Distribution Patterns and Diversity of Sedimental Microbial Communities in the Tianxiu Hydrothermal Field of Carlsberg Ridge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Geochemical Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Geochemical Characterization of the Sediments
3.2. Microbial Community Diversity and Structures
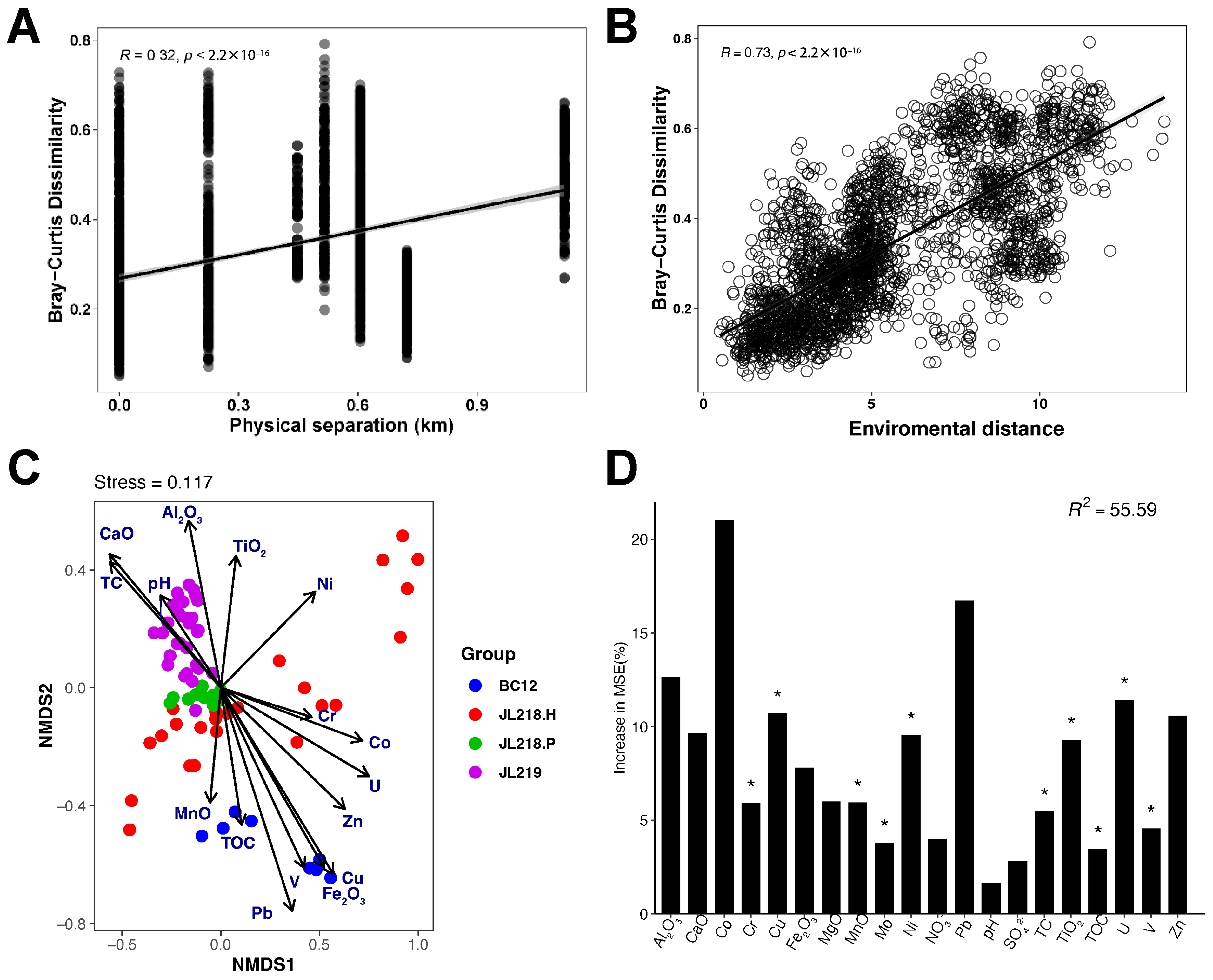
3.3. Environmental Factors Shaping the Community Compositions
3.4. Assembly Process of Microbial Community Structure
4. Discussion
4.1. Microbial Community Composition in Response to Geochemistry
4.2. Microbial Community Assembly in Response to Hydrothermal Activity
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dick, G.J. The microbiomes of deep-sea hydrothermal vents: Distributed globally, shaped locally. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Früh-Green, G.L.; Kelley, D.S.; Lilley, M.D.; Cannat, M.; Chavagnac, V.; Baross, J.A. Diversity of magmatism, hydrothermal processes and microbial interactions at mid-ocean ridges. Nat. Rev. Earth. Environ. 2022, 3, 852–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.F.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Y. Microbial diversity of sediments from an inactive hydrothermal vent field, Southwest Indian Ridge. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2020, 2, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Alain, K.; Shao, Z.Z. Microorganisms from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Mar. Life Sci. Techol. 2021, 3, 204–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvan, J.B.; Pyenson, B.C.; Rouxel, O.; German, C.R.; Edwards, K.J. Time-series analysis of two hydrothermal plumes at 9°50′N East Pacific Rise reveals distinct, heterogeneous bacterial populations. Geobiology 2012, 10, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haalboom, S.; Price, D.M.; Mienis, F.; van Bleijswijk, J.D.L.; de Stigter, H.C.; Witte, H.J.; Reichart, G.J.; Duineveld, G.C.A. Patterns of (trace) metals and microorganisms in the Rainbow hydrothermal vent plume at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 2499–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.E.; Beltrán, M.T.; Hallam, S.J.; Baross, J.A. Microbial community structure across fluid gradients in the Juan de Fuca Ridge hydrothermal system. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 83, 324–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppa Baskaran, D.K.; Umale, S.; Zhou, Z.; Raman, K.; Anantharaman, K. Metagenome-based metabolic modelling predicts unique microbial interactions in deep-sea hydrothermal plume microbiomes. ISME Commun. 