Advancements in Semi-Supervised Deep Learning for Brain Tumor Segmentation in MRI: A Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pseudo-Labeling Methods
2.1. Self-Training
2.2. Co-Training
2.3. Tri-Training
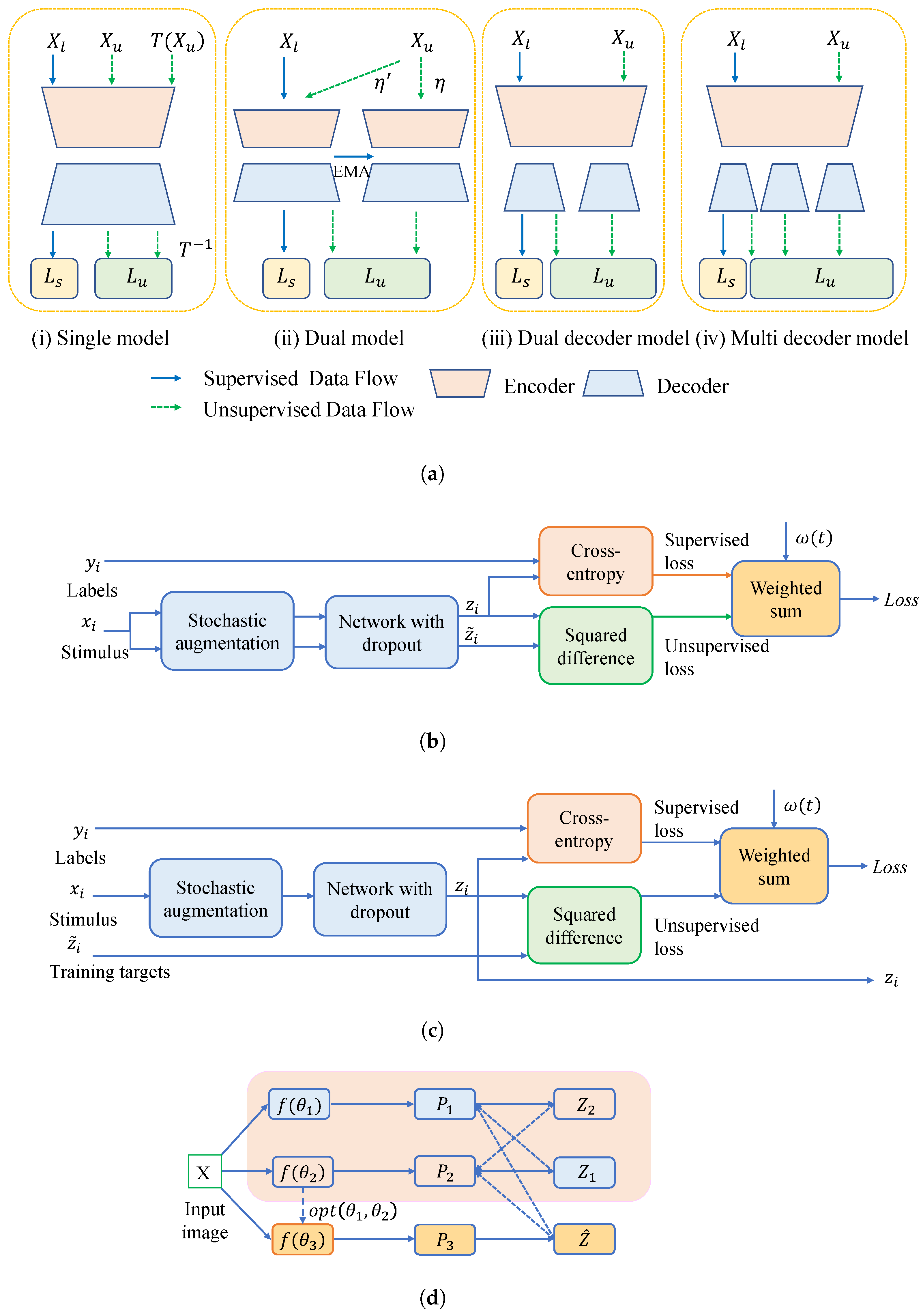
3. Consistency Regularization
3.1. Network-Level Consistency Regularization
3.1.1. Single Model
3.1.2. Dual Model
3.1.3. Dual Decoder and Multiple Decoders
3.1.4. Uncertainty-Aware Approaches
3.2. Data-Level Consistency Regularization
3.3. Task-Level Consistency Regularization
3.4. Other Consistency Regularization
4. Contrastive Learning
4.1. Image-Level CL
4.2. Pixel-Level CL
4.3. Bi-Level CL
5. Adversarial Learning
6. Holistic Approach
7. Summary of Semi-Supervised Approaches and Future Challenges
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC-MT | Ambiguity-consensus mean teacher |
| ASC | Area-similarity constrastive |
| CAD | Computer-aided diagnosis |
| CAT | Constrained Adversarial Training |
| CL | Contrastive Learning |
| CSF | Cererospinal fluid |
| CTM | Constrastive Training Module |
| CPCL | Cyclic prototype consistency learning |
| DL | Deep learning |
| DHC | Dual-biased Heterogeneous Co-training |
| DIffDW | Difficult-aware debiased weighting |
| DistDW | Distribution-aware debiased weighting |
| DSC | Dice Similarity Coefficient |
| DST | Dempster-Shafer theory |
| DTC | Dual-task consistency |
| EMA | Exponential moving average |
| ET | Enhanced tumor |
| FDCT | Fusion-Guided Dual-View Consistency Training |
| FLAIR | Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery sequence |
| FSM | Feature similarity module |
| GANs | Generative Adversarial Networks |
| GBM | Glioblastoma |
| GenSeg | Generative segmentation |
| GM | Gray metter |
| IDH | Isocitrate dehydrogenase |
| Inter-PRL | Inter-patch ranked loss |
| Intra-PRL | Intra-patch ranked loss |
| L2U | Labeled-to-unlabeled |
| MC | Monte Carlo |
| MC-Net | Mutual consistency network |
| MetaSeg | Meta-learning-based semantic segmentation |
| MLP | Multi-layer perceptron |
| MT | Mean teacher |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| MVCM | Mixing Volume Consistency Module |
| PReL | Pseudo-label relearning |
| PReLu | Parametric Rectified Linear Unit |
| REM | Region enhancement module |
| SASSNet | Semantic segmentation algorithm for volumeric medical images |
| SDF | Signed distance field |
| SDM | Signature distance map |
| SEFNet | Semi-supervised evidence fusion framework |
| SegNet | Segmentation network |
| Semi-CML | Semi-supervised contrast mutual learning |
| SSL | Semi-supervised learning |
| TC | Tumor core |
| U2L | Unlabeled-to-labeled |
| UA-MT | Uncertainty-aware mean teacher |
| UPS | Uncertainty-aware pseudo-label selection |
| URCA | Uncertainty-Based Region Clipping |
| UWI | Uncertainty-weighted integration |
| WM | White matter |
| WT | Whole tumor |
| VRC | Voxel Reliability Constraint |
References
- Wacker, J.; Ladeira, M.; Nascimento, J.E.V. Transfer Learning for Brain Tumor Segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1912.12452. [Google Scholar]
- Pellerino, A.; Caccese, M.; Padovan, M.; Cerretti, G.; Lombardi, G. Epidemiology, risk factors, and prognostic factors of gliomas. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2022, 10, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Feo, M.S.; Granese, G.M.; Conte, M.; Palumbo, B.; Panareo, S.; Frantellizzi, V.; De Vincentis, G.; Filippi, L. Immuno-PET for Glioma Imaging: An Update. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S. Deep Learning with Radiogenomics Towards Personalized Management of Gliomas. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 16, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbarzadeh, R.; Caputo, A.; Tirkolaee, E.B.; Ghoushchi, S.J.; Bendechache, M. Brain tumor segmentation of MRI images: A comprehensive review on the application of artificial intelligence tools. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 152, 106405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathimathul Rajeena, P.P.; Sivakumar, R. Brain Tumor Classification Using Image Fusion and EFPA-SVM Classifier. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2023, 35, 2837–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevelegas, A.; Papanikolaou, N. Imaging Modalities in Brain Tumors. In Imaging of Brain Tumors with Histological Correlations; Drevelegas, A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakas, S.; Reyes, M.; Jakab, A.; Bauer, S.; Rempfler, M.; Crimi, A.; Shinohara, R.T.; Berger, C.; Ha, S.M.; Rozycki, M.; et al. Identifying the Best Machine Learning Algorithms for Brain Tumor Segmentation, Progression Assessment, and Overall Survival Prediction in the BRATS Challenge. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1811.02629. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, Y.M.A.; El Garouani, S.; Jellouli, I. A survey of methods for brain tumor segmentation-based MRI images. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2023, 10, 266–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulakshmi, M.; Lakshmi Priya, G.G. Automated brain tumour segmentation techniques—A review. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2017, 27, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baid, U.; Ghodasara, S.; Mohan, S.; Bilello, M.; Calabrese, E.; Colak, E.; Farahani, K.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Kitamura, F.C.; Pati, S.; et al. The RSNA-ASNR-MICCAI BraTS 2021 Benchmark on Brain Tumor Segmentation and Radiogenomic Classification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.02314. [Google Scholar]
- Menze, B.H.; Jakab, A.; Bauer, S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Farahani, K.; Kirby, J.; Burren, Y.; Porz, N.; Slotboom, J.; Wiest, R.; et al. The Multimodal Brain Tumor Image Segmentation Benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 1993–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakas, S.; Akbari, H.; Sotiras, A.; Bilello, M.; Rozycki, M.; Kirby, J.S.; Freymann, J.B.; Farahani, K.; Davatzikos, C. Advancing The Cancer Genome Atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Long, Y.; Han, Z.; Liu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, W.; Chen, L. Swin Unet3D: A three-dimensional medical image segmentation network combining vision transformer and convolution. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2023, 23, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, J.; Ma, P. Two-Branch network for brain tumor segmentation using attention mechanism and super-resolution reconstruction. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 157, 106751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.04597. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. arXiv 2023, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Chaitanya, K.; Erdil, E.; Karani, N.; Konukoglu, E. Local contrastive loss with pseudo-label based self-training for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 87, 102792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Tian, B.; Lukasiewicz, T.; Xu, Z. Multi-modal contrastive mutual learning and pseudo-label re-learning for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 83, 102656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, F.; Tang, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, J. Artificial intelligence multiprocessing scheme for pathology images based on transformer for nuclei segmentation. Complex Intell. Syst. 2024, 10, 5831–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapelle, O.; Schölkopf, B.; Zien, A. Introduction to semi-supervised learning. In Semi-Supervised Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Song, Z.; King, I.; Xu, Z. A Survey on Deep Semi-supervised Learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 35, 8934–8954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, L.; Xue, B.; Zhang, J.; Cai, R.; Jin, C. Learning with limited annotations: A survey on deep semi-supervised learning for medical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 169, 107840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Sheng, V.S.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, C.; Ma, S.; Liu, Z. Deep semi-supervised learning for medical image segmentation: A review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 245, 123052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, L.; Hallinan, J.; Zhang, S.; Makmur, A.; Cai, Q.; Ooi, B.C. BoostMIS: Boosting Medical Image Semi-supervised Learning with Adaptive Pseudo Labeling and Informative Active Annotation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 20634–20644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lu, D.; Luo, X.; Yan, J.; Zheng, Y.; Tong, R.K. Ambiguity-selective consistency regularization for mean-teacher semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 88, 102880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, M.H.; Norman, G.; Nyholm, T.; Lofstedt, T. A Data-Adaptive Loss Function for Incomplete Data and Incremental Learning in Semantic Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 41, 1320–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizve, M.N.; Duarte, K.; Rawat, Y.S.; Shah, M. In Defense of Pseudo-Labeling: An Uncertainty-Aware Pseudo-label Selection Framework for Semi-Supervised Learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.06329. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Cheng, J.; Gao, H.; Xiong, W.; Ren, H. Federated Semi-Supervised Learning for Medical Image Segmentation via Pseudo-Label Denoising. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2023, 27, 4672–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-H. Pseudo-Label: The Simple and Efficient Semi-Supervised Learning Method for Deep Neural Networks. 2013. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:18507866 (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Long, J.; Yang, C.; Ren, Y.; Zeng, Z. Semi-supervised medical image segmentation via feature similarity and reliable-region enhancement. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 167, 107668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Tamura, S. Key information-guided networks for medical image segmentation in medical systems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 121851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Socher, R.; Hoi, S.C.H. DivideMix: Learning with Noisy Labels as Semi-supervised Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.07394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, W.; Yuan, Y. DiffRect: Latent Diffusion Label Rectification for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.09918. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Yao, L.; Cheng, W.; Yu, M.; Shi, W.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Z. Co-training semi-supervised medical image segmentation based on pseudo-label weight balancing. Med. Phys. 2025, 52, 3854–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, M.; Susan, S. Tackling class imbalance in computer vision: A contemporary review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56 (Suppl. S1), 1279–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Ruan, S.; Denœux, T. Semi-supervised multiple evidence fusion for brain tumor segmentation. Neurocomputing 2023, 535, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, A.P. Upper and lower probability inferences based on a sample from a finite univariate population. Biometrika 1967, 54, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, J.; Kuang, H.; Wang, J. A Fully Automated Multimodal MRI-Based Multi-Task Learning for Glioma Segmentation and IDH Genotyping. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 41, 1520–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, C.; de Groot, M.; Alexander, D.C.; Oxtoby, N.P.; Hu, Y.; Jacob, J. Expectation maximisation pseudo labels. Med. Image Anal. 2024, 94, 103125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. URCA: Uncertainty-based region clipping algorithm for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2024, 254, 108278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, B.; Shirani, S.; Keshavarz-Motamed, Z. Semi-supervised segmentation of medical images focused on the pixels with unreliable predictions. Neurocomputing 2024, 610, 128532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, A.; Mitchell, T. Combining Labeled and Unlabeled Data with Co-Training. In Proceedings of the Eleventh Annual Conference on Computational Learning Theory (COLT’98), Madison, WI, USA, 24–26 July 1998; pp. 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Peiris, H.; Hayat, M.; Chen, Z.; Egan, G.; Harandi, M. Uncertainty-guided dual-views for semi-supervised volumetric medical image segmentation. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2023, 5, 724–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Estrada, G.; Pedersoli, M.; Desrosiers, C. Deep co-training for semi-supervised image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 107, 107269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Chen, J.; Song, T.; Wang, G. Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation through Dual-task Consistency. AAAI 2021, 35, 8801–8809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B.H.; Caterina, G.D.; Voisey, J.P. Pseudo-Label Refinement Using Superpixels for Semi-Supervised Brain Tumour Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 19th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Kolkata, India, 28–31 March 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X. DHC: Dual-debiased Heterogeneous Co-training Framework for Class-imbalanced Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.11960. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.H.; Li, M. Tri-training: Exploiting unlabeled data using three classifiers. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2005, 17, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Gao, C.; Zhou, J. Weighted fuzzy rough sets-based tri-training and its application to medical diagnosis. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 124, 109025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Gan, W.; Wang, F.; Yang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Gan, H. Tri-correcting: Label noise correction via triple CNN ensemble for carotid plaque ultrasound image classification. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 91, 105981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Hayashi, Y.; Oda, M.; Kitasaka, T.; Mori, K. TriMix: A General Framework for Medical Image Segmentation from Limited Supervision. In Computer Vision—ACCV 2022; Wang, L., Gall, J., Chin, T.-J., Sato, I., Chellappa, R., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 13846, pp. 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hou, Y.; Liu, H.; Ye, Z.; Zhao, R.; Shen, H. FDCT: Fusion-Guided Dual-View Consistency Training for semi-supervised tissue segmentation on MRI. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 160, 106908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelen, J.E.V.; Hoos, H.H. A survey on semi-supervised learning. Mach. Learn 2020, 109, 373–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, S.; Aila, T. Temporal Ensembling for Semi-Supervised Learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1610.02242. [Google Scholar]
- Tarvainen, A.; Valpola, H. Mean teachers are better role models: Weight-averaged consistency targets improve semi-supervised deep learning results. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 1195–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, M.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, T.; Zeng, X.; Ye, C. Semi-supervised Brain Lesion Segmentation with an Adapted Mean Teacher Model. In Information Processing in Medical Imaging; Chung, A.C.S., Gee, J.C., Yushkevich, P.A., Bao, S., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11492, pp. 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.; Wang, D.; Yan, Q.; Ren, J.; Lau, R.W.H. Dual Student: Breaking the Limits of the Teacher in Semi-supervised Learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.01804. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, M.; Zhang, Z.; Hariharan, B.; Snavely, N.; Freeman, W.T. Unsupervised Semantic Segmentation by Distilling Feature Correspondences. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.08414. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, M.; Ge, Z.; Cai, J.; Zhang, L. Semi-supervised Left Atrium Segmentation with Mutual Consistency Training. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.02911. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Ge, Z.; Zhang, D.; Xu, M.; Zhang, L.; Xia, Y.; Cai, J. Mutual Consistency Learning for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2109.09960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Wang, T. Coarse-Refined Consistency Learning Using Pixel-Level Features for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2023, 27, 3970–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, T.; Zhou, R.; Yang, G. Mutually aided uncertainty incorporated dual consistency regularization with pseudo label for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Neurocomputing 2023, 548, 126411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lian, S.; Luo, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, S. Contour-aware consistency for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 89, 105694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lu, K.; Xue, J.; Wang, S.; Lu, J. Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation with Voxel Stability and Reliability Constraints. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2023, 27, 3912–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Fu, C.-W.; Heng, P.-A. Uncertainty-aware Self-ensembling Model for Semi-supervised 3D Left Atrium Segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.07034. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, A.; Gal, Y. What Uncertainties Do We Need in Bayesian Deep Learning for Computer Vision? arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.04977. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Zhan, B.; Zu, C.; Wu, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y. Semi-supervised medical image segmentation via a tripled-uncertainty guided mean teacher model with contrastive learning. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 79, 102447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yang, Y.; Xia, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S. Dual Uncertainty-Guided Mixing Consistency for Semi-Supervised 3D Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Big Data 2023, 9, 1156–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Sui, B.; Wang, C.; Dou, Q.; Qin, J. Adaptive feature aggregation based multi-task learning for uncertainty-guided semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 232, 120836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiao, R.; Liao, Q.; Li, D.; Zhang, J. Uncertainty-guided mutual consistency learning for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Artif. Intell. Med. 2023, 138, 102476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, X.; Xie, L.; He, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Li, H.; Tian, Q. ATSO: Asynchronous Teacher-Student Optimization for Semi-Supervised Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cisse, M.; Dauphin, Y.N.; Lopez-Paz, D. mixup: Beyond Empirical Risk Minimization. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1710.09412. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, S.; Han, D.; Chun, S.; Oh, S.J.; Yoo, Y.; Choe, J. CutMix: Regularization Strategy to Train Strong Classifiers with Localizable Features. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 6022–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, T.; Xu, K.; Zhu, J. Mixup Inference: Better Exploiting Mixup to Defend Adversarial Attacks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1909.11515. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, V.; Kawaguchi, K.; Lamb, A.; Kannala, J.; Solin, A.; Bengio, Y.; Lopez-Paz, D. Interpolation consistency training for semi-supervised learning. Neural Netw. 2022, 145, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelot, D.; Carlini, N.; Goodfellow, I.; Papernot, N.; Oliver, A.; Raffel, C. MixMatch: A Holistic Approach to Semi-Supervised Learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.02249. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, K.; Berthelot, D.; Li, C.-L.; Zhang, Z.; Carlini, N.; Cubuk, E.D.; Kurakin, A.; Zhang, H.; Raffel, C. FixMatch: Simplifying Semi-Supervised Learning with Consistency and Confidence. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 596–608. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2020/hash/06964dce9addb1c5cb5d6e3d9838f733-Abstract.html (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Cubuk, E.D.; Zoph, B.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. RandAugment: Practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.13719. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, Y.; Li, H.; Xiao, B.; Bi, X.; Li, W. Cross-Mix Monitoring for Medical Image Segmentation with Limited Supervision. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 25, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Lu, B.; Shi, J.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Xia, Y.; Pan, Z.; Lin, Y. Motion-artifact-augmented pseudo-label network for semi-supervised brain tumor segmentation. Phys. Med. Biol. 2024, 69, 055023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Meng, Z. A self-adaptive framework of reducing domain bias under distribution shift for semi-supervised domain generalization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2025, 175, 113087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Debattista, K.; Han, J. Semi-Supervised Unpaired Medical Image Segmentation Through Task-Affinity Consistency. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2023, 42, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Guo, D.; Wang, L.; Yang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Shapey, J.; Vercauteren, T.; Bisdas, S.; Bradford, R.; Saeed, S.; et al. TISS-net: Brain tumor image synthesis and segmentation using cascaded dual-task networks and error-prediction consistency. Neurocomputing 2023, 544, 126295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lu, D.; Yu, L.; Yan, J.; Luo, J.; Ma, K.; Zheng, Y.; Tong, R.K.-y. All-Around Real Label Supervision: Cyclic Prototype Consistency Learning for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 3174–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Dong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tang, H.; Hong, L. Multi-resolution consistency semi-supervised active learning framework for histopathology image classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 259, 125266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, L.; Tan, T.; Tong, T. PCDAL: A Perturbation Consistency-Driven Active Learning Approach for Medical Image Segmentation and Classification. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2025, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Gu, X.; Henderson, P.; Deligianni, F. Multi-Scale Cross Contrastive Learning for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.14293. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zendehdel, N.; Leu, M.C.; Yin, Z. Fine-grained activity classification in assembly based on multi-visual modalities. J. Intell. Manuf. 2024, 35, 2215–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Qi, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Wu, X.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, L. RCPS: Rectified Contrastive Pseudo Supervision for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2024, 28, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitanya, K.; Erdil, E.; Karani, N.; Konukoglu, E. Contrastive learning of global and local features for medical image segmentation with limited annotations. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.10511. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Zeng, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, P.; Wu, X.; Ren, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y. Semi-supervised medical image segmentation via hard positives oriented contrastive learning. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 146, 110020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, T.; Chen, J.; Jiang, B.; Li, H.; Zhang, N.; Yang, G.; Chai, S. GLRP: Global and local contrastive learning based on relative position for medical image segmentation on cardiac MRI. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2024, 34, e22992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2014; Available online: https://papers.nips.cc/paper_files/paper/2014/hash/f033ed80deb0234979a61f95710dbe25-Abstract.html (accessed on 13 March 2024).
- Li, S.; Zhang, C.; He, X. Shape-aware Semi-supervised 3D Semantic Segmentation for Medical Images. Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv. 2020, 12261, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorontsov, E.; Molchanov, P.; Gazda, M.; Beckham, C.; Kautz, J.; Kadoury, S. Towards annotation-efficient segmentation via image-to-image translation. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 82, 102624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Assier, M.A.d.; Vorontsov, E.; Kadoury, S. M-GenSeg: Domain Adaptation For Target Modality Tumor Segmentation with Annotation-Efficient Supervision. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2212.07276. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Shen, X.; Lukasiewicz, T.; Xu, Z. Multi-ConDoS: Multimodal Contrastive Domain Sharing Generative Adversarial Networks for Self-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2024, 43, 76–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Peng, J.; Pedersoli, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Desrosiers, C. CAT: Constrained Adversarial Training for Anatomically-plausible Semi-supervised Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2023, 42, 2146–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Yan, S.; Guan, Y.; Cai, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Tian, B. Semi-Supervised Dual Stream Segmentation Network for Fundus Lesion Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2023, 42, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Han, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, S. BMAnet: Boundary Mining with Adversarial Learning for Semi-Supervised 2D Myocardial Infarction Segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2023, 27, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aralikatti, R.C.; Pawan, S.J.; Rajan, J. A Dual-Stage Semi-Supervised Pre-Training Approach for Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2023, 5, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, S.; Qu, Y.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, W. Consistency and adversarial semi-supervised learning for medical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 161, 107018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, A.K.; Bhandari, A.K. Advances in Deep Learning Models for Resolving Medical Image Segmentation Data Scarcity Problem: A Topical Review. Arch. Computat. Methods Eng. 2024, 31, 1701–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Weng, Y.; Lund, J. Applications of Explainable Artificial Intelligence in Diagnosis and Surgery. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangalathu, S.; Karthikeyan, K.; Feng, D.-C.; Jeon, J.-S. Machine-learning interpretability techniques for seismic performance assessment of infrastructure systems. Eng. Struct. 2022, 250, 112883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehsin, S.; Nasir, I.M.; Damaševičius, R.; Maskeliūnas, R. DaSAM: Disease and Spatial Attention Module-Based Explainable Model for Brain Tumor Detection. BDCC 2024, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Adams, L.C.; Papaioannou, J.-M.; Grundmann, P.; Oberhauser, T.; Figueroa, A.; Löser, A.; Truhn, D.; Bressem, K.K. MedAlpaca: An Open-Source Collection of Medical Conversational AI Models and Training Data. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2304.08247. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, R.; Li, F. Deep learning for surgical workflow analysis: A survey of progresses, limitations, and trends. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, J.J.d.C.; Marques, A.G.; Souza, L.d.N.; Dourado Junior, C.M.J.d.M.; Barros, A.C.d.S.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C.; de Freitas Sousa, L.F. A novel generative model for brain tumor detection using magnetic resonance imaging. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2025, 121, 102498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, J.; Camp, C.; Pezeshk, S. On the application of machine learning techniques to derive seismic fragility curves. Comput. Struct. 2019, 218, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, M.; Ruggieri, S.; Buitrago, M.; Nettis, A.; Adam, J.M.; Uva, G. An ML-based framework for predicting prestressing force reduction in reinforced concrete box-girder bridges with unbonded tendons. Eng. Struct. 2025, 325, 119400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Foundational Theory | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-Labeling | Perform pseudo-labeling of unannotated images and iteratively train, along with annotated data. | The model structure is simple and does not require too many modifications. | The quality requirements for pseudo-labels are high, and overfitting leads to information loss. |
| Consistency Regularization | Encourage prediction consistency under various perturbations. | Strong robustness, even under motion artifacts. | High computational costs for complex models, and choosing the appropriate hyperparameters is challenging. |
| Contrastive Learning | Maximize positive pair affinity and minimize negative pair correlation. | No need for additional data augmentation or negative sampling. | Exhibits a longer training time. |
| Adversarial Learning | Encourage predictive segmentation of unlabeled data closer to that of labeled data with a generator and a discriminator. | Strengthen the model’s ability to generalize and resist perturbations. | It may be challenging in terms of convergence. |
| Reference | Dataset | Backbone | Dice | Type | Highlights | Shortcomings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GenSeg [75] | BraTS 2017 | nn-UNet | 85.00 (1%) | GAN | Employs image-to-image translation to leverage unsegmented data. | Modalities are not considered. |
| SegPL [29] | BraTS 2018 | 3D U-Net | – | Pseudo-label | Generates Bayesian pseudo-labels by learning a threshold to select high-quality pseudo labels. | The model may overfit, resulting in information loss and overconfidence. |
| UG-MCL [56] | BraTS 2019 | V-Net | 83.61 (20%) | Consistency regulation | Leverages intra- and cross-task consistency guided by uncertainty estimation. | Limited to single-class tasks on small-scale datasets. |
| AC-MT [17] | BraTS 2019 | 3D U-Net | 84.63 (20%) | Consistency regulation | Incorporates uncertain regions from unlabeled data into the consistency loss. | Limited compatibility with holistic approaches. |
| URCA [30] | BraTS 2019 | U-Net | 87.58 (20%) | Pseudo-label | Enhances pseudo-label reliability and mitigates label bias via uncertainty-guided region clipping. | Model complexity remains to be optimized. |
| SPPL [35] | BraTS 2020 | nn-UNet | 82.4 (1.9%) | Pseudo-label | Refines the pseudo-labels using the features and edges of the super-pixel maps. | Robustness needs to be enhanced. |
| DUMC [54] | BraTS 2020 | 3D-UNet | 86.67 (30%) | Consistency regulation and Contrastive Learning | Employs a dual uncertainty-guided mixing consistency model. | High computational costs. |
| M-GenSeg [76] | BraTS 2020 | nn-UNet | 86.1 (25%) | GAN | Cross-modality tumor segmentation on unpaired bi-modal datasets. | Used 2D slices instead of full 3D images. |
| MAPSS [66] | BraTS 2020 | 3D U-Net | 85.33 (20%) | Consistency regularization | Enhance the performance and robustness on limited labeled datasets affected by motion artifacts | Bring large computation costs. |
| Co-BioNet [32] | BraTS 2022 | V-Net | 80.30 (40%) | Co-training to generate pseudo-label | Implements co-training with two segmentation and critic networks under uncertainty guidance. | Increased computational cost over the semi-supervised baselines. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, C.; Ng, T.F.; Ibrahim, H. Advancements in Semi-Supervised Deep Learning for Brain Tumor Segmentation in MRI: A Literature Review. AI 2025, 6, 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6070153
Jin C, Ng TF, Ibrahim H. Advancements in Semi-Supervised Deep Learning for Brain Tumor Segmentation in MRI: A Literature Review. AI. 2025; 6(7):153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6070153
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Chengcheng, Theam Foo Ng, and Haidi Ibrahim. 2025. "Advancements in Semi-Supervised Deep Learning for Brain Tumor Segmentation in MRI: A Literature Review" AI 6, no. 7: 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6070153
APA StyleJin, C., Ng, T. F., & Ibrahim, H. (2025). Advancements in Semi-Supervised Deep Learning for Brain Tumor Segmentation in MRI: A Literature Review. AI, 6(7), 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6070153







