AI Advancements: Comparison of Innovative Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Evolution of AI Techniques
2.1. Emergence of Deep Learning and Its Impact
2.2. Transition from Rule-Based Systems to Data-Driven Approaches
3. Core AI Techniques
3.1. Reinforcement Learning
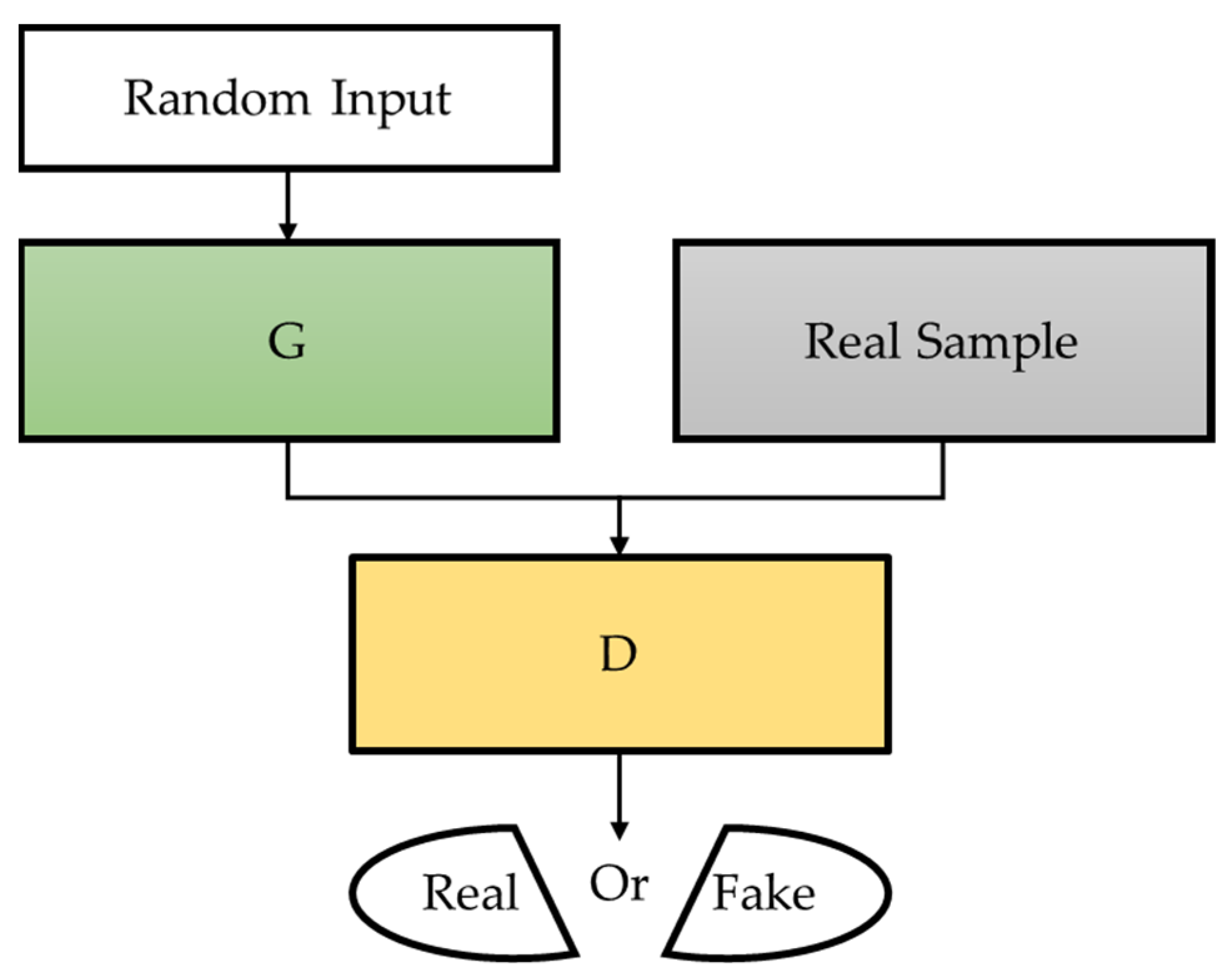
3.2. Generative Adversarial Networks
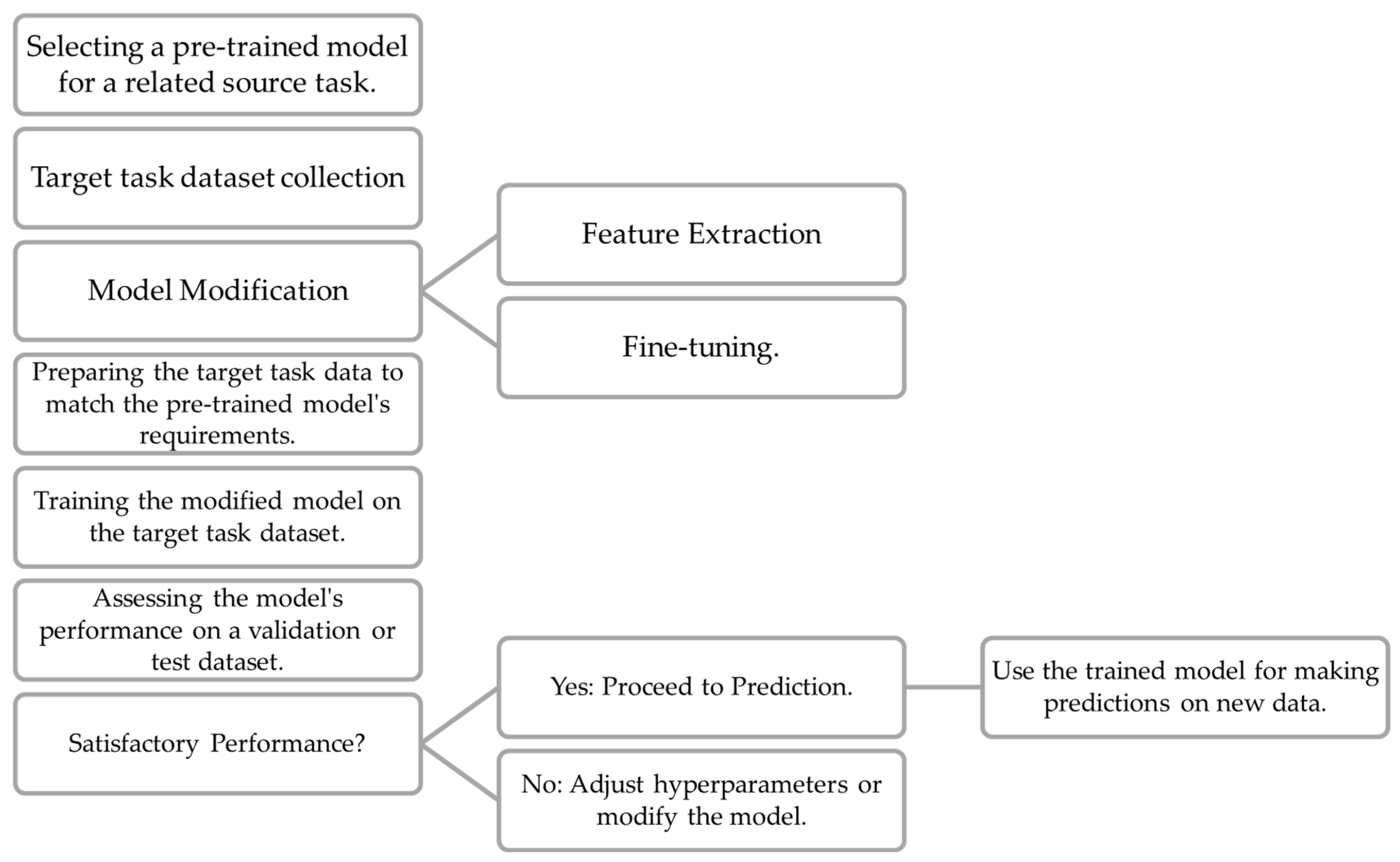
3.3. Transfer Learning
3.4. Neuroevolution
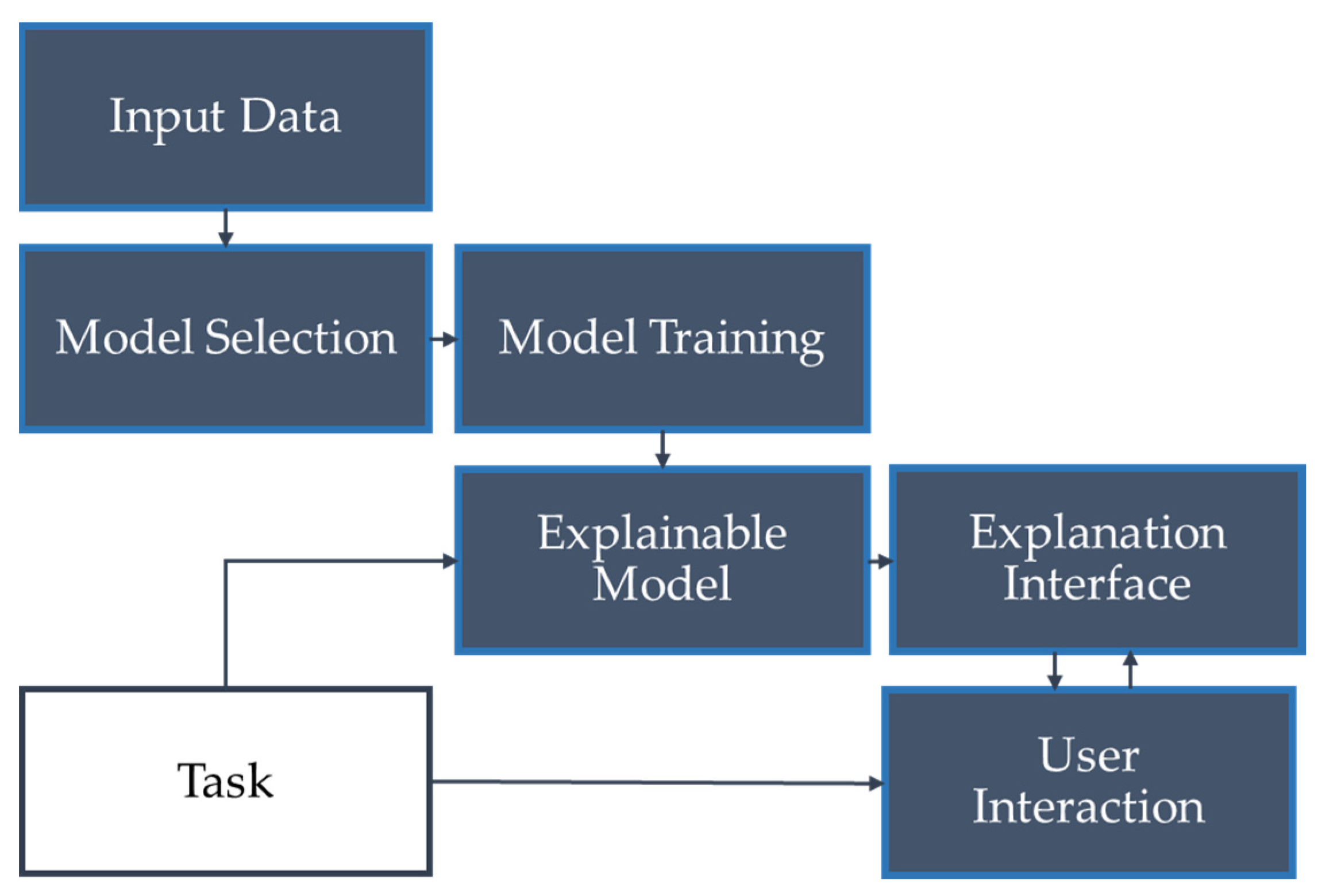
4. Explainable AI
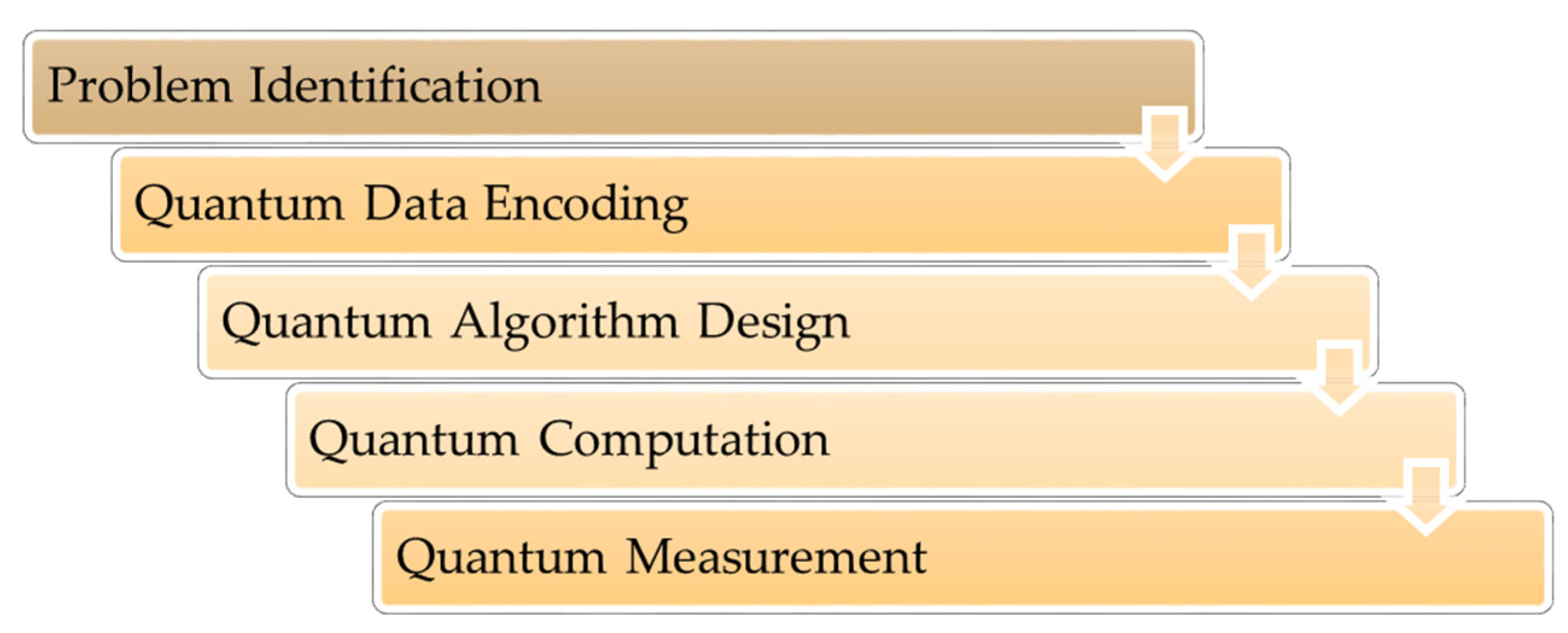
5. Quantum AI
6. Literature Comparison
7. Ethical Considerations and Future Prospects
7.1. Ethical Concerns Related to AI Advancements
7.2. Mitigating Potential Risks and Unintended Consequences
7.3. Future Advancements