2023, 3, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesniewski, R.A.; Jain, S.; Anantharaman, K.; Schloss, P.D.; Dick, G.J. The metatranscriptome of a deep-sea hydrothermal plume is dominated by water column methanotrophs and lithotrophs. ISME J. 2012, 6, 2257–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaman, K.; Breier, J.A.; Dick, G.J. Metagenomic resolution of microbial functions in deep-sea hydrothermal plumes across the Eastern Lau Spreading Center. ISME J. 2016, 10, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namirimu, T.; Park, M.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lim, D.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, A.; Kim, D.; Kwon, K.K. Microbial Diversity of Deep-sea Sediments from Three Newly Discovered Hydrothermal Vent Fields in the Central Indian Ridge. Ocean Sci. J. 2023, 58, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.K.; Krishnan, K.P.; Thomas, F.A.; Binish, M.B.; Mohan, M.; Kurian, P.J. Polyphasic approach revealed complex bacterial community structure and function in deep sea sediment of ultra-slow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Yang, J.Y.; Sun, M.X.; Su, L.; Wang, H.; Gao, J.Q.; Bai, S.J. Distribution and Succession of Microbial Communities Along the Dispersal Pathway of Hydrothermal Plumes on the Southwest Indian Ridge. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 581381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; St. John, E.; Anantharaman, K.; Reysenbach, A.-L. Global patterns of diversity and metabolism of microbial communities in deep-sea hydrothermal vent deposits. Microbiome 2022, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Jian, H.H.; Leng, H.; Xiao, X. Microbial Community Structure of Deep-sea Hydrothermal Vents on the Ultraslow Spreading Southwest Indian Ridge. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.C.; Tran, P.Q.; Adams, A.M.; Kieft, K.; Breier, J.A.; Fortunato, C.S.; Sheik, C.S.; Huber, J.A.; Li, M.; Dick, G.J.; et al. Sulfur cycling connects microbiomes and biogeochemistry in deep-sea hydrothermal plumes. ISME J. 2023, 17, 1194–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mara, P.; Geller-McGrath, D.; Edgcomb, V.; Beaudoin, D.; Morono, Y.; Teske, A. Metagenomic profiles of archaea and bacteria within thermal and geochemical gradients of the Guaymas Basin deep subsurface. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Teske, A.P.; MacGregor, B.J.; McKay, L.J.; Mendlovitz, H.; Albert, D.; Ma, Z.L.; Li, J.T. Thermal Selection of Microbial Communities and Preservation of Microbial Function in Guaymas Basin Hydrothermal Sediments. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2023, 89, e00018–e00023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.R.; Wang, L.S.; Saren, G.W.; Yu, X.K.; Li, Y.J. Variable Microbial Communities in the Non-Hydrothermal Sediments of the Mid-Okinawa Trough. Geomicrobiol. J. 2020, 37, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Cui, J.M.; Yang, Q.H.; Cui, G.J.; Wei, B.B.; Wu, Z.J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.Y. Oxidative Weathering and Microbial Diversity of an Inactive Seafloor Hydrothermal Sulfide Chimney. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Sievert, S.M.; Wang, Y.; Seewald, J.S.; Natarajan, V.P.; Wang, F.; Xiao, X. Microbial succession during the transition from active to inactive stages of deep-sea hydrothermal vent sulfide chimneys. Microbiome 2020, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.C.; Gonnella, G.; Adam, N.; Schippers, A.; Burkhardt, L.; Kurtz, S.; Schwarz-Schampera, U.; Franke, H.; Perner, M. Hydrothermal chimneys host habitat-specific microbial communities: Analogues for studying the possible impact of mining seafloor massive sulfide deposits. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djurhuus, A.; Mikalsen, S.O.; Giebel, H.A.; Rogers, A.D. Cutting through the smoke: The diversity of microorganisms in deep-sea hydrothermal plumes. Roy. Soc. Open. Sci. 2017, 4, 160829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Han, X.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Wu, X.T.; Zong, T.; Yu, X.; Liu, J.Q.; Li, H.L.; Qiu, Z.Y. Hydrothermal alteration of basalts in the ultramafic-associated Tianxiu Vent Field, Carlsberg Ridge. Mar. Geol. 2023, 463, 107113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Zhou, H.Y.; Fang, J.S.; Wu, Z.J.; Peng, X.T. Microbial Distribution in a Hydrothermal Plume of the Southwest Indian Ridge. Geomicrobiol. J. 2016, 33, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Han, X.; Wei, M.C.; Qiu, Z.Y.; Dong, C.Q.; Wu, Y.H.; Wu, X.T.; Juan, Y. Characteristics and evolution of bacterial communities in the Wocan hydrothermal plume-influenced zone, Carlsberg Ridge, northwestern Indian Ocean. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2022, 62, 1974–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Han, X.; Xie, Q.; Wei, M.; Yu, J. Spatio-temporal variations of archaeal communities in the Wocan hydrothermal plume-influenced zone, Carlsberg Ridge, northwest Indian Ocean. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2024, 64, 1848–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, P.; Zhu, Y.X.; Wang, J.; Song, L.; Han, X.Q.; Huang, Y. Biogeography and potential ecological functions of prokaryotes in the hydrothermal and non-hydrothermal field sediments of the Indian Ocean Ridges. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1072569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namirimu, T.