Abstract
Ideally, dental implants should be placed parallel to each other and perpendicular to the occlusal forces. However, they might be implanted with undesirable angulations due to anatomic limitations such as proximity to infra alveolar nerve or maxillary sinus or dentist incompetency. Improper angulation is often addressed at the prosthetic stage of the treatment via using angled abutments. However, severely angled implants could be more challenging regarding the restoration of both esthetics and function. This article presents a cost effective, simple and practical method for fabricating customized angled abutments for restoring severely angled abutments.
1. Introduction
Implant-supported restorations are expected to meet the long-term esthetic and functional demands of patients [1]. However, both of these parameters could be affected by implant positioning and angulation. Ideally, implants should be aligned with the occlusal axial forces to reduce the exerted stresses on the prosthesis, implant and the bone [2,3]. However, some anatomic limitations such as unfavorable width, height and angle of the residual ridge, the presence of bony undercuts, the arch shape, the relationships between mandible and maxilla, the position of the mandibular canal and proximity to the sinus may prevent ideal implant placement, especially when additional surgical corrections are not practical [4,5]. Intentional angular placement of implants and cantilevers is also well documented in the literature as in the All-on-4 technique [6].
Correction of the misalignment of tilted implants is usually possible through the use of prefabricated or customized angled abutments [6,7]. In comparison to straight abutments, there is no conclusive agreement on the adverse effects of angled abutments [6,7,8,9]. Using prefabricated angled abutments could be accompanied by some complications such as the screw access channel being limited by the anti-rotational feature of the implant [1]. Moreover, a deeper implant placement is necessary for esthetics due to the thicker labial metal collar of the abutment [1]. Using dynamic abutments is also a more recent innovation for correcting the misalignment of implants by up to 28 degrees [1]; however, this is only useful for some implant brands.
One of the possible risks associated with tilted implants and abutments is the possible overloading of the implants and the surrounding bone [8,9]. Splinting implant restorations could help to distribute the resulting eccentric