Abstract
Leptin, an adipocyte-derived hormone, plays a central role in the regulation of energy homeostasis by acting on distinct hypothalamic nuclei. This review explores recent advances in our understanding of leptin’s region-specific actions within the arcuate nucleus, ventromedial hypothalamus, dorsomedial hypothalamus, and lateral hypothalamus, highlighting their contributions to appetite regulation, energy expenditure, and neuroendocrine function. In the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus, leptin’s differential regulation of pro-opiomelanocortin and agouti-related peptide/neuropeptide Y neurons is now complemented by the identification of novel leptin-responsive neuronal populations—such as those expressing prepronociceptin, basonuclin 2, and Pirt—as well as a growing array of cellular and molecular modulators, including secreted factors like angiopoietin-like growth factor, zinc-α2-glycoprotein, and spexin, intracellular regulators such as Rap1, growth factor receptor-bound protein 10, and spliced X-box binding protein 1. In the ventromedial hypothalamus, leptin integrates with both peripheral (e.g., cholecystokinin) and central (e.g., pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide) signals, while epigenetic mechanisms, such as those mediated by Jumonji domain-containing protein D3, regulate leptin receptor expression and sensitivity. The dorsomedial hypothalamus is increasingly recognized for coordinating leptin’s effects on metabolism, circadian rhythms, and respiration through distinct neuronal populations, including a subset of neurons co-expressing GLP-1 receptors that mediate leptin’s metabolic effects. In the lateral hypothalamus, leptin modulates reward-driven feeding via GABAergic neuronal populations—circuits that are particularly susceptible to disruption following early life trauma. Together, these insights reveal a sophisticated neurobiological framework through which leptin orchestrates systemic physiology. Understanding the heterogeneity of leptin signaling opens new avenues for restoring leptin sensitivity and developing personalized therapeutic strategies to combat obesity and related metabolic disorders.
1. Introduction
The discovery of leptin in 1994 by Jeffrey M. Friedman’s research group, identifying it as the protein product of the ob gene—nonfunctional in ob/ob mice—sparked intense interest in the scientific community [1]. Over three decades later, leptin is recognized not only as a critical regulator of energy homeostasis but also as a key modulator of reproductive, neuroendocrine, immune, and metabolic processes (Figure 1) [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Leptin is synthesized as a 167-amino-acid polypeptide containing a 21-amino-acid N-terminal signal sequence that directs its secretion. Following translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum, the signal peptide is cleaved, yielding the mature hormone, a 146-amino-acid peptide with a molecular mass of approximately 14–16 kDa [3]. Human leptin shares 84% sequence identity with its murine counterpart and 83% with rat leptin. Crystallographic studies have revealed that leptin adopts a four-helix bundle conformation characteristic of the long-chain helical cytokine family. The hormone is encoded by the LEP gene, located on human chromosome 7q31.3 [3]. While white adipose tissue is its principal source, leptin is also expressed in several other tissues, including the placenta, ovaries, mammary epithelium, bone marrow, and lymphoid organs [2,9,10].
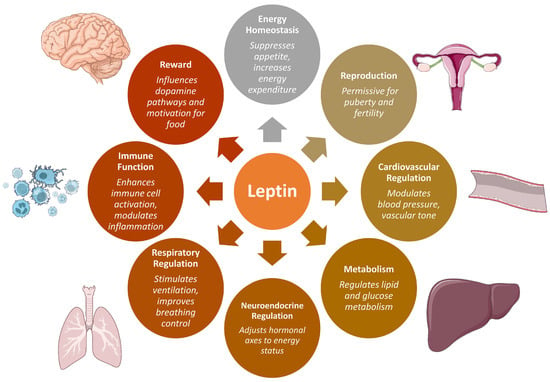
Figure 1.
Overview of the pleiotropic physiological functions of leptin. Beyond its well-established role in energy homeostasis, leptin regulates diverse processes including reproduction, cardiovascular and respiratory regulation, metabolism, immune function, neuroendocrine control, and reward-related pathways influencing feeding behavior.
Among adipose-derived hormones, leptin is one of the most extensively studied and well-characterized. It plays a fundamental role in suppressing appetite and promoting energy expenditure. Rare homozygous mutations in the leptin (LEP) or leptin receptor (LEPR) genes have been identified in humans with severe early-onset obesity, often accompanied by hyperphagia and endocrine abnormalities, while heterozygous variants may present with milder phenotypes [2,5]. Circulating leptin levels reflect total body fat mass and are dynamically regulated by changes in caloric intake [2,10,11]. In the context of diet-induced obesity—where leptin levels are chronically elevated—this feedback system often becomes disrupted, leading to a state of impaired leptin responsiveness termed leptin resistance [12,13]. This condition, characterized by a blunted ability of leptin to reduce food intake and body weight, has been well-documented in rodent models of diet-induced obesity. These models are widely used to study mechanisms underlying human obesity [12,13,14,15]. Although leptin resistance is a well-established concept, its precise molecular basis remains incompletely understood. Contributing factors include impaired transport of leptin across the blood–brain barrier and defects in intracellular signaling—referred to as cellular leptin resistance [12,13].
Leptin exerts its physiological effects through binding to leptin receptors (LepRs), which are widely distributed throughout the central nervous system (CNS) and in select peripheral tissues [2,10,11]. At least six isoforms of the leptin receptor have been identified—LepRa, LepRb, LepRc, LepRd, LepRe, and LepRf—all of which share identical extracellular domains but differ in their intracellular signaling capabilities. The long isoform, LepRb, is the principal signaling receptor and is essential for mediating leptin’s central effects (Figure 2) [16,17]. LepRb is a member of the class I cytokine receptor family and consists of three domains: an extracellular ligand-binding region, a transmembrane segment, and an intracellular domain that transduces the leptin signal. Unlike receptor tyrosine kinases, LepRb lacks intrinsic enzymatic activity and requires the non-receptor tyrosine kinase Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) for signal transduction. Upon leptin binding, JAK2 becomes activated and phosphorylates tyrosine residues on the intracellular tail of LepRb, initiating several downstream signaling cascades. The JAK2/STAT3 pathway is among the most critical for mediating leptin’s actions on energy balance and neuroendocrine regulation [17]. Other important pathways include the PI3K/Akt pathway, which modulates cellular activity through post-translational modifications, and the MAPK pathway (particularly ERK1/2), which influences neuronal excitability, feeding behavior, and thermogenesis. Leptin also engages the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway and the CREB-regulated transcription coactivator system, both of which contribute to the hormone’s metabolic and reproductive effects [17,18].
