Abstract
Fetal hypoxia is a condition characterized by a lack of oxygen supply in a developing fetus in the womb. It can cause potential risks, leading to abnormalities, birth defects, and even mortality. Cardiotocograph (CTG) monitoring is among the techniques that can detect any signs of fetal distress, including hypoxia. Due to the critical importance of interpreting the results of this test, it is essential to accompany these tests with the evolving available technology to classify cases of hypoxia into three cases: normal, suspicious, or pathological. Furthermore, Machine Learning (ML) is a blossoming technique constantly developing and aiding in medical studies, particularly fetal health prediction. Notwithstanding the past endeavors of health providers to detect hypoxia in fetuses, implementing ML and Deep Learning (DL) techniques ensures more timely and precise detection of fetal hypoxia by efficiently and accurately processing complex patterns in large datasets. Correspondingly, this review paper aims to explore the application of artificial intelligence models using cardiotocographic test data. The anticipated outcome of this review is to introduce guidance for future studies to enhance accuracy in detecting cases categorized within the suspicious class, an aspect that has encountered challenges in previous studies that holds significant implications for obstetricians in effectively monitoring fetal health and making informed decisions.
1. Introduction
Fetal distress is a condition caused by intrauterine fetal hypoxia during late pregnancy or labor and is closely associated with changes in Fetal Heart Rate (FHR) signals [1]. Fetal distress can tragically lead to cerebral palsy or neonatal death via hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy [2]. If fetal distress is not promptly identified and treated, the vital organs of the fetus can be harmed before delivery. Therefore, it is critical to enhance the monitoring of the fetal condition within the womb throughout pregnancy to safeguard the safety of both the unborn child and the expectant mother. A study conducted at King Fahd Hospital in Saudi Arabia examined prenatal mortality rates over 10 years spanning from January 1987 to December 1996 [3]. In that study, 19.2 deaths per 1000 live births were found to be the total perinatal mortality rate and Lethal anomalies accounted for 21.1% of fetal deaths. Furthermore, 49.5% of the remaining deaths took place during pregnancy, 16.5% during labor, and 34% happened within the first week after delivery. The findings highlight the complex nature of perinatal mortality and the various factors contributing to adverse outcomes. Understanding the prevalence and effects of hypoxia that can occur during labor and delivery is essential for tackling neonatal mortality rates and the serious effects on the baby’s survival and well-being [4].
CTG monitoring is the most widely used technique for fetal status monitoring in clinical services [5]. The FHR and Uterine Contraction (UC) curves combine to form the CTG signal. CTG can be identified as normal, suspect, or pathological depending on the FHR, heart rate variability, accelerations, and decelerations, according to the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) guidelines [6]. Through CTG monitoring, medical professionals can identify fetal distress early on and take appropriate actions to safeguard the fetus’s health. Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. AI techniques are widely used in various fields and such AI algorithms can analyze medical images, such as X-rays, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans, and CT scans much faster than human radiologists. These AI systems help in detecting anomalies such as tumors, fractures, or diseases like pneumonia, often at early stages, thereby facilitating prompt and effective treatment, which enhances traditional methods [7]. As a result, there is a need for advanced technologies that enable the proactive diagnosis of these diseases by utilizing AI techniques, namely ML and DL. ML, a subset of AI, involves the development of algorithms and statistical models that enable computers to improve their performance on a specific task. DL is a specialized subset of ML that utilizes a Neural Network (NN) with multiple layers to progressively extract higher-level features from raw data, allowing the computer to learn from large amounts of unlabeled data. Moreover, scholars from across the world are committed to developing systems that use ML and DL to assist in the detection of fetal health conditions. These tools are intended to facilitate medical practitioners’ evaluation of CTG signals appropriately and objectively.
In addition, some cases can be missed by health professionals; the early detection of such cases would have allowed the physician to perform a C-section, potentially avoiding negative outcomes. Moreover, it might be difficult to identify and diagnose hypoxia patients promptly, especially in remote and underserved areas. The present approaches for detecting hypoxia rely on subjective human-error-prone manual symptom assessment. As a result, there is a need for a more accurate method for detecting hypoxia in infants using ML algorithms applied to CTG data. By using ML techniques, we can efficiently analyze large volumes of data and improve the precision and effectiveness of fetal health detection and prediction.
Hence, the objective of this research paper is to conduct a narrative review of past studies focused on fetal hypoxia detection using ML techniques during pregnancy and labor stage. To enhance the field’s expertise and proficiency in fetal health monitoring, Figure 1 shows the increase use of the ML from 2012 to 2023 in maternal healthcare. By synthesizing the existing literature in chronological order, this paper aims to identify gaps, limitations, and opportunities in current methodologies.
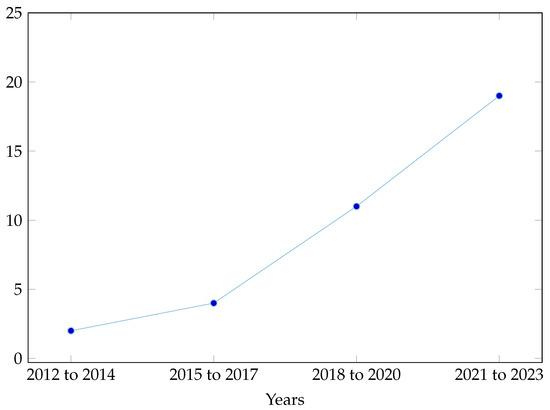
Figure 1.
The increased use of ML over the years.
This paper is structured as follows: Section 2 discusses previous studies, followed by the gap analysis in Section 3. Moreover, Section 4 include a summary of literature, Section 5 illustrates the literature review analysis and Section 6 discusses future work and Section 7 summarizes the key findings and provides a conclusion.
2. Review of the Literature
Several studies have been conducted addressing the use of ML- and DL-based techniques for fetal hypoxia detection. This section presents the existing literature by summarizing previous studies. Figure 2 shows how the summaries are organized based on the techniques used, either ML, DL or ensemble, which are divided into two subsections: during pregnancy and during delivery.
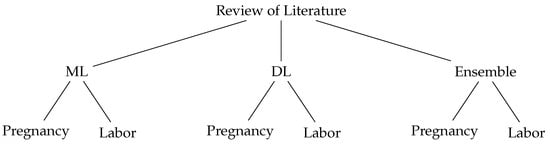
Figure 2.
Review of Literature Taxonomy.
