Risk-Based Decision Making: A Systematic Scoping Review of Animal Models and a Pilot Study on the Effects of Sleep Deprivation in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Systematic Scoping Review
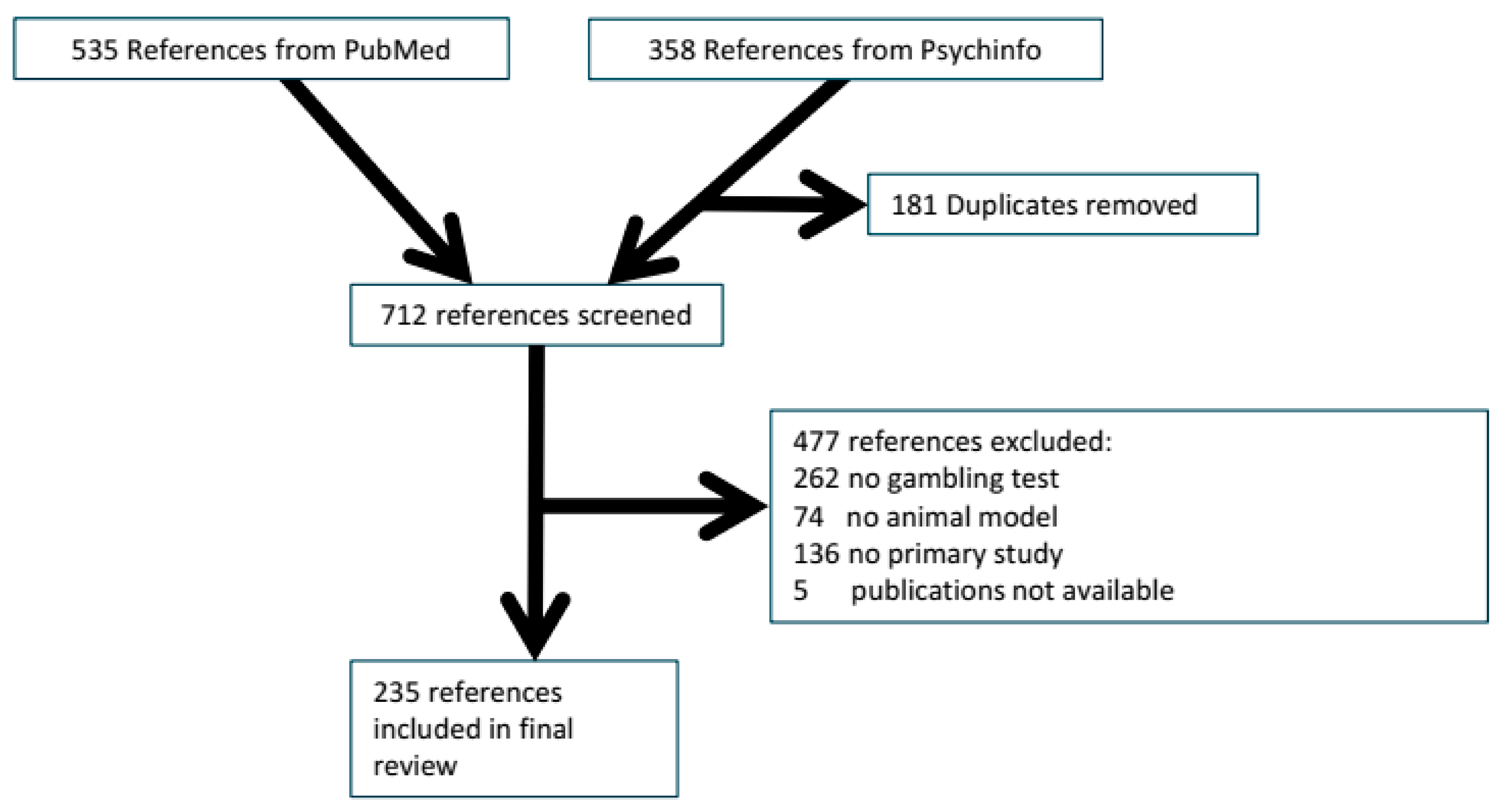
2.1.1. Reference Flow
2.1.2. Narrative Summary of Animal Models for Risk-Based Decision Making
Probability Discounting
Animal Versions of the Iowa Gambling Task
The Balloon Analogue Risk Task
Internal and External Validity of Animal Risk-Based Decision Making Tasks
2.2. Pilot Experiment
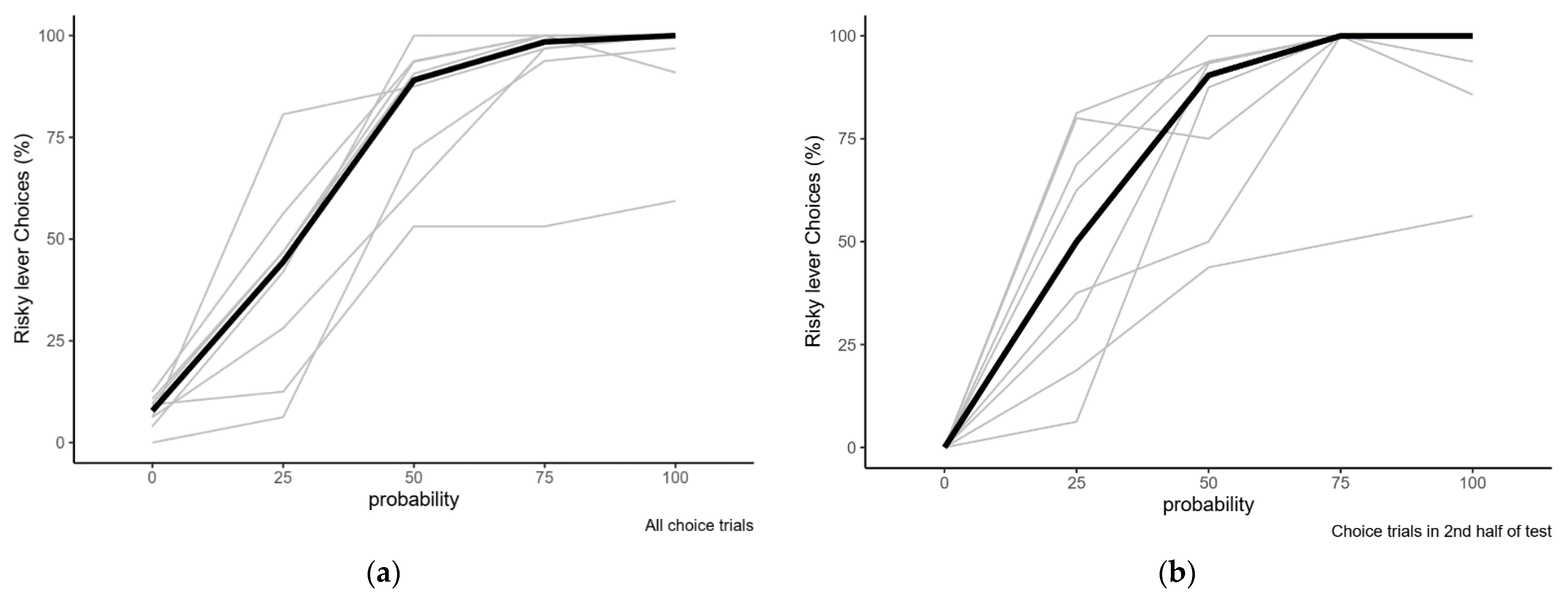
2.2.1. Variation in Risk Preference with Varying Reward Probabilities
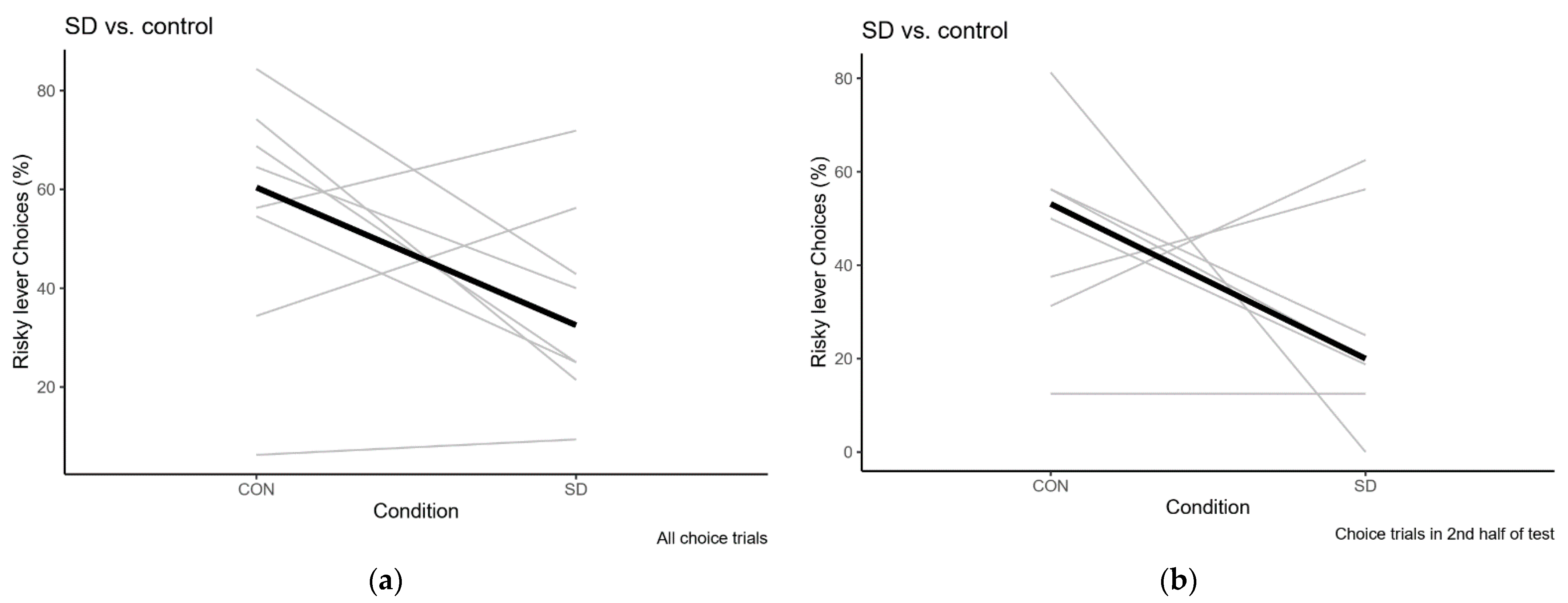
2.2.2. Sleep Deprivation
Sleep Deprivation Compared to Control Condition
Sleep Deprivation Compared to Baseline
2.2.3. Control Condition
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Systematic Scoping Review
4.2. Pilot Experiment
4.2.1. Animals and Husbandry
4.2.2. General Behavioural Test Procedures
4.2.3. Training
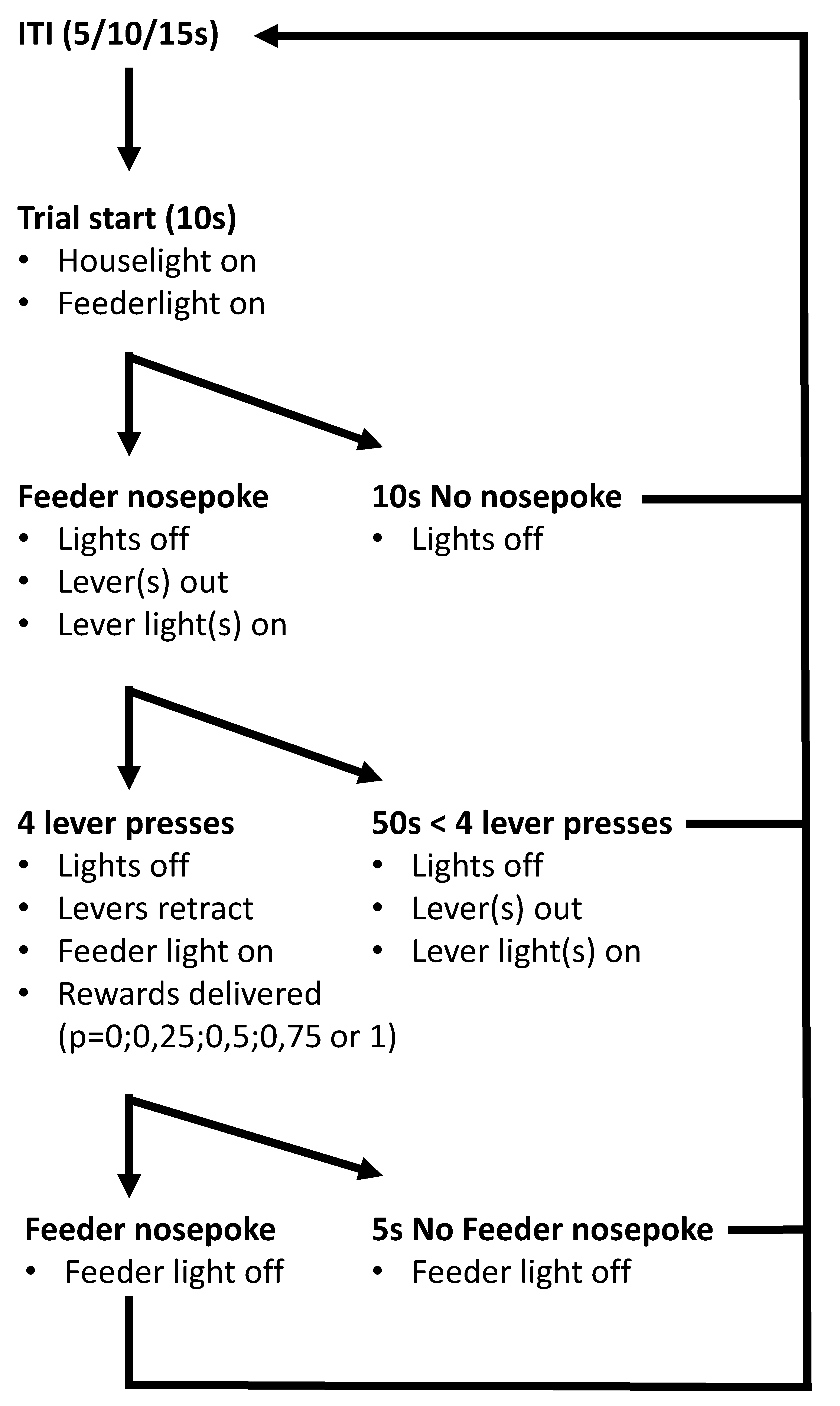
4.2.4. Probability Discounting Choice Task
4.2.5. Risk Preference at Different Probability Levels
4.2.6. Sleep Deprivation
4.2.7. Experimental Design
4.2.8. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BART | Balloon Analog Risk Task |
| FR | Fixed Ratio |
| IGT | Iowa Gambling Task |
| ITI | InterTrial Interval |
| NHP | Non-Human Primate |
| NP | NosePoke |
| SDD | Sleep Deprivation Device |
| VR | Variable Ratio |
References
- Mowinckel, A.M.; Pedersen, M.L.; Eilertsen, E.; Biele, G. A meta-analysis of decision-making and attention in adults with ADHD. J. Atten. Disord. 2015, 19, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paulus, M.P. Decision-making dysfunctions in psychiatry—Altered homeostatic processing? Science 2007, 318, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahman, S.; Sahakian, B.J.; Cardinal, R.N.; Rogers, R.; Robbins, T. Decision making and neuropsychiatry. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2001, 5, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, J.R. Examining the neurochemical underpinnings of animal models of risky choice: Methodological and analytic considerations. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 27, 178–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, K.; Hook, R.; Wickham, K.; Grant, J.E.; Chamberlain, S.R. Impulsivity in Gambling Disorder and problem gambling: A meta-analysis. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 44, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyonka, E.G.E.; Schutte, N.S. Probability discounting and gambling: A meta-analysis. Addiction 2018, 113, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, T.W.; McMullin, S.D.; Mulhauser, K.; Weinstock, J.; Weller, J.A. Diurnal cortisol and decision making under risk in problem gambling. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2020, 34, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kraplin, A.; Dshemuchadse, M.; Behrendt, S.; Scherbaum, S.; Goschke, T.; Buhringer, G. Dysfunctional decision-making in pathological gambling: Pattern specificity and the role of impulsivity. Psychiatry Res. 2014, 215, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, P.; Chen, T.; Su, H.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, M. Risky decision-making in individuals with substance use disorder: A meta-analysis and meta-regression review. Psychopharmacology 2020, 237, 1893–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, B.S.; Dickinson, D.L.; Orff, H.J.; Drummond, S.P. The effects of one night of sleep deprivation on known-risk and ambiguous-risk decisions. J. Sleep Res. 2007, 16, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, J.F.; McNeil, J.; Doucet, E.; Forest, G. The association between REM sleep and decision-making: Supporting evidences. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 225, 113109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killgore, W.D.; Balkin, T.J.; Wesensten, N.J. Impaired decision making following 49 h of sleep deprivation. J. Sleep Res. 2006, 15, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.R.; Liu, Y.R.; Fan, D.Q.; Lei, X.; Liu, Q.Y.; Yu, J. Deciphering Age Differences in Experience-Based Decision-Making: The Role of Sleep. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2020, 12, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salfi, F.; Lauriola, M.; Tempesta, D.; Calanna, P.; Socci, V.; De Gennaro, L.; Ferrara, M. Effects of Total and Partial Sleep Deprivation on Reflection Impulsivity and Risk-Taking in Deliberative Decision-Making. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2020, 12, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, M.A.; Weber, N. Sleep duration and risk-taking in adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 41, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Millar, B.M.; Parsons, J.T.; Redline, S.; Duncan, D.T. What’s Sleep Got to Do with It?: Sleep Health and Sexual Risk-Taking Among Men Who have Sex with Men. AIDS Behav. 2019, 23, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusnac, N.; Spitzenstetter, F.; Tassi, P. Chronic sleep loss and risk-taking behavior: Does the origin of sleep loss matter? Behav. Sleep Med. 2019, 17, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Meth. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leenaars, C.; Tsaioun, K.; Stafleu, F.; Rooney, K.; Meijboom, F.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Bleich, A. Reviewing the animal literature: How to describe and choose between different types of literature reviews. Lab. Anim. 2020, 0023677220968599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonder Haar, C. Challenges and opportunities in animal models of gambling-like behavior. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2020, 31, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselme, P. Dopamine, motivation, and the evolutionary significance of gambling-like behaviour. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 256, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, M.R.; Simpson, E.H.; Balsam, P.D. Neural substrates underlying effort, time, and risk-based decision making in motivated behavior. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2016, 133, 233–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrus, M.M.; Winstanley, C.A. Preclinical models and neurocircuitry of gambling and impulsive behavior. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2017, 13, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeland, C.M.; Knes, A.S.; Robinson, M.J.F. Translating concepts of risk and loss in rodent models of gambling and the limitations for clinical applications. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2020, 31, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persons, A.L.; Tedford, S.E.; Celeste, T. Mirtazapine and ketanserin alter preference for gambling-like schedules of reinforcement in rats. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 77, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farashahi, S.; Azab, H.; Hayden, B.; Soltani, A. On the Flexibility of Basic Risk Attitudes in Monkeys. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 4383–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishii, H.; Onodera, M.; Ohara, S.; Tsutsui, K.I.; Iijima, T. Sex Differences in Risk Preference and c-Fos Expression in Paraventricular Thalamic Nucleus of Rats During Gambling Task. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, M.; Takatsuru, S.; Saeki, D. Choice between constant and variable alternatives by rats: Effects of different reinforcer amounts and energy budgets. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 2000, 73, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leblond, M.; Fan, D.; Brynildsen, J.K.; Yin, H.H. Motivational state and reward content determine choice behavior under risk in mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parker, J.G.; Wanat, M.J.; Soden, M.E.; Ahmad, K.; Zweifel, L.S.; Bamford, N.S.; Palmiter, R.D. Attenuating GABA(A) receptor signaling in dopamine neurons selectively enhances reward learning and alters risk preference in mice. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 17103–17112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, J.; Monteiro, T.; Vasconcelos, M.; Kacelnik, A. Cognitive mechanisms of risky choice: Is there an evaluation cost? Behav. Process. 2012, 89, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, M.S.; Schuck-Paim, C.; Kacelnik, A. Risk sensitivity for amounts of and delay to rewards: Adaptation for uncertainty or by-product of reward rate maximising? Behav. Process. 2012, 89, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafir, S.; Reich, T.; Tsur, E.; Erev, I.; Lotem, A. Perceptual accuracy and conflicting effects of certainty on risk-taking behaviour. Nature 2008, 453, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drezner-Levy, T.; Shafir, S. Parameters of variable reward distributions that affect risk sensitivity of honey bees. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, E.; Kraak, L.; van den Broek, J.; Nordquist, R.E.; van der Staay, F.J. Decision-making under risk and ambiguity in low-birth-weight pigs. Anim. Cogn. 2015, 18, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onge, J.R.; Ahn, S.; Phillips, A.G.; Floresco, S.B. Dynamic fluctuations in dopamine efflux in the prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens during risk-based decision making. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 16880–16891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haun, D.B.; Nawroth, C.; Call, J. Great apes’ risk-taking strategies in a decision making task. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayden, B.Y.; Heilbronner, S.R.; Nair, A.C.; Platt, M.L. Cognitive influences on risk-seeking by rhesus macaques. Judgm. Decis. Mak. 2008, 3, 389–395. [Google Scholar]
- Morgado, P.; Marques, F.; Silva, M.B.; Sousa, N.; Cerqueira, J.J. A novel risk-based decision-making paradigm. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pele, M.; Broihanne, M.; Thierry, B.; Call, J.; Dufour, V. To bet or not to bet? Decision-making under risk in non-human primates. J. Risk Uncertain. 2014, 49, 141–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, A.G.; Hare, B. Chimpanzees and bonobos exhibit emotional responses to decision outcomes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimp, K.G.; Mitchell, M.R.; Beas, B.; Bizon, J.L.; Setlow, B. Affective and cognitive mechanisms of risky decision making. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2015, 117, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Constantinople, C.M.; Piet, A.T.; Brody, C.D. An Analysis of Decision under Risk in Rats. Curr. Biol. CB 2019, 29, 2066–2074.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riviere, J.; Stomp, M.; Augustin, E.; Lemasson, A.; Blois-Heulin, C. Decision-making under risk of gain in young children and mangabey monkeys. Dev. Psychobiol. 2018, 60, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zentall, T.R.; Andrews, D.M.; Case, J.P. Prior commitment: Its effect on suboptimal choice in a gambling-like task. Behav. Process. 