Resting-State Functional Connectivity Predicts Attention Problems in Children: Evidence from the ABCD Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. ADHD Background
1.2. Neuroimaging and ADHD
1.3. Current Work
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. fMRI Acquisition and Data Preprocessing
2.3. Measures
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
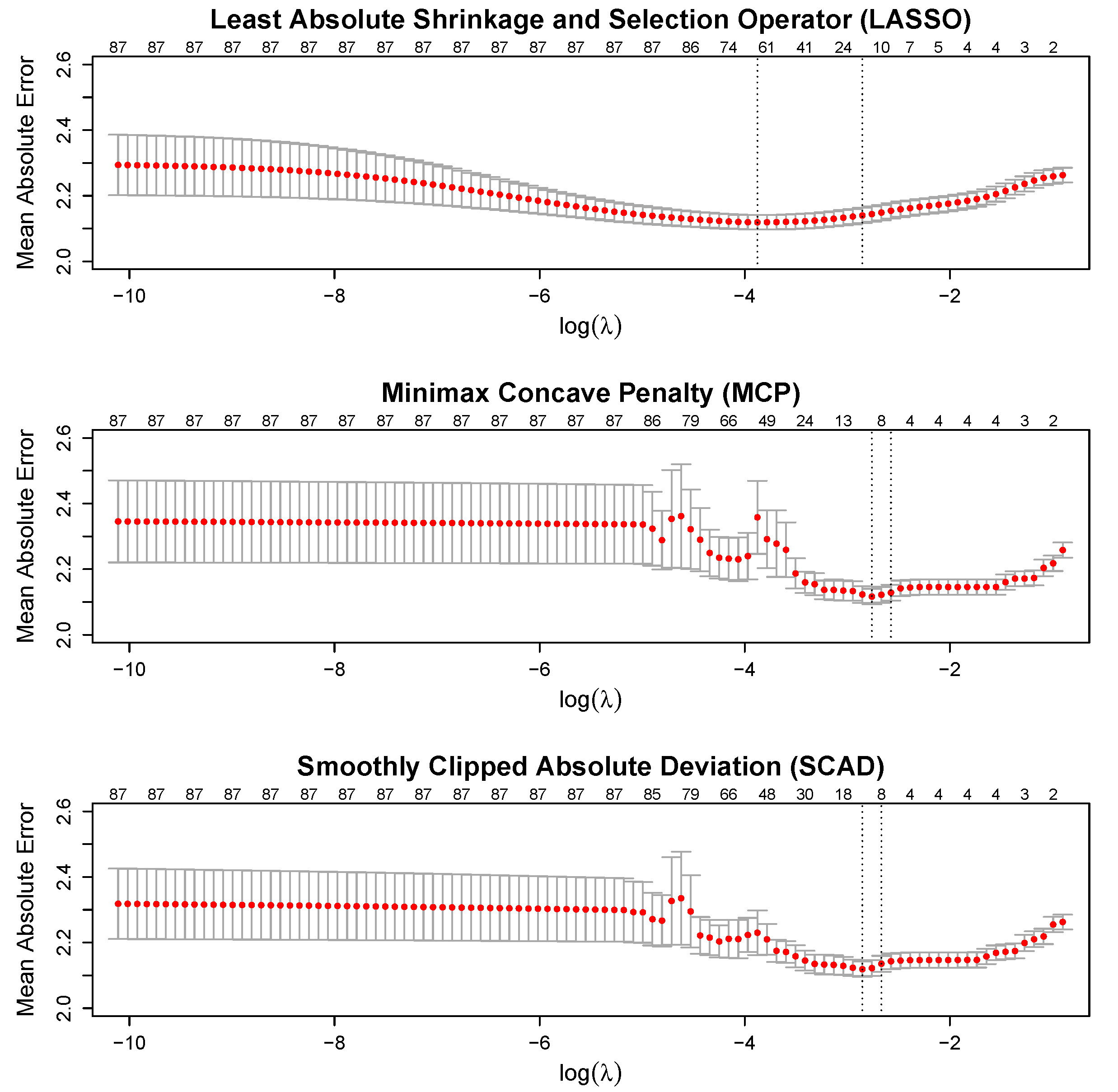
3.1. Cross-Validation
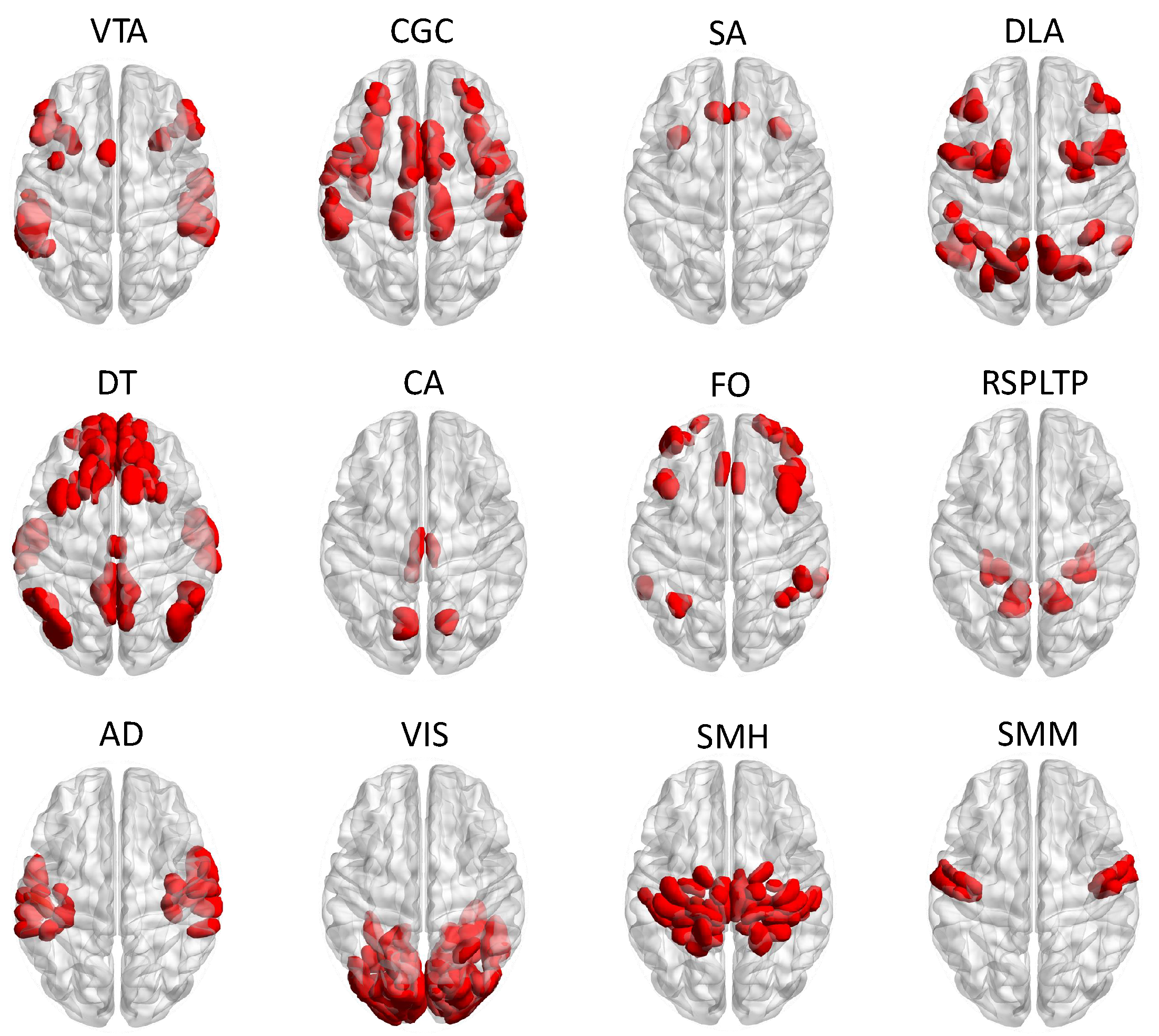
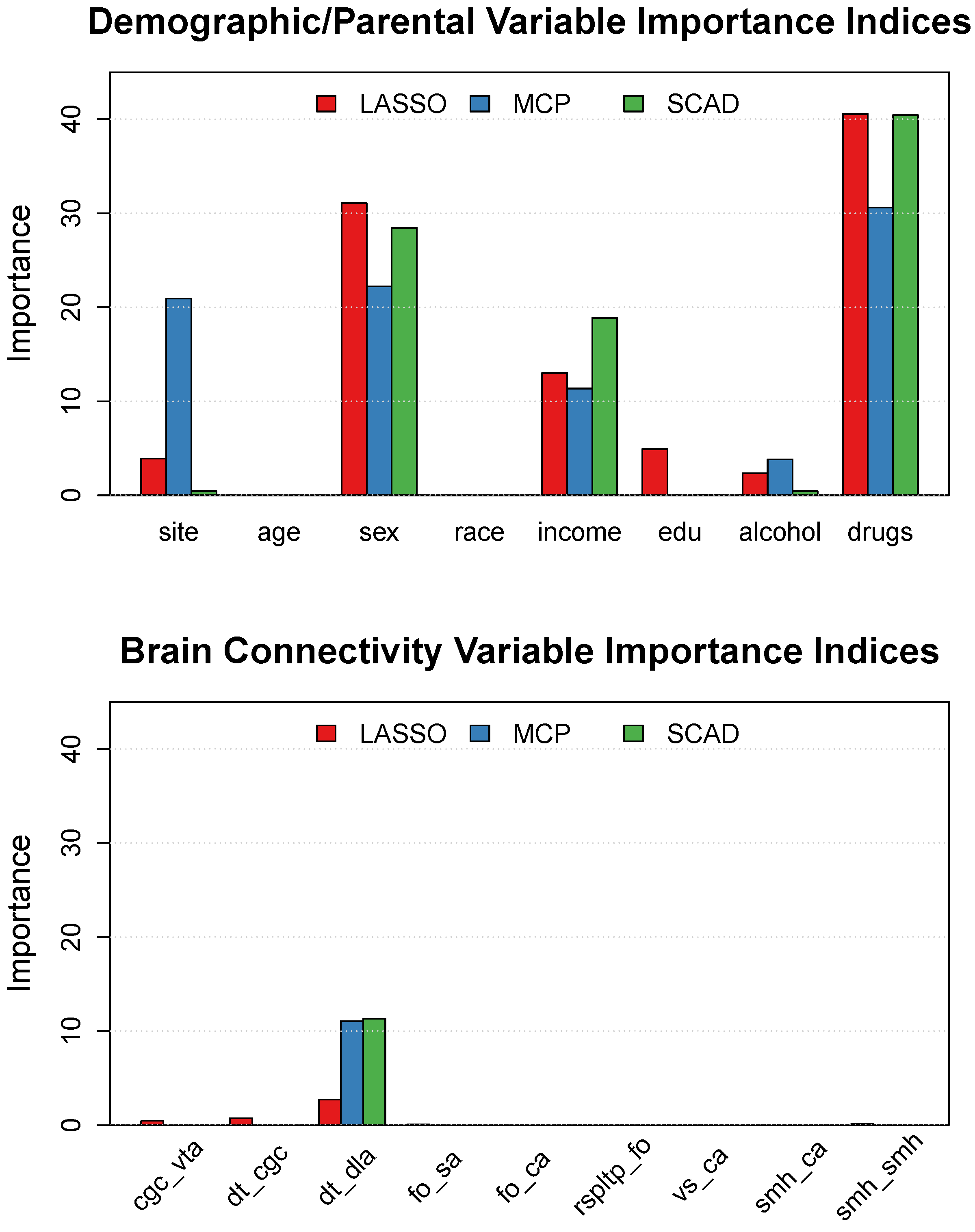
3.2. Variable Selection and Importance
3.3. Demographic and Parental History Effects
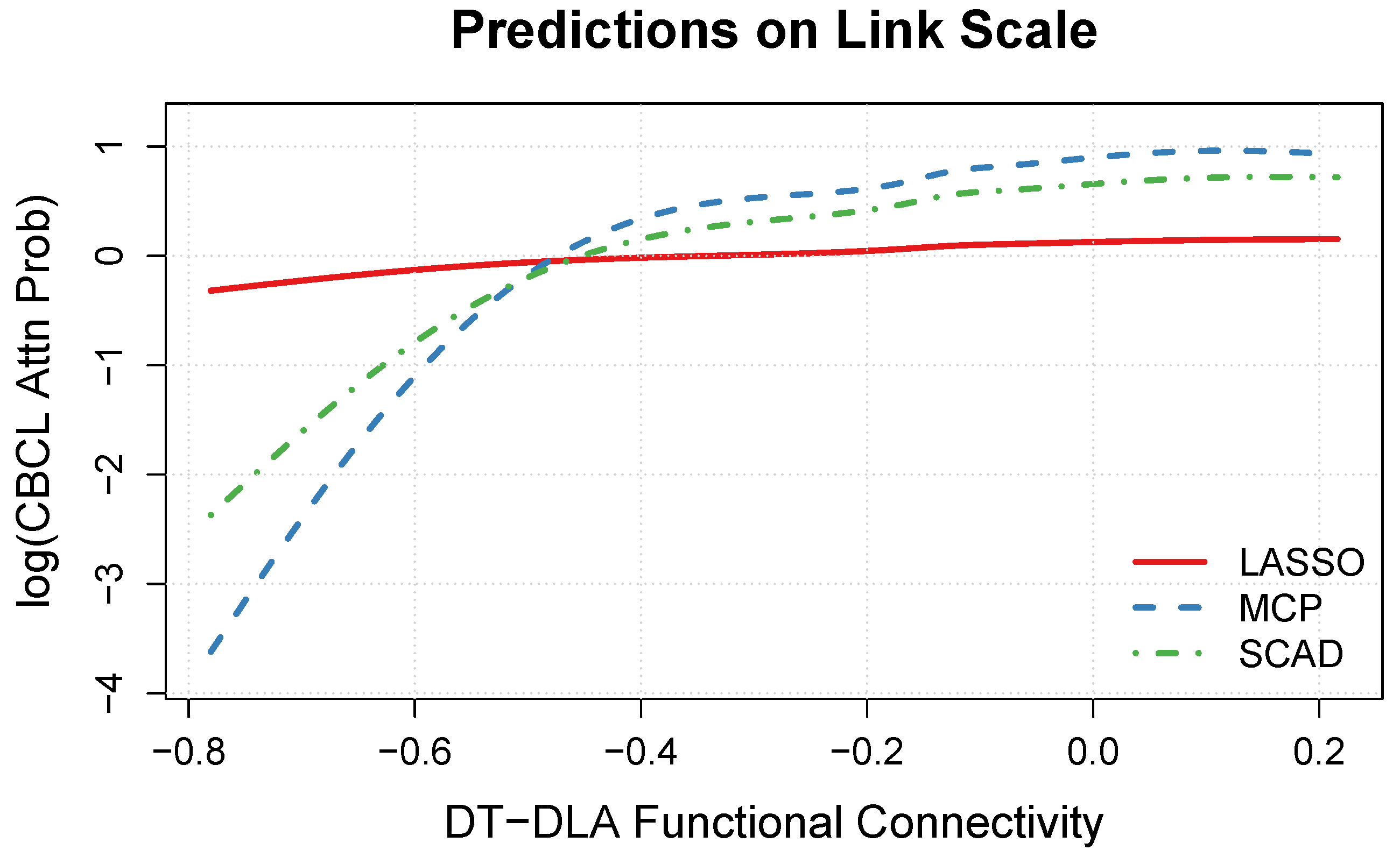
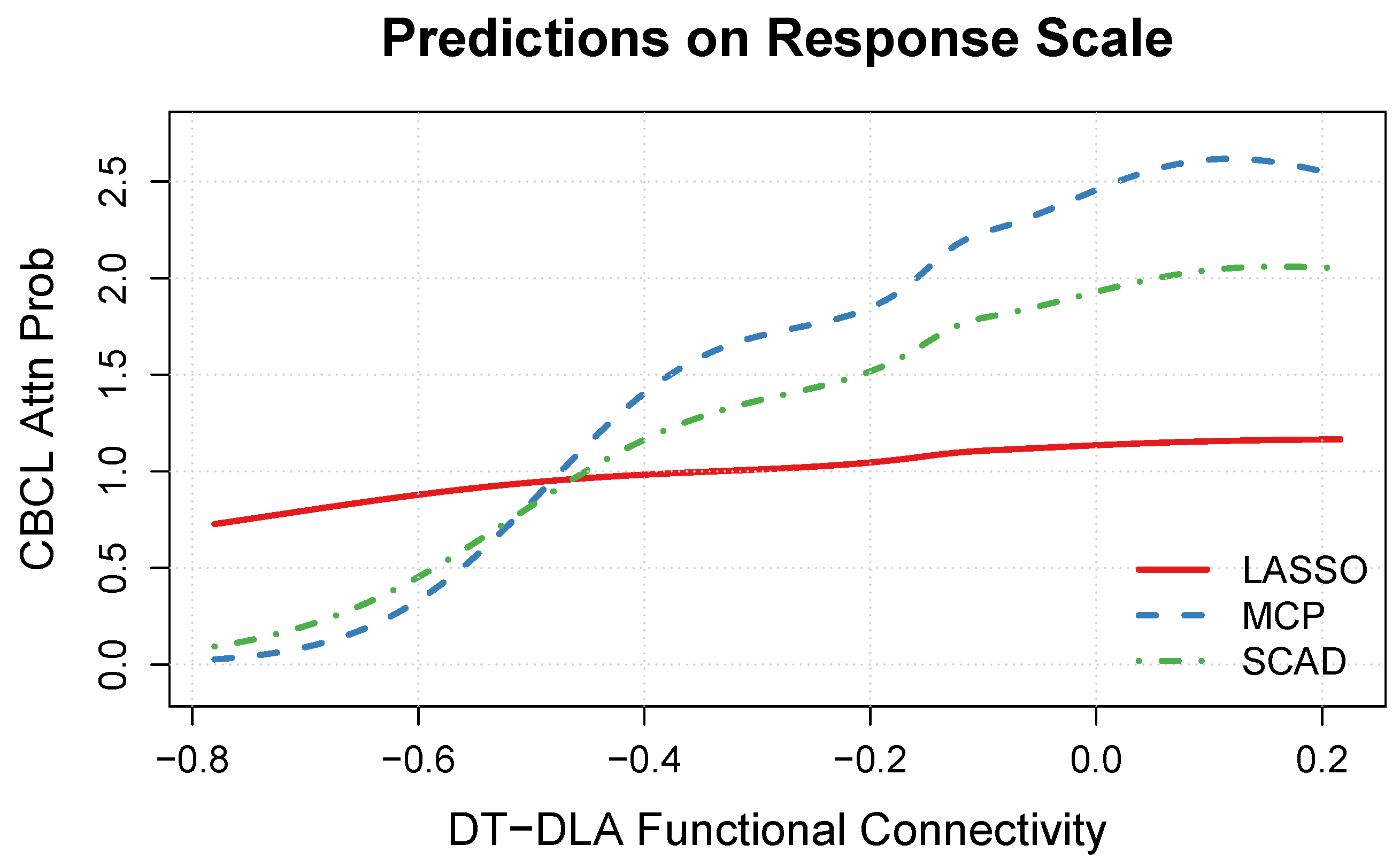
3.4. DT-DLA Functional Connectivity Effect
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Findings
4.2. Strengths, Limitations, and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Auditory network |
| CA | Cingulo-parietal network |
| CGC | Cingulo-opercular network |
| DLA | Dorsal attention network |
| DT | Default network |
| FO | Fronto-parietal network |
| RSPLTP | Retrosplenial temporal network |
| SA | Salience network |
| SMH | Somatomotor hand network |
| SMM | Somatomotor mouth network |
| VIS | Visual network |
| VTA | Ventral attention network |
| ABCD | Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development Study |
| ADHD | Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder |
| CBCL | Child Behavior Checklist |
| fMRI | Functional magnetic resonance imaging |
| LASSO | Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator |
| MAE | Mean absolute error |
| MCP | Minimax concave penalty |
| QC | Quality control |
| ROIs | Regions of interest |
| rs-FC | Resting-state functional connectivity |
| rs-fMRI | Resting-state fMRI |
| SCAD | Smoothly clipped absolute deviation |
Appendix A
References
- Scahill, L.; Schwab-Stone, M. Epidemiology of ADHD in School-Age Children. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 9, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willcutt, E.G. The Prevalence of DSM-IV Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Meta-Analytic Review. Neurotherapeutics 2012, 9, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanczyk, G.V.; Willcutt, E.G.; Salum, G.A.; Kieling, C.; Rohde, L.A. ADHD prevalence estimates across three decades: An updated systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogman, M.; Bralten, J.; Hibar, D.P.; Mennes, M.; Zwiers, M.P.; Schweren, L.S.J.; van Hulzen, K.J.E.; Medland, S.E.; Shumskaya, E.; Jahanshad, N.; et al. Subcortical brain volume differences in participants with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adults: A cross-sectional mega-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2017, 4, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubillo, A.; Halari, R.; Smith, A.; Taylor, E.; Rubia, K. A review of fronto-striatal and fronto-cortical brain abnormalities in children and adults with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and new evidence for dysfunction in adults with ADHD during motivation and attention. Cortex 2012, 48, 194–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plichta, M.M.; Scheres, A. Ventral-striatal responsiveness during reward anticipation in ADHD and its relation to trait impulsivity in the healthy population: A meta-analytic review of the fMRI literature. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 38, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posner, J.; Park, C.; Wang, Z. Connecting the Dots: A Review of Resting Connectivity MRI Studies in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2014, 24, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, B.D.; Miranda-Dominguez, O.; Mills, K.L.; Earl, E.; Cordova, M.; Painter, J.; Karalunas, S.L.; Nigg, J.T.; Fair, D.A. ADHD and attentional control: Impaired segregation of task positive and task negative brain networks. Netw. Neurosci. 2018, 2, 200–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konrad, K.; Eickhoff, S.B. Is the ADHD brain wired differently? A review on structural and functional connectivity in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2010, 31, 904–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fair, D.A.; Posner, J.; Nagel, B.J.; Bathula, D.; Dias, T.G.C.; Mills, K.L.; Blythe, M.S.; Giwa, A.; Schmitt, C.F.; Nigg, J.T. Atypical Default Network Connectivity in Youth with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 68, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, C.; He, Y.; Zang, Y.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, Y. Altered small-world brain functional networks in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Sun, J.; Yu, G.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liang, M.; Liu, X. Global and local brain network reorganization in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Brain Imaging Behav. 2014, 8, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, H.; Chang, Z.; D’Onofrio, B.M.; Lichtenstein, P. The heritability of clinically diagnosed attention deficit hyperactivity disorder across the lifespan. Psychol. Med. 2014, 44, 2223–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, A.E.; Ford, T.; Williams, R.; Russell, G. The Association between Socioeconomic Disadvantage and Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): A Systematic Review. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2016, 47, 440–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopik, V.S.; Sparrow, E.P.; Madden, P.A.F.; Bucholz, K.K.; Hudziak, J.J.; Reich, W.; Slutske, W.S.; Grant, J.D.; McLaughlin, T.L.; Todorov, A.; et al. Contributions of parental alcoholism, prenatal substance exposure, and genetic transmission to child ADHD risk: A female twin study. Psychol. Med. 2005, 35, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, D.B.; Moss, H.B.; Kirisci, L.; Mezzich, A.C.; Miles, R.; Ott, P. Psychopathology in Preadolescent Sons of Fathers With Substance Use Disorders. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 1997, 36, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronis, A.M.; Lahey, B.B.; Pelham, W.E.; Kipp, H.L.; Baumann, B.L.; Lee, S.S. Psychopathology and Substance Abuse in Parents of Young Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2003, 42, 1424–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahey, B.B.; Piacentini, J.C.; McBurnett, K.; Stone, P.; Hartdaghn, S.; Hynd, G. Psychopathology in the Parents of Children with Conduct Disorder and Hyperactivity. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 1988, 27, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luman, M.; Tripp, G.; Scheres, A. Identifying the neurobiology of altered reinforcement sensitivity in ADHD: A review and research agenda. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, M.; Grant, S.J.; London, E.D.; Contoreggi, C.S.; Kimes, A.S.; Spurgeon, L. Decision Making in Adolescents with Behavior Disorders and Adults with Substance Abuse. Am. J. Psychiatry 2003, 160, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawe, S.; Loxton, N.J. The role of impulsivity in the development of substance use and eating disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2004, 28, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigg, J.T.; Wong, M.M.; Martel, M.M.; Jester, J.M.; Puttler, L.I.; Glass, J.M.; Adams, K.M.; Fitzgerald, H.E.; Zucker, R.A. Poor Response Inhibition as a Predictor of Problem Drinking and Illicit Drug Use in Adolescents at Risk for Alcoholism and Other Substance Use Disorders. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2006, 45, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanraud, S.; Pitel, A.L.; Pfefferbaum, A.; Sullivan, E.V. Disruption of Functional Connectivity of the Default-Mode Network in Alcoholism. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 2272–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, N.; Liu, Y.; Fu, X.M.; Li, N.; Wang, C.X.; Zhang, H.; Qian, R.B.; Xu, H.S.; Hu, X.; Zhang, D.R. Abnormal Brain Default-Mode Network Functional Connectivity in Drug Addicts. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos, F.X.; Aoki, Y. Intrinsic functional connectivity in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A science in development. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2016, 1, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, C.Z.; Zang, Y.F.; Cao, Q.J.; Yan, C.G.; He, Y.; Jiang, T.Z.; Sui, M.Q.; Wang, Y.F. Fisher discriminative analysis of resting-state brain function for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. NeuroImage 2008, 40, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulini, A.A.; Kerr, W.T.; Loo, S.K.; Lenartowicz, A. Classification Accuracy of Neuroimaging Biomarkers in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Effects of Sample Size and Circular Analysis. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2019, 4, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The ADHD-200 Consortium. The ADHD-200 Consortium: A model to advance the translational potential of neuroimaging in clinical neuroscience. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The ADHD-200 Consortium. Results of the ADHD-200 Competition. 2012. Available online: https://fcon_1000.projects.nitrc.org/indi/adhd200/ (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Eloyan, A.; Muschelli, J.; Nebel, M.B.; Liu, H.; Han, F.; Zhao, T.; Barber, A.D.; Joel, S.; Pekar, J.J.; Mostofsky, S.H.; et al. Automated diagnoses of attention deficit hyperactive disorder using magnetic resonance imaging. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.R.G.; Sidhu, G.S.; Greiner, R.; Asgarian, N.; Bastani, M.; Silverstone, P.H.; Greenshaw, A.J.; Dursun, S.M. ADHD-200 Global Competition: Diagnosing ADHD using personal characteristic data can outperform resting state fMRI measurements. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang-James, Y.; Helminen, E.C.; Liu, J.; Franke, B.; Hoogman, M.; Faraone, S.V.; The ENIGMA-ADHD Working Group. Evidence for similar structural brain anomalies in youth and adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A machine learning analysis. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogman, M.; Muetzel, R.; Guimaraes, J.P.; Shumskaya, E.; Mennes, M.; Zwiers, M.P.; Jahanshad, N.; Sudre, G.; Wolfers, T.; Earl, E.A.; et al. Brain Imaging of the Cortex in ADHD: A Coordinated Analysis of Large-Scale Clinical and Population-Based Samples. Am. J. Psychiatry 2019, 176, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Shuai, D.; Bu, X.; Hu, X.; Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Hu, X.; Lu, L.; Gong, Q.; et al. Impairments of large-scale functional networks in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A meta-analysis of resting-state functional connectivity. Psychol. Med. 2019, 49, 2475–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutcubasi, B.; Metin, B.; Kurban, M.K.; Metin, Z.E.; Beser, B.; Sonuga-Barke, E. Resting-state network dysconnectivity in ADHD: A system-neuroscience-based meta-analysis. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 21, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortese, S.; Aoki, Y.Y.; Itahashi, T.; Castellanos, F.X.; Eickhoff, S.B. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis: Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2021, 60, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Sanchez, V.; Castellanos, F.X. Neuroimaging in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2021, 34, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, M.M.; Allgaier, N.; Hahn, S.; Yuan, D.; Albaugh, M.; Adise, S.; Chaarani, B.; Ortigara, J.; Juliano, A.; Potter, A.; et al. Multimethod investigation of the neurobiological basis of ADHD symptomatology in children aged 9-10: Baseline data from the ABCD study. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Hastie, T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 2005, 67, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helwig, N.E. Versatile descent algorithms for group regularization and variable selection in generalized linear models. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, L.J.; Sudre, G.; Price, J.; Shastri, G.G.; Shaw, P. Evidence from “big data” for the default-mode hypothesis of ADHD: A mega-analysis of multiple large samples. Neuropsychopharmacology 2023, 48, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, E.M.; Laumann, T.O.; Adeyemo, B.; Huckins, J.F.; Kelley, W.M.; Petersen, S.E. Generation and Evaluation of a Cortical Area Parcellation from Resting-State Correlations. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 26, 288–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.; Wang, J.; He, Y. BrainNet Viewer: A Network Visualization Tool for Human Brain Connectomics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, B.; Cannonier, T.; Conley, M.I.; Cohen, A.O.; Barch, D.M.; Heitzeg, M.M.; Soules, M.E.; Teslovich, T.; Dellarco, D.V.; Garavan, H.; et al. The Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study: Imaging acquisition across 21 sites. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2018, 32, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagler, D.J.; Hatton, S.; Cornejo, M.D.; Makowski, C.; Fair, D.A.; Dick, A.S.; Sutherland, M.T.; Casey, B.; Barch, D.M.; Harms, M.P.; et al. Image processing and analysis methods for the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development Study. NeuroImage 2019, 202, 116091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biederman, J.; Faraone, S.V.; Doyle, A.; Lehman, B.K.; Kraus, I.; Perrin, J.; Tsuang, M.T. Convergence of the Child Behavior Checklist with Structured Interview-based Psychiatric Diagnoses of ADHD Children with and without Comorbidity. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 1993, 34, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Tsai, P.S. Diagnostic Accuracy of Rating Scales for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20152749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, W.K.; Barch, D.M.; Bjork, J.M.; Gonzalez, R.; Nagel, B.J.; Nixon, S.J.; Luciana, M. The structure of cognition in 9 and 10 year-old children and associations with problem behaviors: Findings from the ABCD study’s baseline neurocognitive battery. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2019, 36, 100606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helwig, N.E. Precise tensor product smoothing via spectral splines. Stats 2024, 7, 34–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helwig, N.E. grpnet: Group Elastic Net Regularized GLMs and GAMs, R package version 0.3; 2024. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/grpnet/index.html (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization Paths for Generalized Linear Models via Coordinate Descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helwig, N.E. Spectrally sparse nonparametric regression via elastic net regularized smoothers. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2021, 30, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression Shrinkage and Selection Via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Li, R. Variable Selection via Nonconcave Penalized Likelihood and its Oracle Properties. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2001, 96, 1348–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.H. Nearly unbiased variable selection under minimax concave penalty. Ann. Stat. 2010, 38, 894–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Yu, B. On Model Selection Consistency of Lasso. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2006, 7, 2541–2563. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, N.; Xu, Q.S. Multi-step adaptive elastic-net: Reducing false positives in high-dimensional variable selection. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2015, 85, 3755–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helwig, N.E. Multiple and Generalized Nonparametric Regression. In SAGE Research Methods Foundations; Atkinson, P., Delamont, S., Cernat, A., Sakshaug, J.W., Williams, R.A., Eds.; SAGE: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinshausen, N.; Bühlmann, P. High-dimensional graphs and variable selection with the Lasso. Ann. Stat. 2006, 34, 1436–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek, S.; Tervo-Clemmens, B.; Nielsen, A.N.; Wheelock, M.D.; Miller, R.L.; Laumann, T.O.; Earl, E.; Foran, W.W.; Cordova, M.; Doyle, O.; et al. Identifying reproducible individual differences in childhood functional brain networks: An ABCD study. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2019, 40, 100706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markon, K.E.; Chmielewski, M.; Miller, C.J. The reliability and validity of discrete and continuous measures of psychopathology: A quantitative review. Psychol. Bull. 2011, 137, 856–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, H.; Anckarsater, H.; Råstam, M.; Chang, Z.; Lichtenstein, P. Childhood attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder as an extreme of a continuous trait: A quantitative genetic study of 8,500 twin pairs: ADHD as an extreme of a continuous trait. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2012, 53, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salum, G.A.; Sonuga-Barke, E.; Sergeant, J.; Vandekerckhove, J.; Gadelha, A.; Moriyama, T.S.; Graeff-Martins, A.S.; Manfro, G.G.; Polanczyk, G.; Rohde, L.A.P. Mechanisms underpinning inattention and hyperactivity: Neurocognitive support for ADHD dimensionality. Psychol. Med. 2014, 44, 3189–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordova, M.M.; Antovich, D.M.; Ryabinin, P.; Neighbor, C.; Mooney, M.A.; Dieckmann, N.F.; Miranda-Dominguez, O.; Nagel, B.J.; Fair, D.A.; Nigg, J.T. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Restricted Phenotypes Prevalence, Comorbidity, and Polygenic Risk Sensitivity in the ABCD Baseline Cohort. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2022, 61, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, J.D.; Barnes, K.A.; Snyder, A.Z.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Petersen, S.E. Spurious but systematic correlations in functional connectivity MRI networks arise from subject motion. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 2142–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couvy-Duchesne, B.; Ebejer, J.L.; Gillespie, N.A.; Duffy, D.L.; Hickie, I.B.; Thompson, P.M.; Martin, N.G.; de Zubicaray, G.I.; McMahon, K.L.; Medland, S.E.; et al. Head motion and inattention/hyperactivity share common genetic influences: Implications for fMRI studies of ADHD. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146271. [Google Scholar]

| Variable | Factor Levels | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 49.994 |
| Female | 50.006 | |
| Race/Ethnicity | White | 56.937 |
| Black/African-American | 12.094 | |
| Native American/Alaska Native | 0.251 | |
| Asian/Pacific Islander | 1.466 | |
| Hispanic/Latino | 19.539 | |
| Multiple Races/Other | 9.713 | |
| Household Income | <50 k | 27.334 |
| 50–100 k | 28.688 | |
| >100 k | 43.978 | |
| Parental Education | HS Diploma or Less | 11.342 |
| Some College | 25.116 | |
| Bachelor’s | 26.983 | |
| Graduate | 36.559 | |
| Parental Alcohol Use | None | 85.061 |
| Father Only | 11.067 | |
| Mother Only | 2.231 | |
| Both Parents | 1.642 | |