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russell, S. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, eBook, Global Edition; Pearson Education, Limited: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Doshi-Velez, F.; Kim, B. Towards a rigorous science of interpretable machine learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.08608. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, J.; Minsky, M.L.; Rochester, N.; Shannon, C.E. A proposal for the dartmouth summer research project on artificial intelligence, 31 August 1955. AI Mag. 2006, 27, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Turing, A. Computing machinery and intelligence. Mind 1950, 59, 433–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.-H.; Lim, B.P. The artificial intelligence renaissance: Deep learning and the road to human-level machine intelligence. APSIPA Trans. Signal Inf. Process. 2018, 7, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, J.; de Miguel, I.; Duran, R.J.; Merayo, N.; Singh, S.K.; Jukan, A.; Chamania, M. Artificial intelligence (AI) methods in optical networks: A comprehensive survey. Opt. Switch. Netw. 2018, 28, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Došilović, F.K.; Brčić, M.; Hlupić, N. Explainable artificial intelligence: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2018 41st International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 210–215. [Google Scholar]
- Von Krogh, G. Artificial intelligence in organizations: New opportunities for phenomenon-based theorizing. Acad. Manag. Discov. 2018, 4, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bughin, J.; Hazan, E.; Lund, S.; Dahlström, P.; Wiesinger, A.; Subramaniam, A. Skill shift: Automation and the future of the workforce. McKinsey Glob. Inst. 2018, 1, 3–84. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, A.; Gans, J.S.; Goldfarb, A. Exploring the impact of artificial intelligence: Prediction versus judgment. Inf. Econ. Policy 2019, 47, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legg, S.; Hutter, M. A collection of definitions of intelligence. Front. Artif. Intell. Appl. 2007, 157, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Taherdoost, H. An overview of trends in information systems: Emerging technologies that transform the information technology industry. Cloud Comput. Data Sci. 2023, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.J. Artificial Intelligence a Modern Approach; Pearson Education, Inc.: London, UK, 2010; Available online: https://cse.sc.edu/~mgv/csce580sp15/Newell_Issues1983.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2023).