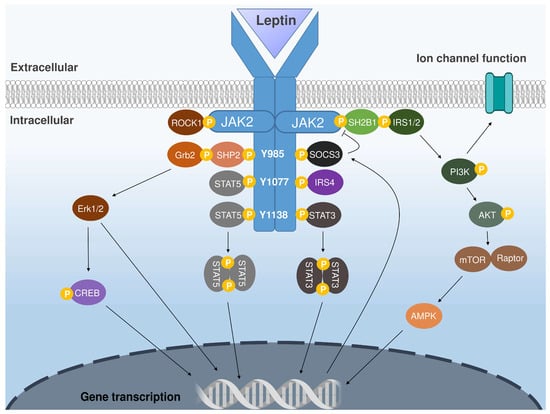
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the major intracellular signaling pathways activated by leptin binding to its receptor (LepRb). Ligand binding induces conformational changes that activate the receptor-associated Janus kinase 2, leading to phosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues (Y985, Y1077, Y1138) and recruitment of downstream signaling molecules. These pathways include the STAT3/STAT5 transcriptional cascades, the PI3K–AKT–mTOR axis, MAPK/ERK signaling, and AMPK activation, as well as modulation of ion channel activity [8,10,17,18]. Abbreviations: JAK2—Janus kinase 2; Y—tyrosine; ROCK1—Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1; Grb2—growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; SHP2—Src homology region 2-containing phosphatase-2; STAT—signal transducer and activator of transcription; CREB—cAMP response element-binding protein; SOCS3—suppressor of cytokine signaling 3; IRS—insulin receptor substrate; SH2B1—SH2B adaptor protein 1; PI3K—phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT—protein kinase B; mTOR—mechanistic target of rapamycin; Raptor—regulatory associated protein of mTOR; AMPK—AMP-activated protein kinase; ERK—extracellular signal-regulated kinase; IRS4—insulin receptor substrate 4.
Expression of LepRb is highest in the CNS, particularly in the hypothalamus—a central hub for the integration of metabolic and hormonal signals [19,20,21]. LepRb-expressing neurons are located in several functionally distinct hypothalamic regions, including the arcuate nucleus (ARC), preoptic area, supraoptic nucleus, paraventricular nucleus, ventral premammillary nucleus, ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH), dorsomedial hypothalamus (DMH), and lateral hypothalamus (LH). These interconnected regions serve as the primary sites where leptin integrates peripheral metabolic cues to coordinate feeding behavior, energy expenditure, thermoregulation, and neuroendocrine function [19,20].
This review focuses on leptin’s actions within key hypothalamic areas, emphasizing recent discoveries and emerging insights. It examines major regions involved in metabolic regulation, including the ARC, DMH, VMH, and LH, with attention to newly identified intracellular signaling pathways, novel molecular mediators with therapeutic potential, and recently characterized leptin-responsive neuronal populations (Table 1 and Table 2). By integrating region-specific effects of leptin on appetite, energy expenditure, glucose homeostasis, and broader metabolic functions, the discussion aims to provide a cohesive understanding of how this hormone coordinates metabolic control and how these insights may inform targeted therapies for obesity, type 2 diabetes, and related disorders.
This narrative review is based on a comprehensive literature search in PubMed, Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science for articles published up to May 2025 using the keywords “leptin”, “hypothalamus”, “energy homeostasis”, “obesity” and the names of specific hypothalamic nuclei. Both original research and review articles were considered, with preference for studies from the last five years, although older seminal works were included when relevant. Given the diversity of research designs and outcomes in this field, a narrative rather than systematic approach was chosen to integrate recent mechanistic insights with established knowledge.
2. The Arcuate Nucleus as a Leptin-Sensing Hub: An Emerging Player in Appetite and Energy Balance Regulation
The ARC of the hypothalamus is a critical site for leptin action (Figure 3) [2,14,21,22]. Leptin acts on two major populations of neurons in the ARC. It directly stimulates proopiomelanocortin (POMC)-expressing neurons, which produce the precursor protein POMC. POMC is cleaved into several biologically active peptides including α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), an anorexigenic neuropeptide that suppresses food intake through activation of melanocortin-3 and melanocortin-4 receptors (MC3R and MC4R). Leptin also promotes the release of the cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) from POMC neurons which further contributes to appetite suppression [11,12]. In parallel, leptin inhibits another neuronal population in the ARC—those expressing agouti-related peptide (AgRP) and neuropeptide Y (NPY), which are potent orexigenic factors. AgRP antagonizes α-MSH signaling at MC4Rs, while NPY increases food intake and decreases energy expenditure [11,12]. Ghrelin and leptin generally exert opposing effects on appetite regulation, with ghrelin activating AgRP/NPY neurons and leptin inhibiting them [13]. However, studies in Ghsr knockout mice indicate no direct modulation of leptin sensitivity by ghrelin signaling [23].
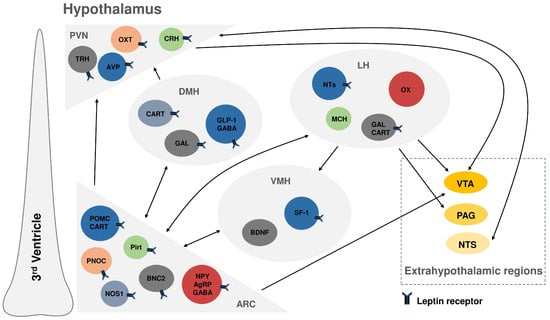
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of major leptin receptor-expressing neuronal populations within the arcuate nucleus (ARC), paraventricular nucleus (PVN), ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH), dorsomedial hypothalamus (DMH), and lateral hypothalamus (LH), along with their principal intra-hypothalamic connections and projections to extrahypothalamic regions, including the ventral tegmental area (VTA), periaqueductal gray (PAG), and nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) [2,7,10]. Abbreviations: POMC—pro-opiomelanocortin; CART—cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript; PNOC—prepronociceptin; BNC2—basonuclin 2; Pirt—phosphoinositide-interacting regulator of TRP channels; NOS1—neuronal nitric oxide synthase; NPY—neuropeptide Y; AgRP—agouti-related peptide; GABA—gamma-aminobutyric acid; OX—orexin; MCH—melanin-concentrating hormone; GAL—galanin; AVP—arginine vasopressin; OXT—oxytocin; TRH—thyrotropin-releasing hormone; CRH—corticotropin-releasing hormone; SF-1—steroidogenic factor 1; NTs—neurotensin; BDNF—brain-derived neurotrophic factor; GLP-1—glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor.
Recent discoveries have revealed greater complexity in leptin signaling within the ARC. Although earlier models suggested that leptin regulates energy balance through direct activation of POMC neurons, newer observations show that POMC neurons are heterogeneous and that leptin’s effects on energy homeostasis may be mediated indirectly. For example, leptin appears to regulate glucose metabolism via direct action on POMC neurons, while its anorexigenic effects likely involve other LepRb-expressing neuronal populations [22]. Interestingly, the effects of leptin on ARC neurons differ during early postnatal development. In neonates, leptin has a trophic role, promoting axonal outgrowth of NPY/AgRP/GABA neurons. During this stage, leptin depolarizes rather than inhibits these neurons, likely providing an orexigenic signal to support rapid growth. This excitatory action transitions to inhibitory around weaning, in parallel with the maturation of ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Thus, leptin’s developmental effects in the ARC are dynamic and age-dependent [24].