and horizontal forces among the implants more evenly [10].The other advantages of splinting the restorations include better force distribution in implants and bone, reducing the risk of screw loosening in abutments and increasing the stability and retention of the restorations [10,11,12].
This article describes a simple and practical method to restore excessively angled implants using customized casting abutments. This method not only resolves the problem of implant misalignment but also results in an esthetically pleasant and retrievable restoration.
2. Technique Report
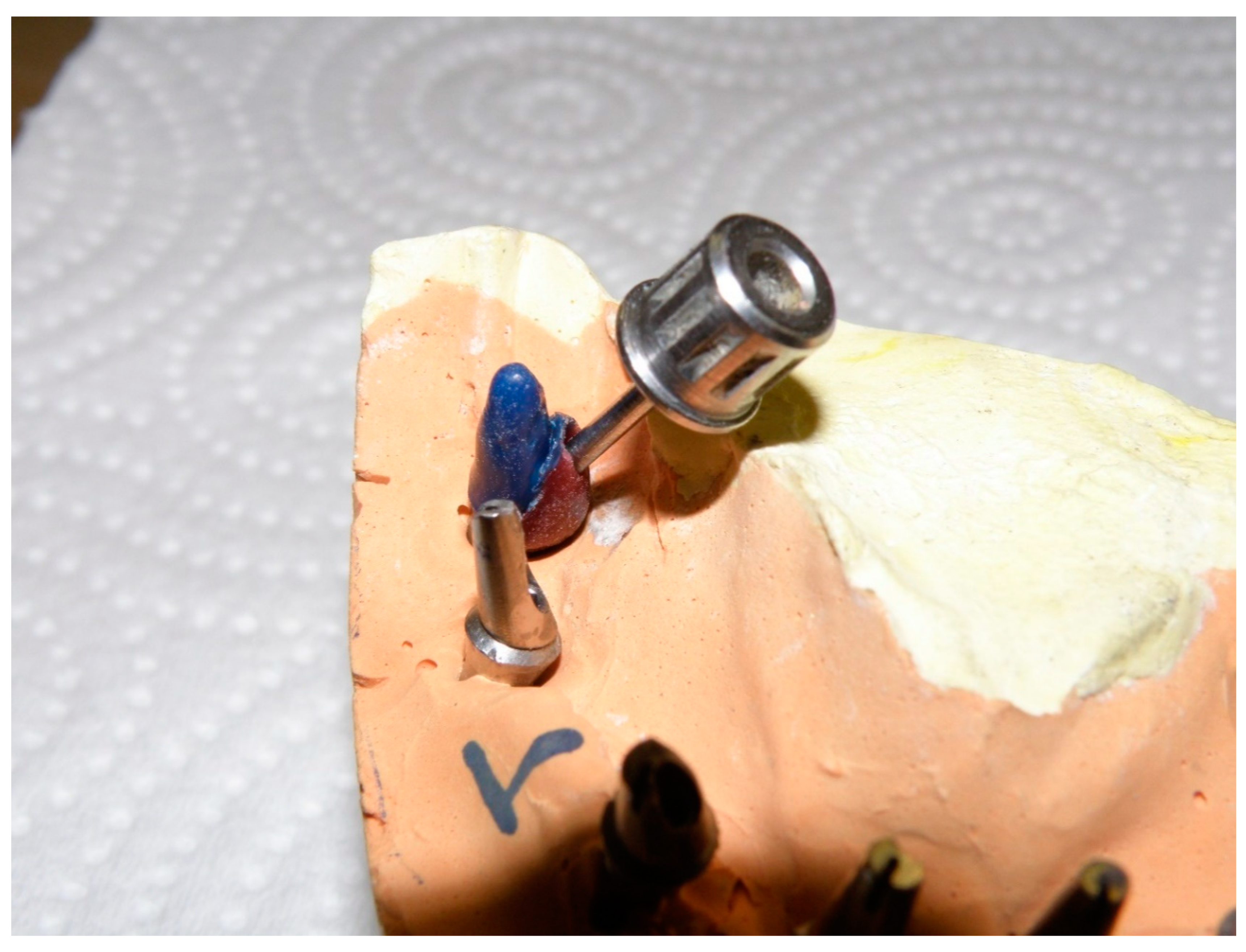
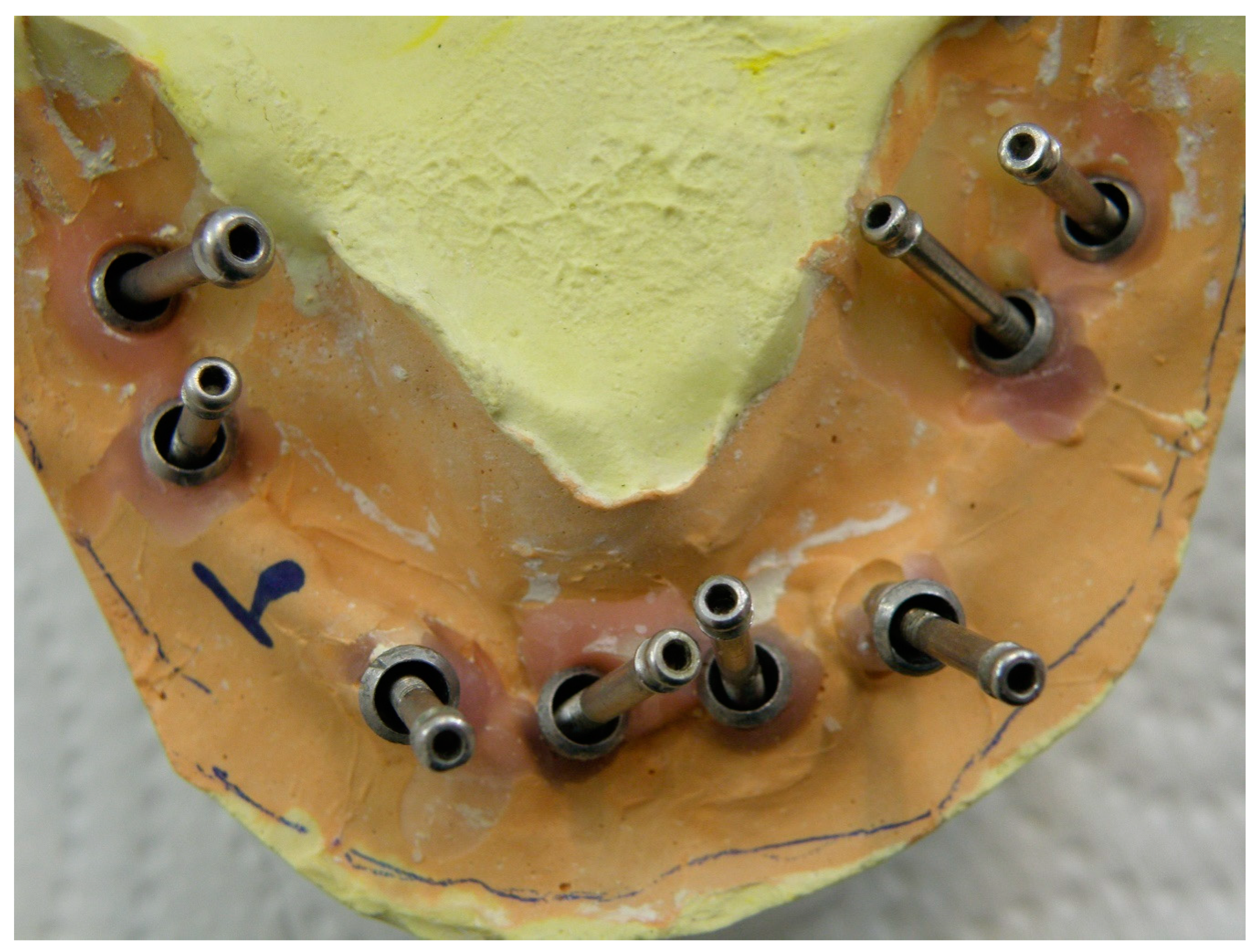
Excessive lingual angulations of distal implants #31 and 19 (Superline II, Dentium, Seoul, South Korea) were first noticed at the time of impression making and then confirmed upon fastening the central pin of impression copings on the master cast (Figure 1). To correct the excessive angulations, using angled abutments would have been necessary. However, due to the severe angulations of the implants, using prefabricated angled abutments was not possible.
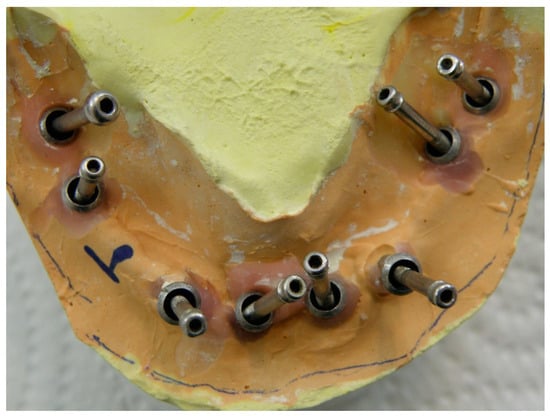
Figure 1.
Severe angulations of distal implants shown using central screw of impression copings.
