Assessment of a Machine Learning Algorithm Using Web Images for Flood Detection and Water Level Estimates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
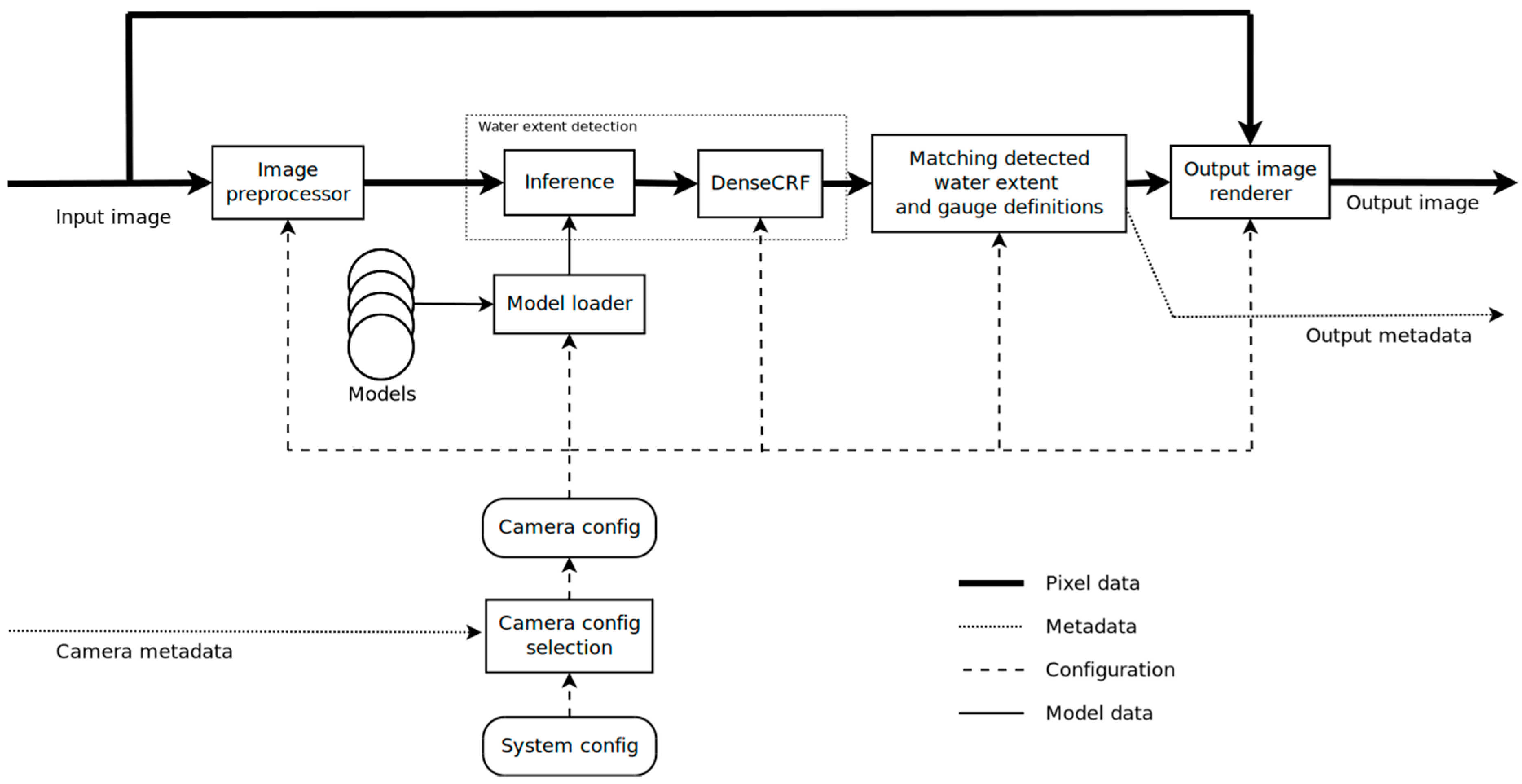
2.1. Machine Learning Algorithm
2.2. USGS Datasets
3. Results
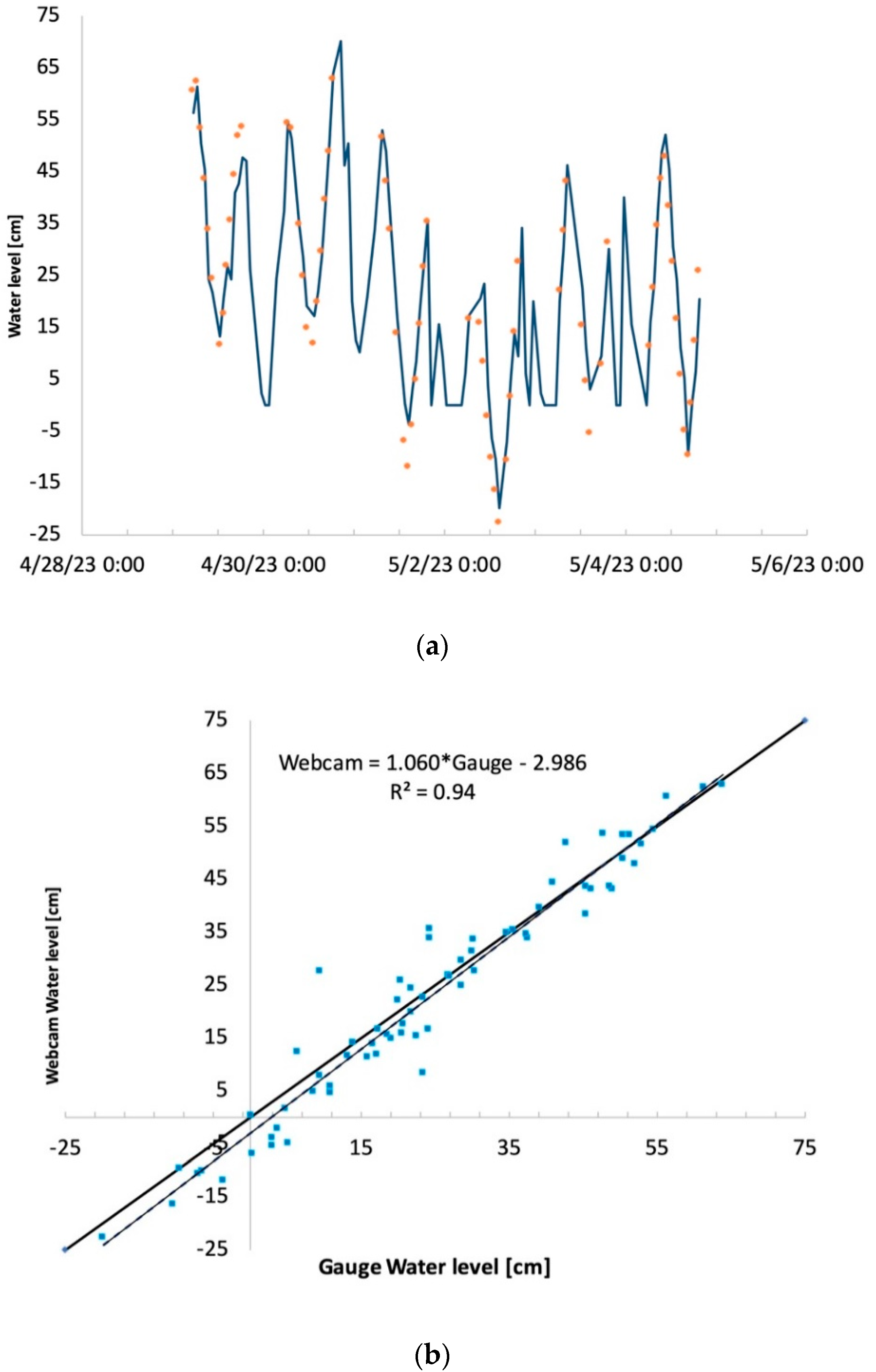
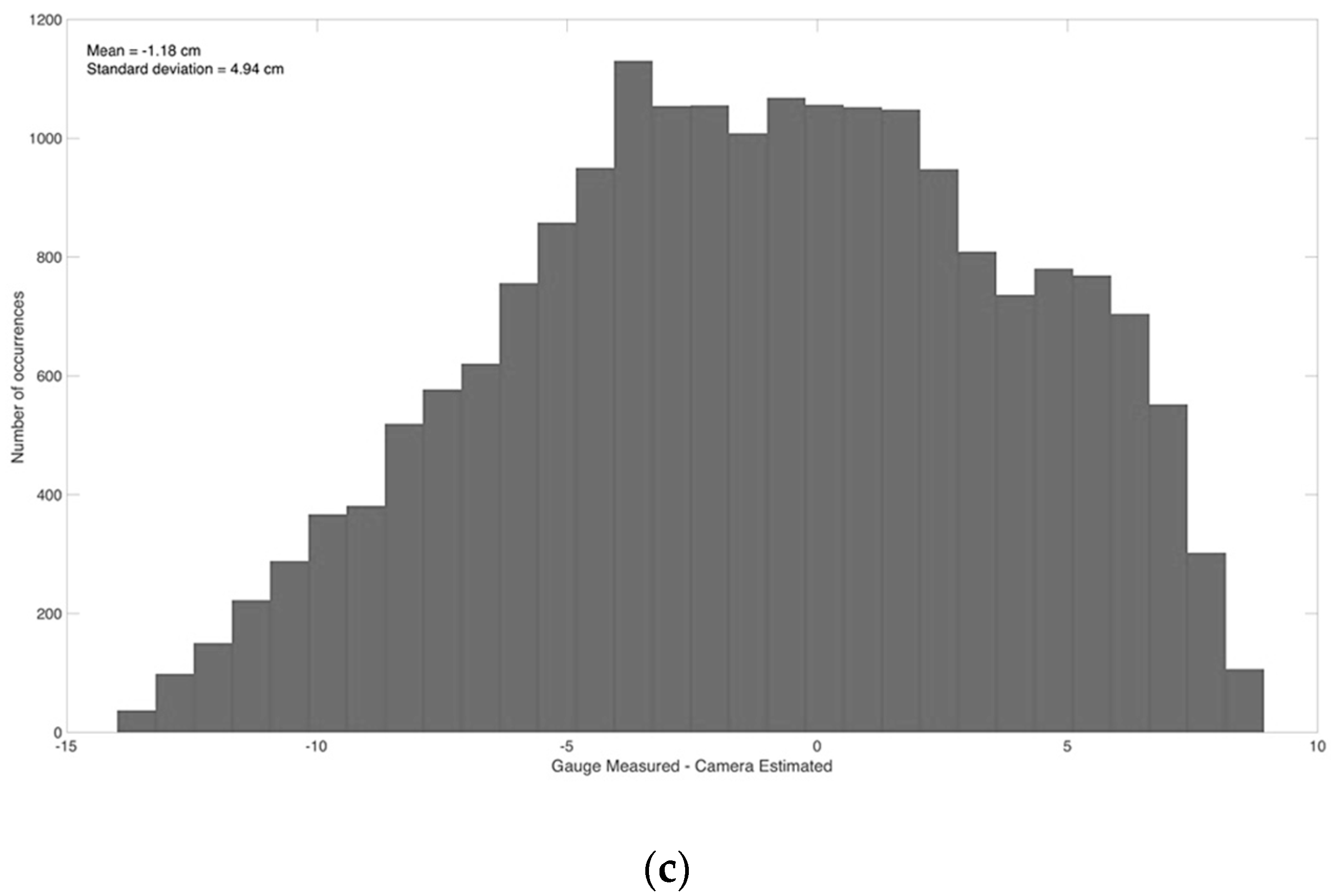