A key recent finding is the identification of a population of prepronociceptin (PNOC)-expressing neurons in the ARC as critical mediators of leptin’s regulatory effects. Loss of leptin receptor expression in ARC PNOC neurons leads to hyperphagia and obesity, while restoring LepRb expression in these neurons on a leptin receptor-null background significantly reduces body weight. These PNOC neurons regulate NPY expression and feeding behavior, identifying ARCPNOC/NPY neurons as a new therapeutic target for obesity [25]. Another novel ARC population responsive to leptin includes neurons expressing basonuclin 2 (BNC2). BNC2 neurons suppress appetite by directly inhibiting AgRP neurons. Leptin modulates their activity based on nutritional status and sensory food cues. Deletion of LepRb in BNC2 neurons causes hyperphagia and obesity, similar to that observed with AgRP neuron-specific LepRb knockout, positioning BNC2 neurons as an essential component of the appetite-regulatory circuit [26]. Leptin also acts on a distinct population of neurons in the ARC that express the phosphoinositide-interacting regulator of TRP channels (Pirt) [27,28]. These LepRbPirt neurons are functionally and molecularly distinct from other ARCLepRb populations, such as POMC and AgRP neurons, and respond to leptin via the leptin receptor. Rather than regulating feeding behavior, LepRbPirt neurons project to the median eminence and influence reproductive hormone secretion, particularly luteinizing hormone. Disrupting leptin signaling in these neurons does not affect food intake but impairs certain aspects of female reproductive function, likely through interactions with GnRH terminals or other hypothalamic targets [27]. Recent data further reveal that activation of ARCPirt neurons reduces brown adipose tissue thermogenesis, core body temperature, and oxygen consumption, indicating a role in suppressing metabolism. These results suggest that ARCPirt neurons contribute to lowering energy expenditure [28].
Recent studies have identified several intracellular and secreted factors that modulate leptin signaling in POMC neurons of the ARC, contributing to the regulation of energy homeostasis (Table 1). One such factor is angiopoietin-like growth factor (AGF), a peripheral protein also expressed in hypothalamic POMC neurons. AGF expression is upregulated by leptin via STAT3 phosphorylation and depends on intact leptin signaling pathways, suggesting that AGF may act as an anorexigenic mediator downstream of leptin in POMC neurons [29]. Another leptin-related factor, zinc-α2-glycoprotein (AZGP1), has also been shown to modulate metabolism in a POMC-specific manner. Overexpression of Azgp1 in POMC neurons under high-fat diet (HFD) conditions reduces food intake, increases energy expenditure, enhances peripheral leptin and insulin sensitivity, alleviates hepatic steatosis, and promotes adipose tissue browning. Conversely, conditional deletion of Azgp1 in POMC neurons leads to increased susceptibility to diet-induced obesity. Mechanistically, AZGP1 enhances leptin–JAK2–STAT3 signaling by interacting with acylglycerol kinase and preventing its ubiquitin-mediated degradation, thereby increasing POMC neuron excitability [30]. Additionally, recent work has identified a role for spexin, a neuropeptide implicated in energy homeostasis, in mediating hypothalamic leptin action. Leptin stimulates hypothalamic spexin expression via STAT3 signaling. Inhibition of hypothalamic spexin synthesis blocks leptin-induced reductions in food intake and body weight gain, as well as leptin-induced increases in Pomc mRNA expression [31].
Leptin sensitivity in ARC neurons is also shaped by several intracellular regulators. Ras-related protein 1 (Rap1), a small GTPase, acts as a negative modulator of leptin action. In tamoxifen-inducible, POMC-specific Rap1 knockout mice, deletion of Rap1a and Rap1b enhanced leptin sensitivity, improved glucose homeostasis, and reduced weight gain under HFD conditions. Acute Rap1 deletion in obese mice improved hyperglycemia and insulin sensitivity without causing significant weight loss, highlighting its therapeutic potential for leptin resistance and metabolic dysfunction [32]. Additionally, mTOR signaling in POMC neurons has been identified as a crucial driver of leptin resistance in diet-induced obesity. Pharmacological inhibition of mTOR with rapamycin restored leptin sensitivity, reduced fat mass, and improved metabolic parameters in diet-induced obese mice—but not in animals with defective leptin or melanocortin signaling, indicating that intact upstream and downstream components are required [33]. Another critical modulator is growth factor receptor-bound protein 10 (Grb10), an adaptor protein that interacts with insulin and leptin receptors. Grb10 overexpression reduces food intake and body weight, while its deletion promotes obesity. Mechanistically, Grb10 amplifies leptin’s excitatory effect on POMC neurons and inhibitory effect on AgRP neurons, partly through modulation of ion channel activity, identifying it as a key leptin sensitizer [34]. Finally, dysregulation of the unfolded protein response and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress have emerged as key contributors to hypothalamic leptin and insulin resistance. Activation of the inositol-requiring enzyme 1/X-box binding protein 1 (IRE1-Xbp1) pathway within AgRP neurons, specifically the expression of spliced X-box binding protein 1 (Xbp1s), has been shown to prevent and even reverse diet-induced obesity, improve insulin sensitivity, and restore leptin responsiveness. These effects occur despite continued ER stress, suggesting a pivotal role for Xbp1s in mediating adaptive responses. These observations reveal that modulation of ER stress responses in AgRP neurons offers a potential therapeutic avenue for obesity and diabetes [35].
3. Leptin Action in the Ventromedial Hypothalamus: Synergistic Hormonal Signaling and Epigenetic Regulation
The VMH is a key hypothalamic region that plays a critical role in energy homeostasis and serves as a major target for leptin action [2,14,22]. Interestingly, subchronic peripheral infusion of low-dose leptin (for 9 days) results in a transient suppression of food intake, which correlates with STAT3 activation specifically in the VMH and the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS), but not in the medial or lateral ARC or the DMH. When food intake normalizes but body weight remains suppressed, only the NTS remains activated. These results suggest that, while leptin’s initial effects on appetite are mediated by hypothalamic sites such as the VMH, long-term metabolic changes that maintain reduced adiposity are sustained by hindbrain structures like the NTS [36]. Nevertheless, evidence from longer-term studies indicates that the initial reduction in body weight is gradually lost over time [37].
Within the VMH, leptin has been shown to upregulate the expression of two anorexigenic neuropeptides: steroidogenic factor-1 and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) (Figure 3) [2,38]. Recent studies have demonstrated that astrocytic BDNF signaling in the VMH modulates neuronal activity in response to changes in energy status, primarily through the truncated TrkB.T1 receptor. During fasting or upon central BDNF depletion, enhanced astrocytic glutamate clearance reduces excitatory neurotransmission and lowers neuronal activity. Moreover, selective deletion of TrkB.T1 in VMH astrocytes blunts the neuronal response to energy status, leptin, glucose, and lipids. These effects are mediated by increased astrocyte coverage of excitatory synapses, enhanced glutamate reuptake, and consequent suppression of neuronal excitability. These findings underscore the role of the BDNF/TrkB.T1 signaling in VMH astrocytes as a critical mechanism for maintaining energy and glucose homeostasis [39].