2017, 145, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, A.; Damasio, H.; Tranel, D.; Damasio, A.R. Deciding advantageously before knowing the advantageous strategy. Science 1997, 275, 1293–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bechara, A.; Damasio, A.R.; Damasio, H.; Anderson, S.W. Insensitivity to future consequences following damage to human prefrontal cortex. Cognition 1994, 50, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bos, R.; Lasthuis, W.; den Heijer, E.; van der Harst, J.; Spruijt, B. Toward a rodent model of the Iowa gambling task. Behav. Res. Methods 2006, 38, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Visser, L.; Homberg, J.R.; Mitsogiannis, M.; Zeeb, F.D.; Rivalan, M.; Fitoussi, A.; Galhardo, V.; van den Bos, R.; Winstanley, C.A.; Dellu-Hagedorn, F. Rodent versions of the iowa gambling task: Opportunities and challenges for the understanding of decision-making. Front. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Staay, F.; van Zutphen, J.A.; de Ridder, M.M.; Nordquist, R.E. Effects of environmental enrichment on decision-making behavior in pigs. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2017, 194, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laude, J.R.; Pattison, K.F.; Zentall, T.R. Hungry pigeons make suboptimal choices, less hungry pigeons do not. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2012, 19, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strait, C.E.; Hayden, B.Y. Preference patterns for skewed gambles in rhesus monkeys. Biol. Lett. 2013, 9, 20130902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilbronner, S.R.; Hayden, B.Y. The description-experience gap in risky choice in nonhuman primates. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2016, 23, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.S.; Madden, G.J.; Brewer, A.T.; Pinkston, J.W.; Fowler, S.C. Effects of acute pramipexole on preference for gambling-like schedules of reinforcement in rats. Psychopharmacology 2011, 213, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goldshmidt, J.N. Risk taking and resource scarcity: An integrative approach to foraging problems. Diss. Abstr. Int. Sect. B Sci. Eng. 1998, 58, 4431. [Google Scholar]
- Lauriola, M.; Panno, A.; Levin, I.P.; Lejuez, C.W. Individual Differences in Risky Decision Making: A Meta-analysis of Sensation Seeking and Impulsivity with the Balloon Analogue Risk Task. J. Behav. Dec. Mak. 2014, 27, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Vyas, A. Toxoplasma gondii infection and testosterone congruently increase tolerance of male rats for risk of reward forfeiture. Horm. Behav. 2016, 79, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblond, M.; Sukharnikova, T.; Yu, C.; Rossi, M.A.; Yin, H.H. The role of pedunculopontine nucleus in choice behavior under risk. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 39, 1664–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozga-Hess, J.E.; Anderson, K.G. Differential effects of d-amphetamine and atomoxetine on risk-based decision making of Lewis and Fischer 344 rats. Behav. Pharmacol. 2019, 30, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdue, B.M.; Brown, E.R. Irrational choice behavior in human and nonhuman primates. Anim. Cogn. 2018, 21, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludvig, E.A.; Madan, C.R.; Pisklak, J.M.; Spetch, M.L. Reward context determines risky choice in pigeons and humans. Biol. Lett. 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDevitt, M.A.; Diller, J.W.; Pietrzykowski, M.O. Human and pigeon suboptimal choice. Learn. Behav. 2019, 47, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Enkhuizen, J.; Henry, B.L.; Minassian, A.; Perry, W.; Milienne-Petiot, M.; Higa, K.K.; Geyer, M.A.; Young, J.W. Reduced dopamine transporter functioning induces high-reward risk-preference consistent with bipolar disorder. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 39, 3112–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselme, P. Does reward unpredictability reflect risk? Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 280, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.H.; Cheng, C.P.; Liao, R.M. Effects of d-amphetamine on risk choice in rats depend on the manner in which the expected reward value is varied. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2018, 171, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, W.R.; Lak, A.; Bossaerts, P.; Schultz, W. Economic choices reveal probability distortion in macaque monkeys. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 3146–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tryon, V. Investigating the Contributions of Hippocampal Memory and Reward Valuation Systems to Cost-Benefit Decision Making. Diss. Abstr. Int. Sect. B Sci. Eng. 2018, 79. Available online: https://digital.lib.washington.edu/researchworks/handle/1773/40291 (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Tryon, V.L.; Penner, M.R.; Heide, S.W.; King, H.O.; Larkin, J.; Mizumori, S.J.Y. Hippocampal neural activity reflects the economy of choices during goaldirected navigation. Hippocampus 2017, 27, 743–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenaars, C.H.; Pels, E.G.M.; Joosten, R.N.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M. Wistar rats do not show preference for either of two commonly used nutritionally sound food rewards in a T-maze. J. Vet. Behav. 2019, 32, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbrook, S.R.; Hankosky, E.R.; Dwyer, M.R.; Gulley, J.M. Age and sex differences in behavioral flexibility, sensitivity to reward value, and risky decision-making. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 132, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoratto, F.; Laviola, G.; Adriani, W. The subjective value of probabilistic outcomes: Impact of reward magnitude on choice with uncertain rewards in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 617, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittaras, E.; Callebert, J.; Dorey, R.; Chennaoui, M.; Granon, S.; Rabat, A. Mouse Gambling Task reveals differential effects of acute sleep debt on decision-making and associated neurochemical changes. Sleep 2018, 41, zsy168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acheson, A.; Richards, J.B.; de Wit, H. Effects of sleep deprivation on impulsive behaviors in men and women. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 91, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killgore, W.D.; Grugle, N.L.; Balkin, T.J. Gambling when sleep deprived: Don’t bet on stimulants. Chronobiol. Int. 2012, 29, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menz, M.M.; Buchel, C.; Peters, J. Sleep deprivation is associated with attenuated parametric valuation and control signals in the midbrain during value-based decision making. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 6937–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkatraman, V.; Chuah, Y.M.; Huettel, S.A.; Chee, M.W. Sleep deprivation elevates expectation of gains and attenuates response to losses following risky decisions. Sleep 2007, 30, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maric, A.; Montvai, E.; Werth, E.; Storz, M.; Leemann, J.; Weissengruber, S.; Ruff, C.C.; Huber, R.; Poryazova, R.; Baumann, C.R. Insufficient sleep: Enhanced risk-seeking relates to low local sleep intensity. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Vries, R.B.; Hooijmans, C.R.; Tillema, A.; Leenaars, M.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M. Updated version of the Embase search filter for animal studies. Lab. Anim. 2014, 48, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hooijmans, C.R.; Tillema, A.; Leenaars, M.