Can Artificial Intelligence Aid Diagnosis by Teleguided Point-of-Care Ultrasound? A Pilot Study for Evaluating a Novel Computer Algorithm for COVID-19 Diagnosis Using Lung Ultrasound
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Telemedicine in the Time of the Pandemic
3. The Role of POCUS in the Management of COVID-19 Patients
4. Teleguided POCUS for Remote Monitoring of COVID-19 Patients
5. AI Can Improve Teleguided POCUS Monitoring of COVID-19 Patients
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Annis, T.; Pleasants, S.; Hultman, G.; Lindemann, E.; Thompson, J.A.; Billecke, S.; Badlani, S.; Melton, G.B. Rapid implementation of a COVID-19 remote patient monitoring program. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2020, 27, 1326–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silberzahn, T. Remote Patient Monitoring for Safe and Effective Management of COVID-19 Patients. HealthManagement.org J. 2020, 20, 513–514. [Google Scholar]
- Tabacof, L.; Kellner, C.; Breyman, E.; Dewil, S.; Braren, S.; Nasr, L.; Tosto, J.; Cortes, M.; Putrino, D. Remote Patient Monitoring for Home Management of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in New York: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study. Telemed. E-Health 2021, 27, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britton, N.; Miller, M.A.; Safadi, S.; Siegel, A.; Levine, A.R.; McCurdy, M.T. Tele-ultrasound in resource-limited settings: A systematic review. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, A.; Tupchong, K.; Verceles, A.C.; Mccurdy, M.T. Point-of-Care Teleultrasound: A Systematic Review. Telemed. E-Health 2020, 26, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonsenso, D.; Moro, F.; Inchingolo, R.; Smargiassi, A.; Demi, L.; Soldati, G.; Moroni, R.; Lanzone, A.; Scambia, G.; Testa, A.C. Effectiveness of rapid lung ultrasound training program for gynecologists and obstetricians managing pregnant women with suspected COVID-19. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 56, 110–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigotti, F.N.; Di Benedetto, C.; Fop, F.; Bianco, S.; Bilucaglia, D.; Cesano, G. Lung ultrasonography performed by nephrologist: COVID-19 as an opportunity to reveal ultrasound’s full potential and usefulness in the dialysis room. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 16, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, T.J.; Kaproth-Joslin, K.; Ambrosini, R.; Baran, T.M.; Dozier, A.M.; Zhao, Y.T.; Satheesh, M.; Mahony Reátegui-Rivera, C.; Sifuentes, W.; Rios-Mayhua, G.; et al. Volume sweep imaging lung teleultrasound for detection of COVID-19 in Peru: A multicentre pilot study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e061332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, A.W.; McKee, I.; McKee, J.L.; Ma, I.; McBeth, P.B.; Roberts, D.J.; Wurster, C.L.; Parfitt, R.; Ball, C.G.; Oberg, S.; et al. Remote just-in-time telementored trauma ultrasound: A double-factorial randomized controlled trial examining fluid detection and remote knobology control through an ultrasound graphic user interface display. Am. J. Surg. 2016, 211, 894–902.