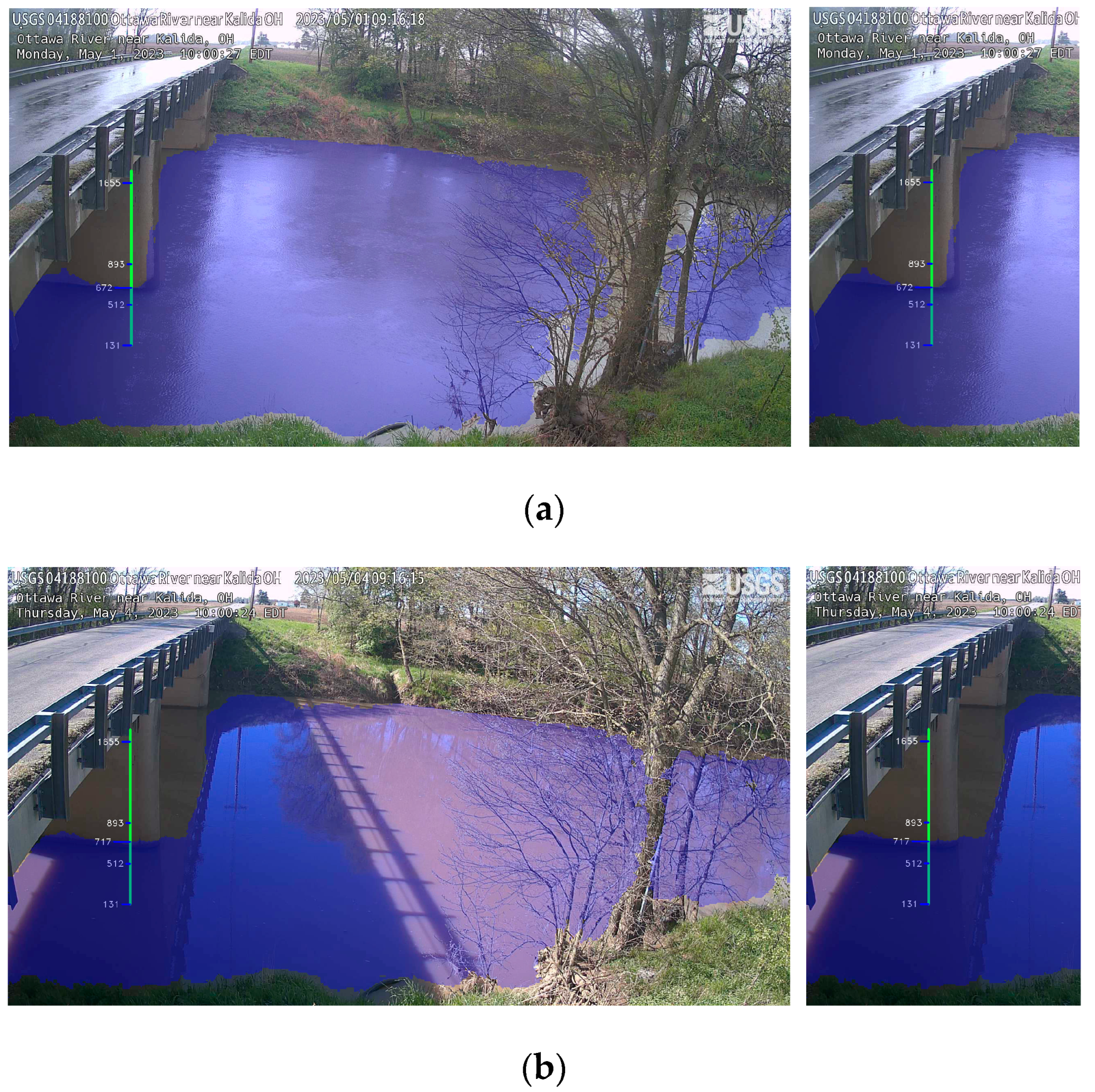
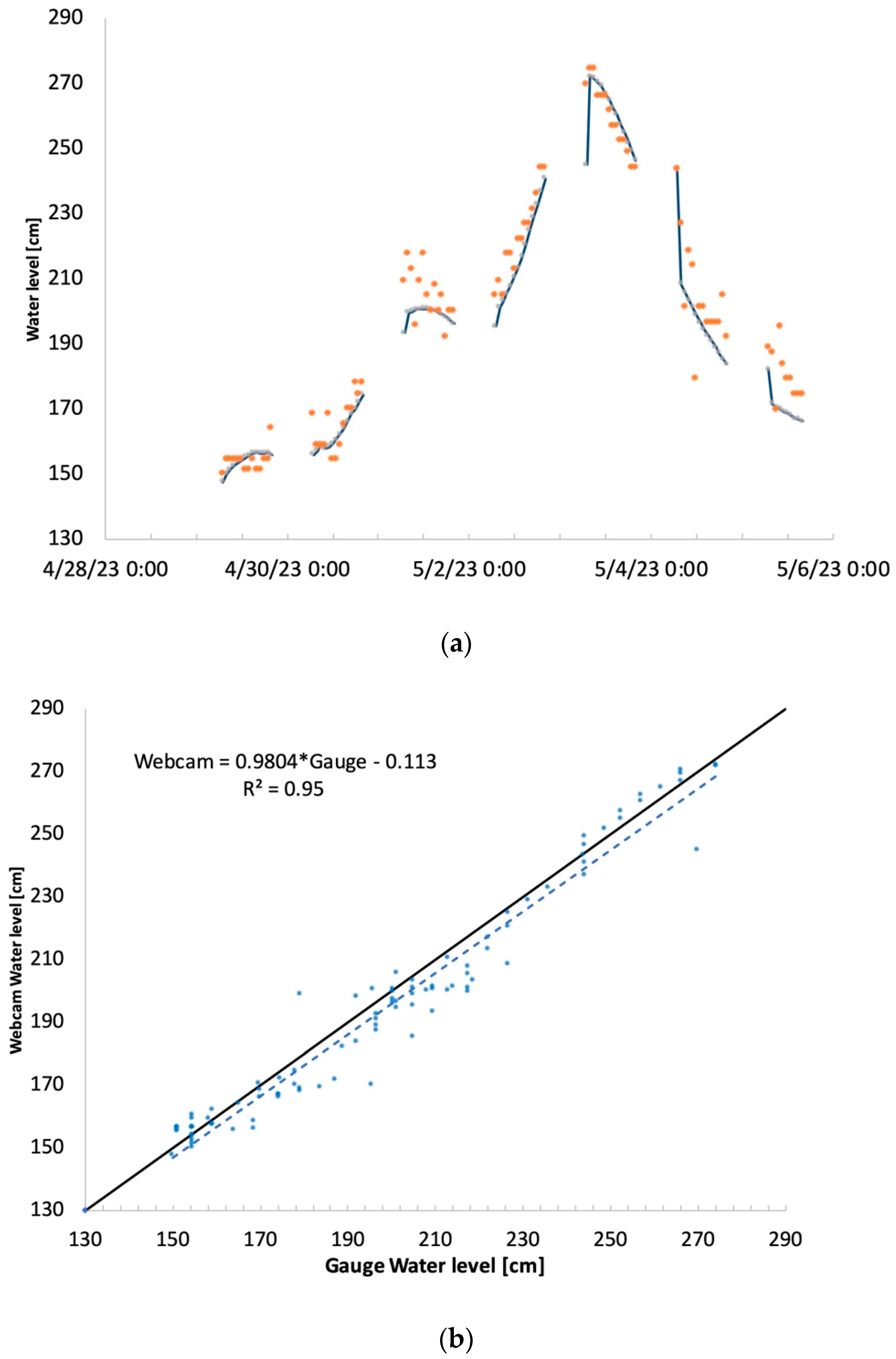
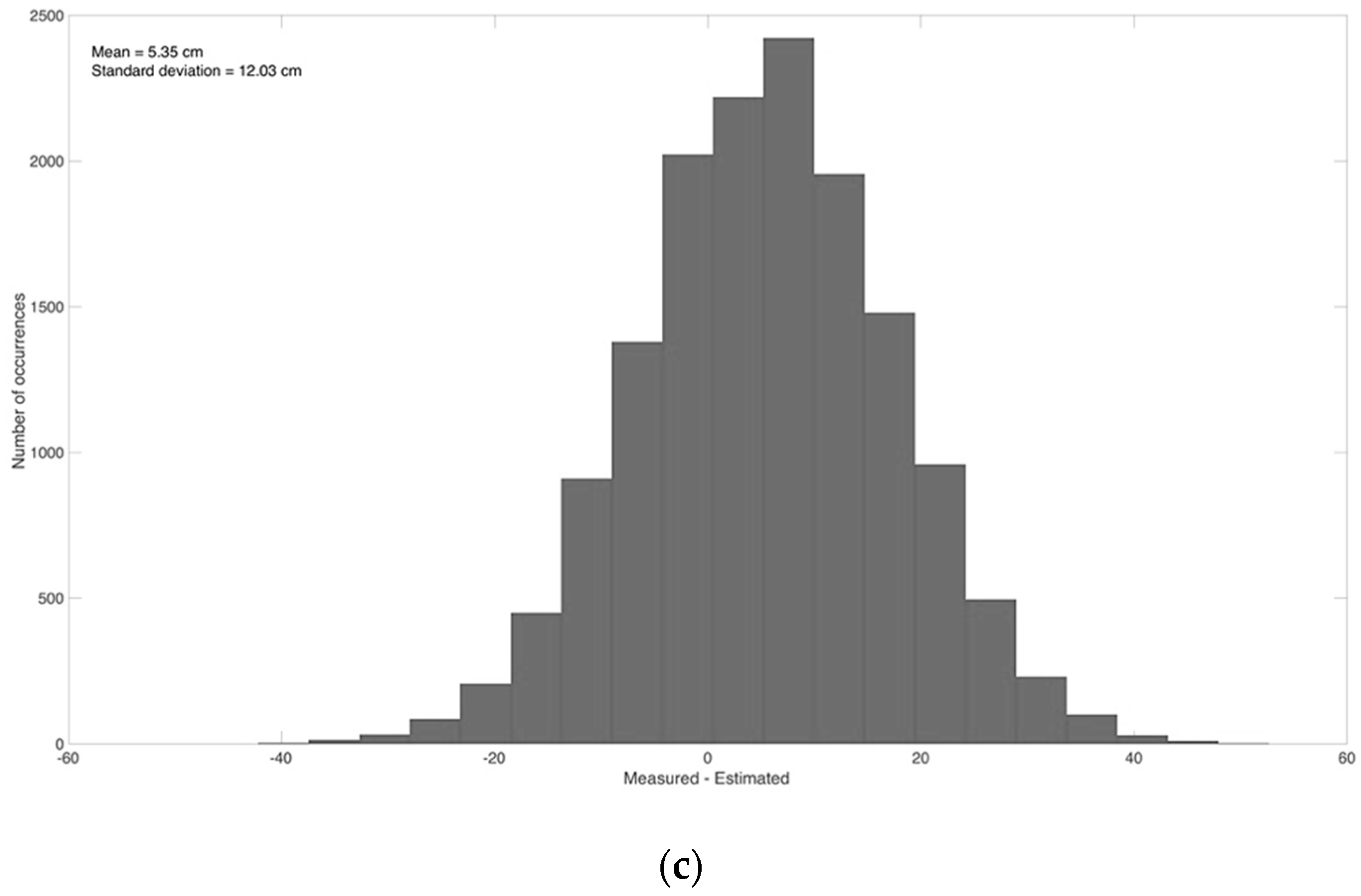
3.1. Comparison between Web Camera-Estimated and Gauge Data