To begin with, a general study was performed by M’Barek et al. [8], which aimed to explore the potential of computerized systems in assisting practitioners during labor and pregnancy. The study emphasized the use of ML and DL techniques in analyzing CTG data. The study involved a comprehensive literature search. The selected publications provided insights into the status of computerized CTG analysis, focusing on ML and DL approaches. The results of the study highlighted the potential of advanced computerized systems in assisting practitioners and improving neonatal outcomes.
2.1. Fetal Hypoxia during Pregnancy Using ML
Firstly, in a paper prepared by Karabulut and Ibrikci [9], they stated that CTG is a common technique used for monitoring changes in FHR and UC. It is crucial to assess CTG data to prevent fetal hypoxia, which is a condition related to the lack of oxygen in a fetus. Furthermore, the dataset that is extracted from the UCI ML Repository contains 2126 records and 21 attributes were used to build the model with attributes classified as normal, suspicious, or pathological. The model itself was built using Adaptive Boosting (AdaBoost), which is a popular variant of the boosting ensemble method. In the ensemble method, multiple classifiers are trained and each one contributes to the final decision of the system. As for the results, Mean Absolute Error (MAE), kappa statistics, and accuracy were utilized to evaluate the model, with the Decision Tree (DT) reaching the highest performance with an accuracy of 95.01%, a kappa of 0.86, and an MAE of 0.034. Finally, the study addresses the need for simultaneous contributions to ML applications in the medical field to achieve the highest performance possible.
Abbas et al. [10] discussed the use of ML to classify fetal hypoxia as acute or chronic to prevent its risks as it is one of the factors for cesarean sections and the third most common cause for newborn deaths. The data utilized are an open source, consisting of eight parameters and only the Ph value was concentrated on in this study. Moreover, 70% of data were reserved for model training and several models were tested namely, DT, Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM), Random Forest (RF), Support Vector Machine (SVM), GLMNET, and K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN). It was found that the RF model yielded an accuracy of 95%, which is the highest among other classifiers, while KNN appeared to be the weakest model.
Additionally, Improta et al. [11] discussed the use of ML to predict the kind of delivery that may lead to solving the problem of unnecessary cesarean sections. In the study, a dataset consisting of 300 CTG scan signals that lasted 20 min was employed, with the use of automated analysis software as a preprocessing to recover FHR. As for the algorithms, J48, ADA-B for ensemble, RF, and Gradient Boosted Tree (GBT) were implemented with 17 features and 10-fold cross validation and researchers found that the RF algorithm scored the highest accuracy, which is 87.6%, while GBT was the highest in recall. Sensitivity, also known as recall, measures the proportion of actual positive cases that were correctly identified by a model. The authors mentioned a limitation caused by the limited data, which leaves room for improvements by using multiple datasets consisting of a decent amount of data to train the model.
Quite interestingly, Zhao et al. [12] aimed to utilize scalable ML algorithms for developing a perinatal hypoxia diagnostic system. The study employed big data and various ML techniques. The study implements the model using the data from [9]. The researchers utilized Spark for dataset analysis. Feature engineering involved combining input features into a single vector using Vector Assembler. ML algorithms such as SVM, RF, and Logistic Regression (LR) were implemented using Python and PySpark models. A comparison was made between straightforward SVM and RF with Sparks. Performance evaluation was performed using the K-fold technique and Spark RF achieved a higher accuracy of 97%, recall of 99%, F1 score of 98%, and an Area Under the ROC Curve (AUC) of 0.97, which refers to a metric used to evaluate the performance of a binary classification model. However, the study did not explore the potential of further exploration of big data computations or utilization of unsupervised or reinforced ML algorithms. Furthermore, the exploration of DL models was not undertaken.
Also utilizing SVM, Cömert et al. [13] discussed that the two biophysical signals that compose CTG are UC and FHR. Computerized systems were typically used in this field of research to produce more objective and reproducible outcomes. The introduction of an open-access intrapartum CTG dataset was available for download from PhysioNet. Additionally, DTs, SVMs, Artificial Neural Network (ANN), and KNN are also examples of ML models that are used. Using the 10-fold cross-validation approach, the effectiveness of the feature selection methods was evaluated. As a result, the SVM yielded the highest accuracy of 88.58%, sensitivity was 77.40%, and specificity, which measures the proportion of actual negative cases that were correctly identified by a model was 93.86%. The study’s limitations are that it does not consider any other fetal surveillance methods or alternative strategies for enhancing fetal well-being monitoring.
Furthermore, Arif et al. [14] analyzed the DT method’s classification of the fetal state code from the Cardio graphic dataset. The study implements the model using the data from [9]. Furthermore, the popular supervised learning algorithm Classification and Regression Trees (CART) is utilized as a DT strategy for classification. A binary tree structure is applied in research to display algorithms and the Gini index is used to choose the attribute containing the most information. As a result, the entire experiment’s accuracy was 98.7%. These findings demonstrated the effectiveness of CART as well as their potential for making more predictions.
Alsaggaf et al. [15] proposed a fetal hypoxia diagnostic model to aid the field’s experts. The study was carried out on a CTG dataset that has a total of 552 raw samples and preprocessed by using the Hermite spline interpolation technique to fix the missing beats problem. Furthermore, the implementation included three ML algorithms, which are, SVM, KNN, and ANN with three basic layers. Consequently, it was found that the SVM model yielded an accuracy of 94.75%, which is the highest among other classifiers.
Moreover, Sajal Baxi [16] developed an accurate and sensitive decision-support model that can identify pathological features based on FHR recordings taken during pregnancy. The dataset used consists of FHR recordings along with 10 other variables obtained from 1800 pregnant women in their third trimester. Furthermore, the approach used in the study involves two stages. In the first stage, the Boruta algorithm was used to identify important variables for predicting the outcome of the test set. In the second stage, the RF algorithm was used to construct the model based on the variables obtained from the first stage. Regarding the results of the study, the RF model achieved an accuracy of 94.71% on the test set. As for the limitations, the study did not consider other factors that may affect fetal hypoxia, such as maternal health conditions and lifestyle factors.
Nonetheless, Pini et al. [17] addressed the use of ML to examine a fetal pathological condition caused by hypoxia. The dataset used was acquired from a CTG scan and data preprocessing was applied to treat the data and use it in training. For training, the SVM algorithm was used, which resulted in 93% accuracy, 93% sensitivity, and 84% specificity. The researchers mentioned a complexity domain, which is the application of nonlinear methodologies.
