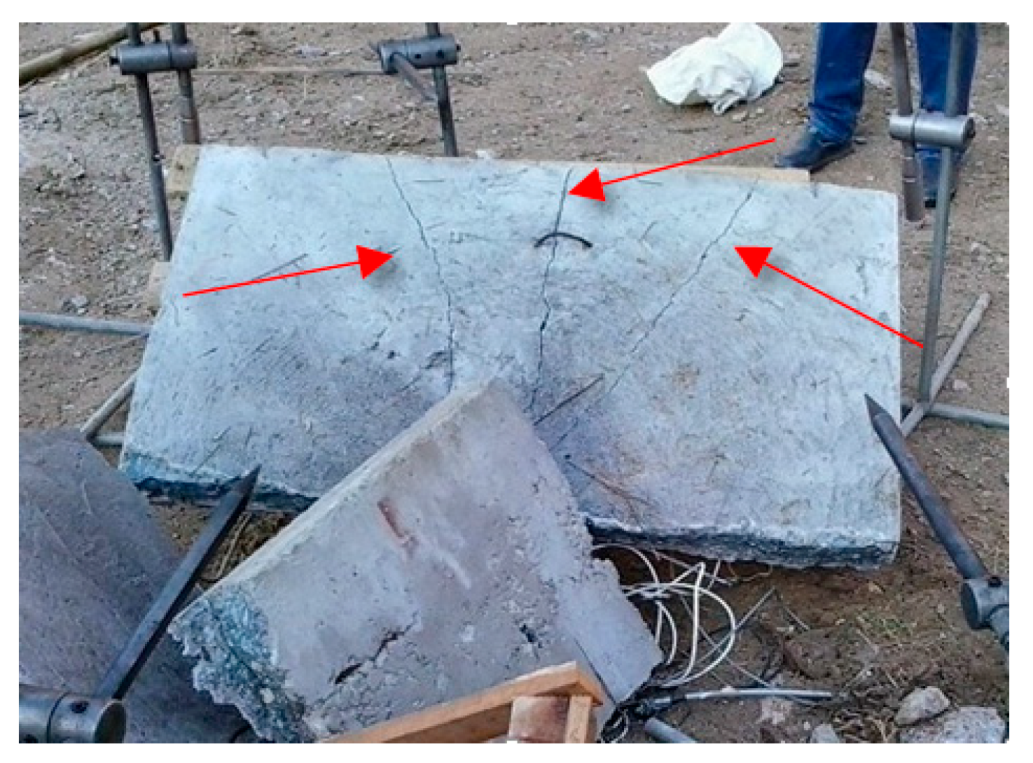
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Data Availability Statement
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ASCE. Design of Blast-Resistant Buildings in Petrochemical Facilities, 2nd ed.; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mostert, F.J. Challenges in blast protection research. Def. Technol. 2018, 14, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiquito, M.; Castedo, R.; López, L.M.; Santos, A.P.; Mancilla, J.M.; Yenes, J.I. Blast Wave Characteristics and TNT Equivalent of Improvised Explosive Device at Small-scaled Distances. Def. Sci. J. 2019, 69, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Elshenawy, T.; Seoud, M.A.; Abdo, G.M. Ballistic Protection of Military Shelters from Mortar Fragmentation and Blast Effects using a Multi-layer Structure. Def. Sci. J. 2019, 69, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajek, R.; Foglar, M.; Fladr, J. Influence of barrier material and barrier shape on blast wave mitigation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 120, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, F.B.; Urgessa, G.S.; Dutra, R.L.; Boschi, R.F.; Iha, K.; Rocco, J.A.F.F. EPS foam blast attenuation in full-scale field test of reinforced concrete slabs. Acta Sci. Civ. Eng. 2020, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, I.S.; Thangadurai, M.; Alegaonkar, P.S.; Saroha, D.R. Mitigation of Blast Induced Acceleration using Open Cell Natural Rubber and Synthetic Foam. Def. Sci. J. 2019, 69, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Qi, X.; Gu, Y.; Lawan, I.A.; Qu, Y. Numerical evaluation of blast resistance of RC slab strengthened with AFRP. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 178, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, A.S. Modelagem Computacional do Efeito de Onda de Choque de Alto Explosivo Sobre Laje de Concreto Armado. Master’s Thesis, Aeronautical Institute of Technology, São José dos Campos, São Paulo, Brazil, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Syed, Z.I.; Raman, S.N.; Ngo, T.; Mendis, P.; Pham, T. The Failure Behaviour of Reinforced Concrete Panels Under Far-field and Near-field Blast Effects. Structures 2018, 14, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, F.B.; Urgessa, G.S.; Rocco, J.A.F.F. Blast Response of 60 MPa Reinforced Concrete Slabs Subjected to Non-Confined Plastic Explosives. In Proceedings of the Structures Congress 2017—ASCE, Denver, CO, USA, 6–8 April 2017; pp. 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABNT, NBR 12655/96. Concreto-Preparo, Controle e Recebimento; ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1996; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- ABNT, NBR 6118/14. Projeto de Estruturas de Concreto-Procedimento; ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, 2014; p. 256. [Google Scholar]
- ABNT, NBR 14931/04. Execução de Estruturas de Concreto-Procedimento; ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, 2004; p. 53. [Google Scholar]
- Urgessa, G.; Mendonca, F.B.; Rocco, J.A.F.F. Experimental Records from Blast Tests of Ten Reinforced Concrete Slabs; George Mason University: Fairfax, VA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonca, F.B.; Urgessa, G.; Iha, K.; Rocha, R.J.; Rocco, J.A.F.F. Comparison of Predicted and Experimental Behaviour of RC Slabs Subjected to Blast using SDOF Analysis. Def. Sci. J. 2018, 68, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, F.B.; Urgessa, G.S. Pre-Test and Analysis of a Reinforced Concrete Slab Subjected to Blast from a Non-Confined Explosive. In Energetic Materials Research, Applications and New Technologies, 1st ed.; Gonçalves, R.F.B., Rocco, J.A.F.F., Iha, K., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, G.F.; Graham, K.J. Explosive Shocks in Air, 2nd ed.; Springer Science: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, W.C.L. Blast–Efeitos da Onda de Choque no ser Humano e Nas Estruturas. Master’s Thesis, Aeronautical Institute of Technology, São José dos Campos, São Paulo, Brazil, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, M.D.; Matsagar, V.A.; Gupta, A.K.; Marburg, S. An abridged review of blast wave parameters. Def. Sci. J. 2012, 62, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simulia. Abaqus. Dassault Systèmes, Vélizy-Villacoublay. 2014. Available online: https://www.3ds.com/products-services/simula/products/abaqus (accessed on 8 February 2020).
