Non-HLA Abs in Solid Organ Transplantation
Abstract
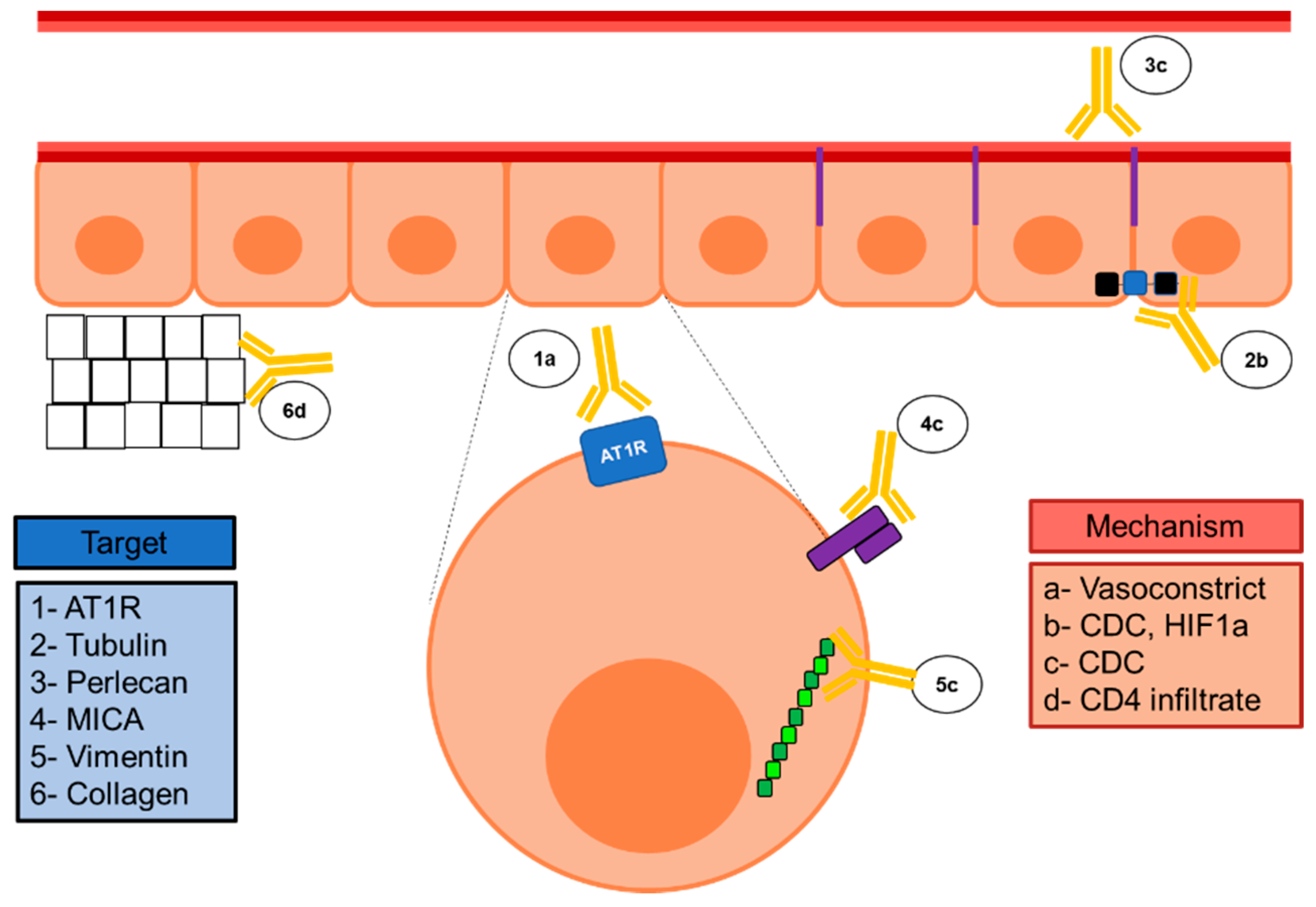
:1. Introduction
2. Non-HLA Abs
2.1. Anti-MICA Abs
2.1.1. Anti-MICA Abs in Renal Transplantation
2.1.2. Anti-MICA Abs in Lung Transplantation
2.1.3. Anti-MICA Abs in Liver Transplantation
2.1.4. Anti-MICA Abs in Heart Transplantation
2.2. Anti-Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor (AT1R) Abs and Anti-Endothelin Receptor (ETAR) Abs
2.2.1. Anti-Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor (AT1R) Abs and anti-Endothelin Receptor (ETAR) Abs in Kidney Transplantation
2.2.2. Anti-AT1R Abs in Heart Transplantation
2.2.3. Anti-AT1R Abs in Lung Transplantation
2.3. Anti-Perlecan (LG3) Abs in Kidney Transplantation
2.4. Anti-Collagen Abs and Anti-K-Alpha-Tubulin Abs
2.4.1. Anti-K-Alpha 1 Tubulin and Anti-Collagen Abs in Lung Transplantation
2.4.2. Anti-K-Alpha 1 Tubulin and Anti-Collagen Abs in Heart Transplantation
2.4.3. Anti-Collagen Abs in Kidney Transplantation
2.5. Anti-Vimentin Abs
2.5.1. Anti-Vimentin Abs in Kidney Transplantation
2.5.2. Anti-Vimentin Abs in Heart Transplantation
2.6. H-Y Antibodies in Solid Organ Transplantation
2.7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABMR | Antibody Mediated Rejection |
| BOS | Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome |
| CAV | coronary allograft vasculopathy |
| DSA | Donor Specific Antibody |
| HLA | Human Leukocyte Antigens |
| IFTA | Interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy |
| IRI | Ischemia/reperfusion injury |
| MCS | Mechanical circulatory support devices |
| MHC | Major Histocompatibility Complex |
| MICA | MHC class I-related chain gene A |
| PGD | Primary graft disfunction |
| PRA | Panel Reactive Antibody |
| TCAD | Accelerated transplant coronary artery disease |
| TCMR | T Cell Mediated Rejection |
| TG | Transplant glomerulopathy |
References
- Bouquegneau, A.; Loheac, C.; Aubert, O.; Bouatou, Y.; Viglietti, D.; Empana, J.P.; Ulloa, C.; Murad, M.H.; Legendre, C.; Glotz, D.; et al. Complement-activating donor-specific anti-HLA antibodies and solid organ transplant survival: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grafft, C.A.; Cornell, L.D.; Gloor, J.M.; Cosio, F.G.; Gandhi, M.J.; Dean, P.G.; Stegall, M.D.; Amer, H. Antibody-mediated rejection following transplantation from an HLA-identical sibling. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2010, 25, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Opelz, G.; Susal, C.; Ruhenstroth, A.; Dohler, B. Impact of HLA compatibility on lung transplant survival and evidence for an HLA restriction phenomenon: A collaborative transplant study report. Transplantation 2010, 90, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, M.; Loupy, A.; Lefaucheur, C.; Roufosse, C.; Glotz, D.; Seron, D.; Nankivell, B.J.; Halloran, P.F.; Colvin, R.B.; Akalin, E.; et al. The Banff 2017 Kidney Meeting Report: Revised diagnostic criteria for chronic active T cell-mediated rejection, antibody-mediated rejection, and prospects for integrative endpoints for next-generation clinical trials. Am. J. Transplant. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2018, 18, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reinsmoen, N.L. Immunological Risk Stratification by Assessing Both the HLA and Non-HLA-Specific Antibodies: Time to Include Testing for Non-HLA Antibodies in the Routine Clinical Antibody Analysis Profile? Transplantation 2017, 101, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragun, D.; Hegner, B. Non-HLA antibodies post-transplantation: Clinical relevance and treatment in solid organ transplantation. Contrib. Nephrol. 2009, 162, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragun, D.; Philippe, A.; Catar, R. Role of non-HLA antibodies in organ transplantation. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2012, 17, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahram, S.; Bresnahan, M.; Geraghty, D.E.; Spies, T. A second lineage of mammalian major histocompatibility complex class I genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 6259–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leelayuwat, C.; Townend, D.C.; Degli-Esposti, M.A.; Abraham, L.J.; Dawkins, R.L. A new polymorphic and multicopy MHC gene family related to nonmammalian class I. Immunogenetics 1994, 40, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Cai, J.; Liu, X. MICA genetic polymorphism and HLA-A,C,B,MICA and DRB1 haplotypic variation in a southern Chinese Han population: Identification of two new MICA alleles, MICA*060 and MICA*062. Hum. Immunol. 