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBeth, P.B.; Crawford, I.; Blaivas, M.; Hamilton, T.; Musselwhite, K.; Panebianco, N.; Melniker, L.; Ball, C.G.; Gargani, L.; Gherdovich, C.; et al. Simple, almost anywhere, with almost anyone: Remote low-cost telementored resuscitative lung ultrasound. J. Trauma 2011, 71, 1528–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiteri, A.; Muratori, L.; Faggiano, C.; Alvisi, M.; Serio, I.; Piscaglia, F. Efficacy of a short course of lung ultrasound for primary care physicians in the assessment of COVID-19-positive patients. Fam. Pract. 2022, 39, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, A.B.; Gervasi, S.; Song, H.; Bond, A.M.; Chen, A.T.; Bergman, A.; David, G.; Bailey, J.M.; Brooks, R.; Smith-McLallen, A. Telemedicine Catches on: Changes in the Utilization of Telemedicine Services during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Am. J. Manag. Care 2022, 28, e1–e6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thornton, J. The “virtual wards” supporting patients with covid-19 in the community. BMJ 2020, 369, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khawam, E.; Khouli, H.; Pozuelo, L. Treating acute anxiety in patients with COVID-19: Posted April 26, 2020. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2020, 87, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.; DeCara, J.M. Point-of-Care Ultrasound. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2020, 22, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, R.C.; Onega, T.; Lee, C.I. Addressing Potential Health Disparities in the Adoption of Advanced Breast Imaging Technologies. Acad. Radiol. 2018, 25, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Addison, R.; Rogers, P.; Stone-McLean, J.; Boyd, S.; Hoover, K.; Pollard, M.; Dubrowski, A.; Parsons, M. Remote mentoring of point-of-care ultrasound skills to inexperienced operators using multiple telemedicine platforms: Is a cell phone good enough? J. Ultrasound Med. 2018, 37, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Via, G.; Melniker, L.; Goffi, A.; Tavazzi, G.; Neri, L.; Villen, T.; Hoppmann, R.; Mojoli, F.; Noble, V.; et al. Multi-organ point-of-care ultrasound for COVID-19 (PoCUS4COVID): International expert consensus. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demi, L.; Mento, F.; Di Sabatino, A.; Fiengo, A.; Sabatini, U.; Macioce, V.N.; Robol, M.; Tursi, F.; Sofia, C.; Di Cienzo, C.; et al. Lung Ultrasound in COVID-19 and Post-COVID-19 Patients, an Evidence-Based Approach. J. Ultrasound Med. 2022, 41, 2203–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, L.R.; Sehgal, C.M. A Review of Early Experience in Lung Ultrasound in the Diagnosis and Management of COVID-19. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 2530–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldati, G.; Smargiassi, A.; Perrone, T.; Torri, E.; Mento, F.; Demi, L.; Inchingolo, R. There is a Validated Acquisition Protocol for Lung Ultrasonography in COVID-19 Pneumonia. J. Ultrasound Med. 2021, 40, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, T.; Soldati, G.; Padovini, L.; Fiengo, A.; Lettieri, G.; Sabatini, U.; Gori, G.; Lepore, F.; Garolfi, M.; Palumbo, I.; et al. A New Lung Ultrasound Protocol Able to Predict Worsening in Patients Affected by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Pneumonia. J. Ultrasound Med. 2021, 40, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smargiassi, A.; Soldati, G.; Borghetti, A.; Scoppettuolo, G.; Tamburrini, E.; Testa, A.C.; Moro, F.; Natale, L.; Larici, A.R.; Buonsenso, D.; et al. Lung ultrasonography for early management of patients with respiratory symptoms during COVID-19 pandemic. J. Ultrasound 2020, 23, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldati, G.