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, M.J.; Lim, D.; Lee, J.H.; Kwon, K.K. Microbial Community Structure and Functional Potential of Deep-Sea Sediments on Low Activity Hydrothermal Area in the Central Indian Ridge. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 09, 784807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Han, X.Q.; Zhou, Y.D.; Qiu, Z.Y.; Yu, X.; Petersen, S.; Li, H.L.; Yang, M.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.Q.; et al. The Daxi Vent Field: An active mafic-hosted hydrothermal system at a non-transform offset on the slow-spreading Carlsberg Ridge, 6°48′N. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 129, 103888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. First Ultramafic-Hosted Hydrothermal Sulfide Deposit Discovered on the Carlsberg Ridge, Northwest Indian Ocean; The Third InterRidge Theoretical Insitute: Hangzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Han, X.Q.; Li, H.L.; Yu, X.; Cui, R.Y.; Li, M.; Chen, X.G.; Liu, J.Q. Discovery and characterization of a new hydrothermal field at 2°N on the slow-spreading Carlsberg Ridge. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2024, 42, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Han, X.Q.; Petersen, S.; Frische, M.; Qiu, Z.Y.; Li, H.M.; Li, H.L.; Wu, Z.C.; Cui, R.Y. Mineralogy and trace element geochemistry of sulfide minerals from the Wocan Hydrothermal Field on the slow-spreading Carlsberg Ridge, Indian Ocean. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 84, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.Y.; Fan, W.J.; Han, X.Q.; Chen, X.G.; Yin, X.B. Distribution, speciation and mobility of metals in sediments of the Tianxiu hydrothermal field, Carlsberg Ridge, Northwest Indian Ocean. J. Mar. Syst. 2023, 237, 103826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.Y.; Han, X.Q.; Fan, W.J.; Wang, Y.J.; Li, M.; Cai, Y.Y. Hydrothermal signatures and prospecting indicators in sediments along the Carlsberg Ridge. Sediment. Geol. 2023, 458, 106536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Han, X.Q.; Qiu, Z.Y.; Fan, W.J.; Wang, Y.J.; Li, H.L.; Chen, H.L.; Hu, H. Sea-Level Fall Driving Enhanced Hydrothermal and Tectonic Activities: Evidence From a Sediment Core Near the Tectonic-Controlled Tianxiu Vent Field, Carlsberg Ridge. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2022GL101599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeberg-Elverfeldt, J.; Schlüter, M.; Feseker, T.; Kölling, M. Rhizon sampling of porewaters near the sediment-water interface of aquatic systems. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2005, 3, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Williams, E.; Vennes, C.; Hijmans, M.R.J. Package ‘geosphere’. Spherical Trigonometry 2017, 1, 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, B.; Simpson, G.