High-Q Terahertz Perfect Absorber Based on a Dual-Tunable InSb Cylindrical Pillar Metasurface
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structure Design
2.1. Meta-Atom Description
2.2. Material Description
2.2.1. Isotropic Response ()
2.2.2. Magnetically Biased Response ()
2.3. Numerical Implementation
3. Electromagnetic Response Analysis
3.1. Absorption Mechanism and Impedance Matching
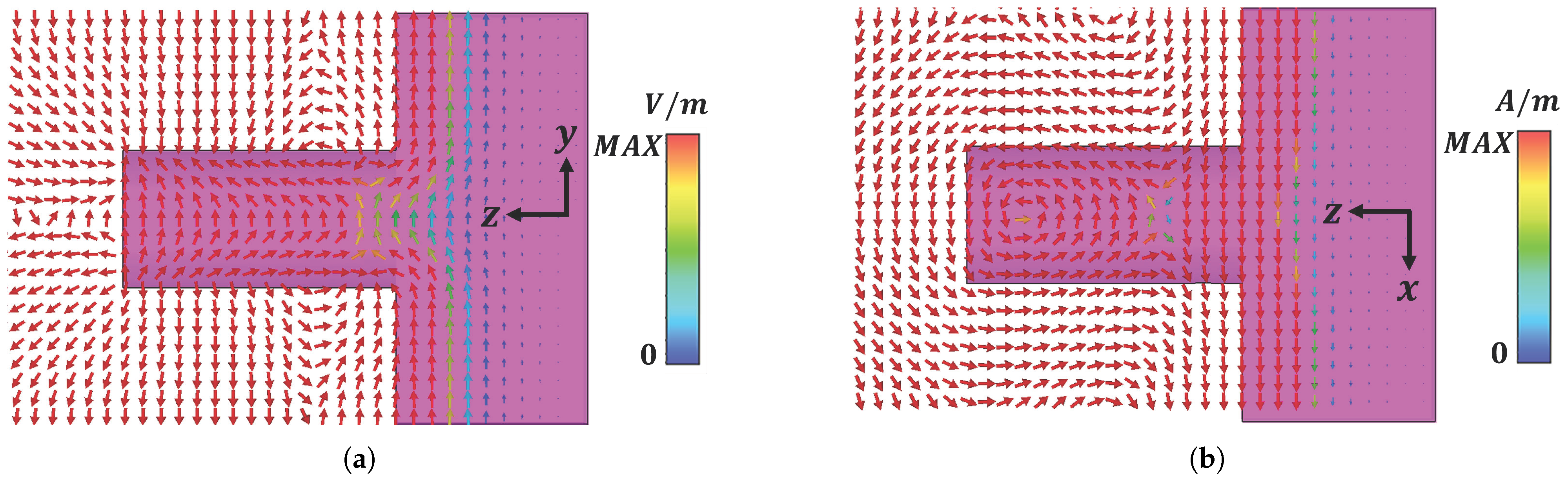
3.2. Field Distribution and Resonance Characterization
- Electric field, y–z plane—Figure 3a: The electric vector circulates around the InSb cylinder, forming a closed loop that signifies the excitation of a magnetic-dipole mode. The loop axis is oriented along , i.e., parallel to the incident magnetic field.
- Magnetic field, x–z plane—Figure 3b: A vortex-like pattern appears, characteristic of an electric-dipole resonance that is driven by the oscillating surface charges on the cylinder.