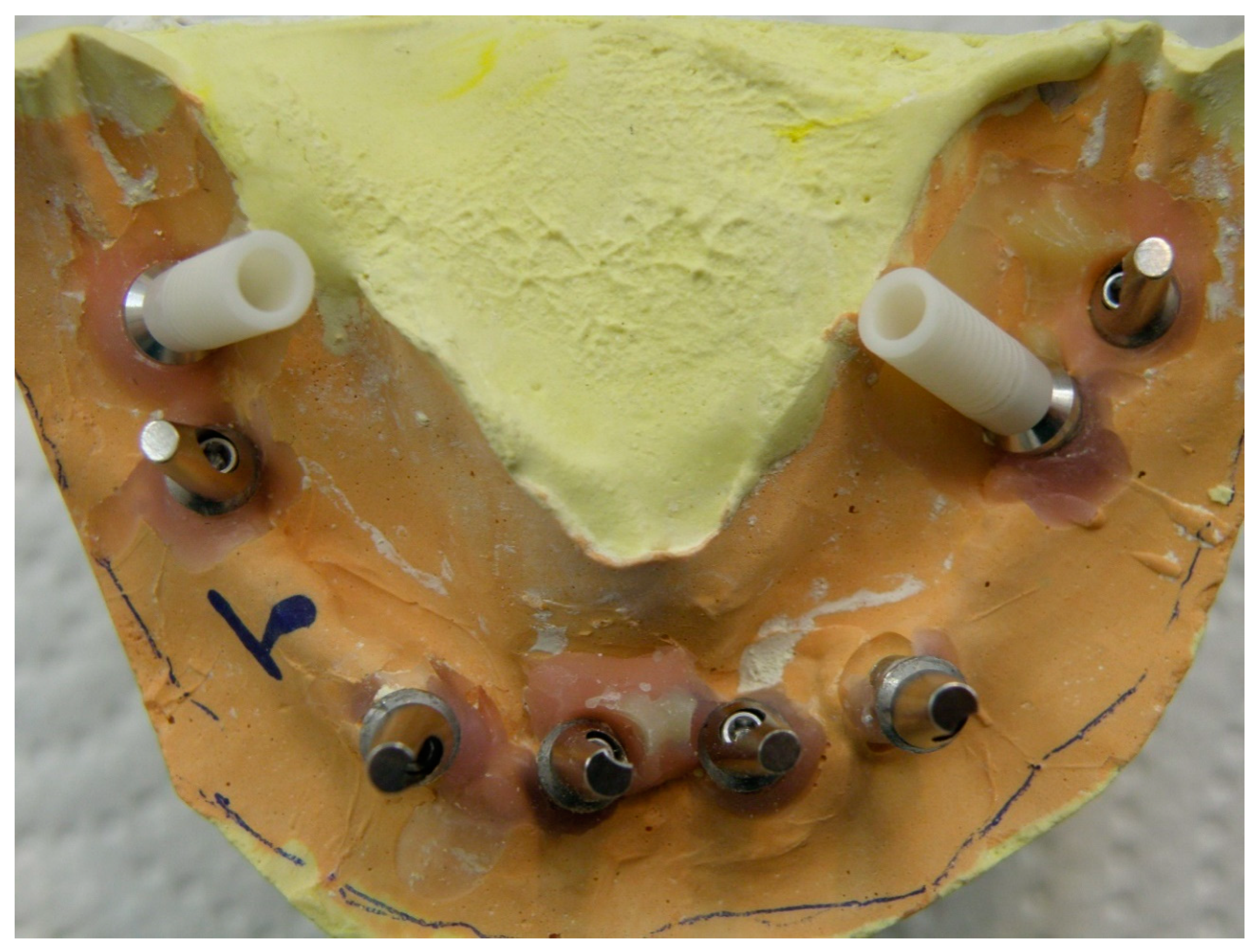
In order to correct the severe misalignment of the implants and also provide an esthetically pleasing result, a modified wax up was implemented using casting plastic abutments (Superline II, Dentium, Seoul, South Korea) for distal implants (Figure 2) to create a final dual screw-cemented-retained restoration. In order to make the alignment of the severely lingually angled implants parallel with other abutments, the buccal part of the plastic abutments was waxed up parallel to the adjacent abutments. On the other hand, the access channel of the abutment screw was considered lingually as the angulation of the implant mandated (Figure 3).
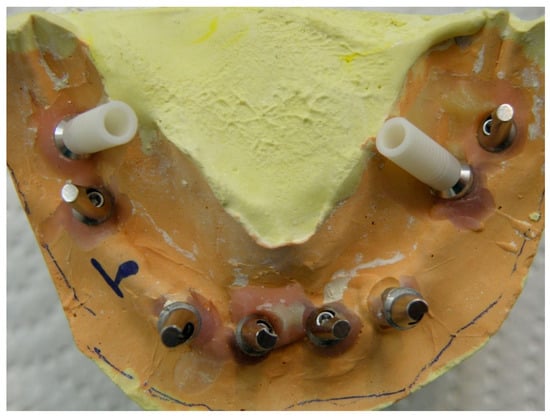
Figure 2.
