Paraneoplastic Hypereosinophilia Revealing Disseminated Colorectal Signet Ring Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
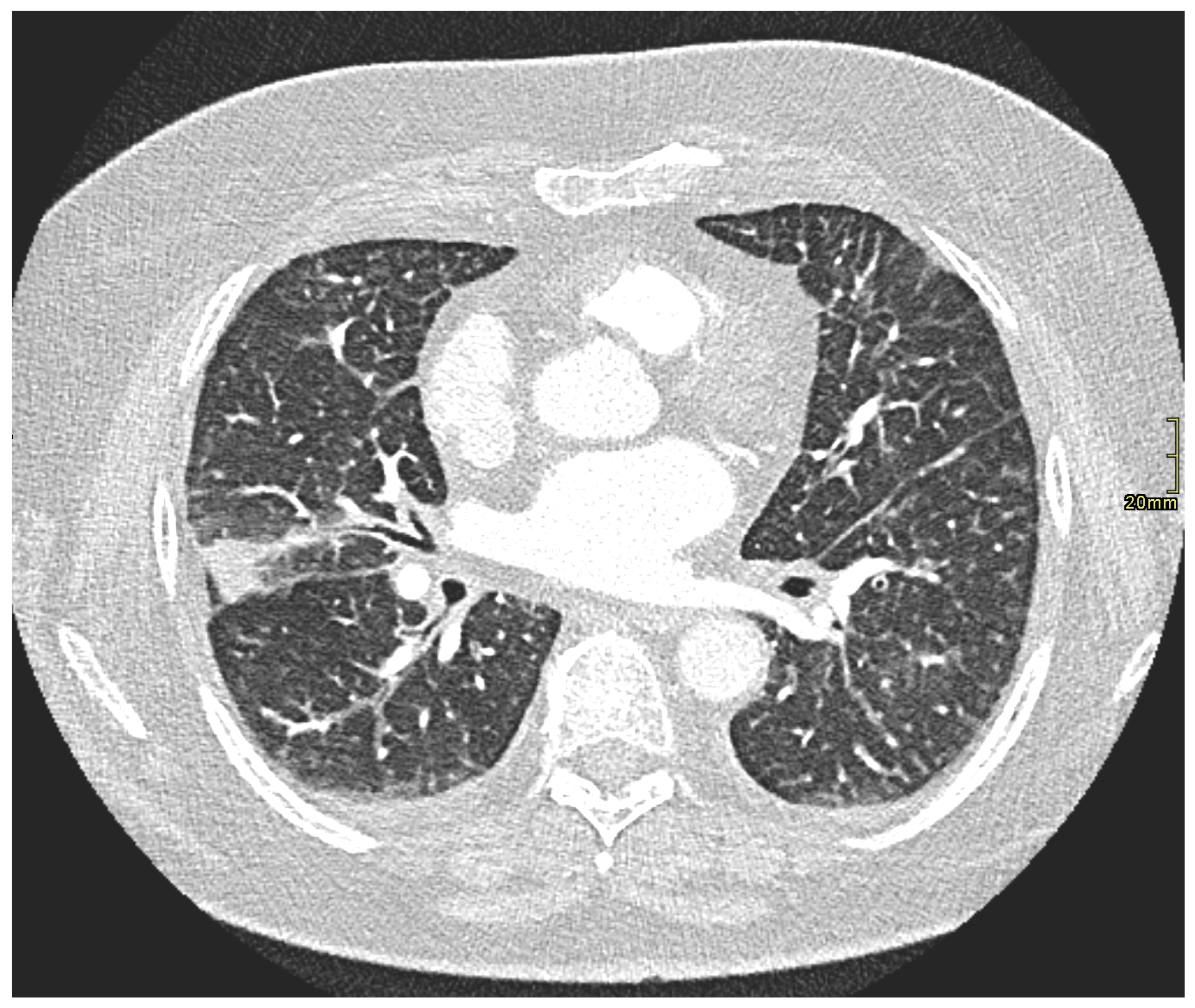
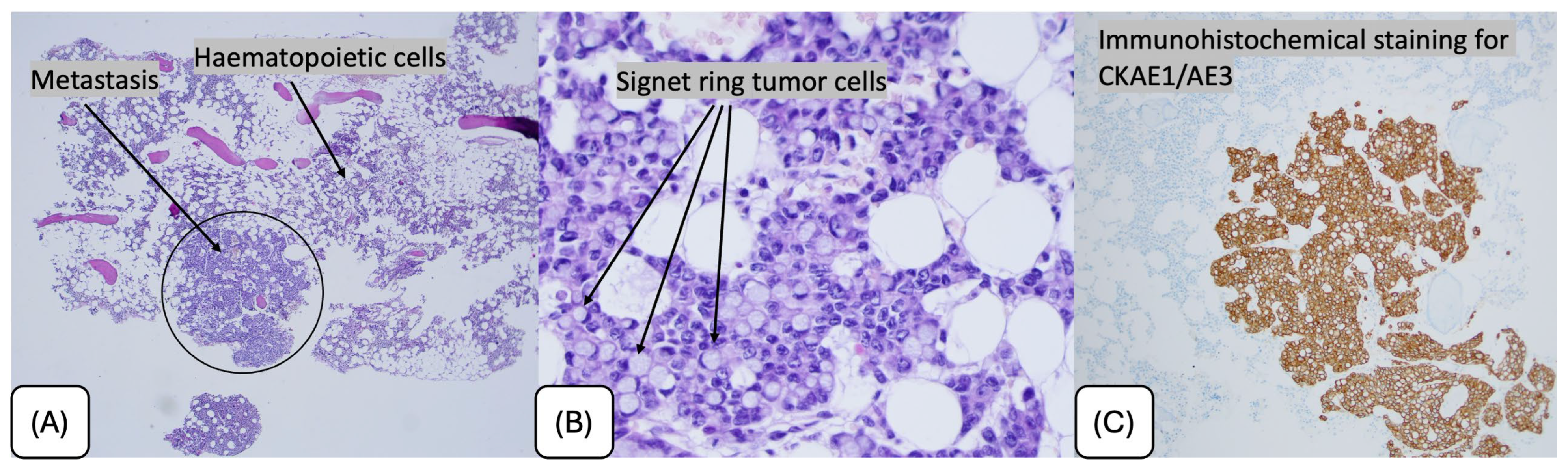
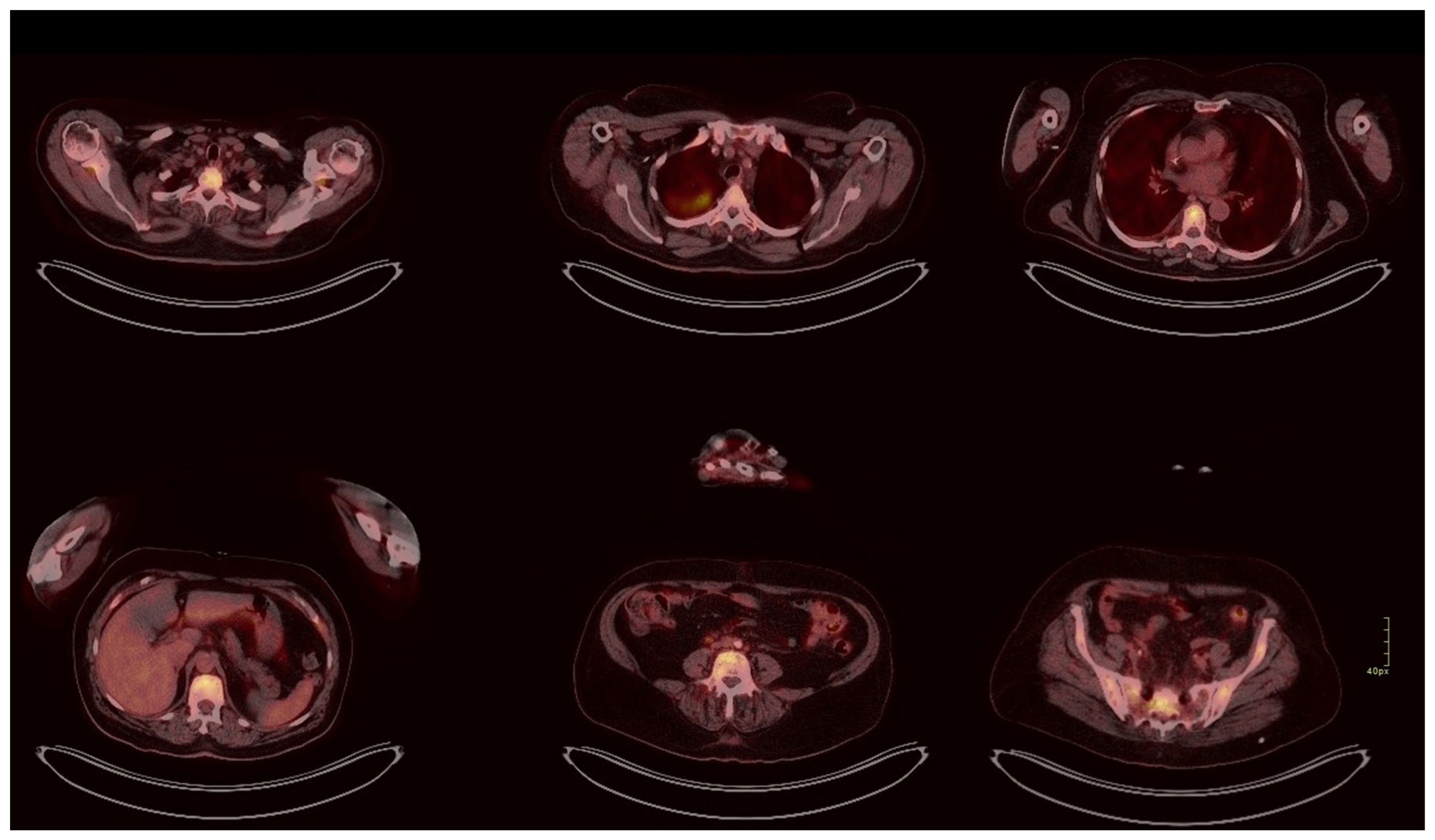
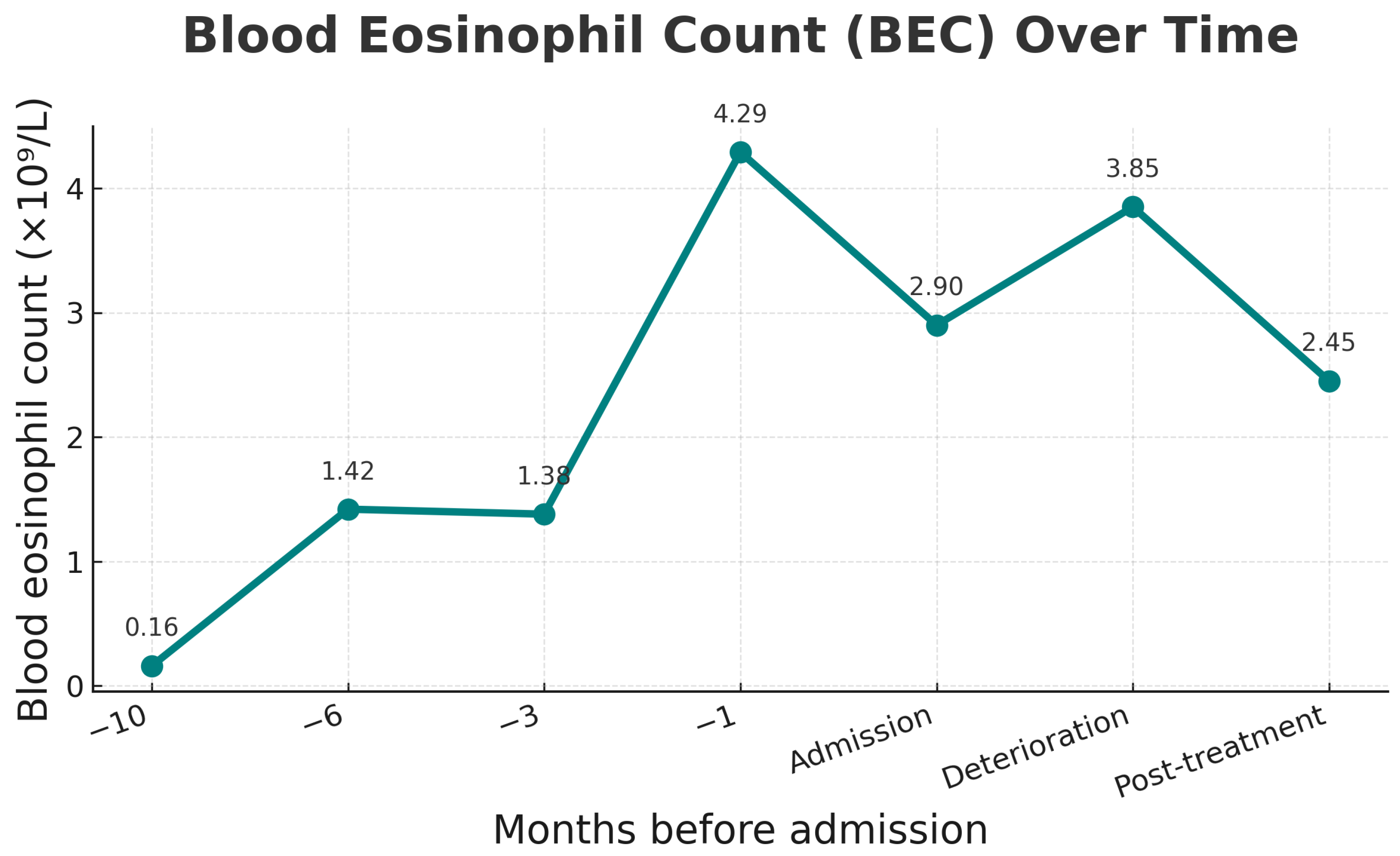
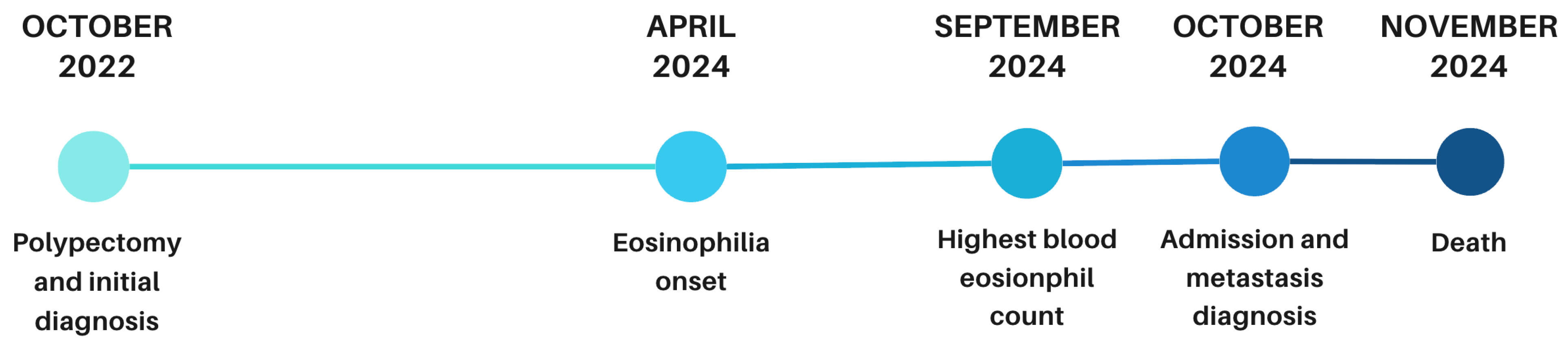
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATS | American Thoracic Society |
| BEC | Blood Eosinophil Count |
| CEA | Carcinoembryonic Antigen |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| ERS | European Respiratory Society |
| FEV1 | Forced expiratory volume in 1st second |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LDH | Lactate Dehydrogenase |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal pro–B-type Natriuretic Peptide |
| PCT | Procalcitonin |
| PET/CT | Positron Emission Tomography–Computed Tomography |
| SRCC | Signet Ring Cell Carcinoma |
References
- Shomali, W.; Gotlib, J. World Health Organization and International Consensus Classification of Eosinophilic Disorders: 2024 Update on Diagnosis, Risk Stratification, and Management. Am. J. Hematol. 