2011, 72, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Alvarez, B.; Fernandez-Sanchez, A.; Lopez-Vazquez, A.; Coto, E.; Ortega, F.; Lopez-Larrea, C. NKG2D and its ligands: Active factors in the outcome of solid organ transplantation? Kidney Int. Suppl. 2011, 1, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zwirner, N.W.; Dole, K.; Stastny, P. Differential surface expression of MICA by endothelial cells, fibroblasts, keratinocytes, and monocytes. Hum. Immunol. 1999, 60, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Lu, J.; Wei, L.; Long, D.; Guo, J.Y.; Shan, J.; Li, F.S.; Lu, P.Y.; Li, P.Y.; Feng, L. The role of HIF-1 in up-regulating MICA expression on human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells during hypoxia/reoxygenation. BMC Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sumitran-Holgersson, S.; Wilczek, H.E.; Holgersson, J.; Soderstrom, K. Identification of the nonclassical HLA molecules, mica, as targets for humoral immunity associated with irreversible rejection of kidney allografts. Transplantation 2002, 74, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mizutani, K.; Terasaki, P.; Bignon, J.D.; Hourmant, M.; Cesbron-Gautier, A.; Shih, R.N.; Pei, R.; Lee, J.; Ozawa, M. Association of kidney transplant failure and antibodies against MICA. Hum. Immunol. 2006, 67, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Stastny, P.; Susal, C.; Dohler, B.; Opelz, G. Antibodies against MICA antigens and kidney-transplant rejection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panigrahi, A.; Gupta, N.; Siddiqui, J.A.; Margoob, A.; Bhowmik, D.; Guleria, S.; Mehra, N.K. Post transplant development of MICA and anti-HLA antibodies is associated with acute rejection episodes and renal allograft loss. Hum. Immunol. 2007, 68, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Zapardiel, E.; Castro-Panete, M.J.; Mancebo, E.; Morales, P.; Laguna-Goya, R.; Morales, J.M.; Apaza, J.; de Andres, A.; Talayero, P.; Paz-Artal, E. Early renal graft function deterioration in recipients with preformed anti-MICA antibodies: Partial contribution of complement-dependent cytotoxicity. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2016, 31, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemy, A.; Andrien, M.; Wissing, K.M.; Ryhahi, K.; Vandersarren, A.; Racape, J.; Heylen, C.; Ghisdal, L.; Broeders, E.; Vereerstraeten, P.; et al. Major histocompatibility complex class 1 chain-related antigen a antibodies: Sensitizing events and impact on renal graft outcomes. Transplantation 2010, 90, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Zapardiel, E.; Castro-Panete, M.J.; Castillo-Rama, M.; Morales, P.; Lora-Pablos, D.; Valero-Hervas, D.; Ruiz-Garcia, R.; Apaza, J.; Talayero, P.; Andres, A.; et al. Harmful effect of preformed anti-MICA antibodies on renal allograft evolution in early posttransplantation period. Transplantation 2013, 96, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhry, M.; Makroo, R.N.; Singh, M.; Kumar, M.; Thakur, Y.; Sharma, V. Role of Anti-MICA Antibodies in Graft Survival of Renal Transplant Recipients of India. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 3434050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.W.; Lee, H.; Choi, B.S.; Park, C.W.; Yang, C.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Oh, E.J.; Chung, B.H. Clinical Impact of Pre-transplant Antibodies Against Angiotensin II Type I Receptor and Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I-Related Chain A in Kidney Transplant Patients. Ann. Lab. Med. 2018, 38, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Luo, M.; Qiu, J.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Jahr, F.M.; Cai, J.; Terasaki, P.I. Detection of antibodies against major histocompatibility complex class I-related chain A in long-term renal graft recipients. Exp. Clin. Transplant. Off. J. Middle East Soc. Organ Transplant. 2012, 10, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, Q.C.; Wang, W.; Li, X.B.; Yin, H.; Zhang, X.D. Expression characteristics of major histocompatibility complex class I-related chain A antibodies and immunoadsorption effect in sensitized recipients of kidney transplantation. Chin. Med. J. 2011, 124, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Li, C.; Yuan, X.N.; Zhang, J.L.; Li, Y.; Wei, X.D.; Hou, J.Q. Anti-human leukocyte antigens and anti-major histocompatibility complex class I-related chain A antibody expression in kidney transplantation during a four-year follow-up. Chin. Med. J. 2013, 126, 2815–2820. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.W.; Peng, Z.G.; Xian, W.H.; Cui, X.Q.; Sun, H.B.; Li, E.G.; Geng, L.N.; Zhao, P.; Tian, J. Association of de novo human leukocyte antigen and major histocompatibility complex class I chain-related gene-A antibodies and proteinuria with graft survival 5 years after renal transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2013, 45, 3249–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemy, A.; Andrien, M.; Lionet, A.; Labalette, M.; Noel, C.; Hiesse, C.; Delahousse, M.; Suberbielle-Boissel, C.; De Meyer, M.; Latinne, D.; et al. Posttransplant major histocompatibility complex class I chain-related gene A antibodies and long-term graft outcomes in a multicenter cohort of 779 kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation 2012, 93, 1258–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciszek, M.; Mucha, K.; Foroncewicz, B.; Zochowska, D.; Kosieradzki, M.; Grochowiecki, T.; Durlik, M.; Gorski, A.; Paczek, L. Immune biomarkers and longterm graft survival: A prospective followup of 457 kidney transplant recipients. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2017, 127, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akgul, S.U.; Oguz, F.S.; Caliskan, Y.; Kekik, C.; Cagatay, P.; Turkmen, A.; Nane, I.; Aydin, F.; Temurhan, S. The effect of anti-human leukocyte antigen, anti-major histocompatibility complex class 1 chain-related antigen a, and anti-glutathione transferase-T1 antibodies on the long-term survival of renal allograft. Transplant. Proc. 2013, 45, 890–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, S.T.; Stephens, H.A.; Fernando, R.; Karasu, A.; Harber, M.; Howie, A.J.; Powis, S.; Zou, Y.; Stastny, P.; Madrigal, J.A.; et al. Major histocompatibility complex class I-related chain A allele mismatching, antibodies, and rejection in renal transplantation. Hum. Immunol. 2011, 72, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angaswamy, N.; Saini, D.; Ramachandran, S.; Nath, D.S.; Phelan, D.; Hachem, R.; Trulock, E.; Patterson, G.A.; Mohanakumar, T. Development of antibodies to human leukocyte antigen precedes development of antibodies to major histocompatibility class I-related chain A and are significantly associated with development of chronic rejection after human lung transplantation. Hum. Immunol. 2010, 71, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uzunel, M.; Kasimu, H.; Joshi, M.; Ge, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, B.; Jaksch, M.; Jorns, C.; Nowak, G.; Sumitran-Holgersson, S. Evidence for no relevance of anti-major histocompatibility complex class I-related chain a antibodies in liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Study Liver Dis. Int. Liver Transplant. Soc. 2008, 14, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciszek, M.; Foroncewicz, B.; Mucha, K.; Zochowska, D.; Ziarkiewicz-Wroblewska, B.; Krawczyk, M.; Paczek, L. Anti-HLA and anti-MICA antibodies in liver transplant recipients: Effect on long-term graft survival. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 828201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, D.S.; Angaswamy, N.; Basha, H.I.; Phelan, D.; Moazami, N.; Ewald, G.A.; Mohanakumar, T. Donor-specific antibodies to human leukocyte antigens are associated with and precede antibodies to major histocompatibility complex class I-related chain A in antibody-mediated rejection and cardiac allograft vasculopathy after human cardiac transplantation. Hum. Immunol. 2010, 71, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Cecka, J.M.; Gjertson, D.W.; Ge, P.; Rose, M.L.; Patel, J.K.; Ardehali, A.; Kobashigawa, J.A.; Fishbein, M.C.; Reed, E.F. HLA and MICA: Targets of antibody-mediated rejection in heart transplantation. Transplantation 2011, 91, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Luo, L.; Guo, Y.; Long, D.; Wei, L.; Shan, J.; Feng, L.; Li, S.; Yang, X.; Lu, Y.; et al. The effect of MICA antigens on transplant outcomes: A systematic review. J. Evid.-Based Med. 2011, 4, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Cheng, D.; Chen, J.; Ji, S.; Wen, J.; Zheng, C.; Liu, Z. De novo development of circulating anti-endothelial cell antibodies rather than pre-existing antibodies is associated with post-transplant allograft rejection. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehle, K.; Kroher, J.; Kolat, P.; von Susskind-Schwendi, M.; Schmid, C.; Haneya, A.; Rupprecht, L.; Hirt, S. Existence of circulating anti-endothelial cell antibodies after heart transplantation is associated with post-transplant acute allograft rejection. Heart Vessel. 