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M. Enhancing search efficiency by means of a search filter for finding all studies on animal experimentation in PubMed. Lab. Anim. 2010, 44, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hart, E.E.; Izquierdo, A. Quantity versus quality: Convergent findings in effort-based choice tasks. Behav. Process. 2019, 164, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, A.I.; Malhotra, G. Mechanistic models must link the field and the lab. Behav. Brain Sci. 2019, 42, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, A.; Minamimoto, T. Trait and State-Dependent Risk Attitude of Monkeys Measured in a Single-Option Response Task. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hart, E.E.; Gerson, J.O.; Izquierdo, A. Persistent effect of withdrawal from intravenous methamphetamine self-administration on brain activation and behavioral economic indices involving an effort cost. Neuropharmacology 2018, 140, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellberg, S.N.; Levit, J.D.; Robinson, M.J.F. Under the influence: Effects of adolescent ethanol exposure and anxiety on motivation for uncertain gambling-like cues in male and female rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 337, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.J.F.; Clibanoff, C.; Freeland, C.M.; Knes, A.S.; Cote, J.R.; Russell, T.I. Distinguishing between predictive and incentive value of uncertain gambling-like cues in a Pavlovian autoshaping task. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 371, 111971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsenbardt, D.N.; Smoker, M.P.; Janetsian-Fritz, S.S.; Lapish, C.C. Impulsivity in rodents with a genetic predisposition for excessive alcohol consumption is associated with a lack of a prospective strategy. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 17, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, N.A.; McGhee, K.E. Boldness is affected by recent experience with predation cues and body size in mosquitofish. Behav. Process. 2019, 164, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, A.O.; Hofmann, G.; Mettke-Hofmann, C. Gouldian finches are followers with black-headed females taking the lead. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.H.; Martens, K.M.; Bashir, A.; Cheung, H.; Stukas, S.; Gibbs, E.; Namjoshi, D.R.; Button, E.B.; Wilkinson, A.; Barron, C.J.; et al. CHIMERA repetitive mild traumatic brain injury induces chronic behavioural and neuropathological phenotypes in wild-type and APP/PS1 mice. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2019, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faure, A.; Zoratto, F.; Chirico, D.; Romano, E.; Mancinelli, R.; Saso, L.; Callebert, J.; Laviola, G.; Granon, S.; Adriani, W. Reduced adolescent risk-assessment and lower nicotinic beta-2 expression in rats exposed to nicotine through lactation by forcedly drinking dams. Neuroscience 2019, 413, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Villegas, P.; Rodriguez, V.M.; Giordano, M.; Juarez, J. Risk-taking, locomotor activity and dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens and medial prefrontal cortex in male rats treated prenatally with alcohol. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2017, 153, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, M.A.; Ardid, D.; Henrie, J.A.; Tamashiro, K.; Blanchard, D.C.; Blanchard, R.J. Amygdala lesions produce analgesia in a novel, ethologically relevant acute pain test. Physiol. Behav. 