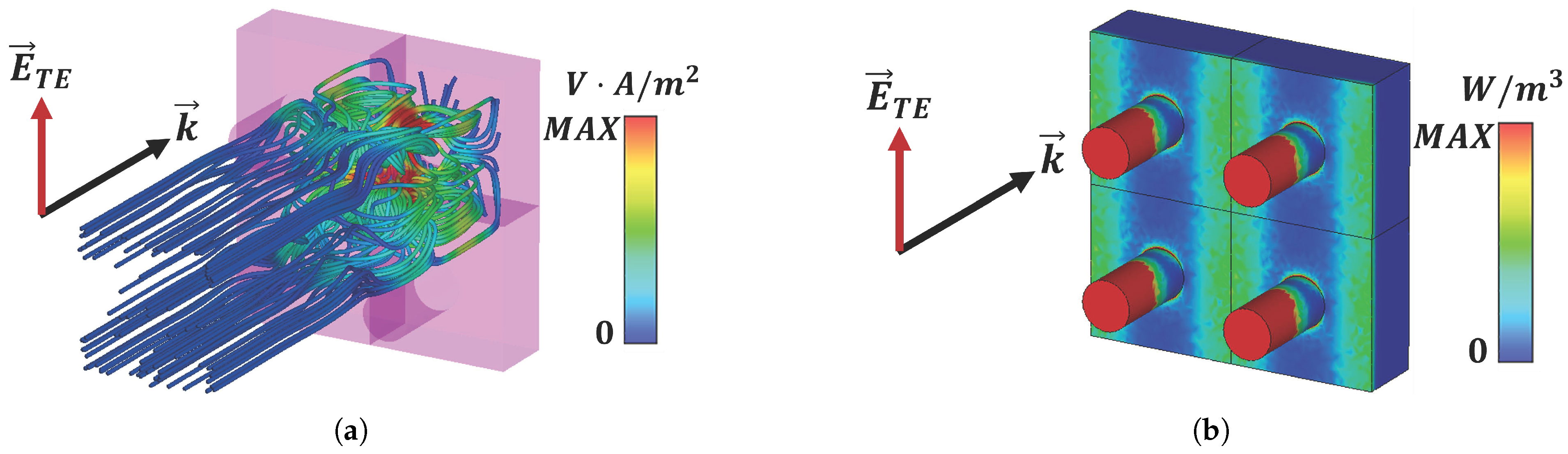
3.3. Power Flow and Loss Distribution
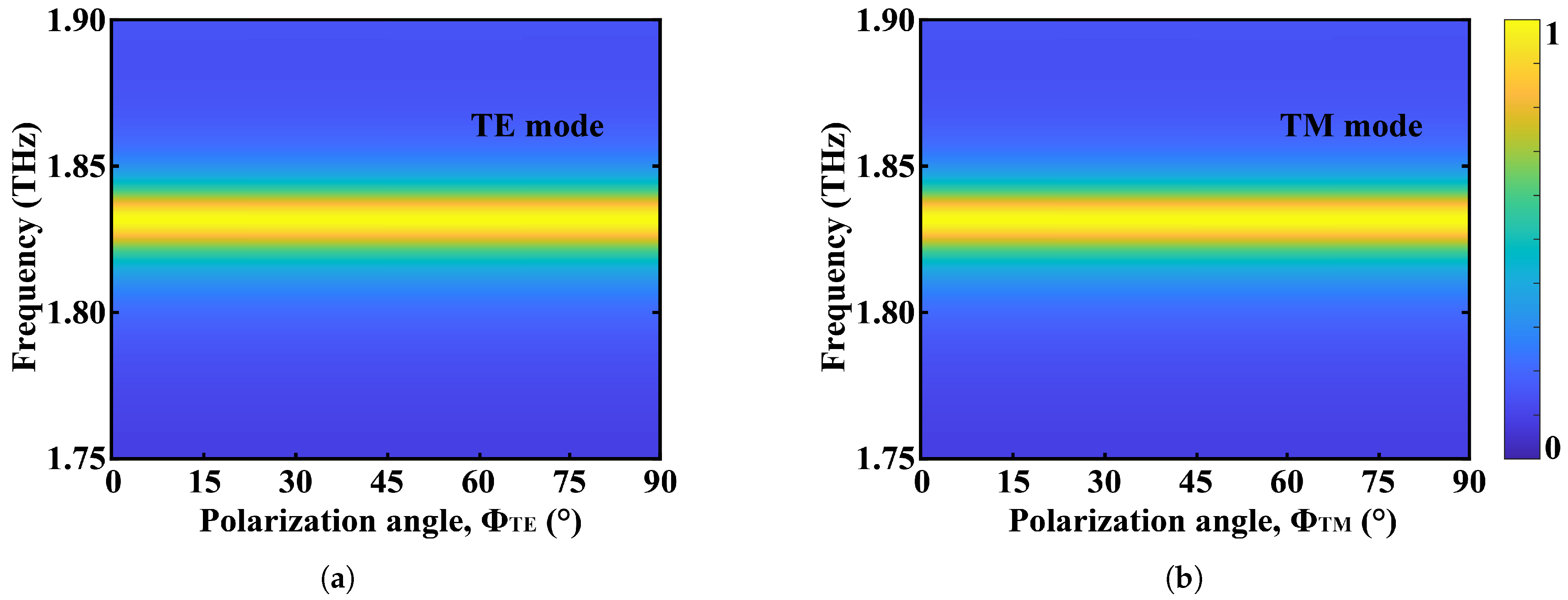
3.4. Polarization Robustness
3.5. Influence of Geometrical Parameters
- (i)
- Substrate thickness h
- (ii)
- Pillar height t
- (iii)
- Pillar radius R
- Design insight. Once the substrate is thicker than the THz skin depth, the absorber’s response is governed primarily by the aspect ratio of the InSb pillar. Varying the height t changes the inductive path length and provides a fine tuning knob: a deviation shifts the resonance by only a few GHz. However, moving away from the optimal height () also degrades the impedance match, causing the peak absorbance to drop from 100% to and broadening the linewidth.