2016, 31, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, P.; Aires, P.; Sampaio, S.; Mendes, C.; Monteiro, M.; Alves, H.; Oliveira, G. XM-ONE detection of endothelium cell antibodies identifies a subgroup of HLA-antibody negative patients undergoing acute rejection. Transplant. Proc. 2011, 43, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Zapardiel, E.; Mancebo, E.; Diaz-Ordonez, M.; de Jorge-Huerta, L.; Ruiz-Martinez, L.; Serrano, A.; Castro-Panete, M.J.; Utrero-Rico, A.; de Andres, A.; Morales, J.M.; et al. Isolated De Novo Antiendothelial Cell Antibodies and Kidney Transplant Rejection. Am. J. kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2016, 68, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, N.; LaMarca, B.; Cunningham, M.W., Jr. The Role of Agonistic Autoantibodies to the Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor (AT1-AA) in Pathophysiology of Preeclampsia. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2018, 19, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kill, A.; Tabeling, C.; Undeutsch, R.; Kuhl, A.A.; Gunther, J.; Radic, M.; Becker, M.O.; Heidecke, H.; Worm, M.; Witzenrath, M.; et al. Autoantibodies to angiotensin and endothelin receptors in systemic sclerosis induce cellular and systemic events associated with disease pathogenesis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehta, P.K.; Griendling, K.K. Angiotensin II cell signaling: Physiological and pathological effects in the cardiovascular system. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C82–C97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinsmoen, N.L. Role of angiotensin II type 1 receptor-activating antibodies in solid organ transplantation. Hum. Immunol. 2013, 74, 1474–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinsmoen, N.L.; Lai, C.H.; Heidecke, H.; Haas, M.; Cao, K.; Ong, G.; Naim, M.; Wang, Q.; Mirocha, J.; Kahwaji, J.; et al. Anti-angiotensin type 1 receptor antibodies associated with antibody mediated rejection in donor HLA antibody negative patients. Transplantation 2010, 90, 1473–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giral, M.; Foucher, Y.; Dufay, A.; Van Huyen, J.P.; Renaudin, K.; Moreau, A.; Philippe, A.; Hegner, B.; Dechend, R.; Heidecke, H.; et al. Pretransplant sensitization against angiotensin II type 1 receptor is a risk factor for acute rejection and graft loss. Am. J. Transplant. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2013, 13, 2567–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Rebellato, L.M.; Cai, J.; Hopfield, J.; Briley, K.P.; Haisch, C.E.; Catrou, P.G.; Bolin, P.; Parker, K.; Kendrick, W.T.; et al. Higher risk of kidney graft failure in the presence of anti-angiotensin II type-1 receptor antibodies. Am. J. Transplant. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2013, 13, 2577–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasik, M.; Boratynska, M.; Koscielska-Kasprzak, K.; Kaminska, D.; Bartoszek, D.; Zabinska, M.; Myszka, M.; Zmonarski, S.; Protasiewicz, M.; Nowakowska, B.; et al. The influence of non-HLA antibodies directed against angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) on early renal transplant outcomes. Transpl. Int. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Organ Transplant. 2014, 27, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, J.W.; Park, H.; Rho, E.Y.; Shin, S.; Park, K.U.; Park, M.H.; Song, E.Y. Anti-angiotensin type 1 receptor antibodies associated with antibody-mediated rejection in patients without preformed HLA-donor-specific antibody. Transplant. Proc. 2014, 46, 3371–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philogene, M.C.; Bagnasco, S.; Kraus, E.S.; Montgomery, R.A.; Dragun, D.; Leffell, M.S.; Zachary, A.A.; Jackson, A.M. Anti-Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor and Anti-Endothelial Cell Antibodies: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Pathological Findings in Allograft Biopsies. Transplantation 2017, 101, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuss, A.; Hope, C.M.; Deayton, S.; Bennett, G.D.; Holdsworth, R.; Carroll, R.P.; Coates, P.T. C4d-negative antibody-mediated rejection with high anti-angiotensin II type I receptor antibodies in absence of donor-specific antibodies. Nephrology 2015, 20, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Huh, K.H.; Park, Y.; Park, B.G.; Yang, J.; Jeong, J.C.; Lee, J.; Park, J.B.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, S.; et al. The clinicopathological relevance of pretransplant anti-angiotensin II type 1 receptor antibodies in renal transplantation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2017, 32, 1244–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Gimferrer, I.; Warner, P.; Nelson, K.; Sibulesky, L.; Bakthavatsalam, R.; Leca, N. Preformed Angiotensin II Type-1 Receptor Antibodies Are Associated With Rejection After Kidney Transplantation: A Single-Center, Cohort Study. Transplant. Proc. 2018, 50, 3467–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gareau, A.J.; Wiebe, C.; Pochinco, D.; Gibson, I.W.; Ho, J.; Rush, D.N.; Nickerson, P.W. Pre-transplant AT1R antibodies correlate with early allograft rejection. Transpl. Immunol. 