SLASSY—An Assistance System for Performing Design for Manufacturing in Sheet-Bulk Metal Forming: Architecture and Self-Learning Aspects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. KBS for the Assessment of Manufacturability
- The well-known “inscribed circles method” of Heuvers [17] (see e.g., Campbell [18] for an English explanation of Heuvers’ circles) can be used to find and correct casting cross sections that require sufficient feeding via a riser. This method has been formalized for computer-aided support by Ransing et al. [19].
- In design for the machining (milling, turning) of metal parts, the golden rule ’never deviate from the primary tool axis’ Hodgson and Pitts [22] is still valid to ensure single-set-up machining [23]. For modern processes, such as free form machining, Korosec et al. [24] developed an approach to evaluate the manufacturability based on artificial neural networks.
| Name | Purpose | Use Case | CAD Integration | Institution | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KS mfk | engineering design system, design for manufacturing | shafts, casted workpieces, sheet metal parts | Pro/E® | University of Erlangen | 1990 | [27] |
| WYCAD | engineering design system | hydraulic excavator | n. a. | Zhejiang University of Hangzhou | 1990 | [28] |
| WISKON | engineering design system | mechanical drive train systems | n. a. | University of Kassel | 1995 | [29] |
| Predictive Engineering | engineering workbench for multi-criteria design analysis | car door system | Pro/E® | University of Erlangen | 2000 | [13] |
| DEKAS | decision making support tool | security facilities | n. a. | University of Strathclyde Glasgow | 2001 | [30] |
| RRCDPE | variant design system | universal rotational connection | SolidEdge®, Unigraphics® | University of Ljubljana | 2002 | [31] |
| ProKon | agent-based system, pro-active support of design engineer | shaft-hub connection | Pro/E® | University of Stuttgart | 2010 | [10] |
| LeanCost | design-task oriented system | design cost estimation | SolidEdge® | University of Ancona | 2011 | [32] |
| PKA assistance system | configuration and dimensioning | follow-on composite tools, handling module | SolidWorks® | Technical University of Vienna | 2011 | [33] |
1.2. Contribution Structure
2. Research on Sheet-Bulk Metal Forming
- increased design freedom due to the merger of sheet and bulk metal forming;
- maximizing functional density with different design features per part;
- realization of narrow tolerances and thus increased robustness of the part’s function fulfillment;
- easier adoption of part design to new requirements due to shortened process chain.
3. Knowledge-Based Systems in Engineering Design
3.1. General Architecture of KBS