4. Tunability and Sensitivity
4.1. Thermal Tunability
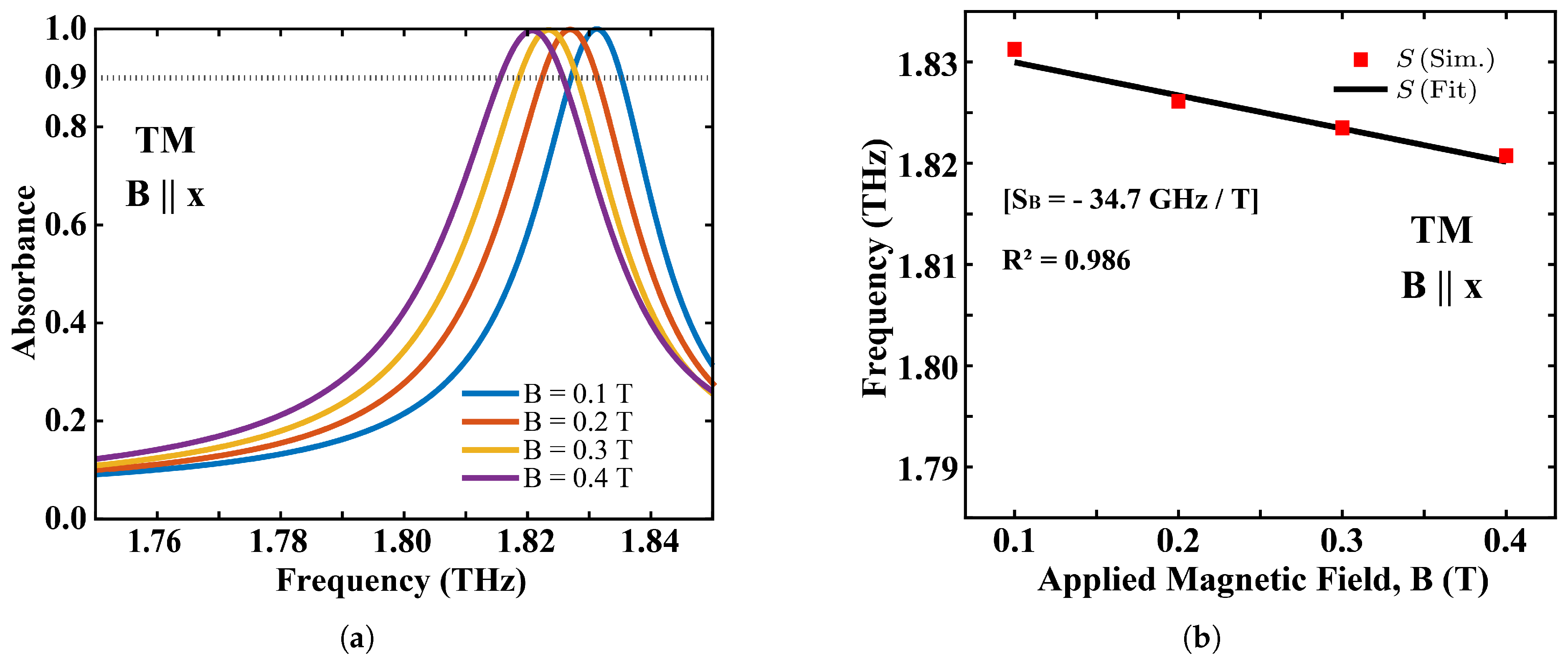
4.2. Magnetic Tunability
5. Discussion
5.1. Spectral Selectivity
5.2. Dual Linear Tunability
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- 3rd Generation Partnership Project. 5G NR; Physical Channels and Modulation (Release 17). 3GPP TS 38.211. 2022. Available online: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_ts/138200_138299/138211/17.01.00_60/ts_138211v170100p.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Rappaport, T.S.; Xing, Y.; Kanhere, O.; Ju, S.; Madanayake, A.; Mandal, S.; Alkhateeb, A.; Trichopoulos, G.C. Wireless communications and applications above 100 GHz: Opportunities and challenges for 6G and beyond. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 78729–78757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Wang, C.-X.; Huang, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Towards 6G wireless communication networks: Vision, enabling technologies, and new paradigm shifts. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2021, 64, 110301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tataria, H.; Shafi, M.; Molisch, A.F.; Dohler, M.; Sjöland, H.; Tufvesson, F. 6G wireless systems: Vision, requirements, challenges, insights, and opportunities. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 1166–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landy, N.I.; Sajuyigbe, S.; Mock, J.J.; Smith, D.R.; Padilla, W.J. Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 207402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Starr, T.; Starr, A.F.; Padilla, W.J. Infrared spatial and frequency selective metamaterial with near-unity absorbance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 207403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; He, F.; Liu, J.; Shu, F.; Fang, B.; Lang, T.; Jing, X.; Hong, Z. Ultra-high-Q resonances in terahertz all-silicon metasurfaces based on bound states in the continuum. Photonics Res. 2022, 10, 2743–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Chen, X.; Cai, G.; Zhu, J.; Liu, N.; Liu, Q.H. Electrically tunable broadband terahertz absorption with hybrid-patterned graphene metasurfaces. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charca-Benavente, R.; Kumar, R.; Rubio-Noriega, R.; Clemente-Arenas, M. Thermally tunable bi-functional metasurface based on InSb for terahertz applications. Materials 2025, 18, 2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, W.O.F.; Moncada-Villa, E.; Mejía-Salazar, J.R.; Spadoti, D.H. Dynamic terahertz beamforming based on magnetically switchable hyperbolic materials. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2024, 57, 175001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, H. Temperature tunable narrow-band terahertz metasurface absorber based on InSb micro-cylinder arrays for enhanced sensing application. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 82981–82988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Cheng, Y. Thermally tunable terahertz metasurface absorber based on all dielectric indium antimonide resonator structure. Opt. Mater. 2020, 102, 109801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Arenas, M.; Rubio-Noriega, R.E.; Urbina, J.V.; Lakhtakia, A. Non-metallic magnetostatically tunable metasurface absorber for terahertz waves. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2024, 41, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wei, R.; Taplin, J.; Zhang, W. Terahertz metasurfaces exploiting the phase transition of vanadium dioxide. Materials 2023, 16, 7106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Feng, L.; Li, Z.; Bai, J.; Wang, S.