The Effect of 12 Hour Shifts, Time of Day, and Sleepiness on Emotional Empathy and Burnout in Medical Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Descriptive Statistics
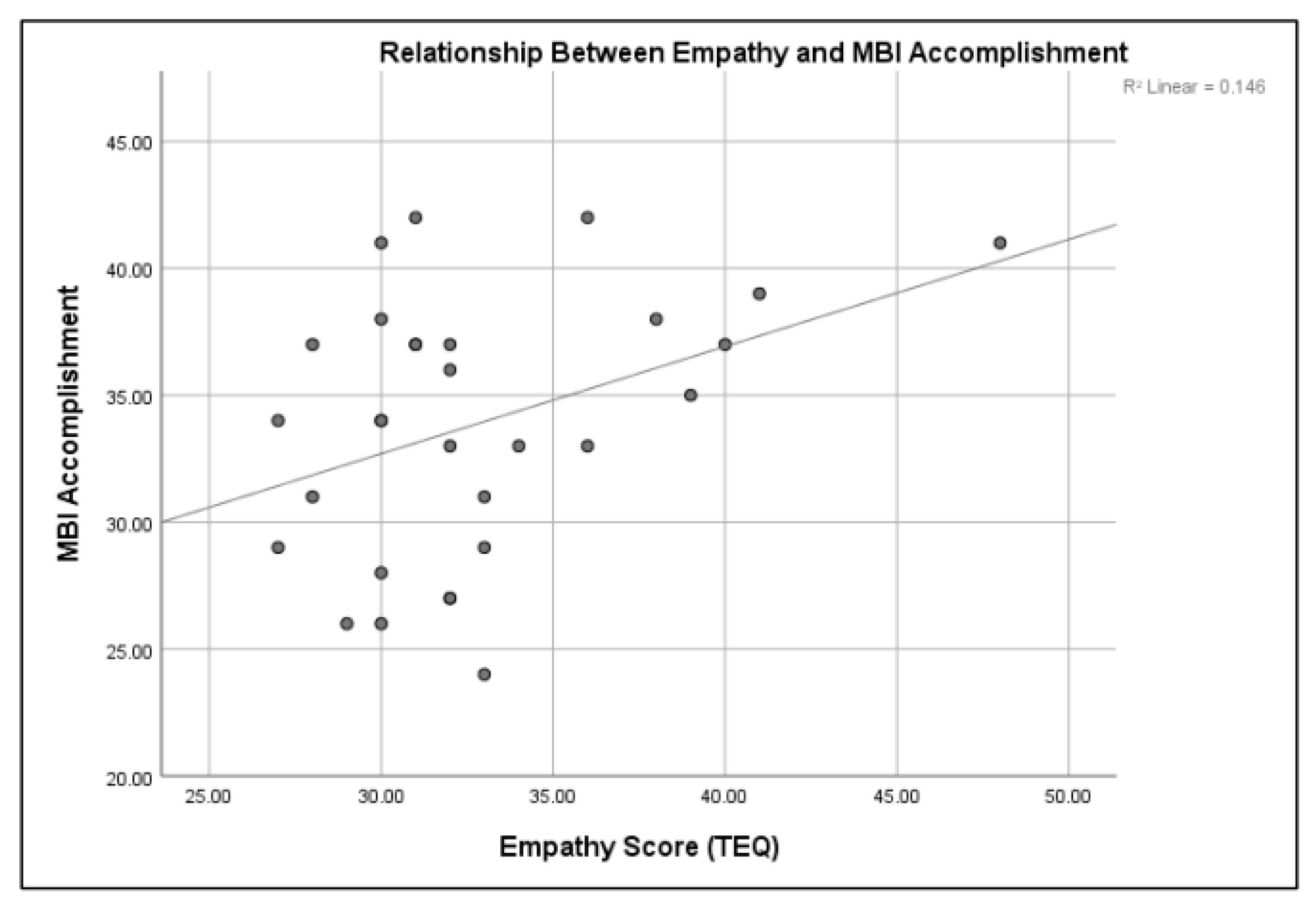
2.2. Inferential Statistics
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SSS | Stanford Sleepiness Scale |
| TEQ | Toronto Empathy Questionnaire |
| MBI-SS | Maslach Burnout Inventory-Student Survey |
References
- Landrigan, C.P.; Rothschild, J.M.; Cronin, J.W.; Kaushal, R.; Burdick, E.; Katz, J.T.; Lilly, C.M.; Stone, P.H.; Lockley, S.W.; Bates, D.W.; et al. Effect of reducing interns’ work hours on serious medical errors in intensive care units. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1838–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pigeon, W.R.; Sateia, M.J.; Ferguson, R.J. Distinguishing between excessive daytime sleepiness and fatigue: Toward improved detection and treatment. J. Psychosom. Res. 2003, 54, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, A.; Shen, J.; Shapiro, C.M. Measurements of sleepiness and fatigue. J. Psychosom. Res. 2010, 69, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Barbera, J.; Shapiro, C.M. Distinguishing sleepiness and fatigue: Focus on definition and measurement. Sleep Med. Rev. 2006, 10, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, O.P. Sustained work, fatigue, sleep loss and performance: A review of the issues. Work Stress 1989, 3, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, D.; Reid, K. Fatigue, alcohol and performance. Nature 1997, 288, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basner, M.; Dinges, D.F.; Shea, J.A.; Small, D.S.; Zhu, J.; Norton, L.; Ecker, A.J.; Novak, C.; Bellini, L.M.; Volpp, K.G. Sleep and alertness in medical interns and residents: An observational study on the role of extended shifts. Sleep 2017, 40, zsx027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, K.K.; Stoller, E.P.; Sage, P.; Aikens, J.E.; Owens, J.; Avidan, A.; Phillips, B.; Rosen, R.; Strohl, K.P. The effects of sleep loss and fatigue on resident–physicians: A multi-institutional, mixed-method study. Acad. Med. 2004, 79, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barger, L.K.; Ayas, N.T.; Cade, B.E.; Cronin, J.W.; Rosner, B.; Speizer, F.E.; Czeisler, C.A. Impact of extended-duration shifts on medical errors, adverse events, and attentional failures. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Approved Major Revisions to Program Requirements, Section VI; Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education: Chicago, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Brick, C.A.; Seely, D.L.; Palermo, T.M. Association between sleep hygiene and sleep quality in medical students. Behav. Sleep Med. 2010, 8, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrber, K.; Dresler, M.; Niedermaier, S.; Steiger, A.; Genze, L. The interaction between sleep quality and academic performance. Psychiatr. Res. 2012, 46, 1618–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, T.; Lamm, C. The social neuroscience of empathy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1156, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Kaplowitz, S.; Johnston, M.V. The effects of physician empathy on patient satisfaction and compliance. Eval. Health Prof. 2004, 27, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojat, M.; Gonnella, J.S.; Nasca, T.J.; Mangione, S.; Vergare, M.; Magee, M. Physician empathy: Definition, components, measurement, and relationship to gender and specialty. Am. J. Psychiatry 2002, 159, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojat, M.; Mangione, S.; Nasca, T.J.; Rattner, S.; Erdmann, J.B.; Gonnella, J.S.; Magee, M. An empirical study of decline in empathy in medical school. Med. Ed. 2004, 38, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, R.M.; Street, R.J. The values and value of patient-centered care. Ann. Fam. Med. 2011, 9, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J. Perspective: Does medical education promote professional alexithymia? A call for attending to the emotions of patients and self in medical training. Acad. Med. 2011, 86, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamay-Tsoory, S.G. The neural bases for empathy. Neuroscientist 2011, 17, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, S.D.; de Waal, F.B. Empathy: Its ultimate and proximate bases. Behav. Brain Sci. 2002, 25, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Collette, F.; Cajochen, C.; Peigneux, P. A time to think: Circadian rhythms in human cognition. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 2007, 24, 755–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoia-Caraballa, R.; Rye, M.S.; Pan, W.; Brown, K.J.; Lutz-Zois, C.; Lyons, A. Negative affect and anger rumination as mediators between forgiveness and sleep quality. J. Behav. Med. 2008, 31, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minkel, J.; Htaik, O.; Banks, S.; Dinges, D. Emotional expressiveness in sleep-deprived healthy adults. Behav. Sleep Med. 2010, 9, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guadagni, V.; Burles, F.; Ferrara, M.; Iaria, G. The effects of sleep deprivation on emotional empathy. J. Sleep Res. 2014, 23, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, M.; Sheppes, G.; Sadeh, A. Sleep and emotions: Bidirectional links and underlying mechanisms. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2013, 89, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilcher, J.J.; Huffcutt, A.J. Effects of sleep deprivation on performance: A meta-analysis. Sleep 1996, 19, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojat, M.; Vergare, M.; Isenberg, G.; Cohen, M.; Spandorfer, J. Underlying construct of empathy, optimism, and burnout in medical students. Int. J. Med. Educ. 2015, 6, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanafelt, T.D.; Hasan, O.; Dyrebye, L.N.; Sinsky, C.; Satele, D.; Sloan, J.; West, C.P. Changes in burnout and satisfaction with work-life balance in physicians and the general US working population between 2011 and 2014. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 1600–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, R.; Schonfeld, I.S.; Laurent, E. Burnout-depression overlap: A review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2015, 36, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreskovich, M.R.; Kaups, K.L.; Balch, C.M.; Hanks, J.B.; Satele, D.; Sloan, J.; Meredith, C.; Buhl, A.; Dyrbye, L.N.; Shanafelt, T.D. Prevalence of alcohol use disorders among american sureons. Arch. Surg. 2012, 147, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, C.P.; Dyrbye, L.N.; Shanafelt, T.D. Physician burnout: Contributors, consequences and solutions. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 283, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, C.P.; Tan, A.D.; Shanafelt, T.D. Association of resident fatigue and distress with occupational blood and body fluid exposures and motor vehicle incidents. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2012, 87, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslach, C.; Jackson, S.E.; Leiter, M.P. Maslach Burnout Inventory Manual, 3rd ed.; Consulting Psychologists Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- McHill, A.W.; Czeisler, C.A.; Shea, S.A. Resident physician extended work hours and burnout. Sleep 2018, 41, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soderstrom, M.; Jeding, K.; Ekstedt, M.; Perski, A.; Akerstedt, T. Insufficient sleep predicts clinical burnout. J. Occup. Health Psychol. 