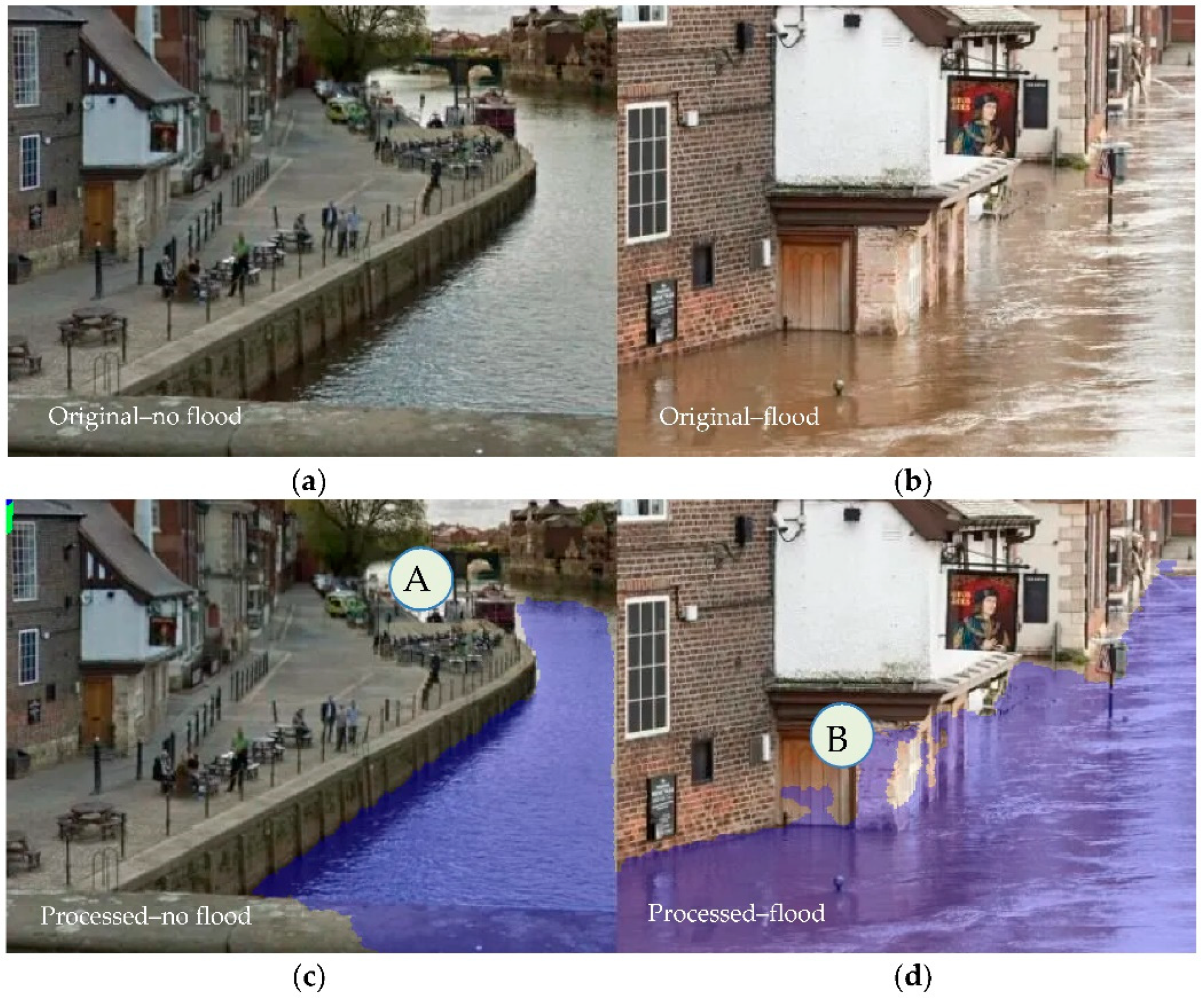
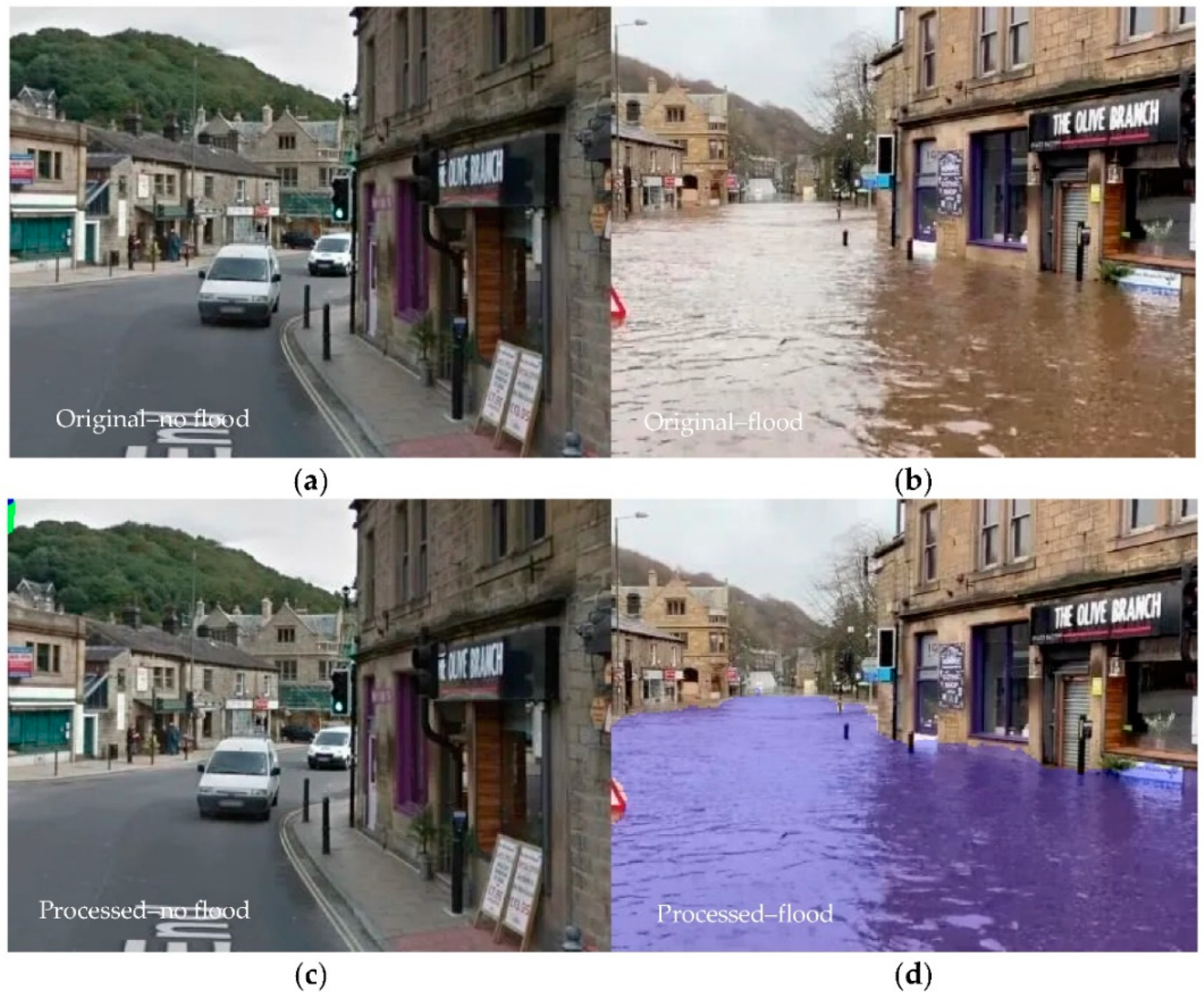
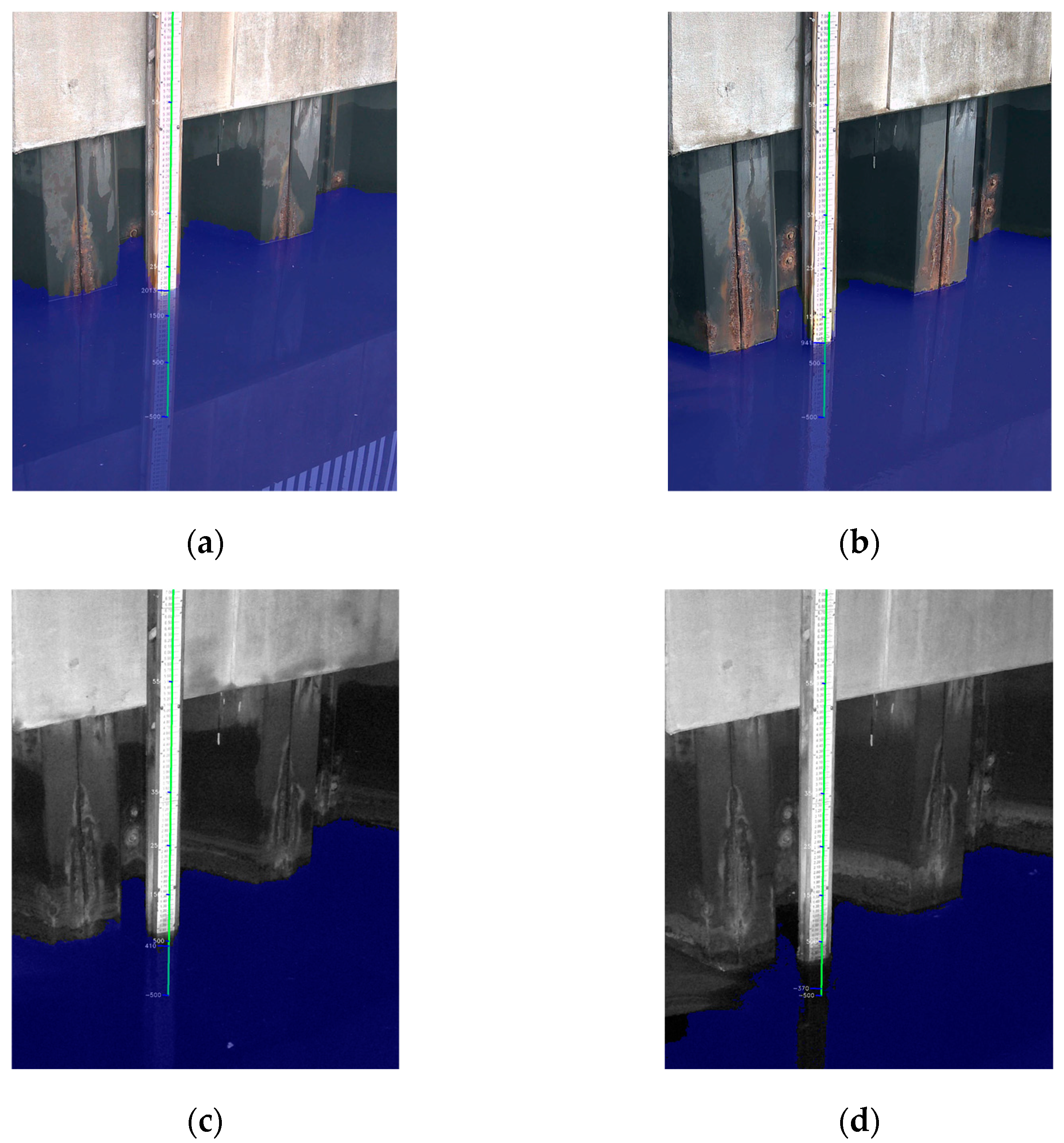
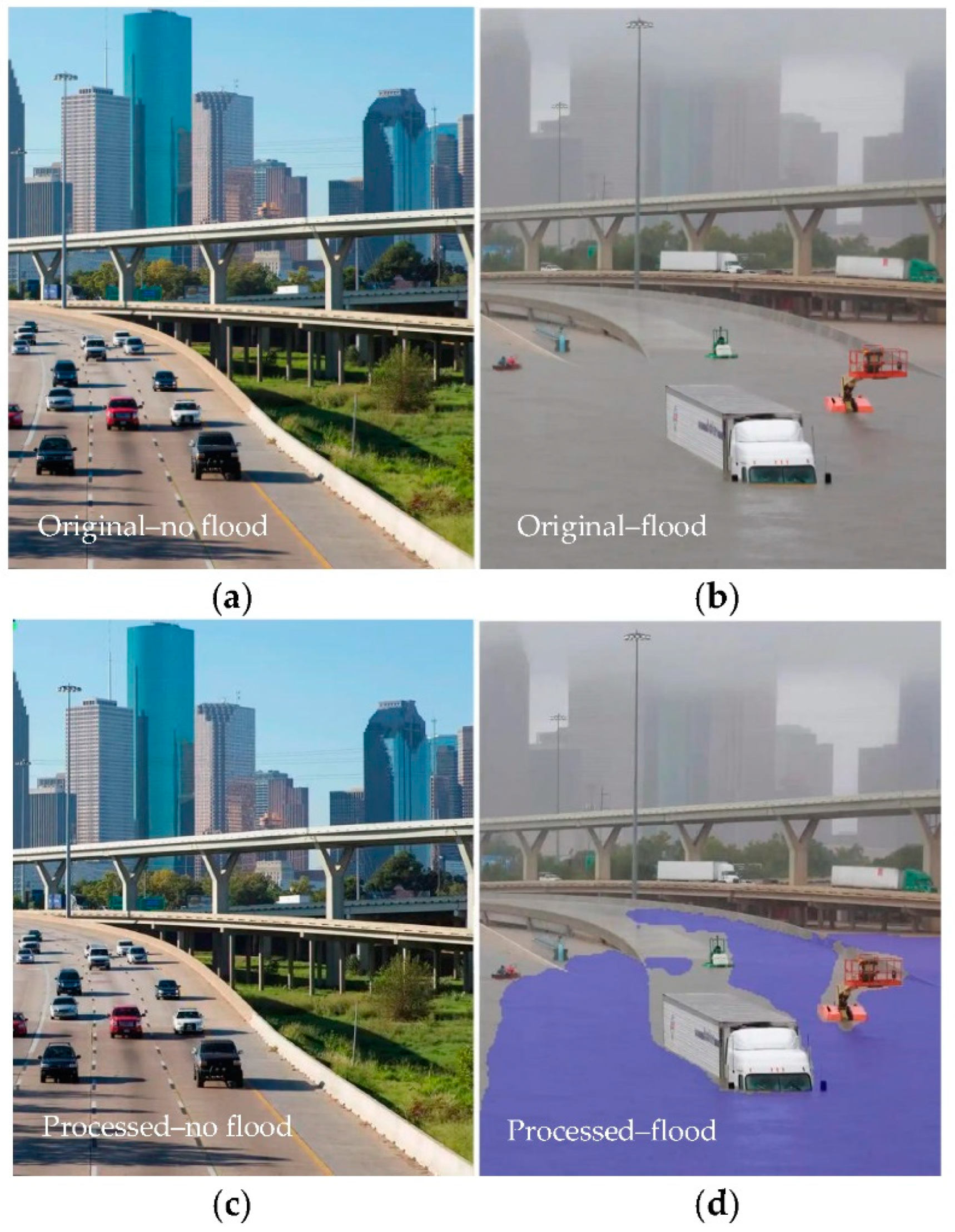