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Yao, W. A review of the preparation, properties and applications of VO2 thin films with the reversible phase transition. Front. Mater. 2024, 11, 1341518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, A.D.; Gao, X.; Du, J.; Han, Z.; Seo, D.H.; Cooper, J.S.; Murdock, A.T.; Lam, S.K.H.; Zhang, T.; van der Laan, T. Electrically tuneable terahertz metasurface enabled by a graphene/gold bilayer structure. Commun. Mater. 2022, 3, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Guo, C.; Xu, W.; Liu, K.; Yuan, X.; Qin, S. Broadband terahertz absorber based on multi-band continuous plasmon resonances in geometrically gradient dielectric-loaded graphene plasmon structure. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Cao, W.; He, X. Hybrid plasmonic waveguides with tunable ENZ phenomenon supported by 3D Dirac semimetals. Laser Photonics Rev. 2024, 18, 2400167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cao, W.; He, X. 3D Dirac semimetal elliptical fiber supported THz tunable hybrid plasmonic waveguides. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2023, 29, 8400207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wu, L.; Tao, J. Research progress on two-photon 3D printed metasurface optical devices. Study Opt. Commun. 2023, 49, 11–31. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Kuang, D.; Fan, F.; Chang, S.; Lin, L. Subwavelength B-shaped metallic hole array terahertz filter with InSb bar as thermally tunable structure. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 7098–7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ren, G.; Gao, Y.; Lian, Y.; Qi, Y.; Jian, S. Tunable subwavelength terahertz plasmon-induced transparency in the InSb slot waveguide side-coupled with two stub resonators. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 3918–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moridsadat, M.; Golmohammadi, S.; Baghban, H. Tunable multiband plasmonic response of indium antimonide touching microrings in the terahertz range. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 4368–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oszwałldowski, M.; Zimpel, M. Temperature dependence of intrinsic carrier concentration and density of states effective mass of heavy holes in InSb. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1988, 49, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W.; Han, J. Terahertz surface magnetoplasmons modulation with magnetized InSb hole array sheet. Opt. Commun. 2019, 446, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lakhtakia, A.; Tian, Z.; Lu, X.; Zhang, W. Magnetic and magnetothermal tunabilities of subwavelength-hole arrays in a semiconductor sheet. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 1465–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Sultana, J.; Biabanifard, M.; Vafapour, Z.; Nine, M.J.; Dinovitser, A.; Cordeiro, C.M.B.; Ng, B.W.-H.; Abbott, D. Tunable localized surface plasmon graphene metasurface for multiband superabsorption and terahertz sensing. Carbon 2020, 158, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Ma, W.; Wu, T.; Li, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Duan, J.; Li, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, W.; Gao, Y.; et al. Metasurface terahertz perfect absorber with strong multi-frequency selectivity. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 36712–36727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K. Multi-band terahertz resonant absorption based on an all-dielectric grating metasurface for chlorpyrifos sensing. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 13563–13575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, D.; Belling, S.W.; Cheng, H.; Kats, M.A.; Fan, S.; Povinelli, M.L.; Yu, Z. Inverse design of metasurfaces based on coupled-mode theory and adjoint optimization. ACS Photonics 2021, 8, 2265–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, R.; Ouyang, Z. Terahertz absorber with dynamically switchable dual-broadband based on a hybrid metamaterial with vanadium dioxide and graphene. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 20839–20850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozar, D.M. Microstrip antennas. Proc. IEEE 2002, 80, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lang, T.; Zhu, F. High-sensitivity temperature sensor based on the perfect metamaterial absorber in the terahertz band. Photonics 2023, 10, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, Y.-F.C.; Chao, C.-T.C.; Huang, H.J.; Anwar, U.; Lim, C.M.; Voo, N.Y.; Mahadi, A.H.; Kumara, N.T.R.N.; Chiang, H.-P. Plasmonic perfect absorber based on metal nanorod arrays connected with veins. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Cheng, Z. Terahertz perfect absorber based on InSb metasurface for both temperature and refractive index sensing. Opt. Mater. 2021, 117, 111129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Lakhtakia, A.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Jain, P.K. Magnetically tunable metasurface comprising InAs and InSb pixels for absorbing terahertz radiation. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 9673–9680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, P.; Singh, R.K.; Mitharwal, R. A highly sensitive terahertz temperature sensor based on polarization insensitive perfect metamaterial absorber with tunable characteristics. Opt. Mater. 2024, 148, 114940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| T (K) | (GHz) | (GHz) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 295 | 0.999 | 1832 | 8.3 |
| 300 | 0.997 | 1849 | 7.0 |
| 305 | 0.992 | 1864 | 5.0 |
| 310 | 0.984 | 1875 | 4.0 |
| 315 | 0.983 | 1888 | 3.3 |
| B (T) | (GHz) | (GHz) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.999 | 1830 | 8.5 |
| 0.2 | 0.999 | 1820 | 10.0 |
| 0.3 | 0.997 | 1808 | 11.8 |
| 0.4 | 0.997 | 1790 | 14.8 |
| Reference | Resonator/Tuning Method | (THz) | Peak A (%) | Q | (GHz/K) | (GHz/T) | Pol. Indep. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This work | InSb cylindrical pillar/B and T tuning | 1.832 | ≈100 | 72.3 | 2.8 | 132.7 | Yes |
| Luo & Cheng 2020 [12] | InSb star-shaped/T tuning | 1.430 | 99.9 | 26.9 | 9.6 | — | Yes |
| Cheng et al., 2021 [35] | InSb micro-rod/T tuning | 1.757 | 99.9 | 53.2 | 4.2 | — | Yes |
| Sharma et al., 2020 [36] | Pixelated InAs/InSb/B tuning | 2–4 | 95–99 | — | — | 300 | — |
| Binda et al., 2024 [37] | Curved InSb microstrip/T tuning | 1.846 | 99.9 | — | 16.1 | — | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Charca-Benavente, R.; Lezama-Calvo, J.; Clemente-Arenas, M. High-Q Terahertz Perfect Absorber Based on a Dual-Tunable InSb Cylindrical Pillar Metasurface. Telecom 2025, 6, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6030070
Charca-Benavente R, Lezama-Calvo J, Clemente-Arenas M. High-Q Terahertz Perfect Absorber Based on a Dual-Tunable InSb Cylindrical Pillar Metasurface. Telecom. 2025; 6(3):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6030070
Chicago/Turabian StyleCharca-Benavente, Rafael, Jinmi Lezama-Calvo, and Mark Clemente-Arenas. 2025. "High-Q Terahertz Perfect Absorber Based on a Dual-Tunable InSb Cylindrical Pillar Metasurface" Telecom 6, no. 3: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6030070
APA StyleCharca-Benavente, R., Lezama-Calvo, J., & Clemente-Arenas, M. (2025). High-Q Terahertz Perfect Absorber Based on a Dual-Tunable InSb Cylindrical Pillar Metasurface. Telecom, 6(3), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6030070