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Buonsenso, D.; Perrone, T.; Briganti, D.F.; Perlini, S.; Torri, E.; Mariani, A.; Mossolani, E.E.; et al. Proposal for International Standardization of the Use of Lung Ultrasound for Patients With COVID-19: A Simple, Quantitative, Reproducible Method. J. Ultrasound Med. 2020, 39, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Wodnicki, R.; Kang, H.; Zhang, J.; Tchelepi, H.; Zhou, Q. Current Ultrasound Technologies and Instrumentation in the Assessment and Monitoring of COVID-19 Positive Patients. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2020, 67, 2230–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orosz, G.; Gyombolai, P.; Tóth, J.T.; Szabó, M. Reliability and clinical correlations of semi-quantitative lung ultrasound on BLUE points in COVID-19 mechanically ventilated patients: The ‘BLUE-LUSS’-A feasibility clinical study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Rodríguez, J.; Martos-Ruiz, M.; Benavente-Fernández, A.; Aranda-Laserna, P.; Montero-Alonso, M.Á.; Peregrina-Rivas, J.A.; Fernández-Reyes, D.; Martínez de Victoria-Carazo, J.; Guirao-Arrabal, E.; Hernández-Quero, J. Lung ultrasound score severity cut-off points in COVID-19 pneumonia. A systematic review and validating cohort. Med. Clin. 2023, 160, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazic, I.; Cogliati, C.; Flor, N.; Frija, G.; Kawooya, M.; Umbrello, M.; Ali, S.; Baranne, M.L.; Cho, Y.J.; Pitcher, R.; et al. The use of lung ultrasound in COVID-19. ERJ Open Res. 2023, 9, 00196-2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Yang, Z.; Peng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Feng, C.; Huang, X.; Jiang, N.; et al. Semiquantitative lung ultrasound scores in the evaluation and follow-up of critically ill patients with COVID-19: A single-center study. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, 1363–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, S.; Savinelli, C.; Paolucci, E.; Pelagatti, L.; Sibona, E.; Fersini, N.; Buggea, M.; Tozzi, C.; Allescia, G.; Paolini, D.; et al. Point-of-care ultrasound (PoCUS) in the early diagnosis of novel coronavirus 2019 disease (COVID-19) in a first-level emergency department during a SARS-CoV-2 outbreak in Italy: A real-life analysis. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2022, 17, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Cao, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Duan, Y.; Kong, S.; You, M.; Ma, R.; Jiang, L.; et al. Prognostic value of bedside lung ultrasound score in patients with COVID-19. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahier, T.; Meuwly, J.Y.; Pantet, O.; Brochu Vez, M.J.; Gerhard Donnet, H.; Hartley, M.A.; Hugli, O.; Boillat-Blanco, N. Lung Ultrasonography for Risk Stratification in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Prospective Observational Cohort Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e4189–e4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaad, S.; Brahier, T.; Hartley, M.A.; Cordonnier, J.B.; Bosso, L.; Espejo, T.; Pantet, O.; Hugli, O.; Carron, P.N.; Meuwly, J.Y.; et al. Point-of-care lung ultrasonography for early identification of mild COVID-19: A prospective cohort of outpatients in a Swiss screening center. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e060181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanforlin, A.; Strapazzon, G.; Falk, M.; Gallina, V.; Viteritti, A.; Valzolgher, L.; La Guardia, M.; Ferro, F.; Pagani, L.; Vezzali, N. Lung Ultrasound in the Emergency Department for Early Identification of COVID-19 Pneumonia. Respiration 2021, 100, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Gioia, C.C.; Artusi, N.; Xotta, G.; Bonsano, M.; Sisto, U.G.; Tecchiolli, M.; Orso, D.; Cominotto, F.; Amore, G.; Meduri, S.; et al. Lung ultrasound in ruling out COVID-19 pneumonia in the ED: A multicentre prospective sensitivity study. Emerg. Med. J. 2022, 39, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichter, Y.; Topilsky, Y.; Taieb, P.; Banai, A.; Hochstadt, A.; Merdler, I.; Gal Oz, A.; Vine, J.; Goren, O.; Cohen, B.; et al. Lung ultrasound predicts clinical course and outcomes in COVID-19 patients. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1873–1883, Erratum in Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 2128–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombini, V.; Di Capua, M.; Capsoni, N.; Lazzati, A.; Bergamaschi, M.; Gheda, S.; Ghezzi, L.; Cassano, G.; Albertini, V.; Porta, L.; et al. Risk Stratification in COVID-19 Pneumonia—Determining the Role of Lung Ultrasound. Ultraschall Med. 2022, 43, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschiera, E.; Mento, F.; Demi, L. Numerical study on lung ultrasound B-line formation as a function of imaging frequency and alveolar geometries. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 149, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mento, F.; Demi, L. On the influence of imaging parameters on lung ultrasound B-line artifacts, in vitro study. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 148, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldati, G.; Demi, M.; Inchingolo, R.; Smargiassi, A.; Demi, L. On the Physical Basis of Pulmonary Sonographic Interstitial Syndrome. J. Ultrasound Med. 2016, 35, 2075–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mento, F.; Khan, U.; Faita, F.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Perrone, T.; Demi, L. State of the Art in Lung Ultrasound, Shifting from Qualitative to Quantitative Analyses. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2022, 48, 2398–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demi, L.; Demi, M.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Faita, F.; Soldati, G. Ultrasonography in lung pathologies: New perspectives. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2014, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mento, F.; Demi, L. Dependence of lung ultrasound vertical artifacts on frequency, bandwidth, focus and angle of incidence: An in vitro study. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 150, 4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivetta, E.; Girard, E.; Locascio, F.; Lupia, E.; Martin, J.D.; Stone, M. Self-Performed Lung Ultrasound for Home Monitoring of a Patient Positive for Coronavirus Disease 2019. Chest J. 2020, 158, E93–E97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, S.J.; Burbridge, B.E.; Badea, A.; Kanigan, N.; Bustamante, L.; Babyn, P.; Mendez, I. A cross over comparison of standard and telerobotic approaches to prenatal sonography. J. Ultrasound Med. 2018, 37, 2603–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, T.M.; Levine, A.R.; Olivieri, P.P.; McCurdy, M.T.; Papali, A.; Zubrow, M.T.; Rodick, K.M.; Hurley, J.M.; Verceles, A.C. Brief