- Johnson, G.; Holmquist, T. An Improved Computational Constitutive Model for Brittle Materials. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings 309, American Institute of Physics, Melville, NY, USA, 28 June–2 July 1993; pp. 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmquist, T.; Johnson, G.; Cook, W. A Computational Constitutive Model for Concrete Subjected to Large Strains, High Strain Rates, and High Pressures. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Ballistics 14, International Ballistics Society, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 26–29 September 1993; pp. 591–600, ISBN 0961815681. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, G.; Cook, W. A Constitutive Model and Data for Metals Subjected to Large Strains, High Strain Rates and High Temperatures. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Symposium on Ballistics, International Ballistics Society, The Hague, South Holland, The Netherlands, 19–21 April 1983; pp. 541–547. Available online: https://archive.org/details/AConstitutiveModelAndDataForMetals/mode/2up (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Simulia Abaqus Theory Manual; Dassault Systèmes: Vélizy-Villacoublay, France, 2014.
- Hyde, D.W. Conventional Weapons Effect (CONWEP)—Application of TM5-855-1; Department of the Army: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 1988.
- Wang, W.; Zhang, D.; Lu, F.; Wang, S.C.; Tang, F. Experimental study and numerical simulation of the damage mode of a square reinforced concrete slab under close-in explosion. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 27, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharma Rao, V.; Srinivas Kumar, A.; Venkateswara Rao, K.; Krishna Prasad, V.S.R. Theoretical and experimental studies on blast wave propagation in air. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2015, 1, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingery, C.N.; Bulmash, G. Airblast Parameters from TNT Spherical Air Bursts and Hemispherical Surface Bursts. US Technical Report ARBRL-TR-02555; US Army: Harford, MD, USA, 1984.
- Wu, C.; Sheikh, H. A finite element modelling to investigate the mitigation of blast effects on reinforced concrete panel using foam cladding. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2013, 55, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusenberry, D.O. Handbook for Blast-Resistant Design of Buildings, 1st ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.D.; Hetherington, J.G. Blast and Ballistic Loading of Structures, 1st ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Brode, H.L. Numerical solutions of spherical blast waves. J. Appl. Phys. 1955, 26, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrych, J.; Abrahamson, G.R. The Dynamics of Explosion and Its Use, 1st ed.; Elsevier Ltd: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979; Volume 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
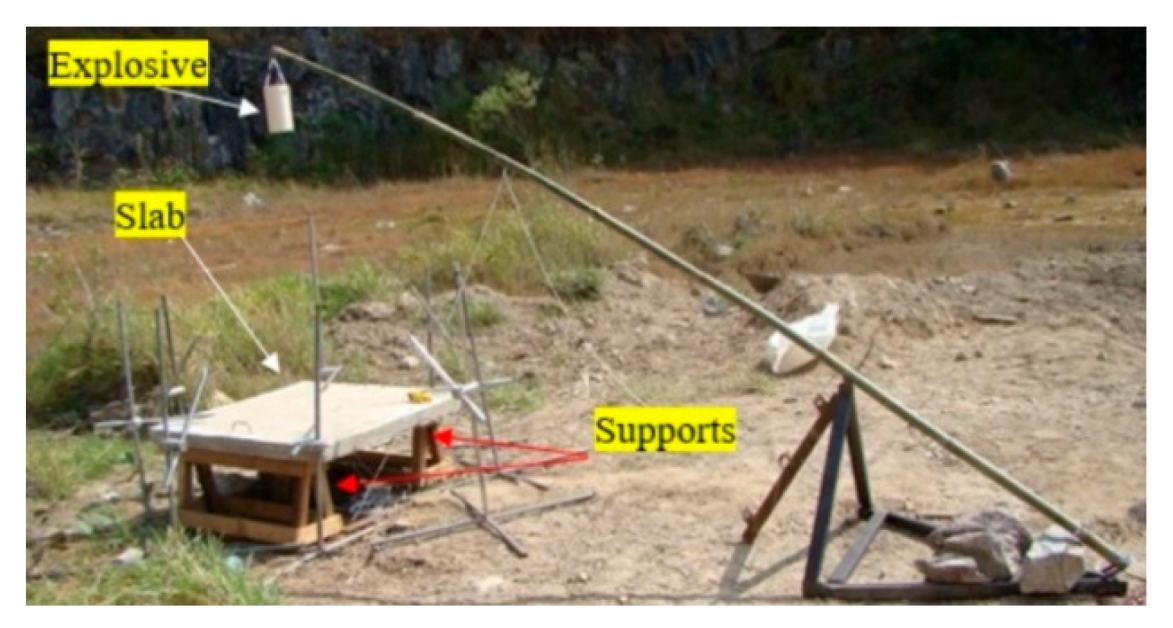
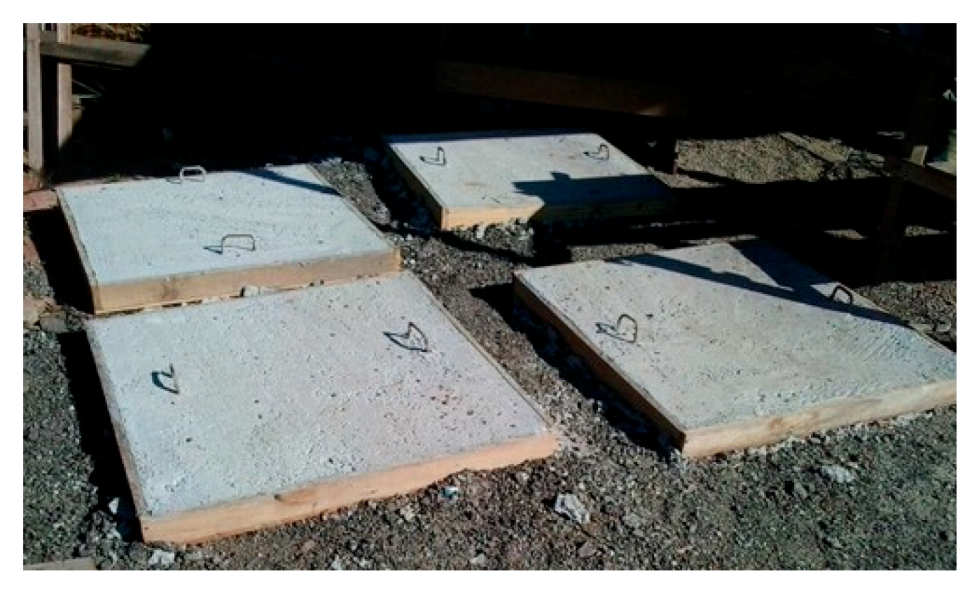
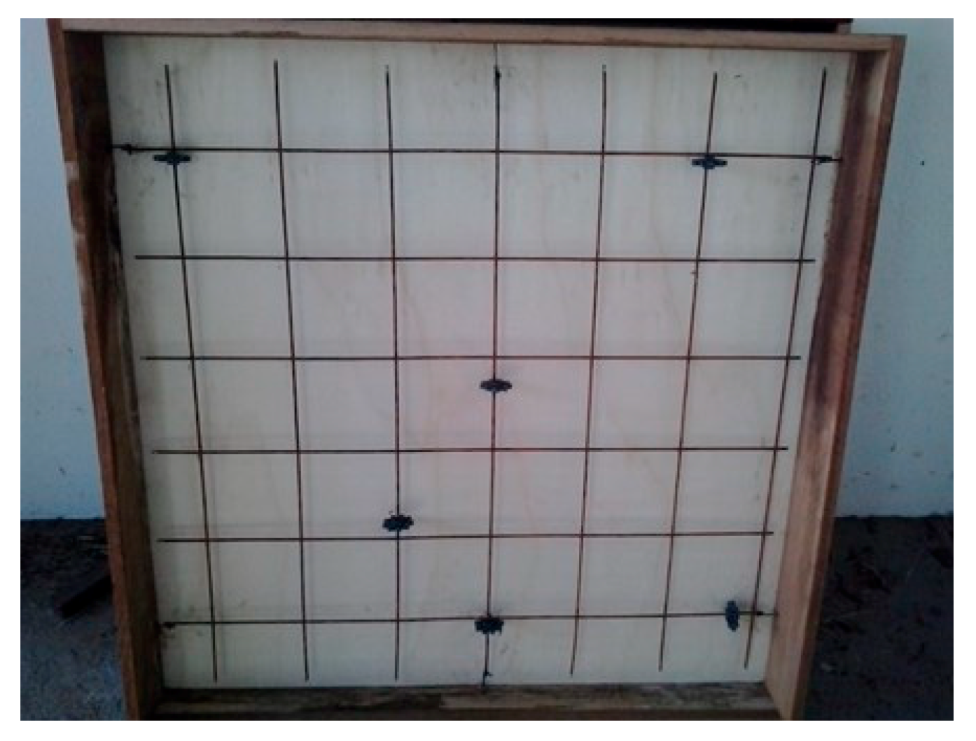
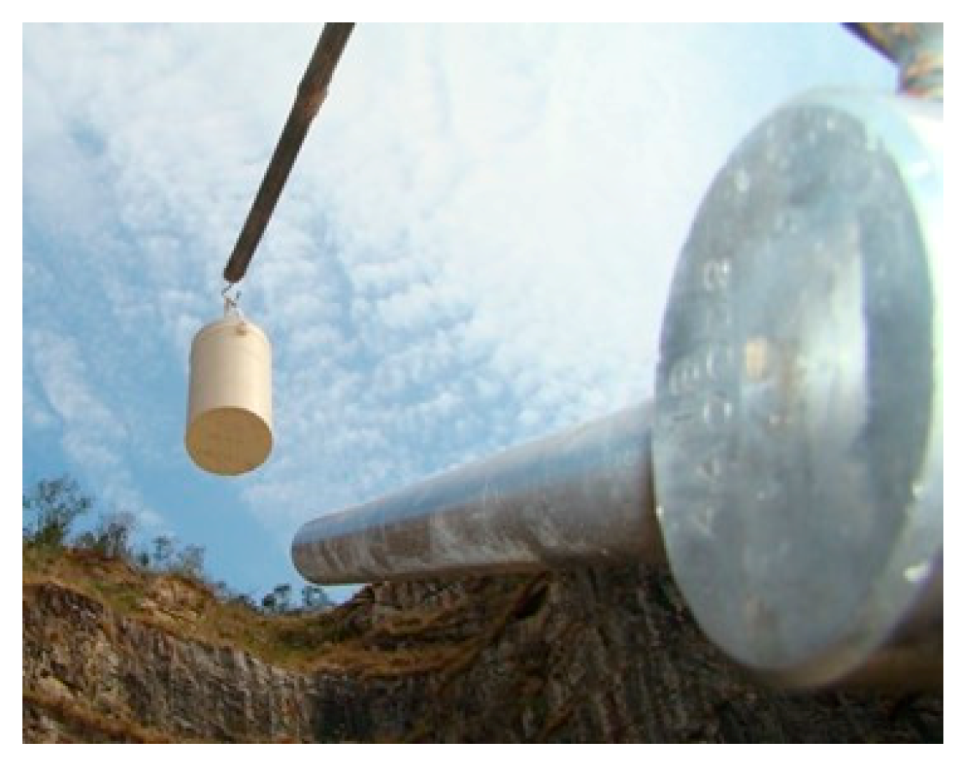
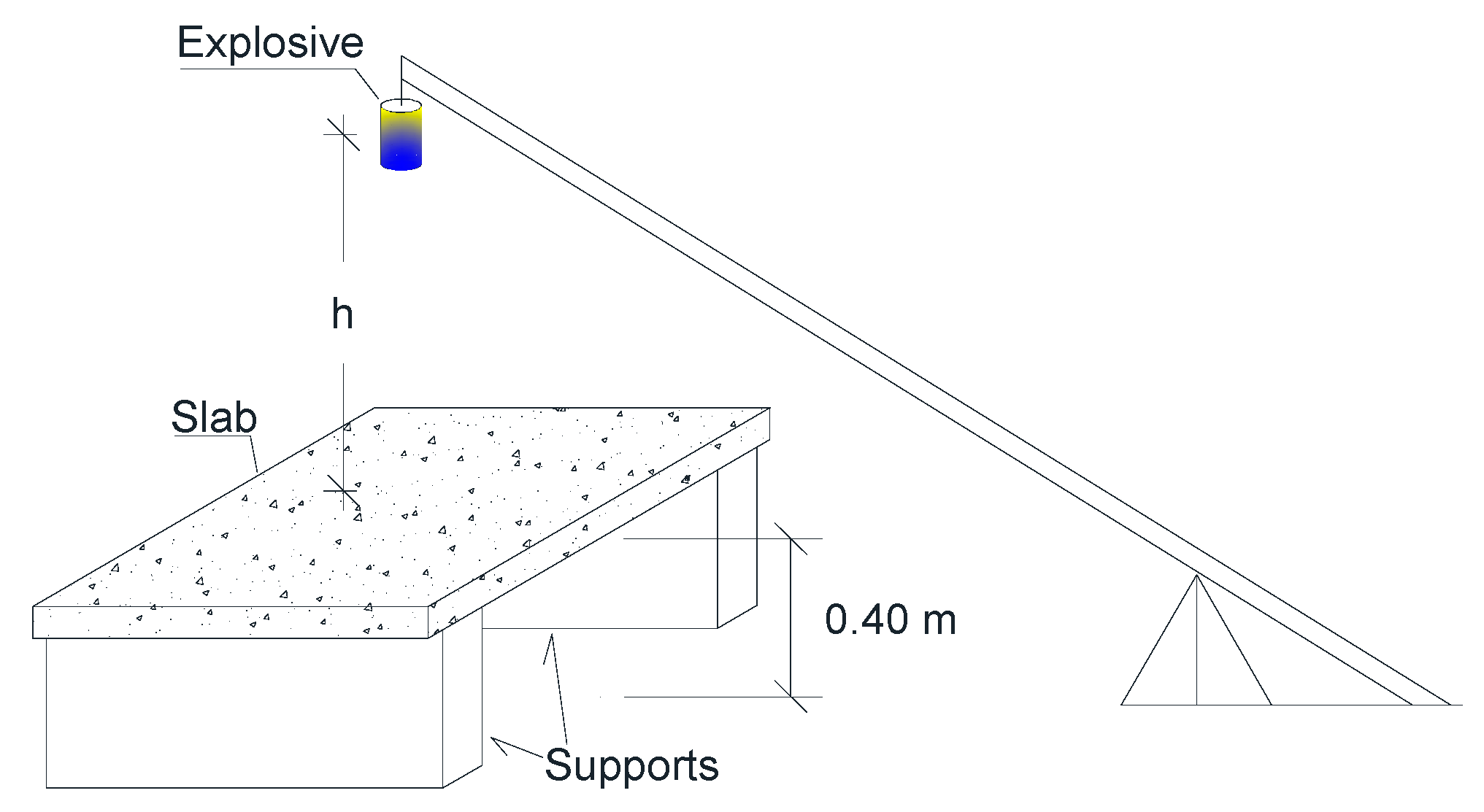


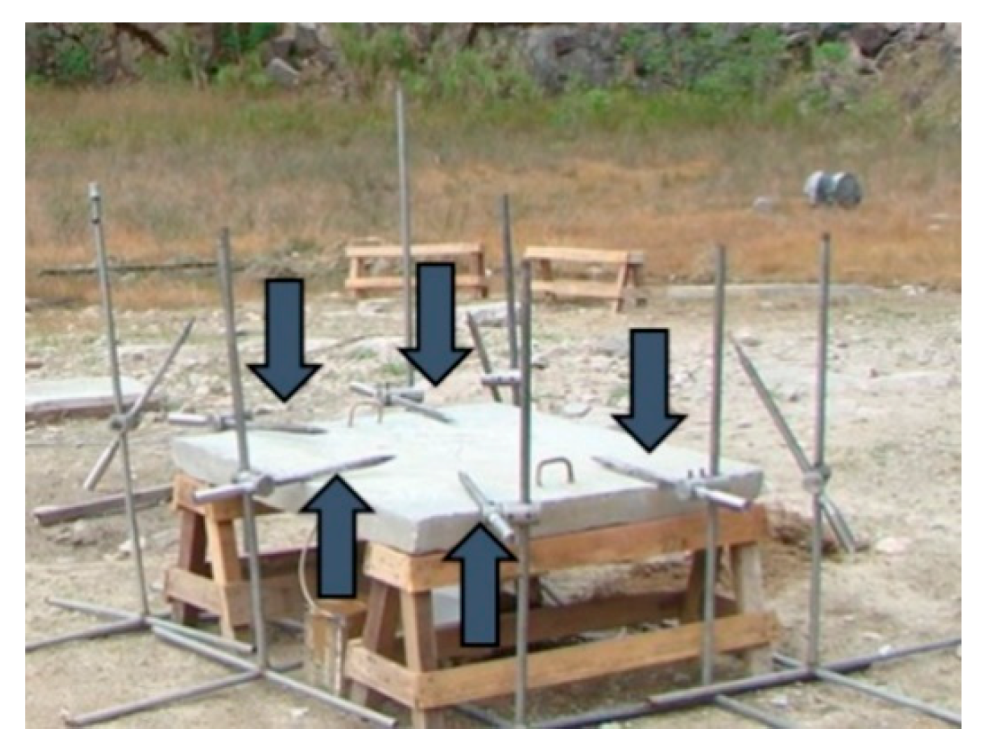




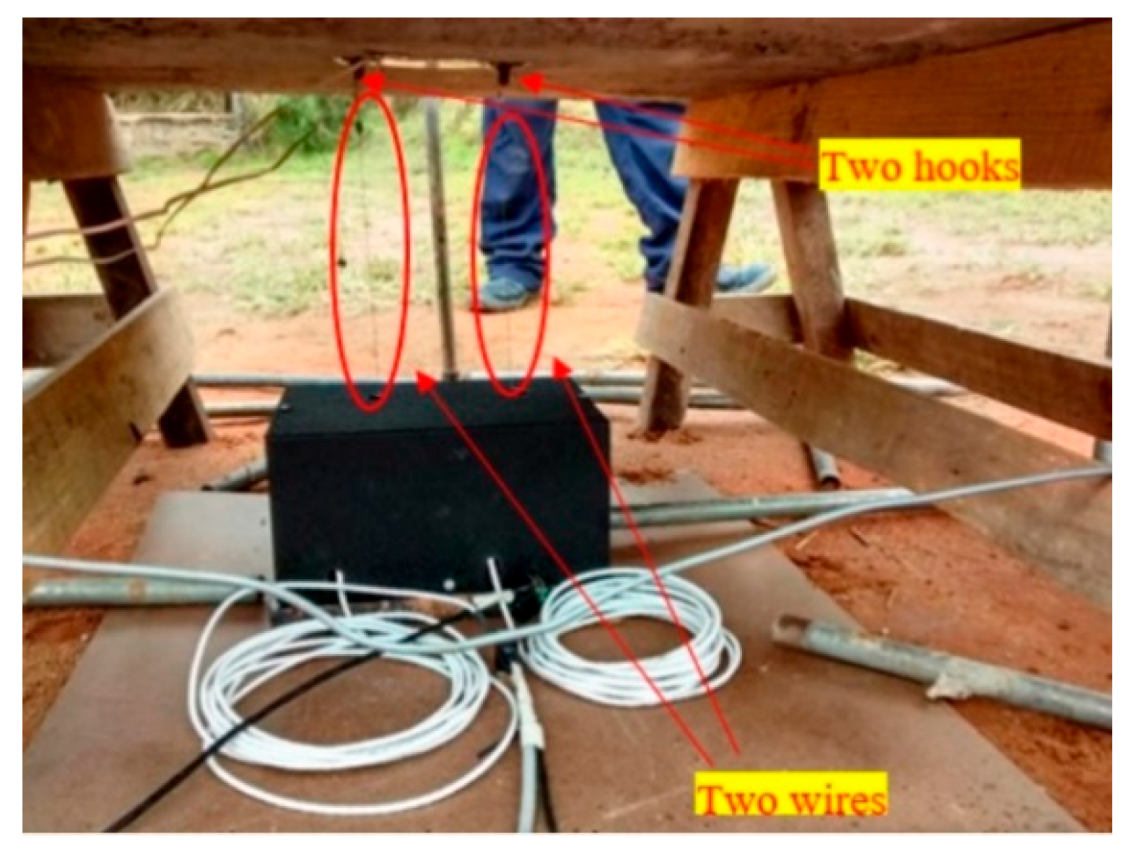
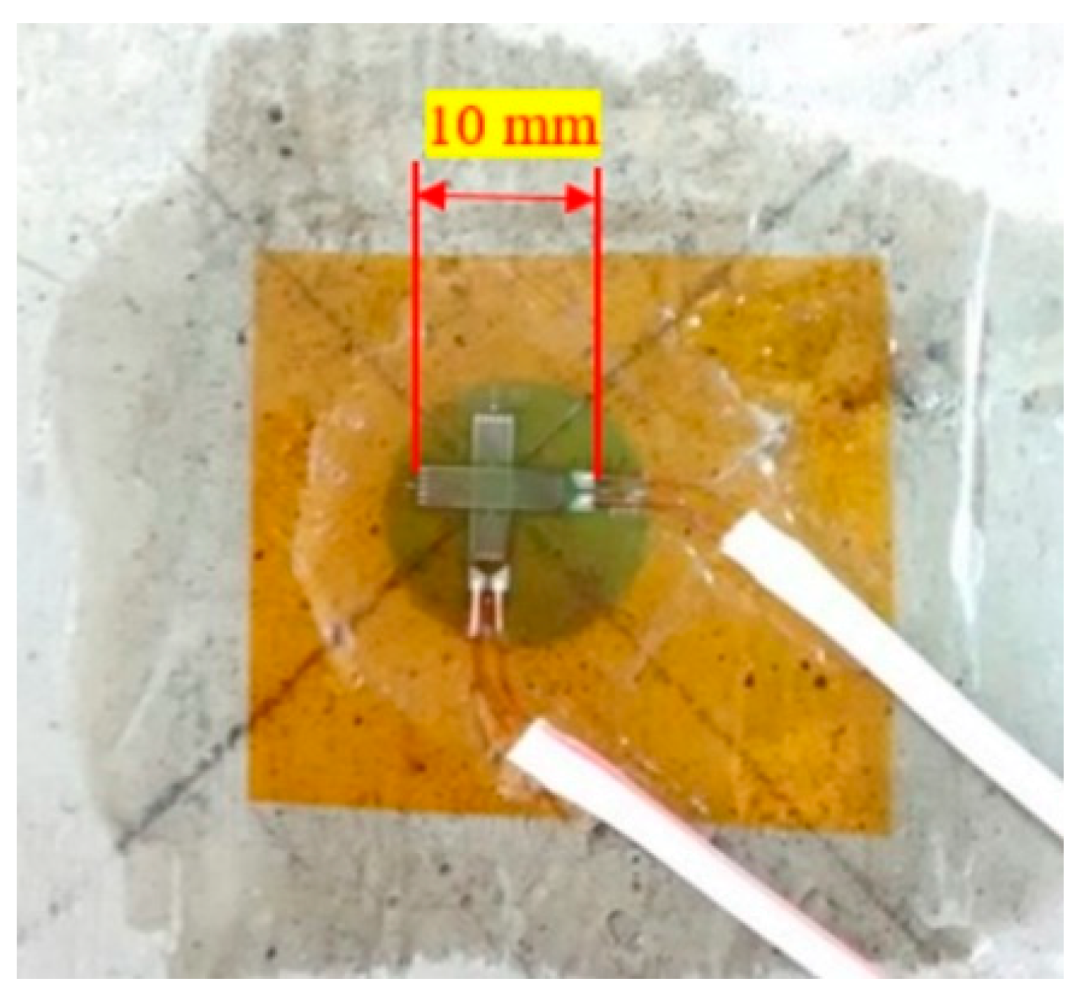