- Kolata, G. How Can Computers Get Common Sense? Two of the founders of the field of artificial intelligence disagree on how to make a thinking machine. Science 1982, 217, 1237–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taherdoost, H.; Madanchian, M. Artificial Intelligence and Knowledge Management: Impacts, Benefits, and Implementation. Computers 2023, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzweil, R. The singularity is near. In Ethics and Emerging Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 393–406. [Google Scholar]
- Simeone, O. Machine Learning for Engineers; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- McClarren, R.G. Machine Learning for Engineers; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A. Intellectual issues in the history of artificial intelligence. Artif. Intell. Crit. Concepts 1982, 25–70. [Google Scholar]
- Kaynak, O. The Golden Age of Artificial Intelligence: Inaugural Editorial; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Edwards, J.S.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Artificial intelligence for decision making in the era of Big Data—Evolution, challenges and research agenda. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 48, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijwil, M.M.; Abttan, R.A. Artificial intelligence: A survey on evolution and future trends. Asian J. Appl. Sci. 2021, 9, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannu, A. Artificial intelligence and its application in different areas. Artif. Intell. 2015, 4, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Sharma, A.; Rana, N.P.; Giannakis, M.; Goel, P.; Dutot, V. Evolution of artificial intelligence research in Technological Forecasting and Social Change: Research topics, trends, and future directions. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2023, 192, 122579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roll, I.; Wylie, R. Evolution and revolution in artificial intelligence in education. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2016, 26, 582–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, P. ‘The Robots are Coming! Perennial problems with technological progress. Des. J. 2017, 20, S4120–S4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Desislavov, R.; Martínez-Plumed, F.; Hernández-Orallo, J. Trends in AI inference energy consumption: Beyond the performance-vs-parameter laws of deep learning. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2023, 38, 100857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvano, C.; Ielmini, D.; Ferrandi, F.; Fiorin, L.; Curzel, S.; Benini, L.; Conti, F.; Garofalo, A.; Zambelli, C.; Calore, E. A survey on deep learning hardware accelerators for heterogeneous hpc platforms. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.15552. [Google Scholar]
- Roddick, T. Learning Birds-Eye View Representations for Autonomous Driving; University of Cambridge: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nabavinejad, S.M.; Baharloo, M.; Chen, K.-C.; Palesi, M.; Kogel, T.; Ebrahimi, M. An overview of efficient interconnection networks for deep neural network accelerators. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2020, 10, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Davis, J.J.; Zhao, R.; Ng, H.-C.; Niu, X.; Luk, W.; Cheung, P.Y.; Constantinides, G.A. Deep neural network approximation for custom hardware: Where we’ve been, where we’re going. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 52, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuther, A.; Michaleas, P.; Jones, M.; Gadepally, V.; Samsi, S.; Kepner, J. Survey and benchmarking of machine learning accelerators. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE High Performance Extreme Computing Conference (HPEC), Westin Hotel, Waltham, MA, USA, 24–26 September 2019; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.; Wang, P.; Abbas, K. A survey on deep learning and its applications. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2021, 40, 100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Humaidi, A.J.; Al-Dujaili, A.; Duan, Y.; Al-Shamma, O.; Santamaría, J.; Fadhel, M.A.; Al-Amidie, M.; Farhan, L. Review of deep learning: Concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, B.; Maurya, M.; Puranik, V.G.; Kumar, A.S. Toward Artificial General Intelligence: Deep Learning, Neural Networks, Generative AI; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Gegov, A.; Stahl, F. Categorization and construction of rule based systems. In Proceedings of the Engineering Applications of Neural Networks: 15th International Conference, EANN 2014, Proceedings 15, Sofia, Bulgaria, 5–7 September 2014; pp. 183–194. [Google Scholar]
- Alty, J.; Guida, G. The use of rule-based system technology for the design of man-machine systems. IFAC Proc. Vol. 1985, 18, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilone, G.; Longo, L. A quantitative evaluation of global, rule-based explanations of post-hoc, model agnostic methods. Front. Artif. Intell. 2021, 4, 717899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, S.; Riggs, H.; Tariq, M.; Sarwat, A.I. Advancements and Challenges in Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Review of Models, Libraries, Applications, and Algorithms. Electronics 2023, 12, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Liu, C.-L.; Suen, C.Y. Towards robust pattern recognition: A review. Proc. IEEE 2020, 108, 894–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, O.; Wang, Q.; Svensen, M.; Dersin, P.; Lee, W.-J.; Ducoffe, M. Potential, challenges and future directions for deep learning in prognostics and health management applications. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 92, 103678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, T.; Himmelstein, D.S.; Beaulieu-Jones, B.K.; Kalinin, A.A.; Do, B.T.; Way, G.P.; Ferrero, E.; Agapow, P.-M.; Zietz, M.; Hoffman, M.M. Opportunities and obstacles for deep learning in biology and medicine. J. R. Soc. Interface 2018, 15, 20170387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann, E.; Hermann, G. Artificial intelligence in research and development for sustainability: The centrality of explicability and research data management. AI Ethics 2022, 2, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.; Dennehy, D.; Conboy, K.; Mikalef, P. Artificial intelligence in information systems research: A systematic literature review and research agenda. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 60, 102383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM). Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence to Advance Earth System Science: Opportunities and Challenges: Proceedings of a Workshop; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Soori, M.; Arezoo, B.; Dastres, R. Artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning in advanced robotics, A review. Cogn. Robot. 2023, 3, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivamayil, K.; Rajasekar, E.; Aljafari, B.; Nikolovski, S.; Vairavasundaram, S.; Vairavasundaram, I. A systematic study on reinforcement learning based applications. Energies 2023, 16, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botvinick, M.; Ritter, S.; Wang, J.X.; Kurth-Nelson, Z.; Blundell, C.; Hassabis, D. Reinforcement learning, fast and slow. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2019, 23, 408–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, J.; Schaal, S. Reinforcement learning of motor skills with policy gradients. Neural Netw. 2008, 21, 682–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, G.; Morimoto, J.; Matsubara, T.; Nakanishi, J.; Cheng, G. Learning CPG-based biped locomotion with a policy gradient method: Application to a humanoid robot. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2008, 27, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.; Fu, W.; Liang, H. Model-based reinforcement learning: A survey. arXiv 2018, arXiv:2006.16712v4. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, D.P.; Amgoth, T.; Annavarapu, C.S.R. Machine learning algorithms for wireless sensor networks: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2019, 49, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankar, N.; Vijayakumar, M. Reinforcement learning algorithms: Survey and classification. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Otterlo, M.; Wiering, M. Reinforcement learning and markov decision processes. In Reinforcement Learning: State-of-the-Art; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 3–42. [Google Scholar]
- Tanveer, J.; Haider, A.; Ali, R.; Kim, A. Reinforcement Learning-Based Optimization for Drone Mobility in 5G and Beyond Ultra-Dense Networks. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 68, 3807–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Yang, Z.; Su, H.; Wang, L. Monte Carlo-based reinforcement learning control for unmanned aerial vehicle systems. Neurocomputing 2022, 507, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hao, Y.; Cao, J. Learning to traverse over graphs with a Monte Carlo tree search-based self-play framework. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 105, 104422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maoudj, A.; Hentout, A. Optimal path planning approach based on Q-learning algorithm for mobile robots. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 97, 106796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intayoad, W.; Kamyod, C.; Temdee, P. Reinforcement learning based on contextual bandits for personalized online learning recommendation systems. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 115, 2917–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27. Available online: https://papers.nips.cc/paper_files/paper/2014/hash/5ca3e9b122f61f8f06494c97b1afccf3-Abstract.html (accessed on 17 December 2023).
- Jin, L.; Tan, F.; Jiang, S. Generative adversarial network technologies and applications in computer vision. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Ge, Z.; Bonnington, C.P.; Zhou, J. Progressive transfer learning and adversarial domain adaptation for cross-domain skin disease classification. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 24, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, B.; Al-Sahaf, H.; Xue, B.; Zhang, M. Transfer learning: A building block selection mechanism in genetic programming for symbolic regression. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference Companion, Prague, Czech Republic, 13–17 July 2019; pp. 350–351. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, N.; Sondhi, A.; Chopra, K.; Singh, G. Transfer learning: Survey and classification. Smart Innovations in Communication and Computational Sciences: Proceedings of ICSICCS 2020. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2021, 1168, 145–155. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.M. A Review Study on Neuro Evolution. Int. J. Sci. Res. Eng. Trends 2021, 7, 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Galván, E.; Mooney, P. Neuroevolution in deep neural networks: Current trends and future challenges. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2021, 2, 476–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes-Filho, S.; Olsen, K.; Yazidi, A.; Riegler, M.A.; Halvorsen, P.; Nichele, S. Towards the Neuroevolution of Low-level artificial general intelligence. Front. Robot. AI 2022, 9, 1007547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doran, D.; Schulz, S.; Besold, T.R. What does explainable AI really mean? A new conceptualization of perspectives. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.00794. [Google Scholar]