- The problem solving component is the interface between the knowledge base and the components that interact with the user and the expert. The processing of expert knowledge is defined by implemented inference strategies;
- A dialogue component is necessary for the communication between the user and the assistance system. It enables the input of a user’s data and controls the output of results, suggestions or information;
- The explanation component shows the KBS’ procedure to both the user and the expert. The former is enabled to comprehend the system’s decisions whereas the latter can search for errors in the knowledge base;
- The knowledge acquisition component enables the transfer of knowledge from different sources into the knowledge base. New knowledge can be integrated and existing knowledge can be changed or removed.
3.2. Examples of KBS in Engineering Design
Engineering Design System mfk
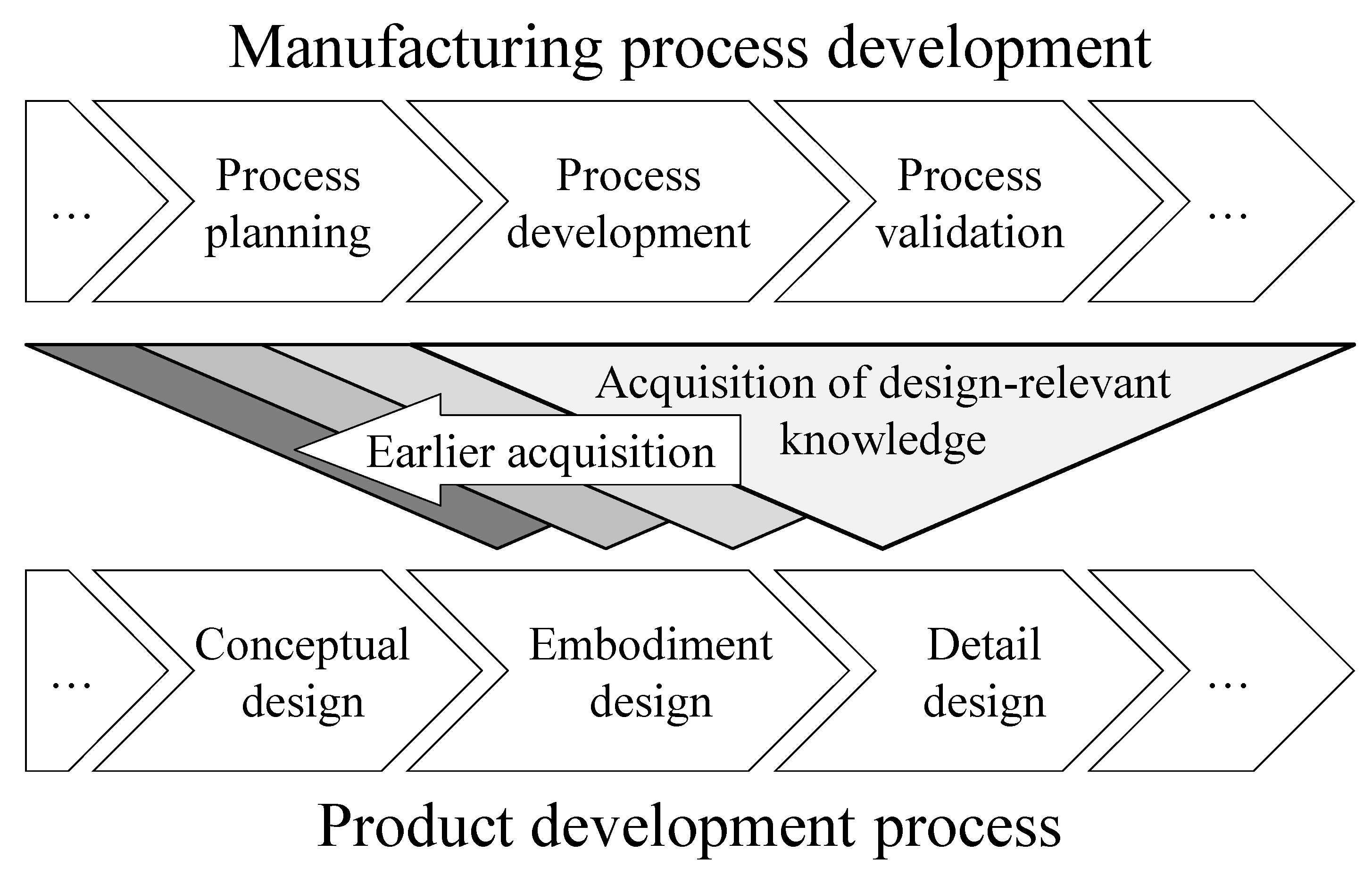
3.3. Knowledge Acquisition Methods
4. SLASSY—The Self-Learning Assistance System
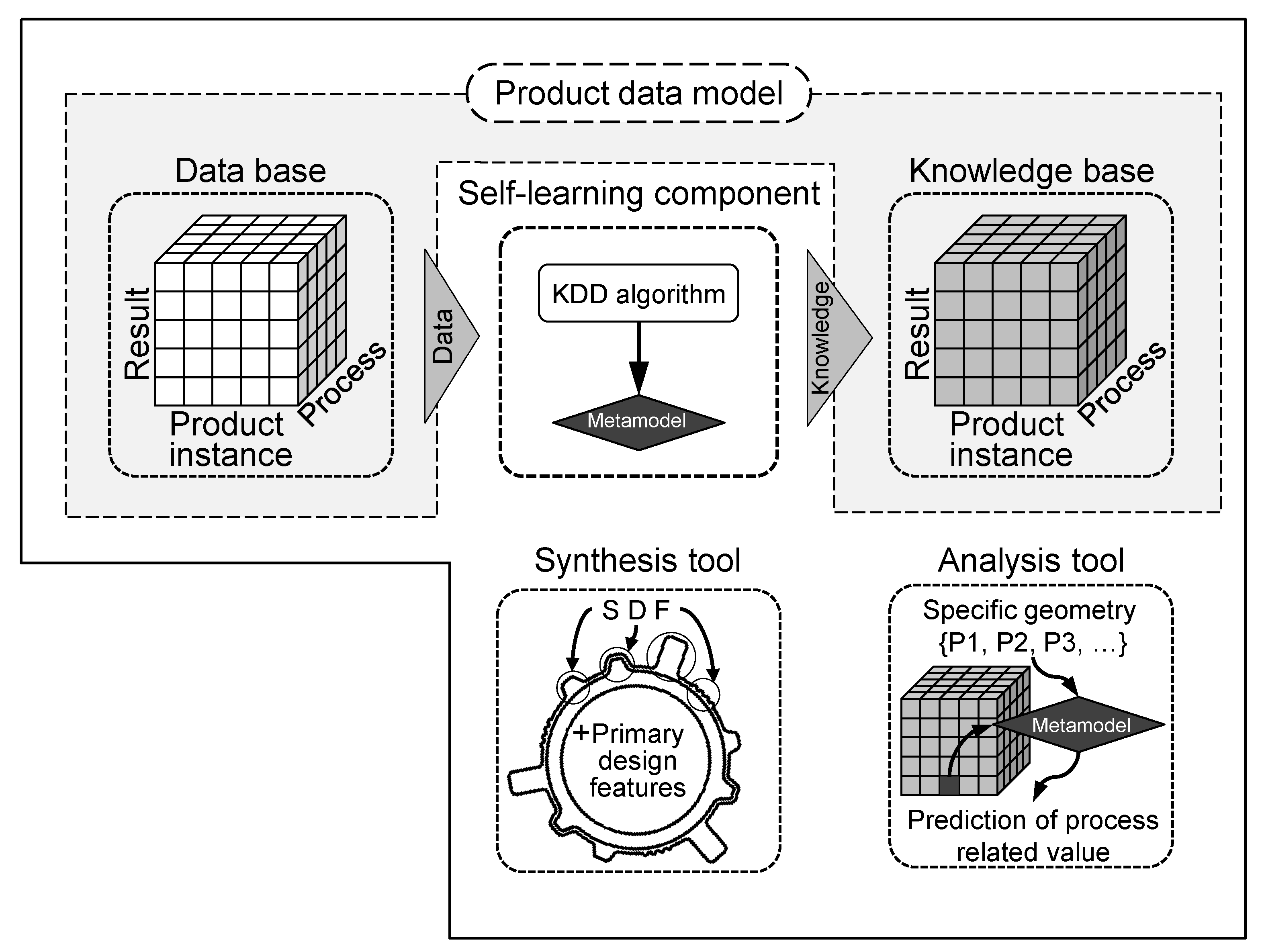
4.1. The Product Data Model
4.2. Synthesis and Analysis Tool
4.3. The KDD-Based Self-Learning Component
4.3.1. Implemented Metamodel Algorithms
4.3.2. Evaluating the Prediction Quality of Metamodels
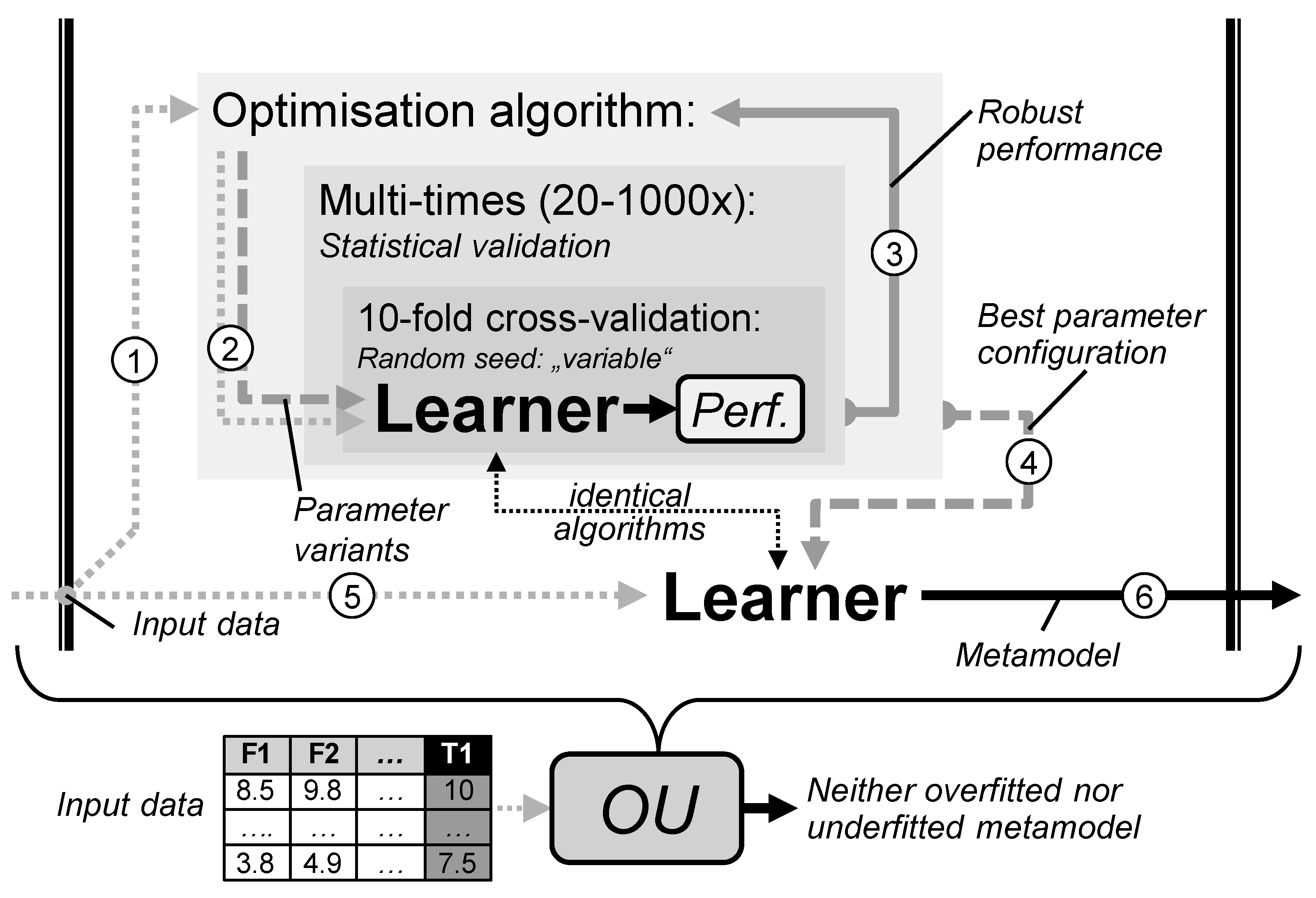
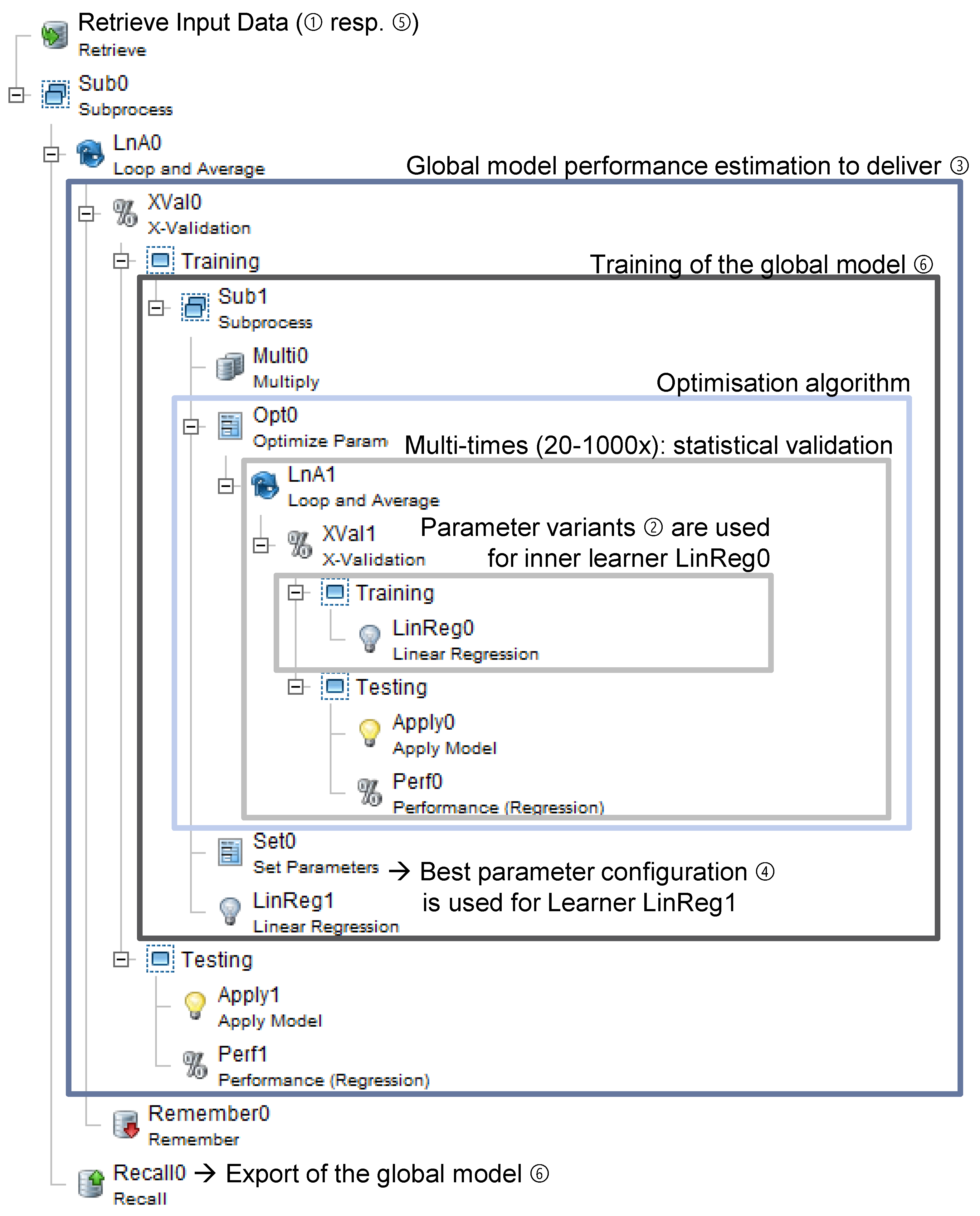
4.3.3. Robust Optimisation and Performance Estimation
4.3.4. Picking the Best
5. Use Case: Sheet-Bulk Metal Forming
5.1. Simulation-Based Parameter Study
5.2. Performing the ROPE Process
5.3. Best Model Derivation
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Terwiesch, C.; Loch, C.H. Managing the process of engineering change orders: The case of the climate control system in automobile development. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 1999, 16, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riviere, A.; DaCunha, C.; Tollenaere, M. Performances in engineering changes management. In Recent Advances in Integrated Design and Manufacturing in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 369–378. [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim, B.W. Lean product development flow. In Systems Engineering; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, B. Concurrent Engineering Fundamentals; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1996; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Rude, S. Wissensbasiertes Konstruieren; Shaker: Aachen, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, S.; Fan, I.S.; Li, G. Achieving Competitive Advantage through Knowledge-Based Engineering: A Best Practice Guide; Prepared for the Dept. of Trade and Industry by Dept. of Enterprise Integration, Cranfield University: Silsoe, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Skarka, W. Application of MOKA methodology in generative model creation using CATIA. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2007, 20, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Laan, A.H. Knowledge Based Engineering Support for Aircraft Component Design; TU Delft, Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lutz, C.; Gerhard, D. Implementation of practice-orientated IT-Systems for knowledge based configuration and design of customised products. In Proceedings of the 43th CIRP International Conference on Manufacturing Systems—CIRP ICMS 2010, Vienna, Austria, 26–28 May 2010; Kuhlang, P., Sihn, W., Eds.; Neuer Wissenschaftlicher Verlag: Wien, Austria, 2010; pp. 1060–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Kratzer, M.; Rauscher, M.; Binz, H.; Groehner, P. An agent-based system for supporting design engineers in the embodiment design phase. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Engineering Design, Denmark, Copenhagen, 15–18 August 2011; McAloone, T.C., Howard, T.J., Eds.; Technical University of Denmark: Denmark, Copenhagen, 2011; pp. 178–189. [Google Scholar]
- Verhagen, W.J.; Garcia, P.B.; Mariot, P.; Cotton, J.P.; Ruiz, D.; Redon, R.; Curran, R. Knowledge-based cost modelling of composite wing structures. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2012, 25, 368–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, S.E.; Corkill, D.D.; Staley, S.M. Designing integrated engineering environments: Blackboard-based integration of design and analysis tools. Concurr. Eng. 1996, 4, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wartzack, S. Predictive Engineering—Assistenzsystem Zur Multikriteriellen Analyse Alternativer Produktkonzepte; VDI: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, M. The application of surface demoldability and moldability to side-core design in die and mold CAD. Comput. Aided Des. 2008, 40, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, R. Automation of strip-layout design for sheet metal work on progressive die. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 195, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigenbaum, E.A. Expert systems in the 1980s. In State of the Art Report on Machine Intelligence; Pergamon-Infotech: Maidenhead, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Heuvers, A. Was hat der Stahlgießer dem Konstrukteur über Lunker-und Rissbildung zu sagen? Stahl Eisen 1929, 49, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J. Castings Practice: The Ten Rules of Castings; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ransing, R.S.; Sood, M.P.; Pao, W. Computer implementation of Heuvers’ circle method for thermal optimisation in castings. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2005, 18, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler GmbH. Metal Forming Handbook; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Meerkamm, H.; Rösch, S.; Storath, E.; Steber, M. A Design System Sheet Metal Parts as a Basis for a Concurrent Engineering Approach. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Sheet Metal, Naples, Italy, 9–12 June 1996; pp. 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson, B.; Pitts, G. Designing for CNC manufacture. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 1989, 203, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spur, G.; Stoferle, T. Handbook of Production Techniques. Volume 3/2: Machining (Handbuch der Fertigungstechnik. Band 3/2: Machining). (Book). (Retroactive Coverage); Carl Hanser Verlag: Munich, Germany, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Korosec, M.; Balic, J.; Kopac, J. Neural network based manufacturability evaluation of free form machining. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merklein, M.; Koch, J.; Schneider, T.; Opel, S.; Vierzigmann, U. Manufacturing of complex functional components with variants by using a new metal forming process–sheet-bulk metal forming. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2010, 3, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatti, S.; Laperrière, L.; Reinhart, G.; Tolio, T. (Eds.) Plate Forging. In CIRP Encyclopedia of Production Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; p. 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerkamm, H. Design system mfk—An important step towards an engineering workbench. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J. Eng. Manuf. 1993, 207, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingzhi, H. Introduce Engineering Constraint to Graphic Parametrization for Process Parametrization. Manuf. Autom. 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Eulenbach, D. Konstruktionssystem WISKON: Ein Beitrag zur Weiterentwicklung von CAD-Systemen; VDI-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- West, G.; Strachan, S.; McDonald, J.; Duffy, A.; Farrell, J.; Gwyn, B. DEKAS-an evolutionary case-based reasoning system to support protection scheme design. Des. Manag. Process. Inf. Issues 2001, 2, 123. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiba, P.; Prebil, I.; Novak, A. Upgrading a CAD System with expert system. In Proceedings of the 7th International Design Conference (DESIGN 2002), Dubrovnik, Croatia, 14–17 May 2002; pp. 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Germani, M.; Cicconi, P.; Mandolini, M. Manufacturing cost estimation during early phases of machine design. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Engineering Design (ICED 11), Impacting Society through Engineering Design, Volume 5: Design for X/Design to X, Lyngby/Copenhagen, Denmark, 15–19 August 2011; pp. 198–209. [Google Scholar]