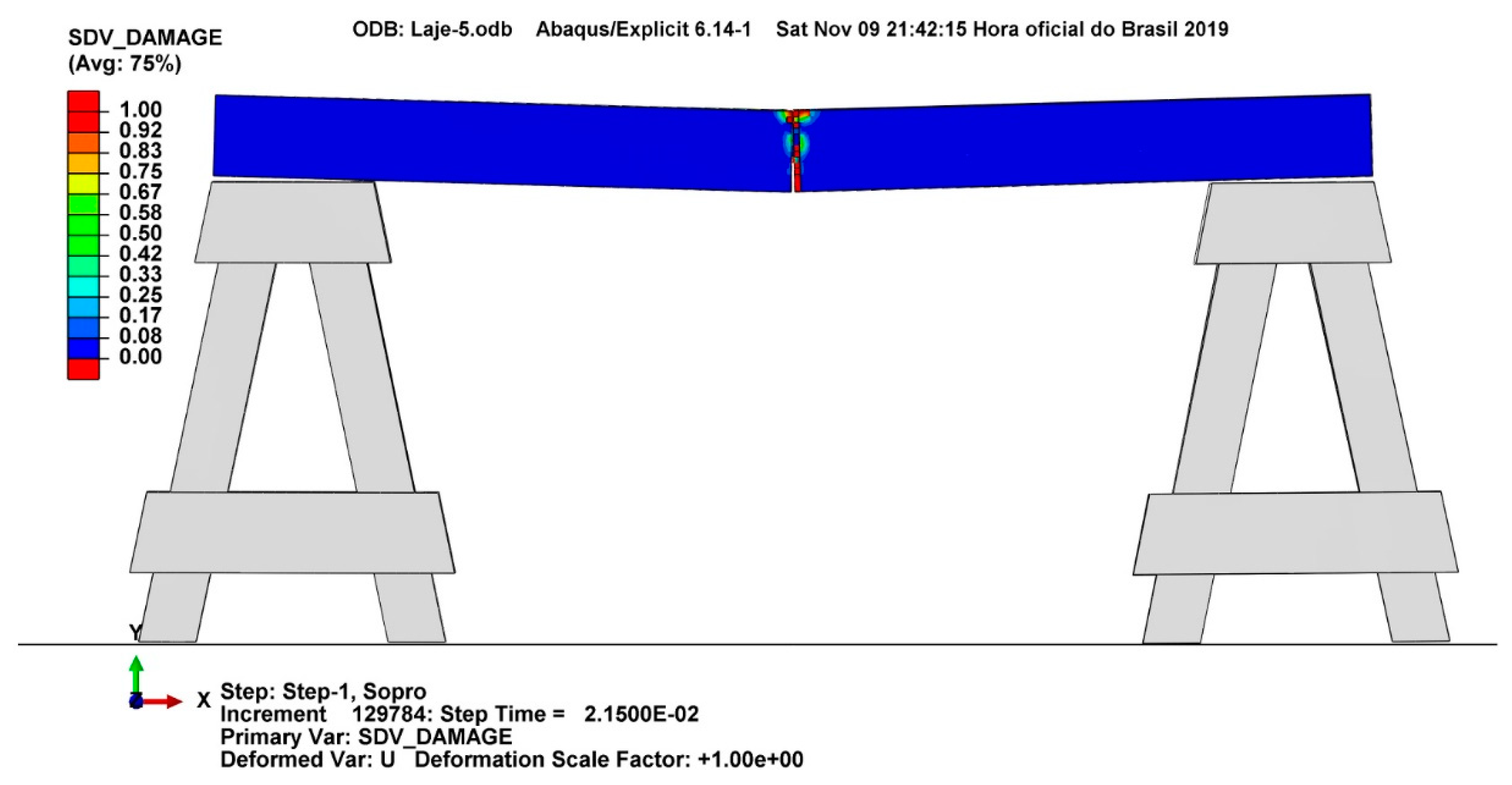
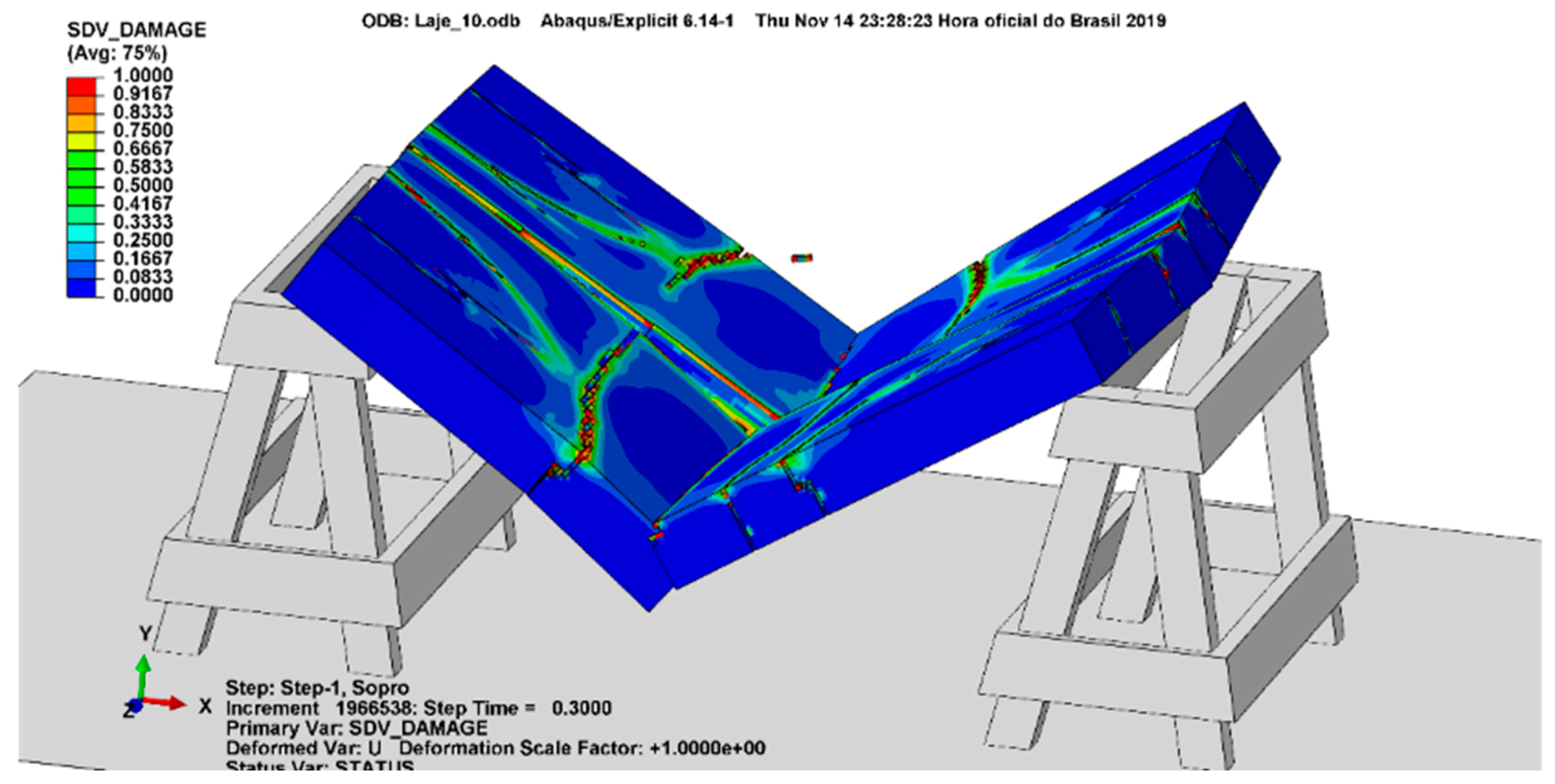
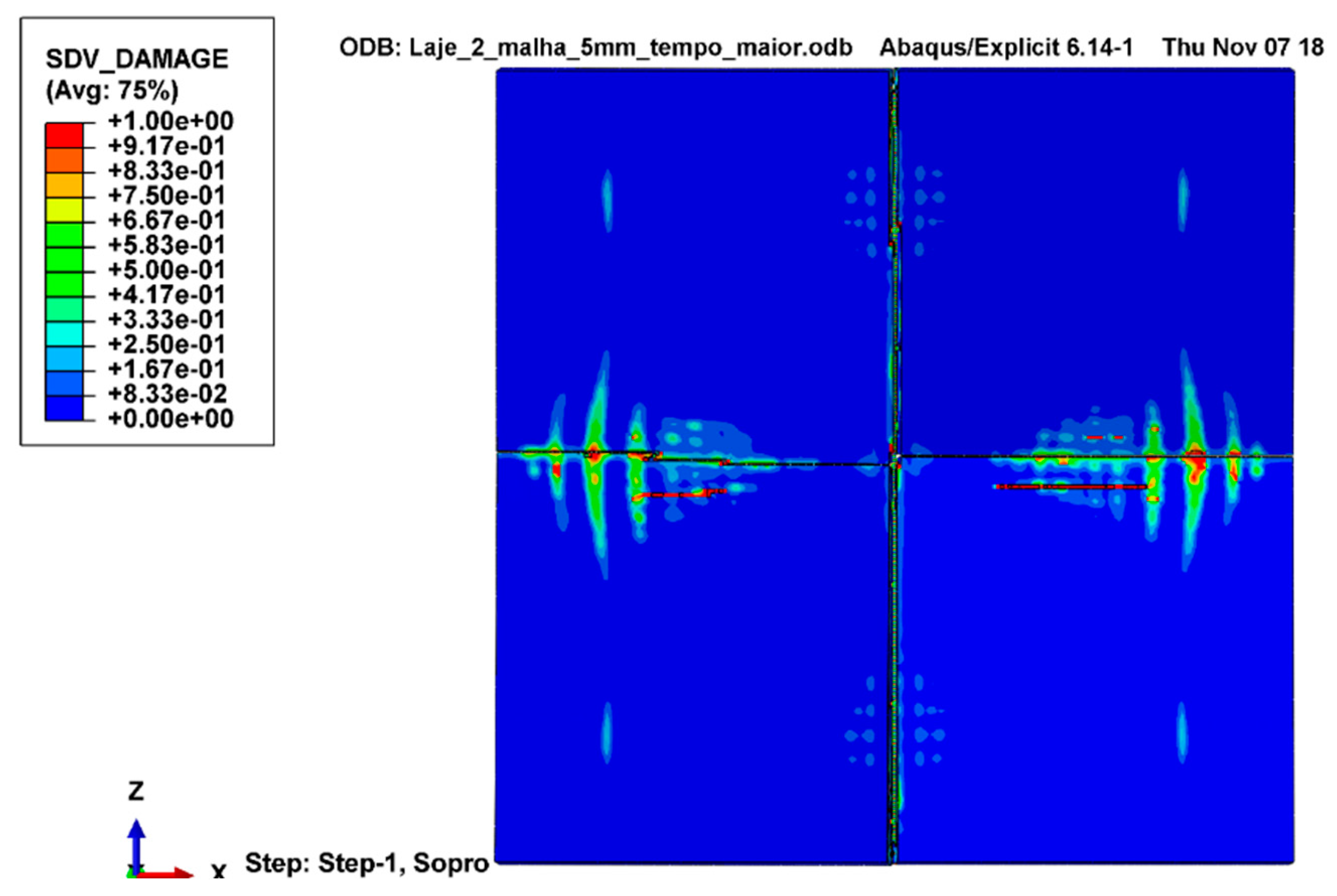
| Slab | fck (MPa) | Bar Diam. (mm) | Rebar Spacing (cm) | Rebar Direct. | Reinforc. Ratio | TNT Mass (kg) | Stand-off Distance (m) | Z (m/kg1/3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40 | 5 | 15 | Two way | 0.17% | 2.76 | 1.3 | 0.93 |
| 2 | 50 | 5 | 15 | Two way | 0.17% | 2.72 | 2 | 1.43 |
| 10 | 10 | One way | 0.37% | |||||
| 3 * | 50 | 5 | 15 | Two way | 0.17% | 2.71 | 2 | 1.43 |
| 10 | 10 | One way | 0.37% | |||||
| 4 | 60 | 5 | 10 | Two way | 0.25% | 2.69 | 2 | 1.44 |
| 5 | 50 | 5 | 15 | Two way | 0.17% | 2.58 | 2 | 1.46 |
| 10 | 10 | One way | 0.37% | |||||
| 6 * | 50 | 5 | 15 | Two way | 0.17% | 2.72 | 2 | 1.43 |
| 10 | 10 | One way | 0.37% | |||||
| 7 | 60 | 5 | 10 | Two way | 0.25% | 2.60 | 2 | 1.45 |
| 8 * | 60 | 5 | 10 | Two way | 0.25% | 2.76 | 2 | 1.42 |
| 9 | 60 | 5 | 10 | Two way | 0.25% | 2.72 | 2 | 1.43 |
| 10 | 40 | 5 | 15 | Two way | 0.17% | 2.60 | 1.6 | 1.16 |
| Sensor | Distance from Explosive (cm) | Pso (Measured) (kPa) | Pso (Predicted) (kPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 66 | 917 | |
| B | 66 | 866 | |
| C | 62 | 746 | |
| D | 65 | 1052 | |
| Average | 895 | 780 | |
| E | 56 | 1365 | |
| F | 57 | 961 | |
| G | 59 | 637 | |
| H | 56 | 879 | |
| Average | 960 | 1025 |
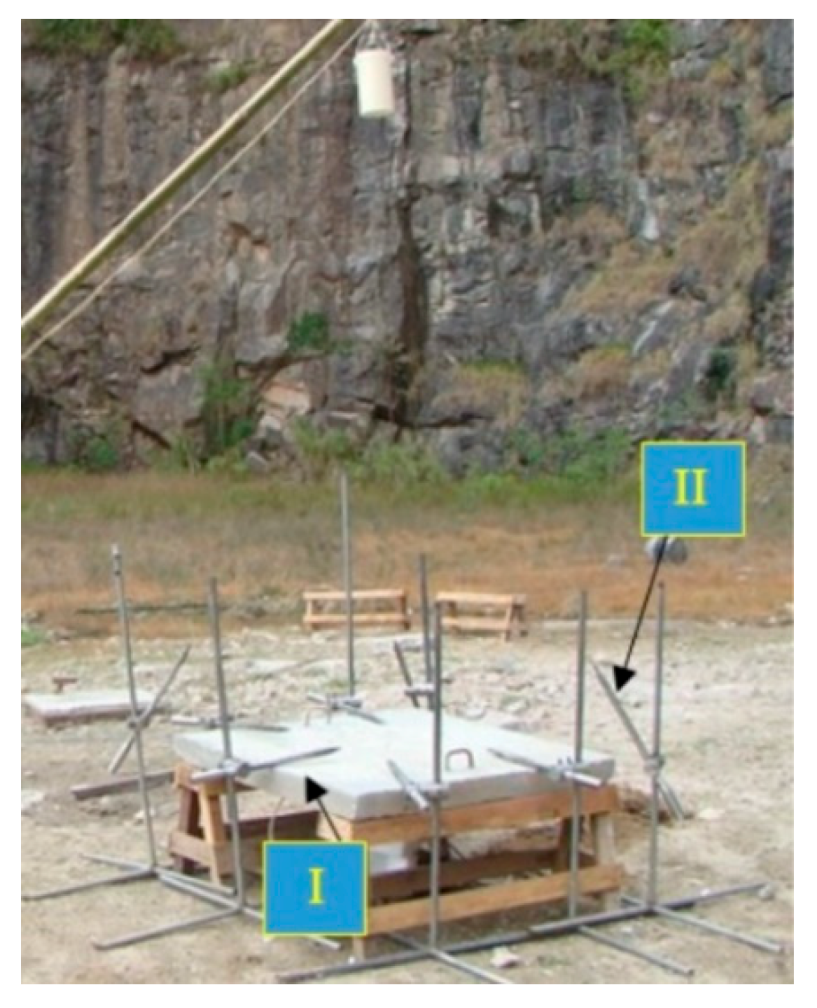
| Sensor | Position | Peak Pressure (kPa) | Time of Duration (ms) | Impulse (kPa-ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | II | 1578 | 0.5 | 462 |
| 2 | I | 844 | 1.01 | 485 |
| 3 | II | 1310 | 0.53 | 379 |
| 4 | II | 1012 | 0.93 | 505 |