| Parental Drug Use | None | 69.207 |
| Father Only | 8.059 | |
| Mother Only | 16.155 | |
| Both Parents | 6.580 |
| Variable | Factor Levels | LASSO | MCP | SCAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 1.15 | 1.17 | 1.18 |
| Female | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.85 | |
| Income | <50 k | 1.10 | 1.13 | 1.16 |
| 50–100 k | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| >100 k | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.87 | |
| Alcohol | None | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.98 |
| Father Only | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.99 | |
| Mother Only | 1.00 | 1.03 | 1.00 | |
| Both Parents | 1.11 | 1.19 | 1.04 | |
| Drugs | None | 0.79 | 0.76 | 0.75 |
| Father Only | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 | |
| Mother Only | 1.10 | 1.12 | 1.12 | |
| Both Parents | 1.24 | 1.27 | 1.29 |
| Site | LASSO | MCP | SCAD |
|---|---|---|---|
| site01 | 0.93 | 0.77 | 0.98 |
| site02 | 0.94 | 0.81 | 0.98 |
| site03 | 1.09 | 1.37 | 1.03 |
| site04 | 1.05 | 1.17 | 1.01 |
| site05 | 1.01 | 1.06 | 1.00 |
| site06 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.00 |
| site07 | 1.04 | 1.15 | 1.01 |
| site08 | 1.02 | 1.09 | 1.01 |
| site09 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.99 |
| site10 | 0.94 | 0.79 | 0.98 |
| site11 | 1.04 | 1.14 | 1.01 |
| site12 | 1.04 | 1.13 | 1.01 |
| site13 | 0.97 | 0.90 | 0.99 |
| site14 | 0.94 | 0.80 | 0.98 |
| site15 | 1.04 | 1.12 | 1.01 |
| site16 | 1.02 | 1.13 | 1.01 |
| site17 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 1.00 |
| site18 | 0.98 | 0.91 | 0.99 |
| site19 | 0.96 | 0.86 | 0.99 |
| site20 | 1.00 | 1.04 | 1.00 |
| site21 | 1.01 | 1.05 | 1.00 |
| site22 | 1.03 | 1.08 | 1.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duffy, K.A.; Helwig, N.E. Resting-State Functional Connectivity Predicts Attention Problems in Children: Evidence from the ABCD Study. NeuroSci 2024, 5, 445-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5040033
Duffy KA, Helwig NE. Resting-State Functional Connectivity Predicts Attention Problems in Children: Evidence from the ABCD Study. NeuroSci. 2024; 5(4):445-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5040033
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuffy, Kelly A., and Nathaniel E. Helwig. 2024. "Resting-State Functional Connectivity Predicts Attention Problems in Children: Evidence from the ABCD Study" NeuroSci 5, no. 4: 445-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5040033
APA StyleDuffy, K. A., & Helwig, N. E. (2024). Resting-State Functional Connectivity Predicts Attention Problems in Children: Evidence from the ABCD Study. NeuroSci, 5(4), 445-461. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5040033