1999, 67, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcutt, S.E.; Proctor, D.; Berman, S.M.; de Waal, F.B.M. Chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) Are More Averse to Social Than Nonsocial Risk. Psychol. Sci. 2019, 30, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubner, C.; Czaczkes, T.J. Risk preference during collective decision making: Ant colonies make risk-indifferent collective choices. Anim. Behav. 2017, 132, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nentwig, T.B.; Starr, E.M.; Chandler, L.J.; Glover, E.J. Absence of compulsive drinking phenotype in adult male rats exposed to ethanol in a binge-like pattern during adolescence. Alcohol (Fayetteville N.Y.) 2019, 79, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocker, P.J.; Hosking, J.G.; Murch, W.S.; Clark, L.; Winstanley, C.A. Activation of dopamine D4 receptors within the anterior cingulate cortex enhances the erroneous expectation of reward on a rat slot machine task. Neuropharmacology 2016, 105, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocker, P.J.; Lin, M.Y.; Barrus, M.M.; Le Foll, B.; Winstanley, C.A. The agranular and granular insula differentially contribute to gambling-like behavior on a rat slot machine task: Effects of inactivation and local infusion of a dopamine D4 agonist on reward expectancy. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 3135–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafa, D.; Kregiel, J.; Popik, P.; Rygula, R. Effects of optimism on gambling in the rat slot machine task. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 300, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islas-Preciado, D.; Wainwright, S.R.; Sniegocki, J.; Lieblich, S.E.; Yagi, S.; Floresco, S.B.; Galea, L.A.M. Risk-based decision making in rats: Modulation by sex and amphetamine. Horm. Behav. 2020, 125, 104815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, C.A.; Willis, M.L.; Gilbert, R.J.; Bizon, J.L.; Setlow, B. Sex differences in a rat model of risky decision making. Behav. Neurosci. 2016, 130, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinal, R.N.; Howes, N.J. Effects of lesions of the nucleus accumbens core on choice between small certain rewards and large uncertain rewards in rats. BMC Neurosci. 2005, 6, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Leenaars, C.H.; Dematteis, M.; Joosten, R.N.; Eggels, L.; Sandberg, H.; Schirris, M.; Feenstra, M.G.; Van Someren, E.J. A new automated method for rat sleep deprivation with minimal confounding effects on corticosterone and locomotor activity. J. Neurosci. Methods 2011, 196, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R_Core_Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Bryan, J. readxl: Read Excel Files. R Package Version 1.3.1. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=readxl (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Wickham, H.; François, R.; Henry, L.; Müller, K. dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation. R Package Version 0.8.5. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dplyr (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]



| Task Category | Animal Species Tested | Brief Description | Comparable Tests in Humans |
|---|---|---|---|
| Probability Discounting (PD) | Rats, NHPs, Pigeons, Mice, Starlings, Bees, Pigs. | Choices between safe and risky options. | Human PD tests; tests with safe and risky options. |
| Iowa Gambling Task (IGT) | Rats, Mice, Pigs, Pigeons, Macaques. | Repetitive choices between options that are on average advantageous or disadvantageous, with a risk for loss/punishment at each option. | Human IGT, picking cards that will result in gains or losses from 4 card decks. Two decks are on average advantageous, the others are on average disadvantageous. |
| Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART) | Rats. | Pressing on one of two levers increases the size of a reward, but at a risk of losing everything. Pressing the other lever results in receiving the build-up reward. | Human BART; pressing a button to inflate a virtual balloon at the risk of popping it, or another button to cash out a reward proportional to the balloon size. |
| Probability of Reward at Risky Lever | Overall % Risky Choice | Risky Choices in 2nd Half of Session |
|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 7.8 (0–12.5) | 0 (0–0) |
| 0.25 | 44.4 (6.3–80.6) | 50 (6.3–81.3) |
| 0.50 | 89.1 (53.1–100) | 90.4 (43.8–100) |
| 0.75 | 98.4 (53.1–100) | 100 (50–100) |
| 1.00 | 100 (59.4–100) | 100 (56.3–100) |
| Test | Overall % Risky Choice | Risky Choices in 2nd Half of Session |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 62.5 (6.3–93.8) | 62.5 (6.3–93.8) |
| Sleep Deprivation | 32.5 (9.4–71.9) | 20 (0–62.5) |
| Recovery | 62.5 (6.3–87.1) | 46.9 (6.3–86.7) |
| Test | Overall % Risky Choice | Risky Choices in 2nd Half of Session |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 44.4 (9.4–80.6) | 46.9 (6.3–80) |
| Control housing in SDDs | 60.4 (6.3–84.4) | 53.1 (12.5–81.3) |
| Recovery | 46.9 (28.1–84.4) | 50 (37.5–75) |
| Database | Last Update | Risk Task Search String |
|---|---|---|
| PubMed (legacy) | 6 August 2020 | ((risk taking [mesh] OR risk taking [tiab] OR risk preference [tiab] OR risk-based [tiab] OR risk tolerance [tiab]) AND (decision making [mesh] OR decision making [tiab])) OR (choice behavior [majr] AND risk [tiab]) |
| Psychinfo | 10 August 2020 | ((Risk taking/OR gambling/OR (risk taking OR risk preference OR risk-based OR risk tolerance).mp.) AND ((decision making/OR decision making.mp.) OR (choice behavior/AND risk.mp.))) |
| Phase | Task | Session Length | FR | # Sessions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autoshaping | Press lever | 60 min or 64 trials | 1 | 5–8 |
| Progressive ratio | Press lever at FR | 64 trials | 1–4 | 1 |
| Trial initiation | NP for trial start | 64 trials | 4 | 7 |
| Stable risk preference | Final task | 96 trials | 4 | 38 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leenaars, C.H.C.; Van der Mierden, S.; Joosten, R.N.J.M.A.; Van der Weide, M.A.; Schirris, M.; Dematteis, M.; Meijboom, F.L.B.; Feenstra, M.G.P.; Bleich, A. Risk-Based Decision Making: A Systematic Scoping Review of Animal Models and a Pilot Study on the Effects of Sleep Deprivation in Rats. Clocks & Sleep 2021, 3, 31-52. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep3010003
Leenaars CHC, Van der Mierden S, Joosten RNJMA, Van der Weide MA, Schirris M, Dematteis M, Meijboom FLB, Feenstra MGP, Bleich A. Risk-Based Decision Making: A Systematic Scoping Review of Animal Models and a Pilot Study on the Effects of Sleep Deprivation in Rats. Clocks & Sleep. 2021; 3(1):31-52. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep3010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeenaars, Cathalijn H.C., Stevie Van der Mierden, Ruud N.J.M.A. Joosten, Marnix A. Van der Weide, Mischa Schirris, Maurice Dematteis, Franck L.B. Meijboom, Matthijs G.P. Feenstra, and André Bleich. 2021. "Risk-Based Decision Making: A Systematic Scoping Review of Animal Models and a Pilot Study on the Effects of Sleep Deprivation in Rats" Clocks & Sleep 3, no. 1: 31-52. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep3010003
APA StyleLeenaars, C. H. C., Van der Mierden, S., Joosten, R. N. J. M. A., Van der Weide, M. A., Schirris, M., Dematteis, M., Meijboom, F. L. B., Feenstra, M. G. P., & Bleich, A. (2021). Risk-Based Decision Making: A Systematic Scoping Review of Animal Models and a Pilot Study on the Effects of Sleep Deprivation in Rats. Clocks & Sleep, 3(1), 31-52. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep3010003