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, H.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 2, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Ning, D.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Shan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Brown, M.R.; Li, Z.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; et al. Global diversity and biogeography of bacterial communities in wastewater treatment plants. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijewski, T.; Zbawicka, M.; Strand, J.; Kautsky, H.; Kotta, J.; Rätsep, M.; Wenne, R. Random forest assessment of correlation between environmental factors and genetic differentiation of populations: Case of marine mussels. Oceanologia 2019, 61, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Doebeli, M. Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 2016, 353, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, W.T.; Lunn, M.; Woodcock, S.; Head, I.M.; Nee, S.; Curtis, T.P. Quantifying the roles of immigration and chance in shaping prokaryote community structure. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.J.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.Y.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Ning, D.L. Stochastic Community Assembly: Does It Matter in Microbial Ecology? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00002–e00017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, T.; Doi, H.; Uramoto, G.I.; Wörmer, L.; Adhikari, R.R.; Xiao, N.; Morono, Y.; D’Hondt, S.; Hinrichs, K.U.; Inagaki, F. Global diversity of microbial communities in marine sediment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 27587–27597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinke, C.; Schwientek, P.; Sczyrba, A.; Ivanova, N.N.; Anderson, I.J.; Cheng, J.F.; Darling, A.; Malfatti, S.; Swan, B.K.; Gies, E.A.; et al. Insights into the phylogeny and coding potential of microbial dark matter. Nature 2013, 499, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.Y.; Greening, C.; Rattray, J.E.; Chakraborty, A.; Chuvochina, M.; Mayumi, D.; Dolfing, J.; Li, C.; Brooks, J.M.; Bernard, B.B.; et al. Metabolic potential of uncultured bacteria and archaea associated with petroleum seepage in deep-sea sediments. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagostina, L.; Frandsen, S.; MacGregor, B.J.; Glombitza, C.; Deng, L.H.; Fiskal, A.; Li, J.Q.; Doll, M.; Geilert, S.; Schmidt, M.; et al. Interactions between temperature and energy supply drive microbial communities in hydrothermal sediment. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, Z.M.; Li, J.T.; Bougouffa, S.; Tian, R.M.; Bajic, V.B.; Qian, P.Y. Draft genome of an bacterium reveals a facultative lifestyle in deep-sea anaerobic sediments. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, S.; Hirai, M.; Matsui, Y.; Makabe, A.; Minegishi, H.; Tsuda, M.; Juliarni; Rastelli, E.; Danovaro, R.; Corinaldesi, C.; et al. Microbial community and geochemical analyses of trans-trench sediments for understanding the roles of hadal environments. ISME J. 2020, 14, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazejak, A.; Schippers, A. High abundance of JS-1-and -related in deeply buried marine sediments revealed by quantitative, real-time PCR. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 72, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Saez, G.V.; Ristova, P.P.; Sievert, S.M.; Elvert, M.; Hinrichs, K.U.; Bühring, S.I. Relative Importance of Chemoautotrophy for Primary Production in a Light Exposed Marine Shallow Hydrothermal System. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozanov, A.S.; Bryanskaya, A.V.; Ivanisenko, T.V.; Malup, T.K.; Peltek, S.E. Biodiversity of the microbial mat of the Garga hot spring. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleary, D.F.R.; Polónia, A.R.M.; Becking, L.E.; de Voogd, N.J.; Purwanto; Gomes, H.; Gomes, N.C.M. Compositional analysis of bacterial communities in seawater, sediment, and sponges in the Misool coral reef system, Indonesia. Mar. Biodivers. 2018, 48, 1889–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, D.F.R.; Coelho, F.J.R.C.; Oliveira, V.; Gomes, N.C.M.; Polónia, A.R.M. Sediment depth and habitat as predictors of the diversity and composition of sediment bacterial communities in an inter-tidal estuarine environment. Mar. Ecol. 2017, 38, e12411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barosa, B.; Ferrillo, A.; Selci, M.; Giardina, M.; Bastianoni, A.; Correggia, M.; di Iorio, L.; Bernardi, G.; Cascone, M.; Capuozzo, R.; et al. Mapping the microbial diversity associated with different geochemical regimes in the shallow-water hydrothermal vents of the Aeolian archipelago, Italy. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1134114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.M.; Idei, A.; Terajima, S.; Kakegawa, T.; Fischer, W.W.; McGlynn, S.E. Microbial diversity and iron oxidation at Okuoku-hachikurou Onsen, a Japanese hot spring analog of Precambrian iron formations. Geobiology 2017, 15, 817–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Wang, L.; Mbadinga, S.M.