Digital Literacy and Technology Adoption in Agriculture: A Systematic Review of Factors and Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of the Systematic Literature Review
2.2. Research Questions
- Population (P): Farmers and their process of technology adoption in agriculture.
- Intervention (I): Digital literacy, technology training, training strategies.
- Comparison (C): Differences in adoption with and without digital literacy, different theoretical models, and applied strategies.
- Outcome (O): Level of technology adoption, influencing factors, effective strategies, existing barriers, and impact on the agricultural sector.
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- -
- Published between 2015 and 2025, to capture recent evidence reflecting rapid changes in digital technologies applied to agriculture.
- -
- Written in English, in order to incorporate relevant literature from global contexts.
- -
- Open access (except in IEEE Xplore, where all relevant articles were considered due to limited availability in OA).
- -
- That explicitly addressed digital literacy in agricultural contexts and its relationship to technology adoption.
- -
- Articles that were not available in full text.
- -
- Articles that did not refer directly to agricultural contexts.
- -
- Studies not related to digital skills or technology adoption in agricultural contexts.
- -
- Editorials, non-systematic reviews, non-scientific essays, or unrefereed theses.
2.4. Sources of Information
- Scopus: for its multidisciplinary coverage and editorial rigor.
- ScienceDirect: for its high presence of research in agricultural sciences and technology.
- IEEE Xplore: for its technical focus on engineering, computer science, and emerging technologies.
2.5. Search Strategy
2.6. Study Selection Process
2.7. Methodological Quality Assessment
2.8. Data Extraction
2.9. Data Synthesis and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bibliometric Analysis of Scientific Output
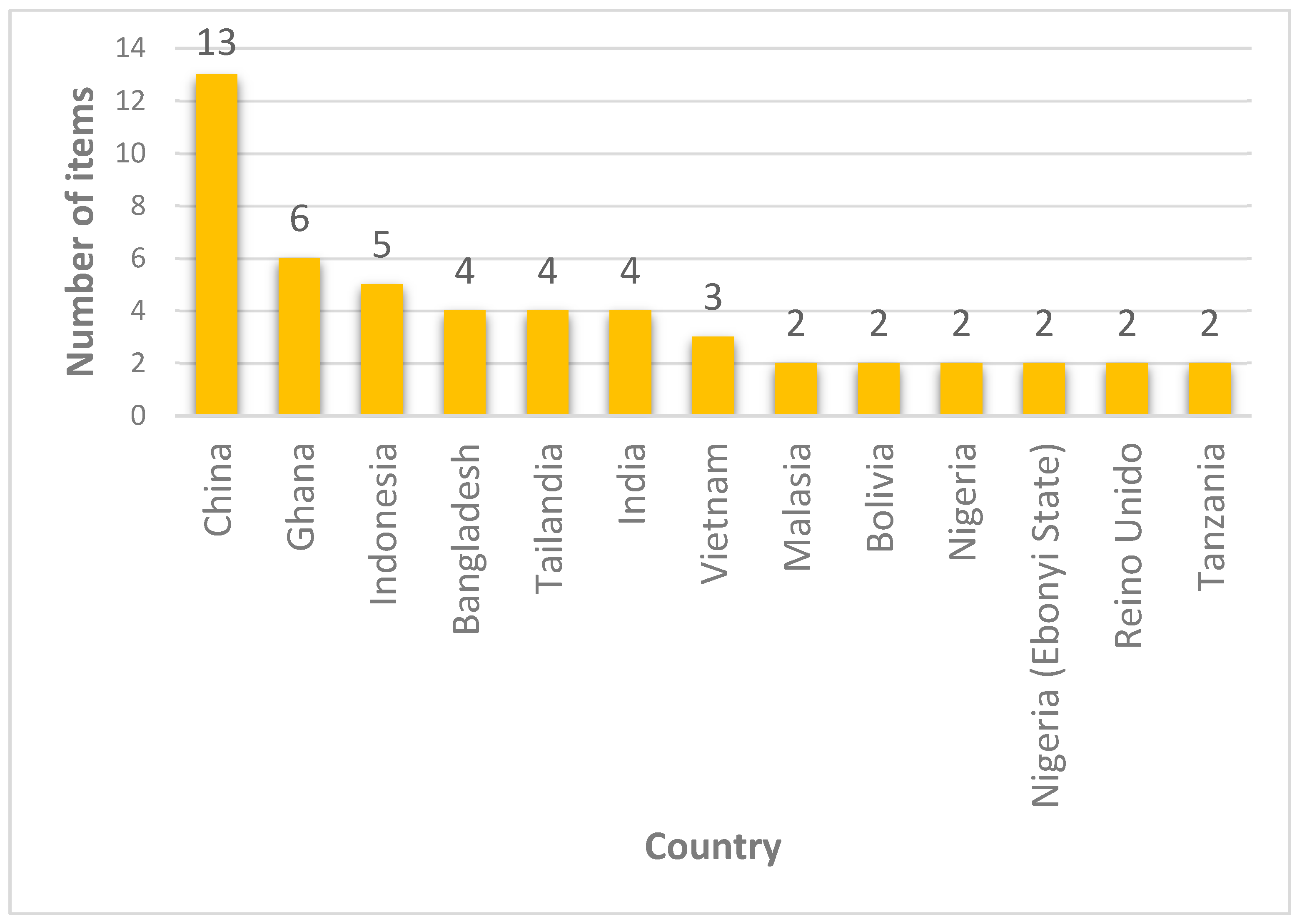
3.1.1. Scientific Output by Country with Two or More Articles
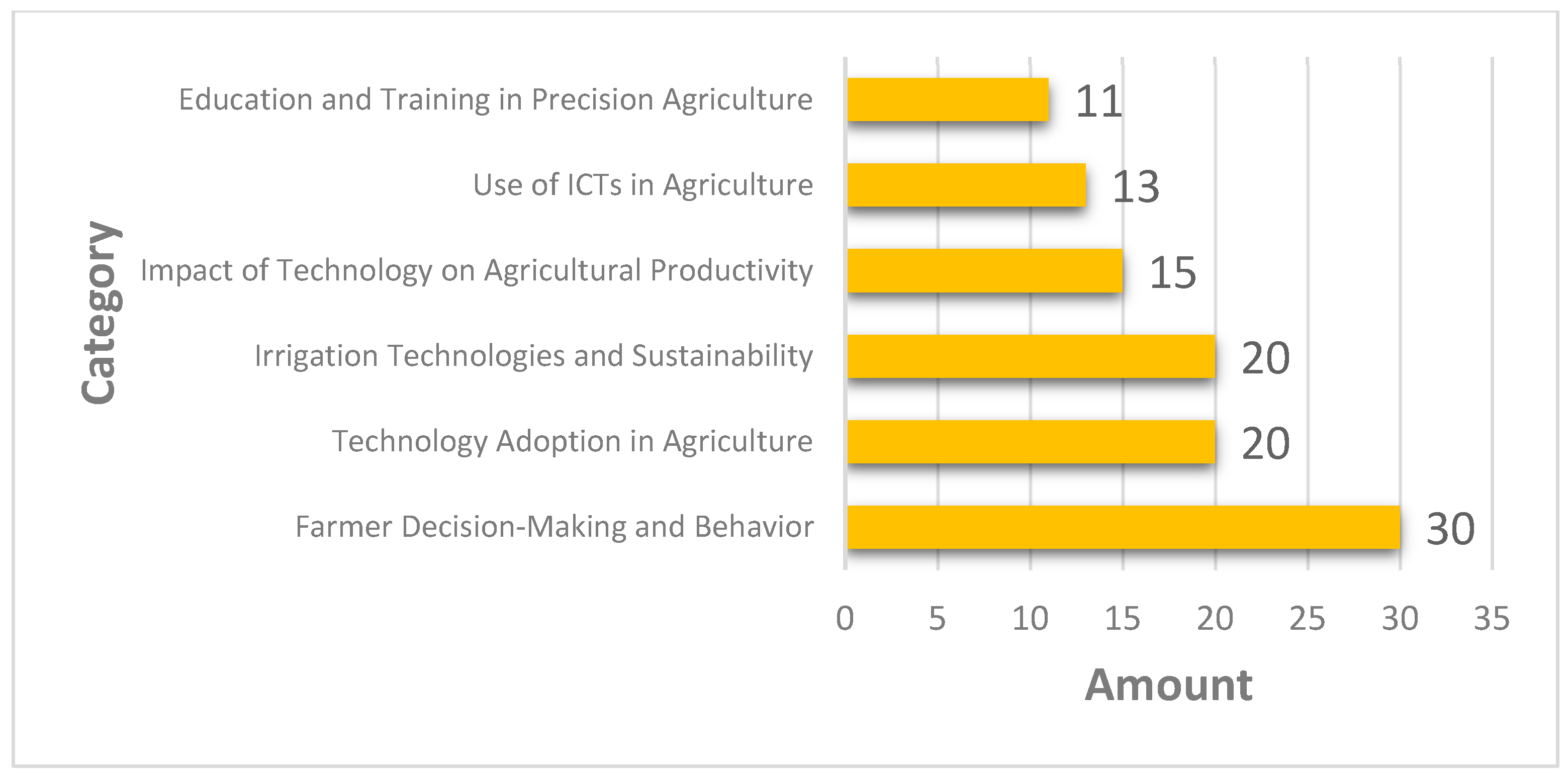
3.1.2. Thematic Categories of Articles
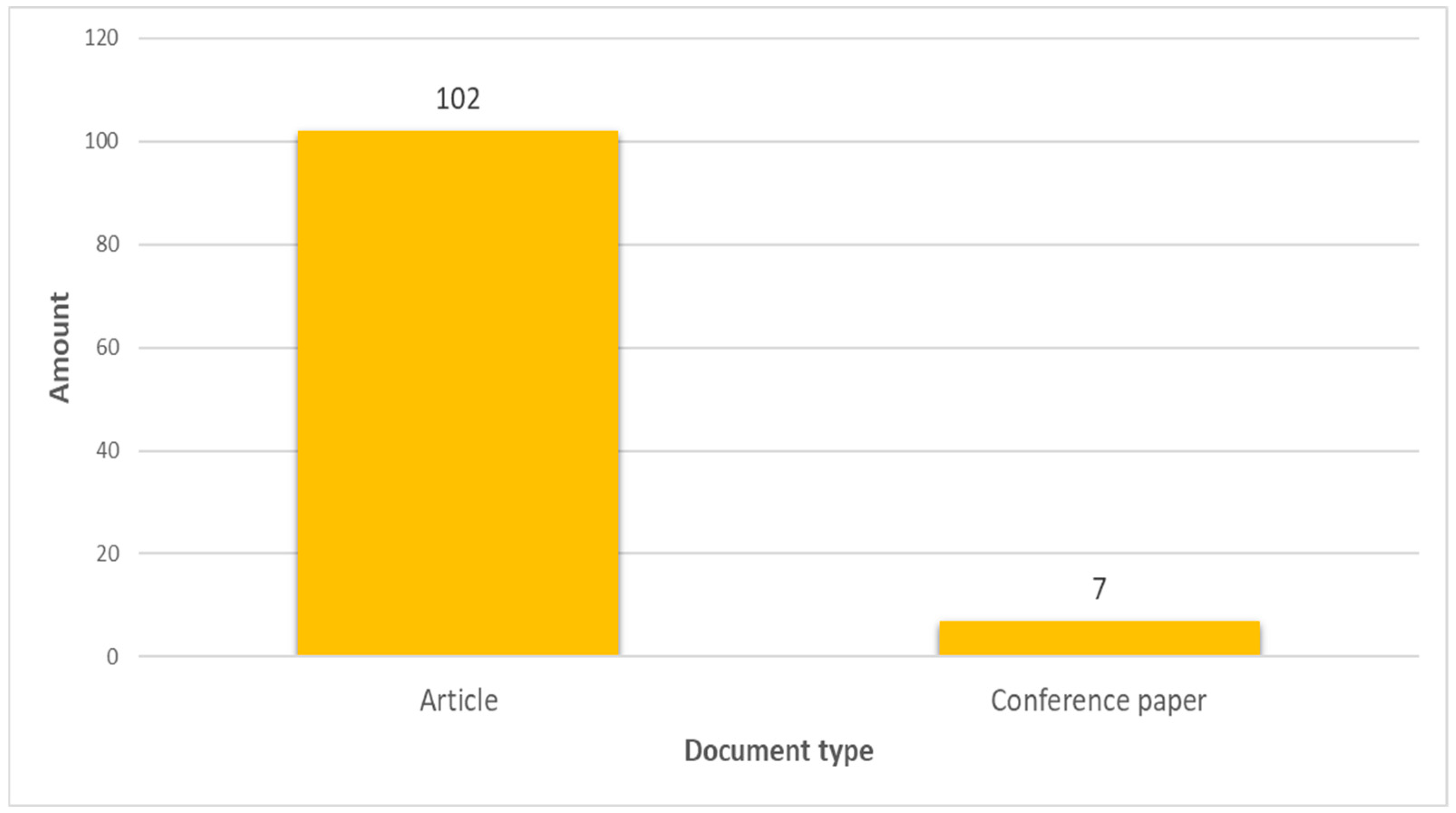
3.1.3. Types of Documents Reviewed
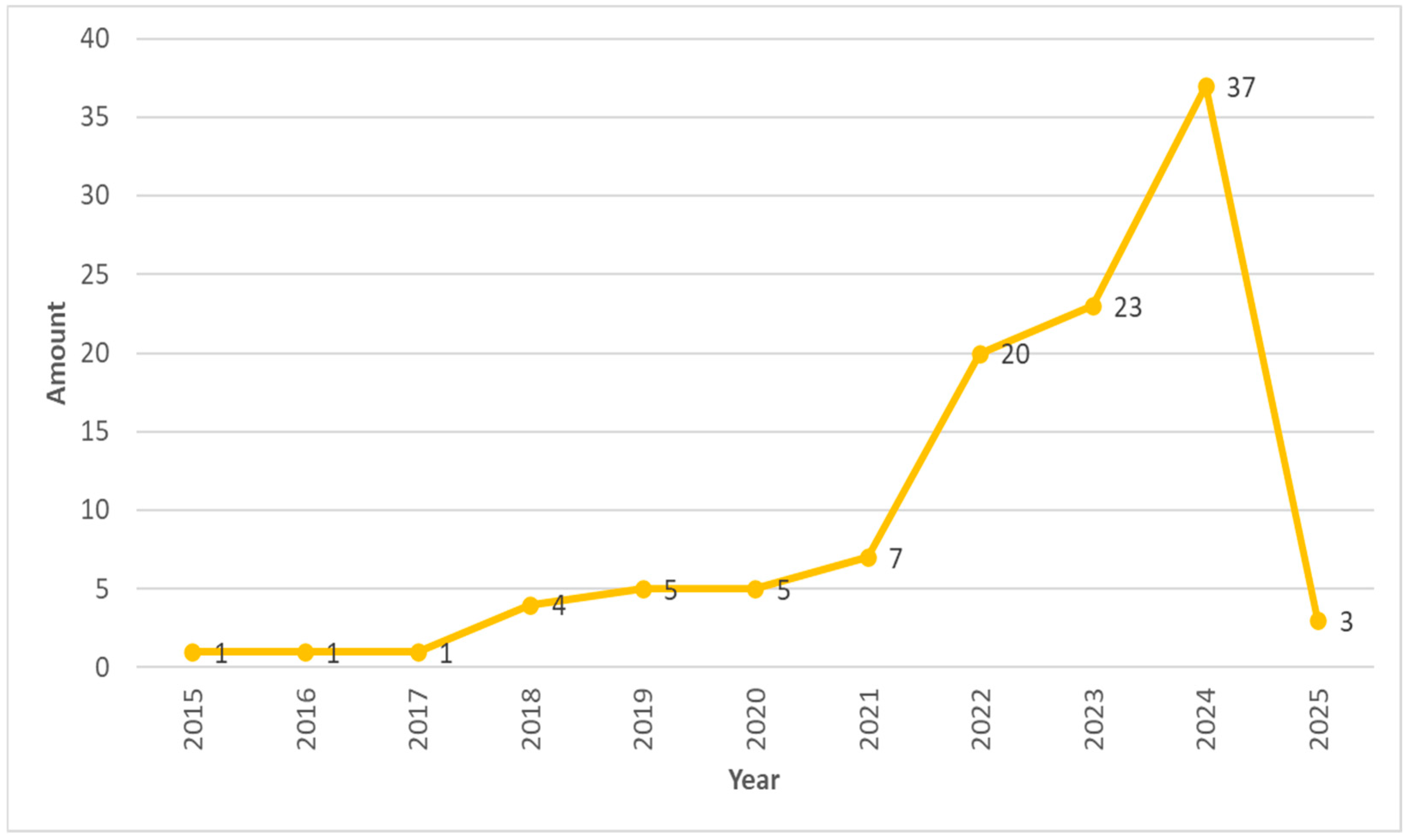
3.1.4. Scientific Production by Year