| 5 | I | 1997 | 1.35 | 1112 |
| 6 | II | 821 | 0.43 | 319 |
| 7 | I | 847 | 0.92 | 633 |
| 8 | I | 686 | 0.93 | 481 |
| Equation | Reference | Pso Value (kPa) |
|---|---|---|
| [18] | 1187 | |
| [33] | 1007 | |
| [34] | 898 | |
| Blast wave curves | [29] | 1105 |
| Sensors First Recorded Pressure Value (kPa) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S 01 | S02 | S 03 | S 04 | S 05 | S 06 | S 07 | S 08 |
| Failed | 257 | 696 | 938 | 279 | 233 | 292 | 632 |
| Equation | Reference | Pso Value (kPa) |
|---|---|---|
| [18] | 451 | |
| [33] | 335 | |
| [34] | 353 | |
| Blast wave curves | [29] | 414 |
| Sensor | Position | Peak Pressure (kPa) | Time of Duration (ms) | Impulse (kPa-ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | II | - | - | - |
| 2 | II | 718 | 0.62 | 310 |
| 3 | I | 2634 | 1.07 | 842 |
| 4 | I | 3801 | 2.24 | 1966 |
| 5 | II | 1303 | 3.00 | 1363 |
| 6 | I | 2215 | 0.76 | 789 |
| 7 | I | 2159 | 0.63 | 856 |
| 8 | I | 1327 | 0.73 | 568 |
| Sensors First Recorded Pressure Value (kPa) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S 01 | S02 | S 03 | S 04 | S 05 | S 06 | S 07 | S 08 |
| 227 | 226 | 407 | 600 | 279 | 370 | 567 | 416 |
| Sensor | Position | Peak Pressure (kPa) | Time of Duration (ms) | Impulse (kPa-ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | II | 579 | 0.93 | 352 |
| 2 | II | 496 | 0.63 | 263 |
| 3 | I | 1440 | 1.37 | 767 |
| 4 | I | 1934 | 0.99 | 839 |
| 5 | II | 881 | 2.59 | 1245 |
| 6 | I | 1130 | 1.20 | 632 |
| 7 | I | 1850 | 1.37 | 1150 |
| 8 | I | 1070 | 46.54 | 3652 |
| Sensors First Recorded Pressure Value (kPa) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S 01 | S02 | S 03 | S 04 | S 05 | S 06 | S 07 | S 08 |
