Automatic Supplement Weighing Units for Monitoring the Time of Accessing Mineral Block Supplements by Rangeland Cattle in Northern Queensland, Australia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Sites
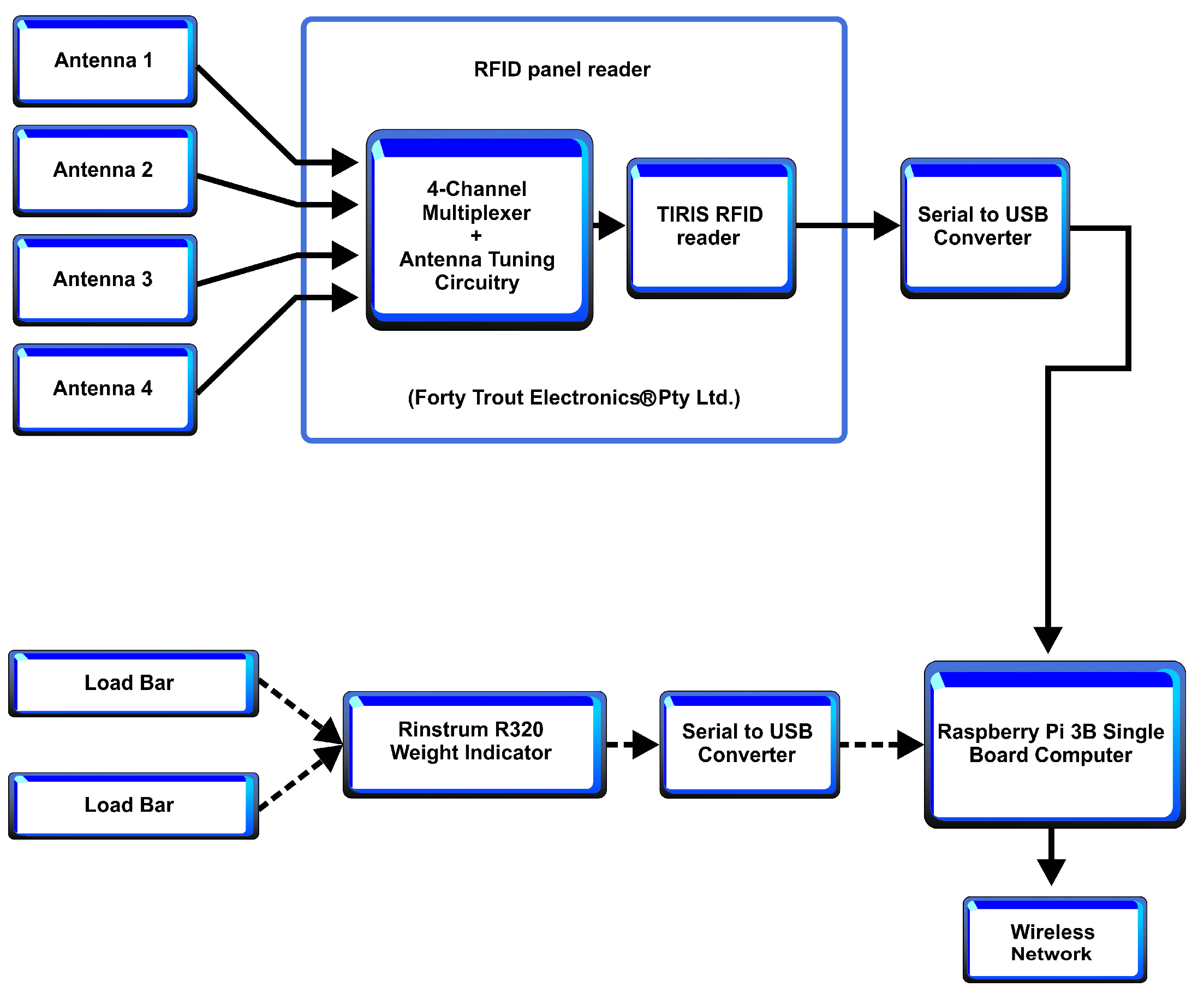
2.2. Automatic Supplement Weighing Units
2.3. Experimental Procedures
2.4. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Time Spent at the Automatic Supplement Weighing Units
3.2. Number of Cows and Individual Time Spent Accessing the Sites
3.3. Visiting Time of Cows to the Sites and Automatic Supplement Weighing Units
3.4. Relationship between Time Spent at the ASW Units and Mineral Block Intakes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunt, L.P.; McIvor, J.G.; Grice, A.C.; Bray, S.G. Principles and guidelines for managing cattle grazing in the grazing lands of northern Australia: Stocking rates, pasture resting, prescribed fire, paddock size and water points—A review. Rangeland J. 2014, 36, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIvor, J.G.; Guppy, C.; Probert, M.E. Phosphorus requirements of tropical grazing systems: The northern Australian experience. Plant Soil 2011, 349, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, M.K.; Chudleigh, F.; Dixon, R.M.; Sullivan, M.T.; Schatz, T.; Oxley, T. The economics of phosphorus supplementation of beef cattle grazing northern Australian rangelands. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2020, 60, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.M.; Anderson, S.T.; Kidd, L.J.; Fletcher, M.T. Management of phosphorus nutrition of beef cattle grazing seasonally dry rangelands: A review. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2020, 60, 863–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggington, A.R.; McCosker, T.H.; Graham, C.A. Intake of lick block supplements by cattle grazing native monsoonal tallgrass pastures in the Northern Territory. Rangeland J. 1990, 12, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.M.; White, A.; Fry, P.; Petherick, J.C. Effects of supplement type and previous experience on variability in intake of supplements by heifers. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2003, 54, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, J.G.P.; Sowell, B.F. Delivery method and supplement consumption by grazing ruminants: A review. J. Anim. Sci. 1997, 75, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, T.; Chen, C.; Larsen, M.L.V.; Berckmans, D. Precision livestock farming: Building ‘digital representations’ to bring the animals closer to the farmer. Animal 2019, 13, 3009–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culbertson, M.M. Genetic Selection for Feed Intake and Efficiency in Beef Cattle. Ph.D. Thesis, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, B.R.; Ribas, M.N.; Machado, F.S.; Lima, J.A.M.; Cavalcanti, L.F.L.; Chizzotti, M.L.; Coelho, S.G. Validation of a system for monitoring individual feeding and drinking behaviour and intake in young cattle. Animal 2018, 12, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockwill, C.L.; McAllister, T.A.; Olson, M.E.; Milligan, D.N.; Ralston, B.J.; Huisma, C.; Hand, R.K. Individual intake of mineral and molasses supplements by cows, heifers and calves. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2000, 80, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaz, J.A.; García, S.; González, L.A. Application of in-paddock technologies to monitor individual self-fed supplement intake and liveweight in beef cattle. Animals 2020, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, R.R.; Moffet, C.A.; Horn, G.W.; Zimmerman, S.; Billars, M. TECHNICAL NOTE: Daily variation in intake of a salt-limited supplement by grazing steers. Prof. Anim. Sci. 2017, 33, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, K.L.; Underdahl, S.R.; Undi, M.; Becker, S.; Dahlen, C.R. Utilizing an electronic feeder to measure mineral and energy supplement intake in beef heifers grazing native range. Trans. Anim. Sci. 2019, 3, 1719–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanungkalit, G.; Hegarty, R.S.; Cowley, F.C.; McPhee, M.J. Evaluation of remote monitoring units for estimating body weight and supplement intake of grazing cattle. Animal 2020, 14, s332–s340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.J.; McIvor, J.G.; Jones, P.; Smith, D.R.; Mayer, D.G. Comparison of stocking methods for beef production in northern Australia: Seasonal diet quality and composition. Rangeland J. 2017, 38, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; François, R.; Henry, L.; Müller, K. dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation, 0.8.5. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dplyr (accessed on 7 March 2021).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. lmerTest package: Tests in linear mixed effects models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.R.; Moore, S.T.; Bishop-Hurley, G.J.; Swain, D.L. A sensor-based solution to monitor grazing cattle drinking behaviour and water intake. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 168, 105141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.M.; Anderson, A.; Petherick, J.C. Inclusion of cottonseed meal into loose mineral mix supplements increases the voluntary intake of the supplement by grazing heifers. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2017, 57, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Garcia, L.; Lunadei, L. The role of RFID in agriculture: Applications, limitations and challenges. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2011, 79, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.R.; Fox, D.R.; Bishop-Hurley, G.J.; Swain, D.L. Use of radio frequency identification (RFID) technology to record grazing beef cattle water point use. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 156, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, L.E.; Paterson, J.A.; Clark, R.; Harbac, M.; Kellom, A. Readability of thirteen different radio frequency identification ear tags by three different multi-panel reader systems for use in beef cattle. Prof. Anim. Sci. 2008, 24, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartzkopf-Genswein, K.S.; Huisma, C.; McAllister, T.A. Validation of a radio frequency identification system for monitoring the feeding patterns of feedlot cattle. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1999, 60, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowell, B.F.; Mosley, J.C.; Bowman, J.G.P. Social behavior of grazing beef cattle: Implications for management. J. Anim. Sci. 2000, 77, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, R.M.; Fisher, L.J. Variability in individual animal’s intake of minerals offered free-choice to grazing ruminants. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 1996, 62, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgour, R.J. In pursuit of “normal”: A review of the behaviour of cattle at pasture. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 138, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesley, R.L.; Cibils, A.F.; Mulliniks, J.T.; Pollak, E.R.; Petersen, M.K.; Fredrickson, E.L. An assessment of behavioural syndromes in rangeland-raised beef cattle. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 139, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neave, H.W.; Weary, D.M.; Von Keyserlingk, M.A.G. Individual variability in feeding behaviour of domesticated ruminants. Animal 2018, 12, s419–s430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujović, V.; Maksimović, M. Raspberry Pi as a Wireless Sensor node: Performances and constraints. In Proceedings of the 2014 37th International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 26–30 May 2014; pp. 1013–1018. [Google Scholar]






| Experimental Sites | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bore + Eldons | Bore | Eldons | ||||
| CTS (min) | n-Day 2 | CTS (min) | n-Day 2 | CTS (min) | n-Day 2 | |
| n1 | 133 | 142 | 155 | |||
| Minimum | 4.9 | 4 | 2.2 | 1 | 2.7 | 1 |
| Maximum | 2047.3 | 51 | 1547.4 | 60 | 1675.8 | 50 |
| Median | 201.7 | 27 | 178.2 | 30 | 169.3 | 20 |
| Mean | 323.0 | 25 | 276.8 | 29 | 284.1 | 19 |
| SD | 345.17 | 13.1 | 299.24 | 13.7 | 301.68 | 11.2 |
| Sites | Time Spent at the ASW Units (min/day) 1 | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASW 1 | ASW 2 | ASW 3 | ASW 4 | ASW 5 | ||
| Bore | 10.7 ± 14.9 a | 7.1 ± 14.1 b | 8.7 ± 14.4 c | 6.7 ± 8.7 ad | 3.7 ± 5.5 e | <0.001 |
| Eldons | 28.9 ± 36.7 f | 8.9 ± 12.1 g | 1.6 ± 3.1 h | 4.8 ± 9.2 bi | 0.1 ± 0.1 ij | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simanungkalit, G.; Bremner, G.; Cowley, F.; Barwick, J.; Dawson, B.; Dobos, R.; Hegarty, R. Automatic Supplement Weighing Units for Monitoring the Time of Accessing Mineral Block Supplements by Rangeland Cattle in Northern Queensland, Australia. AgriEngineering 2021, 3, 218-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering3020014
Simanungkalit G, Bremner G, Cowley F, Barwick J, Dawson B, Dobos R, Hegarty R. Automatic Supplement Weighing Units for Monitoring the Time of Accessing Mineral Block Supplements by Rangeland Cattle in Northern Queensland, Australia. AgriEngineering. 2021; 3(2):218-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering3020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimanungkalit, Gamaliel, Graeme Bremner, Frances Cowley, Jamie Barwick, Bradley Dawson, Robin Dobos, and Roger Hegarty. 2021. "Automatic Supplement Weighing Units for Monitoring the Time of Accessing Mineral Block Supplements by Rangeland Cattle in Northern Queensland, Australia" AgriEngineering 3, no. 2: 218-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering3020014
APA StyleSimanungkalit, G., Bremner, G., Cowley, F., Barwick, J., Dawson, B., Dobos, R., & Hegarty, R. (2021). Automatic Supplement Weighing Units for Monitoring the Time of Accessing Mineral Block Supplements by Rangeland Cattle in Northern Queensland, Australia. AgriEngineering, 3(2), 218-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering3020014