Furthermore, Gude and Corns. [18] created an integrated model that recognizes patterns in fetal heart rate and uses an LSTM to forecast values that are subsequently classified using an ensemble approach. Additionally, the CTG data and related pH values for approximately 8000 individuals were submitted by the Phelps County Regional Medical Centre. This model classified the CTG recording using SVM, RF, and NN. For each method, hyperparameter tuning was conducted via a grid search. The algorithms are compared using three performance measures: specificity, sensitivity, and accuracy. Moreover, to prevent overfitting, a five-fold cross-validation was applied. Consequently, 72.22% accuracy, 66.66% sensitivity, and 85.71% specificity are achieved using the SVM. The study is limited due to the ensemble model’s lesser accuracy discussed in this paper and the dataset’s small size of 94 samples.
Kedia et al. [19] enhanced prenatal healthcare for mothers as well as infants using CTG-based fetal health categorization. The study’s dataset was used similar to [8]. Furthermore, the methodology of this study was an ML-based classification model for fetal health based on CTG to predict the overall fetal health. The proposed ML models used were the SVM, RF, LR, Naïve Bayes (NB), and eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) algorithm. RF was the most accurate prediction model, with 96% accuracy. The datasets utilized in the study were restricted to a specific population.
Finally, Jones et al. [20] developed the first acML algorithm to identify high-risk pre-term pregnancies using FHR monitoring. The study sourced 4867 antepartum FHR traces from pregnancies that were assigned to at least 1 of 10 adverse conditions and 4014 normal pregnancies. Furthermore, six ML algorithms were trained using k-fold cross-validation to identify each trace as either normal or high risk. The RF classifier was the most effective model, yielding a sensitivity of 76.2%, a specificity of 87.5%, and an F1 score of 81.7%, indicating a high discriminative ability between pregnancy outcomes. The F1 score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall used when dealing with imbalanced datasets.
2.2. Fetal Hypoxia during Labor Using ML
Firstly, a study by Mooney et al. [21] aimed to develop an ML algorithm that can predict the occurrence of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in infants with perinatal asphyxia. The data for this study were collected from 409 single-birth infants, including 237 males and 172 females, who were clinically and biochemically diagnosed with the condition within the first 72 h from birth. The data were split into two models: one with features like pH, lactate, and base deficit removed (Model 1) and the other with infants without these features removed. The researchers applied the RF algorithm to both sets of data. The results showed that the RF models highest accuracy reached was 94%. The study was limited by a bias in the dataset for the second model, as not all infants with perinatal asphyxia underwent postnatal blood gas analysis.
Additionally, Zhong et al. [22] examined the effectiveness of using AI to analyze FHR signals to calculate a baseline value, spot accelerations, and decelerations using electronic fetal monitoring during labor. In addition, the dataset is The NanFang Hospital of Southern Medical University provided a total of 43,888 CTG recordings of female patients undergoing deliveries. The SVM classifier is the algorithm that was used in this investigation. Furthermore, 10-fold cross-validation was used to evaluate the computations. Consequently, in terms of the automatic analysis of FHR based on CTG data, the suggested AI-based system, CTGNet, performs well. The F1-measure (86.85) of the suggested technique was better than those of the best traditional method presented by Mantel.
Next, Das et al. [23] proposed an ML-based model and applied it independently to the two stages of labor and classified the CTG. In this model, the OB TraceVue System was used to collect 552 intrapartum data for the Czech Technical University and University Hospital of Brno datasets between 27 April and 6 August 2012. ML algorithms such as Multilayer Perceptron (MLP), SVM, RF, and Bagging were used for classification. Additionally, the authors examined the k-value selection for the k-fold cross-validation to assess its robustness. As a result, the RF algorithm produced the best results, with a sensitivity of 96.4% and a specificity of 98.4%. The study’s difficulties were that the models were trained on a small amount of data, which caused overfitting.
M’Barek et al. [24] introduced DeepCTG® 1.0, a model that can infer with fetal acidity from CTG signals. It was built and evaluated using three datasets, CTU-UHB, Beaujon Hospital, and SPaM. For instance, the algorithm Dawes and Redman published was employed in the model. Several multivariate logistic regression models were trained and evaluated using k-fold cross-validation using five folds on the three datasets. The optimal result that the model achieved is AUC = 0.756 with cubic Hermite spline interpolation and 0.760 with linear interpolation.
Finally, Mennickent et al. [25] presented the current level of knowledge about the application of ML to diseases and difficulties associated with pregnancy. The datasets in the ML model were typically from the biological area. The model was developed by comparing the performance of multiple ML classification models such as boosted DT, Bayes point machine, decision forest, decision jungle, locally deep SVM, LR, NN, SVM, and RF. In this study, XGBoost with cross-validation was used as a validation technique. In addition, with a 45% correct prediction rate for stillbirths, XGBoost produced the best results. For spontaneous cases, LR produced the best outcomes, with validation AUC during the first and second trimesters of 59.4% and 64.5%, respectively. The best performances in preterm birth were from RF, with AUC of 0.92 and 0.89 in the testing dataset.
2.3. Fetal Hypoxia during Pregnancy Using DL
Firstly, Sundar [26] evaluated some of the statistical and ML techniques used to classify CTG data. The study implements the model using the data from [8]. Additionally, a supervised learning model was used to build the network, where a set of labeled data was used for training the ANN model and then evaluating the model on the testing data. The ANN model provided significant performance as it could identify the three fetal states, which are normal, suspicious, or pathological, with precision, recall, and F1-scores of 97.06%, 99.10%, and 97.84%, respectively. As for the limitations of the study, the ANN model could not perform well in the case of a suspicious classification.
Simultaneously, Ersen Yilmaz [27] discussed the implementation of ANNs to detect the state of a fetus using the dataset mentioned in the paper [8]. In the application of ANN, several models were tested such as MLP and Probabilities Neural Network Probabilities Neural Network (PNN). To evaluate the models, 10-fold cross-validation was used to compare the performance of these two models. The study showed a slow conversion rate as a serious drawback when training MLP. As a result, PNN yielded the highest accuracy of 92.15%.
Furthermore, Cömert Z. and Kocamaz A. F. [28] aimed to investigate and compare the behaviors and performances of various ANN training algorithms for the classification of CTG signals. The goal was to determine the most efficient and fastest training algorithm for CTG signal classification. The study used a database similar to [8]. The study employed five different training algorithms for artificial neural networks: GD, RB, Conjugate Gradient, Quasi-Newton, and Levenberg-Marquardt (LM). Two experimental setups were performed during the training and testing stages. According to the results of the study, all of the training algorithms produced satisfactory results. The best classification performances were achieved with the LM backpropagation and Recurrence Plot Recurrence Plot (RP) algorithms. The geometric mean values of RP and LM were obtained as 89.69% and 86.14%, respectively. One limitation of the study is that it did not explore the combinations of feature selection techniques and different ML algorithms.