2018, 46, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deltombe, C.; Gillaizeau, F.; Anglicheau, D.; Morelon, E.; Trebern-Launay, K.; Le Borgne, F.; Rimbert, M.; Guerif, P.; Malard-Castagnet, S.; Foucher, Y.; et al. Is pre-transplant sensitization against angiotensin II type 1 receptor still a risk factor of graft and patient outcome in kidney transplantation in the anti-HLA Luminex era? A retrospective study. Transpl. Int. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Organ Transplant. 2017, 30, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malheiro, J.; Tafulo, S.; Dias, L.; Martins, S.; Fonseca, I.; Beirao, I.; Castro-Henriques, A.; Cabrita, A. Deleterious effect of anti-angiotensin II type 1 receptor antibodies detected pretransplant on kidney graft outcomes is both proper and synergistic with donor-specific anti-HLA antibodies. Nephrology 2019, 24, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, E.; Arreola-Guerra, J.M.; Hernandez-Mendez, E.A.; Salcedo, I.; Castelan, N.; Uribe-Uribe, N.O.; Vilatoba, M.; Contreras-Saldivar, A.G.; Sanchez-Cedillo, A.I.; Ramirez, J.B.; et al. Pretransplant angiotensin II type 1-receptor antibodies are a risk factor for earlier detection of de novo HLA donor-specific antibodies. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2016, 31, 1738–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Kim, J.I.; Moon, I.S.; Chung, B.H.; Yang, C.W.; Kim, Y.; Han, K.; Oh, E.J. Investigation of Serum Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Antibodies at the Time of Renal Allograft Rejection. Ann. Lab. Med. 2015, 35, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banasik, M.; Boratynska, M.; Koscielska-Kasprzak, K.; Krajewska, M.; Mazanowska, O.; Kaminska, D.; Bartoszek, D.; Zabinska, M.; Myszka, M.; Nowakowska, B.; et al. The impact of non-HLA antibodies directed against endothelin-1 type A receptors (ETAR) on early renal transplant outcomes. Transpl. Immunol. 2014, 30, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marian, U.; Slavcev, A.; Gazdic, T.; Ivak, P.; Netuka, I. The impact of Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor antibodies on morbidity and mortality in Heart Mate II supported recipients. Biomed. Papers Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky Olomouc Czechoslov. 2016, 160, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Mirocha, J.; Aintablian, T.; Dimbil, S.; Moriguchi, J.; Arabia, F.; Kobashigawa, J.A.; Reinsmoen, N. Revealing a new mode of sensitization induced by mechanical circulatory support devices: Impact of anti-AT1 R antibodies. Clin. Transplant. 2018, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiemann, N.E.; Meyer, R.; Wellnhofer, E.; Schoenemann, C.; Heidecke, H.; Lachmann, N.; Hetzer, R.; Dragun, D. Non-HLA antibodies targeting vascular receptors enhance alloimmune response and microvasculopathy after heart transplantation. Transplantation 2012, 94, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinsmoen, N.L.; Lai, C.H.; Mirocha, J.; Cao, K.; Ong, G.; Naim, M.; Wang, Q.; Haas, M.; Rafiei, M.; Czer, L.; et al. Increased negative impact of donor HLA-specific together with non-HLA-specific antibodies on graft outcome. Transplantation 2014, 97, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinsmoen, N.L.; Mirocha, J.; Ensor, C.R.; Marrari, M.; Chaux, G.; Levine, D.J.; Zhang, X.; Zeevi, A. A 3-Center Study Reveals New Insights Into the Impact of Non-HLA Antibodies on Lung Transplantation Outcome. Transplantation 2017, 101, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, C.Y.; Lord, M.S.; Melrose, J.; Rees, M.D.; Knox, S.M.; Freeman, C.; Iozzo, R.V.; Whitelock, J.M. Heparan sulfate-dependent signaling of fibroblast growth factor 18 by chondrocyte-derived perlecan. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 5524–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cailhier, J.F.; Sirois, I.; Laplante, P.; Lepage, S.; Raymond, M.A.; Brassard, N.; Prat, A.; Iozzo, R.V.; Pshezhetsky, A.V.; Hebert, M.J. Caspase-3 activation triggers extracellular cathepsin L release and endorepellin proteolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 27220–27229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardinal, H.; Dieude, M.; Brassard, N.; Qi, S.; Patey, N.; Soulez, M.; Beillevaire, D.; Echeverry, F.; Daniel, C.; Durocher, Y.; et al. Antiperlecan antibodies are novel accelerators of immune-mediated vascular injury. Am. J. Transplant. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2013, 13, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulez, M.; Pilon, E.A.; Dieude, M.; Cardinal, H.; Brassard, N.; Qi, S.; Wu, S.J.; Durocher, Y.; Madore, F.; Perreault, C.; et al. The perlecan fragment LG3 is a novel regulator of obliterative remodeling associated with allograft vascular rejection. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Dieude, M.; Hamelin, K.; Henault-Rondeau, M.; Patey, N.; Turgeon, J.; Lan, S.; Pomerleau, L.; Quesnel, M.; Peng, J.; et al. Anti-LG3 Antibodies Aggravate Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Long-Term Renal Allograft Dysfunction. Am. J. Transplant. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2016, 16, 3416–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesco, L.; Irure, J.; Rodrigo, E.; Guiral, S.; Ruiz, J.C.; Gomez, J.; Lopez-Hoyos, M.; San Segundo, D. Anti-perlecan antibodies and acute humoral rejection in hypersensitized patients without forbidden HLA specificities after kidney transplantation. Transpl. Immunol. 2019, 52, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharat, A.; Saini, D.; Steward, N.; Hachem, R.; Trulock, E.P.; Patterson, G.A.; Meyers, B.F.; Mohanakumar, T. Antibodies to self-antigens predispose to primary lung allograft dysfunction and chronic rejection. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 90, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tiriveedhi, V.; Gautam, B.; Sarma, N.J.; Askar, M.; Budev, M.; Aloush, A.; Hachem, R.; Trulock, E.; Myers, B.; Patterson, A.G.; et al. Pre-transplant antibodies to Kalpha1 tubulin and collagen-V in lung transplantation: Clinical correlations. J. Heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Society Heart Transplant. 2013, 32, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hachem, R.R.; Tiriveedhi, V.; Patterson, G.A.; Aloush, A.; Trulock, E.P.; Mohanakumar, T. Antibodies to K-alpha 1 tubulin and collagen V are associated with chronic rejection after lung transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2012, 12, 2164–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, D.; Weber, J.; Ramachandran, S.; Phelan, D.; Tiriveedhi, V.; Liu, M.; Steward, N.; Aloush, A.; Hachem, R.; Trulock, E.; et al. Alloimmunity-induced autoimmunity as a potential mechanism in the pathogenesis of chronic rejection of human lung allografts. J. Heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Society Heart Transplant. 2011, 30, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akbarpour, M.; Bharat, A. Lung Injury and Loss of Regulatory T Cells Primes for Lung-Restricted Autoimmunity. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 37, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, M.; Xu, Z.; Nayak, D.K.; Sharma, M.; Hachem, R.; Walia, R.; Bremner, R.M.; Smith, M.A.; Mohanakumar, T. Donor-Derived Exosomes With Lung Self-Antigens in Human Lung Allograft Rejection. Am. J. Transplant. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2017, 17, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nath, D.S.; Tiriveedhi, V.; Basha, H.I.; Phelan, D.; Moazami, N.; Ewald, G.A.; Mohanakumar, T. A role for antibodies to human leukocyte antigens, collagen-V, and K-alpha1-Tubulin in antibody-mediated rejection and cardiac allograft vasculopathy. Transplantation 2011, 91, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angaswamy, N.; Klein, C.; Tiriveedhi, V.; Gaut, J.; Anwar, S.; Rossi, A.; Phelan, D.; Wellen, J.R.; Shenoy, S.; Chapman, W.C.; et al. Immune responses to collagen-IV and fibronectin in renal transplant recipients with transplant glomerulopathy. Am. J. Transplant. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2014, 14, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilalic, S.; Michlmayr, A.; Gruber, V.; Buchberger, E.; Burghuber, C.; Bohmig, G.A.; Oehler, R. Lymphocyte activation induces cell surface expression of an immunogenic vimentin isoform. Transpl. Immunol. 2012, 27, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayet, W.J.; Wandel, E.; Hermann, E.; Dumann, H.; Kohler, H. Antibodies to cytoskeletal components in patients undergoing long-term hemodialysis detected by a sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin. Nephrol. 1990, 33, 272–278. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, V.; Howell, W.M. Vimentin antibody production in transplant patients and immunomodulatory effects of vimentin in-vitro. Hum. Immunol. 