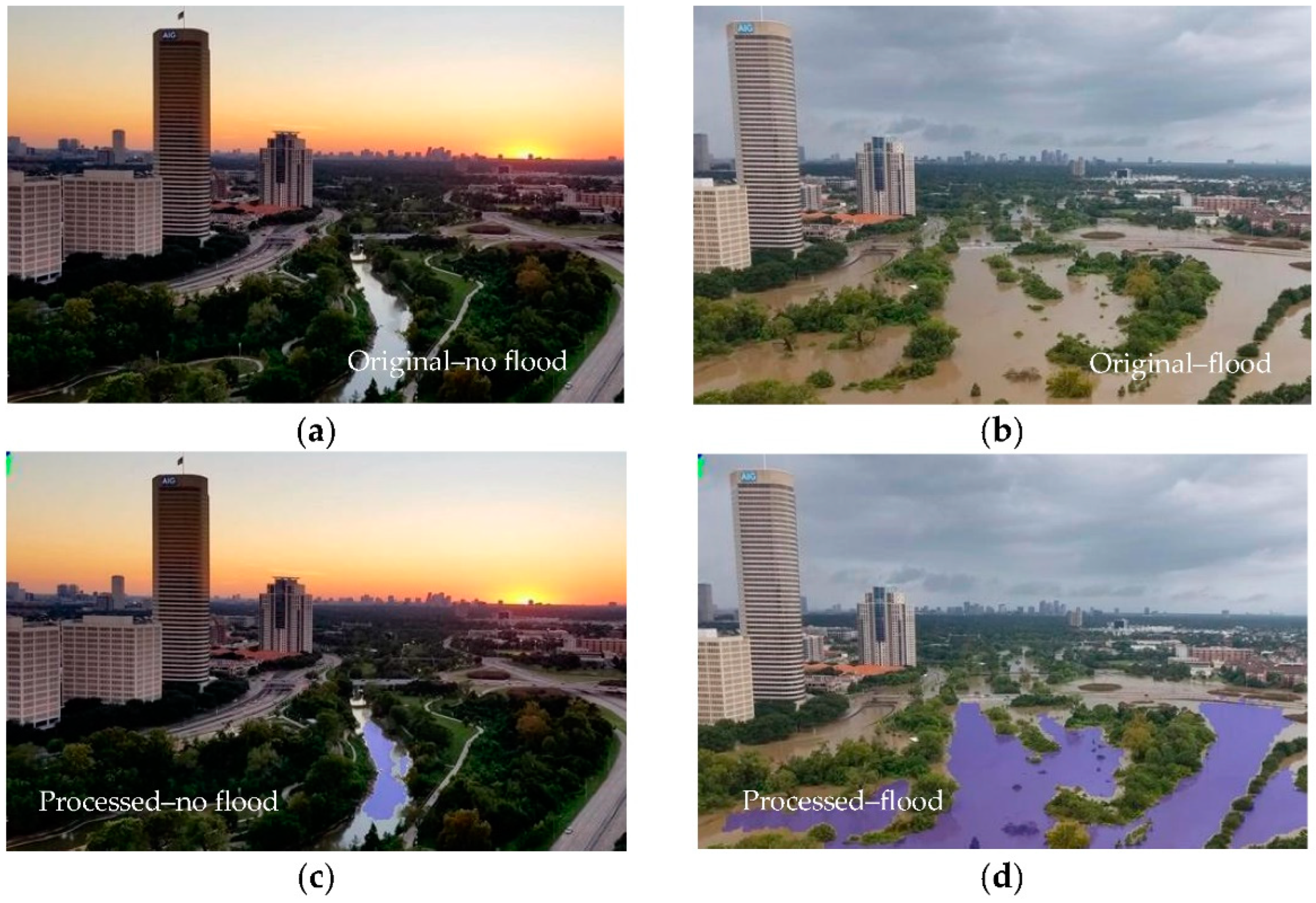
3.2. Assessment of Water Detection Skills of the Algorithm
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colgan, C.S.; Beck, M.W.; Narayan, S. Financing Natural Infrastructure for Coastal Flood Damage Reduction; Lloyd’s Tercentenary Research Foundation: London, UK, 2017; Available online: https://www.middlebury.edu/institute/sites/www.middlebury.edu.institute/files/2018-07/6.13.17.LLYODS.Financing%20Natural%20Infrastructure%201.JUN_.2017_Lo%20Res.pdf (accessed on 9 May 2023).