In addition to its independent anorexigenic effects, leptin in the VMH has been shown to facilitate the satiety-inducing actions of cholecystokinin (CCK), a gut-derived hormone. Experimental data indicate that a basal level of VMH leptin receptor activation is required for the full satiety response to CCK, particularly in animals consuming high-fat diets. Disruption of leptin signaling in the VMH abolishes CCK-induced hypophagia, whereas intact leptin signaling enhances the response. These observations highlight a synergistic interaction between central leptin and peripheral CCK pathways, suggesting that VMH leptin receptors are critical for integrating hormonal cues involved in short- and long-term energy regulation [40]. Recent evidence also implicates pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) in leptin-like functions within the VMH. PACAP reduces food intake and modulates energy metabolism in a manner that mirrors leptin’s effects. Notably, PACAP administration into the VMH induces STAT3 phosphorylation and upregulates SOCS3 mRNA expression—both of which are classic markers of leptin receptor activation. Furthermore, both leptin and PACAP increase BDNF mRNA levels in the VMH. Blockade of PACAP receptors completely abolishes the behavioral and molecular effects of leptin injections into this region. Electrophysiological studies further confirm that leptin’s actions on VMH neurons are dependent on intact PACAP signaling. These results suggest that leptin and PACAP may share a convergent signaling cascade in the VMH, allowing for the integration of systemic hormonal cues with centrally released neuropeptides [41].
Epigenetic mechanisms have gained attention in understanding obesity and metabolic syndrome, yet the interaction between obesogenic diets and the epigenetic reprogramming of hypothalamic circuits governing leptin action remains poorly understood. It has been shown that Jumonji D3 (JMJD3)—a histone lysine demethylase containing a Jmjc domain—is a key epigenetic regulator of leptin signaling [42]. In HFD-fed obese mice, JMJD3 expression is significantly reduced in the VMH compared to chow-fed controls. Overexpression of JMJD3 in the VMH via lentiviral delivery (LV-CMV-JMJD3) leads to reduced body weight, fat mass, blood glucose, insulin levels, and food intake. These changes are accompanied by enhanced leptin sensitivity, as evidenced by elevated pSTAT3 levels, suggesting that JMJD3 promotes leptin signaling. Mechanistically, JMJD3 overexpression results in demethylation of the repressive histone mark H3K27me3 at the LepRb promoter in the VMH, leading to increased LepRb mRNA expression. These findings reveal that JMJD3 enhances leptin signaling by epigenetically upregulating LepRb, positioning JMJD3 as a critical mediator in hypothalamic leptin responsiveness. Targeting JMJD3 in the VMH may represent a promising therapeutic strategy to reverse leptin resistance in obesity [42].

Table 1.
Modulators of leptin signaling: sites and mechanisms of action.
Table 1.
Modulators of leptin signaling: sites and mechanisms of action.
| Modulator | Site of Action | Mechanism | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Angiopoietin-like growth factor (AGF) | ARC (POMC neurons) | A peripheral promoter of energy expenditure that counteracts obesity. Leptin induces AGF expression via STAT3 phosphorylation. | [29] |
| Zinc-α2-glycoprotein | ARC (POMC neurons) | Increases energy expenditure, improves leptin and insulin sensitivity, alleviates hepatic steatosis, and promotes adipose browning. | [30] |
| Spexin | ARC (POMC neurons) | Leptin induces spexin expression, and inhibition of hypothalamic spexin blocks leptin’s effects on food intake, body weight, and Pomc expression. | [31] |
| Ras-related protein 1 (Rap1) | ARC (POMC neurons) | POMC-specific Rap1 deletion enhances leptin sensitivity, improves glucose homeostasis, and reduces weight gain under high-fat diet. | [32] |
| Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) | ARC (POMC neurons) | mTOR signaling in POMC neurons drives leptin resistance in diet-induced obesity. Inhibition with rapamycin restores leptin sensitivity, reduces fat mass, and improves metabolism. | [33] |
| Growth factor receptor-bound protein 10 (Grb10) | ARC (POMC/AgRP neurons) | Overexpression of Grb10 reduces food intake and body weight by enhancing leptin’s excitatory effect on POMC neurons and inhibitory effect on AgRP neurons, while its deletion promotes obesity. | [34] |
| Spliced X-box binding protein 1 | ARC (AgRP neurons) | Prevents diet-induced obesity and enhances leptin sensitivity. | [35] |
| Jumonji D3 (JMJD3), a histone lysine demethylase containing a Jmjc domain | VMH neurons | Enhances leptin signaling by demethylating H3K27me3 at the LepRb promoter, increasing LepRb expression. Overexpression of JMJD3 in obese mice reduces body weight, fat mass, food intake, and glucose levels. | [42] |
4. The Dorsomedial Hypothalamus: Integrating Leptin’s Roles in Metabolism, Circadian Rhythms, and Respiratory Control
The DMH is a critical site for the integration of thermoregulatory, metabolic, and circadian signals. Neurons in this region that express LepRb have emerged as key players in these physiological processes [2,43,44,45].
Recent evidence indicates that DMHLepR neurons comprise both glutamatergic and GABAergic subpopulations, each projecting to distinct brain regions. Interestingly, selective activation of either subpopulation can increase energy expenditure, yet only leptin receptor activation yields broader beneficial metabolic effects, suggesting a unique and integrative role of these neurons in leptin-mediated metabolic regulation [46]. A conserved population of GABAergic LepRb neurons that also express GLP-1 receptors (LepRbGlp1r) is enriched in the DMH and plays a central role in regulating food intake and body weight (Figure 3) [47]. Experimental ablation of Lepr in LepRbGlp1r neurons induces hyperphagic obesity without affecting energy expenditure. Conversely, reactivation of Lepr in GABAergic Glp1r-expressing neurons in otherwise Lepr-null mice largely normalizes energy balance. Furthermore, restoring Glp1r expression in LepRbGlp1r neurons in Glp1r-null mice reinstates the anorexigenic response to liraglutide, a GLP-1R agonist. These results underscore the critical role of this GABAergic LepRbGlp1r neuronal population in mediating the anorexigenic effects of both leptin and GLP-1R agonists [47]. Moreover, the existence of LepRbGlp1r neurons in the DMH of nonhuman primates indicates potential translational relevance. Based on this, researchers developed a dual GLP-1R/LepR agonist and demonstrated its efficacy in reducing food intake and body weight in leptin- and Lepr-deficient mice. Ablation of Lepr in Glp1r-expressing neurons abolished these effects, while reintroducing Glp1r in Lepr neurons restored responsiveness, further validating LepRbGlp1r neurons as effective targets for dual agonist therapies [48].
DMHLepR neurons also coordinate feeding-related circadian rhythms. Using a viral approach, silencing DMHLepR neurons in adult mice not only led to increased adiposity and body weight, but also phase-advanced diurnal rhythms of feeding and metabolism. These mice exhibited diminished locomotor activity during the dark phase and failed to adapt to time-restricted feeding schedules [49]. Single-nucleus RNA sequencing during scheduled feeding revealed that DMHLepR neurons upregulate circadian entrainment genes and show increased calcium activity prior to an anticipated meal. Leptin administration, as well as silencing or chemogenetic activation of these neurons, disrupted food-anticipatory behavioral rhythms. Anatomical and functional data demonstrated that a subpopulation of these neurons projects to the suprachiasmatic nucleus, providing a direct link between metabolic signals and the master circadian clock [50].