However, Kaur et al. [29] aimed to develop a CAD system for detecting fetal hypoxia using FHR signals. The research utilized a dataset similar to [8]. The proposed system integrated Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). The FHR signals were preprocessed and transformed into two-dimensional images using RP, capturing non-linear characteristics. CNN could automatically learn features from the data without manual feature engineering. The optimized CNN model achieved an average performance across 10-fold, with an accuracy of 98.69%, sensitivity of 99.29%, specificity of 98.10%, and an AUC of 98.70%. A limitation of the study was that the dataset included only images, limiting the analysis to visual information.
Also using CNNs, Ma’sum et al. [30] proposed a DL approach that was followed to detect hypoxia in fetuses using FHR and UC using 552 data collected from a CTG scan of 552 pregnant women. The study implements the model using the data from [9]. Various DL methods such as DenseNet and CNN were used with pre-processing for the data where missing values were assigned a zero while noise remained with no treatment. In the study, different strategies such as data-scaling, representation input, classifier layers increasing, and up-sampling were tested for improving detection in five scenarios that concluded in achieving an 81% f1-score with standard DenseNet, which was the highest among all of the scenarios. It can be observed that the study has a limitation of using raw signals other than data with features extracted.
Mohan and V [31] explored the relevance of CTG signals to fetal hypoxia. The main goal of the study was to use CNN models and CTG signals to identify fetal hypoxia. The dataset used in this study is similar to [12]. The dataset included 447 normal cases and 105 hypoxic cases. This study followed a methodology that included preprocessing the CTG signals to remove noise and artifacts. The preprocessed signals are then converted into recurrence plots and fed into three different CNN models (VGG16, Residual Network (ResNet), and CNN) for the classification of normal or hypoxic signals. The authors compared the performance of VGG16, ResNet, and CNN models on the RP data and found that VGG16 achieved the best accuracy of 82.02%. The main limitation of the study is the imbalance in the dataset.
Another paper by Obaidullah et al. [32] compared four ML models, namely MLP, RF, NB, and SLR, to suggest a classification strategy for FHR deceleration. Furthermore, the model used two feature sets, each with 12 event points and the baseline of FHR. The MLP achieved the highest accuracy of 97.94% with the first feature set and RF achieved an accuracy of 63.92% with the second feature set. Furthermore, the study used a dataset similar to [9]. Concerning the study’s shortcomings, the model failed to distinguish several patterns within the gray zone while integrating curtain features derived from the dataset.
Nonetheless, Lin et al. [33] developed an automatic analysis system named Long-term Antepartum Risk Analysis system (LARA) for continuous FHR monitoring, combining DL and information fusion methods. The dataset used for the study was collected from April 2019 to December 2018 at Peking University Third Hospital, consisting of 114 sequences of long-term monitoring from 86 singleton deliveries. Furthermore, the methodology involved a labeling process to classify the monitoring data as normal or abnormal. Afterward, the LARA model was developed after preprocessing the labeled data. As for the evaluation, the LARA model obtained an AUC of 0.872, an accuracy of 81.6%, specificity of 81.1%, a precision of 0.271, and an F1 score of 0.415.
2.4. Fetal Hypoxia during Labor Using DL
Firstly, Fergus et al. [34] aimed to demonstrate a proof-of-concept approach for differentiating between cesarean sections and normal deliveries based on FHR signals using AI techniques. The study utilized an open-source dataset similar to [12]. Various ML algorithms, including RF, DT, NB, SVM, and ANN, were trained and validated. The results showed that ANN achieved a sensitivity of 94%, a specificity of 91%, an AUC of 99%, an F-score of 100%, and a Mean Squared Error (MSE) of 1%. However, it is important to note that the study is limited by its dataset size and used oversampled data. Additionally, it did not consider other significant clinical factors that may impact the classification performance.
In another study by Petrozziello et al. [35], the aim was to develop a DL technique to evaluate electronic fetal monitoring (EFM) during labor. The model was built using a dataset that was obtained from Oxford University and contains 35,429 EFM records. Moreover, the authors utilized CNNs and LSTM networks to analyze the EFM traces and predict fetal compromise. The results showed that CNN outperformed the results of the clinical practice and showed robust performance with a TPR of 44% and a FPR of 15%, which is higher than the clinical practice with a TPR of 31%. As for the limitations of the study, they include the use of EFM signals at 0.25 Hz, analysis only on the last hour of EFM, and no mention of the labor stage. In addition, training datasets, network sizes, and the incorporation of clinical risk factors may significantly improve the accuracy of the model.
Another paper by Alkanan [36] aimed to examine several approaches to overcoming the difficulties associated with CTG and anticipate any issues that could affect the mother’s and fetus’s safety and health during pregnancy and delivery. The dataset used for this study included more than 37,000 CTG records that were acquired from multiple hospitals between 2012 and 2017 as part of a clinical trial. Moreover, both DL and ML algorithms were employed, such as SVM, RF, DT, ANN, and CNN. As for the result, utilizing an RF yielded the best AUC of 0.89 in identifying high-risk deliveries, whereas utilizing CNN produced an AUC of 0.958 in categorizing newborns with low Apgar scores. However, it is worth noting that the dataset used in the study suffered from imbalances and C-sections deliveries were excluded from the research.
Furthermore, a study by Francis et al. [37] recommended utilizing the Apgar score in the ML model as a hypoxia measure. The study’s primary objective was to use ML algorithms to identify fetal hypoxia at delivery. The dataset used in the study is similar to [9]. Furthermore, five ML algorithms were used, including a DT, RF, SVM, k-nearest neighbor, and ANN. The findings demonstrated that AUROC, F1 score, precision, and recall were used to evaluate the performances. The recall (100%) was highest for the ANN with four deep layers, whereas the F1 (97%), AUROC (99.73%), and precision (97%) were highest for the RF classifier. The study was limited to a limited number of samples, which led to oversampling.
2.5. Fetal Hypoxia during Pregnancy Using Ensemble
Firstly, Mishra [38] aimed to use ML techniques to classify fetal hypoxia based on CTG data. The study implements the model using the data from [9]. Furthermore, ANN, SVM, RF, and SL with the AdaBoost ensemble approach and 10-fold cross-validation were utilized for robustness verification. A stacking of the algorithms was performed, obtaining the highest accuracy of 98.79%. Additionally, while testing over a larger dataset can be beneficial, obtaining such large amounts of data is challenging due to the confidentiality of the patient’s information. Moreover, the Stack 2 implemented in the study can be used on different medical datasets to verify its performance.