2013, 74, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nankivell, B.J.; Borrows, R.J.; Fung, C.L.; O’Connell, P.J.; Allen, R.D.; Chapman, J.R. The natural history of chronic allograft nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 2326–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Besarani, D.; Cerundolo, L.; Smith, J.D.; Procter, J.; Barnardo, M.C.; Roberts, I.S.; Friend, P.J.; Rose, M.L.; Fuggle, S.V. Role of anti-vimentin antibodies in renal transplantation. Transplantation 2014, 98, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, M.; Maw, T.T.; Santos, R.D.; Shenoy, S.; Wellen, J.; Mohanakumar, T. Immunoglobulin isotype switching of antibodies to vimentin is associated with development of transplant glomerulopathy following human renal transplantation. Transpl. Immunol. 2017, 45, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mewar, D.; Wilson, A.G. Autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2006, 60, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Soler, R.I.; Borgia, J.A.; Kanangat, S.; Fhied, C.L.; Conti, D.J.; Constantino, D.; Ata, A.; Chan, R.; Wang, Z. Anti-vimentin Antibodies Present at the Time of Transplantation May Predict Early Development of Interstitial Fibrosis/Tubular Atrophy. Transplant. Proc. 2016, 48, 2023–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fhied, C.; Kanangat, S.; Borgia, J.A. Development of a bead-based immunoassay to routinely measure vimentin autoantibodies in the clinical setting. J. Immunol. Methods 2014, 407, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.K.; Dale, B.; Russell, S.D.; Zachary, A.A.; Tedford, R.J. Incidence and early outcomes associated with pre-transplant antivimentin antibodies in the cardiac transplantation population. Clin. Transplant. 2015, 29, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nath, D.S.; Ilias Basha, H.; Tiriveedhi, V.; Alur, C.; Phelan, D.; Ewald, G.A.; Moazami, N.; Mohanakumar, T. Characterization of immune responses to cardiac self-antigens myosin and vimentin in human cardiac allograft recipients with antibody-mediated rejection and cardiac allograft vasculopathy. J. Heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Society Heart Transplant. 2010, 29, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miklos, D.B.; Kim, H.T.; Zorn, E.; Hochberg, E.P.; Guo, L.; Mattes-Ritz, A.; Viatte, S.; Soiffer, R.J.; Antin, J.H.; Ritz, J. Antibody response to DBY minor histocompatibility antigen is induced after allogeneic stem cell transplantation and in healthy female donors. Blood 2004, 103, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorn, E.; Miklos, D.B.; Floyd, B.H.; Mattes-Ritz, A.; Guo, L.; Soiffer, R.J.; Antin, J.H.; Ritz, J. Minor histocompatibility antigen DBY elicits a coordinated B and T cell response after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasone, H.; Tian, L.; Sahaf, B.; Kawase, T.; Schoenrock, K.; Perloff, S.; Ryan, C.E.; Paul, J.; Popli, R.; Wu, F.; et al. Allogeneic HY antibodies detected 3 months after female-to-male HCT predict chronic GVHD and nonrelapse mortality in humans. Blood 2015, 125, 3193–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paul, J.; Nakasone, H.; Sahaf, B.; Wu, F.; Wang, K.; Ho, V.; Wu, J.; Kim, H.; Blazar, B.; Ritz, J.; et al. A confirmation of chronic graft-versus-host disease prediction using allogeneic HY antibodies following sex-mismatched hematopoietic cell transplantation. Haematologica 2019, 104, e314–e317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratwohl, A.; Dohler, B.; Stern, M.; Opelz, G. H-Y as a minor histocompatibility antigen in kidney transplantation: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2008, 372, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Gill, J.S. H-Y incompatibility predicts short-term outcomes for kidney transplant recipients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2009, 20, 2025–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.C.; Kim, J.P.; Chertow, G.M.; Grumet, F.C.; Desai, M. Donor-recipient sex mismatch in kidney transplantation. Gend. Med. 2012, 9, 335–347.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lepeytre, F.; Dahhou, M.; Zhang, X.; Boucquemont, J.; Sapir-Pichhadze, R.; Cardinal, H.; Foster, B.J. Association of Sex with Risk of Kidney Graft Failure Differs by Age. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2017, 28, 3014–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dierselhuis, M.P.; Spierings, E.; Drabbels, J.; Hendriks, M.; Alaez, C.; Alberu, J.; Alvarez, M.B.; Burlingham, W.; Campos, E.; Christiaans, M.; et al. Minor H antigen matches and mismatches are equally distributed among recipients with or without complications after HLA identical sibling renal transplantation. Tissue Antigens 2013, 82, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.C.; Wadia, P.P.; Coram, M.; Grumet, F.C.; Kambham, N.; Miller, K.; Pereira, S.; Vayntrub, T.; Miklos, D.B. H-Y antibody development associates with acute rejection in female patients with male kidney transplants. Transplantation 2008, 86, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, Y.; Mirbaha, F.; Lazaro, A.; Zhang, Y.; Lavingia, B.; Stastny, P. MICA is a target for complement-dependent cytotoxicity with mouse monoclonal antibodies and human alloantibodies. Hum. Immunol. 2002, 63, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiriveedhi, V.; Gelman, A.E.; Mohanakumar, T. HIF-1alpha signaling by airway epithelial cell K-alpha1-tubulin: Role in fibrosis and chronic rejection of human lung allografts. Cell. Immunol. 2012, 273, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burlingham, W.J.; Love, R.B.; Jankowska-Gan, E.; Haynes, L.D.; Xu, Q.; Bobadilla, J.L.; Meyer, K.C.; Hayney, M.S.; Braun, R.K.; Greenspan, D.S.; et al. IL-17-dependent cellular immunity to collagen type V predisposes to obliterative bronchiolitis in human lung transplants. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 3498–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahesh, B.; Leong, H.S.; McCormack, A.; Sarathchandra, P.; Holder, A.; Rose, M.L. Autoantibodies to vimentin cause accelerated rejection of cardiac allografts. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Specificity | Type of Solid Organ Transplantation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renal | Lung | Liver | Heart | |
| MICA | [17,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30] | [31] | [32,33] | [34,35,36] |
| AT1R/ETAR | [22,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59] | [64] | [60,61,62,63] | |
| Perlecan (LG3) | [67,68,69,70] | |||
| Collagen/K-alpha-tubulin | [73,74,78] | [71,72,73,74,75,76] | [77] | |
| Vimentin | [81,82,83,84,86,87] | [88,89] | ||
| Antibody | Solid Organ Transplant | Detection Technique | Cellular Location | Proposed Mechanism | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renal | Lung | Heart | |||||
| MICA | Pre | unclear association with graft survival and ABMR | - | unclear | Luminex | Ligand in NKG2D receptor | Complement-dependent cytotoxicity? [100] |
| Post | unclear association with graft survival and ABMR | BOS, synergistic with HLA | ABMR synergistic with HLA, CAV | ||||
| AT1R | Pre | Acute rejection | Graft failure | Not associated with rejection | Commercially available ELISA | GPCR in endothelia, promoted by ischemic injury | Endothelial damage, vasoconstriction [44] |
| Post | ABMR and decreased graft survival | Possible ABMR and CMR | ABMR and CMR | ||||
| Perlecan | Pre | AVR | - | - | Home made ELISA (also available for Luminex) | Vessel wall component acts as neoantigen after caspase-dependent cleavage | CD3, NK cell infiltrate and C4d deposition [67] |
| Post | ABMR, impaired graft function | - | - | ||||
| Tubulin | Pre | - | BOS, PGD | - | Home made ELISA | Gap junctions, cytoskeletal protein | Complement activation, also HIF-1a and pro-fibrotic growth factors [101] |
| Post | - | ABMR driven by donor HLA, BOS | CAV, ABMR | ||||
| Collagen | Pre | - | BOS, PGD | - | Home made ELISA | Connective tissues | In lung, Ab to collagen type V result in CD4 infiltrate and IL-17 production, resulting in BOS [102] |
| Post | TG | ABMR driven by donor HLA, BOS | CAV, ABMR | ||||
| Vimentin | Pre | IFTA (IgG isotype) | - | Not associated with rejection | ELISA and/or LUMINEX | Cytoskeletal, intermediate filament | CD3, CD4, cell infiltrate and C3d deposition [103] |
| Post | TG (IgG isotype), rejection | - | ABMR and CAV driven by donor HLA | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutiérrez-Larrañaga, M.; López-Hoyos, M.; Renaldo, A.; San Segundo, D. Non-HLA Abs in Solid Organ Transplantation. Transplantology 2020, 1, 24-41. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology1010003
Gutiérrez-Larrañaga M, López-Hoyos M, Renaldo A, San Segundo D. Non-HLA Abs in Solid Organ Transplantation. Transplantology. 2020; 1(1):24-41. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology1010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutiérrez-Larrañaga, María, Marcos López-Hoyos, André Renaldo, and David San Segundo. 2020. "Non-HLA Abs in Solid Organ Transplantation" Transplantology 1, no. 1: 24-41. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology1010003
APA StyleGutiérrez-Larrañaga, M., López-Hoyos, M., Renaldo, A., & San Segundo, D. (2020). Non-HLA Abs in Solid Organ Transplantation. Transplantology, 1(1), 24-41. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology1010003