training increases nurses’ comfort using tele-ultrasound: A feasibility study. Intensive Crit. Care Nurs. 2019, 51, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demi, L.; Wolfram, F.; Klersy, C.; De Silvestri, A.; Ferretti, V.V.; Muller, M.; Miller, D.; Feletti, F.; Wełnicki, M.; Buda, N.; et al. New International Guidelines and Consensus on the use of Lung Ultrasound. J. Ultrasound Med. 2022, 42, 309–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, F.L.; Bergamini, C.; Allegrini, A.; Scopelliti, M.; Secco, G.; Miccoli, M.; Boni, S.; Brigada, R.; Perlini, S. Bedside wireless lung ultrasound for the evaluation of COVID-19 lung injury in senior nursing home residents. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2020, 90, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.R.; McCurdy, M.T.; Zubrow, M.T.; Papali, A.; Mallemat, H.A.; Verceles, A.C. Tele-intensivists can instruct non-physicians to acquire high-quality ultrasound images. J. Crit. Care 2015, 30, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, T.E.; Levine, A.R.; Verceles, A.C.; Buchner, J.A.; Lantry, J.H.; Papali, A.; Zubrow, M.T.; Colas, L.N.; Augustin, M.E.; McCurdy, M.T. Remote tele-mentored ultrasound for non-physician learners using FaceTime: A feasibility study in a low-income country. J. Crit. Care 2017, 40, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieveld, A.W.; Kok, B.; Azijli, K.; Schuit, F.H.; van de Ven, P.M.; de Korte, C.L.; Nijveldt, R.; van den Heuvel, F.M.; Teunissen, B.P.; Hoefsloot, W.; et al. Assessing COVID-19 pneumonia—clinical extension and risk with point-of-care ultrasound: A multicenter, prospective, observational study. J. Am. Coll. Emerg. Physicians Open 2021, 2, e12429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, F.; Wang, J.; Shi, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Z.; He, K.; Shi, Y.; Shen, D. Review of Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Imaging Data Acquisition, Segmentation, and Diagnosis for COVID-19. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 14, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syeda, H.B.; Syed, M.; Sexton, K.W.; Syed, S.; Begum, S.; Syed, F.; Prior, F.; Yu, F., Jr. Role of Machine Learning Techniques to Tackle the COVID-19 Crisis: Systematic Review. JMIR Med. Inform. 2021, 9, e23811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, V.V.; Chadaga, K.; Sampathila, N.; Prabhu, S.; Chadaga, R.; Umakanth, S. Diagnosing COVID-19 using artificial intelligence: A comprehensive review. Netw. Model. Anal. Health Inform. Bioinform. 2022, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccialli, F.; di Cola, V.S.; Giampaolo, F.; Cuomo, S. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Fighting the COVID-19 Pandemic. Inf. Syst. Front. 2021, 23, 1467–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, N.; Mento, F.; Zanforlin, A.; Smargiassi, A.; Torri, E.; Perrone, T.; Demi, L. Human-to-AI Interrater Agreement for Lung Ultrasound Scoring in COVID-19 Patients. J. Ultrasound Med. 2023, 42, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.; Afrakhteh, S.; Mento, F.; Fatima, N.; De Rosa, L.; Custode, L.L.; Azam, Z.; Torri, E.; Soldati, G.; Tursi, F.; et al. Benchmark methodological approach for the application of artificial intelligence to lung ultrasound data from COVID-19 patients: From frame to prognostic-level. Ultrasonics 2023, 132, 106994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custode, L.L.; Mento, F.; Tursi, F.