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.; Gu, J.; Mu, B. Anaerolineaceae and Methanosaeta turned to be the dominant microorganisms in alkanes-dependent methanogenic culture after long-term of incubation. AMB Express 2015, 5, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, N.; Perner, M. Microbially Mediated Hydrogen Cycling in Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vents. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.S.; LaRowe, D.E.; Amend, J.P. Bioenergetic potentials in terrestrial, shallow-sea and deep-sea hydrothermal systems. Chem Geol 2021, 583, 120449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmkvist, L.; Ferdelman, T.G.; Jørgensen, B.B. A cryptic sulfur cycle driven by iron in the methane zone of marine sediment (Aarhus Bay, Denmark). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 3581–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, R.; Roy, H.; Augustin, N.; Gennerich, H.H.; Peters, M.; Wenzhoefer, F.; Amann, R.; Meyerdierks, A. Bacterial sulfur cycling shapes microbial communities in surface sediments of an ultramafic hydrothermal vent field. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 2633–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, C.; Seyfried, W. Hydrothermal Processes. In The Oceans and Marine Geochemistry; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2013; Volume 9, pp. 191–233. [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta, S.; Peng, X.; Ta, K. Interaction between Microbes, Minerals, and Fluids in Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Systems. Minerals 2021, 11, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, A.J.; Estes, E.R.; Gartman, A.; Yücel, M.; Kamyshny, A.; Luther, G.W. Iron and sulfide nanoparticle formation and transport in nascent hydrothermal vent plumes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, W.B.; Li, W.; Xiong, W.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Y.P.; Miao, Y.Z.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhang, N.; Shen, Q.R.; Zhang, R.F. Diversity-triggered deterministic bacterial assembly constrains community functions. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, K.; Nakamura, K. Archaeal diversity and community development in deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colman, D.R.; Keller, L.M.; Arteaga-Pozo, E.; Andrade-Barahona, E.; St. Clair, B.; Shoemaker, A.; Cox, A.; Boyd, E.S. Covariation of hot spring geochemistry with microbial genomic diversity, function, and evolution. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reysenbach, A.-L.; Shock, E. Merging Genomes with Geochemistry in Hydrothermal Ecosystems. Science 2002, 296, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
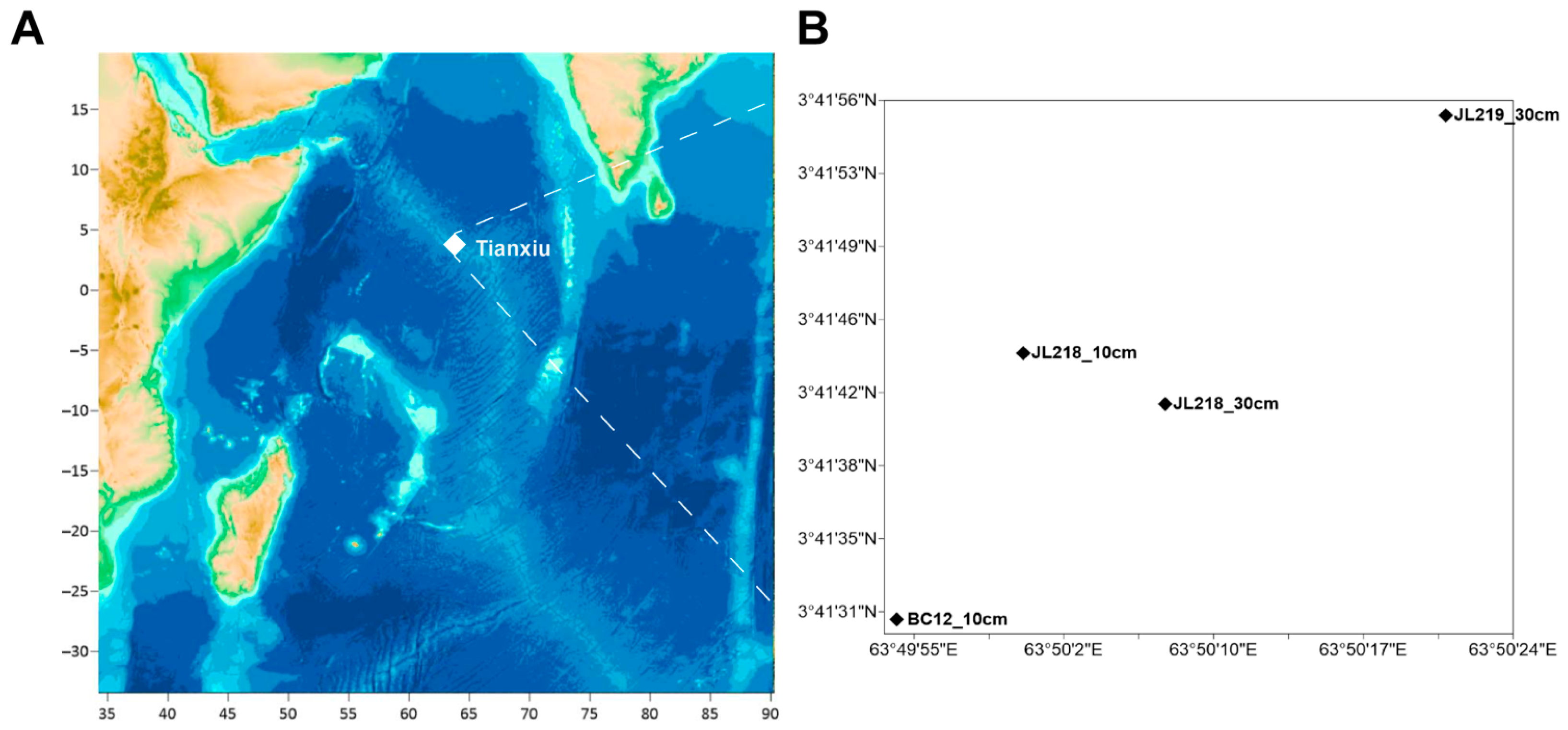
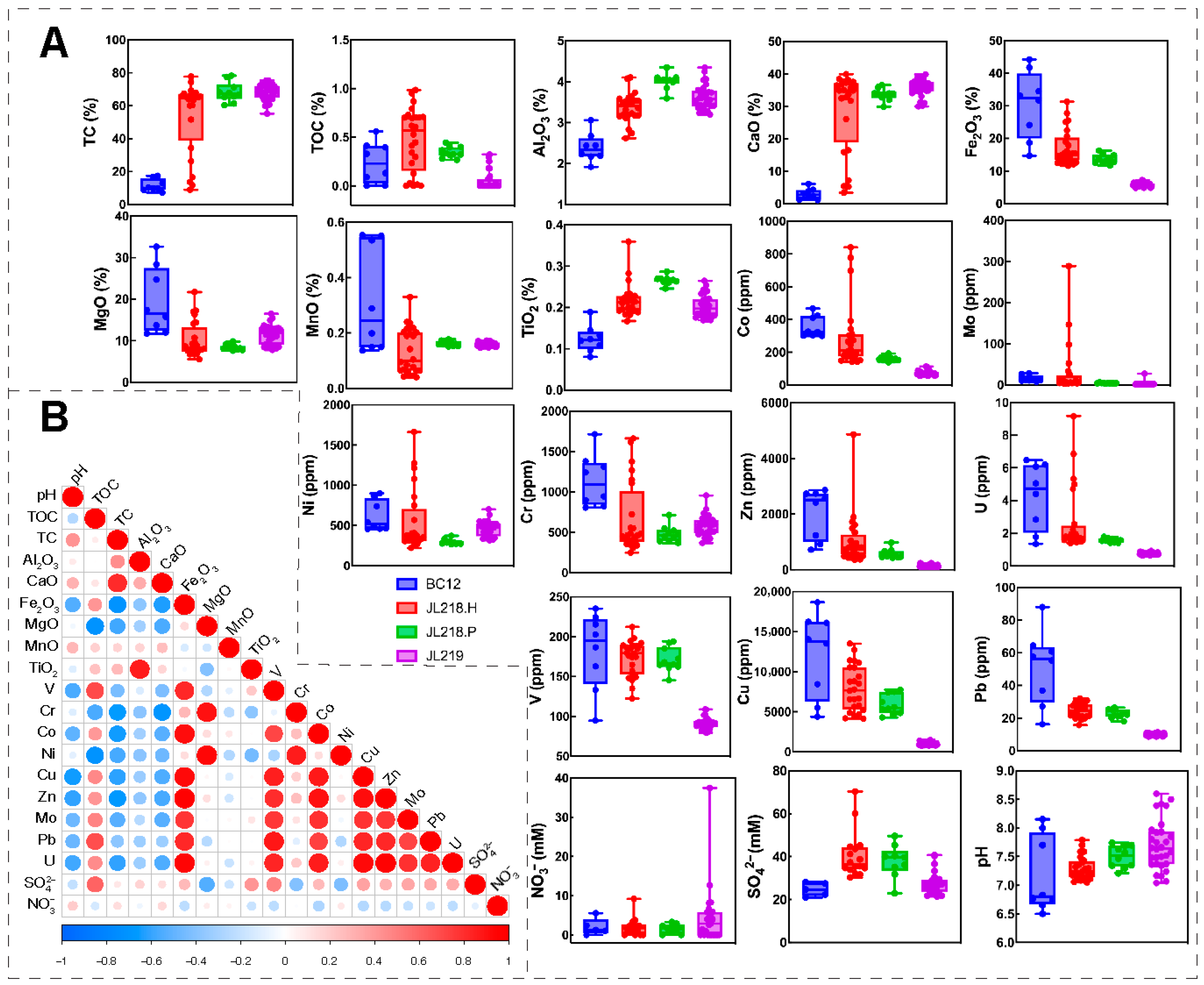
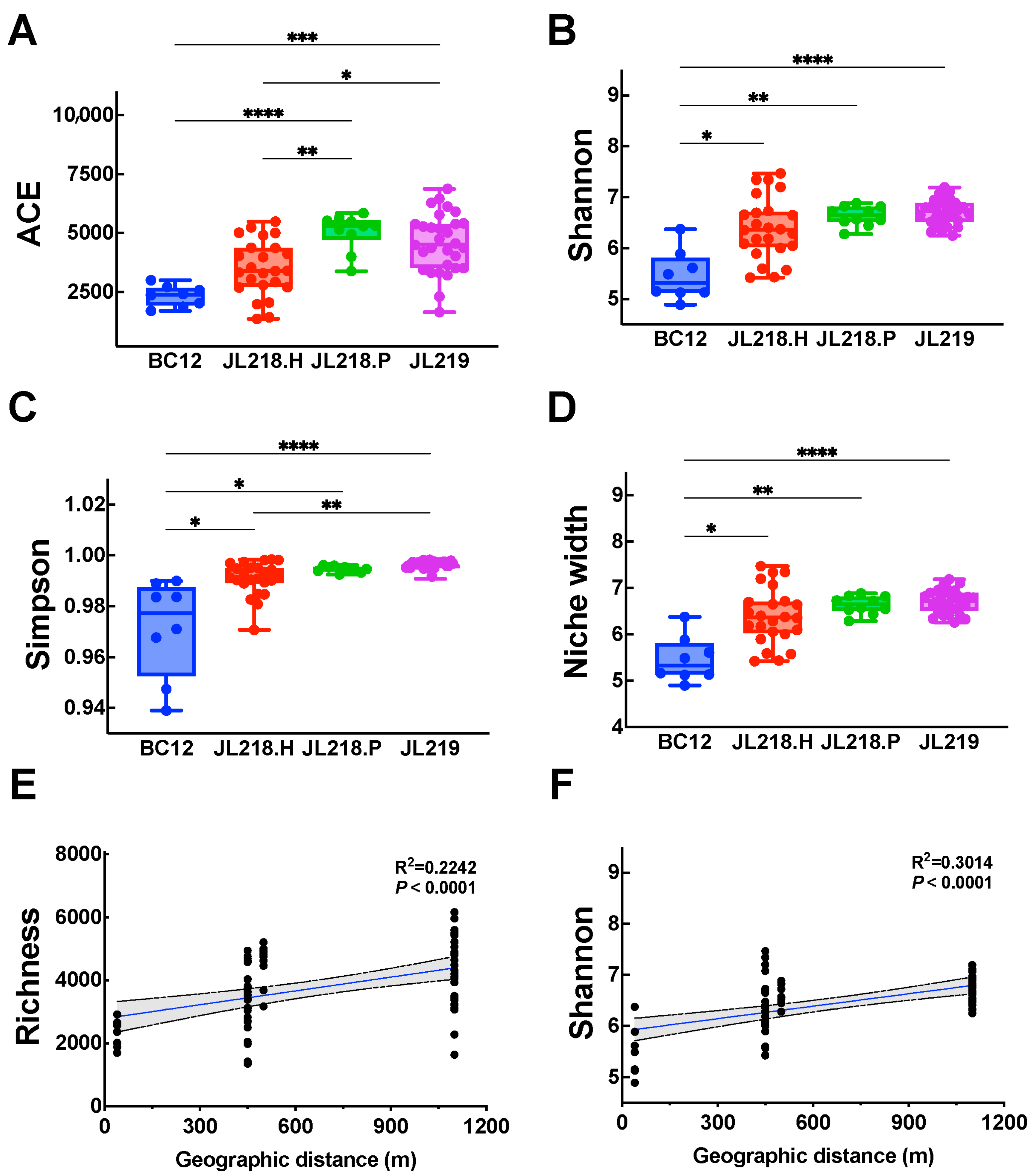

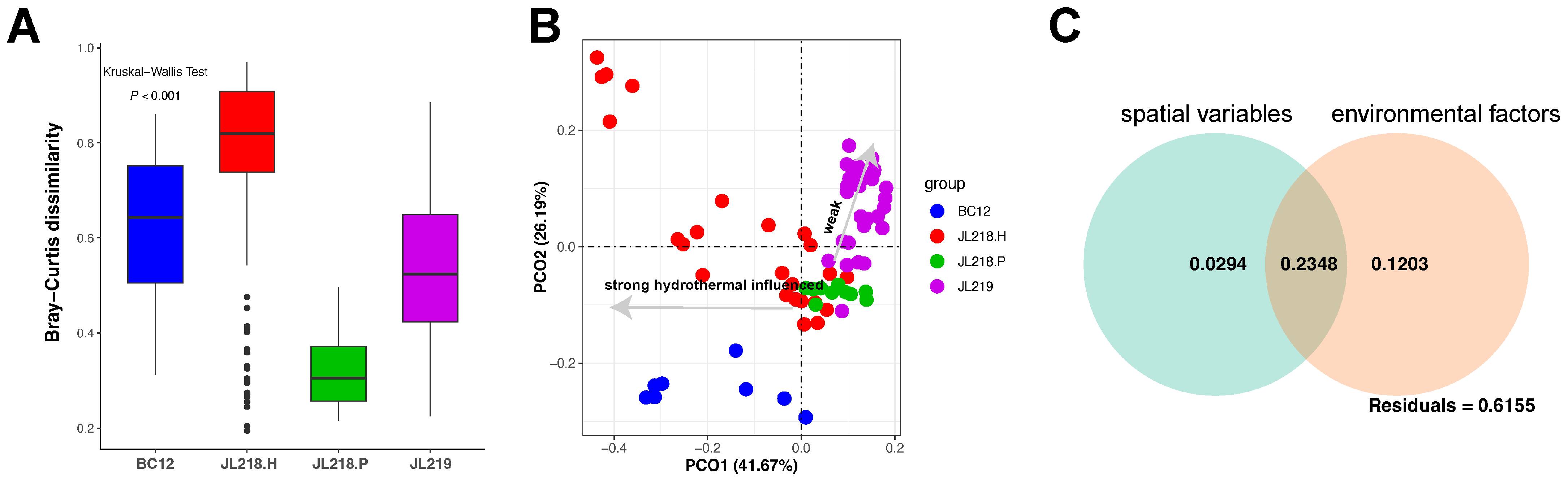