- Xafoulis, N.; Kontos, Y.; Farsirotou, E.; Kotsopoulos, S.; Perifanos, K.; Alamanis, N.; Dedousis, D.; Katsifarakis, K. Evaluation of Various Resolution DEMs in Flood Risk Assessment and Practical Rules for Flood Mapping in Data-Scarce Geospatial Areas: A Case Study in Thessaly, Greece. Hydrology 2023, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billah, M.; Islam, A.S.; Bin Mamoon, W.; Rahman, M.R. Random forest classifications for landuse mapping to assess rapid flood damage using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2023, 30, 100947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, E.; Peter, B.G.; Munoz, D.F.; Moftakhari, H.; Moradkhani, H. Fast Flood Extent Monitoring with SAR Change Detection Using Google Earth Engine. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refice, A.; D’Addabbo, A.; Capolongo, D. (Eds.) Methods, Techniques and Sensors for Precision Flood Monitoring Through Remote Sensing. In Flood Monitoring through Remote Sensing; Springer Remote Sensing/Photogrammetry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, M.; McAlpine, S.; Porter, J.R. Exposure of real estate properties to the 2018 Hurricane Florence flooding. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, L.; Hostache, R.; Matgen, P.; Schumann, G.J.; Bates, P.D.; Mason, D.C. A change detection approach to flood mapping in urban areas using TerraSAR-X. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 2417–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windheuser, L.; Karanjit, R.; Pally, R.; Samadi, S.; Hubig, N.C. An End-To-End Flood Stage Prediction System Using Deep Neural Networks. Earth Space Sci. 2023, 10, e2022EA002385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Q.-C.; Le, M.-Q.; Tran, M.-K.; Le, N.-Q.; Tran, M.-T. FL-Former: Flood Level Estimation with Vision Transformer for Images from Cameras in Urban Areas. In Multimedia Modeling; Dang-Nguyen, D.-T., Gurrin, C., Larson, M., Smeaton, A.F., Rudinac, S., Dao, M.-S., Trattner, C., Chen, P., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 13833, pp. 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donratanapat, N.; Samadi, S.; Vidal, J.; Tabas, S.S. A national scale big data analytics pipeline to assess the potential impacts of flooding on critical infrastructures and communities. Environ. Model. Softw. 2020, 133, 104828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, X.; Tsai, B.; Chen, Q.; Jafari, N. V-FloodNet: A video segmentation system for urban flood detection and quantification. Environ. Model. Softw. 2023, 160, 105586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandaele, R.; Dance, S.L.; Ojha, V. Deep learning for automated river-level monitoring through river-camera images: An approach based on water segmentation and transfer learning. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 4435–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Fuentes, L.; Rossi, C.; Skinnemoen, H. River segmentation for flood monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Boston, MA, USA, 11–14 December 2017; pp. 3746–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhadi, N.A.; Abdullah, A.F.; Bejo, S.K.; Mahadi, M.R.; Mijic, A. Deep Learning Semantic Segmentation for Water Level Estimation Using Surveillance Camera. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H. Visual Measurement of Water Level under Complex Illumination Conditions. Sensors 2019, 19, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, G.; Yang, M.; Wang, H. A Water Level Measurement Approach Based on YOLOv5s. Sensors 2022, 22, 3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltner, A.; Elias, M.; Sardemann, H.; Spieler, D. Automatic Image-Based Water Stage Measurement for Long-Term Observations in Ungauged Catchments. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 10362–10371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muste, M.; Ho, H.-C.; Kim, D. Considerations on direct stream flow measurements using video imagery: Outlook and research needs. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2011, 5, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.-W.; Wu, J.-H.; Lin, F.-P.; Hsu, C.-H. Visual Sensing for Urban Flood Monitoring. Sensors 2015, 15, 20006–20029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoener, G. Time-Lapse Photography: Low-Cost, Low-Tech Alternative for Monitoring Flow Depth. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2018, 23, 06017007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Lin, Y.-C.; Han, J.-Y. Automatic water-level detection using single-camera images with varied poses. Measurement 2018, 127, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Yuchou, L.; Youjie, Y.; Xurui, L. IP Camera-Based LSPIV System for On-Line Monitoring of River Flow. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 13th International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments (ICEMI), Yangzhou, China, 20–22 October 2017; pp. 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, C. Water Level Estimation Based on Image of Staff Gauge in Smart City. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE SmartWorld, Ubiquitous Intelligence & Computing, Advanced & Trusted Computing, Scalable Computing & Communications, Cloud & Big Data Computing, Internet of People and Smart City Innovation (SmartWorld/SCALCOM/UIC/ATC/CBDCom/IOP/SCI), Guangzhou, China, 8–12 October 2018; pp. 1341–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc, P.; Ashmore, P.; Sjogren, D. Technical note: Stage and water width measurement of a mountain stream using a simple time-lapse camera. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubaki, R.; Fujita, I.; Tsutsumi, S. Measurement of the flood discharge of a small-sized river using an existing digital video recording system. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2011, 5, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creutin, J.; Muste, M.; Bradley, A.; Kim, S.; Kruger, A. River gauging using PIV techniques: A proof of concept experiment on the Iowa River. J. Hydrol. 2003, 277, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.-H.; Li, W.; Liao, Q.; Tang, H.-L.; Wang, M.-Y. Application of an automated LSPIV system in a mountainous stream for continuous flood flow measurements: LSPIV for Mountainous Flood Monitoring. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 3014–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, A.; Augereau, E.; Delacourt, C.; Bonnier, J. Photogrammetric discharge monitoring of small tropical mountain rivers: A case study at Rivière des Pluies, Réunion Island. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 4550–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Fu, R.; Ai, X.; Huang, C.; Cong, L.; Li, X.; Jiang, J.; Pei, Q. An Integrated Method for River Water Level Recognition from Surveillance Images Using Convolution Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, G.; Chen, R.; Han, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J. Research on Water-Level Recognition Method Based on Image Processing and Convolutional Neural Networks. Water 2022, 14, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krähenbühl, P.; Koltun, V. Efficient Inference in Fully Connected CRFs with Gaussian Edge Potentials. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1210.5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tedesco, M.; Radzikowski, J. Assessment of a Machine Learning Algorithm Using Web Images for Flood Detection and Water Level Estimates. GeoHazards 2023, 4, 437-452. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards4040025
Tedesco M, Radzikowski J. Assessment of a Machine Learning Algorithm Using Web Images for Flood Detection and Water Level Estimates. GeoHazards. 2023; 4(4):437-452. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards4040025
Chicago/Turabian StyleTedesco, Marco, and Jacek Radzikowski. 2023. "Assessment of a Machine Learning Algorithm Using Web Images for Flood Detection and Water Level Estimates" GeoHazards 4, no. 4: 437-452. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards4040025
APA StyleTedesco, M., & Radzikowski, J. (2023). Assessment of a Machine Learning Algorithm Using Web Images for Flood Detection and Water Level Estimates. GeoHazards, 4(4), 437-452. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards4040025