- Lutz, C.; Gerhad, D. IT-based configurationand dimensioning of customer specific products-towards a framework for implementing knowledge-based design assistant systems. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Engineering Design (ICED 11), Impacting Society through Engineering Design, Volume 5: Design for X/Design to X, Lyngby/Copenhagen, Denmark, 15–19 August 2011; Volume 6. pp. 192–199. [Google Scholar]
- Hildenbrand, P.; Schneider, T.; Merklein, M. Flexible Rolling of Process Adapted Semi-Finished Parts and its Application in a 101 Sheet-Bulk Metal Forming Process. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publ: Durnten-Zurich, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 639, pp. 259–266. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, C.; Hetzner, H.; Tremmel, S.; Hilpert, F.; Durst, K. Tailored mechanical properties and residual stresses of aC: H: W Coatings. In Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publ: Durnten-Zurich, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 996, pp. 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, E.; Faßmann, D.; Loehnert, S.; Schaper, M.; Wriggers, P. Texture development and formability prediction for pre-textured cold rolled body-centred cubic steel. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2013, 68, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, F.; Blum, H.; Kumor, D.; Rademacher, A.; Willner, K.; Schneider, T. Experimental and Simulative Investigations of Tribology in Sheet-Bulk Metal Forming. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publ: Durnten-Zurich, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 639, pp. 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, N.J. Principles of Artificial Intelligence; Morgan Kaufmann: San Mateo, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Verhagen, W.J.; Bermell-Garcia, P.; van Dijk, R.E.; Curran, R. A critical review of Knowledge-Based Engineering: An identification of research challenges. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2012, 26, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestel, P.; Wartzack, S. Wissensbasierter Aufbau konstruktionsbegleitender Finite-Elemente-Analysen durch ein FEA-Assistenzsystem. In Entwerfen Entwickeln Erleben—Beiträge zu Virtuellen Produktentwicklung und Konstruktionstechnik; TUD Press: Dresden, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, R. Knowledge-based systems. Science 1986, 231, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahl, G.; Beitz, W.; Blessing, L.; Feldhusen, J.; Grote, K.H.; Wallace, K. Engineering Design: A Systematic Approach, 3rd ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wartzack, S.; Meerkamm, H. Durchgängige Rechnerunterstützung in der Produktentwicklung aufgrund des Einsatzes semantisch hochwertiger Features. Konstruktion 2000, 52, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, C. CPM/PDD–An extended theoretical approach to modelling products and product development processes. In 2nd German-Israeli Symposium on Advances in Methods and Systems for Development of Products and Processes; Bley, H., Jansen, H., Krause, F.L., Shpitalni, M., Eds.; Fraunhofer-IRB-Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2005; pp. 159–179. [Google Scholar]
- Kleijnen, J.P. Statistical Tools for Simulation Practitioners; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, R.; Chen, W.; Simpson, T.W. Comparative studies of metamodelling techniques under multiple modelling criteria. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2001, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, C.; Schleich, B.; Wartzack, S. Simultaneous Development of a Self-learning Engineering Assistance System. In Sheet Bulk Metal Forming. Research Results of the TCRC73; Marion Merklein, A., Erman Tekkaya, B.A.B., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Production Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, G.; Hall, M.; Frank, E. Generating Rule Sets from Model Trees. In Proceedings of the Twelfth Australian Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Canberra, Australia, 29–30 November 1999; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E.; Hall, M.A. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques, 3rd ed.; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, P.N.; Steinbach, M.; Kumar, V. Introduction to Data Mining, Pearson International ed.; Pearson/Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Kamber, M.; Pei, J. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques, 2nd ed.; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan, J.R. Learning with continuous classes. In Proceedings of the 5th Australian joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Hobart, Tasmania, 16–18 November 1992; World Scientific: Singapore, 1992; Volume 92, pp. 343–348. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Witten, I.H. Inducing Model Trees for Continuous Classes. In Proceedings of the Ninth European Conference on Machine Learning, Prague, Czech Republic, 23–25 April 1997; pp. 128–137. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, D.; Butler, D. Statistical validation. Ecol. Model. 