| Cores ID | Sample Abbreviation | Sampling Method | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Water Depth (m) | Distance from the Vent (m) | Number of Subsamples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC12_10 cm | BC12 | box corer | 3.691895 | 63.831765 | 3400 | 40 | 8 |
| JL218_30 cm | JL218.H | push-corer | 3.694844 | 63.835352 | 3508.8 | 450 | 24 |
| JL218_10 cm | JL218.P | push-corer | 3.695543 | 63.833459 | 3524.1 | 500 | 10 |
| JL219_30 cm | JL219 | push-corer | 3.698796 | 63.839103 | 3640 | 1100 | 30 |
| Sample | LREE | HREE | ΣREE | δEu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC12 (n = 8) | Min. | 7.19 | 2.85 | 10.04 | 2.29 |
| Max. | 25.41 | 7.53 | 32.94 | 3.55 | |
| Average | 16.94 | 5.01 | 21.95 | 2.86 | |
| Standard deviation | 1.52 | 5.98 | 7.48 | 0.50 | |
| JL218.H (n = 24) | Min. | 16.63 | 6.12 | 22.75 | 1.32 |
| Max. | 49.79 | 11.92 | 61.71 | 1.90 | |
| Average | 39.11 | 9.91 | 49.02 | 1.47 | |
| Standard deviation | 1.74 | 9.74 | 11.42 | 0.17 | |
| JL218.P (n = 10) | Min. | 36.12 | 9.67 | 45.79 | 1.25 |
| Max. | 47.38 | 12.03 | 59.40 | 1.37 | |
| Average | 43.35 | 11.07 | 54.43 | 1.31 | |
| Standard deviation | 0.62 | 3.32 | 3.92 | 0.04 | |
| JL219 (n = 30) | Min. | 32.15 | 7.92 | 40.07 | 1.16 |
| Max. | 49.07 | 12.02 | 61.09 | 1.32 | |
| Average | 40.10 | 9.71 | 49.81 | 1.22 | |
| Standard deviation | 1.08 | 4.16 | 5.23 | 0.04 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, F.; Liu, X.; Hou, W.; Dong, H.; Hu, J.; Chen, H.; Ding, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, X. Distribution Patterns and Diversity of Sedimental Microbial Communities in the Tianxiu Hydrothermal Field of Carlsberg Ridge. Oceans 2025, 6, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans6040061
Li F, Liu X, Hou W, Dong H, Hu J, Chen H, Ding Y, Wu Y, Xu X. Distribution Patterns and Diversity of Sedimental Microbial Communities in the Tianxiu Hydrothermal Field of Carlsberg Ridge. Oceans. 2025; 6(4):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans6040061
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Fangru, Xiaolei Liu, Weiguo Hou, Hailiang Dong, Jinglong Hu, Hongyu Chen, Yi Ding, Yuehong Wu, and Xuewei Xu. 2025. "Distribution Patterns and Diversity of Sedimental Microbial Communities in the Tianxiu Hydrothermal Field of Carlsberg Ridge" Oceans 6, no. 4: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans6040061
APA StyleLi, F., Liu, X., Hou, W., Dong, H., Hu, J., Chen, H., Ding, Y., Wu, Y., & Xu, X. (2025). Distribution Patterns and Diversity of Sedimental Microbial Communities in the Tianxiu Hydrothermal Field of Carlsberg Ridge. Oceans, 6(4), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans6040061