- Gunning, D.; Aha, D. DARPA’s explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) program. AI Mag. 2019, 40, 44–58. [Google Scholar]
- Chaddad, A.; Peng, J.; Xu, J.; Bouridane, A. Survey of explainable AI techniques in healthcare. Sensors 2023, 23, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, H.W.; Ooi, C.P.; Seoni, S.; Barua, P.D.; Molinari, F.; Acharya, U.R. Application of explainable artificial intelligence for healthcare: A systematic review of the last decade (2011–2022). Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 107161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, Z.; Alizadehsani, R.; Cifci, M.A.; Kausar, S.; Rehman, R.; Mahanta, P.; Bora, P.K.; Almasri, A.; Alkhawaldeh, R.S.; Hussain, S. A Brief Review of Explainable Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.01543. [Google Scholar]
- Band, S.S.; Yarahmadi, A.; Hsu, C.-C.; Biyari, M.; Sookhak, M.; Ameri, R.; Dehzangi, I.; Chronopoulos, A.T.; Liang, H.-W. Application of explainable artificial intelligence in medical health: A systematic review of interpretability methods. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2023, 226, 101286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, F.; Delmastro, F. Explainable AI for clinical and remote health applications: A survey on tabular and time series data. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 5261–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glisic, S.G.; Lorenzo, B. Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing for Advanced Wireless Networks; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Marella, S.T.; Parisa, H.S.K. Introduction to quantum computing. Quantum Comput. Commun. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgarbas, K.N. The road to quantum artificial intelligence. arXiv 2007, arXiv:0705.3360. [Google Scholar]
- Zeguendry, A.; Jarir, Z.; Quafafou, M. Quantum machine learning: A review and case studies. Entropy 2023, 25, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krenn, M.; Landgraf, J.; Foesel, T.; Marquardt, F. Artificial intelligence and machine learning for quantum technologies. Phys. Rev. A 2023, 107, 010101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaelbling, L.P.; Littman, M.L.; Moore, A.W. Reinforcement learning: A survey. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 1996, 4, 237–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.K.; Ostrovski, G. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, S.; Pastor, P.; Krizhevsky, A.; Ibarz, J.; Quillen, D. Learning hand-eye coordination for robotic grasping with deep learning and large-scale data collection. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2018, 37, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Metz, L.; Chintala, S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.06434. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Brock, A.; Donahue, J.; Simonyan, K. Large scale GAN training for high fidelity natural image synthesis. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.11096. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.J.; Yang, Q. A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2009, 22, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosinski, J.; Clune, J.; Bengio, Y.; Lipson, H. How transferable are features in deep neural networks? Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 3320–3328. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.; Sun, F.; Kong, T.; Zhang, W.; Yang, C.; Liu, C. A survey on deep transfer learning. In Proceedings of the Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning–ICANN 2018: 27th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Proceedings, Part III 27, Rhodes, Greece, 4–7 October 2018; pp. 270–279. [Google Scholar]
- Oquab, M.; Bottou, L.; Laptev, I.; Sivic, J. Learning and transferring mid-level image representations using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1717–1724. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, K.O.; Miikkulainen, R. Evolving neural networks through augmenting topologies. Evol. Comput. 2002, 10, 99–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Real, E.; Moore, S.; Selle, A.; Saxena, S.; Suematsu, Y.L.; Tan, J.; Le, Q.V.; Kurakin, A. Large-scale evolution of image classifiers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 2902–2911. [Google Scholar]
- Clune, J.; Stanley, K.O.; Pennock, R.T.; Ofria, C. On the performance of indirect encoding across the continuum of regularity. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2011, 15, 346–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouret, J.-B.; Clune, J. Illuminating search spaces by mapping elites. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1504.04909. [Google Scholar]