1993, 68, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Most, T.; Will, J. Metamodel of Optimal Prognosis-an automatic approach for variable reduction and optimal metamodel selection. Proc. Weimar. Optim. Und Stochastiktage 2008, 5, 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Küstner, C.; Breitsprecher, T.; Wartzack, S. Die Auswirkung der Reihenfolge von Mess- und Simulationsdaten auf das Ergebnis der Kreuzvalidierung in KDD Prozessen. In Proceedings of the 24th Symposium Design for X, 19–20th, Hamburg, Germany, 19–20 September 2013; pp. 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Prekopcsák, Z.; Henk, T.; Gáspár-Papanek, C. Cross-validation: The illusion of reliable performance estimation. In Proceedings of the RCOMM RapidMiner Community Meeting and Converence, Dortmund, Germany, 13–16 September 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.C.; Runger, G.C. Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Durivage, M.A. Practical Engineering, Process, and Reliability Statistics; ASQ Quality Press: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, S.L.; Abramowitz, S.K. Statistics Using SPSS: An Integrative Approach; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, R.J. A Primer of Multivariate Statistics; Psychology Press: Hove, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhauer, J.G. Degrees of freedom. Teach. Stat. 2008, 30, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkle, D.E.; Wiersma, W.; Jurs, S.G. Applied Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences; Houghton Mifflin: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tukey, J.W. Comparing individual means in the analysis of variance. Biometrics 1949, 5, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.A. The Design of Experiments; Oliver Boyd: Edinburgh, UK, 1935. [Google Scholar]
- Pituch, K.A.; Whittaker, T.A.; Stevens, J.P. Intermediate Statistics: A Modern Approach; Routledge: New Delhi, India, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, R.D. Multivariate Statistical Methods in Behavioral Research; Scientific Software International: Lincolnwood, IL, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, M.A. EDF statistics for goodness of fit and some comparisons. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1974, 69, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Criteria | Direct | Indirect | Automatic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Availability of knowledge source |  |  |  |
| Formalization of knowledge |  |  |  |
| Susceptibility to errors |  |  |  |
| Minimizing effort w. r. t. time and cost |  |  |  |
 rather insufficient,
rather insufficient, 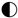 barely sufficient,
barely sufficient,  moderately sufficient,