| 231 | 294 | 568 | 410 | 267 | 172 | 541 | 403 |
| Sensor | Position | Peak Pressure (kPa) | Time of Duration (ms) | Impulse (kPa-ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | II | 913 | 0.82 | 389 |
| 2 | II | 755 | 0.60 | 295 |
| 3 | I | 4073 | 1.13 | 929 |
| 4 | I | 2374 | 1.33 | 912 |
| 5 | II | 986 | 1.75 | 908 |
| 6 | I | 3593 | 0.64 | 835 |
| 7 | I | 2317 | 0.92 | 912 |
| 8 | I | 1986 | 0.76 | 456 |
| Sensors First Recorded Pressure Value (kPa) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S 01 | S02 | S 03 | S 04 | S 05 | S 06 | S 07 | S 08 |
| 292 | 352 | 498 | 748 | 372 | 382 | 985 | 370 |
| Sensor | Position | Peak Pressure (kPa) | Time of Duration (ms) | Impulse (kPa-ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | II | 799 | 0.67 | 381 |
| 2 | II | 937 | 0.61 | 385 |
| 3 | I | 1390 | 0.76 | 633 |
| 4 | I | 2000 | 0.84 | 753 |
| 5 | II | 1497 | 1.60 | 947 |
| 6 | II | 933 | 0.71 | 384 |
| 7 | I | 2114 | 0.77 | 1084 |
| 8 | I | 1691 | 1.16 | 556 |
| Sensors First Recorded Pressure Value (kPa) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S 01 | S02 | S 03 | S 04 | S 05 | S 06 | S 07 | S 08 |
| 262 | 271 | 334 | 332 | 278 | 352 | 602 | 268 |
| Sensor | Position | Peak Pressure (kPa) | Time of Duration (ms) | Impulse (kPa-ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | II | 480 | 0.46 | 257 |
| 2 | II | 307 | 0.54 | 145 |
| 3 | I | 998 | 0.63 | 388 |
| 4 | I | 1026 | 1.08 | 709 |
| 5 | II | 1071 | 5.40 | 2453 |
| 6 | II | 413 | 1.21 | 385 |
| 7 | I | 1219 | 2.67 | 1393 |
| 8 | I | 961 | 1.62 | 597 |