2024, 99, 946–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, A.; Ozawa, H.; Oki, M.; Yanagi, H.; Nabeshima, K.; Nakamura, N. Helicobacter pylori-Negative Advanced Gastric Cancer with Massive Eosinophilia. Intern. Med. 2018, 57, 1715–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Arora, R.; Das, P.; Singh, M.K. Deeply Eosinophilic Cell Variant of Signet-Ring Type of Gastric Carcinoma: A Diagnostic Dilemma. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 13, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, T.; George, R.; Rodriguez-Bigas, M.; Petrelli, N.J. Primary Signet-Ring Cell Carcinoma of the Colon and Rectum. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 1996, 3, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitsche, U.; Zimmermann, A.; Späth, C.; Müller, T.; Maak, M.; Schuster, T.; Slotta-Huspenina, J.; Käser, S.A.; Michalski, C.W.; Janssen, K.P.; et al. Mucinous and Signet-Ring Cell Colorectal Cancers Differ from Classical Adenocarcinomas in Tumor Biology and Prognosis. Ann. Surg. 2013, 258, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalewska, E.; Obołończyk, Ł.; Sworczak, K. Hypereosinophilia in Solid Tumors—Case Report and Clinical Review. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 639395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciesielski, W.; Kupryś-Lipińska, I.; Kumor-Kisielewska, A.; Grząsiak, O.; Borodacz, J.; Niedźwiecki, S.; Hogendorf, P.; Durczyński, A.; Strzelczyk, J.; Majos, A. Peripheral Eosinophil Count May Be the Prognostic Factor for Overall Survival in Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Undergoing Surgical Treatment. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.; Saha, A.; Kuykendall, A.; Zhang, L. Clinical and Therapeutic Intervention of Hypereosinophilia in the Era of Molecular Diagnosis. Cancers 2024, 16, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Sui, P.; Han, B. Gastric Signet-Ring Cell Carcinoma with Paraneoplastic Eosinophilia: A Case Report and Literature Review. Oncol. Transl. Med. 2022, 8, 264–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.W.; Cho, M.Y.; Park, C. Expression of Eosinophil Chemotactic Factors in Stomach Cancer. Yonsei