Plastic abutments screwed to severely angled implants before customizing the wax up.
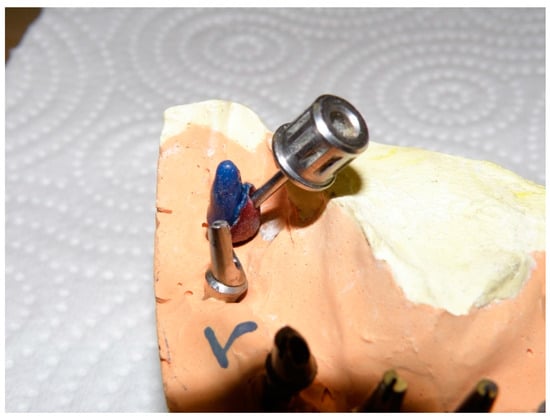
Figure 3.
Waxed up customized abutments showing screw access direction in relation to the body of the abutment.
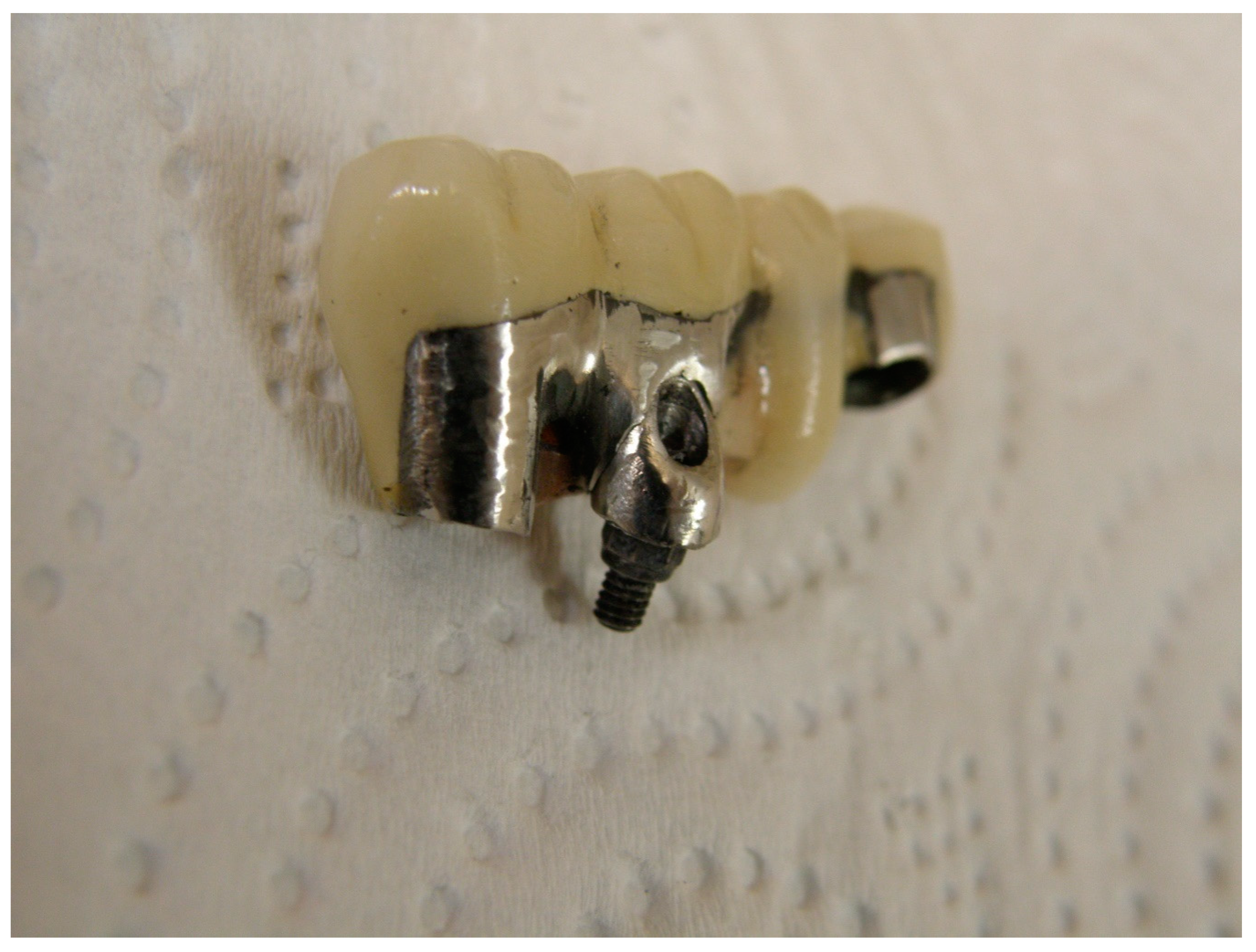
The finalized plastic abutments were cast and then checked on the master cast (Figure 4). The final metal–ceramic restorations were made (Figure 5) and evaluated on the custom abutments. The abutments were then torqued to the recommended force by the manufacturer (30 N·cm) and the abutment screw holes were filled with Teflon tape (SITCO, Fujian China) and composite resin material (Filtek Z250, 3M ESPE, St. Paul, MN, USA). The restorations were cemented on the abutments using a temporary cement (Temp Bond® NE, Kerr Corp, Orange, CA, USA).
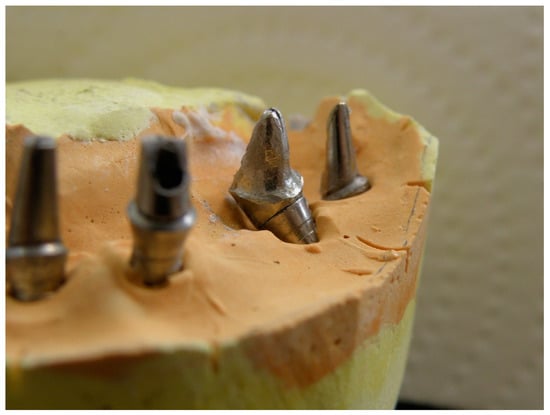

Figure 4.
Finalized customized dual abutment prepared before fabricating the final restoration.
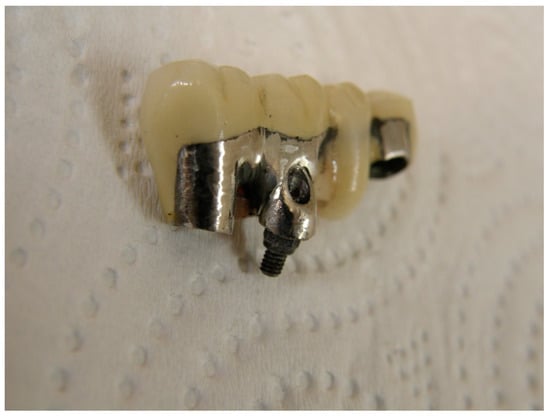
Figure 5.
Final restoration tried on the customized dual abutment.
Using angled abutments has been widely studied and proven to have a survival rate of 98.6% over a 5-year period and 98.2% rate cover a 14-year period [7]. Moreover, no significant difference was found between angled and standard abutments in terms of clinical parameters such as probing depths, gingival level, gingival index and mobility [5]. Additionally, even higher removal torque values have been reported for angled abutments [9].
The main benefits of implant-supported cement-retained and screw-retained restorations are their esthetics and retrievability, respectively [13]. This article suggested a simple manual method to create a dual (cement-screw) angled abutment for restoring severely angled implants with the use of affordable casting plastic abutments. The advantages of this method include preserving restoration retrievability, providing an acceptable esthetic outcome and also being applicable for all implant systems. These abutments could also be designed using CAD/CAM systems with additional advantages due to eliminating the casting procedure limitations.