2012, 17, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilgore, W.D.; Kahn-Greene, E.T.; Lipizzi, E.L.; Newman, R.A.; Kamimori, G.H.; Balkin, T.J. Sleep deprivation reduces perceived emotional intelligence and constructive thinking skills. Sleep Med. 2008, 9, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Helm, E.; Gujar, N.; Walker, M.P. Sleep deprivation impairs the accurate recognition of human emotions. Sleep 2010, 33, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempesta, D.; Couyoumdjian, A.; Curcio, G. Lack of sleep affects the evaluation of emotional stimuli. Brain Res. Bull. 2010, 82, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Guadagni, V.; Cook, E.; Hart, C.; Burles, F.; Iaria, G. Poor sleep quality affects empathic responses in experienced paramedics. Sleep Biol. Rhythm. 2018, 16, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerstedt, T.; Knutsson, A.; Westerholm, P.; Theorells, T.; Alfredsson, L.; Kecklund, G. Mental fatigue, work and sleep. J. Psychosom. Res. 2004, 57, 247–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleitman, N.; Titelbaum, S.; Feiveson, P. The effect of body temperature on reaction time. Am. J. Physiol. 1938, 121, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christov-Moore, L.; Simpson, E.A.; Coude, G.; Grigatyte, K.; Iacoboni, M.; Ferrari, P.F. Empathy: Gender effects in brain and behavior. Neurosci. Behav. Rev. 2014, 46, 604–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoddes, E.; Zarcone, V.; Smythe, H.; Phillips, R.; Dement, W.C. Quantification of sleepiness: A new approach. Psychophysiology 1973, 10, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoddes, E.; Dement, W.; Zarcone, V. The development and use of the stanford sleeping scale (SSS). Psychophysiology 1972, 9, 150. [Google Scholar]
- Herscovitch, J.; Broughton, R. Sensitivity of the Stanford sleepiness scale to the effects of cumulative partial sleep deprivation and recovery oversleeping. Sleep 1981, 4, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spreng, R.N.; McKinnon, M.C.; Mar, R.A.; Levine, B. The Toronto empathy questionnaire: Scale development and initial validation of a factor-analytic solution to multiple empathy measures. J. Personal. Assess. 2009, 91, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron-Cohen, S.; Wheelwright, S. The empathy quotient: An investigation of adults with Asperger syndrome or high functioning autism, and normal sex differences. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2004, 34, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufeli, W.B.; Martinez, I.M.; Pinto, A.M.; Salanova, M.; Bakker, A.B. Burnout and engagement in university students: A cross-national study. J. Cross-Cult. Psychol. 