- Lipton, Z.C. The mythos of model interpretability: In machine learning, the concept of interpretability is both important and slippery. Queue 2018, 16, 31–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruana, R.; Lou, Y.; Gehrke, J.; Koch, P.; Sturm, M.; Elhadad, N. Intelligible models for healthcare: Predicting pneumonia risk and hospital 30-day readmission. In Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Sydney, Australia, 10–13 August 2015; pp. 1721–1730. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. “Why should I trust you? ” Explaining the predictions of any classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 1135–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Preskill, J. Quantum computing in the NISQ era and beyond. Quantum 2018, 2, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArdle, S.; Endo, S.; Aspuru-Guzik, A.; Benjamin, S.C.; Yuan, X. Quantum computational chemistry. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2020, 92, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, A.M.; Gosset, D.; Webb, Z. Universal computation by multiparticle quantum walk. Science 2013, 339, 791–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandala, A.; Mezzacapo, A.; Temme, K.; Takita, M.; Brink, M.; Chow, J.M.; Gambetta, J.M. Hardware-efficient variational quantum eigensolver for small molecules and quantum magnets. Nature 2017, 549, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobin, A.; Ienca, M.; Vayena, E. The global landscape of AI ethics guidelines. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2019, 1, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzioni, A.; Etzioni, O. Incorporating ethics into artificial intelligence. J. Ethics 2017, 21, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belenguer, L. AI bias: Exploring discriminatory algorithmic decision-making models and the application of possible machine-centric solutions adapted from the pharmaceutical industry. AI Ethics 2022, 2, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, R.R.; Nakeshimana, A.; Olubeko, O. Addressing fairness, bias, and appropriate use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in global health. Front. Artif. Intell. 2021, 3, 561802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartneck, C.; Lütge, C.; Wagner, A.; Welsh, S. Privacy issues of AI. Introd. Ethics Robot. AI 2021, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, N.; Hameed, B.; Shetty, D.K.; Swain, D.; Shah, M.; Paul, R.; Aggarwal, K.; Ibrahim, S.; Patil, V.; Smriti, K. Legal and ethical consideration in artificial intelligence in healthcare: Who takes responsibility? Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. Ethics and discrimination in artificial intelligence-enabled recruitment practices. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Keyword (Search in Title) | Results | Main Subject Area | Main Document Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| “Reinforcement learning” | 28,412 documents | Computer Science (21,583 documents) | Conference paper (14,973 documents) |
| “Generative adversarial network” | 8186 documents | Computer Science (5841 documents) | Article (4310 documents) |
| “Transfer learning” | 11,633 documents | Computer Science (8165 documents) | Article (5863 documents) |
| “Neuroevolution” OR “Neuro evolution” | 338 documents | Computer Science (269 documents) | Conference paper (198 documents) |
| “Explainable AI” OR “Explainable artificial intelligence” | 1479 documents | Computer Science (1075 documents) | Article (695 documents) |
| “Quantum AI” OR “Quantum artificial intelligence” | 8 documents | Computer Science (6 documents) | Conference paper (5 documents) |
| AI Technique | Strengths | Weaknesses | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reinforcement Learning | Dynamic effectiveness in complex tasks, achieving superhuman performance in game playing and robotics. | High computational requirements, sensitivity to tuning, exploration-exploitation trade-off, and substantial data needs. | [49,81,82,83] |
| Generative Adversarial Networks | Generates realistic, high-quality data with versatile applications like image-to-image translation. Encourages robust model generation. | Training instability, mode collapse reducing output diversity, vulnerability to adversarial attacks, and difficulty in controlling specific features. | [61,84,85,86] |
| Transfer Learning | Transfers knowledge for improved new task performance, saving resources, effective in limited labeled data scenarios. Facilitates specialized models based on a common backbone. | Success depending on domain/task similarity, fine-tuning leading to overfitting, transfer of biases impacting fairness, and compatibility issues between architectures. | [87,88,89,90] |
| Neuroevolution | Evolves neural network architectures, optimizes complex structures, and discovers novel solutions. | Computationally expensive for large-scale problems, prone to premature convergence, requires careful fitness function design, and struggles with high-dimensional, continuous tasks. | [91,92,93,94] |
| XAI | Enhances transparency and interpretability, crucial for critical applications, builds trust, and identifies/corrects biases. | May reduce model complexity and predictive performance. Interpretability not universally applicable, balancing complexity and interpretability is challenging, and providing explanations for complex decisions is difficult. | [2,95,96,97] |
| Quantum AI | Potentially outperforms classical algorithms, efficient simulation of quantum systems for chemistry, etc., holds promise for exponential speedup. | Quantum hardware faces technical challenges, limited availability of quantum computers, specialized quantum algorithms, and requires high expertise in quantum mechanics. | [98,99,100,101] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taherdoost, H.; Madanchian, M. AI Advancements: Comparison of Innovative Techniques. AI 2024, 5, 38-54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai5010003
Taherdoost H, Madanchian M. AI Advancements: Comparison of Innovative Techniques. AI. 2024; 5(1):38-54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai5010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaherdoost, Hamed, and Mitra Madanchian. 2024. "AI Advancements: Comparison of Innovative Techniques" AI 5, no. 1: 38-54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai5010003
APA StyleTaherdoost, H., & Madanchian, M. (2024). AI Advancements: Comparison of Innovative Techniques. AI, 5(1), 38-54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai5010003