In another research paper written by Fergus et al. [39], the aim was to develop ans ML-based decision support system for accurately classifying delivery types using CTG traces. The researchers utilized an open dataset same as [9], extracted 13 features from raw CTG fetal heart rate traces, and employed feature set engineering techniques. To address the imbalanced class distribution, a synthetic minority oversampling technique was used and RF and SVM algorithms. An ensemble classifier (RF, SVM) achieved results with 87% and 95%, sensitivity, 90% specificity, 96% AUC, and a 0.9 mean square error. Two limitations of the study should be noted. Firstly, the dataset used in the study was relatively small and not normally distributed. Secondly, the study focused solely on the FHR signal.
In addition, Riskyana et al. [40] employed ensemble learning methods and DL methods to detect hypoxia. They developed and implemented ensemble learning methods (Bagging Tree (BT), AdaBoost, and Voting Classifier) with classifier methods (DT, SVM, SGD, GLVQ, and NB). They also used DL methods (specifically CNN and DenseNet) to detect hypoxia in fetal conditions based on CTG data analysis. Data from CTG were employed in the study, with a particular emphasis on the FHR signal. The dataset had matching labels that listed the pH values, which served as the benchmark for classification. The BT approach combined with the NB classifier produced the best results. The F1-score for the normal class was 0.76, while the F1-score for the hypoxia class was 0.45. The paper did not disclose details about the dataset used due to the private nature of the research and it did not provide any information regarding how the noise present in the dataset was handled.
Simultaneously, Hoodbhoy et al. [41] aimed to assess the precision of ML algorithms in identifying high-risk fetuses based on CTG data. The study implements the model using the data from [9]. In this study, various ML algorithms, including MLP, SVM, K-nearest neighbors, XGBoost classifier, AdaBoost classifier, RF, LR, Gaussian NB, and DT, were employed. To address the imbalanced nature of the dataset, the Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE) was applied as a balancing technique. This technique aimed to prevent overfitting of the ML models on skewed classes. Although the results showed that the fetal state could be predicted more accurately using five features, these factors included the percentage of time with abnormal short-term variability, the percentage of time with abnormal long-term variability, the number of (AC), the mean value of short-term variability, and UCs. These five factors were found to carry the greatest importance in predicting the fetal state. Furthermore, the XGBoost model achieved the highest sensitivity (92%) in predicting a pathological state. The model had limitations in accurately predicting the suspect fetal state as the sensitivity dropped to 73%.
Next, Dixit [42] intended to create ML algorithms that can predict fetal health using data from CTG scans and classify the fetal state into three categories, normal, suspicious, or pathological. The dataset used in [8] was utilized in the study to implement multiple ML models. Additionally, the study uses SelectKBest from the scikit-learn library’s univariate feature selection technique to choose the dataset’s most pertinent features based on their statistical significance. Additionally, the Extra Trees model outperformed the others with an accuracy of 93.66% and recall and precision of 93.66% and 93.82%, respectively. The dataset alone does not take into consideration the intricacy of a fetus’s health; hence, the study has certain limitations in this regard.
Research by Chidambaram and Joy [43] aimed to analyze different classifiers and ensemble techniques to enhance fetal health prediction. In the study, a dataset similar to [9] was used. To carry out the analysis, testing data were set to size 30% and fed into five classification algorithms which are SVM, KN, DT, Gaussian Naive Bayes, and Linear Discriminant Analysis. Moreover, after comparing the models and setting the highest accuracy, different ensemble methods were tested to optimize that performance. The results showed that the DT model scored the maximum base accuracy of 92.63%, whereas the Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LightGBM) improved that base accuracy to 95.90%.
2.6. Fetal Hypoxia during Labor Using Ensemble
Firstly, Pavel et al. [44] predicted infants with electrographic seizures in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy at an early stage using ML algorithms. Furthermore, the dataset used in the study contained 162 infants with hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy who used multichannel EEG monitoring to predict seizures based on various clinical and EEG features. Additionally, the models used in this study were developed using RF for clinical and qualitative EEG features. GBM was used for quantitative EEG features, which were evaluated using the Matthews correlation coefficient and area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve. Furthermore, the missing data were replaced with mean values and features with over 50% missing data were excluded. The highest result was achieved by the clinical and gradient boosting quantitative EEG models, with a Matthews correlation coefficient of 0.513 and an AUC of 0.746.
Next, in a study by Al Duhayyim et al. [45], the paper aimed to identify the abnormal, suspicious, and pathological fetus readings in the CTG results that are imbalanced. Moreover, automating the process of classifying fetal health is necessary in order to obtain a prompt and precise diagnosis of both fetal and maternal health. The dataset used in the study is similar to [9]. Furthermore, the proposed model used five ensemble learners: RF, AdaBoost, XGBoost, CatBoost, and LightGBM. The CTG data were then balanced using the random oversampling technique to train the ensemble models. Consequently, each classifier assesses AUROC values, F1-scores, accuracy, precision, and recall. The XGBoost, LightGBM, and CatBoost classifiers produced results with 99% accuracy.
In another study by Asfaw et al. [46], the authors considered the problem of developing DL techniques to predict adverse birth outcomes. Specifically, the study focuses on using early labor data and cardiotocography data, which consist of infant extracted features delivered at the John Radcliffe Hospital in Oxford between 1993 and 2012. The main technique applied is a multimodal DL approach that combines 1D CNNs, LSTMs, and two CNNs. The multimodal architecture combining 1D-CNN-LSTM and 2D-CNN was evaluated using Partial AUC, TPR, and FPR with a best performance of 0.85, 0.67, and 5%, respectively. Moreover, one of the limitations of the study is that it utilizes data augmentation, which presents the potential of amplifying label noise within the dataset. Moreover, the classification performance could be improved by analyzing longer traces, incorporating uterine contraction signals and incorporating clinical risk factors into the model.