Leptin action in the DMH also plays a vital role in respiratory control [51]. Obesity-associated conditions such as obstructive sleep apnea and obesity hypoventilation syndrome are linked to impaired central leptin signaling, although the precise mechanisms have remained unclear [51,52,53]. Targeted expression of LepRb in DMH of LepRb-deficient db/db mice—an animal model of sleep-disordered breathing—led to a sustained increase in minute ventilation during NREM sleep following intracerebroventricular leptin infusion. These obese mice typically exhibit chronic alveolar hypoventilation, resembling human obesity hypoventilation syndrome. Adenoviral vector-mediated transfection resulted in LepRb expression specifically in DMH neurons, which were also MC4-positive. The leptin-induced hyperventilation occurred without a corresponding rise in CO2 production (VCO2), suggesting that the effect was due to stimulation of central respiratory control mechanisms rather than increased metabolic demand [54]. Chemogenetic activation of LepRb-positive DMH neurons increased respiratory rate and ventilation during REM sleep, particularly during inspiratory flow limitation—indicating a role in relieving airway obstruction [55,56]. Importantly, leptin’s respiratory effects were linked to projections from DMHLepR neurons to serotonergic neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus. Optogenetic stimulation of these DMH neurons evoked excitatory postsynaptic currents in dorsal raphe neurons, and the ventilatory response to hypercapnia was enhanced by leptin and suppressed by serotonin receptor antagonism. These results suggest that leptin promotes breathing and maintains upper airway patency via LepRb-expressing neurons in the DMH, potentially through serotonergic modulation [55,56].
5. The Lateral Hypothalamus: Leptin’s Regulation of Feeding Motivation and Reward Pathways
The LH is a critical integrative hub that regulates feeding behavior, energy homeostasis, water intake, reward processing, sleep–wake cycles, locomotor activity, pain, and neuroendocrine functions [57,58]. Within the LH, two major populations of orexigenic neurons—orexin/hypocretin-expressing and melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH)-expressing neurons—are indirectly inhibited by leptin (Figure 3) [59,60,61,62]. Several subpopulations of LepR-expressing neurons in the LH (LHLepR) mediate distinct neurophysiological and behavioral effects of leptin. These neurons co-express feeding-related neuropeptides such as neurotensin and galanin. For instance, galanin-expressing LHLepR neurons may suppress orexin neurons to modulate nutrient reward [62]. Similarly, neurotensin-expressing LHLepR neurons project to both orexin neurons in the LH and dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and substantia nigra, thereby contributing to leptin’s regulation of energy balance via inhibition of orexin activity and modulation of the mesolimbic dopamine system [60,61]. Leptin reduces excitatory synaptic input onto MCH- and orexin-expressing LH neurons that project to the VTA, potentially altering dopamine signaling and feeding motivation. This synaptic regulation appears to be presynaptic and is highly sensitive to energy status: both acute fasting and HFD-induced obesity impair leptin’s effects. These findings support an inverted “U-shaped” model for leptin’s influence on LH-VTA circuitry, dependent on metabolic state and plasma glucose levels [63].
Despite their low abundance, LHLepR neurons are pivotal in regulating feeding and reward. To better characterize them, researchers used TRAP (translating ribosome affinity purification) in LepR-Cre mice injected with Cre-dependent GFP in the LH, followed by RNA sequencing of hypothalamic tissue from fed and 24-h food-restricted mice. This approach identified known markers of LHLepR neurons and novel genes associated with energy balance and metabolic disease (e.g., Acvr1c, Npy1r, Itgb1) as well as genes responsive to energy deficit (e.g., Fam46a, Rrad), providing a rich molecular profile of these neurons [64].
Functional studies have identified LHLepR neurons, a subset of GABAergic cells in the LH, as key regulators of motivation. Activation of these neurons enhances performance on progressive ratio tasks, indicating increased motivational drive, whereas their inhibition reduces operant responding for both food and water, suggesting a broad role in goal-directed behaviors [65]. Further work has revealed behavioral distinctions between broader LH GABAergic neurons (LHVGAT) and the LHLepR subset. While ablation of LHVGAT neurons reduces food intake and weight gain, specific ablation of LHLepR neurons disrupts Pavlovian appetitive learning without affecting baseline feeding. In cue discrimination tasks, only LHLepR activity encodes learned associations, and modulation of LHLepR→VTA projections leads to distinct behavioral outcomes. Notably, inhibition of LHLepR neurons does not alter cocaine-conditioned place preference but attenuates cocaine sensitization, suggesting specificity for non-drug rewards [66]. In male mice, fiber photometry and microendoscope imaging show that LHLepR neurons are differentially activated during voluntary food-seeking versus consumption. Two subpopulations were identified: one time-locked to seeking and another to consummatory behavior. NPY appears to act as a tonic permissive gate, enhancing LHLepR neuronal activity. These data reveal a fine-tuned leptin-regulated circuit underlying motivated behavior [67].
Early life trauma (ELT) is a well-established risk factor for the development of binge eating and obesity later in life, yet the underlying neural circuits remained unclear until recently [68,69]. In a study using a mouse model, it was demonstrated that ELT leads to downregulation of Lepr expression in the LH, contributing to increased susceptibility to binge-like eating and obesity upon HFD exposure [70]. The sustained hyperactivity of LH LepR-expressing neurons was found to encode this maladaptive feeding behavior. Inhibition of LHLepr neurons projecting to the ventrolateral periaqueductal gray (vlPAG) normalizes these behaviors. Moreover, activation of proenkephalin-expressing vlPAG neurons—which are inhibited by LHLepr input—rescues maladaptive eating. These findings uncover a stress-sensitive LH-vlPAG circuit linking early life adversity to pathological feeding behavior and obesity risk [70].

Table 2.
Novel insights into hypothalamic leptin-responsive neurons and their functional roles.
Table 2.
Novel insights into hypothalamic leptin-responsive neurons and their functional roles.
| Hypothalamic Region | Neuronal Population | Functions | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARC | LepRb PNOC neurons | Mediate leptin’s effects on feeding by regulating NPY; LepRb loss causes obesity, restoration reduces body weight. | [25] |
| LepRb BNC2 neurons | Suppress appetite by inhibiting AgRP neurons; LepRb loss causes obesity, highlighting their key role in appetite control. | [26] | |
| LepRb Pirt neurons | Regulate reproduction and suppress energy expenditure; LepRb loss impairs female fertility but not feeding. | [27,28] | |
| VMH | LepRb neurons | Enable CCK-induced satiety, especially on high-fat diets, integrating central leptin and peripheral CCK signals for energy regulation. | [40] |
| LepRb neurons | Require intact PACAP signaling to mediate leptin’s effects on satiety, metabolism, and associated molecular responses. | [41] | |
| DMH | LepRb Glp1r neurons | Essential for regulating food intake and body weight, mediating the anorexigenic effects of both leptin and GLP-1R agonists. | [47,48] |
| LepRb neurons | Coordinate feeding-related circadian rhythms, linking leptin signaling to metabolic timing. | [49,50] | |
| LepRb neurons | Crucial for central respiratory control, promoting ventilation and maintaining airway patency. | [54,55,56] | |
| LH | LepRb GABA neurons | Regulate motivated behavior rather than baseline feeding. Their activation enhances goal-directed actions, while inhibition disrupts Pavlovian appetitive learning and attenuates reward-specific behaviors. | [65,66,67] |
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Leptin, a critical regulator of energy homeostasis, exerts multifaceted effects across hypothalamic regions—including the arcuate nucleus, ventromedial hypothalamus, dorsomedial hypothalamus, and lateral hypothalamus—to modulate appetite, energy expenditure, glucose metabolism, and neuroendocrine function [71,72]. In the arcuate nucleus, leptin differentially regulates POMC and AgRP/NPY neurons, with recent discoveries identifying novel leptin-responsive populations—such as neurons expressing prepronociceptin, basonuclin 2, and Pirt—and both secreted and intracellular mediators, including angiopoietin-like growth factor, zinc-α2-glycoprotein, spexin, Rap1, growth factor receptor-bound protein 10, and spliced X-box binding protein 1, that influence leptin sensitivity.