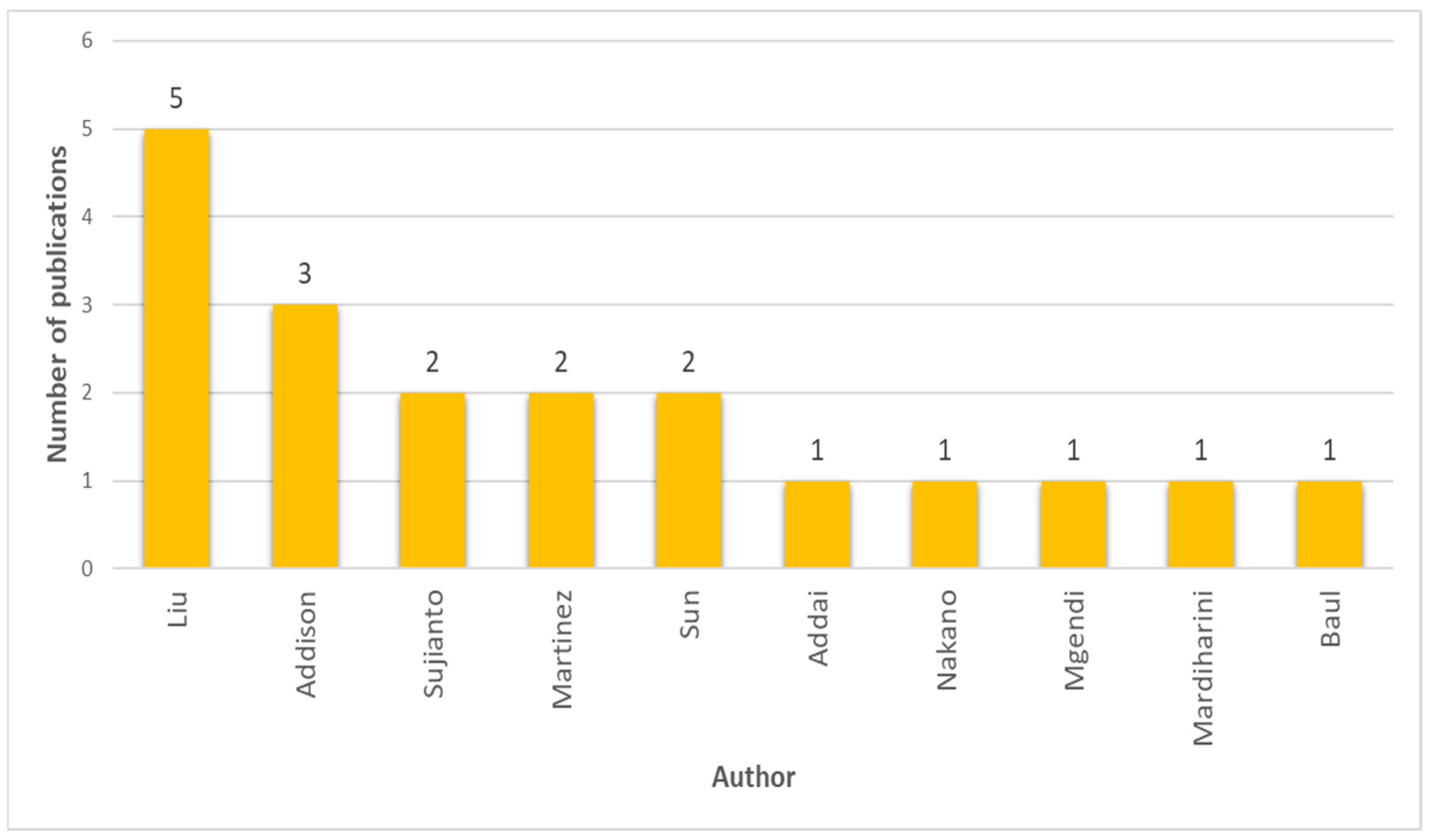
3.1.5. Most Productive Authors
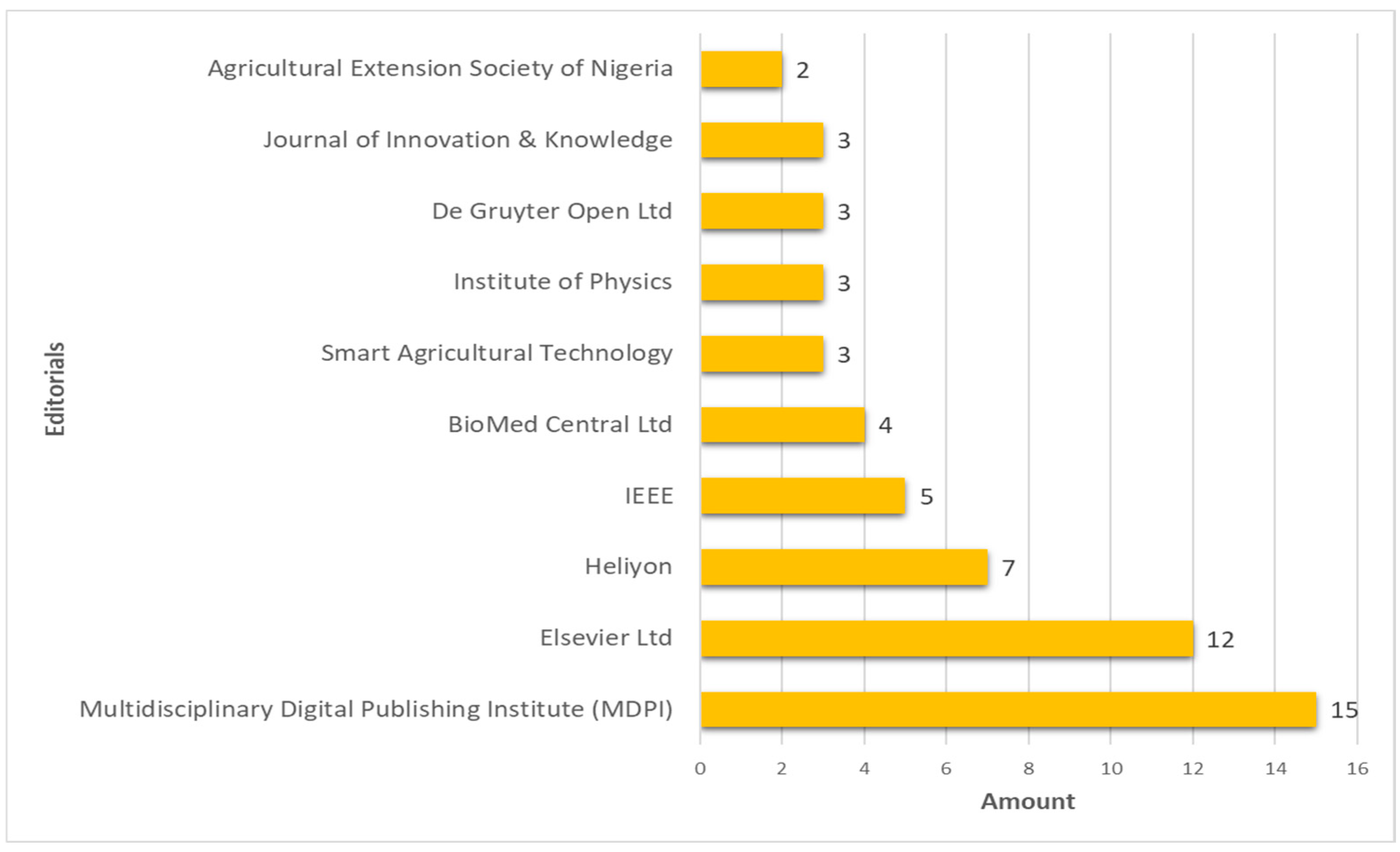
3.1.6. Publishers with the Most Articles Published
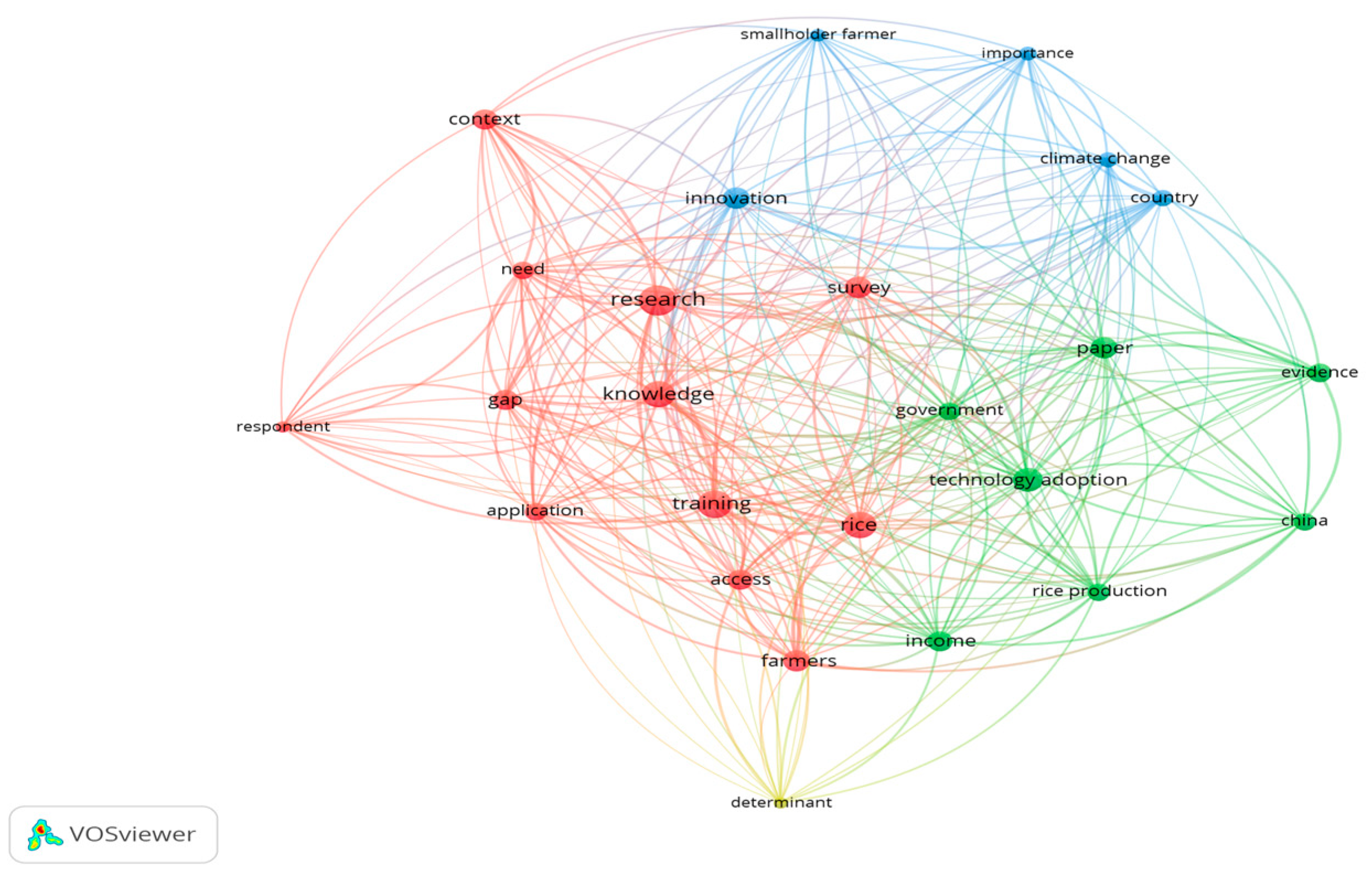
3.1.7. VosViewer Analysis
- -
- Red cluster: Focused on topics related to knowledge, research, gaps, and training. Concepts such as research, training, knowledge, gap, and application are grouped in this category, indicating an academic and training approach to digital literacy and the training needs of farmers.
- -
- Green cluster: Associated with topics related to technology adoption, agricultural outcomes, and governance. Terms such as technology adoption, government, rice, income, China, and evidence stand out, reflecting research focused on the effects of agricultural technology adoption in specific contexts, especially related to rice production.
- -
- Blue cluster: Represents terms related to the global and climate context, such as climate change, country, importance, and smallholder farmer. This cluster connects the topic with broader structural challenges, such as sustainability and rural vulnerability.
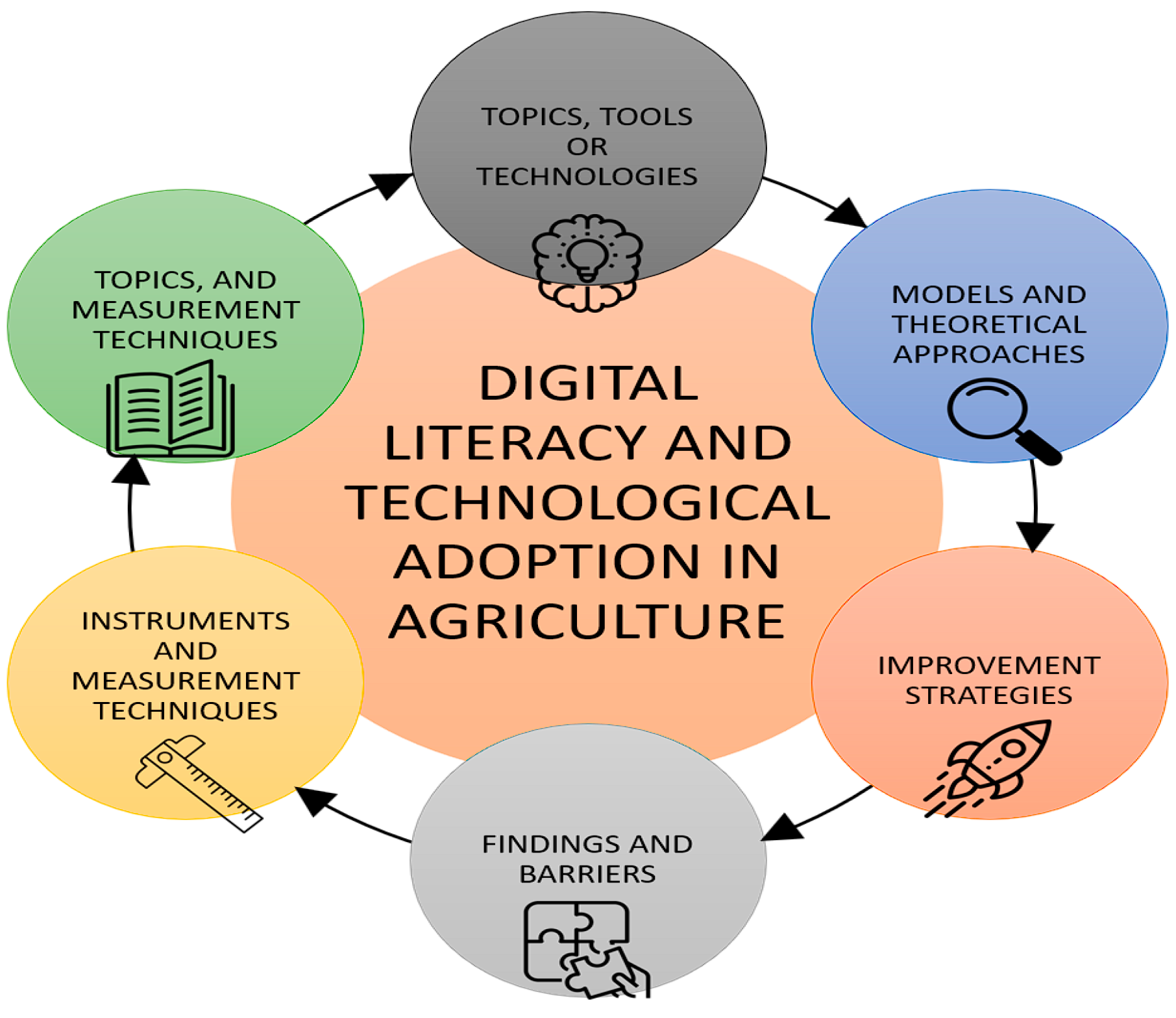
3.2. Response to Research Objectives
3.2.1. OBJ01: Describe the Main Topics, Tools, or Technologies Addressed in Digital Literacy for Farmers
3.2.2. OBJ02: Identify the Instruments and Techniques Used to Measure the Impact of Digital Literacy on the Adoption of Agricultural Technology
3.2.3. OBJ03: Analyze the Models and Theoretical Approaches That Have Been Applied to Study the Adoption of Agricultural Technologies Based on Digital Literacy
3.2.4. OBJ04: Determine the Main Factors Influencing Farmers’ Digital Literacy and Its Relationship with the Adoption of Agricultural Technology
3.2.5. OBJ05: Synthesize the Main Findings and Barriers Regarding the Relationship Between Digital Literacy and the Adoption of Agricultural Technologies Reported in the Scientific Literature
3.2.6. OBJ06: Examine the Strategies Implemented to Improve Farmers’ Digital Literacy and Their Impact on the Adoption of Emerging Technologies
3.3. Comparative Analysis by Region: Europe, Asia, Latin America, and Africa
3.3.1. Factors Influencing Digital Literacy and Technology Adoption by Region
3.3.2. Strategies to Improve Digital Literacy by Region
3.4. Limitations, Barriers, and Challenges by Region