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Perrone, T.; Demi, L.; Iacca, G. Multi-objective automatic analysis of lung ultrasound data from COVID-19 patients by means of deep learning and decision trees. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 133, 109926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.; Mento, F.; Nicolussi Giacomaz, L.; Trevisan, R.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Perrone, T.; Demi, L. Deep Learning-Based Classification of Reduced Lung Ultrasound Data From COVID-19 Patients. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2022, 69, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, O.; Schipper, N.; Vaturi, M.; Soldati, G.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Torri, E.; Perrone, T.; Mento, F.; Demi, L.; et al. Integrating Domain Knowledge Into Deep Networks for Lung Ultrasound With Applications to COVID-19. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 41, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshankhah, R.; Karbalaeisadegh, Y.; Greer, H.; Mento, F.; Soldati, G.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Torri, E.; Perrone, T.; Aylward, S.; et al. Investigating training-test data splitting strategies for automated segmentation and scoring of COVID-19 lung ultrasound images. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 150, 4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mento, F.; Perrone, T.; Fiengo, A.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Soldati, G.; Demi, L. Deep learning applied to lung ultrasound videos for scoring COVID-19 patients: A multicenter study. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 149, 3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhou, B.; Sohn, J.J.; Zhou, J.; Jacob, J.T.; Higgins, K.A.; Bradley, J.D.; Liu, T. Review of Machine Learning in Lung Ultrasound in COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faucoz, O.; Standarovski, D.; Aguersif, A.; Bouharaoua, S.; Sarton, B.; Silva, S.; The MAGELLAN Study Group. Moving beyond the lines: Lung ultrasound pixel-wise computer-assisted analysis for critically ill patients. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, M.R.; Hagens, L.A.; Heijnen, N.F.L.; Pisani, L.; Cherpanath, T.G.V.; Dongelmans, D.A.; de Grooth, H.S.; Pierrakos, C.; Tuinman, P.R.; Zimatore, C.; et al. Lung Ultrasound Prediction Model for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Multicenter Prospective Observational Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveenkumar, E.; Dhiyanesh, B.; Kanna, R.R.; Diwakar, P.S.; Murali, M.; Radha, R. Detection of Lung Ultrasound COVID-19 Disease Patients based Convolution Multifacet Analytics using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Smart Energy (ICAIS), Coimbatore, India, 23–25 February 2022; pp. 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Hu, B.; Feng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, X.; Shao, H.; Wang, H.; Jin, L.; Ai, S.; Ji, Y. An ensemble deep learning model for risk stratification of invasive lung adenocarcinoma using thin-slice CT. NPJ Digit. Med. 2023, 6, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, T.I.A.; Oyelade, O.N.; Ezugwu, A.E. Automatic detection and classification of lung cancer CT scans based on deep learning and ebola optimization search algorithm. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, L.R.; Chen, Y.T.; Cary, T.W.; Ashi, K.; Sehgal, C.M. Quantitative pleural line characterization outperforms traditional lung texture ultrasound features in detection of COVID-19. J. Am. Coll. Emerg. Phys. Open 2021, 2, e12418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, C.M.; Sultan, L.R.; Cary, T.W. Analysis of Pleural Lines for the Diagnosis of Lung Conditions. U.S. Patent Application No. 17/951,985, 23 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.; Menapace, W.; Oei, S.; Luijten, B.; Fini, E.; Saltori, C.; Huijben, I.; Chennakeshava, N.; Mento, F.; Sentelli, A. Deep learning for classification and localization of COVID-19 markers in point-of-care lung ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2676–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanti, H.; Suprijanto. Image Processing Framework for Pleural Line (A-Line) Detection in Video Lung Ultrasonography. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE-EMBS Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (IECBES), Langkawi Island, Malaysia, 1–3 March 2021; pp. 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrer, L.; Donini, E.; Marinelli, D.; Zanetti, M.; Mento, F.; Torri, E.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Soldati, G.; Demi, L.; et al. Automatic Pleural Line Extraction and COVID-19 Scoring From Lung Ultrasound Data. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2020, 67, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.E.; Desai, S.K.; Georgiadis, A.L.; Tekle, W.G. Augmented reality enhanced tele-proctoring platform to intraoperatively support a neuro-endovascular surgery fellow. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2021, 28, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, T.; Wilczewski, H.; Paige, S.R.; Soni, H.; Welch, B.M.; Bunnell, B.E. Extended Reality for Enhanced Telehealth During and Beyond COVID-19: Viewpoint. JMIR Serious Games 2021, 9, e26520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparwasser, P.; Haack, M.; Frey, L.; Haferkamp, A.; Borgmann, H. Virtual und Augmented Reality in der Urologie [Virtual and augmented reality in urology]. Urologe A 2022, 61, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forte, M.P.; Gourishetti, R.; Javot, B.; Engler, T.; Gomez, E.D.; Kuchenbecker, K.J. Design of interactive augmented reality functions for robotic surgery and evaluation in dry-lab lymphadenectomy. Int. J. Med. Robot. 2021, 18, e2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oulefki, A.; Agaian, S.; Trongtirakul, T.; Benbelkacem, S.; Aouam, D.; Zenati-Henda, N.; Abdelli, M.-L. Virtual Reality visualization for computerized COVID-19 lesion segmentation and interpretation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 73, 103371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amara, K.; Aouf, A.; Kennouche, H.; Djekoune, A.O.; Zenati, N.; Kerdjidj, O.; Ferguene, F. COVIR: A virtual rendering of a novel NN architecture O-Net for COVID-19 Ct-scan automatic lung lesions segmentation. Comput. Graph. 2022, 104, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, K.; Kerdjidj, O.; Guerroudji, M.A.; Zenati, N.; Djekoune, O. Augmented Reality Visualization and Interaction for COVID-19 CT-Scan NN Automated Segmentation: A Validation Study. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 12114–12123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