moderately sufficient,  very sufficient
very sufficient| Parameter | Description | Unit | Input/ Output | Mean | Std | Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X_T0_A0 | angle of tooth | (degree) | input | 55.833 | 3.128 | |
| X_T0_W0 | tooth width | mm | input | 2.50 | 0.410 | |
| X_T0_L0 | tooth length | mm | input | 2.75 | 0.251 | |
| X_T0_R1 | top radius | mm | input | 0.60 | 0.246 | |
| X_T0_R2 | radius at tooth addendum | mm | input | 0.367 | 0.17 | |
| achieved forming force | kN | output | 1950 | 287.93 |
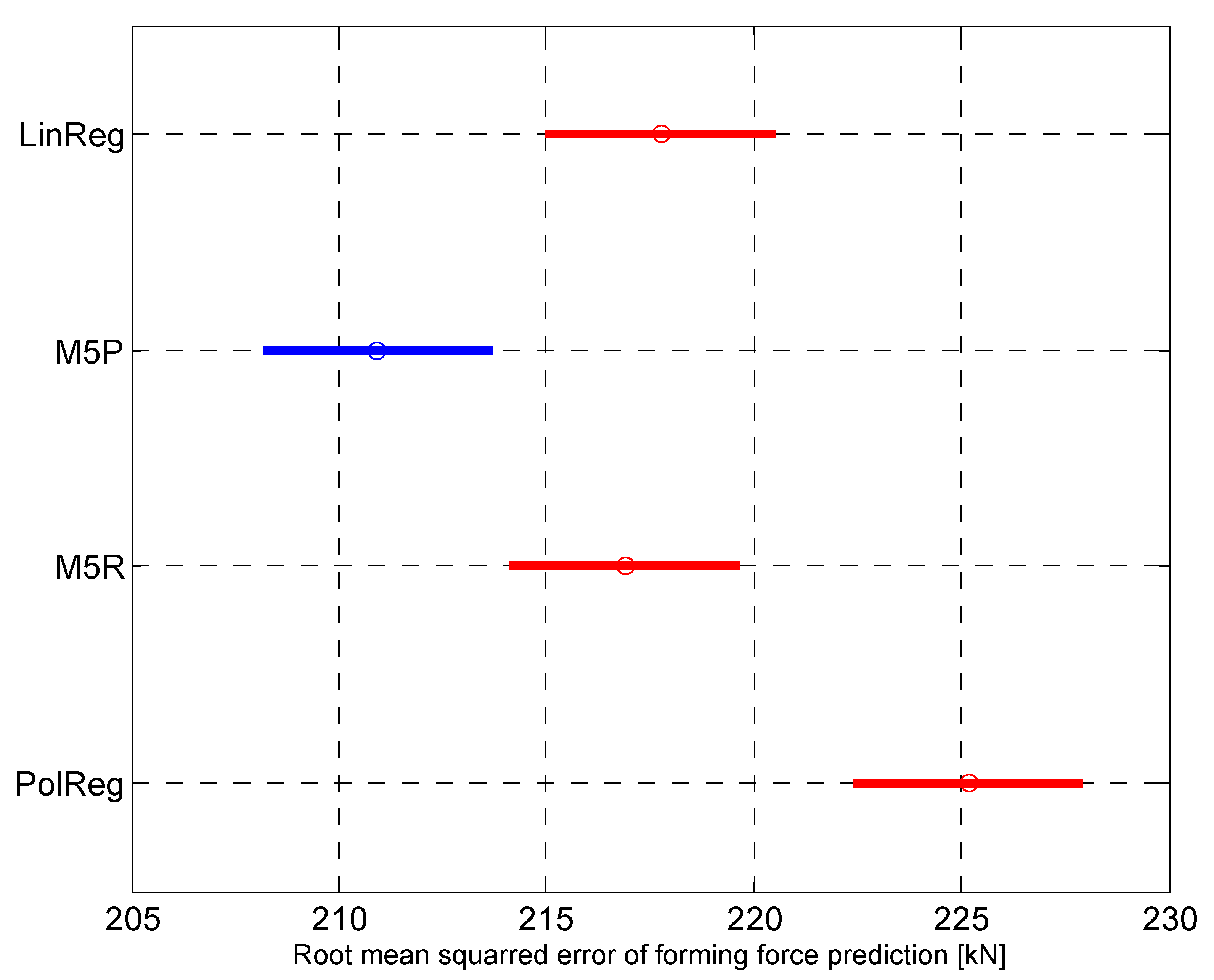
| Name | Min | Max | Mean | Std |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear reg. | 178.24 | 261.46 | 217.76 | 15.84 |
| M5P | 159.06 | 264.46 | 210.92 | 18.05 |
| M5R | 192.76 | 241.72 | 216.90 | 8.45 |
| Polynomial reg. | 185.95 | 266.54 | 225.17 | 16.22 |
| Source | SS | DoF | MS | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | 10,240 | 3 | 3414 | 14.72 | 4.19 × 10 |
| Error | 91,880 | 396 | 232.01 | ||
| Total | 102,120 | 399 |
| A | B | Lower Limit | Mean Diff. | Upper Limit | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LinReg | → | M5P | 1.299 | 6.833 | 12.367 | 0.0082 |
| LinReg | → | M5R | −4.676 | 0.858 | 6.390 | 0.9786 |
| LinReg | → | PolReg | −12.95 | −7.42 | −1.883 | 0.0032 |
| M5P | → | M5R | −11.51 | −5.97 | −0.441 | 0.0284 |
| M5P | → | PolReg | −19.79 | −14.25 | −8.717 | 0.0000 |
| M5R | → | PolReg | −13.81 | −8.28 | −2.742 | 0.0007 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sauer, C.; Breitsprecher, T.; Küstner, C.; Schleich, B.; Wartzack, S. SLASSY—An Assistance System for Performing Design for Manufacturing in Sheet-Bulk Metal Forming: Architecture and Self-Learning Aspects. AI 2021, 2, 307-329. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai2030019
Sauer C, Breitsprecher T, Küstner C, Schleich B, Wartzack S. SLASSY—An Assistance System for Performing Design for Manufacturing in Sheet-Bulk Metal Forming: Architecture and Self-Learning Aspects. AI. 2021; 2(3):307-329. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai2030019
Chicago/Turabian StyleSauer, Christopher, Thilo Breitsprecher, Christof Küstner, Benjamin Schleich, and Sandro Wartzack. 2021. "SLASSY—An Assistance System for Performing Design for Manufacturing in Sheet-Bulk Metal Forming: Architecture and Self-Learning Aspects" AI 2, no. 3: 307-329. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai2030019
APA StyleSauer, C., Breitsprecher, T., Küstner, C., Schleich, B., & Wartzack, S. (2021). SLASSY—An Assistance System for Performing Design for Manufacturing in Sheet-Bulk Metal Forming: Architecture and Self-Learning Aspects. AI, 2(3), 307-329. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai2030019