2002, 33, 464–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.A.; Jordani, P.C.; Zucoloto, M.L.; Bonafe, F.S.; Maroco, J. Burnout in dental students: Effectiveness of different methods. Rev. Odontol. UNESP 2013, 42, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maslach, C.; Leiter, M.P. Burnout. In Stress: Concepts, Cognition, Emotion, and Behavior; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 351–357. [Google Scholar]

| Sleepiness | Empathy | Burnout | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Exhaustion | Cynicism | Accomplishment | |
| Time of Day | |||||||
| AM (N = 30) | 2.27 (1.55) | 4.45 (1.81) | 31.26 (3.41) | 35.27 (6.13) | 19.81 (6.30) | 9.00 (3.29) | 34.91 (5.80) |
| PM (N = 30) | 3.12 (1.49) | 3.29 (1.83) | 35.5 (5.23) | 34.42 (3.46) | 21.58 (5.26) | 9.53 (4.44) | 33.35 (4.89) |
| Time of Shift | |||||||
| Day (N = 19) | 3.00 (1.49) | 3.21 (1.84) | 31.47 (3.45) | 32.57 (3.47) | 21.16 (5.47) | 9.79 (5.03) | 33.74 (4.66) |
| Night (N = 11) | 2.36 (1.63) | 4.72 (1.61) | 35.18 (5.62) | 35.00 (6.26) | 19.63 (6.32) | 9.00 (3.28) | 34.09 (6.11) |
| Gender | |||||||
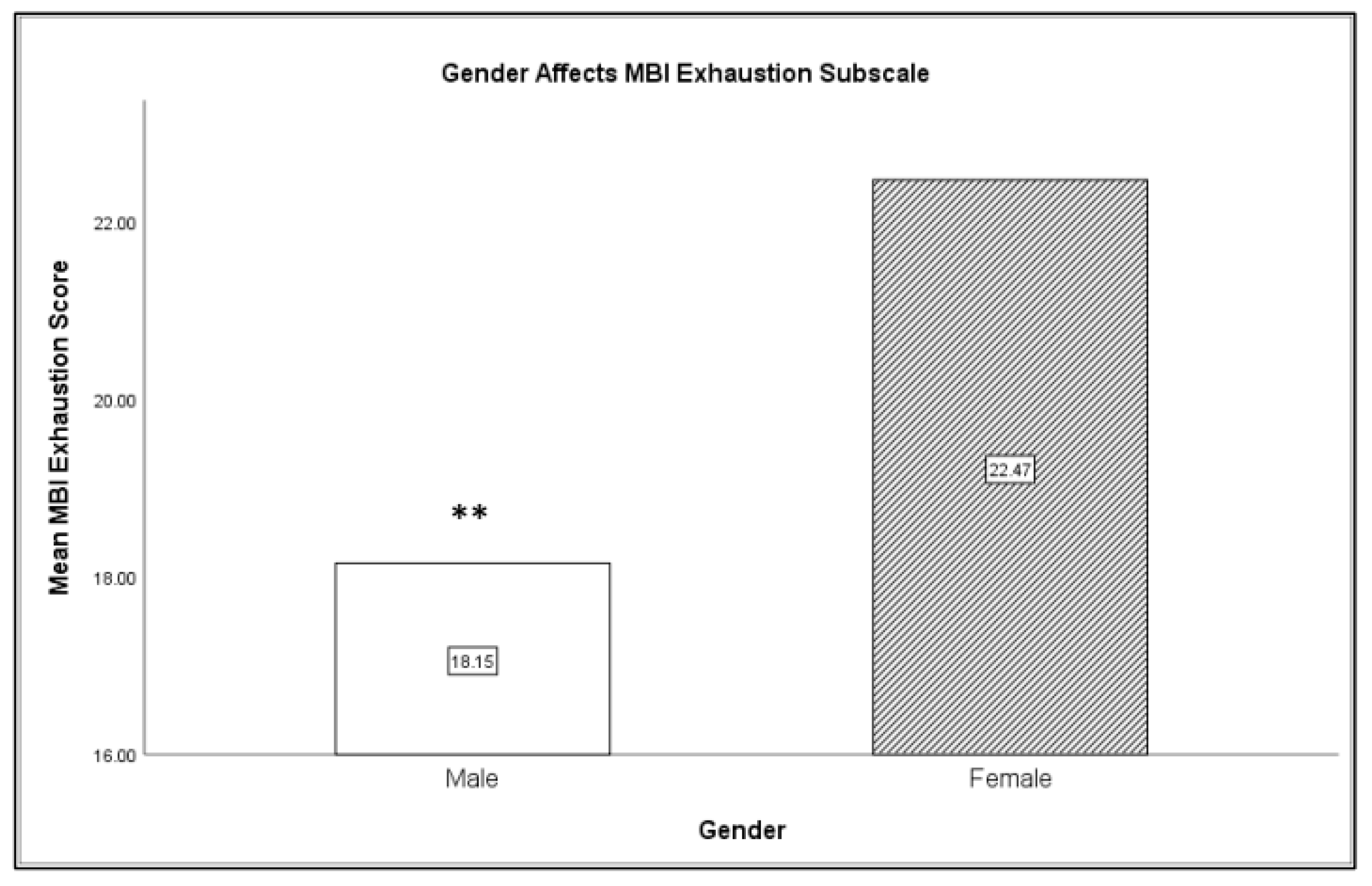
| Male (N = 12) | 2.08 (.86) | 3.84 (1.99) | 32.69 (4.44) | 33.85 (3.93) | 18.15 (3.69) | 9.31 (4.42) | 34.85 (4.78) |
| Female (N = 16) | 3.29 (1.76) | 3.71 (1.86) | 32.82 (4.92) | 33.18 (5.36) | 22.47 (6.40) | 9.65 (4.55) | 33.12 (5.41) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fowler, L.A.; Ellis, S. The Effect of 12 Hour Shifts, Time of Day, and Sleepiness on Emotional Empathy and Burnout in Medical Students. Clocks & Sleep 2019, 1, 501-509. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep1040038
Fowler LA, Ellis S. The Effect of 12 Hour Shifts, Time of Day, and Sleepiness on Emotional Empathy and Burnout in Medical Students. Clocks & Sleep. 2019; 1(4):501-509. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep1040038
Chicago/Turabian StyleFowler, Lauren A., and Shannon Ellis. 2019. "The Effect of 12 Hour Shifts, Time of Day, and Sleepiness on Emotional Empathy and Burnout in Medical Students" Clocks & Sleep 1, no. 4: 501-509. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep1040038
APA StyleFowler, L. A., & Ellis, S. (2019). The Effect of 12 Hour Shifts, Time of Day, and Sleepiness on Emotional Empathy and Burnout in Medical Students. Clocks & Sleep, 1(4), 501-509. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep1040038