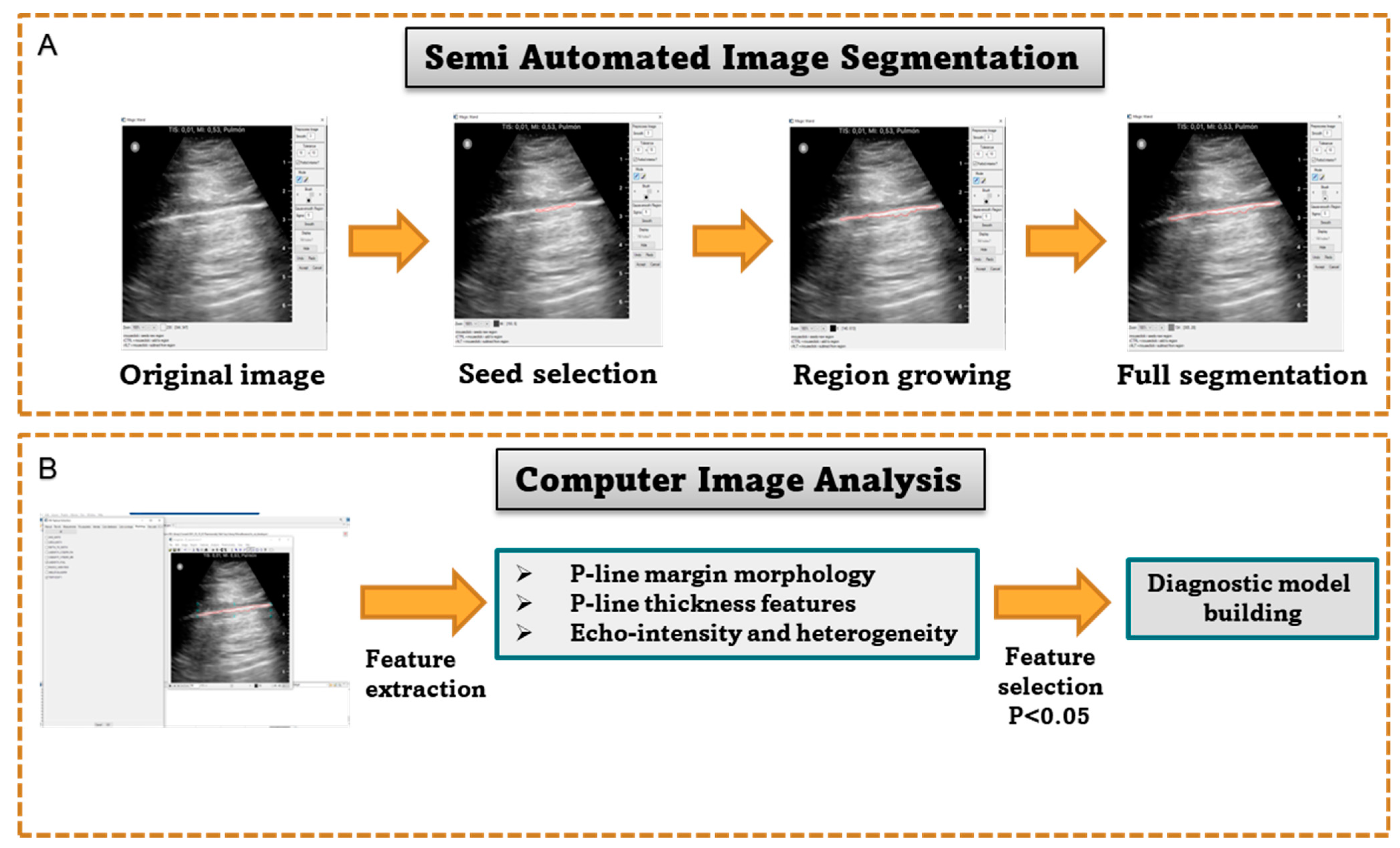
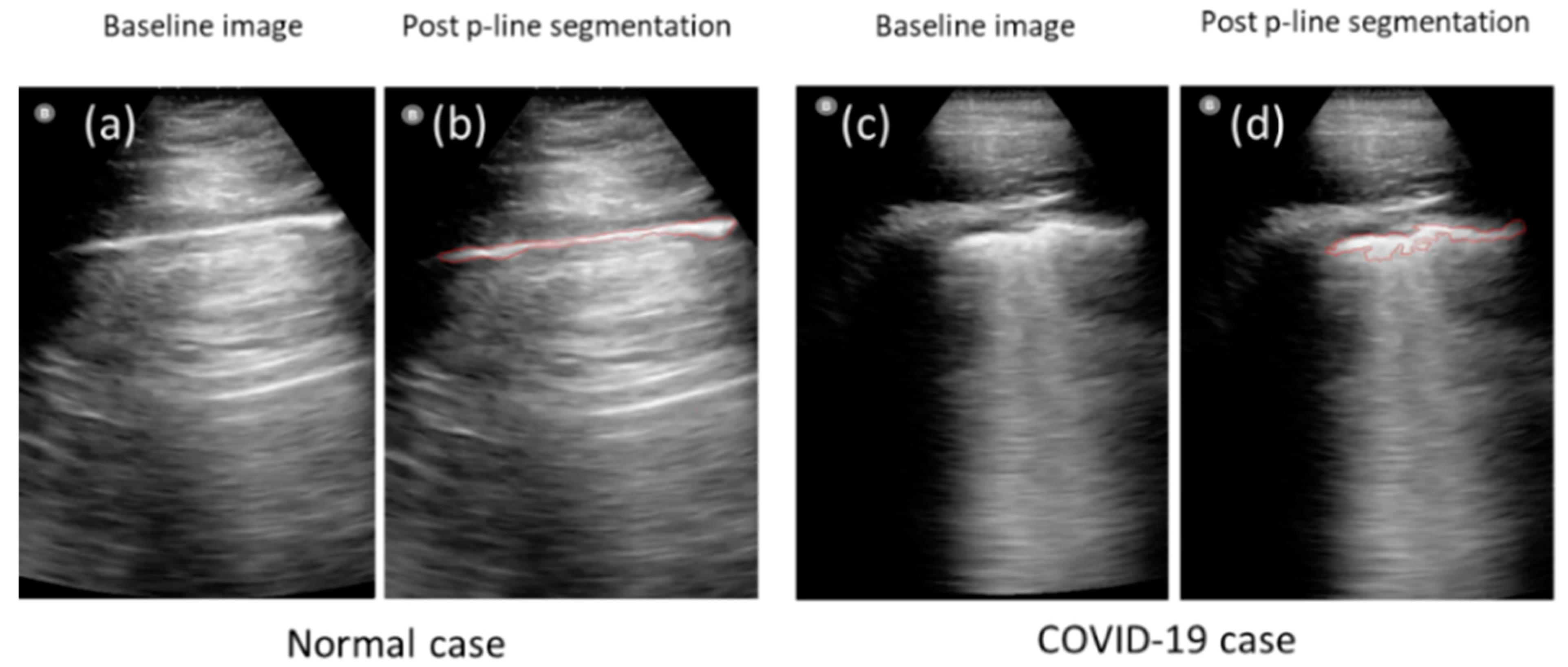
| Years of Clinical Experience | Experience in Diagnostic Methods | Experience with Ultrasound Technologies | Educational Background | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| User 1 | None | >30 years | >30 years | PhD |
| User 2 | >5 years | >5 years | >5 years | MD |
| User 3 | >5 years | >1 years | >1 years | MD |
| User 4 | None | >20 years | >20 years | PhD |
| User 5 | 10 years | 10 years | 10 years | MD |
| Thickness | Thickness Variation | PID | Nonlinearity | Tortuosity | Echo Intensity | Echo Heterogeneity | Overall Performance (AUC) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| User 1 | COVID-19 | 5.20 | 0.23 | 2.68 | 0.25 | 1.54 | 186.86 | 18.45 | |
| Normal | 1.80 | 0.06 | 0.70 | 0.81 | 1.04 | 195.06 | 14.69 | 0.96 | |
| p-value | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.47 | 0.12 | ||
| User 2 | COVID-19 | 4.62 | 1.97 | 2.45 | 0.20 | 1.46 | 184.79 | 20.96 | |
| Normal | 1.41 | 0.36 | 0.49 | 0.90 | 1.01 | 197.41 | 18.60 | 0.98 | |
| p-value | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.30 | 0.43 | ||
| User 3 | COVID-19 | 6.03 | 0.25 | 2.45 | 0.23 | 1.33 | 129.20 | 34.46 | |
| Normal | 2.51 | 0.06 | 0.59 | 0.74 | 1.08 | 137.74 | 32.38 | 0.92 | |
| p-value | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.20 | 0.53 | ||
| User 4 | COVID-19 | 4.69 | 0.67 | 1.62 | 0.23 | 1.51 | 202.21 | 13.91 | |
| Normal | 1.10 | 0.85 | 1.84 | 0.79 | 1.16 | 212.31 | 11.50 | 0.84 | |
| p-value | 0.00 | 0.69 | 0.84 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.51 | 0.06 | ||
| User 5 | COVID-19 | 5.84 | 1.40 | 3.03 | 0.13 | 1.10 | 167.21 | 34.62 | |
| Normal | 2.16 | 0.44 | 0.93 | 0.78 | 1.04 | 182.48 | 27.56 | 0.99 | |
| p-value | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.22 | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sultan, L.R.; Haertter, A.; Al-Hasani, M.; Demiris, G.; Cary, T.W.; Tung-Chen, Y.; Sehgal, C.M. Can Artificial Intelligence Aid Diagnosis by Teleguided Point-of-Care Ultrasound? A Pilot Study for Evaluating a Novel Computer Algorithm for COVID-19 Diagnosis Using Lung Ultrasound. AI 2023, 4, 875-887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai4040044
Sultan LR, Haertter A, Al-Hasani M, Demiris G, Cary TW, Tung-Chen Y, Sehgal CM. Can Artificial Intelligence Aid Diagnosis by Teleguided Point-of-Care Ultrasound? A Pilot Study for Evaluating a Novel Computer Algorithm for COVID-19 Diagnosis Using Lung Ultrasound. AI. 2023; 4(4):875-887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai4040044
Chicago/Turabian StyleSultan, Laith R., Allison Haertter, Maryam Al-Hasani, George Demiris, Theodore W. Cary, Yale Tung-Chen, and Chandra M. Sehgal. 2023. "Can Artificial Intelligence Aid Diagnosis by Teleguided Point-of-Care Ultrasound? A Pilot Study for Evaluating a Novel Computer Algorithm for COVID-19 Diagnosis Using Lung Ultrasound" AI 4, no. 4: 875-887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai4040044
APA StyleSultan, L. R., Haertter, A., Al-Hasani, M., Demiris, G., Cary, T. W., Tung-Chen, Y., & Sehgal, C. M. (2023). Can Artificial Intelligence Aid Diagnosis by Teleguided Point-of-Care Ultrasound? A Pilot Study for Evaluating a Novel Computer Algorithm for COVID-19 Diagnosis Using Lung Ultrasound. AI, 4(4), 875-887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai4040044