| Sensors First Recorded Pressure Value (kPa) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S 01 | S02 | S 03 | S 04 | S 05 | S 06 | S 07 | S 08 |
| 215 | 245 | 336 | 297 | 209 | 275 | 515 | 244 |
| Sensor | Position | Peak Pressure (kPa) | Time of Duration (ms) | Impulse (kPa-ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | II | 821 | 0.84 | 430 |
| 2 | II | 495 | 0.74 | 241 |
| 3 | I | 2654 | 0.74 | 960 |
| 4 | I | 1687 | 0.62 | 603 |
| 5 | II | 1543 | 1.65 | 1001 |
| 6 | II | 956 | 0.95 | 367 |
| 7 | I | 2239 | 2.34 | 1203 |
| 8 | I | 2180 | 0.41 | 654 |
| Sensors First Recorded Pressure Value (kPa) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S 01 | S02 | S 03 | S 04 | S 05 | S 06 | S 07 | S 08 |
| 234 | 226 | 285 | 253 | 267 | 243 | 533 | 363 |
| Sensor | Position | Peak Pressure (kPa) | Time of Duration (ms) | Impulse (kPa-ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | II | 740 | 0.28 | 202 |
| 2 | II | 596 | 0.44 | 176 |
| 3 | I | 825 | 0.47 | 258 |
| 4 | I | 1057 | 2.41 | 841 |
| 5 | II | 1296 | 2.75 | 1821 |
| 6 | II | 763 | 0.47 | 341 |
| 7 | I | 1450 | 2.41 | 1477 |
| 8 | I | 1984 | 1.39 | 839 |
| Sensors First Recorded Pressure Value (kPa) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S 01 | S02 | S 03 | S 04 | S 05 | S 06 | S 07 | S 08 |
| 245 | 316 | 300 | 403 | 314 | 268 | 221 | 506 |
| Sensor | Position | Peak Pressure (kPa) | Time of Duration (ms) | Impulse (kPa-ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | II | 1052 | 0.31 | 299 |
| 2 | II | 442 | 0.78 | 291 |
| 3 | I | 2029 | 0.65 | 844 |
| 4 | I | 1874 | 0.66 | 883 |
| 5 | II | 1216 | 1.55 | 1116 |
| 6 | II | 746 | 0.92 | 472 |
| 7 | I | 1831 | 2.23 | 1069 |