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagesh, O.S.; Budaraju, R.R.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Vinay, M.; Ajibade, S.-S.M.; Chopra, M.; Jawarneh, M.; Kaliyaperumal, K. Boosting enabled efficient machine learning technique for accurate prediction of crop yield towards precision agriculture. Discov. Sustain. 2024, 5, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Wu, Z.; Yan, Q.; Feng, X.; Zhao, Z. Improving soil organic carbon mapping in farmlands using machine learning models and complex cropping system information. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2024, 36, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Gao, Q.; Ju, K.; Ma, Y. How digital skills affect farmers’ agricultural entrepreneurship? An explanation from factor availability. J. Innov. Knowl. 2024, 9, 100477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajalakshmi, R.; Faizal, S.; Sivasankaran, S.; Geetha, R. RiceSeedNet: Rice seed variety identification using deep neural network. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 16, 101062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Dong, M.; Chen, F.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, J.; Chen, P.; Xie, Y.; Yuan, C.; Qiao, Z.; et al. Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer Reduction Combined with Foliar Fertilizer Application on the Physiological Characteristics and Yield of High-Quality Japonica Rice. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2024, 18, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, Z.; Fu, Z.; Jia, L.; Li, Q.; Song, J. Impact of digital technology adoption on technological innovation in grain production. J. Innov. Knowl. 2024, 9, 100520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashane, M.F.; Senanayake, I.P. Developing a two-decadal time-record of rice field maps using Landsat-derived multi-index image collections with a random forest classifier: A Google Earth Engine based approach. Inf. Process. Agric. 2024, 11, 260–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SaberiKamarposhti, M.; Ng, K.-W.; Yadollahi, M.; Kamyab, H.; Cheng, J.; Khorami, M. Cultivating a sustainable future in the artificial intelligence era: A comprehensive assessment of greenhouse gas emissions and removals in agriculture. Environ. Res. 2024, 250, 118528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sethi, I. Computer Vision-Based Automated Detection and Severity Grading of Rice Spot Disease for Precision Management. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Interdisciplinary Approaches in Technology and Management for Social Innovation (IATMSI), Gwalior, India, 14–16 March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Munaganuri, R.K.; Rao, Y.N. PAMICRM: Improving Precision Agriculture Through Multimodal Image Analysis for Crop Water Requirement Estimation Using Multidomain Remote Sensing Data Samples. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 52815–52836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryavanshi, A.; Kukreja, V.; Dogra, A.; Bordoloi, D.; Joshi, K. A CNN and Random Forest Fusion with Optimized Convolutional Layers for Accurate Disease Identification in Rice Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Interdisciplinary Approaches in Technology and Management for Social Innovation (IATMSI), Gwalior, India, 14–16 March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Husin, N.A.; Sivajiganason, V.A.L.; Kamaruzzaman, N.N.; Mazlan, N.; Sitanggang, I.S. iRICE Decision Support System: Time-Series Forecasting Model for the Risk Management System. J. Adv. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2024, 33, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, M.; Bonuedi, I.; Arhin, A.A.; Wadei, B.; Owusu-Addo, E.; Fredua Antoh, E.; Mensah-Odum, N. Exploring the impact of agricultural digitalization on smallholder farmers’ livelihoods in Ghana. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addai, K.N.; Temoso, O.; Ng’ombe, J.N. Heterogeneous Effects of Agricultural Technology Adoption on Smallholder Household Welfare in Ghana. J. Agric. Appl. Econ. 2023, 55, 283–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Kabir, K.H.; McQuire, M.; Bureau, D.P. The dynamics of digital technology adoption in rainbow trout aquaculture: Exploring multi-stakeholder perceptions in Ontario using Q methodology and the theory of planned behaviour. Aquaculture 2025, 594, 741460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollerenshaw, A.; Robinson, N.; Chadha, A.; Channon, J. A smart agriculture information system delivering research data for adoption by the Australian grains industry. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 9, 100610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, E.; Hanees, A.; Shanmuganathan, B.; Kareem Basha, M.I. Precision Agriculture: A Novel Approach on AI-Driven Farming. In Intelligent Robots and Drones for Precision Agriculture; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, J.; Jamali, M.H.; Kaly Sitthan, V.; Tagang, R.R.; Ibrahim, M.H. Farmers’ Perception Towards Agroforestry Practices in Siburan: Perception of Agroforestry in Siburan. Borneo J. Resour. Sci. Technol. 2024, 14, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekhar, V.; Arulselvi, G.; Babu, K.S. Design an optimization based ensemble machine learning framework for detecting rice leaf diseases. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 84401–84424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangaiah, A.K.; Yu, F.; Lin, Y.; Shen, W.; Sharma, A. UAV T-YOLO-Rice: An Enhanced Tiny Yolo Networks for Rice Leaves Diseases Detection in Paddy Agronomy. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2024, 11, 5201–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, S.; Savita; Ganguly, S. AI for Agro-Business in the Identification of Rice Diseases. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (IC2PCT), Greater Noida, India, 9–10 February 2024; pp. 976–982. [Google Scholar]
- Sagar, L.; Maitra, S.; Singh, S.; Sairam, M. Advanced strategies for optimization of primary nutrients requirement in rice—A review. Plant Sci. Today 2024, 11, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusharki, M.B.; Muhammad-Bello, B.L. AIoT-Enabled Precision Agriculture for Sustainable Crop Disease Management: Advancing SDGs Through Graph Attention Neural Networks. In Artificial Intelligence of Things for Achieving Sustainable Development Goals; Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 192, pp. 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.; Chen, D.; Tian, Y. Unveiling the environmental and socioeconomic benefits of precision nitrogen management for paddy fields in subtropical China. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 142, 126663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PRISMA Statement. PRISMA 2020 Statement. Available online: https://www.prisma-statement.org/prisma-2020 (accessed on 3 February 2025).