However, making the restoration parallel to other implants could result in a bucco-lingual cantilever. Therefore, in order to compensate the resulted bucco-lingual cantilever, some measures should be taken into consideration, including employing a cross-bite occlusion, a narrowed occlusal table especially in non-esthetic regions, reducing cusp inclinations, splinting tilted implants and reducing the bucco-lingual length of cantilever as much as possible [14,15]. Moeover, infra-occlusion (100 μm) contacts in the centric occlusal position and removing working/non-working occlusal contacts’ lateral excursive movements on the cantilever segment is recommended for a full-arch fixed implant prosthesis [14,16,17].
3. Conclusions
There are several anatomical situations that could potentially force positioning the implants with less than optimal angulations. Although surgical corrections such as bone augmentation of the alveolar ridge, sinus elevation or nerve repositioning could result in the opportunity for ideal placement of implants, they might not always be practical due to patient refusal or economic problems. Using customized dual angled abutment through manual wax up or using CAD-CAM technology results in acceptable esthetic and functional outcomes. However, it is still recommended to reduce the the effect of non-axial forces by splint ing and occlusal contact reduction of the restorations.
Author Contributions
The patient treatment was performed by A.S. and the article was prepared by E.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Berroeta, E.; Zabalegui, I.; Donovan, T.; Chee, W. Dynamic abutment: A method of redirecting screw access for implant-supported restorations: Technical details and a clinical report. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2015, 113, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunder, U.; Gracis, S.; Capelli, M. Influence of the 3-D bone-to-implant relationship on esthetics. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2005, 25, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Tarnow, D.P.; Cho, S.C.; Wallace, S.S. The effect of inter-implant distance on theheight of inter-implant bone crest. J. Periodontol. 2000, 71, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, Y.; Madjar, D. Prosthetic treatment for severely misaligned implants: A clinical report. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2002, 88, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eger, D.E.; Gunsolley, J.C.; Feldman, S. Comparison of angled and standard abutments and their effect on clinical outcomes: A preliminary report. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2000, 15, 819–823. [Google Scholar]
- Malo, P.; Rangert, B.; Nobre, M. All-on-four immediate-function concept with Branemark system implants for completely edentulous mandibles: A retrospective clinical study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2003, 5, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, A.; Kaus, T.; Sochor, P.; Axmann-Krcmar, D. Evolution of theconcept of angulated abutments in implant dentistry: 14-year clinical data. Implant. Dent. 2002, 11, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, J., Jr.; Greenstein, G. Angled implant abutments: A practical application of available knowledge. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2011, 142, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, C.Y.; Lim, Y.J.; Kim, M.J.; Choi, J.H. The influence of abutment angulation onscrew loosening of implants in the anterior maxilla. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2011, 26, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Guichet, D.L.; Yoshinobu, D.; Caputo, A.A. Effect of splinting and interproximal contact tightness on load transfer by implant restorations. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2002, 87, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, Y.; Finger, I.M.; Block, M.S. Indications for splinting implant restorations. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 63, 1642–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.M.; Leu, L.J.; Wang, J.; Lin, L.D. Effects of prosthesis materials and prosthesis splinting on periimplant bone stress around implants in poor quality bone: A numeric analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2002, 17, 231–237. [Google Scholar]
- Nematollahi, F.; Beyabanaki, E.; Alikhasi, M. Cement Selection for Cement-Retained Implant-Supported Prostheses: A Literature Review. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 25, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundgren, D.; Laurell, L. Biomechanical aspects of fixed bridgework supported by natural teeth and endosseous implants. Periodontology 2000 1994, 4, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S.; Kum, Y.L.; Bae, J.M. Biomechanical comparison of axial and tilted implants for mandibular full arch fixed prosthesis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2011, 26, 976–984. [Google Scholar]
- Falk, H.; Laurell, L.; Lundgren, D. Occlusal interferences and cantilever joint stress in implant-supported prostheses occluding with complete dentures. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1990, 5, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren, D.; Falk, H.; Laurell, L. Influence of number and distribution of occlusal cantilever contacts on closing and chewing forces in dentitions with implant-supported fixed prostheses occluding with complete dentures. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1989, 4, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).