| 8 | I | 1490 | 0.37 | 355 |
| Sensors First Recorded Pressure Value (kPa) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S 01 | S02 | S 03 | S 04 | S 05 | S 06 | S 07 | S 08 |
| 314 | 217 | 1000 | 876 | 327 | 364 | 913 | 309 |
| Sensor | Position | Peak Pressure (kPa) | Time of Duration (ms) | Impulse (kPa-ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | II | 1107 | 0.45 | 286 |
| 2 | II | 538 | 0.72 | 206 |
| 3 | I | 2944 | 0.34 | 533 |
| 4 | I | 3066 | 2.26 | 1779 |
| 5 | II | 971 | 1.47 | 964 |
| 6 | II | 2472 | 2.43 | 1416 |
| 7 | I | 3084 | 2.35 | 1481 |
| 8 | I | 1699 | 0.35 | 443 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendonça, F.B.; Urgessa, G.S.; Augusto, A.S.; Rocco, J.A.F.F. Experimental Records from Blast Tests of Ten Reinforced Concrete Slabs. CivilEng 2020, 1, 51-74. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng1020005
Mendonça FB, Urgessa GS, Augusto AS, Rocco JAFF. Experimental Records from Blast Tests of Ten Reinforced Concrete Slabs. CivilEng. 2020; 1(2):51-74. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng1020005
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendonça, Fausto B., Girum S. Urgessa, Anselmo S. Augusto, and José A. F. F. Rocco. 2020. "Experimental Records from Blast Tests of Ten Reinforced Concrete Slabs" CivilEng 1, no. 2: 51-74. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng1020005
APA StyleMendonça, F. B., Urgessa, G. S., Augusto, A. S., & Rocco, J. A. F. F. (2020). Experimental Records from Blast Tests of Ten Reinforced Concrete Slabs. CivilEng, 1(2), 51-74. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng1020005