The ventromedial hypothalamus integrates leptin signaling with peripheral inputs such as cholecystokinin and central modulators like pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide, while epigenetic regulators, including Jumonji domain-containing protein D3, enhance leptin responsiveness through modulation of receptor expression.
The dorsomedial hypothalamus emerges as a hub for leptin’s metabolic and circadian effects, with LepRbGlp1r neurons mediating both leptin and GLP-1 agonist actions. Additionally, leptin receptor–expressing neurons in this region contribute to respiratory control, linking leptin to obesity-associated breathing disorders.
In the lateral hypothalamus, leptin modulates reward and motivational circuits through orexin/melanin-concentrating hormone neurons and distinct GABAergic LepRb subpopulations, with disruptions in this network implicated in maladaptive feeding behaviors, particularly following early life trauma.
Despite significant advances, key questions remain—particularly regarding the molecular mechanisms underlying leptin resistance in obesity. Emerging insights into intracellular signaling, neuronal heterogeneity, and epigenetic regulation offer promising therapeutic avenues. Future research should focus on translating these results into targeted interventions that restore leptin sensitivity, including combinatorial approaches such as dual GLP-1/leptin agonists. This integrative perspective highlights the need to target discrete hypothalamic circuits to achieve effective, personalized treatments for metabolic disorders, paving the way for precision medicine strategies that address the complex interplay between metabolism, behavior, and systemic physiology.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Acknowledgments
The author gratefully acknowledges the use of professional language editing services to improve the clarity and readability of the manuscript. For the preparation of Figure 1, images were adapted from Servier Medical Art (https://smart.servier.com/ (accessed on 13 August 2025)), licensed under CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), and from the NIH BioArt Source.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| α-MSH | α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone |
| AGF | Angiopoietin-like growth factor |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| ARC | Arcuate nucleus |
| AZGP1 | Zinc-α2-glycoprotein |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| CCK | Cholecystokinin |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CREB | cAMP response element-binding protein |
| DMH | Dorsomedial hypothalamus |
| ELT | Early life trauma |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| ERK1/2 | Extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 |
| GABA | Gamma-aminobutyric acid |
| GFP | Green fluorescent protein |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| GLP-1R | Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor |
| Grb10 | Growth factor receptor-bound protein 10 |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
| JAK2 | Janus kinase 2 |
| LH | Lateral hypothalamus |
| LepR/LepRb | Leptin receptor/Leptin receptor long isoform |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MC3R | Melanocortin-3 receptor |
| MC4R | Melanocortin-4 receptor |
| MCH | Melanin-concentrating hormone |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| NREM | Non-rapid eye movement (sleep) |
| NPY | Neuropeptide Y |
| NTS | Nucleus of the solitary tract |
| PACAP | Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| Pirt | Phosphoinositide-interacting regulator of TRP |
| PNOC | Prepronociceptin |
| POMC | Proopiomelanocortin |
| Rap1 | Ras-related protein 1 |
| REM | Rapid eye movement (sleep) |
| SOCS3 | Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| VMH | Ventromedial hypothalamus |
| vlPAG | Ventrolateral periaqueductal gray |
| VTA | Ventral tegmental area |
| Xbp1s | Spliced X-box binding protein 1 |
References
- Zhang, Y.; Proenca, R.; Maffei, M.; Barone, M.; Leopold, L.; Friedman, J.M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994, 372, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzoros, C.S.; Magkos, F.; Brinkoetter, M.; Sienkiewicz, E.; Dardeno, T.A.; Kim, S.Y.; Hamnvik, O.P.; Koniaris, A. Leptin in human physiology and pathophysiology. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 301, E567–E584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prolo, P.; Wong, M.L.; Licinio, J. Leptin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1998, 30, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J. Novel Leptin-Based Therapeutic Strategies to Limit Synaptic Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yupanqui-Lozno, H.; Bastarrachea, R.A.; Yupanqui-Velazco, M.E.; Alvarez-Jaramillo, M.; Medina-Méndez, E.; Giraldo-Peña, A.P.; Arias-Serrano, A.; Torres-Forero, C.; Garcia-Ordoñez, A.M.; Mastronardi, C.A.; et al. Congenital Leptin Deficiency and Leptin Gene Missense Mutation Found in Two Colombian Sisters with Severe Obesity. Genes 2019, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, M.; Lazarov, L. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase or cystathionine gamma-lyase abolishes leptin-induced fever in male rats. J. Therm. Biol. 2023, 112, 103443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Swieten, M.M.; Pandit, R.; Adan, R.A.; van der Plasse, G. The neuroanatomical function of leptin in the hypothalamus. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2014, 61–62, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wauman, J.; Zabeau, L.; Tavernier, J. The Leptin Receptor Complex: Heavier Than Expected? Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, A.M.; Holland, O.J.; Hryciw, D.H. Link Between Umbilical Cord Blood Adipokines and Early Childhood Health. Endocrines 2025, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münzberg, H.; Morrison, C.D. Structure, production and signaling of leptin. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2015, 64, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppari, R.; Bjørbæk, C. Leptin revisited: Its mechanism of action and potential for treating diabetes. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 692–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.G.; Cowley, M.A.; Münzberg, H. Mechanisms of leptin action and leptin resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2008, 70, 537–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; López, M.; Rahmouni, K. The cellular and molecular bases of leptin and ghrelin resistance in obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, M.; Landzhov, B.; Yakimova, K. Cafeteria diet-induced obesity reduces leptin-stimulated NADPH-diaphorase reactivity in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus of rats. Acta Histochem. 2020, 122, 151616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, M.; Landzhov, B.; Nikolov, R.; Yakimova, K. Central, but not systemic, thermoregulatory effects of leptin are impaired in rats with obesity: Interactions with GABAB agonist and antagonist. Amino Acids 2019, 51, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.H.; Proenca, R.; Montez, J.M.; Carroll, K.M.; Darvishzadeh, J.G.; Lee, J.I.; Friedman, J.M. Abnormal splicing of the leptin receptor in diabetic mice. Nature 1996, 379, 632–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.C.; Lord, R.A.; Anderson, G.M. Multiple Leptin Signalling Pathways in the Control of Metabolism and Fertility: A Means to Different Ends? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, J.; Frazão, R., Jr.; Elias, C.F. The PI3K signaling pathway mediates the biological effects of leptin. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. E Metabol. 2010, 54, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hâkansson, M.L.; Brown, H.; Ghilardi, N.; Skoda, R.C.; Meister, B. Leptin receptor immunoreactivity in chemically defined target neurons of the hypothalamus. J Neurosci. 1998, 18, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.M.; Lachey, J.L.; Sternson, S.M.; Lee, C.E.; Elias, C.F.; Friedman, J.M.; Elmquist, J.K. Leptin targets in the mouse brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 514, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi-Lozano, M.; Roa, J.; Ruiz-Pino, F.; Piet, R.; Garcia-Galiano, D.; Pineda, R.; Zamora, A.; Leon, S.; Sanchez-Garrido, M.A.; Romero-Ruiz, A.; et al. Defining a novel leptin-melanocortin-kisspeptin pathway involved in the metabolic control of puberty. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, O.; Michael, N.J.; Caron, A. A critical update on the leptin-melanocortin system. J. Neurochem. 2023, 165, 467–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perello, M.; Scott, M.M.; Sakata, I.; Lee, C.E.; Chuang, J.C.; Osborne-Lawrence, S.; Rovinsky, S.A.; Elmquist, J.K.; Zigman, J.M. Functional implications of limited leptin receptor and ghrelin receptor coexpression in the brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2012, 520, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquero, A.F.; de Solis, A.J.; Lindsley, S.R.; Kirigiti, M.A.; Smith, M.S.; Cowley, M.A.; Zeltser, L.M.; Grove, K.L. Developmental switch of leptin signaling in arcuate nucleus neurons. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 9982–9994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solheim, M.H.; Stroganov, S.; Chen, W.; Subagia, P.S.; Bauder, C.A.; Wnuk-Lipinski, D.; Del Río-Martín, A.; Sotelo-Hitschfeld, T.; Beddows, C.A.; Klemm, P.; et al. Hypothalamic PNOC/NPY neurons constitute mediators of leptin-controlled energy homeostasis. Cell 2025, 188, 3550–3566.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.L.; Yin, L.; Tan, Y.; Ivanov, J.; Plucinska, K.; Ilanges, A.; Herb, B.R.; Wang, P.; Kosse, C.; Cohen, P.; et al. Leptin-activated hypothalamic BNC2 neurons acutely suppress food intake. Nature 2024, 636, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santinga, J. The Role of Lepr/Pirt Neurons in the Control of Reproductive Function by Leptin. Bachelor’s Thesis in Neuroscience with Honors, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 30 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Onoharigho, R.; Campbell, J. A novel neuron population that selectively controls metabolism. Physiology 2025, 40 (Suppl. S1), 0789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Heo, J.Y.; Lee, M.J.; Zhu, J.; Seo, C.; Go, D.H.; Yoon, S.K.; Yukari, D.; Oike, Y.; Sohn, J.-W.; et al. Angiopoietin-Like Growth Factor Involved in Leptin Signaling in the Hypothalamus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, D.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, H.; Yang, G.; Li, L.; Yang, M. AZGP1 in POMC neurons modulates energy homeostasis and metabolism through leptin-mediated STAT3 phosphorylation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, B.; Kim, K.-K.; Lee, T.-H.; Kim, H.-R.; Park, B.-S.; Park, J.-W.; Jeong, J.-K.; Seong, J.-Y.; Lee, B.-J. Spexin Regulates Hypothalamic Leptin Action on Feeding Behavior. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K.; Lu, W.; Xu, Y.; Morozov, A.; Fukuda, M. The small GTPase Rap1 in POMC neurons regulates leptin actions and glucose metabolism. Mol. Metab. 2025, 95, 102117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Hedbacker, K.; Kelly, L.; Zhang, Z.; Moura-Assis, A.; Luo, J.D.; Rabinowitz, J.D.; Friedman, J.M. A cellular and molecular basis of leptin resistance. Cell Metab. 2025, 37, 723–741.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; He, Y.; Bai, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; Yang, Y.; Luo, H.; Yu, M.; Liu, H.; Tu, L.; et al. Hypothalamic Grb10 enhances leptin signalling and promotes weight loss. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajwani, J.; Hwang, E.; Portillo, B.; Lieu, L.; Wallace, B.; Kabahizi, A.; He, Z.; Dong, Y.; Grose, K.; Williams, K.W. Upregulation of Xbp1 in NPY/AgRP neurons reverses diet-induced obesity and ameliorates leptin and insulin resistance. Neuropeptides 2024, 108, 102461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.B.S. Low-dose peripheral leptin infusion produces selective activation of ventromedial hypothalamic and hindbrain STAT3. American journal of physiology. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 325, E72–E82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravussin, Y.; LeDuc, C.A.; Watanabe, K.; Mueller, B.; Skowronski, A.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R. Effects of chronic leptin infusion on subsequent body weight and composition in mice: Can body weight set point be reset? Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, H.; Zigman, J.M.; Ye, C.; Lee, C.E.; McGovern, R.A.; Tang, V.; Kenny, C.D.; Christiansen, L.M.; White, R.D.; Edelstein, E.A.; et al. Leptin directly activates SF1 neurons in the VMH, and this action by leptin is required for normal body-weight homeostasis. Neuron 2006, 49, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameroso, D.; Meng, A.; Chen, S.; Felsted, J.; Dulla, C.G.; Rios, M. Astrocytic BDNF signaling within the ventromedial hypothalamus regulates energy homeostasis. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, W.; Latremouille, J.; Harris, R.B.S. Leptin receptor-expressing cells in the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus contribute to enhanced CCK-induced satiety following central leptin injection. American journal of physiology. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 323, E267–E280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, M.M.; Anderson, E.M.; Chen, C.; Maunze, B.; Hess, E.M.; Block, M.E.; Patel, N.; Cooper, Z.; McCoy, R.; Dabra, T.; et al. Acute Blockade of PACAP-Dependent Activity in the Ventromedial Nucleus of the Hypothalamus Disrupts Leptin-Induced Behavioral and Molecular Changes in Rats. Neuroendocrinology 2020, 110, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladun, B.T.; Kim, M.H. Epigenetic Regulation of Leptin Signaling by Hypothalamic JMJD3 Mitigates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2024, 8 (Suppl. S2), 103638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enriori, P.J.; Sinnayah, P.; Simonds, S.E.; Garcia Rudaz, C.; Cowley, M.A. Leptin action in the dorsomedial hypothalamus increases sympathetic tone to brown adipose tissue in spite of systemic leptin resistance. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 12189–12197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, G.T.; Worth, A.A.; Nunn, N.; Korpal, A.K.; Bechtold, D.A.; Allison, M.B.; Myers, M.G.; Statnick, M.A., Jr.; Luckman, S.M. The thermogenic effect of leptin is dependent on a distinct population of prolactin-releasing peptide neurons in the dorsomedial hypothalamus. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kerman, I.A.; Laque, A.; Nguyen, P.; Faouzi, M.; Louis, G.W.; Jones, J.C.; Rhodes, C.; Münzberg, H. Leptin-receptor-expressing neurons in the dorsomedial hypothalamus and median preoptic area regulate sympathetic brown adipose tissue circuits. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 1873–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, M.; Kaiser, L.; He, Y.; Xu, Y.; Salbaum, J.M.; Yu, S.; Morrison, C.D.; Berthoud, H.R.; Münzberg, H. Leptin receptor neurons in the dorsomedial hypothalamus require distinct neuronal subsets for thermogenesis and weight loss. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2025, 163, 156100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupp, A.C.; Tomlinson, A.J.; Affinati, A.H.; Yacawych, W.T.; Duensing, A.M.; True, C.; Lindsley, S.R.; Kirigiti, M.A.; MacKenzie, A.; Polex-Wolf, J.; et al. Suppression of food intake by Glp1r/Lepr-coexpressing neurons prevents obesity in mouse models. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e157515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polex-Wolf, J.; Deibler, K.; Hogendorf, W.F.J.; Bau, S.; Glendorf, T.; Stidsen, C.E.; Tornøe, C.W.; Tiantang, D.; Lundh, S.; Pyke, C.; et al. Glp1r-Lepr coexpressing neurons modulate the suppression of food intake and body weight by a GLP-1/leptin dual agonist. Sci. Transl. Med. 2024, 16, eadk4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, C.L.; Deem, J.D.; Phan, B.A.; Doan, T.P.; Ogimoto, K.; Mirzadeh, Z.; Schwartz, M.W.; Morton, G.J. Leptin receptor neurons in the dorsomedial hypothalamus regulate diurnal patterns of feeding, locomotion, and metabolism. eLife 2021, 10, e63671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Godschall, E.; Brennan, C.D.; Zhang, Q.; Abraham-Fan, R.J.; Williams, S.P.; Güngül, T.B.; Onoharigho, R.; Buyukaksakal, A.; Salinas, R.; et al. Leptin receptor neurons in the dorsomedial hypothalamus input to the circadian feeding network. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadh9570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Pho, H.; Kirkness, J.; Ladenheim, E.E.; Bi, S.; Moran, T.H.; Fuller, D.D.; Schwartz, A.R.; Polotsky, V.Y. Localizing Effects of Leptin on Upper Airway and Respiratory Control during Sleep. Sleep 2016, 39, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.; Polotsky, V.Y. Leptin and Leptin Resistance in the Pathogenesis of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Possible Link to Oxidative Stress and Cardiovascular Complications. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 5137947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phipps, P.R.; Starritt, E.; Caterson, I.; Grunstein, R.R. Association of serum leptin with hypoventilation in human obesity. Thorax 2002, 57, 75–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pho, H.; Berger, S.; Freire, C.; Kim, L.J.; Shin, M.K.; Streeter, S.R.; Hosamane, N.; Cabassa, M.E.; Anokye-Danso, F.; Dergacheva, O.; et al. Leptin receptor expression in the dorsomedial hypothalamus stimulates breathing during NREM sleep in db/db mice. Sleep 2021, 44, zsab046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, M.R.; Wang, X.; Pho, H.; Bevans-Fonti, S.; Anokye-Danso, F.; Escobar, J.; Dergacheva, O.; Branco, L.G.; Mendelowitz, D.; Polotsky, V.Y. Activation of Leptin-Receptor-Expressing Neurons in the Dorsomedial Hypothalamus Increases Hypercapcnic Ventilatory Response and Relieves Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Obese Mice. FASEB J. 2022, 36, R2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, M.R.; Wang, X.; Aung, O.; Bevans-Fonti, S.; Anokye-Danso, F.; Ribeiro, C.; Escobar, J.; Freire, C.; Pho, H.; Dergacheva, O.; et al. Leptin signaling in the dorsomedial hypothalamus couples breathing and metabolism in obesity. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnavion, P.; Mickelsen, L.E.; Fujita, A.; de Lecea, L.; Jackson, A.C. Hubs and spokes of the lateral hypothalamus: Cell types, circuits and behaviour. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 6443–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhoury, M.; Salman, I.; Najjar, W.; Merhej, G.; Lawand, N. The Lateral Hypothalamus: An Uncharted Territory for Processing Peripheral Neurogenic Inflammation. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goforth, P.B.; Leinninger, G.M.; Patterson, C.M.; Satin, L.S.; Myers, M.G., Jr. Leptin acts via lateral hypothalamic area neurotensin neurons to inhibit orexin neurons by multiple GABA-independent mechanisms. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 11405–11415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinninger, G.M.; Opland, D.M.; Jo, Y.H.; Faouzi, M.; Christensen, L.; Cappellucci, L.A.; Rhodes, C.J.; Gnegy, M.E.; Becker, J.B.; Pothos, E.N.; et al. Leptin action via neurotensin neurons controls orexin, the mesolimbic dopamine system and energy balance. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opland, D.; Sutton, A.; Woodworth, H.; Brown, J.; Bugescu, R.; Garcia, A.; Christensen, L.; Rhodes, C.; Myers, M.; Leinninger, G., Jr. Loss of neurotensin receptor-1 disrupts the control of the mesolimbic dopamine system by leptin and promotes hedonic feeding and obesity. Mol. Metab. 2013, 2, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laque, A.; Yu, S.; Qualls-Creekmore, E.; Gettys, S.; Schwartzenburg, C.; Bui, K.; Rhodes, C.; Berthoud, H.R.; Morrison, C.D.; Richards, B.K.; et al. Leptin modulates nutrient reward via inhibitory galanin action on orexin neurons. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Bello, N.T.; Pang, Z.P. Presynaptic Regulation of Leptin in a Defined Lateral Hypothalamus-Ventral Tegmental Area Neurocircuitry Depends on Energy State. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 11854–11866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakava-Georgiadou, N.; Drkelic, V.; Garner, K.M.; Luijendijk, M.C.M.; Basak, O.; Adan, R.A.H. Molecular profile and response to energy deficit of leptin-receptor neurons in the lateral hypothalamus. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffino, F.L.; Siemian, J.N.; Petrella, M.; Laing, B.T.; Sarsfield, S.; Borja, C.B.; Gajendiran, A.; Zuccoli, M.L.; Aponte, Y. Activation of a lateral hypothalamic-ventral tegmental circuit gates motivation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemian, J.N.; Arenivar, M.A.; Sarsfield, S.; Borja, C.B.; Russell, C.N.; Aponte, Y. Lateral hypothalamic LEPR neurons drive appetitive but not consummatory behaviors. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, K.S.; Jang, M.; Song, H.Y.; Jung, S.H.; Ha, D.S.; Park, J.S.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.M.; et al. Lateral hypothalamic leptin receptor neurons drive hunger-gated food-seeking and consummatory behaviours in male mice. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, S.; Jaussent, I.; Maimoun, L.; Ryst, A.; Seneque, M.; Villain, L.; Hamroun, D.; Lefebvre, P.; Renard, E.; Courtet, P. Associations between adverse childhood experiences and clinical characteristics of eating disorders. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brustenghi, F.; Mezzetti, F.A.F.; Di Sarno, C.; Giulietti, C.; Moretti, P.; Tortorella, A. Eating Disorders: The Role of Childhood Trauma and the Emotion Dysregulation. Psychiatr. Danub. 2019, 31 (Suppl. S3), 509–511. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.; You, I.J.; Jeong, M.; Bae, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Cawley, M.L.; Han, A.; Lim, B.K. Early adversity promotes binge-like eating habits by remodeling a leptin-responsive lateral hypothalamus-brainstem pathway. Nat. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hristov, M.; Landzhov, B.; Yakimova, K. Effect of leptin on nitrergic neurons in the lateral hypothalamic area and the supraoptic nucleus of rats. Biotech. Histochem. Off. Publ. Biol. Stain Comm. 2024, 99, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, M.; Landzhov, B.; Yakimova, K. Increased NADPH-diaphorase reactivity in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus and tanycytes following systemic administration of leptin in rats. Acta Histochem. 2019, 121, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).