3. Gap Analysis
Based on an extensive literature review, previous studies have primarily concentrated on identifying and preventing fetal hypoxia. However, it is worth noting that the datasets presented in some of the papers, such as [11,18,19,21,23,31,35,36,38,39,40,43], have limited data and imbalanced samples, which may have affected the study’s bias. Additionally, in [29], the analysis was restricted to visual data because the dataset only contained images. An additional significant deficiency observed in the research’s findings was the inadequate management of data preprocessing procedures. For instance, the handling of noise present in the dataset is not addressed in the research paper [43]. Data augmentation is used in the study [46], which raises the possibility of increasing label noise in the dataset. Referring to the papers [26,32,42], it was found that accuracy was impacted by the absence of proper handling of missing data. Moreover, the models used could not perform well in the case of a suspicious classification. Additionally, in the paper [30], an important preliminary technique, which is future extraction, was missing and they used a raw signal. Also, in [28], the study failed to investigate the interaction between various ML algorithms and feature selection strategies. In the paper [9], more concurrent contributions to ML applications are required in the medical domain. Additionally, there is need to investigate DL models [11]. The studies [12,15,18] did not take into account any other fetal surveillance methods or alternative strategies for enhancing fetal well-being monitoring. According to [34], regression analysis with a wider number of classes should be used in the study instead of merely differentiating between a vaginal delivery and a cesarean section to predict the predicted time to delivery. Based on the gaps that have been found in prior studies, this paper provides an overall analysis and evaluation of techniques employed in the detection of fetal hypoxia during the third trimester and labor. It explores a range of methods and examines their respective strengths and limitations.
4. Summary Tables of Earlier Utilized Algorithm
This review emphasizes the importance of analyzing CTG data using a variety of ML and DL techniques. The understanding of prenatal monitoring is greatly advanced by these studies, and the health of mothers and fetuses is greatly enhanced. As a result of critical insights from CTG data being uncovered by researchers using ML and DL algorithms, more precise diagnoses and customized treatment regimens have been made. A thorough assessment of performance metrics is carried out in every study, including the phases of pregnancy and childbirth. These evaluation metrics include accuracy, AUC, sensitivity, and F1 score. Such metrics are vital for clinical management and decision-making, shedding light on the predictive capabilities of each algorithm concerning pregnancy- and labor-related outcomes. Table 1 presents the ML summary table of earlier utilized algorithms; Table 2 features the DL summary table of earlier utilized algorithms; and Table 3 showcases the ensemble summary table of earlier utilized algorithms. These tables collectively provide a comprehensive overview of the diverse ML, DL, and ensemble techniques applied in CTG data analysis, contributing significantly to the enhancement of fetal health care.

Table 1.
ML summary table of earlier utilized algorithm.

Table 2.
DL summary table of earlier utilized algorithm.

Table 3.
Ensemble summary table of earlier utilized algorithm.
5. Discussion
From the summary tables of the reviewed literature, Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3, numerous pivotal insights have been discerned. The RF algorithm is established as a widely employed and effective method, as evidenced by studies [9,10,11,15,18,19,22,24,33], denoting its robust utility during pregnancy and labor stages. However, avenues for advancement are noticeable within the domains of DT and SVM, particularly when SVMs have not exceeded a 94% accuracy benchmark in research [12,14,16,17,21]. This suggests room for further methodological enhancement. Concurrently, DL methodologies, including ANN, CNN, and MLP, have delivered promising results in classifying fetal hypoxia cases. Nonetheless, the prevalent reliance on a single dataset in studies [25,26,27,28] highlights a significant research gap, underscoring the imperative of employing more diverse datasets to substantiate these models’ validity. In the context of ensemble techniques, especially Gradient Boosting (GB) models, studies [41,43,44,45] have yielded outstanding results. Yet, the repeated use of similar datasets, with study [44] being an exception as it utilized a unique private dataset, raises concerns about the diversity of datasets. Notably, the incorporation of base models, often regarded as suboptimal, into ensemble methods for improved predictive accuracy, as shown in study [17], embodies an innovative and progressive stance in the field. Despite significant advancements and accuracy rates in various studies, the homogeneity of datasets employed across different models constrains the generalizability of these insights, thereby highlighting the need for future research to focus on diversifying datasets, investigating novel ML and DL models, and refining extant methodologies. The need for comprehensive and varied data collection is a recurrent theme, with many studies limited by the range and diversity of their datasets, leading to potential biases or model overfitting. Collaborative endeavors with healthcare providers to gather more inclusive and representative data are posited as a viable solution to mitigate this constraint. Figure 3 shows the proportion of models that were used in the reviewed papers, while Figure 4 shows the number of samples used for each technique.
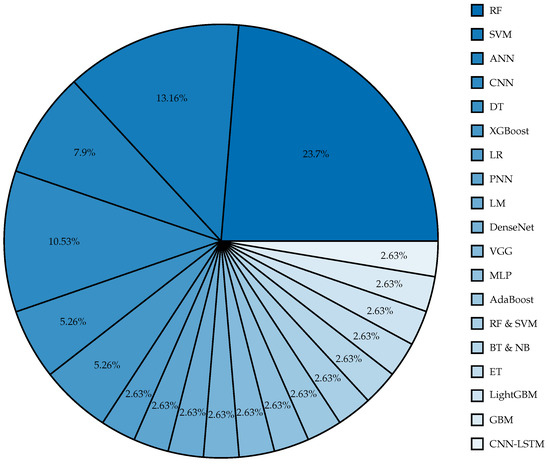
Figure 3.
Proportion of models used in previous studies.
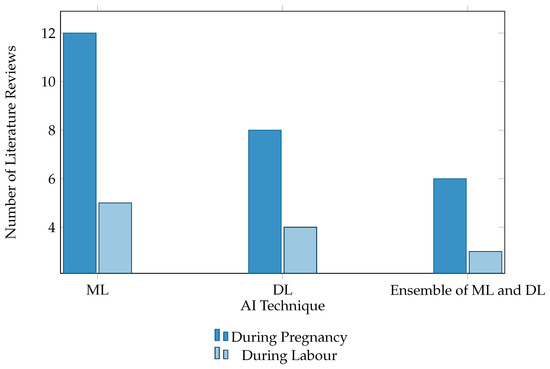
Figure 4.
Number of samples of each class. This figure presents a bar chart illustrating the utilization trends of AI technologies, mainly ML, DL, and ensembles of ML and DL, throughout the stages of pregnancy and childbirth. This visual representation offers insights into AI applications in maternal healthcare, showcasing advancements and innovations.