- Heitkämper, K.; Reissig, L.; Bravin, E.; Glück, S.; Mann, S. Digital technology adoption for plant protection: Assembling the environmental, labour, economic and social pieces of the puzzle. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 4, 100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieti, J.; Waema, T.M.; Baumüller, H.; Ndemo, E.B.; Omwansa, T.K. What really impedes the scaling out of digital services for agriculture? A Kenyan users’ perspective. Smart Agric. Technol. 2022, 2, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.L.H.; Khuu, D.T.; Halibas, A.; Nguyen, T.Q. Factors That Influence the Intention of Smallholder Rice Farmers to Adopt Cleaner Production Practices: An Empirical Study of Precision Agriculture Adoption. Eval. Rev. 2024, 48, 692–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panyasit, K.; Singhavara, M.; Srihirun, J.; Wangsathian, S.; Nonthapot, S. A study to assess the readiness of rice farmers to use agricultural technology for production in Nong Khai Province, Thailand. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Stud. 2024, 7, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, M.A.; Paul, S.K.; Naim, J. Farmers Adaptation Strategies to Adverse Impacts of Drought on Agriculture of the Central Barind Tract of Bangladesh: An Empirical Study. IDRiM J. 2023, 13, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mgendi, G.; Mao, S.; Qiao, F. Is a Training Program Sufficient to Improve the Smallholder Farmers’ Productivity in Africa? Empirical Evidence from a Chinese Agricultural Technology Demonstration Center in Tanzania. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheampong, L.D.; Nsiah Frimpong, B.; Adu-Appiah, A.; Asante, B.O.; Asante, M.D. Assessing the information seeking behaviour and utilization of rice farmers in the Ejisu-Juaben municipality of Ashanti Region of Ghana. Agric. Food Secur. 2017, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhun, S.; Kumar, V.; Martin, R.J.; Srean, P.; Hadi, B.A.R. Weed management practices of smallholder rice farmers in Northwest Cambodia. Crop Prot. 2020, 135, 104793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awotide, B.A.; Karimov, A.A.; Diagne, A. Agricultural technology adoption, commercialization and smallholder rice farmers’ welfare in rural Nigeria. Agric. Econ. 2016, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayhan, S.J.; Rahman, M.S.; Lyu, K. The Role of Rural Credit in Agricultural Technology Adoption: The Case of Boro Rice Farming in Bangladesh. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileiou, M.; Kyrgiakos, L.S.; Kleisiari, C.; Kleftodimos, G.; Vlontzos, G.; Belhouchette, H.; Pardalos, P.M. Transforming weed management in sustainable agriculture with artificial intelligence: A systematic literature review towards weed identification and deep learning. Crop Prot. 2024, 176, 106522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alant, B.P.; Bakare, O.O. A case study of the relationship between smallholder farmers’ ICT literacy levels and demographic data w.r.t. their use and adoption of ICT for weather forecasting. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithra, S.; Singh, A.; Singh, H.; Burman, R.R. Can Access to Institutional Credit Promote Adoption of Improved Technology? A Case of Biofertiliser Use Among the Indian Paddy Farmers. Indian J. Agric. Econ. 2024, 79, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campenhout, B.V. The Role of Information in Agricultural Technology Adoption: Experimental Evidence from Rice Farmers in Uganda. Econ. Dev. Cult. Change 2021, 69, 1239–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, M.; Musshoff, O. A tobit regression model for the timing of smartphone adoption in agriculture. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanko, M.; Muhammed, M.A.; Ismaila, S. Reshapping agriculture technology adoption thinking: Malthus, Borlaug and Ghana’s fail green revolution. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Q. How Digital Business Penetration Influences Farmers’ Sense of Economic Gain: The Role of Farmers’ Entrepreneurial Orientation and Market Responsiveness. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 187744–187753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Quan, Y.; Fu, Y. Risk preferences and the low-carbon agricultural technology adoption: Evidence from rice production in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 2577–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbemavo, C.D.S.J.; Toffa, J.; Tchakpa, C.; Loko, Y.L.E.; Djedatin, G.; Ewedje, E.-E.; Orobiyi, A.; Sedah, P.; Sabot, F. Rice farmers’ perceptions and response to climate variability, and determinants of adaptation strategies in the Republic of Benin. Int. J. Clim. Change Strateg. Manag. 2022, 14, 332–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, H. Farmers’ adoption of agriculture green production technologies: Perceived value or policy-driven? Heliyon 2024, 10, e23925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardiharini, M.; Jamal, E.; Rohaeni, E.S.; Indrawanto, C.; Indraningsih, K.S.; Gunawan, E.; Ramadhan, R.P.; Fahmid, I.M.; Wardana, Ï.P.; Ariningsih, E. Indonesian rice farmers’ perceptions of different sources of information and their effect on farmer capability. Open Agric. 2023, 8, 20220200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, M.; Shahzad, M.S.; Khan, F.U.; Luqman, M.; Saleem, U.; Nasir, S. Public Sector Advisory Services for Rice Productivity: A Case Study of Farmers’ Awareness in Tehsil Shakargarh of Pakistan. Sarhad J. Agric. 2021, 38, 1–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-D.; Chen, F. Socio-economic factors influencing the adoption of low carbon technologies under rice production systems in China. Carbon Balance Manag. 2022, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susanti, E.; Safrida; Nabila, N.P.; Iskandar, E. The adoption of combine harvester and its determinant factors for sustainable rice production in Aceh Besar District, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1290, 012052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeh, A.N.; Eze, A.V.; Eze, E.O. Extension Agents’ Use of Mobile Phone Applications for Agricultural Extension Service Delivery in Ebonyi State Agricultural Development Programme, Nigeria. J. Agric. Ext. 2021, 25, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yang, S. The Effect of Social Network on Controlled-Release Fertilizer Use: Evidence from Rice Large-Scale Farmers in Jiangsu Province, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulai, S.; Zakariah, A.; Donkoh, S.A. Adoption of rice cultivation technologies and its effect on technical efficiency in Sagnarigu District of Ghana. Cogent Food Agric. 2018, 4, 1424296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Nayak, S.; Mohapatra, S.; Trivedi, P.; Waza, S.A. Women-led community institutions as a potential vehicle for the adoption of varieties and improved seed practices: An impact case from India. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2024, 5, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janc, K.; Czapiewski, K.; Wójcik, M. In the starting blocks for smart agriculture: The internet as a source of knowledge in transitional agriculture. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2019, 90–91, 100309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hota, J.; Verma, V.K. Challenges to Adoption of Digital Agriculture in India. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Maintenance and Intelligent Asset Management (ICMIAM), Anand, India, 13–15 December 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yangchen, U.; Suebsombut, P.; Lhamo, T.; Dorji, P.; Chernbumroong, S.; Sureephong, P.; Touchard, S. Preliminary study on Smart farming literacy: A case study in Barp gewog, Punakha District, Bhutan. In Proceedings of the 2021 Joint International Conference on Digital Arts, Media and Technology with ECTI Northern Section Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Computer and Telecommunication Engineering, Cha-am, Thailand, 3–6 March 2021; pp. 340–345. [Google Scholar]
- Sujianto; Gunawan, E.; Saptana; Syahyuti; Darwis, V.; Ashari; Syukur, M.; Ariningsih, E.; Saliem, H.P.; Mardianto, S.; et al. Farmers’ perception, awareness, and constraints of organic rice farming in Indonesia. Open Agric. 2022, 7, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommey, R.E.; Fombad, M.C. Knowledge sharing technologies for rice farmers: A perspective from the Eastern Region of Ghana. Knowl. Manag. E-Learn. Int. J. 2024, 16, 355–378. [Google Scholar]
- Ashoori, D.; Allahyari, M.S.; Bagheri, A.; Damalas, C.A. Adoption Determinants of Modern Rice Cultivars among Smallholders of Northern Iran. Agriculture 2019, 9, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tra Vinh University; Bang, P.V.; Khanh, P.T.; Tung, D.T. The influence of cultural factors on the acceptance of alternate wetting and drying technology among rice farmers in the Vietnamese Mekong delta. J. Sustain. Sci. Manag. 2022, 17, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shazwan Azizul, A.; El Pebrian, D.; Mustaffha, S.; Mariam Shamsi, S.; Zahari, M.K.; Aziera Ruslan, N. The use of drone for rice cultivation in Malaysia: Identification of factors influencing its farmers’ acceptance. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2023, 22, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goli, I.; Azadi, H.; Miceikienė, A.; Tanaskovik, V.; Stamenkovska, I.J.; Kurban, A.; Viira, A.-H. Training Needs Assessment: The Case of Female Rice Farmers in Northern Iran. Agriculture 2022, 12, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, J.; Maye, D.; Bailye, C.; Barnes, A.; Bear, C.; Bell, M.; Cutress, D.; Davies, L.; De Boon, A.; Dinnie, L.; et al. What are the priority research questions for digital agriculture? Land Use Policy 2022, 114, 105962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, H.; Han, J. Understanding Ecological Agricultural Technology Adoption in China Using an Integrated Technology Acceptance Model—Theory of Planned Behavior Model. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 927668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikri, I.; Firda, I.; Hamid, A.H.; Susanti, E. ICT-based agricultural extension literacy and the needs for agriculture development and sustainability: A case study of rice farmer in Aceh. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1302, 012128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Yang, S.; Pan, G. Innovation practices in agricultural transformation in East China: Exploring the impact and implications of the new professional farmer training model. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suebsombut, P.; Chernbumroong, S.; Sureephong, P.; Jaroenwanit, P.; Phuensane, P.; Sekhari, A. Comparison of Smart Agriculture Literacy of Farmers in Thailand. In Proceedings of the 2020 Joint International Conference on Digital Arts, Media and Technology with ECTI Northern Section Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Computer and Telecommunications Engineering (ECTI DAMT & NCON), Pattaya, Thailand, 11–14 March 2020; pp. 242–245. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, K.N.N. Social Network to Accelerate Agricultural Technology Adoption: Evidence from Hambanthota District, Sri Lanka. Indian J. Ext. Educ. 2023, 59, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, A.; Coniglio, I.M.; Corvello, V.; Longo, F.; Sagawa, J.K.; Solina, V. Exploring small farmers behavioral intention to adopt digital platforms for sustainable and successful agricultural ecosystems. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 204, 123436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Luo, C.; Li, Y.; Tan, Z.; Gao, S. ‘They adopt, I also adopt’: The neighborhood effects and irrigator farmers’ conversion to adopt water-saving irrigation technology. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 305, 109141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyeneke, C.J.; Umeh, G.N.; Onyeneke, R.U. Impact of Climate Information Services on Crop Yield in Ebonyi State, Nigeria. Climate 2022, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmaryani, S.; Soleh, A.; Irmanelly; Wiarta, I. Integration of technology acceptance models and government support to improve digital literacy. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addison, M.; Anyomi, B.K.; Acheampong, P.P.; Wongnaa, C.A.; Amaning, T.K. Key drivers of adoption intensity of selected improved rice technologies in rural Ghana. Sci. Afr. 2023, 19, e01544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oo, S.P.; Usami, K. Farmers’ Perception of Good Agricultural Practices in Rice Production in Myanmar: A Case Study of Myaungmya District, Ayeyarwady Region. Agriculture 2020, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Chen, Y.; Xie, L. How does internet use promote joint adoption of sustainable agricultural practices? Evidence from rice farmers in China. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2023, 21, 2270244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanogo, K.; Touré, I.; Arinloye, D.-D.A.A.; Dossou-Yovo, E.R.; Bayala, J. Factors affecting the adoption of climate-smart agriculture technologies in rice farming systems in Mali, West Africa. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 5, 100283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggins, S.; McCampbell, M.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, R.; Haefele, S.M.; Karki, E.; Hetherington, J.; Smith, J.; Brown, B. How have smallholder farmers used digital extension tools? Developer and user voices from Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia and Southeast Asia. Glob. Food Secur. 2022, 32, 100577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Murtaza, M.; Ahmad, W.; Bibi, N.; Khan, A.; Khan, J. Does Education and Farming Experience Affect Technical Efficiency of Rice Crop Growers? Evidence from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Sarhad J. Agric. 2022, 38, 1147–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.B.; Diep, T.T.; Fock, K.; Nguyen, T.S. Using the Internet of Things to promote alternate wetting and drying irrigation for rice in Vietnam’s Mekong Delta. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 41, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karubanga, G.; Godfrey Agea, J.; Tatenda Rugare, J.; Mubangizi, N. Leveraging video integration for enhanced agricultural extension reforms in Uganda. Cogent Soc. Sci. 2024, 10, 2399936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, D.; Baruah, B. Beer, barley, livestock, milk: Who adopts agricultural innovations in rural Rajasthan? World Dev. Perspect. 2024, 36, 100643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metta, M.; Ciliberti, S.; Obi, C.; Bartolini, F.; Klerkx, L.; Brunori, G. An integrated socio-cyber-physical system framework to assess responsible digitalisation in agriculture: A first application with Living Labs in Europe. Agric. Syst. 2022, 203, 103533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindasombatcharoen, N.; Tsolakis, N.; Kumar, M.; O’Sullivan, E. Navigating psychological barriers in agricultural innovation adoption: A multi-stakeholder perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 475, 143695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Qi, Z.; Tan, L.; Hu, C. How Neighbors Influence Rice–Crayfish Integrated System Adoption: Evidence from 980 Farmers in the Lower and Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Takács-György, K. What is stopping Agriculture 4.0?—Examples from China. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Applied Computational Intelligence and Informatics (SACI), Timisoara, Romania, 23–26 May 2023; pp. 000511–000518. [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsen, K.; Mikalsen, M.; Lilleng, G. A literature review of smart technology domains with implications for research on smart rural communities. Technol. Soc. 2023, 75, 102397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro-Padial, J.; Virgili-Gomá, J.; Gil, R.; Teixidó, M.; García, R. Agriculture data sharing review. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunlerd, A.; Nabumroong, B.; Jantarakomet, K.; Ruttanaprasert, R.; Burana, K. Analyzing Success Factors in Developing Mobile Applications for Farmers in Thailand Using Analytic Hierarchy Process Technique. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Inform. IJEEI 2024, 12, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoy, R.; Nanseki, T.; Chomei, Y. Farmers’ Perceptions of Government’s Rice Export Policy: A Case in Southern Cambodia. J. Fac. Agric. Kyushu Univ. 2018, 63, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, M.; Ohene-Yankyera, K.; Acheampong, P.P.; Wongnaa, C.A. The impact of uptake of selected agricultural technologies on rice farmers’ income distribution in Ghana. Agric. Food Secur. 2022, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Xu, Z.; Xiao, A.; Wang, X.; Skare, M. Overcoming barriers and seizing opportunities in the innovative adoption of next-generation digital technologies. J. Innov. Knowl. 2024, 9, 100622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, Y.; Tsusaka, T.W.; Aida, T.; Pede, V.O. Is farmer-to-farmer extension effective? The impact of training on technology adoption and rice farming productivity in Tanzania. World Dev. 2018, 105, 336–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujianto, S.; Hasibuan, A.M.; Mahendri, I.G.A.P.; Pribadi, E.R.; Pujiharti, Y.; Ardana, I.K.; Ermiati; Sudjarmoko, B.; Sukamto; Gunawan, E. Drivers of Organic Rice Adoption Among Smallholder Farmers: Implications for Sustainable Development. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2024, 19, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baul, T.; Karlan, D.; Toyama, K.; Vasilaky, K. Improving smallholder agriculture via video-based group extension. J. Dev. Econ. 2024, 169, 103267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Carmona, O.; Buján-Carballal, D.; Casado-Mansilla, D.; López-de-Ipiña, D.; Cano-Benito, J.; Cimmino, A.; Poveda-Villalón, M.; García-Castro, R.; Almela-Miralles, J.; Apostolidis, D.; et al. Mind the gap: The AURORAL ecosystem for the digital transformation of smart communities and rural areas. Technol. Soc. 2023, 74, 102304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agussabti, A.; Rahmaddiansyah, R.; Hamid, A.H.; Zakaria, Z.; Munawar, A.A.; Abu Bakar, B. Farmers’ perspectives on the adoption of smart farming technology to support food farming in Aceh Province, Indonesia. Open Agric. 2022, 7, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.H.; Waza, S.A.; Nayak, S.; Chakravorty, R.; Zaidi, N.W.; Hossain, M. Gender focused training and knowledge enhances the adoption of climate resilient seeds. Technol. Soc. 2020, 63, 101388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Huang, Y.; Luo, X. Farmers’ technology preference and influencing factors for pesticide reduction: Evidence from Hubei Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 6424–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiru, I.O. Impact of Extension Services and Input Consultants’ Activities on Crop Yields of Fadama III Additional Financing Farmers in Nigeria. J. Agric. Ext. 2024, 28, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.M.; Labarta, R.A.; Gonzalez, C. Impacts of the joint adoption of improved varieties and chemical fertilizers on rice productivity in Bolivia: Implications for Global Food Systems. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1194930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.M.; Labarta, R.A.; Gonzalez, C.; Lopera, D.C. Joint adoption of rice technologies among Bolivian farmers. Agric. Resour. Econom. Rev. 2021, 50, 252–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, M.-H.; Finger, R.; El Benni, N.; Gocht, A.; Sørensen, C.A.G.; Gusset, M.; Pfeifer, C.; Poppe, K.; Regan, Á.; Rose, D.C.; et al. Scenarios for European agricultural policymaking in the era of digitalisation. Agric. Syst. 2022, 196, 103318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, G.; Dorward, P.; Poskitt, S.; Stern, R.D.; Nyirongo, D.; Fara, K.; Gathenya, J.M.; Staub, C.G.; Trotman, A.; Nsengiyumva, G.; et al. Stimulating small-scale farmer innovation and adaptation with Participatory Integrated Climate Services for Agriculture (PICSA): Lessons from successful implementation in Africa, Latin America, the Caribbean and South Asia. Clim. Serv. 2022, 26, 100298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandeya, S.; Gajurel, A.; Mishra, B.P.; Devkota, K.; Gyawali, B.R.; Upadhaya, S. Determinants of Climate-Smart Agriculture Adoption Among Rice Farmers: Enhancing Sustainability. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamanda, P.J.; Motaung, M.V.; Okorley, E.L. Socio-demographic Characteristics of Smallholder Farmers That Influence Their Competence in Rice Post-Harvest Value Addition, Southern Region of Sierra Leone. Univers. J. Agric. Res. 2023, 11, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetteh Quarshie, P.; Abdulai, A.-R.; Duncan, E.; Bahadur Kc, K.; Roth, R.; Sneyd, A.; Fraser, E.D.G. Myth or reality? The Digitalization of Climate-Smart Agriculture (DCSA) practices in smallholding agriculture in the Bono East Region of Ghana. Clim. Risk Manag. 2023, 42, 100553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratella, V.; Pirelli, T.; Giordano, R.; Pagano, A.; Portoghese, I.; Bea, M.; López-Moya, E.; Di Fonzo, A.; Fabiani, S.; Vanino, S. Stakeholders analysis and engagement to address Water-Ecosystem-Food Nexus challenges in Mediterranean environments: A case study in Italy. Ital. J. Agron. 2023, 18, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begen, N.; Atasoy, H. Technological literacy and employment: An inquiry into the adoption of learning technologies. Telecommun. Policy 2024, 48, 102864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Razman, M.R.; Syed Zakaria, S.Z.; Ern, L.K.; Hussain, A.; Chamola, V. Utilizing ubiquitous learning to foster sustainable development in rural areas: Insights from 6G technology. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2024, 161, 108418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surdianto, Y.; Sutrisna, N.; Nurawan, A.; Hamdani, K.K.; Wiratno, W.; Erythrina, E.; Sugandi, D. Study of Rice (Oryza sativa) Seed Breeding Based on Farmer Groups in Pangandaran Regency, West Java Province, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1364, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.J.; Sarma, P.K.; Begum, I.A.; Connor, J.; Crase, L.; Sayem, S.M.; McKenzie, A.M. Agricultural extension service, technology adoption, and production risk nexus: Evidence from Bangladesh. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiya, N.; Tomitaka, M.; Oizumi, N.; Assenga, A.N.; Jacob, M.K. Farmer-to-Farmer Extension Facilitated by Agricultural Training Institutions: A Case of NERICA Dissemination in Tanzania. Plant Prod. Sci. 2015, 18, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiedu-Ayeh, L.O.; Zheng, X.; Agbodah, K.; Dogbe, B.S.; Darko, A.P. Promoting the Adoption of Agricultural Green Production Technologies for Sustainable Farming: A Multi-Attribute Decision Analysis. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakumanu, K.R.; Kotapati, G.R.; Nagothu, U.S.; Kuppanan, P.; Kallam, S.R. Adaptation to climate change and variability: A case of direct seeded rice in Andhra Pradesh, India. J. Water Clim. Change 2019, 10, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, F.; Li, J.; Jin, J.; Qiu, X. Do Green Production Technologies Improve Household Income? Evidence from Rice Farmers in China. Land 2023, 12, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun Oo, A.; Cho, A.; Yan Naing, S.; Marin, G. Determining factors and barriers to the uptake of climate change adaptation strategies of agriculture and aquaculture farm households in Myanmar. Int. J. Clim. Change Strateg. Manag. 2024, 16, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhan, J.; Chen, Z. Agricultural Insurance and Selection of Soil Testing and Formula Fertilization Technology—An Empirical Study Based on the Main Rice-Producing Areas in China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, N.; Liao, C. Effects of Social Capital on the Adoption of Green Production Technologies by Rice Farmers: Moderation Effects Based on Risk Preferences. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndayambaje, B.; Amuguni, H.; Coffin-Schmitt, J.; Sibo, N.; Ntawubizi, M.; VanWormer, E. Pesticide Application Practices and Knowledge among Small-Scale Local Rice Growers and Communities in Rwanda: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, S.; Baljinder, K.S. Groundwater Depletion and Role of Direct Seeded Rice in Water Saving: A Move Towards Sustainable Agriculture of Punjab. Econ. Aff. 2019, 64, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lyu, J.; Ge, C. Knowledge and Farmers’ Adoption of Green Production Technologies: An Empirical Study on IPM Adoption Intention in Major Indica-Rice-Producing Areas in the Anhui Province of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakitan, B.; Hadi, B.; Herlinda, S.; Siaga, E.; Widuri, L.I.; Kartika, K.; Lindiana, L.; Yunindyawati, Y.; Meihana, M. Recognizing farmers’ practices and constraints for intensifying rice production at Riparian Wetlands in Indonesia. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2018, 85, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Thematic Concept | Keywords/Synonyms | Databases Used |
|---|---|---|
| Digital literacy | “digital literacy,” “digital competence,” “ICT skills,” “digital education,” “e-literacy,” “digital skills” | Scopus, IEEE Xplore, ScienceDirect |
| Technology adoption | “technology adoption,” “technology acceptance,” “innovation adoption,” “technological adoption,” “technology dissemination,” “awareness raising,” “capacity building,” “training” | Scopus, IEEE Xplore, ScienceDirect |
| Technology applied to agriculture | “agriculture,” “precision agriculture,” “smart farming,” “precision farming,” “site-specific agriculture,” “agricultural technology,” “smart agriculture,” “agricultural innovation,” “farm management system,” “digital transformation,” “digitalization,” “tools,” “applications,” “software,” “digital farming” | Scopus, IEEE Xplore, ScienceDirect |
| Subjects (Farmers) | “farmer,” “agriculturist,” “smallholder farmer,” “rural community,” “farming sector” | Scopus |
| Specific crop (rice) | “rice”, “rice farming”, “rice production”, “paddy farming”, “paddy cultivation”, “rice cropping” | Scopus |
| Database | Search String |
|---|---|
| Scopus | TITLE-ABS-KEY (“digital literacy” OR “digital competence” OR “ICT skills” OR “digital education” OR “e-literacy” OR “technology adoption” OR “technology acceptance” OR “innovation adoption” OR “technological adoption” OR “capacity building” OR “awareness raising” OR “technology dissemination” OR “training” OR “digital skills”) AND (“technology” OR “tools” OR “applications” OR “digitalization” OR “software” OR “agricultural innovation” OR “precision agriculture” OR “smart farming” OR “digital transformation” OR “farm management system”) AND (“farmer” OR “agriculturist” OR “smallholder farmer” OR “rural community” OR “farming sector”) AND (“rice” OR “rice farming” OR “rice production” OR “paddy farming” OR “paddy cultivation” OR “rice cropping”) |
| IEEE Xplore | (“digital literacy” OR “digital competence” OR “ICT skills” OR “digital education” OR “e-literacy” OR “technology adoption”) AND (“agriculture” OR “precision agriculture” OR “smart agriculture” OR “digital farming”) |
| ScienceDirect | (“digital literacy” OR “digital competence” OR “ICT skills” OR “e-literacy”) AND (“technology adoption”) AND (“agriculture” OR “precision agriculture” OR “smart agriculture” OR “digital farming”) |
| Database | Identified | Screened | Sought for Retrieval | Assessed for Eligibility | Included in Review |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scopus | 296 | 217 | 76 | 76 | 72 |
| ScienceDirect | 273 | 104 | 45 | 33 | 32 |
| IEEE Xplore | 135 | 123 | 30 | 17 | 5 |
| Total | 704 | 444 | 151 | 126 | 109 |
| Region | Most Frequently Cited Factors | Frequency (No. of Articles) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Europe |
| 10 | [15,26,35,37,38,40,53,54,74,81] |
| Asia |
| 17 | [16,18,28,35,39,40,42,44,48,49,52,57,58,65,82,98] |
| Latin America |
| 8 | [16,45,73,74,77,81,92,94] |
| Africa |
| 3 | [16,49,81] |
| Region | Main Strategies | Frequency (Number of Articles) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Europe |
| 10 | [26,37,38,40,54,74,81,92,93,95] |
| Asia |
| 14 | [18,28,39,40,42,44,49,50,51,53,57,58,82,98] |
| Latin America |
| 5 | [16,45,74,92,94] |
| Africa |
| 1 | [81] |
| Region | Constraints | Barriers | Challenges | Key References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Europe | Limited evidence in isolated rural areas; studies predominantly conducted in countries with high digital infrastructure. | Low participation of older farmers in digital programs. | Incorporate older farmers into training and technological adaptation processes. | [26,37,38,53,54] |
| Asia | High concentration of studies in leading countries (China, India), lower coverage in less developed areas. | Low rural connectivity, unequal access to devices, language barriers. | Develop culturally adapted, low-cost technological solutions; expand rural internet coverage. | [18,28,35,40,42,49] |
| Latin | Lack of longitudinal studies and long-term impact studies. | Lack of local technical support, economic barriers to ICT acquisition. | Implement sustained digital extension programs and foster local technical support networks. | [16,45,73,74,92] |
| Africa | Limited diversity of studies, concentrated in countries with international cooperation. | Limited digital infrastructure, high access costs, gender inequality in access to ICT. | Improve rural digital infrastructure, integrate inclusive programs for women and young people. | [81] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arangurí, M.; Mera, H.; Noblecilla, W.; Lucini, C. Digital Literacy and Technology Adoption in Agriculture: A Systematic Review of Factors and Strategies. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7090296
Arangurí M, Mera H, Noblecilla W, Lucini C. Digital Literacy and Technology Adoption in Agriculture: A Systematic Review of Factors and Strategies. AgriEngineering. 2025; 7(9):296. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7090296
Chicago/Turabian StyleArangurí, María, Huilder Mera, William Noblecilla, and Cristina Lucini. 2025. "Digital Literacy and Technology Adoption in Agriculture: A Systematic Review of Factors and Strategies" AgriEngineering 7, no. 9: 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7090296
APA StyleArangurí, M., Mera, H., Noblecilla, W., & Lucini, C. (2025). Digital Literacy and Technology Adoption in Agriculture: A Systematic Review of Factors and Strategies. AgriEngineering, 7(9), 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7090296