Med. J. 1999, 40, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffari, S.; Rezaei, N. Eosinophils in the Tumor Microenvironment: Implications for Cancer Immunotherapy. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, N.; Hu, W.; Ge, H.; Xie, S.; Ding, C. Tumor-Associated Eosinophilia in a Patient with EGFR-Positive, MET-Amplified Lung Adenocarcinoma Refractory to Targeted Therapy: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 4988–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ream, S.; Natarajan, P.; Gupta, S.; Sotelo-Rafiq, E.; Schuller, D. Paraneoplastic Hypereosinophilia in Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Lung. Cureus 2023, 15, e34386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Wang, S.; Zhong, K.; Xu, F.; Huang, L.; Chen, W.; Cheng, P. Tumor-Associated Tissue Eosinophilia Predicts Favorable Clinical Outcome in Solid Tumors: A Meta-Analysis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.M.; Russeth, T.E.; Thati, N. Hypereosinophilia as a Presenting Sign of Advanced Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Rare, Severe Presentation. BMJ Case Rep. 2023, 16, e256235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rink, S.; Škrgat, S.; Harlander, M.; Mlakar, P. Paraneoplastic Hypereosinophilia Revealing Disseminated Colorectal Signet Ring Cell Carcinoma. Gastrointest. Disord. 2025, 7, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7040074
Rink S, Škrgat S, Harlander M, Mlakar P. Paraneoplastic Hypereosinophilia Revealing Disseminated Colorectal Signet Ring Cell Carcinoma. Gastrointestinal Disorders. 2025; 7(4):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7040074
Chicago/Turabian StyleRink, Saša, Sabina Škrgat, Matevž Harlander, and Polona Mlakar. 2025. "Paraneoplastic Hypereosinophilia Revealing Disseminated Colorectal Signet Ring Cell Carcinoma" Gastrointestinal Disorders 7, no. 4: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7040074
APA StyleRink, S., Škrgat, S., Harlander, M., & Mlakar, P. (2025). Paraneoplastic Hypereosinophilia Revealing Disseminated Colorectal Signet Ring Cell Carcinoma. Gastrointestinal Disorders, 7(4), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7040074