6. Future Work
In future studies, addressing key challenges is crucial to advance the detection of fetal hypoxia. Foremost among these challenges is the availability of comprehensive datasets, as previous studies highlighted limited and unbalanced data. Future efforts must prioritize collaborating with healthcare providers to collect more diverse data. Additionally, researchers should investigate the effectiveness of different DL models and explore the fusion of multiple DL or ML models. Specifically, one avenue for future work of this paper will involve utilizing local Saudi data to build fetal hypoxia detection models using ML techniques. These models would be selected based on the review of literature conducted in this paper. Lastly, there is a need for further exploration into the correlation between specific obstetric procedures, such as labor induction, and the occurrence of fetal hypoxia. By addressing such inquiries, future research can significantly contribute to the development of more accurate models for detecting fetal hypoxia, thereby improving overall maternal health.
7. Conclusions
In conclusion, fetal hypoxia is a serious condition that needs to be identified immediately in order to reduce risks and complications. Additionally, understanding the prevalence and effects of hypoxia during labor and delivery is essential for reducing neonatal mortality rates and ensuring the well-being of newborns. CTG and other continuous monitoring methods are essential for detecting fetal distress early on and enabeling healthcare professionals to respond quickly to protect the mother’s and fetus’ health. The integration of AI methods, such as ML and DL, to fetal health monitoring holds potential for enhancing diagnostic precision and supporting professionals in more efficient CTG signal evaluation. This paper focuses on providing a concise literature survey on recent advancements in the detection of fetal hypoxia, specifically focusing on the use of AI models with CTG data. With the literature findings, this paper has identified the inability of some models to detect cases that fall into the suspicious category. Moreover, the reviewed studies have implemented various models while obtaining high accuracy; however, most of the studies have utilized the same dataset, offering a very limited domain in this research area.
Author Contributions
D.A., H.A., R.A. (Reema Albrahim), R.A. (Reham Alzahrani) and W.A.S. all contributed equally to the design and implementation of the research, to the analysis of the results, and to the writing of the review. N.A. and M.Y. were involved in planning and supervising the work. All authors provided critical feedback and helped shape the research. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
This research does not involve any new empirical data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| AdaBoost | Adaptive Boosting |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| AUC | Area Under the ROC Curve |
| BT | Bagging Tree |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CTG | Cardiotocograph |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DT | Decision Tree |
| EFM | electronic fetal monitoring |
| FHR | Fetal Heart Rate |
| FIGO | International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics |
| GB | Gradient Boosting |
| GBM | Gradient Boosting Machine |
| GBT | Gradient Boosted Tree |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbors |
| LARA | Long-term Antepartum Risk Analysis system |
| LightGBM | Light Gradient Boosting Machine |
| LM | Levenberg-Marquardt |
| LR | Logistic Regression |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MLP | Multilayer Perceptron |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| NB | Naïve Bayes |
| NN | Neural Network |
| PNN | Probabilities Neural Network |
| ResNet | Residual Network |
| RF | Random Forest |
| RP | Recurrence Plot |
| SMOTE | Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| UC | Uterine Contraction |
| XGBoost | eXtreme Gradient Boosting |
References
- Li, X.; Zheng, D.; Zhou, S.; Tang, D.; Wang, C.; Wu, G. Approximate entropy of fetal heart rate variability as a predictor of fetal distress in women at term pregnancy. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2005, 84, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, K.A.; Brandon, D.H. Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: Pathophysiology and experimental treatments. Newborn Infant Nurs. Rev. 2011, 11, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mejhim, F.M.; Al-Najashi, S.S. Trends in perinatal mortality at King Fahd Hospital of the University, Al-Khobar, Saudi Arabia: A ten years study. J. Fam. Community Med. 1998, 5, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Mendis, L.; Palaniswami, M.; Brownfoot, F.; Keenan, E. Computerised Cardiotocography Analysis for the Automated Detection of Fetal Compromise during Labour: A Review. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, S.; Ayres-de Campos, D.; Costa-Santos, C.; Schnettler, W.; Ugwumadu, A.; Da Graça, L.M.; Collaboration, F.C. Agreement and accuracy using the FIGO, ACOG and NICE cardiotocography interpretation guidelines. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2017, 96, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayres-de Campos, D.; Spong, C.Y.; Chandraharan, E. FIGO consensus guidelines on intrapartum fetal monitoring: Cardiotocography. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2015, 131, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, D.; Harrison, A.; Zhang, L.; Yan, K.; Wang, Y.; Cai, J.; Miao, S.; Lu, L. Artificial Intelligence in Radiology. In Artificial Intelligence in Medicine; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 265–289. [Google Scholar]
- Ben M’Barek, I.; Jauvion, G.; Vitrou, J.; Holmström, E.; Koskas, M.; Ceccaldi, P.F. DeepCTG® 1.0: An interpretable model to detect fetal hypoxia from cardiotocography data during labor and delivery. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1190441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabulut, E.M.; Ibrikci, T. Analysis of cardiotocogram data for fetal distress determination by decision tree based adaptive boosting approach. J. Comput. Commun. 2014, 2, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, R.; Hussain, A.; Al-Jumeily, D.; Baker, T.; Khattak, A. Classification of foetal distress and hypoxia using machine learning approaches. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Computing Methodologies: 14th International Conference, ICIC 2018, Wuhan, China, 15–18 August 2018; Part III 14. pp. 767–776. [Google Scholar]
- Improta, G.; Ricciardi, C.; Amato, F.; D’Addio, G.; Cesarelli, M.; Romano, M. Efficacy of machine learning in predicting the kind of delivery by cardiotocography. In Proceedings of the XV Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing–MEDICON 2019: Proceedings of MEDICON 2019, Coimbra, Portugal, 26–28 September 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 793–799. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Comert, Z.; Deng, Y. Computer-aided diagnosis system of fetal hypoxia incorporating recurrence plot with convolutional neural network. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cömert, Z.; Şengür, A.; Budak, Ü.; Kocamaz, A.F. Prediction of intrapartum fetal hypoxia considering feature selection algorithms and machine learning models. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2019, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.Z.; Ahmed, R.; Sadia, U.H.; Tultul, M.S.I.; Chakma, R. Decision tree method using for fetal state classification from cardiotography data. J. Adv. Eng. Comput. 2020, 4, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaggaf, W.; Cömert, Z.; Nour, M.; Polat, K.; Brdesee, H.; Toğaçar, M. Predicting fetal hypoxia using common spatial pattern and machine learning from cardiotocography signals. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 167, 107429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxi, S. Machine learning based clinical decision support system to predict fetal hypoxia in women during antenatal check-up. Paripex Indian J. Res. 2021, 10, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini, N.; Lucchini, M.; Esposito, G.; Tagliaferri, S.; Campanile, M.; Magenes, G.; Signorini, M.G. A machine learning approach to monitor the emergence of late intrauterine growth restriction. Front. Artif. Intell. 2021, 4, 622616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gude, V.; Corns, S. Integrated Deep Learning and Supervised Machine Learning Model for Predictive Fetal Monitoring. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedia, A.; Sanjitha, N.; Agarwal, R.V.; Manasa, T.P.; Naheed, Y. Fetal Health Classification based on CTG using Machine Learning. Int. J. Adv. Res. Innov. Ideas Educ. 2023, 9, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Davis Jones, G.; Cooke, W.; Vatish, M. Identifying high-risk pre-term pregnancies using the fetal heart rate and machine learning. medRxiv 2024, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Mooney, C.; O’Boyle, D.; Finder, M.; Hallberg, B.; Walsh, B.H.; Henshall, D.C.; Boylan, G.B.; Murray, D.M. Predictive modelling of hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy risk following perinatal asphyxia. Heliyon 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, M.; Yi, H.; Lai, F.; Liu, M.; Zeng, R.; Kang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Rong, J.; Wang, H.; Bai, J.; et al. CTGNet: Automatic analysis of fetal heart rate from cardiotocograph using artificial intelligence. Matern.-Fetal Med. 2022, 4, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mukherjee, H.; Roy, K.; Saha, C. Fetal Health Classification from Cardiotocograph for Both Stages of Labor—A Soft-Computing-Based Approach. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben M’Barek, I.; Jauvion, G.; Ceccaldi, P.F. Computerized cardiotocography analysis during labor–A state-of-the-art review. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2023, 102, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mennickent, D.; Rodríguez, A.; Opazo, M.C.; Riedel, C.A.; Castro, E.; Eriz-Salinas, A.; Appel-Rubio, J.; Aguayo, C.; Damiano, A.E.; Guzmán-Gutiérrez, E.; et al. Machine learning applied in maternal and fetal health: A narrative review focused on pregnancy diseases and complications. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1130139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundar, C.; Chitradevi, M.; Geetharamani, G. Classification of cardiotocogram data using neural network based machine learning technique. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2012, 47, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Yılmaz, E. Fetal state assessment from cardiotocogram data using artificial neural networks. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2016, 36, 820–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cömert, Z.; Kocamaz, A. A study of artificial neural network training algorithms for classification of cardiotocography signals. Bitlis Eren Univ. J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Khullar, V.; Singh, H.P.; Bala, M. Perinatal hypoxia diagnostic system by using scalable machine learning algorithms. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2019, 8, 1954–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma’sum, M.; Intan, P.; Jatmiko, W.; Krisnadhi, A.; Setiawan, N.; Suarjaya, I. Improving deep learning classifier for fetus hypoxia detection in cardiotocography signal. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Workshop on Big Data and Information Security (IWBIS), Bali, Indonesia, 11 October 2019; pp. 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Aswathi Mohan, P.P.; Uma, V. Fetal Hypoxia Detection using CTG Signals and CNN Models. Int. Res. J. Adv. Sci. Hub 2023, 5, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidullah, S.M.; Das, S.; Mahmud, M.; Kaiser, M.S.; Roy, K.; Saha, C.K.; Goswami, K. A machine learning pipeline to classify foetal heart rate deceleration with optimal feature set. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Li, R.; Liu, Q.; Ma, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Hong, S. Deep Learning with Information Fusion and Model Interpretation for Health Monitoring of Fetus based on Long-term Prenatal Electronic Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring Data. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.15337. [Google Scholar]
- Fergus, P.; Hussain, A.; Al-Jumeily, D.; Huang, D.S.; Bouguila, N. Classification of caesarean section and normal vaginal deliveries using foetal heart rate signals and advanced machine learning algorithms. Biomed. Eng. Online 2017, 16, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrozziello, A.; Jordanov, I.; Papageorghiou, T.; Redman, W.; Georgieva, A. Deep learning for continuous electronic fetal monitoring in labor. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 5866–5869. [Google Scholar]
- Alkanan, M. A Study on Classifying Fetal Distress from Large-Scale Cardiotocographic (CTG) Data Using Different Machine Learning Approaches. Ph.D. Thesis, Tokyo University of Technology, Hachioji, Japan, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, F.; Wu, H.; Luz, S.; Townsend, R.; Stock, S. Detecting Intrapartum Fetal Hypoxia from Cardiotocography Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 Computing in Cardiology (CinC), Tampere, Finland, 4–7 September 2022; Volume 498, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, K.M. Application of Machine Learning Techniques to Classify Fetal Hypoxia. Ph.D. Thesis, National College of Ireland, Dublin, Ireland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fergus, P.; Selvaraj, M.; Chalmers, C. Machine learning ensemble modelling to classify caesarean section and vaginal delivery types using Cardiotocography traces. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 93, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riskyana, P.; Ma’sum, M.; Alfiany, N.; Jatmiko, W.; Kekalih, A.; Bustamam, A. Ensemble learning versus deep learning for Hypoxia detection in CTG signal. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Workshop on Big Data and Information Security (IWBIS), Bali, Indonesia, 11 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hoodbhoy, Z.; Noman, M.; Shafique, A.; Nasim, A.; Chowdhury, D.; Hasan, B. Use of machine learning algorithms for prediction of fetal risk using cardiotocographic data. Int. J. Appl. Basic Med. Res. 2019, 9, 226. [Google Scholar]
- Dixit, R.R. Predicting Fetal Health using Cardiotocograms: A Machine Learning Approach. J. Adv. Anal. Healthc. Manag. 2022, 6, 43–57. [Google Scholar]
- Chidambaram, M.; Joy, J. Comparative Analysis of Ensemble Learning Methods for Enhancing Fetal Health Prediction using Cardiotocography. Int. J. Sci. Res. Comput. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2022, 8, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, A.M.; O’Toole, J.M.; Proietti, J.; Livingstone, V.; Mitra, S.; Marnane, W.P.; Finder, M.; Dempsey, E.M.; Murray, D.M.; Boylan, G.B.; et al. Machine learning for the early prediction of infants with electrographic seizures in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Duhayyim, M.; Abbas, S.; Al Hejaili, A.; Kryvinska, N.; Almadhor, A.; Mughal, H. Ensemble Learning for Fetal Health Classification. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2023, 47, 823–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaw, D.; Jordanov, I.; Impey, L.; Namburete, A.; Lee, R.; Georgieva, A. Multimodal Deep Learning for Predicting Adverse Birth Outcomes Based on Early Labour Data. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).